Stormwater Biofilters as Barriers against Campylobacter jejuni, Cryptosporidium Oocysts and Adenoviruses; Results from a Laboratory Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Configurations
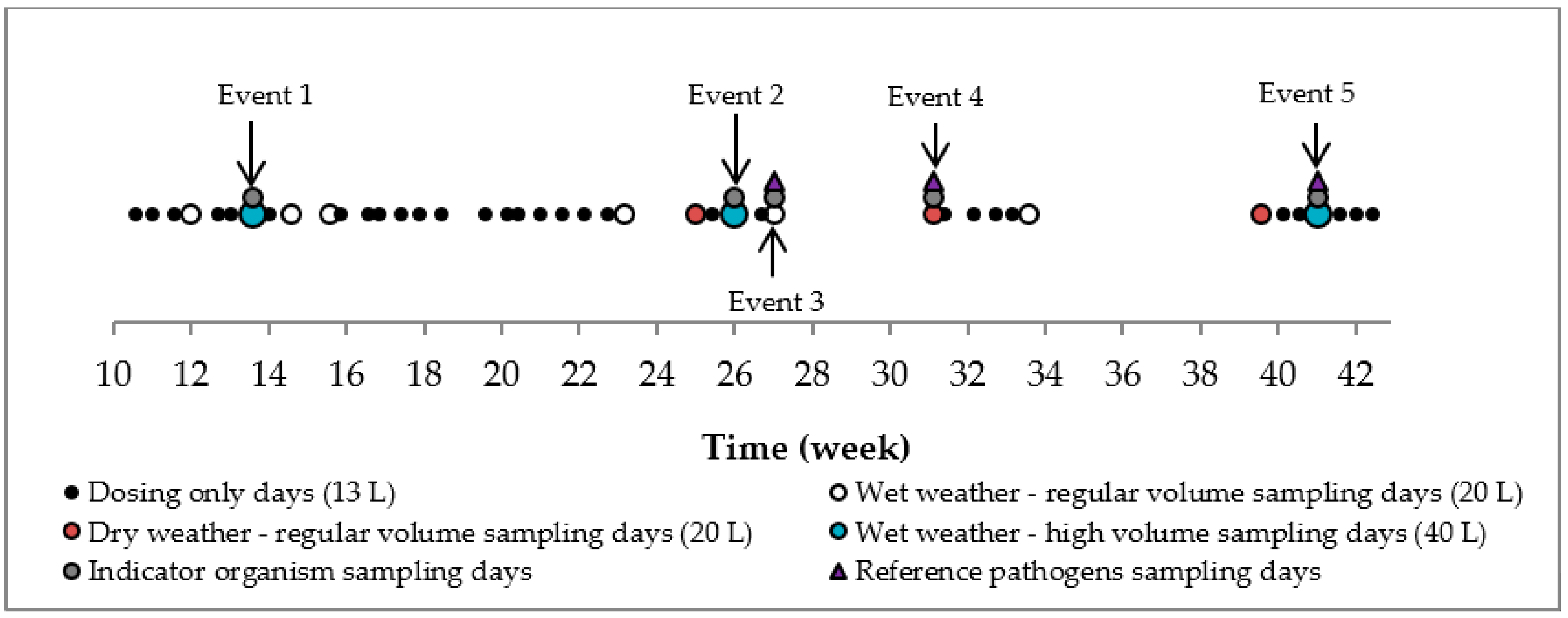
2.2. Dosing and Sampling
2.2.1. Semi-Natural Stormwater Preparation
2.2.2. Dosing Frequency and Volumes
2.2.3. Inflow and Outflow Water Quality Sampling
2.2.4. Infiltration Rate Measurements
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
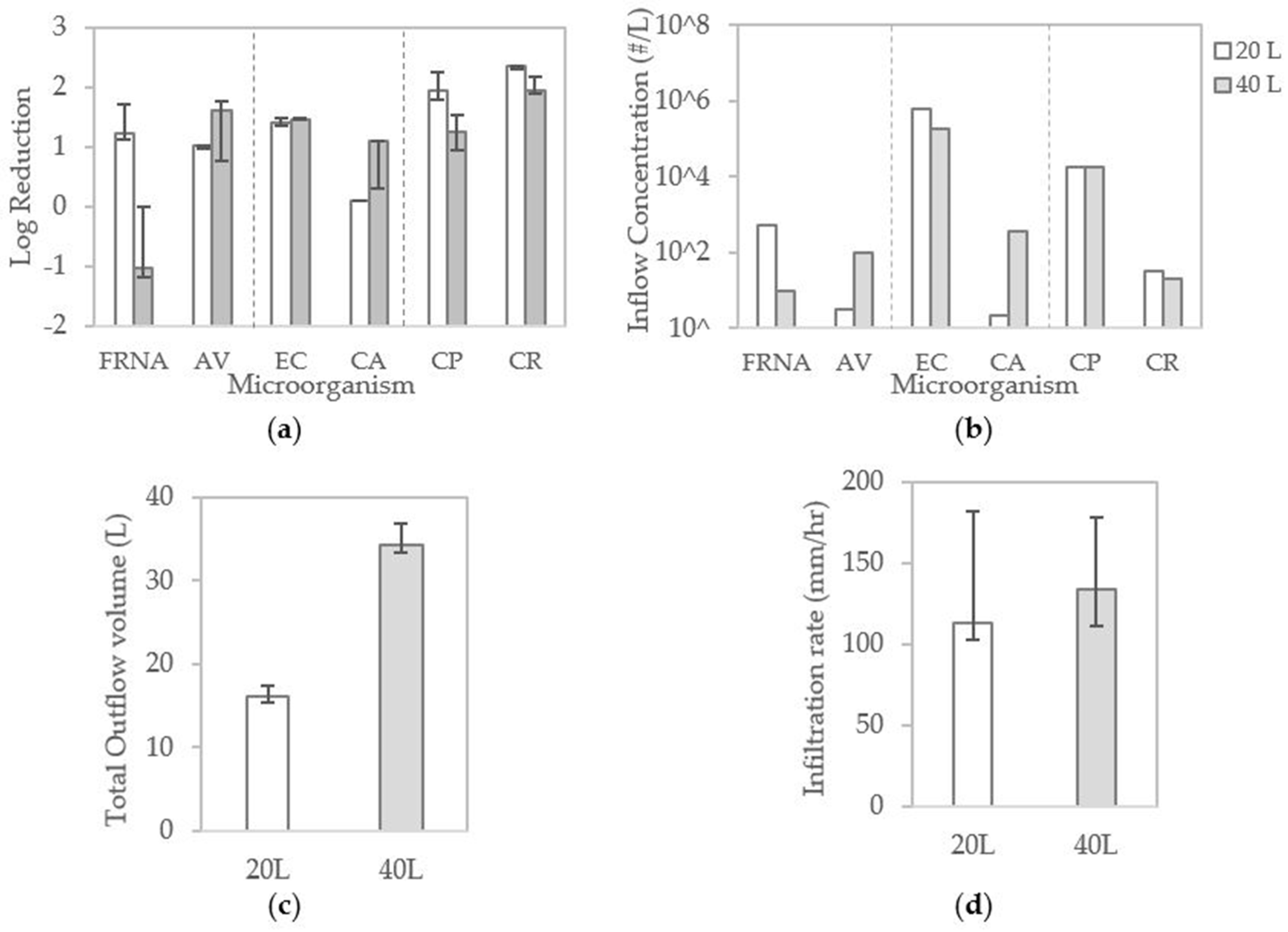
3.1. Overall Removal Performance of Indicators and Reference Pathogens
3.2. Effect of Dry Weather Periods
3.3. Effect of Event Size
3.4. Comparison of Indicator and Reference Pathogen Removal
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, V.G.; Deletic, A.; Fletcher, T.D.; Hatt, B.E.; McCarthy, D.T. Achieving multiple benefits from stormwater harvesting. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban Water Resources Research Council. Pathogens in Urban Stormwater Systems; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC). Australian Guidelines for Water Recycling (Phase 2): Stormwater Harvesting and Reuse; Natural Resource Management Ministerial Council; Environment Protection and Heritage Council; National Health and Medical Research Council: Canberra, Australia, 2009.
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Sharma, H.; Minami, C. Water quality improvement through bioretention media: Nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Water Environ. Res. 2006, 78, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facility for Advancing Water Biofiltration (FAWB). Adoption Guidelines for Stormwater Biofiltration Systems; Facility for Advancing Water Biofiltration, Monash University: Clayton, VIC, Australia, 2009; ISBN 978-0-9805831-1-3. [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway, J.; Hunt, W.; Graves, A.; Wright, J. Field Evaluation of Bioretention Indicator Bacteria Sequestration in Wilmington, North Carolina. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 137, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Deletic, A.; Alcazar, L.; Bratieres, K.; Fletcher, T.D.; McCarthy, D.T. Removal of Clostridium perfringens, Escherichia coli and F-RNA coliphages by stormwater biofilters. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 49, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.K.; Torkelson, A.A.; Dodd, H.; Nelson, K.L.; Boehm, A.B. Engineering Solutions to Improve the Removal of Fecal Indicator Bacteria by Bioinfiltration Systems during Intermittent Flow of Stormwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10791–10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, I.; Atoyan, J.; Amador, J.; Boving, T. Transport of Pathogen Surrogates in Soil Treatment Units: Numerical Modeling. Water 2014, 6, 818–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifman, L.; Kasaraneni, V.; Sullivan, R.; Oyanedel-Craver, V.; Boving, T. Bacteria Removal from Stormwater Runoff Using Tree Filters: A Comparison of a Conventional and an Innovative System. Water 2016, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horan, N.J. Faecal indicator organisms. In The Handbook of Water and Wastewater Microbiology; Mara, D., Horan, N.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA; London, UK, 2003; ISBN 978-0-12-470100-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rippy, M.A. Meeting the criteria: Linking biofilter design to fecal indicator bacteria removal: Linking biofilter design to FIB removal. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2015, 2, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasena, G.I.; Pham, T.; Payne, E.G.; Deletic, A.; McCarthy, D.T. E. coli removal in laboratory scale stormwater biofilters: Influence of vegetation and submerged zone. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; McCarthy, D.T.; Deletic, A. Escherichia coli removal in copper-zeolite-integrated stormwater biofilters: Effect of vegetation, operational time, intermittent drying weather. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifman, L.A.; Kasaraneni, V.K.; Sullivan, R.K.; Oyanedel-Craver, V.; Boving, T.B. New Antimicrobially Amended Media for Improved Nonpoint Source Bacterial Pollution Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14383–14391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasaraneni, V.K.; Schifman, L.A.; Boving, T.B.; Oyanedel-Craver, V. Enhancement of Surface Runoff Quality Using Modified Sorbents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.K.; Cantrell, K.B.; Nelson, K.L.; Boehm, A.B. Efficacy of biochar to remove Escherichia coli from stormwater under steady and intermittent flow. Water Res. 2014, 61, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, M.; Li, X.; Brow, C.N.; Johnson, W.P. Detachment-Influenced Transport of an Adhesion-Deficient Bacterial Strain within Water-Reactive Porous Media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasena, G.I.; Deletic, A.; Lintern, A.; Henry, R.; McCarthy, D.T. Enhancing Escherichia coli removal in stormwater biofilters with a submerged zone: Balancing the impact of vegetation, filter media and extended dry weather periods. Urban Water J. 2017. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Bratieres, K.; Fletcher, T.; Deletic, A.; Somes, N.; Woodcock, T. Hydraulic and pollutant treatment performance of sand based biofilters 2010. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Sustainable Techniques and Strategies in Urban Water Management, Villeurbanne, France, 28 June–1 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bratieres, K.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A.; Zinger, Y. Nutrient and sediment removal by stormwater biofilters: A large-scale design optimisation study. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3930–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, H.P. Urban Stormwater Quality: A Statistical Overview; Cooperative Research Centre for Catchment Hydrology: Melbourne, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.D.; Fletcher, T.D.; Wong, T.H.F.; Breen, P.F.; Duncan, H.P. Nitrogen composition in urban runoff—Implications for stormwater management. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasena, G.I.; Deletic, A.; Ellerton, J.; McCarthy, D.T. Evaluating Escherichia coli removal performance in stormwater biofilters: A laboratory-scale study. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IDEXX-Laboratories. IDEXX-Laboratories Colilert® Test Kit; IDEXX-Laboratories: Westbrook, ME, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Allard, A.; Girones, R.; Juto, P.; Wadell, G. Polymerase chain reaction for detection of adenoviruses in stool samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 2659–2667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- APHA (American Public Health Association); AWWA (American Water Works Association); WPCF (Water Pollution Control Federation). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Pollution Control Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hsomi, M.; Sudo, R. Simultaneous determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in freshwater samples using persulphate digestion. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 1986, 27, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Payne, E.G.; Fletcher, T.D.; Cook, P.L.; Deletic, A.; Hatt, B.E. The influence of vegetation in stormwater biofilters on infiltration and nitrogen removal: Preliminary findings. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD 2012), Melbourne, Australia, 21–23 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasena, G.I.; Deletic, A.; McCarthy, D.T. Biofiltration for stormwater harvesting: Comparison of Campylobacter spp. and Escherichia coli removal under normal and challenging operational conditions. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, R.; Schang, C.; Chandrasena, G.; Deletic, A.; Edmunds, M.; Jovanovic, D.; Kolotelo, P.; Williamson, R.; Schmidt, J.; McCarthy, D. Environmental monitoring of waterborne Campylobacter: Evaluation of the Australian Standard and a hybrid extraction-free MPN-PCR method. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, S.A.; Bettahar, M. Straining, attachment, and detachment of Cryptosporidium oocysts in saturated porous media. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevik, T.K.; Aa, K.; Ausland, G.; Hanssen, J.F. Retention and removal of pathogenic bacteria in wastewater percolating through porous media: A review. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Chu, Y.; Li, Y. Virus removal and transport in saturated and unsaturated sand columns. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2000, 43, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strecker, E.; Quigley, M.; Urbonas, B.; Jones, J.; Clary, J. Determining Urban Storm Water BMP Effectiveness. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2001, 127, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez, C.; Alum, A.; Suarez-Rey, E.M.; Choi, C.Y.; Oron, G.; Gerba, C.P. Bacteriophages MS2 and PRD1 in turfgrass by subsurface drip irrigation. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medema, G.J.; Bahar, M.; Schets, F.M. Survival of Cryptosporidium parvum, Escherichia coli, faecal enterococci and Clostridium perfringens in river water: Influence of temperature and autochthonous microorganisms. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 249–252. [Google Scholar]


| Stormwater Pollutant | Unit | Inflow Concentration | Main Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Measured in the Inflow during This Study 1 | |||
| E. coli | MPN/100 mL | 5.9 × 104 | 2.8 × 104 (4.16) | raw sewage |
| FRNA coliphages | pfu/100 mL | 5.5 | 26.7 (20.83) | laboratory culture |
| C. perfringens | orgs/100 mL | 925 | 1.4 × 103 (1.73) | laboratory culture |
| Campylobacter spp. | MPNIU/L | 33.1 | 65 (19.49) | laboratory culture |
| Adenoviruses | MPNIU/L | 1 | 11 (6.50) | laboratory culture |
| Cryptosporidium oocysts | oocysts/L | 17.6 | 9 (2.53) | laboratory culture |
| Total suspended solids | mg/L | 100 | 86 (1.44) | sediment |
| Total phosphorus | mg/L | 0.35 | 0.42 (1.18) | sediment, KH2PO4 |
| Total nitrogen | mg/L | 2.2 | 2.92 (1.17) | sediment, KNO3, NH4Cl, C6H5O2N |
| Cadmium | mg/L | 4.5 × 10−3 | 8.1 × 10−3 (1.40) | Cd(NO3)2 in HNO3 |
| Chromium | mg/L | 2.5 × 10−2 | 5.4 × 10−2 (1.58) | Cr(NO3)3 |
| Copper | mg/L | 5.0 × 10−2 | 8.0 × 10−2 (1.36) | CuSO4 |
| Lead | mg/L | 1.4 × 10−1 | 2.7 × 10−1 (1.47) | Pb(NO3)2 |
| Manganese | mg/L | 2.3 × 10−1 | 1.9 × 10−1 (1.11) | Mn(NO3)2 |
| Nickel | mg/L | 3.1 × 10−2 | 5.0 × 10−2 (1.30) | Ni(NO3)2 |
| Zinc | mg/L | 2.5 × 10−1 | 2.6 × 10−1 (1.18) | ZnCl2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chandrasena, G.; Deletic, A.; Lintern, A.; Henry, R.; McCarthy, D. Stormwater Biofilters as Barriers against Campylobacter jejuni, Cryptosporidium Oocysts and Adenoviruses; Results from a Laboratory Trial. Water 2017, 9, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120949
Chandrasena G, Deletic A, Lintern A, Henry R, McCarthy D. Stormwater Biofilters as Barriers against Campylobacter jejuni, Cryptosporidium Oocysts and Adenoviruses; Results from a Laboratory Trial. Water. 2017; 9(12):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120949
Chicago/Turabian StyleChandrasena, Gayani, Ana Deletic, Anna Lintern, Rebekah Henry, and David McCarthy. 2017. "Stormwater Biofilters as Barriers against Campylobacter jejuni, Cryptosporidium Oocysts and Adenoviruses; Results from a Laboratory Trial" Water 9, no. 12: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120949
APA StyleChandrasena, G., Deletic, A., Lintern, A., Henry, R., & McCarthy, D. (2017). Stormwater Biofilters as Barriers against Campylobacter jejuni, Cryptosporidium Oocysts and Adenoviruses; Results from a Laboratory Trial. Water, 9(12), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120949





