High Variability Is a Defining Component of Mediterranean-Climate Rivers and Their Biota
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Variability in Abiotic Environmental Conditions
3. Biological Variability in Mediterranean-Climate Rivers
3.1. Population Variability
3.1.1. Macroinvertebrate Populations
3.1.2. Fish Populations
3.2. Community Variability
3.2.1. Macroinvertebrate Communities
3.2.2. Fish Communities
4. Variability Governing Mediterranean River Management
4.1. Biomonitoring in Highly Variable Systems
4.2. Conservation Management in Mediterranean Regions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palmer, M.A.; Hakenkamp, C.C.; Nelson-Baker, K. Ecological Heterogeneity in Streams: Why Variance Matters. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1997, 16, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti-Cecchi, L. The importance of the variance around the mean effect size of ecological processes. Ecology 2003, 84, 2335–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüegg, J.; Chaloner, D.T.; Levi, P.S.; Tank, J.L.; Tiegs, S.D.; Lamberti, G.A. Environmental variability and the ecological effects of spawning Pacific salmon on stream biofilm. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, D.; Andino, P.; Calvez, R.; Cauvy-Fraunié, S.; Espinosa, R.; Dangles, O. Temporal variability in discharge and benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in a tropical glacier-fed stream. Freshw. Sci. 2014, 33, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L.; Cole, J.J.; Findlay, S.E.G.; Fischer, D.T.; Gephart, J.A.; Malcom, H.M.; Pace, M.L.; Rosi-Marshall, E.J. Decadal-scale change in a large-river ecosystem. Bioscience 2014, 64, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Ward, J.V. Implications of Streamflow Variability and Predictability for Lotic Community Structure: A Regional Analysis of Streamflow Patterns. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 46, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgherr, P.; Ward, J.V. Longitudinal and seasonal distribution patterns of the benthic fauna of an alpine glacial stream (Val Roseg, Swiss Alps). Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 1705–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchette, M.L.; Pearson, R.G. Dynamics of habitats and macroinvertebrate assemblages in rivers of the Australian dry tropics. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 742–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Podolak, K.; Grantham, T.E. Restoring mediterranean-climate rivers. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonada, N.; Resh, V.H. Mediterranean-climate streams and rivers: Geographically separated but ecologically comparable freshwater systems. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasith, A.; Resh, V.H. Streams in Mediterranean Climate Regions: Abiotic Influences and Biotic Responses to Predictable Seasonal Events. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1999, 30, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitch, M.J.; Goodfellow, M.; Feirer, S.T. Spatial and temporal variability of rainfall among Mediterranean climate regions across the globe. Water 2016. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Grantham, T.E.; Newburn, D.A.; McCarthy, M.A.; Merenlender, A.M. The role of streamflow and land use in limiting oversummer survival of juvenile steelhead in California streams. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2012, 141, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskoff, R.P. Geomorphological Processes and Characteristic Landforms in the Mediterranean Regions of the World. In Mediterranean Type Ecosystems: Origin and Structure; di Castri, F., Mooney, H.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1973; pp. 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tzoraki, O.; Nikolaidis, N.P. A generalized framework for modeling the hydrologic and biogeochemical response of a Mediterranean temporary river basin. J. Hydrol. 2007, 346, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levick, L.; Fonseca, J.; Goodrich, D.; Hernandez, M.; Semmens, S.; Stromberg, J.; Leidy, R.; Scianni, M.; Guertin, D.P.; Tluczek, M.; et al. The Ecological and Hydrological Significance of Ephemeral and Intermittent Streams in the Arid and Semi-Arid American Southwest; EPA/600/R-08/134; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and USDA/ARS Southwest Watershed Research Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Bonada, N.; Rieradevall, M.; Dallas, H.; Davis, J.; Day, J.; Figueroa, R.; Resh, V.H.; Prat, N. Multi-scale assessment of macroinvertebrate richness and composition in Mediterranean-climate rivers. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 772–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin, J.D.; Bogan, M.T.; Bonada, N.; Ríos-Touma, B.; Lytle, D.A. Seasonality and predictability shape temporal species diversity. Unpublished work. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rieradevall, M.; Bonada, N.; Prat, N. Community structure and water quality in the Mediterranean streams of a natural park (St. Llorenç del Munt, NE Spain). Limnética 1999, 17, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bêche, L.A.; McElravy, E.P.; Resh, V.H. Long-term seasonal variation in the biological traits of benthic-macroinvertebrates in two Mediterranean-climate streams in California, USA. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bêche, L.A.; Connors, P.G.; Resh, V.H.; Merenlender, A.M. Resilience of fishes and invertebrates to prolonged drought in two California streams. Ecography 2009, 32, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, M.F.; Beja, P.; Schlosser, I.J.; Collares-Pereira, M.J. Effects of multi-year droughts on fish assemblages of seasonally drying Mediterranean streams. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1494–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonada, N.; Dolédec, S.; Statzner, B. Taxonomic and biological trait differences of stream macroinvertebrate communities between mediterranean and temperate regions: Implications for future climatic scenarios. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 1658–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershkovitz, Y.; Gasith, A. Resistance, resilience, and community dynamics in mediterranean-climate streams. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, H.F. Ecological status assessment in mediterranean rivers: Complexities and challenges in developing tools for assessing ecological status and defining reference conditions. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resh, V.H.; Bêche, L.A.; Lawrence, J.E.; Mazor, R.D.; McElravy, E.P.; O’Dowd, A.P.; Rudnick, D.; Carlson, S.M. Long-term population and community patterns of benthic macroinvertebrates and fishes in Northern California Mediterranean-climate streams. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettinger, M.D.; Ralph, F.M.; Das, T.; Neiman, P.J.; Cayan, D.R. Atmospheric Rivers, Floods and the Water Resources of California. Water 2011, 3, 445–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-Filled SRTM for the Globe Version 4. Available from the CGIAR-CSI SRTM 90 m Database. 2008. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 17 October 2016).
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Mata, L.J.; Arnell, N.W.; Döll, P.; Jimenez, B.; Oki, T.; Şen, Z.; Shiklomanov, I. The implications of projected climate change for freshwater resources and their management resources and their management. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, B.C.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Wu, S.; Palutikof, J.P. Climate Change and Water. Technical Paper of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC Secretariat: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Döll, P.; Schmied, H.M. How is the impact of climate change on river flow regimes related to the impact on mean annual runoff? A global-scale analysis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 14037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Swain, D.L.; Touma, D. Anthropogenic warming has increased drought risk in California. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3931–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Wang, S.-Y.S.; Gillies, R.R.; Kravitz, B.; Hipps, L.; Rasch, P.J. Increasing water cycle extremes in California and in relation to ENSO cycle under global warming. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dettinger, M.D. Historical and Future Relations Between Large Storms and Droughts in California. San Franc. Estuary Watershed Sci. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupilli, E.; Puig, M.A. Effects of a major flood on the mayfly and stonefly populations in a Mediterranean stream (Matarranya stream, Ebro River basin, North East of Spain). In Research Update on Ephemeroptera and Plecoptera; Gaino, E., Ed.; University of Perugia: Perugia, Italy, 2003; pp. 381–389. [Google Scholar]
- Resh, V.H.; Brown, A.V.; Covich, A.P.; Gurtz, M.E.; Li, H.W.; Minshall, W.G.; Reice, S.R.; Sheldon, A.L.; Wallace, J.B.; Wissmar, R.C. The Role of Disturbance in Stream Ecology. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1988, 7, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resh, V.H. Year-to-year changes in the age structure of a caddisfly population following loss and recovery of a springbrook habitat. Ecography 1992, 15, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feminella, J.W.; Resh, V.H. Hydrologic influences, disturbance, and intraspecific competition in a stream caddisfly population. Ecology 1990, 71, 2083–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rodríguez, M.J.; de Figueroa, J.M.T.; Fenoglio, S.; Bo, T.; Alba-Tercedor, J. Life strategies of 3 Perlodidae species (Plecoptera) in a Mediterranean seasonal stream in southern Europe. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2009, 28, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavert, V.; Zamora-Muñoz, C.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, M.; Fernández-Cortés, A.; Soler, J.J. Climatic conditions, diapause and migration in a troglophile caddisfly. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 1606–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.M.; Magalhães, M.F.; Da Costa, L.M.; Alves, M.J.; Coelho, M.M. Effects of an extreme flash flood on the native fish assemblages across a Mediterranean catchment. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2008, 15, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, C.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Almeida, P.R. Life history of a cyprinid species in non-regulated and regulated rivers from permanent and temporary Mediterranean basins. Ecohydrology 2014, 8, 1137–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woelfle-Erskine, C.; Larsen, L.G.; Carlson, S.M. Abiotic habitat thresholds for salmonid over-summer survival in intermittent streams. Ecosphere 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Magalhães, M.F.; Schlosser, I.J.; Collares-Pereira, M.J. The role of life history in the relationship between population dynamics and environmental variability in two Mediterranean stream fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2003, 63, 300–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorig, R.C.; Marchetti, M.P.; Kopp, G. Spatial and temporal distribution of native fish larvae in seasonal and perennial tributaries of the Sacramento River, CA, USA. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2013, 5060, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, S.M.; Satterthwaite, W.H. Weakened portfolio effect in a collapsed salmon population complex. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwan, J.L.; Carlson, S.M. Fragmentation of an Intermittent Stream During Seasonal Drought: Intra-annual and Interannual Patterns and Biological Consequences. River Res. Appl. 2016, 32, 856–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwan, J.L.; Fernández-Chacón, A.; Buoro, M.; Carlson, S.M. Dry season survival of juvenile salmonids in an intermittent coastal stream. Unpublished work. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Merciai, R. Effects of Global Change on Fish Assemblages in Mediterranean Streams; Universitat de Girona: Catalonia, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Ruiz, A.; Granado-Lorencio, C. Spawning period and migration of three species of cyprinids in a stream with Mediterranean regimen (SW Spain). J. Fish Biol. 1992, 41, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, E.; Sostoa, A. Pattern of movements of adult Barbus haasi in a small Mediterranean stream. J. Fish Biol. 1999, 55, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.P.; Moyle, M.P. Effects of Flow Regime on Fish Assemblages in a California Stream. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.F.; Beja, P.; Magalhães, M.F. Out of pools: Movement patterns of Mediterranean stream fish in relation to dry season refugia. River Res. Appl. 2014, 30, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, M.F.; Beja, P.; Canas, C.; Collares-Pereira, M.J. Functional heterogeneity of dry-season fish refugia across a Mediterranean catchment: The role of habitat and predation. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 1919–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, B.J.; Chester, E.T.; Mitchell, B.D.; Matthews, T.G. Disturbance and the role of refuges in mediterranean climate streams. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaní, A.M.; Sabater, S. Structure and Activity of Rock and Sand Biofilms in a Mediterranean. Ecology 2001, 82, 3232–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, S.; Muñoz, I. Successional dynamics of the phytoplankton in the lower part of the river Ebro. J. Plankton Res. 1990, 12, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornés, E.; Pérez, M.C.; Durán, C.; Sabater, S. Reservoirs override seasonal variability of phytoplankton communities in a regulated Mediterranean river. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 475, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabater, S.; Sabater, F. Longitudinal changes of benthic algal biomass in a mediterranean river during two high production periods. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1992, 124, 475–487. [Google Scholar]
- Guasch, H.; Sabater, S. Seasonal variations in photosynthesis-irradiance reponses by biofilms in Mediterranean streams. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix, D.; García-Berthou, E.; Gascón, S.; Benejam, L.; Tornés, E.; Sala, J.; Benito, J.; Munné, A.; Solà, C.; Sabater, S. Response of community structure to sustained drought in Mediterranean rivers. J. Hydrol. 2010, 383, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyroudi, A.; Chatzinikolaou, Y.; Poirazidis, K.; Lazaridou, M. Do intermittent and ephemeral mediterranean rivers belong to the same river type? Aquat. Ecol. 2009, 43, 465–476. [Google Scholar]
- Buffagni, A.; Erba, S.; Armanini, D.G. The lentic—Lotic character of Mediterranean rivers and its importance to aquatic invertebrate communities. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 72, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, J.C.; Rodríguez-González, P.M.; Dufour, S.; Bendix, J. Riparian vegetation research in Mediterranean-climate regions: Common patterns, ecological processes, and considerations for management. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenda, J.; Gallardo-Mayenco, A. Distribution Patterns, Species Assemblages and Habitat Selection of the Stoneflies (Plecoptera) from Two Mediterranean River Basins in Southern Spain. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 1999, 84, 595–608. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz García, A.; Herrera Grao, A.F.; Ferreras-Romero, M. Distribution of Trichoptera communities in the Hozgarganta catchment (Los Alcornocales Natural Park, SW Spain). Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2006, 91, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntí, T.; Rieradevall, M.; Prat, N. Chironomidae assemblages in reference condition Mediterranean streams: Environmental factors, seasonal variability and ecotypes. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2007, 170, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonada, N.; Rieradevall, M.; Prat, N.; Resh, V.H. Benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages and macrohabitat connectivity in Mediterranean-climate streams of northern California. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2006, 25, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Montoya, M.M.; Suárez, M.L.; Vidal-Abarca, M.R. Seasonal and interannual variability of macroinvertebrate reference communities and its influence on bioassessment in different Mediterranean stream types. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2009, 174, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonada, N.; Rieradevall, M.; Prat, N. Macroinvertebrate community structure and biological traits related to flow permanence in a Mediterranean river network. Hydrobiologia 2007, 589, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemiadou, V.; Statiri, X.; Brouziotis, T.; Lazaridou, M. Ecological quality of small mountainous Mediterranean streams (river type R-M4) and performance of the European intercalibration metrics. Hydrobiologia 2008, 605, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonada, N.; Zamora-Muñoz, C.; Rieradevall, M.; Prat, N. Ecological and historical filters constraining spatial caddisfly distribution in Mediterranean rivers. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Roger, E.M.; Sánchez-Montoya, M.D.M.; Cid, N.; Erba, S.; Karaouzas, I.; Verkaik, I.; Rieradevall, M.; Gómez, R.; Suárez, M.L.; Vidal-abarca, M.R.; et al. Spatial scale effects on taxonomic and biological trait diversity of aquatic macroinvertebrates in Mediterranean streams. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2013, 183, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arscott, D.B.; Larned, S.; Scarsbrook, M.R.; Lambert, P. Aquatic invertebrate community structure along an intermittence gradient: Selwyn River, New Zealand. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 530–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datry, T. Benthic and hyporheic invertebrate assemblages along a flow intermittence gradient: Effects of duration of dry events. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, C.; Bonada, N.; Boulton, A.J.; Hugueny, B.; Larned, S.T.; Vander Vorste, R.; Datry, T. Invertebrate assemblage responses and the dual roles of resistance and resilience to drying in intermittent rivers. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 78, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, A.F.; Lawrence, J.E.; Bonada, N. Vulnerability of stream biota to climate change in mediterranean climate regions: A synthesis of ecological responses and conservation challenges. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, R.D.; Purcell, A.H.; Resh, V.H. Long-Term variability in bioassessments: A twenty-year study from two northern california streams. Environ. Manag. 2009, 43, 1269–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, G.; Bonada, N.; Prat, N. Long-term effects of climatic-hydrological drivers on macroinvertebrate richness and composition in two Mediterranean streams. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 1313–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáinz-Bariáin, M.; Zamora-Muñoz, C.; Soler, J.J.; Bonada, N.; Sáinz-Cantero, C.E.; Alba-Tercedor, J. Changes in Mediterranean high mountain Trichoptera communities after a 20-year period. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 78, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langton, P.H.; Casas, J. Changes in chironomid assemblage composition in two Mediterranean mountain streams over a period of extreme hydrological conditions. Hydrobiologia 1998, 390, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña, V.; Muñoz, I.; Giorgi, A.; Omella, M.; Sabater, F.; Sabater, S. Drought and postdrought recovery cycles in an intermittent Mediterranean stream: Structural and functional aspects. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bêche, L.A.; Resh, V.H. Short-term climatic trends affect the temporal variability of macroinvertebrates in California “Mediterranean” streams. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 2317–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.M.; Cowx, I.G.; Coelho, M.M. Seasonal changes in fish community structure of intermittent streams in the midle reaches of the Guadian basin, Portugal. J. Fish Biol. 1999, 54, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, A.F.; Cowx, I.G.; Collares-Pereira, M.J. Spatial modelling of freshwater fish in semi-arid river systems: A tool for conservation. River Res. Appl. 2002, 18, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.D.; De Sostoa, A.; Freeman, M.C.; Lobon-Cerviá, J. Microhabitat Use in a Mediterranean Riverine Fish Assemblage: Fishes of the Lower Matarraña. Oecologia 1987, 73, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.D.; De Sostoa, A.; Freeman, M.C.; Lobon-Cerviá, J. Microhabitat Use in a Mediterranean Riverine Fish Assemblage: Fishes of the Upper Matarraña. Oecologia 1987, 73, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habit, E.; Belk, M.; Victoriano, P.; Jaque, E. Spatio-temporal distribution patterns and conservation of fish assemblages in a Chilean coastal river. Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 16, 3179–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, C.M.; Ferreira, T.F.; Almeida, P.R. Fish assemblages in non-regulated and regulated rivers from permanent and temporary Iberian systems. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 1042–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matono, P.; Bernardo, J.M.; Oberdorff, T.; Ilhéu, M. Effects of natural hydrological variability on fish assemblages in small Mediterranean streams: Implications for ecological assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, J.M.; Ilhéu, M.; Matono, P.; Costa, A.M. Interannual variation of fish assemblage structure in a Mediterranean river: Implications of streamflow on the dominance of native or exotic species. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiernan, J.; Moyle, P.; Crain, P. Restoring native fish assemblages to a regulated California stream using the natural flow regime concept. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyle, P.B.; Marchetti, M.P.; Baldrige, J.; Taylor, T.L. Fish Health and Diversity: Justifying Flows for a California Stream. Fisheries 1998, 23, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Martí, E.; García-Berthou, E.; Sabater, S.; Tomanova, S.; Muñoz, I. Comparing fish assemblages and trophic ecology of permanent and intermittent reaches in a Mediterranean stream. Hydrobiologia 2010, 657, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.J.; Merciai, R.; Benejam, L.; Sabater, S.; García-Berthou, E. Small Weirs, Big Effects: Disruption of Water Temperature Regimes with Hydrological Alteration in a Mediterranean Stream. River Res. Appl. 2016, 32, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benejam, L.; Angermeier, P.L.; Munné, A.; García-Berthou, E. Assessing effects of water abstraction on fish assemblages in Mediterranean streams. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fronseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonada, N.; Prat, N.; Resh, V.H.; Statzner, B. Developments in Aquatic Insect Biomonitoring I: A Comparative Analysis of Recent Approaches. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 495–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hering, D.; Johnson, R.K.; Kramm, S.; Schmutz, S.; Szoszkiewicz, K.; Verdonschot, P.F.M. Assessment of European streams with diatoms, macrophytes, macroinvertebrates and fish: A comparative metric-based analysis of organism response to stress. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 1757–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2000, L327, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, R.C.; Norris, R.H.; Reynoldson, T.B. Bioassessment of Freshwater Ecosystems. Using the Reference Condition Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Stoddard, J.L.; Larsen, D.P.; Hawkins, C.P.; Johnson, R.K.; Norris, R.H. Setting expectations for the ecological conidition of streams: The concept of refernce condition. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B. The Water Framework Directive: Total environment or political compromise? Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munné, A.; Prat, N. Effects of Mediterranean climate annual variability on stream biological quality assessment using macroinvertebrate communities. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Montoya, M.M.; Vidal-Abarca, M.R.; Puntí, T.; Poquet, J.M.; Prat, N.; Rieradevall, M.; Alba-Tercedor, J.; Zamora-Muñoz, C.; Toro, M.; Robles, S.; et al. Defining criteria to select reference sites in Mediterranean streams. Hydrobiologia 2009, 619, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunde, K.B.; Cover, M.R.; Mazor, R.D.; Sommers, C.A.; Resh, V.H. Identifying reference conditions and quantifying biological variability within benthic macroinvertebrate communities in perennial and non-perennial northern california streams. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feio, M.J.; Ferreira, J.; Buffagni, A.; Erba, S.; Dörflinger, G.; Ferréol, M.; Munné, A.; Prat, N.; Tziortzis, I.; Urbanič, G. Comparability of ecological quality boundaries in the Mediterranean basin using freshwater benthic invertebrates. Statistical options and implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, M.; Dallas, H.F. Bioassessment in ephemeral rivers: Constraints and challenges in applying macroinvertebrate sampling protocols. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 38, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, S.E. Biological monitoring of water quality in Australia: Workshop summary and future directions. Aust. J. Ecol. 1995, 20, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.C.; Norris, R.H. Biological assessment of river quality: Development of AUSRIVAS models and outputs. In Assessing the biological quality of fresh waters: RIVPACS and other techniques. In Proceedings of the International Workshop, Oxford, UK, 16–18 September 1997; pp. 125–142.
- Pennifold, M. Ecological Condition of Streams in South-West Forests; Department of Environment and Conservation, The Government of Western Australia; Information Sheet 63; 2013. Available online: https://www.dpaw.wa.gov.au/images/ScienceInfo63.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2016).
- Cid, N.; Prat, N.; Gallart, F.; Latron, J.; Llorens, P.; Rieradevall, M.; Munné, A.; Solà, C.; Bardina, M.; Estrela, T.; et al. Deliverable 7: A Report of Methods Used Until Now by Water Agencies in the River Basin Management Plans; EU Project LIFE+ TRIVERS (LIFE13 ENV/ES/000341); Universitat de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tal, A.; Al Khateeb, N.; Nagouker, N.; Akerman, H.; Diabat, M.; Nassar, A.; Angel, R.; Sadah, M.A.; Hershkovitz, Y.; Gasith, A.; et al. Chemical and biological monitoring in ephemeral and intermittent streams: A study of two transboundary Palestinian–Israeli watersheds. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2010, 8, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, R.; Bonada, N.; Guevara, M.; Pedreros, P.; Correa-Araneda, F.; Díaz, M.E.; Ruiz, V.H. Freshwater biodiversity and conservation in mediterranean climate streams of Chile. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, N.; Gallart, F.; Von Schiller, D.; Polesello, S.; García-Roger, E.M.; Latron, J.; Rieradevall, M.; Llorens, P.; Barberá, G.G.; Brito, D.; et al. the Mirage Toolbox: An Integrated Assessment Tool for Temporary Streams. River Res. Appl. 2014, 30, 1318–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, R.D.; Stein, E.D.; Ode, P.R.; Schiff, K. Integrating intermittent streams into watershed assessments: Applicability of an index of biotic integrity. Freshw. Sci. 2014, 33, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, A.L.; von Schiller, D.; Tockner, K.; Marshall, J.C.; Bunn, S.E. When the river runs dry: Human and ecological values of dry riverbeds. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Montoya, M.D.M.; von Schiller, D.; Ruhí, A.; Pechar, G.S.; Proia, L.; Miñano, J.; Vidal-Abarca, M.R.; Suárez, M.L.; Tockner, K. Responses of ground-dwelling arthropods to surface flow drying in channels and adjacent habitats along Mediterranean streams. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uys, M.C.; O’Keeffe, J.H. Simple Words and Fuzzy Zones: Early Directions for Temporary River Research in South Africa. Environ. Manag. 1997, 21, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallart, F.; Prat, N.; García-Roger, E.M.; Latron, J.; Rieradevall, M.; Llorens, P.; Barberá, G.G.; Brito, D.; De Girolamo, A.M.; Lo Porto, A.; et al. A novel approach to analysing the regimes of temporary streams in relation to their controls on the composition and structure of aquatic biota. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3165–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallart, F.; Llorens, P.; Latron, J.; Cid, N.; Rieradevall, M.; Prat, N. Validating alternative methodologies to estimate the regime of temporary rivers when flow data are unavailable. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LIFE+ TRIVERS (LIFE13 ENV/ES/000341). Implementing the Water Framework Directive to Temporary Rivers: Tools for the Assessment of Their Ecological Status. Available online: www.lifetrivers.eu (accessed on 15 September 2016).
- Larsen, S.; Mancini, L.; Pace, G.; Scalici, M.; Tancioni, L. Weak Concordance between Fish and Macroinvertebrates in Mediterranean Streams. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermoso, V.; Clavero, M. Threatening processes and conservation management of endemic freshwater fish in the Mediterranean basin: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyle, P.B.; Katz, J.V.E.; Quiñones, R.M. Rapid decline of California’s native inland fishes: A status assessment. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.K.; Klausmeyer, K.R.; Fesenmyer, K.A.; Furnish, J.; Gardali, T.; Grantham, T.E.; Katz, J.V.E.; Kupferberg, S.; McIntyre, P.; Moyle, P.B.; et al. Patterns of freshwater species richness, endemism, and vulnerability in California. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrizo, S.F.; Lengyel, S.; Kapusi, F.; Szabolcs, M.; Kasperidus, H.D.; Scholz, M.; Markovic, D.; Freyhof, J.; Cid, N.; Cardoso, A.C.; et al. Critical catchments for freshwater biodiversity conservation in Europe: Identification, prioritisation and gap-analysis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, T.E.; Figueroa, R.; Prat, N. Water management in mediterranean river basins: A comparison of management frameworks, physical impacts, and ecological responses. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 451–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Morán-Tejeda, E.; Zabalza, J. Recent trends in Iberian streamflows (1945–2005). J. Hydrol. 2012, 414, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrone, K.C.; Hughes, J.D.; Van Niel, T.G.; Silberstein, R.P. Streamflow decline in southwestern Australia, 1950–2008. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrongiello, J.R.; Beatty, S.J.; Bennett, J.C.; Crook, D.A.; Ikedife, D.N.E.N.; Kennard, M.J.; Kerezsy, A.; Lintermans, M.; McNeil, D.G.; Pusey, B.J.; et al. Climate change and its implications for Australia’s freshwater fish. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1082–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandecasteele, I.; Bianchi, A.; Batista e Silva, F.; Lavalle, C.; Batelaan, O. Mapping current and future European public water withdrawals and consumption. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivelli, A.J. Anaecypris Hispanica. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2006: e.T1199A3318827. 2006. Available online: http://www.iucnredlist.org/details/1199/0 (accessed on 13 October 2016).
- Grantham, T.E.; Fesenmyer, K.A.; Peek, R.; Holmes, E.; Quiñones, R.M.; Bell, A.; Santos, N.; Howard, J.K.; Viers, J.H.; Moyle, P.B. Missing the Boat on Freshwater Fish Conservation in California. Conserv. Lett. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, V.; Linke, S.; Prenda, J. Identifying priority sites for the conservation of freshwater fish biodiversity in a Mediterranean basin with a high degree of threatened endemics. Hydrobiologia 2009, 623, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, V.; Ward, D.P.; Kennard, M.J. Prioritizing refugia for freshwater biodiversity conservation in highly seasonal ecosystems. Divers. Distrib. 2013, 19, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, T.E.; Viers, J.H.; Moyle, P.B. Systematic screening of dams for environmental flow assessment and implementation. Bioscience 2014, 64, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, L.; Schmidt-Kloiber, A.; Grenouillet, G.; Graf, W. A trait-based approach to assess the vulnerability of European aquatic insects to climate change. Hydrobiologia 2013, 721, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, D.; Carrizo, S.; Freyhof, J.; Cid, N.; Lengyel, S.; Scholz, M.; Kasperdius, H.; Darwall, W. Europe’s freshwater biodiversity under climate change: Distribution shifts and conservation needs. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, P.A.; Oberdorff, T.; Cornu, J.F.; Beauchard, O.; Brosse, S.; Dürr, H.H.; Grenouillet, G.; Leprieur, F.; Tisseuil, C.; Zaiss, R.; et al. A scenario for impacts of water availability loss due to climate change on riverine fish extinction rates. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, T.E.; Merenlender, A.M.; Resh, V.H. Climatic influences and anthropogenic stressors: An integrated framework for streamflow management in Mediterranean-climate California, U.S.A. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merenlender, A.M.; Matella, M.K. Maintaining and restoring hydrologic habitat connectivity in mediterranean streams: An integrated modeling framework. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Brown, C.M.; Grantham, T.E.; Matthews, J.H.; Palmer, M.A.; Spence, C.M.; Wilby, R.L.; Haasnoot, M.; Mendoza, G.F.; Dominique, K.C.; et al. Sustainable water management under future uncertainty with eco-engineering decision scaling. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, P.A.; Cornu, J.-F.; Hugueny, B.; Oberdorff, T. Freshwater Fish Extinction Rates due to Water Availability Loss from Climate Change. Accessed through the Global Freshwater Biodiversity Atlas. 2013. Available online: http://atlas.freshwaterbiodiversity.eu (accessed on 17 October 2016).
- Lawrence, J.E.; Lunde, K.B.; Mazor, R.D.; Beche, L.A.; McElravy, E.P.; Resh, V.H. Long-term macroinvertebrate responses to climate change: Implications for biological assessment in mediterranean-climate streams. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 1424–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
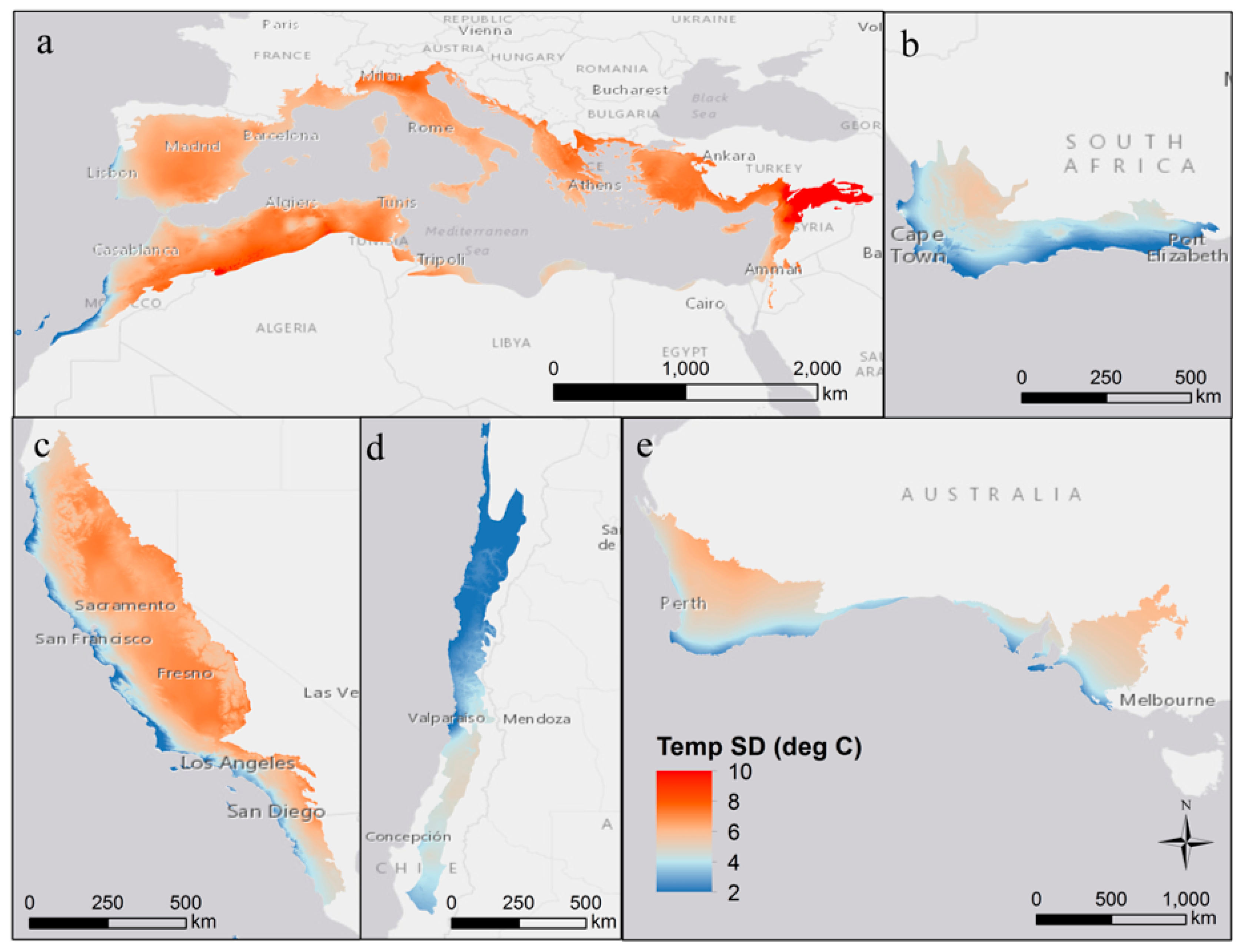
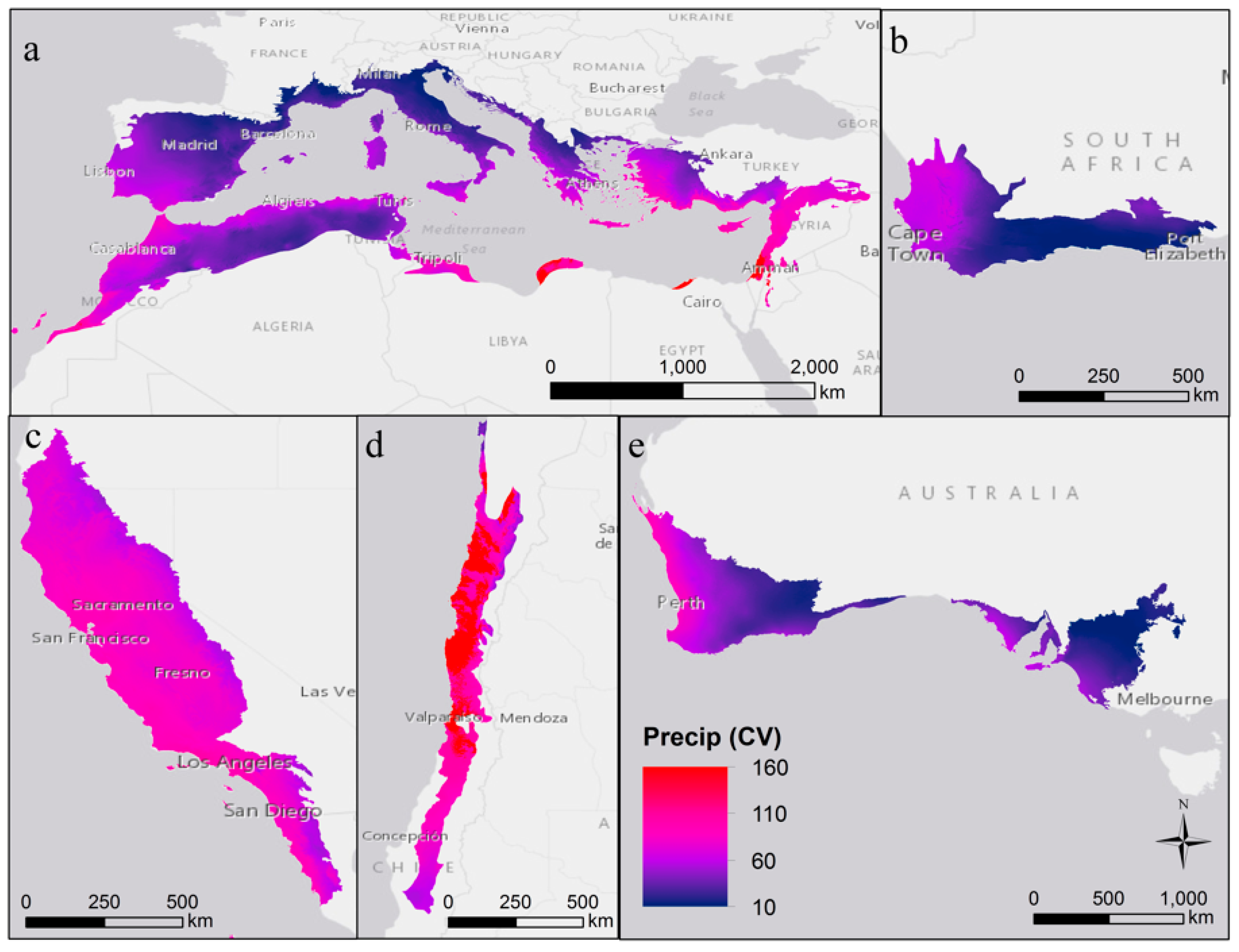


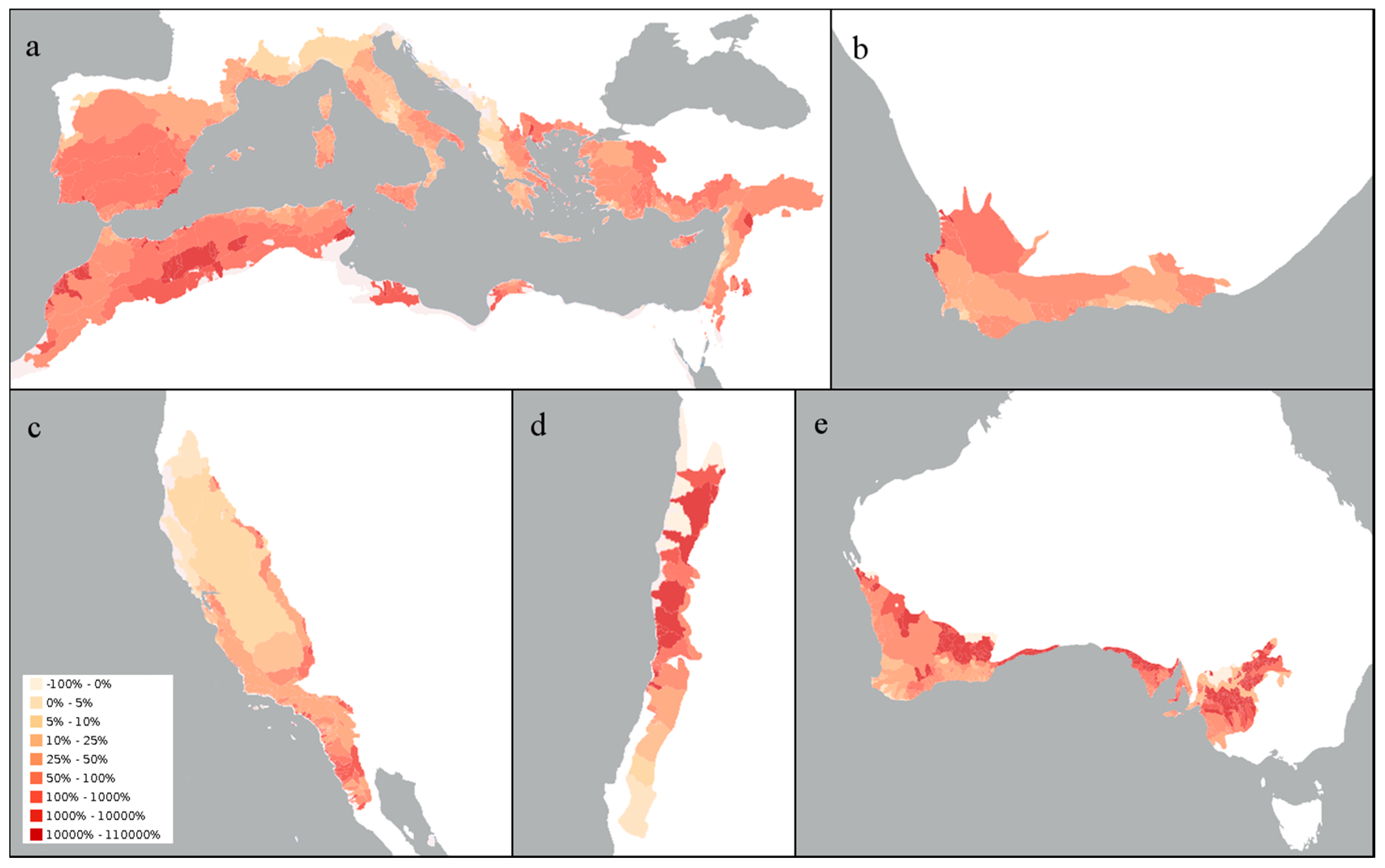
| Region | Mediterranean Basin | California | Chile | Australia | South Africa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | 2,137,100 | 324,900 | 148,400 | 791,300 | 123,100 |
| Elevation (mean ± SD m.a.s.l.) | 640 ± 490 | 800 ± 580 | 980 ± 580 | 200 ± 185 | 530 ± 461 |
| Mean temperature (mean ± SD °C) | 15 ± 3 | 13 ± 4 | 13 ± 3 | 17 ± 2 | 16 ± 2 |
| Mean min. temperature 1 (mean ± SD °C) | 2 ± 3 | 0 ± 4 | 3 ± 4 | 5 ± 1 | 4 ± 2 |
| Mean max. temperature 2 (mean ± SD °C) | 31 ± 4 | 30 ± 5 | 24 ± 4 | 32 ± 3 | 28 ± 3 |
| Annual precipitation (mean ± SD mm) | 560 ± 250 | 700 ± 410 | 420 ± 520 | 390 ± 165 | 430 ± 200 |
| Study and Region | Period Analyzed | Sampling Sites | Hydrological Regime and Available Stream Characteristics | Community Metrics | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [20] California | 1977–1983 (6 years) | 1 | Perennial, spring Stream order = 3 | Richness H’ | 33.2 23.9 |
| 1 | Perennial, summer Stream order = 3 | Richness H’ | 22.2 17.9 | ||
| 1985–2003 (18 years) | 1 | Non-perennial, spring Stream order = 1 | Richness H’ | 21.3 15.4 | |
| 1 | Non-perennial, summer Stream order = 1 | Richness H’ | 22.6 25.4 | ||
| [84] Mediterranean Basin | 2002–2003 (1 year) | 1 | Non-perennial, siliceous | Richness H’ | 7.6 12.2 |
| [80] California | 1984–2003 (20 years) | 2 | Perennial, spring | Richness EPT IBI | 19–26 24–30 24–26 |
| 1 | Perennial, summer | Richness EPT IBI | 23 51 42 | ||
| 2 | Non-perennial, spring | IBI Richness EPT | 22–25 22–29 21–40 | ||
| [71] Mediterranean Basin | 2003–2005 (3 years) | 6 | Perennial, calcareous Mean stream order = 1.7 | Richness H’ EPT IBMWP ICM-11 | 15.3 18.9 16.8 8.7 24.4 |
| 8 | Perennial, siliceous Mean stream order = 1.3 | Richness H’ EPT IBMWP ICM-11 | 7.7 17.5 7.4 7.2 5.6 | ||
| [81] Mediterranean Basin | 1995–2008 (13 years) | 1 | Perennial, spring calcareous dry | EPT | 21.6 |
| 1 | Perennial, spring, calcareous wet | EPT | 25.2 |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cid, N.; Bonada, N.; Carlson, S.M.; Grantham, T.E.; Gasith, A.; Resh, V.H. High Variability Is a Defining Component of Mediterranean-Climate Rivers and Their Biota. Water 2017, 9, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010052
Cid N, Bonada N, Carlson SM, Grantham TE, Gasith A, Resh VH. High Variability Is a Defining Component of Mediterranean-Climate Rivers and Their Biota. Water. 2017; 9(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleCid, Núria, Núria Bonada, Stephanie M. Carlson, Theodore E. Grantham, Avital Gasith, and Vincent H. Resh. 2017. "High Variability Is a Defining Component of Mediterranean-Climate Rivers and Their Biota" Water 9, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010052
APA StyleCid, N., Bonada, N., Carlson, S. M., Grantham, T. E., Gasith, A., & Resh, V. H. (2017). High Variability Is a Defining Component of Mediterranean-Climate Rivers and Their Biota. Water, 9(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010052





