Influence of Extreme Strength in Water Quality of the Jucazinho Reservoir, Northeastern Brazil, PE
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
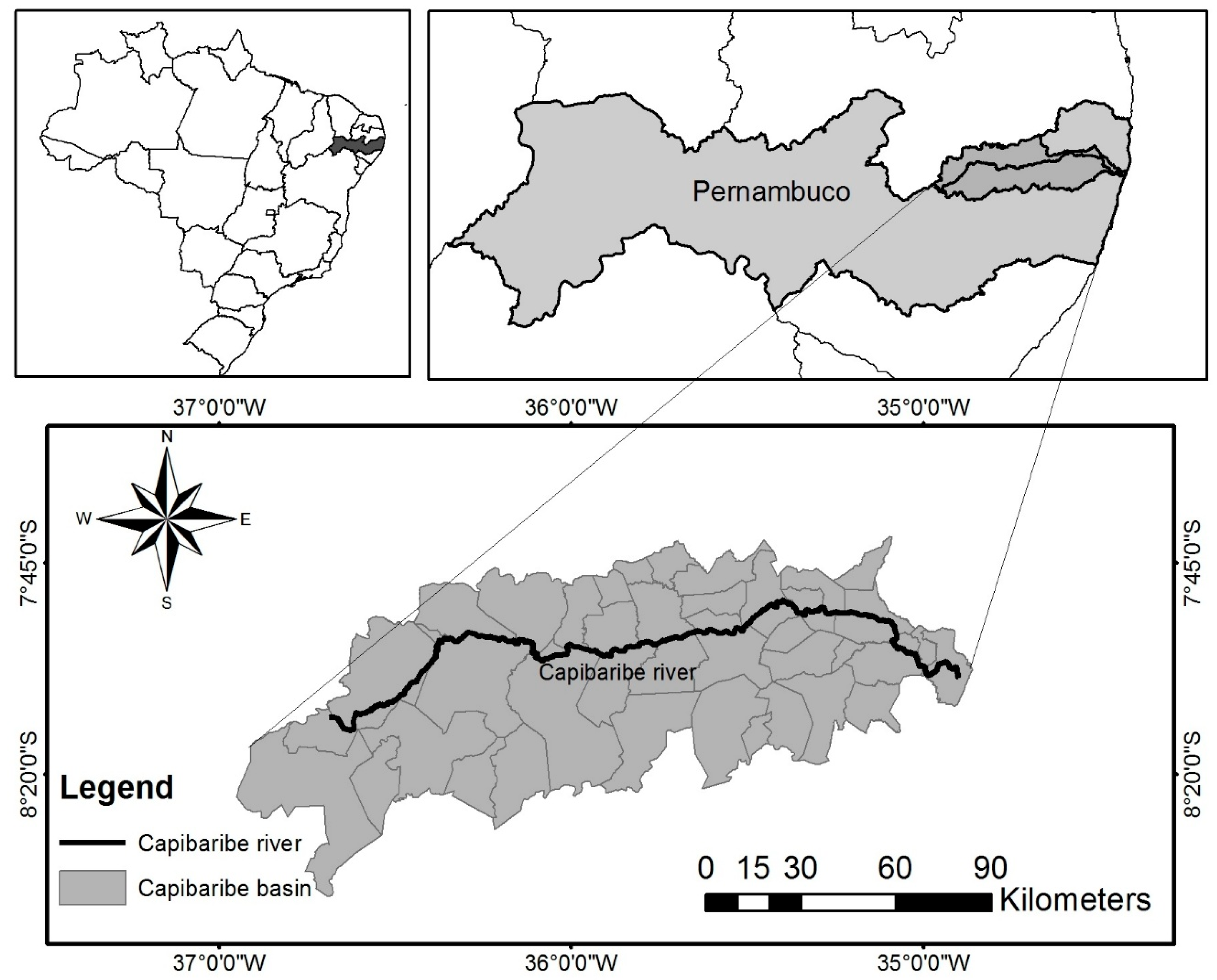
2.1. Spring Studied and Its Area of Hydric Contribution
2.2. Acquisition of Data
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of the Original Variables and Correlations between Variables
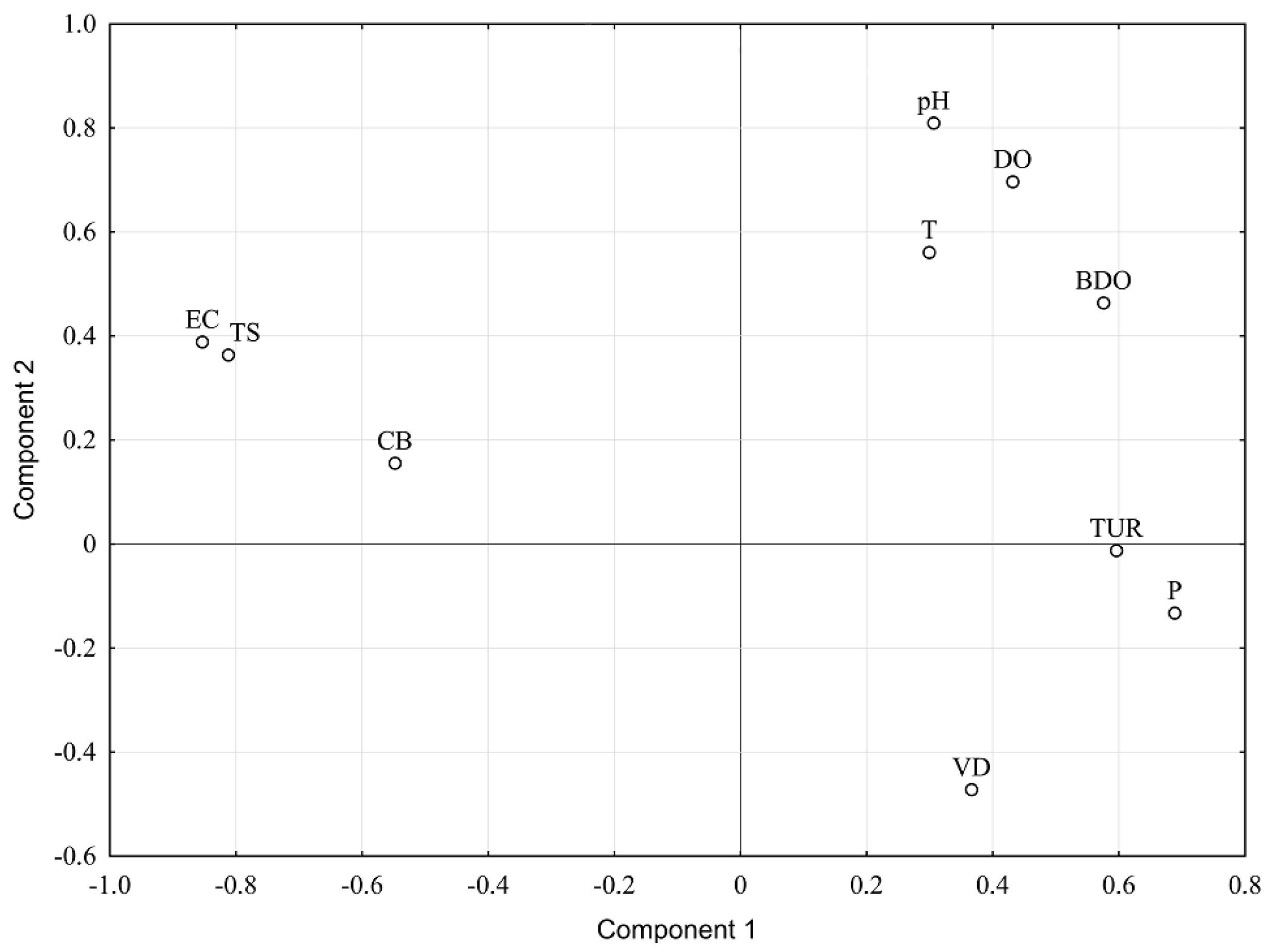
3.2. Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
- The employment of PCA promoted a reduction of 10 parameters of surface water quality in two components, which together explain 55% of total variance, illuminating the main problems that interfere in the temporal variation in water quality.
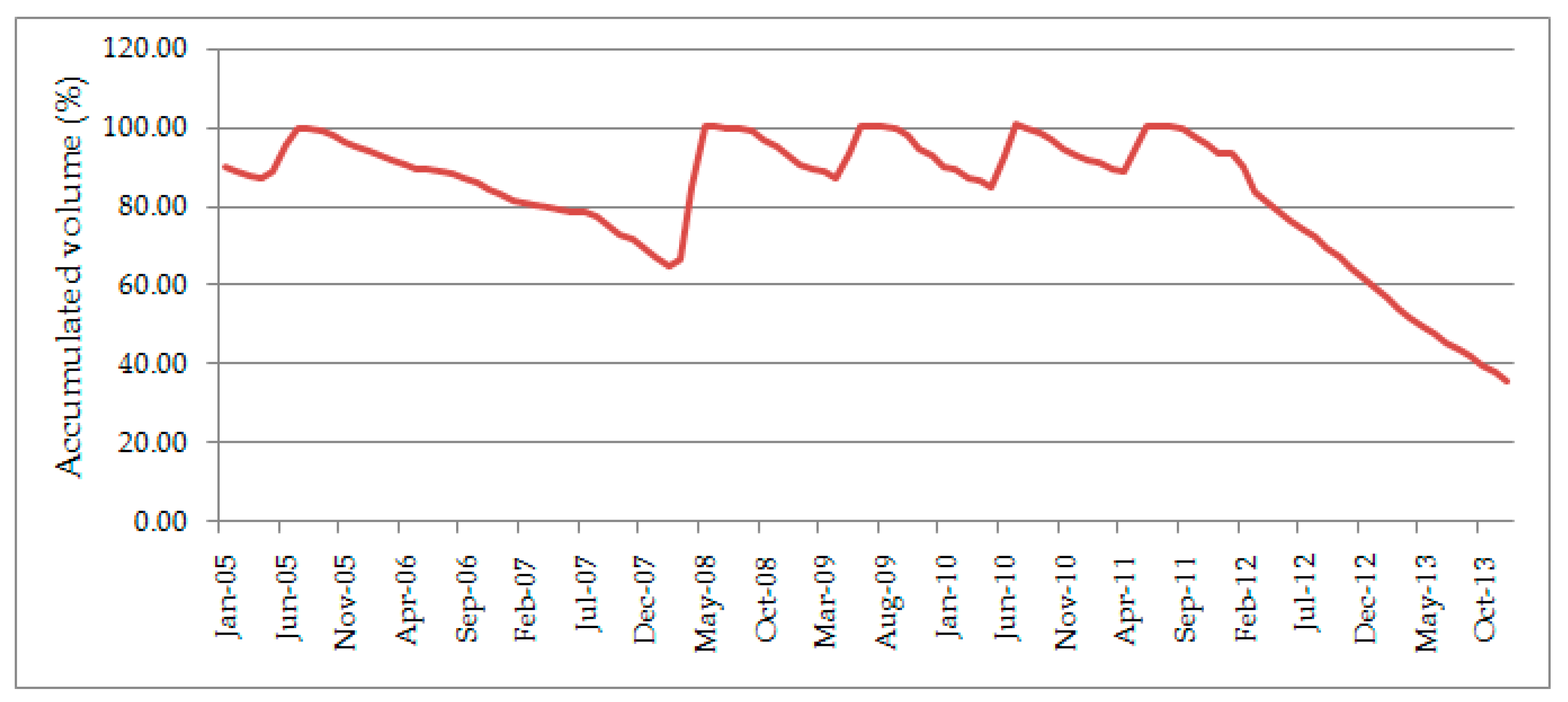
- The results of PCA showed a tendency toward formation over years, and even over months, of similar water quality parameters, conditioned by rainfall, indicating, in general, the temporal variations of the parameters analyzed. The temporal pattern obtained by the analysis shows that two factors are responsible for the variation in water quality during periods of drought, one observed over many years and other observed every six months.
- Wet years increase the inflow to the reservoir, so more domestic and industrial sewage is contributed, which in turn increases the turbidity and the content of phosphorus in the spring. On the other hand, years with little or no precipitation provide low inflow to the reservoir. In these conditions, there is an increase in total solids (dissolved salts) and, consequently, in electrical conductivity in view of the increase of the evaporation of the repressed water volume. An increase photosynthetic activity can also be seen, as is evidenced by the increase in the oxygen content in the water and in pH.
- The research shows the importance of water quality monitoring, where adequate statistical treatment can provide subsidies for better monitoring to preserve water quality for public water supply. In extreme dry periods, the identification of annual and semi-annual variation behavior can assist managers in making decisions regarding reservoir operation, monitoring the most important parameters and actions that minimize the impact of this extreme drought.
- The results of the study were relevant in the conduction of new methodologies for monitoring and management of the reservoir, since the applied statistical treatment shed light on the most recurrent problems of extreme drought, and these findings can be extended to other reservoirs located in the semi-arid of Northeastern Brazil.
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbosa, I.M.B.R.; Cirilo, J.A. Evolução do estado trófico do reservatório Jucazinho, Pernambuco. In Simpósio de Recursos Hidrícos do Nordeste, 1st ed.; [CD-ROM]; 11. 2012, Anais; ABRH: João Pessoa, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, L.A.V.; Paulino, W.D.; Garcez, D.S.; Becker, H.; Sanchez-Botero, J.I. Limnological characteristics of a reservoir in semiarid Northeastern Brazil subjective to intensive tilapia farming (Orechromisniloticus Linnaeus, 1758). Acta Limnol. Bras. 2014, 26, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunkel, G.; Lima, D.; Selge, F.; Sobral, M.; Calado, S. Aquatic ecosstem services of reservoirs in semi-arid áreas: Sustainability and reservoir management. River Basin Manag. 2015, 197, 187–200. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.C. Noções de Hidroquímica. In Hidrologia: Conceitos e Aplicações; Cprm/Labhid-Ufpe: Fortaleza, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.P.C.; Costa, I.A.S. Biomonitoring ecological status of two reservoirs of the Brazilian semi-arid using phytoplankton assemblages (Q index). Acta Limnol. Bras. 2015, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapra, S.C. Surface Water-Quality Modeling; Waveland Press, Inc.: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2008; p. 844. [Google Scholar]
- Esteves, F.A. Fundamentos da Limnologia, 2nd ed.; Interciência: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2011; 602p. [Google Scholar]
- Friese, K.; Schmidt, G.; Lena, J.C.; Nalini, H.A., Jr.; Zachmann, D.W. Anthropogenic influence on the degradation of na urban lake—The Pampulha reservoir in Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Limnologica 2010, 40, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reartes, S.B.R.; Estrada, V.; Bazan, R.; Larossa, N.; Cossavella, A.; Lopez, A.; Busso, F.; Diaz, M.S. Evaluation of ecological effects of anthropogenic nutrient loading scenarios in Los Molinos reservoir through a mathematical model. Ecol. Model. 2016, 320, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, R.I.; Weber, K.F.; Padowski, J.; Boucher, T.; Shemie, D. Estimating watershed degradation over the last centur and its impacto n water-treatment costs for the world’s large cities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9117–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, C.W.K.; Drikas, M.; House, J.; Burch, M.D.; Velzeboer, R.M.A. The impact of conventional water treatment process on cells of the cyanobacteriumMicrocystisaeruginosa. Water Res. 1999, 33, 3253–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, C.N.; Maccarty, P.L.; Parkin, G.F. Chemistry for Environmental Engineering; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2003; 752p. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi, J.V.E.; Lacerda, L.D.; Dórea, J.G.; Landim, P.M.B.; Gomes, J.P.O.; Almeida, R.; Manzatto, A.G.; Bastos, W.R. Aplicação da análise das componentes principais na ordenação dos parâmetros físico-químicos no alto Rio Madeira e afluentes, Amazônia Ocidental. Geochim. Bras. 2009, 23, 1–158. [Google Scholar]
- Norusis, M.J. SPSS Base System User’s Guide; SPSS Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 1990; 520p. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Anderson, R.E.; Tatham, R.L. Análise Multivariada de Dados, 5th ed.; Bookman: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Parinet, B.; Lhote, A.; Legube, B. Principal componentanalysis: An appropriate tool for water quality evaluation andmanagement—Application a tropical lake system. Ecol. Model. 2004, 178, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.W.; Gau, H.S.; Lai, W.L.; Chen, J.J.; Lee, C.G. Identification of pollution of Tapeng Lagoon from neighbouring rivers using multivariate statistical method. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Mohan, D.; Sinha, S. Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—A case study. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3980–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Departamento Nacional de Obras Contra as Secas-DNOCS, Ministério da Integração Nacional. Hidrologia do Reservatório de Jucazinho; Águasolos: Recife, Brazil, 1995; p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaria de Recursos Hídricos e Energéticos. ProjetecBRLi. Plano Hidroambiental da Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio do Capibaribe; TOMO I (vol 1, 2 e 3) e TOMO IV; SRHE: Recife, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, I.B.R.; Cirilo, J.A. Contribuição média de fósforo em reservatório de abastecimento de água—Parte 1. Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental 2015, 20, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieder, C.A.; Nam, S.H.; Martz, T.R.; Levin, L.A. High temporal and spatial variability of dissolved oxygen and pH inanearshore California kelp forest. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 3917–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, E.M.D.; Araújo, L.D.F.; Rosa, M.F.; Disney, W.; Alves, A.B. Surface water quality indicators in low acaraú basin, Ceará, Brazil, using multivariable analysis. Engenharia Agrícola 2007, 27, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palácio, H.A.; Araújo Neto, J.R.; Meireles, A.; Andrade, E.M.; Santos, J.C.; Chaves, L.C. Similaridade e fatores determinantes na salinidade das águas superficiais do Ceará, por técnicas multivariadas. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental 2011, 15, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helena, B.; Pardo, R.; Vega, M.; Barrado, E.; Fernandez, J.M.; Fernandez, L. Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuergariver, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Res. 2000, 34, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministério da Saúde. Dispõe Sobre os Procedimentos de Controle e de Vigilância da Qualidade da Água Para Consumo Humano e Seu Padrão de Potabilidade; Portaria No. 2914; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2011. Available online: http://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/gm/2011/prt2914_12_12_2011.html (accessed on 12 July 2017).
- Luíz, Â.M.E.; Pinto, M.L.C.; Scheffer, E.W. Parâmetros de cor e turbidez como indicadores de impactos resultantes do uso do solo, na bacia hidrográfica do rio Taquaral, São Mateus do Sul-PR. Revista o Espaço Geográfico em Análise 2012, 290–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, M. Application of multivariate statistical techniques in the assessment of water quality in the Southwest New Territories and Kowloon, Hong Kong. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 137, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girão, E.G.; De Andrade, E.M.; de Freitas Rosa, M.; Pereira de Araújo, L.D.F.; Maia Meireles, A.C. Seleção dos indicadores da qualidade de água no Rio Jaibaras pelo emprego da análise da componente principal. Revista Ciência Agronômica 2007, 38, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Palácio, H.A.Q. Índice de Qualidade das Águas na Parte Baixa da Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio Trussu, Ceará. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Ceará, Ceará, Brazil, 2004; 96p. [Google Scholar]
- Ministério de Minas e Energia. Diagnóstico do Município de Santa Cruz do Capibaribe; Ministério de Minas e Energia: Recife, Brazil, 2005. Available online: http://rigeo.cprm.gov.br/xmlui/bitstream/handle/doc/16692/Rel_Santa%20Cruz%20do%20Capibaribe.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 12 July 2017).
- Aragão, N.K.C.V. Taxonomia, Distribuição e Quantificação de Populações de Cianobactérias em Reservatórios do Estado de Pernambuco (Nordeste do Brasil). Master’s Thesis, Departamento deBiologia, Universidade Federal Rural de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil, 2011; 157p. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, V.O.; Cavati, B.; de Oliveira, L.B.; de Souza, B.D.Â. Ecologia de cianobactérias: Fatores promotores e conseqüências das florações. Oecol. Bras. 2009, 13, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.N.; Andrade, E.M.; Araujo Neto, J.R.; Meireles, A.C.M.; Palacio, H.A.Q. Land use and trophic state dynamics in a tropical semi-arid reservoir. Revista Ciência Agronômica 2014, 45, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, H.D.A. Associação da Ocorrência de Cianobactérias às Variações de Parâmetros de Qualidade da Água em Quatro Bacias Hidrográficas de Minas Gerais. Ph.D. Thesis, Mestrado em Saneamento, Meio Ambiente e Recursos Hídricos, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais-Escola de Engenharia, Minas Gerais, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Umetsu, C.A.; Umetsu, R.K.; Munhoz, K.C.A.; Dalmagro, H.J.; Krusche, A.V. Aspectos físico-químicos de dois rios da bacia do Alto Tapajós—Teles Pires e Cristalino—MT, durante período de estiagem e cheia. Revista de Ciências Agro-Ambientais 2007, 5, 59–70. [Google Scholar]

| Variable | Mean | Standard Deviation | Variance | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB (cell mL−1) | 3.81 × 107 | 1.38 × 107 | 1.90 × 107 | 3.62 |
| TUR (UNT) | 5.45 | 4.36 | 19.01 | 0.80 |
| BDO (mg L−1) | 3.26 | 2.03 | 4.11 | 0.62 |
| P (mg L−1) | 0.25 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.38 |
| DO (mg L−1) | 6.85 | 2.05 | 4.21 | 0.30 |
| TS (mg L−1) | 1084.16 | 172.80 | 29,859.41 | 0.16 |
| VD (%) | 88.13 | 13.52 | 182.74 | 0.15 |
| EC (dSm−1) | 1.680 | 0.232 | 0.054 | 0.14 |
| pH | 8.37 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 0.07 |
| T (°C) | 27.66 | 1.23 | 1.52 | 0.04 |
| T | pH | EC | DO | BDO | P | TUR | TS | CB | VD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | 1.000 | |||||||||
| pH | 0.362 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| EC | −0.078 | 0.055 | 1.000 | |||||||
| DO | 0.383 | 0.700 | −0.155 | 1.000 | ||||||
| BDO | 0.279 | 0.500 | −0.262 | 0.427 | 1.000 | |||||
| P | −0.038 | 0.081 | −0.537 | 0.099 | 0.449 | 1.000 | ||||
| TUR | 0.309 | 0.088 | −0.510 | 0.156 | 0.099 | 0.395 | 1.000 | |||
| TS | −0.114 | 0.024 | 0.839 | −0.082 | −0.293 | −0.455 | −0.435 | 1.000 | ||
| CB | 0.000 | −0.036 | 0.421 | −0.141 | −0.195 | −0.375 | −0.220 | 0.390 | 1.000 | |
| VD | −0.137 | −0.107 | −0.537 | 0.009 | −0.011 | 0.097 | −0.061 | −0.483 | −0.105 | 1.000 |
| Components | Eigenvalues | Explained Variance (%) | Accumulated Eingenvalues | Accumulated Explained Variance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 3.35 | 33.52 | 3.35 | 33.52 |
| PC2 | 2.22 | 22.18 | 5.57 | 55.70 |
| PC3 | 1.12 | 11.23 | 6.69 | 66.93 |
| PC4 | 1.02 | 10.22 | 7.72 | 77.15 |
| PC5 | 0.73 | 7.32 | 8.45 | 84.47 |
| PC6 | 0.59 | 5.88 | 9.04 | 90.35 |
| PC7 | 0.34 | 3.38 | 9.37 | 93.73 |
| PC8 | 0.29 | 2.86 | 9.66 | 96.59 |
| PC9 | 0.23 | 2.26 | 9.89 | 98.86 |
| PC10 | 0.11 | 1.14 | 10.00 | 100.00 |
| Components | PC 1 | PC 2 |
|---|---|---|
| T | 0.299 | 0.561 |
| pH | 0.306 | 0.81 |
| EC | −0.853 | 0.389 |
| DO | 0.432 | 0.696 |
| BDO | 0.576 | 0.464 |
| P | 0.688 | −0.133 |
| TUR | 0.596 | −0.012 |
| TS | −0.812 | 0.364 |
| CB | −0.548 | 0.155 |
| VD | 0.366 | −0.472 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Melo, R.R.C.; Rameh Barbosa, I.M.B.; Ferreira, A.A.; Lee Barbosa Firmo, A.; Da Silva, S.R.; Cirilo, J.A.; De Aquino, R.R.B. Influence of Extreme Strength in Water Quality of the Jucazinho Reservoir, Northeastern Brazil, PE. Water 2017, 9, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120955
De Melo RRC, Rameh Barbosa IMB, Ferreira AA, Lee Barbosa Firmo A, Da Silva SR, Cirilo JA, De Aquino RRB. Influence of Extreme Strength in Water Quality of the Jucazinho Reservoir, Northeastern Brazil, PE. Water. 2017; 9(12):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120955
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Melo, Rafael Roney Camara, Ioná Maria Beltrão Rameh Barbosa, Aida Araújo Ferreira, Alessandra Lee Barbosa Firmo, Simone Rosa Da Silva, José Almir Cirilo, and Ronaldo Ribeiro Barbosa De Aquino. 2017. "Influence of Extreme Strength in Water Quality of the Jucazinho Reservoir, Northeastern Brazil, PE" Water 9, no. 12: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120955
APA StyleDe Melo, R. R. C., Rameh Barbosa, I. M. B., Ferreira, A. A., Lee Barbosa Firmo, A., Da Silva, S. R., Cirilo, J. A., & De Aquino, R. R. B. (2017). Influence of Extreme Strength in Water Quality of the Jucazinho Reservoir, Northeastern Brazil, PE. Water, 9(12), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120955






