Calculation of Steady-State Evaporation for an Arbitrary Matric Potential at Bare Ground Surface
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Background and Problem Description
2.2. New Solutions of Evaporation with Arbitrary Surface Matric Potentials
2.2.1. Calculation of Evaporation Rate E with the Modified Gardner [23] Model
2.2.2. Calculation of Evaporation Rate E with the Brooks–Corey [26] Model
3. Results
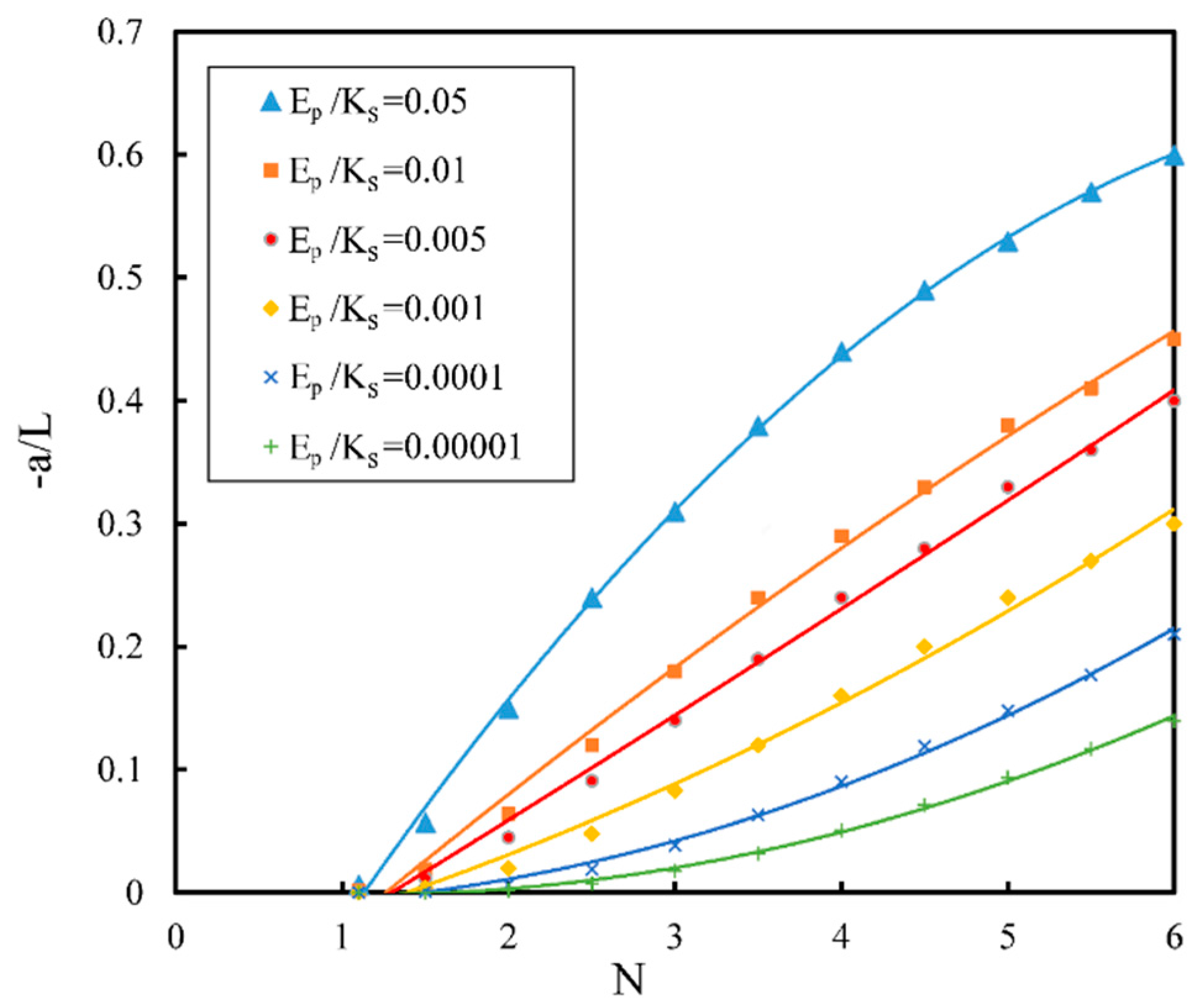
3.1. Check of Applicability of Equations (11) and (12)
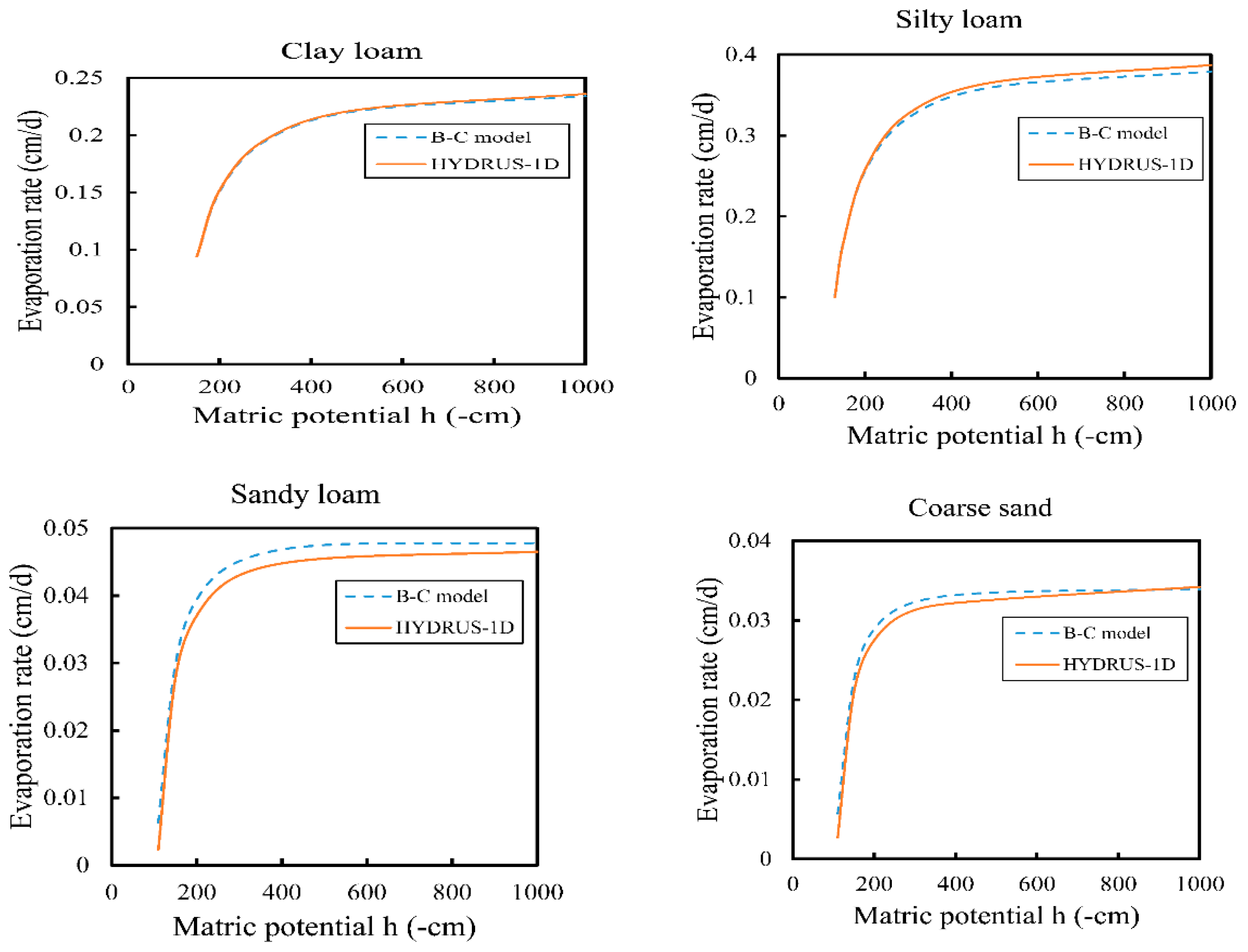
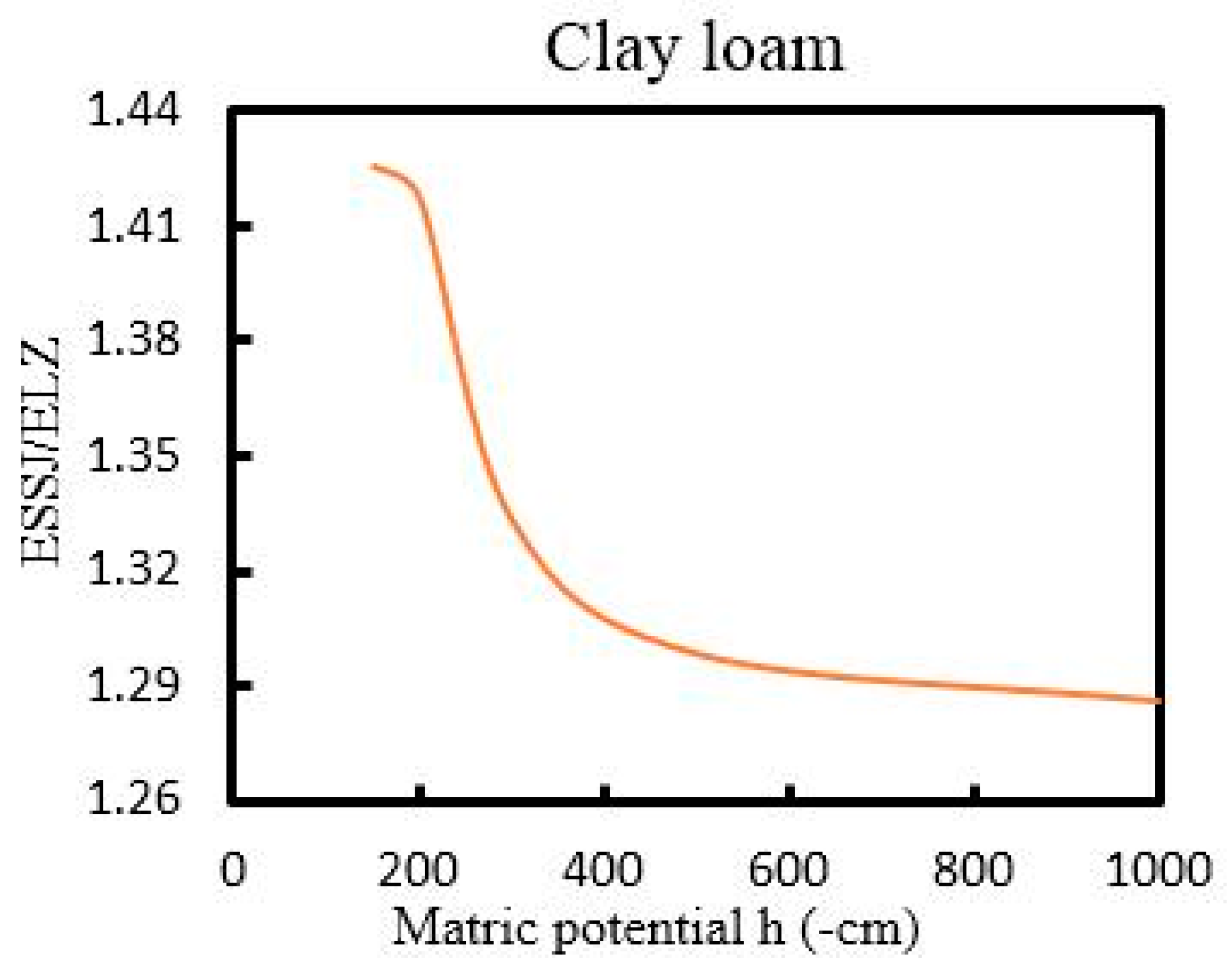
3.2. Results with Brooks–Corey and Modified Gardner Models
3.3. Comparison with Previous Work of Sadeghi et al. [18]
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Chanzy, A.; Bruckler, L. Significance of soil surface moisture with respect to daily bare soil evaporation. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, F.I. Operational estimates of areal evapotranspiration and their significance to the science and practice of hydrology. J. Hydrol. 1983, 66, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbjornsen, H.; Goldsmith, G.R.; Alvarado-Barrientos, M.S.; Rebel, K.; Van Osch, F.P.; Rietkerk, M.; Chen, J.; Gotsch, S.; Tobon, C.; Geissert, D.R.; et al. Ecohydrological advances and applications in plant–water relations research: A review. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 4, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddes, R.A.; de Rooij, G.H.; van Dam, J.C. Unsaturated-Zone Modeling: Progress, Challenges and Applications; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; 364p. [Google Scholar]
- Apollonio, C.; Balacco, G.; Novelli, A.; Tarantino, E.; Piccinni, A.F. Land Use Change Impact on Flooding Areas: The Case Study of Cervaro Basin (Italy). Sustainability 2016, 8, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, A.; Tarantino, E.; Caradonna, G.; Apollonio, C.; Balacco, G.; Piccinni, F. Improving the ANN Classification Accuracy of Landsat Data Through Spectral Indices and Linear Transformations (PCA and TCT) Aimed at LU/LC Monitoring of a River Basin. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications, Beijing, China, 4–7 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dow, C.L.; DeWalle, D.R. Trends in evaporation and Bowen ratio on urbanizing watersheds in eastern United States. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plauborg, F. Evaporation from bare soil in a temperate humid climate—Measurement using micro-lysimeters and time domain reflectometry. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 76, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jury, W.A.; Horton, R. Soil Physics; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Shokri, N.; Salvucci, G.D. Evaporation from porous media in the presence of a water table. Vadose Zone J. 2011, 10, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.A.; Konukcu, F.; Gowing, J.W. Effect of watertable depth on evaporation and salt accumulation from saline groundwater. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2005, 43, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowing, J.W.; Konukcu, F.; Rose, D.A. Evaporative flux from a shallow watertable: The influence of a vapour–liquid phase transition. J. Hydrol. 2006, 321, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Il’ichev, A.T.; Tsypkin, G.G.; Pritchard, D.; Richardson, C.N. Instability of the salinity profile during the evaporation of saline groundwater. J. Fluid Mech. 2008, 614, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, P.; Assouline, S.; Or, D. Characteristic lengths affecting evaporative drying of porous media. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 77, 56309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokri, N.; Lehmann, P.; Or, D. Evaporation from layered porous media. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 45, W10433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Tyler, S.W.; Selker, J.S.; Lunati, I.; Higgins, C.W.; Parlange, M.B. Evaporation from a shallow water table: Diurnal dynamics of water and heat at the surface of drying sand. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4022–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Shokri, N.; Jones, S.B. A novel analytical solution to steady-state evaporation from porous media. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W09516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Tuller, M.; Gohardoust, M.R.; Jones, S.B. Column-scale unsaturated hydraulic conductivity estimates in coarse-textured homogeneous and layered soils derived under steady-state evaporation from a water table. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, P.; Assouline, S.; Or, D. Comment on “Column-scale unsaturated hydraulic conductivity estimates in coarse-textured homogeneous and layered soils derived under steady-state evaporation from a water table” by M. Sadeghi, M. Tuller, MR Gohardoust and SB Jones. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1274–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Tuller, M.; Gohardoust, M.R.; Jones, S.B. Reply to comments on “Column-scale unsaturated hydraulic conductivity estimates in coarse-textured homogeneous and layered soils derived under steady-state evaporation from a water table”[J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1238–1248]. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayek, M. An analytical model for steady vertical flux through unsaturated soils with special hydraulic properties. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.R. Some steady-state solutions of the unsaturated moisture flow equation with application to evaporation from a water table. Soil Sci. 1958, 85, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvucci, G.D. An approximate solution for steady vertical flux of moisture through an unsaturated homogeneous soil. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 3749–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, A.W. Additional solutions for steady-state evaporation from a shallow water table. Soil Sci. 1988, 146, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.H.; Corey, A.T. Hydraulic Properties of Porous Medium; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Bras, R.L. Hydrology: An Introduction to Hydrologic Science; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Burdine, N.T. Relative permeability calculations from pore size distribution data. Int. Pet. Trans. 1953, 198, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, A.W.; Or, D. Soil water concepts. Dev. Agric. Eng. 2007, 13, 27–59. [Google Scholar]
- Haverkamp, R.; Vauclin, M.; Touma, J.; Wierenga, P.J.; Vachaud, G. A comparison of numerical simulation models for one-dimensional infiltration. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formula, Graphs and Mathematical Tables; Dover Publications Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1972; p. 322. [Google Scholar]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, W.R.; Fireman, M. Laboratory studies of evaporation from soil columns in the presence of a water table. Soil Sci. 1958, 85, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hylckama, T.E.A. Evaporation from Vegetated and Fallow Soils. Water Resour. Res. 1966, 2, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M. Dynamics of Soil Water under Non-Isothermal Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Newcastle, Tyne, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M. Water movement through soil in response to water-content and temperature gradients: Evaluation of the theory of Philip and de Vries (1957). J. Eng. Appl. Sci. Pakistan 2000, 19, 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Rijtema, P.E. Soil Moisture Forecasting; University of Wageningen: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Calculation of Steady-State Evaporation for an Arbitrary Matric Potential at Ground Surface. Master’s Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rawls, W.J.; Brakensiek, D.L.; Saxtonn, K.E. Estimation of soil water properties. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1982, 25, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Site/Type | Parameter Value | References |
|---|---|---|
| Chino Clay | N = 2, a = −23.8 cm | [33] |
| Pachappa (fine sandy loam) | N = 3, a = −63.83 cm | [33] |
| Buckeye (fine sand) | N = 5, a = −44.7 cm | [34] |
| Yolo Light Clay | N = 1.77, a = −15.3 cm | [30] |
| L (cm) | 10 | 50 | 100 | 300 | 500 | 1000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chino Clay, Ep/Ks | 3.27 | 0.40 | 0.124 | 0.015 | 0.0056 | <0.0001 |
| Pachappa (fine sandy loam), Ep/Ks | 7.07 | 0.96 | 0.280 | 0.016 | 0.004 | 0.00045 |
| Buckeye (fine sand), Ep/Ks | 4.00 | 0.29 | 0.023 | 0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Yolo Light Clay, Ep/Ks | 2.38 | 0.29 | 0.096 | 0.014 | 0.006 | 0.002 |
| E/Ks Soil | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.0001 | 0.00001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buckeye (fine sand) | 17.8% | 3.9% | 2.0% | 0.4% | 0.04% | 0.004% |
| clay loam | 4.8% | 1.0% | 0.5% | 0.1% | 0.01% | 0.001% |
| silty loam | 9.3% | 2.0% | 1.0% | 0.2% | 0.02% | 0.002% |
| sandy loam | 13.6% | 2.9% | 1.5% | 0.3% | 0.03% | 0.003% |
| coarse sand | 13.6% | 2.9% | 1.5% | 0.3% | 0.03% | 0.003% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhan, H. Calculation of Steady-State Evaporation for an Arbitrary Matric Potential at Bare Ground Surface. Water 2017, 9, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100729
Liu X, Zhan H. Calculation of Steady-State Evaporation for an Arbitrary Matric Potential at Bare Ground Surface. Water. 2017; 9(10):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100729
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xin, and Hongbin Zhan. 2017. "Calculation of Steady-State Evaporation for an Arbitrary Matric Potential at Bare Ground Surface" Water 9, no. 10: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100729
APA StyleLiu, X., & Zhan, H. (2017). Calculation of Steady-State Evaporation for an Arbitrary Matric Potential at Bare Ground Surface. Water, 9(10), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100729






