Source Apportionment of Annual Water Pollution Loads in River Basins by Remote-Sensed Land Cover Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Long-Term Dataset
2.2. Estimating Water Poolution Loads from Different Land Cover Classifications by a Modified Empirical Model
3. Results
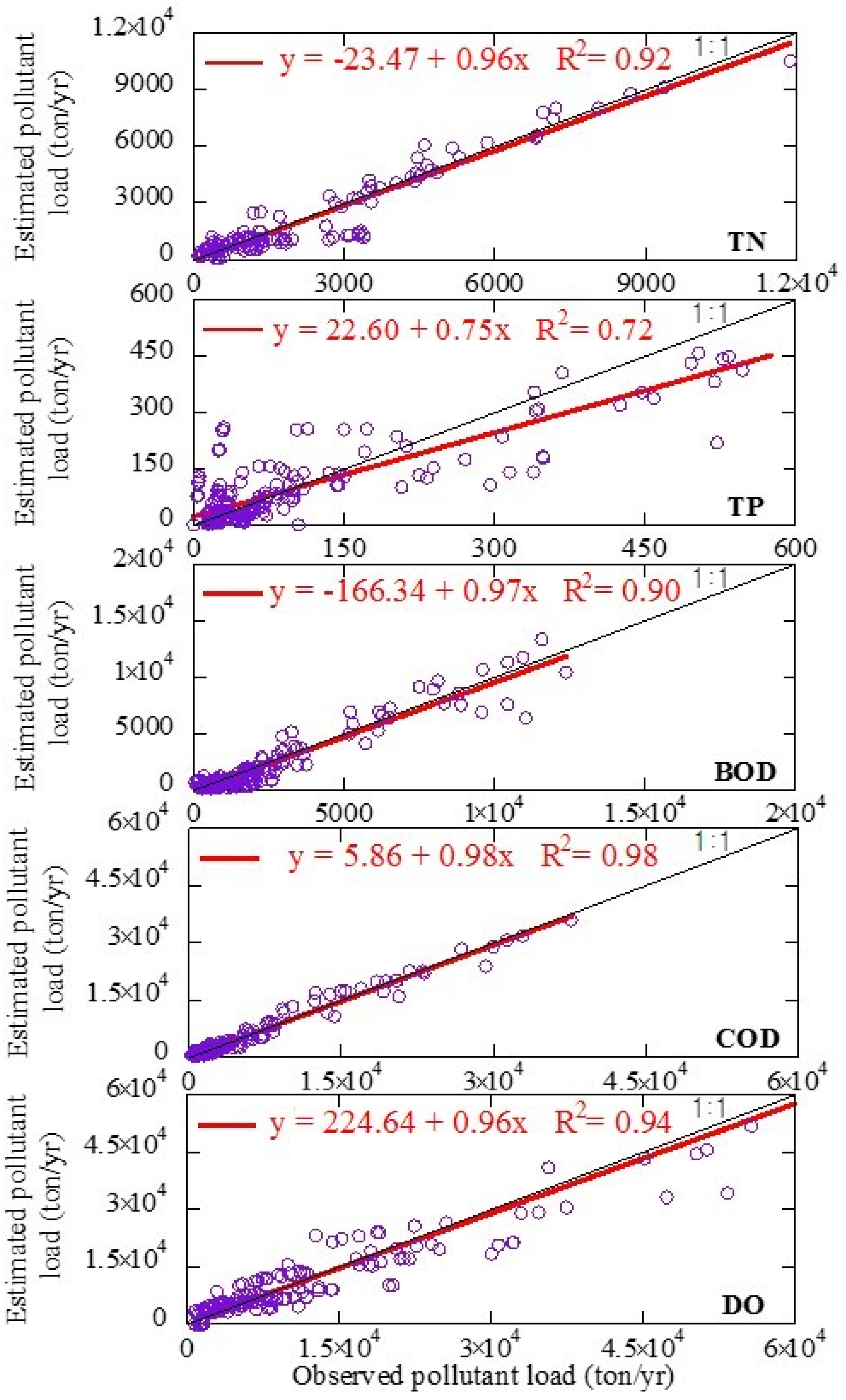
3.1. Model Calibration (1994–1999) and Validation (2000–2004)
3.2. Spatial Comparison of Water Pollution Loads in the 30 Rivers
3.3. Long-Term Variation in Water Pollution Loads Estimated from Different Sources
4. Discussion
4.1. Model Advantage Compared with Conventional Method
4.2. Problems of Water Pollution Loads
4.3. Model Limitation
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Changnon, S.A.; Demissie, M. Detection of changes in streamflow and floods resulting from climate fluctuations and land use-drainage changes. Clim. Chang. 1996, 32, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Wang, Y.; Takase, K.; Mouri, G.; Razafindrabe, B.H. Estimating land use impacts on regional scale urban water balance and groundwater recharge. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 1863–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Nover, D.; Yang, G.; Chen, W.; Meng, H.; Zou, S.; Liu, C. Water Quality Assessment and Pollution Source Identification of the Eastern Poyang Lake Basin Using Multivariate Statistical Methods. Sustainability 2016, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, N.J.; Yates, A.G. Agricultural Best Management Practice Abundance and Location does not Influence Stream Ecosystem Function or Water Quality in the Summer Season. Water 2015, 7, 6861–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoye, E.; Machiwa, J.F. The influence of land-use patterns in the Ruvu river watershed on water quality in the river system. Phys. Chem. Earth A/B/C 2004, 29, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliva, L.; Williams, D.D. Buffer zone versus whole catchment approaches to studying land use impact on river water quality. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3462–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Takara, K.; He, B.; Luo, P.; Nover, D.; Yamashiki, Y. Spatial and temporal trends in estimates of nutrient and suspended sediment loads in the Ishikari River, Japan, 1985 to 2010. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Takara, K.; Luo, P.; Nover, D.; Sahu, N.; Yamashiki, Y. Spatiotemporal evaluation of water quality incidents in Japan between 1996 and 2007. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitzinger, S.P.; Kroeze, C. Global distribution of nitrous oxide production and N inputs in freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1998, 12, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L.; Beighley, R.E.; Thompson, L.C.; Brooks, S.; Nilsson, C.; Pinay, G.; Naiman, R.J. Effects of land cover on stream ecosystems: Roles of empirical models and scaling issues. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.E.; Rabalais, N.N. Linking landscape and water quality in the Mississippi River basin for 200 years. Bioscience 2003, 53, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.V.; Swaney, D.P.; Buddemeier, R.W.; Scarsbrook, M.R.; Weatherhead, M.A.; Humborg, C.; Eriksson, H.; Hannerz, F. River nutrient loads and catchment size. Biogeochemistry 2005, 75, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.J.; Meyer, J.L. Streams in the urban landscape. In Urban Ecology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 207–231. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Oki, T.; Kanae, S.; Mouri, G.; Kodama, K.; Komori, D.; Seto, S. Integrated biogeochemical modelling of nitrogen load from anthropogenic and natural sources in Japan. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 2325–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Kanae, S.; Oki, T.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Yamashiki, Y.; Takara, K. Assessment of global nitrogen pollution in rivers using an integrated biogeochemical modeling framework. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2573–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, E.W.; Goodale, C.L.; Jaworski, N.A.; Howarth, R.W. Anthropogenic nitrogen sources and relationships to riverine nitrogen export in the northeastern USA. In The Nitrogen Cycle at Regional to Global Scales; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 137–169. [Google Scholar]
- Sivertun, Å.; Prange, L. Non-point source critical area analysis in the Gisselö watershed using GIS. Environ. Model. Softw. 2003, 18, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Oki, T.; Sun, F.; Komori, D.; Kanae, S.; Wang, Y.; Kim, H.; Yamazaki, D. Estimating monthly total nitrogen concentration in streams by using artificial neural network. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, L.; Liu, Q.; Peng, Q.; Kang, M. Impacts of Land Use on Surface Water Quality in a Subtropical River Basin: A Case Study of the Dongjiang River Basin, Southeastern China. Water 2015, 7, 4427–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Yoshizawa, K.; Magara, Y. Non-point pollution of Ishikari river, Hokkaido, Japan. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kimura, S.D. Creation of an Eco-Balance Model to Assess Environmental Risks Caused by Nitrogen Load in a Basin-Agroecosystem. Ph.D. Thesis, Hokkaido University, Hokkaido, Japan, 25 March 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, S.D.; Hatano, R. An eco-balance approach to the evaluation of historical changes in nitrogen loads at a regional scale. Agric. Syst. 2007, 94, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.L.; He, B.; Takara, K.; Luo, P.P.; Nover, D.; Hu, M.C. Modeling suspended sediment sources and transport in the Ishikari River basin, Japan, using SPARROW. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, K.; Yasuoka, Y. Mapping the potential annual total nitrogen load in the river basins of Japan with remotely sensed imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3091–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Oki, K.; Wang, Y.; Oki, T. Using remotely sensed imagery to estimate potential annual pollutant loads in river basins. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, H.; Takeuchi, W. Sawada and Takeuchi Laboratory. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda, H.; Fukue, K.; Cho, K.; Matsuoka, R.; Hashimoto, T.; Nemoto, T.; Tokunaga, M.; Tanba, S.; Takagi, M. Development of a software package for ADEOS and NOAA data analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–10 July 1998; Volume 2, pp. 674–676.
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation systems in the great plains with ERTS. In Proceedings of the Third Earth Resources Technology Satellite-1 Symposium, NASA SP-351, Washington, DC, USA, 14 December 1974; pp. 309–317.
- Dubes, R.C.; Jain, A.K. Algorithms for Clustering Data Prentice-Hall; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective; Prentice Hall: Old Tappan, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bolboaca, S.; Jäntschi, L. Pearson versus Spearman, Kendall’s tau correlation analysis on structure-activity relationships of biologic active compounds. Leonardo J. Sci. 2006, 5, 179–200. [Google Scholar]
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A simplex method for function minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H. Numerical Recipes 3rd Edition: The Art of Scientific Computing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, H.; Kashiwagi, N.; Ninomiya, K.; Ogura, H.; Kawai, T. Changes in the State of Water Pollution in Tokyo Bay since 1980-Trend analysis of water quality using monitoring data obtained by Local Governments. Annu. Rep. Tokyo Metrop. Res. Inst. Environ. Prot. 2005, 2005, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
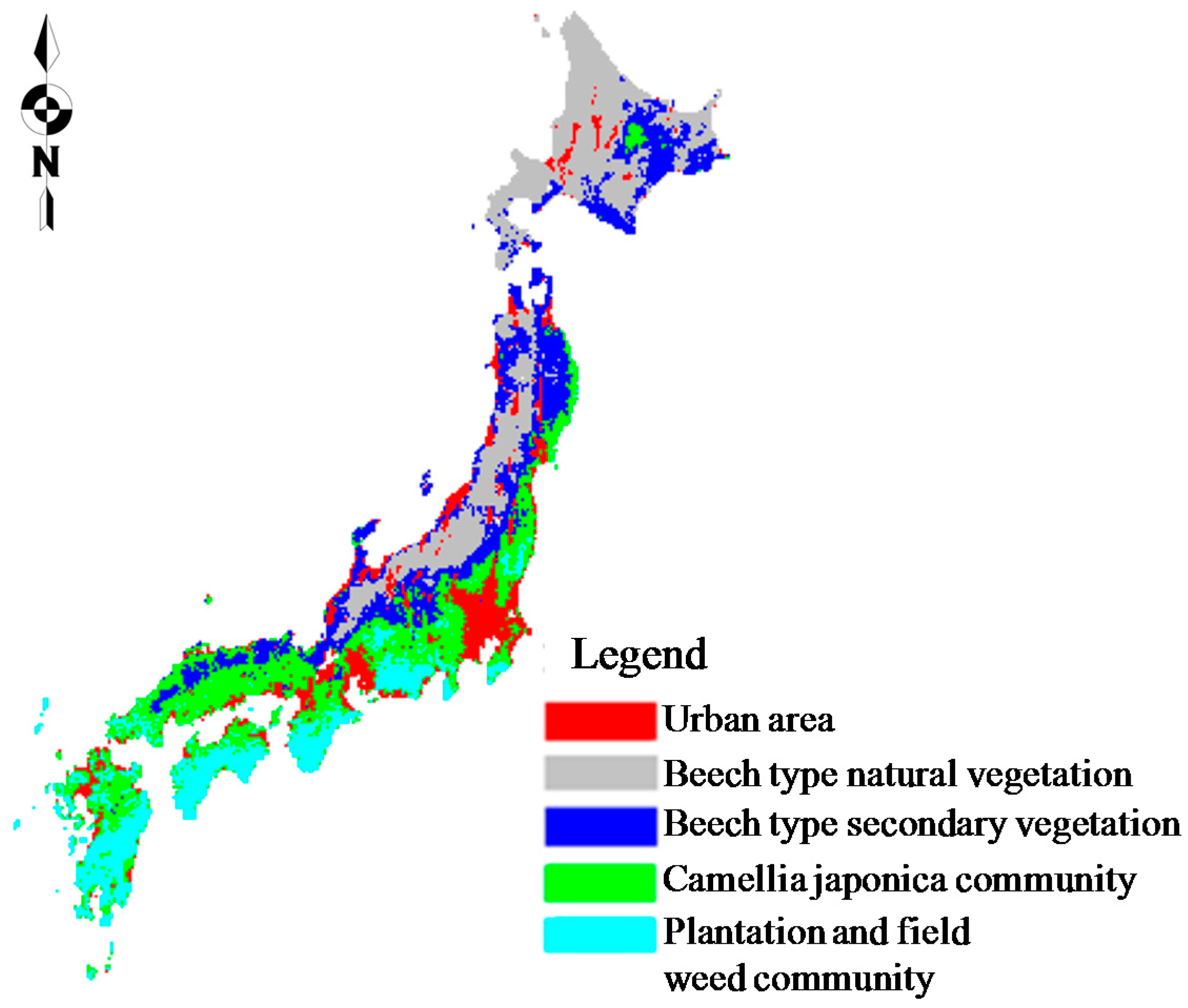
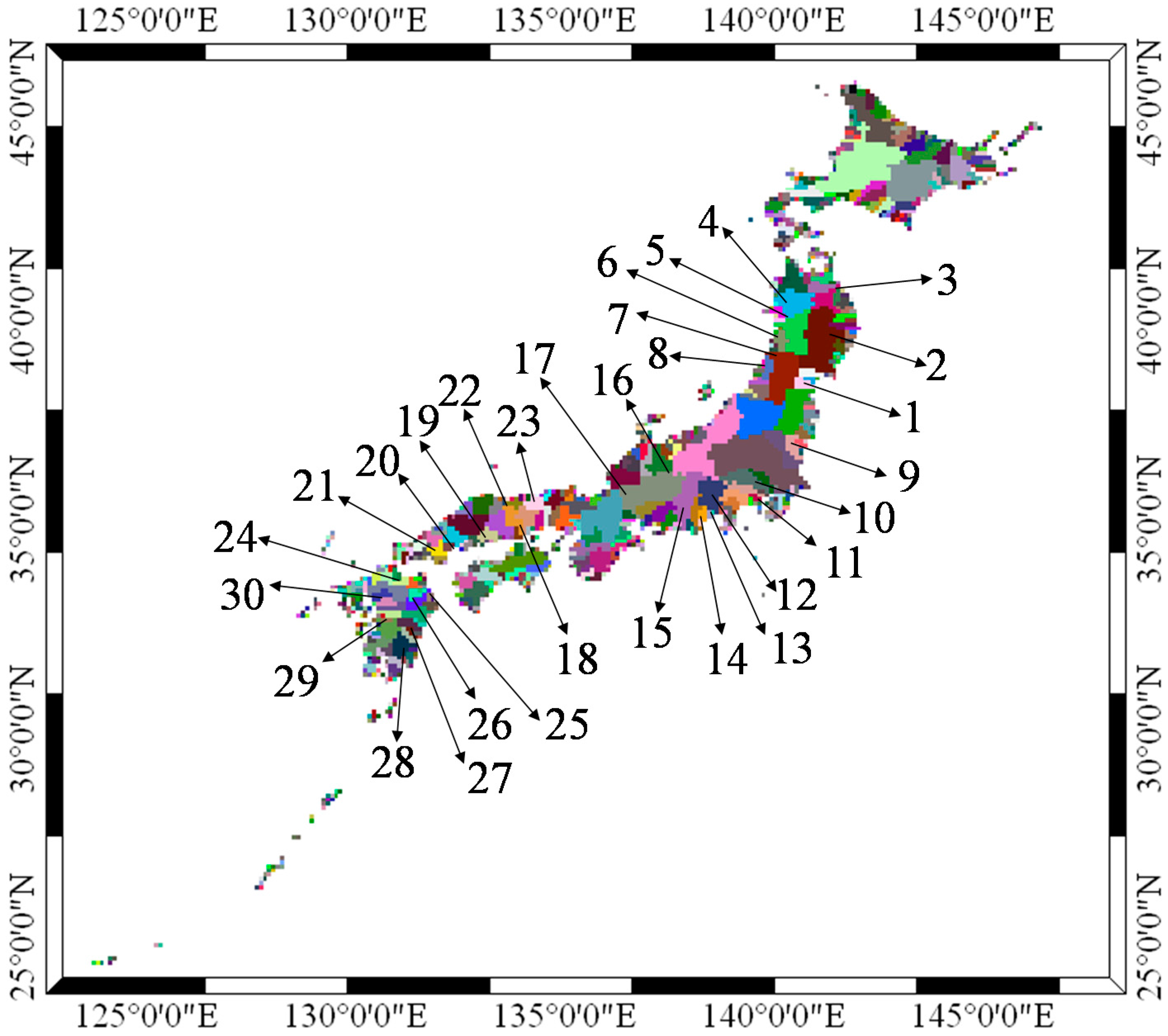
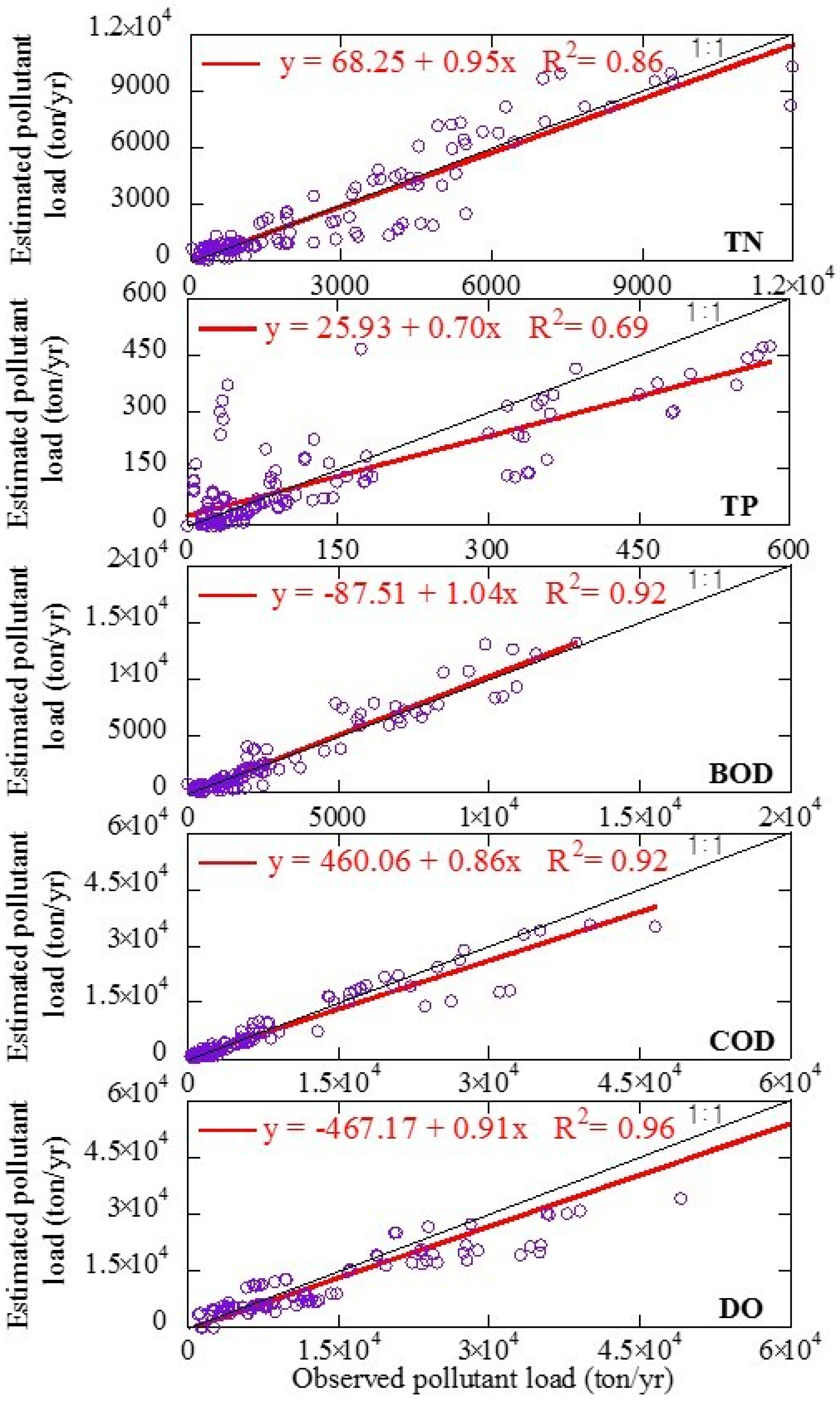
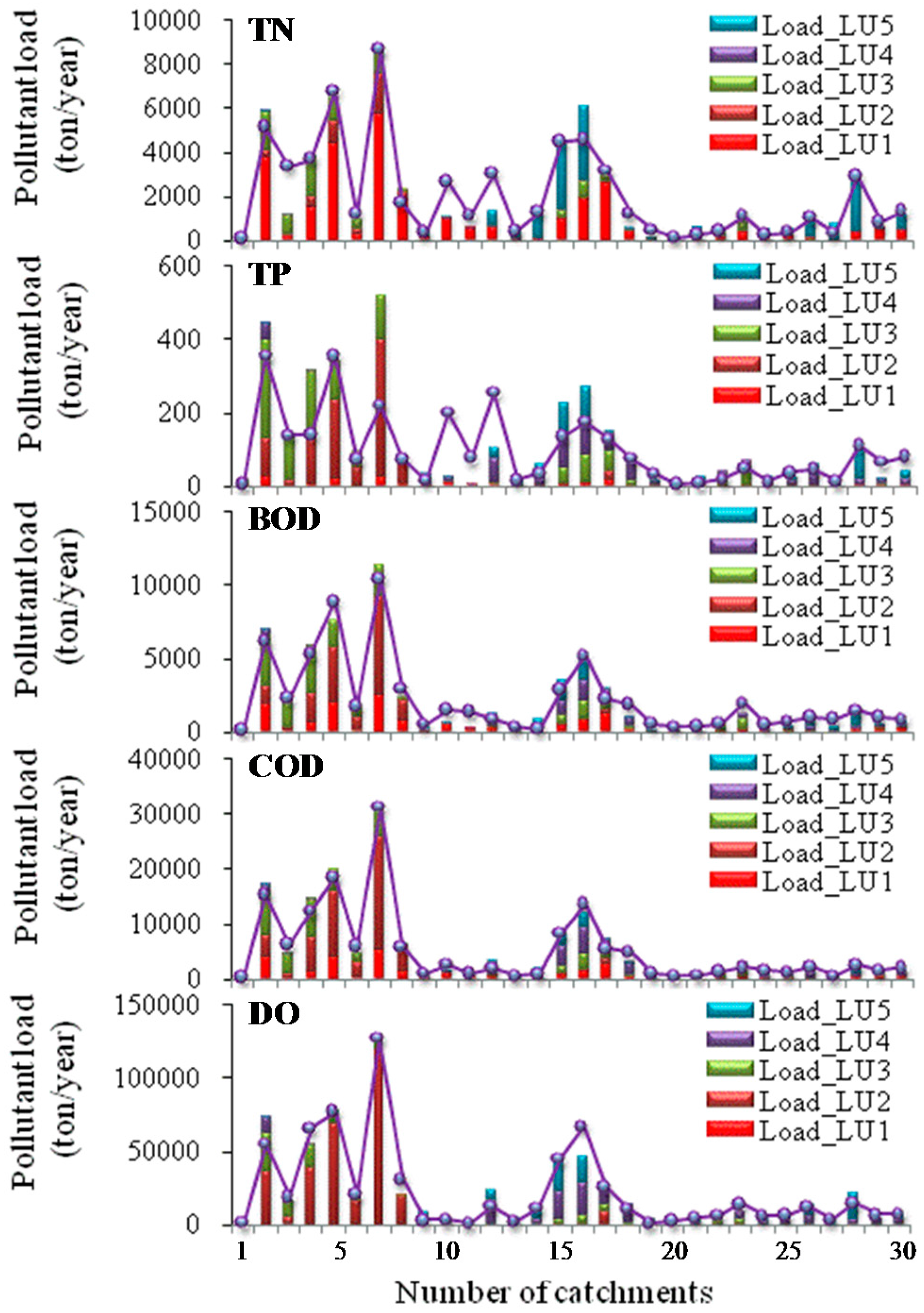
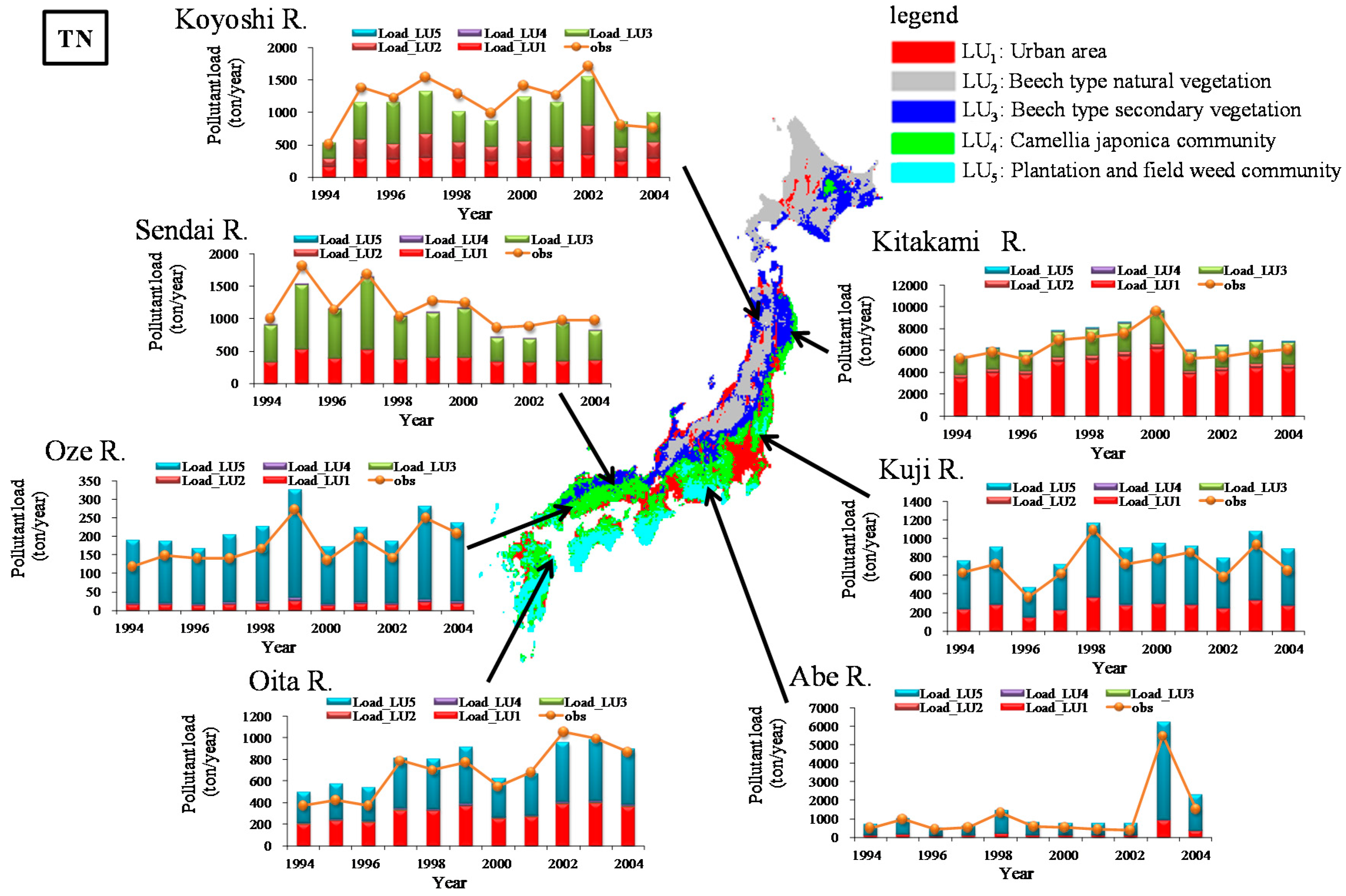

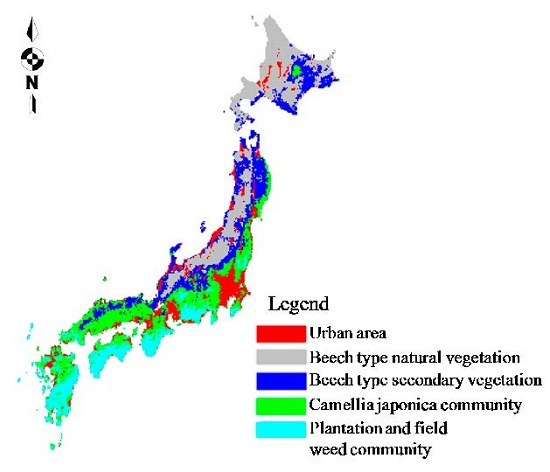
| Variables | Mean | Range | SD | CV% | Mean Percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LU1 (km2) | 222.3 | 4.0–1363.0 | 299.8 | 134.8 | 10.1% |
| LU2 (km2) | 450.2 | <0.01–4721.0 | 1059.7 | 235.4 | 20.4% |
| LU3 (km2) | 579.7 | <0.01–5365.0 | 1091.1 | 188.2 | 26.2% |
| LU4 (km2) | 646.0 | <0.01–2696.0 | 760.6 | 117.7 | 29.2% |
| LU5 (km2) | 311.0 | <0.01–1653.0 | 464.9 | 149.5 | 14.1% |
| Variables | Mean | Range | SD | CV% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN (mg/L) | 1.7 | 0.5–11.3 | 2.2 | 129.7 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.1 | <0.01–0.8 | 0.2 | 162.6 |
| BOD (mg/L) | 1.8 | 0.2–14.2 | 2.5 | 137.9 |
| COD (mg/L) | 2.9 | 0.8–9.5 | 1.9 | 63.5 |
| DO (mg/L) | 10.1 | 6.7–11.7 | 1.0 | 10.3 |
| Catchment | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | 1078 | 10,617 | 2252 | 4198 | 4594 | 1189 | 6869 | 858 | 1539 | 1217 |
| Q (m3/L) | 3.1 | 163.2 | 56.6 | 186.8 | 235.0 | 60.6 | 367.7 | 86.3 | 9.3 | 11.6 |
| Catchment | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| Area (km2) | 237 | 3878 | 582 | 1277 | 4854 | 4762 | 3695 | 2069 | 831 | 361 |
| Q (m3/L) | 3.2 | 40.4 | 6.4 | 34.7 | 132.6 | 205.3 | 80.4 | 40.2 | 4.2 | 6.8 |
| Catchment | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| Area (km2) | 511 | 929 | 1202 | 557 | 650 | 1368 | 509 | 2164 | 510 | 922 |
| Q (m3/L) | 14.1 | 18.6 | 45.1 | 18.5 | 17.9 | 36.7 | 11.3 | 47.0 | 19.3 | 24.2 |
| Parameter | k | n | LU1 | LU2 | LU3 | LU4 | LU5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | 0.09 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.34 |
| TP | 0.17 | 0.44 | 0.36 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.52 | 0.76 |
| BOD | 0.14 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 0.28 |
| COD | 0.19 | 0.70 | 1.50 | 0.97 | 0.76 | 0.55 | 0.50 |
| DO | 1.62 | 0.34 | 0.00 | 115.73 | 33.40 | 47.92 | 71.08 |
| LU1 | LU2 | LU3 | LU4 | LU5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | 0.71 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TP | 0.43 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| BOD | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.60 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| COD | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.66 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| DO | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; He, B.; Duan, W.; Li, W.; Luo, P.; Razafindrabe, B.H.N. Source Apportionment of Annual Water Pollution Loads in River Basins by Remote-Sensed Land Cover Classification. Water 2016, 8, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090361
Wang Y, He B, Duan W, Li W, Luo P, Razafindrabe BHN. Source Apportionment of Annual Water Pollution Loads in River Basins by Remote-Sensed Land Cover Classification. Water. 2016; 8(9):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090361
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi, Bin He, Weili Duan, Weihong Li, Pingping Luo, and Bam H. N. Razafindrabe. 2016. "Source Apportionment of Annual Water Pollution Loads in River Basins by Remote-Sensed Land Cover Classification" Water 8, no. 9: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090361
APA StyleWang, Y., He, B., Duan, W., Li, W., Luo, P., & Razafindrabe, B. H. N. (2016). Source Apportionment of Annual Water Pollution Loads in River Basins by Remote-Sensed Land Cover Classification. Water, 8(9), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090361