Attribution of Runoff Change for the Xinshui River Catchment on the Loess Plateau of China in a Changing Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
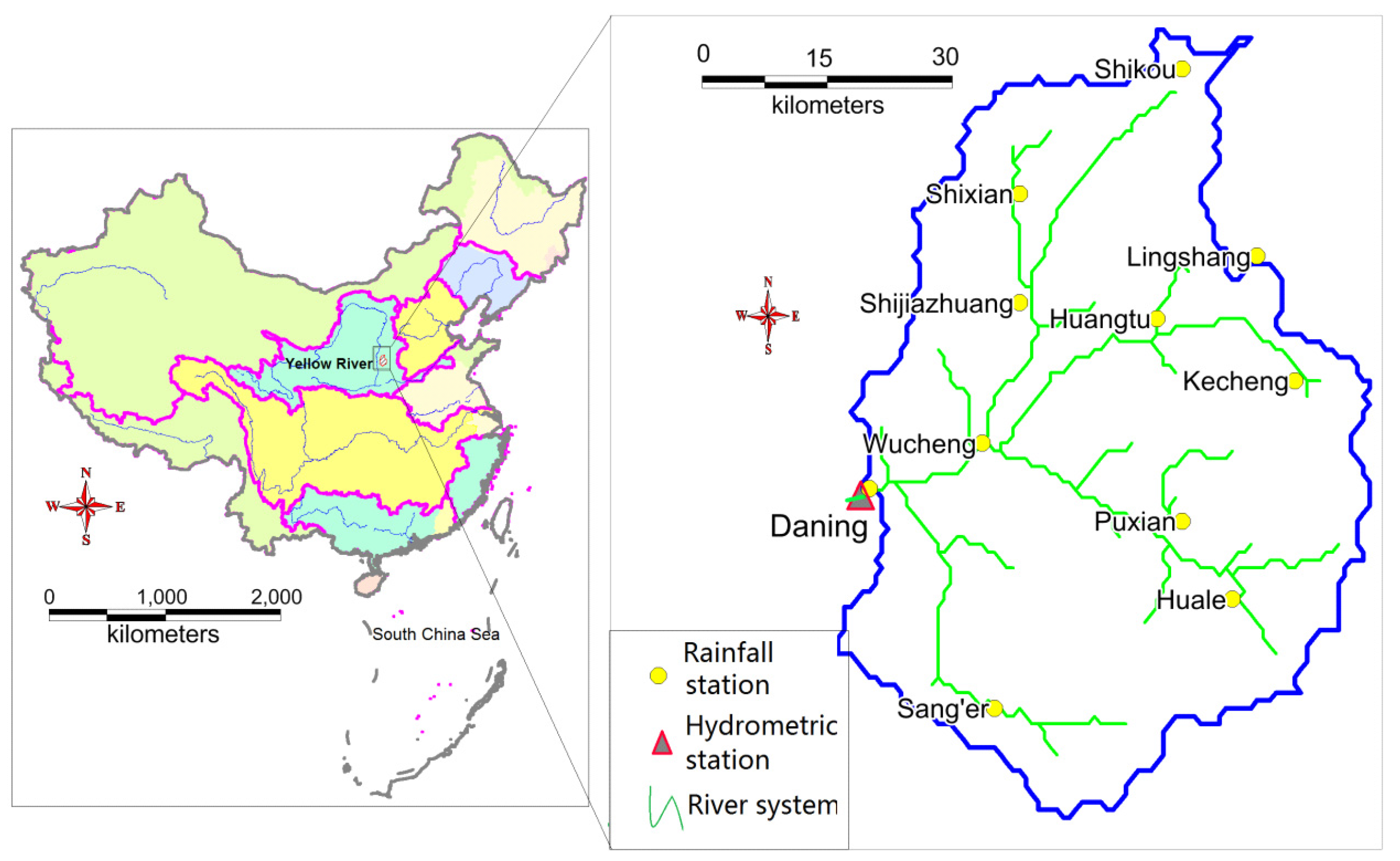
2.1. Description of the Xinshui River Catchment
2.2. Physically-Based Method for Detection of a Natural Period in a Runoff Series
2.3. Quantitative Method for Attribution Analysis of Runoff Change
2.4. Description of a Simplified Water Balance Model
3. Results
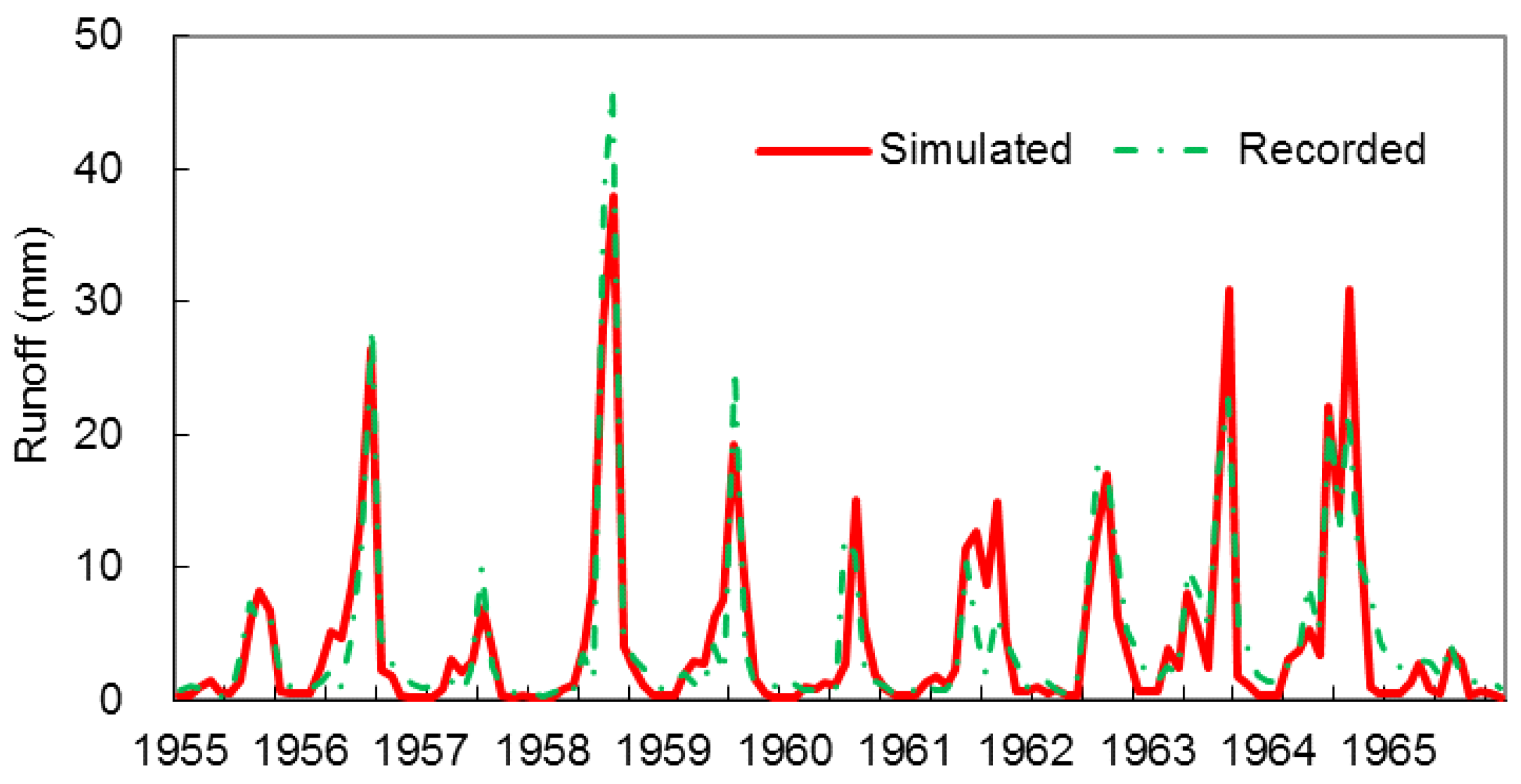
3.1. Inter-Annual Variability of Precipitation, Temperature, and Recorded Runoff During 1955–2008
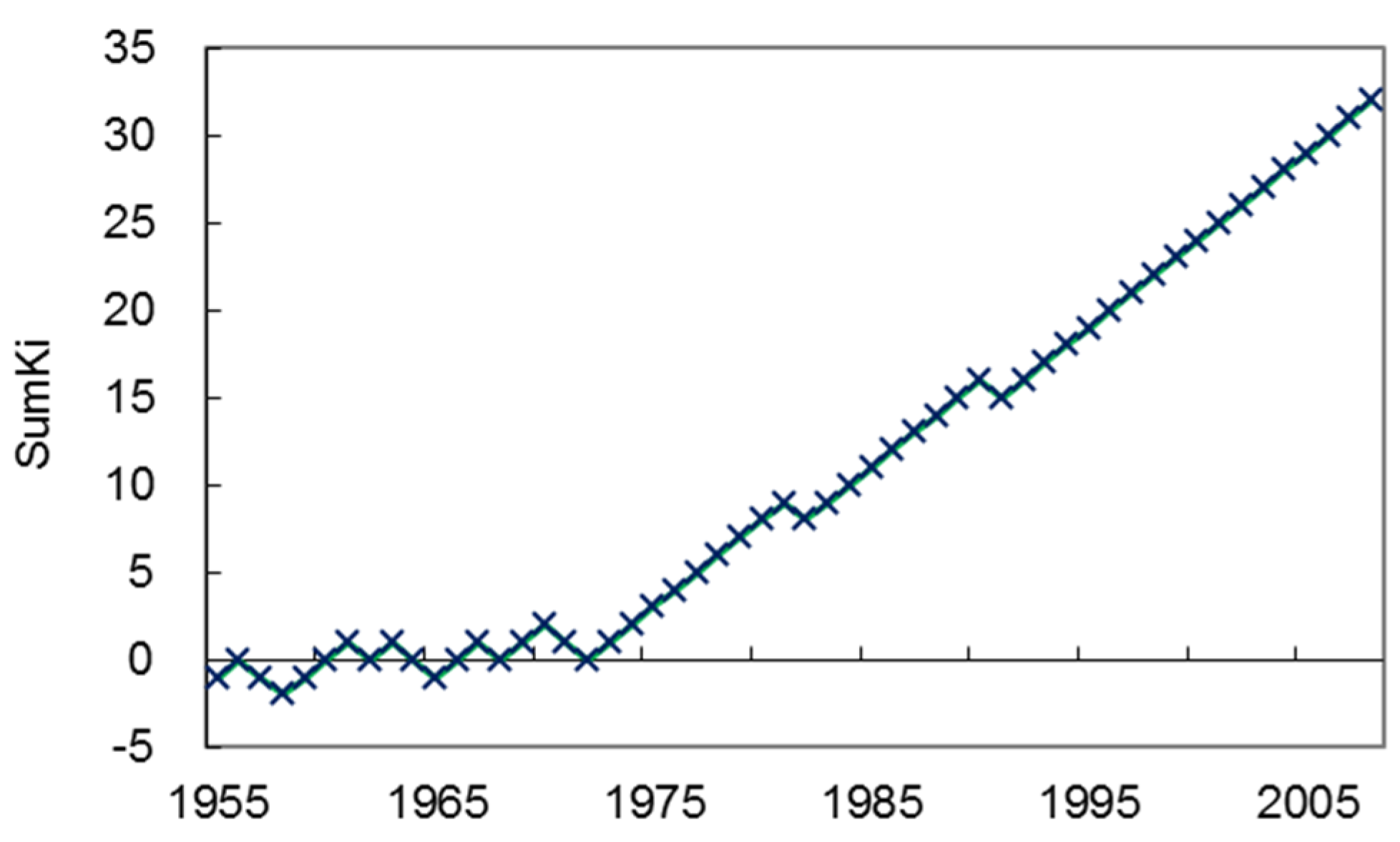
3.2. Detection of Abrupt Change Year in Runoff Series and Selection of Natural Period
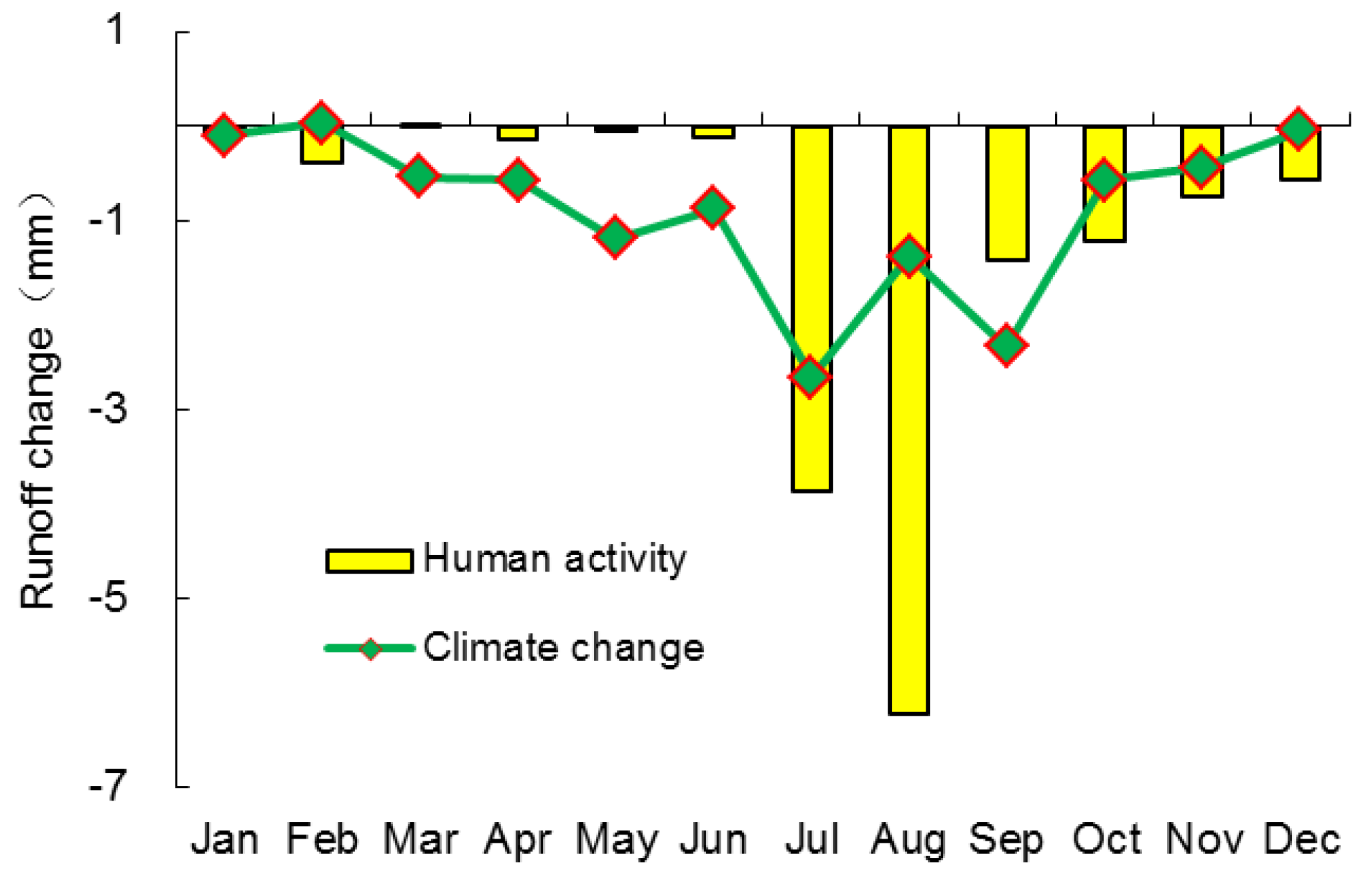
3.3. Attribution Analysis of Changes in Runoff of the Xinshui River Catchment
4. Discussion
4.1. Change Detection Method and Its Limitations
4.2. Needs for Improvement of Attribution Analysis Methods
4.3. Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Runoff and its Seasonal Distribution
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleick, P.H. Water and conflict: Fresh water resources and international security. Int. Secur. 1993, 18, 79–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Wilby, R.L.; Battarbee, R.W.; Kernan, M.; Wade, A.J. A review of the potential impacts of climate change on surface water quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Fang, D. Recent trends in the suspended sediment loads of the world’s rivers. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2003, 39, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Yan, X.L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, C.S.; Jin, J.L.; Bao, Z.X. Detecting evolution trends in the recorded runoffs from the major rivers in China during 1950–2010. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2013, 4, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, G.Q.; He, R.M.; Liu, C.S. Variation trends of runoff in the Middle Yellow River basin and its response to climate change. Adv. Water Sci. 2009, 20, 153–158. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, G.Q. Impacts of Climate Change on Hydrology and Water Resources; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane, D.; Stone, R.; Martens, S.; Thomas, J.; Silberstein, R.; Ali, R.; Hodgson, G. Climate change impacts on water yields and demands in south-western Australia. J. Hydrol. 2012, 475, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, D.; Tan, S.K.; Gao, B.; Hu, Q. Impact of climate variability and human activity on streamflow decrease in the Miyun Reservoir catchment. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhang, L.; Tong, L.; Su, X. Analysis of impacts of climate variability and human activity on streamflow for a river basin in arid region of northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; He, R.; Liu, C.; Ma, T.; Bao, Z.; Liu, Y. Runoff sensitivity to climate change for hydro-climatically different catchments in China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, G.Q. Variation of Stream Flow and Quantitative Identification for Attribution; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, M.S.; Agnès, D.; Jan, P. The impact of global land-cover change on the terrestrial water cycle. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.N.; Wang, Y.Z.; Xu, J.H. Assessment Methods of Soil and Water Conservation Measures Impacting on Water Resources and Sediment for the Middle Reaches of the Yellow River Basin; Yellow River Press: Zhengzhou, China, 2004. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.M.; Zhang, J.Y. Rapid urbanization and changes in spatio-temporal characteristics of precipitation in Beijing metropolitan area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 11250–11271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L. Strategy Study for Water Management in China; Southeast University Press: Nanjing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; He, R.M.; Jiang, N.Q.; Jing, X.A. Runoff reduction due to environmental changes in the Sanchuanhe River basin. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2008, 23, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, G.Q.; Fu, G.B.; He, R.M.; Yan, X.L.; Jin, J.L.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, A.J. Attribution for decreasing streamflow of the Haihe River basin, northern China: Climate variability or human activities? J. Hydrol. 2012, 460, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.H.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Gao, Y.J.; Li, M. Impact of Water Conservancy Projects on Storm Flood and Sediment Yield in the Middle Reaches of the Yellow River; Yellow River Press: Zhengzhou, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.B.; Mohanmad, H. Quantifying the relative contribution of the climate and direct human impacts on mean annual streamflow in the contiguous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.S.; Xia, J.; Chen, J. Quantification of effects of climate variations and human activities on runoff by a monthly water balance model: A case study of the Chaobai River basin in Northern China. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.S.; Jiang, S.S.; Sun, F.B.; Jia, Y.W.; Niu, C.W.; Yue, W.F. Quantitative contribution of climate change and human activities to runoff changes in the Wei River basin, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, N.A.; Tych, W.; Chotai, A.; Bidin, K.; Sinun, W.; Chiew, T.H. BARUMODEL: Combined data based mechanistic models of runoff response in a managed rainforest catchment. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 224, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaiylov, G.K.; Fedorov, V.M. Analysis of long-term variations in the Volga annual runoff. Water Resour. 2001, 28, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J. Separating the impacts of climate variation and human activities on runoff in the Songhua River Basin, Northeast China. Water 2014, 6, 3320–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Rustomji, P.; Hairsine, P. Responses of streamflow to changes in climate and land use/cover in the Loess Plateau, China. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Yang, Y.H.; Han, S.M. Using runoff slope-break to determine dominate factors of runoff decline in Hutuo River Basin, North China. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, T. The influence of climate change on stream flow in Danish rivers. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 226–238. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.H.; Yuan, F.; Duan, Q.Y.; Zheng, J.; Liang, M.L.; Chen, F. Regional Parameter Estimation of the VIC Land Surface Model: Methodology and Application to River Basins in China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, G.Q.; Pagano, T.C.; Jin, J.L.; Liu, C.S.; He, R.M.; Liu, Y.L. Using hydrologic simulation to explore the impacts of climate change on runoff in the Huaihe River basin of China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Niu, C.; Song, X.; Xu, C. The impacts of climate variability and human activities on streamflow in Bai River basin, northern China. Hydrol. Res. 2013, 44, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Ye, A.Z.; Gong, W.; Mao, Y.N.; Miao, C.Y.; Di, Z.H. An estimate of human and natural contributions to flood changes of the Huai River. Global Planet. Chang. 2014, 119, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Amo-Boateng, M.; Deng, P.; Huang, P. Quantitative assessment of the impact of climate variability and human activities on runoff changes for the upper reaches of Weihe River. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk A 2014, 28, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.D.; Zhan, C.S.; Sun, F.B.; Du, H.; Wang, F.Y. Effects of climate change and human activities on surface runoff in the Luan River Basin. Adv. Meteorol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Jin, J.L.; Thomas, C.; Roger, C.; Bao, Z.X.; Liu, C.S.; Liu, Y.L.; Yan, X.L. Assessing water resources in China using PRECIS and VIC model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.D.; Xia, J.; Du, H. Separating the effects of climate change and human activities on runoff over different time scales in the Zhang River basin. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Pagano, T.C.; Liu, Y.L.; Liu, C.S.; Bao, Z.X.; Jin, J.L.; He, R.M. Using hydrologic simulation to detect human-disturbed epoch in runoff series. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Jin, J.L.; Liu, Y.L.; He, R.M.; Bao, Z.X.; Liu, C.S.; Li, Y. Regional calibration of a water balance model for estimating stream flow in ungauged areas of the Yellow River Basin. Quat. Int. 2014, 336, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J. River flow forecasting through conceptual models: Part 1—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]





| Model Parameters | Model Performance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smax (mm) | ks | kg | NSE (%) | RE (%) |
| 180 | 0.12 | 0.005 | 78.6 | −0.32 |
| Period | Recorded Runoff (WHR, mm) | Simulated Runoff (WHN, mm) | Total Runoff Reduction (∆WT, mm) | Human-Induced Change (∆WH) | Climate-Induced Change (∆WC) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | % | mm | % | ||||
| 1955–1972 | 49.37 | 49.41 | – | – | – | – | – |
| 1973–1999 | 26.58 | 39.56 | 22.79 | 12.98 | 56.96 | 9.81 | 43.04 |
| 2000–2008 | 15.68 | 38.63 | 33.68 | 22.94 | 68.11 | 10.74 | 31.89 |
| 1973–2008 | 23.86 | 39.33 | 25.51 | 15.47 | 60.64 | 10.04 | 39.36 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q. Attribution of Runoff Change for the Xinshui River Catchment on the Loess Plateau of China in a Changing Environment. Water 2016, 8, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060267
Wang G, Zhang J, Yang Q. Attribution of Runoff Change for the Xinshui River Catchment on the Loess Plateau of China in a Changing Environment. Water. 2016; 8(6):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060267
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guoqing, Jianyun Zhang, and Qinli Yang. 2016. "Attribution of Runoff Change for the Xinshui River Catchment on the Loess Plateau of China in a Changing Environment" Water 8, no. 6: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060267
APA StyleWang, G., Zhang, J., & Yang, Q. (2016). Attribution of Runoff Change for the Xinshui River Catchment on the Loess Plateau of China in a Changing Environment. Water, 8(6), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060267






