Numerical Simulations of Suspended Sediment Dynamics Due to Seasonal Forcing in the Mekong Coastal Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
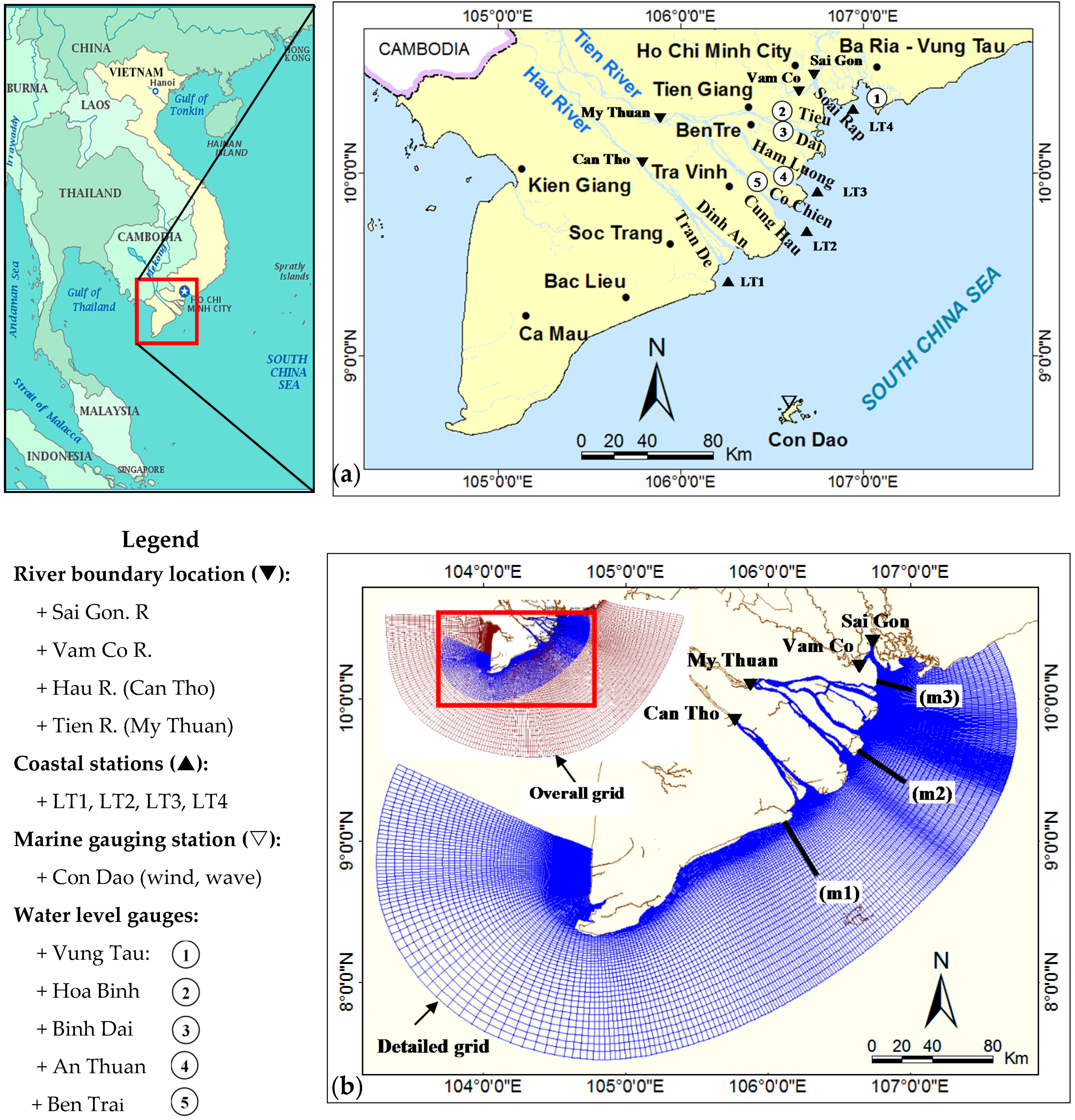
2.1. The Mekong River Delta (MRD)
2.1.1. The Mekong River
2.1.2. Climate and Rainfall
2.1.3. Hydrological Regimes and Sediment Transport
2.1.4. Tides
2.2. Data
2.3. Modelling Strategy
2.3.1. The Delft3D Model
2.3.2. Model Setup
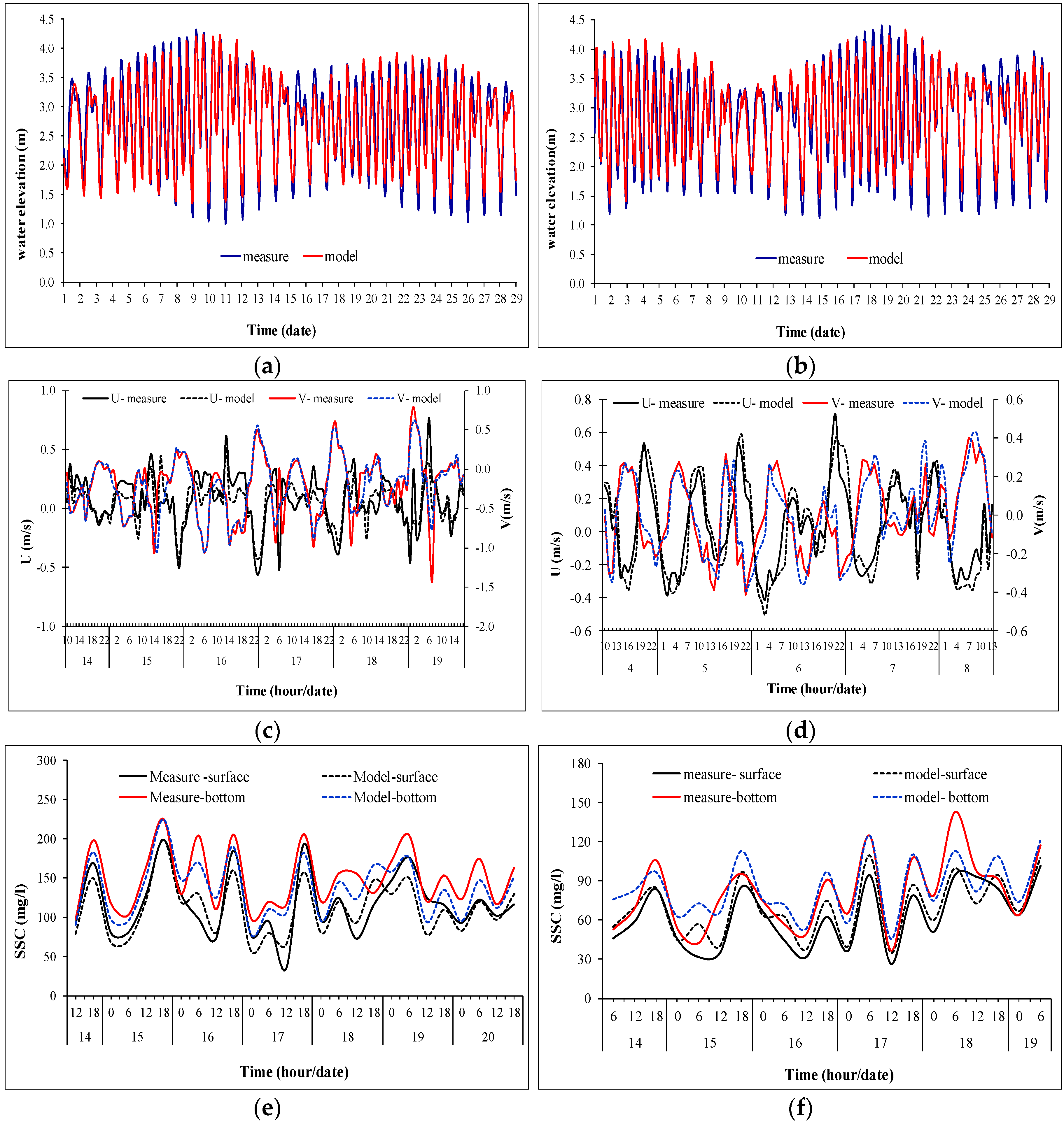
2.3.3. Calibration and Validation Process
2.3.4. Scenario Simulation
- during the low flow season (from December to August), the average water river discharges of 3054 m3·s−1 at My Thuan in the Tien River, 3739 m3·s−1 at Can Tho in the Hau River, 52.5 m3·s−1 in the Vamco River and 546.9 m3·s−1 in the Soai Rap River were imposed, with SSC = 50 mg·L−1 at Can Tho, 53.6 mg·L−1 at My Thuan, 55 mg·L−1 in the Vamco and Soai Rap rivers (Table 1);
- during the flood season (from September to November), the average water river discharges of 12,530 m3·s−1 at My Thuan, 13,130 m3·s−1 at Can Tho, 177.8 m3·s−1 in the Vamco River and 1310 m3·s−1 in the Soai Rap River were considered, with SSC = 67.8 mg·L−1 at Can Tho, 86.5 mg·L−1 at My Thuan and 70 mg·L−1 at Vamco and Soai Rap (Table 2).
3. Results
3.1. Model Validation from Field Measurements
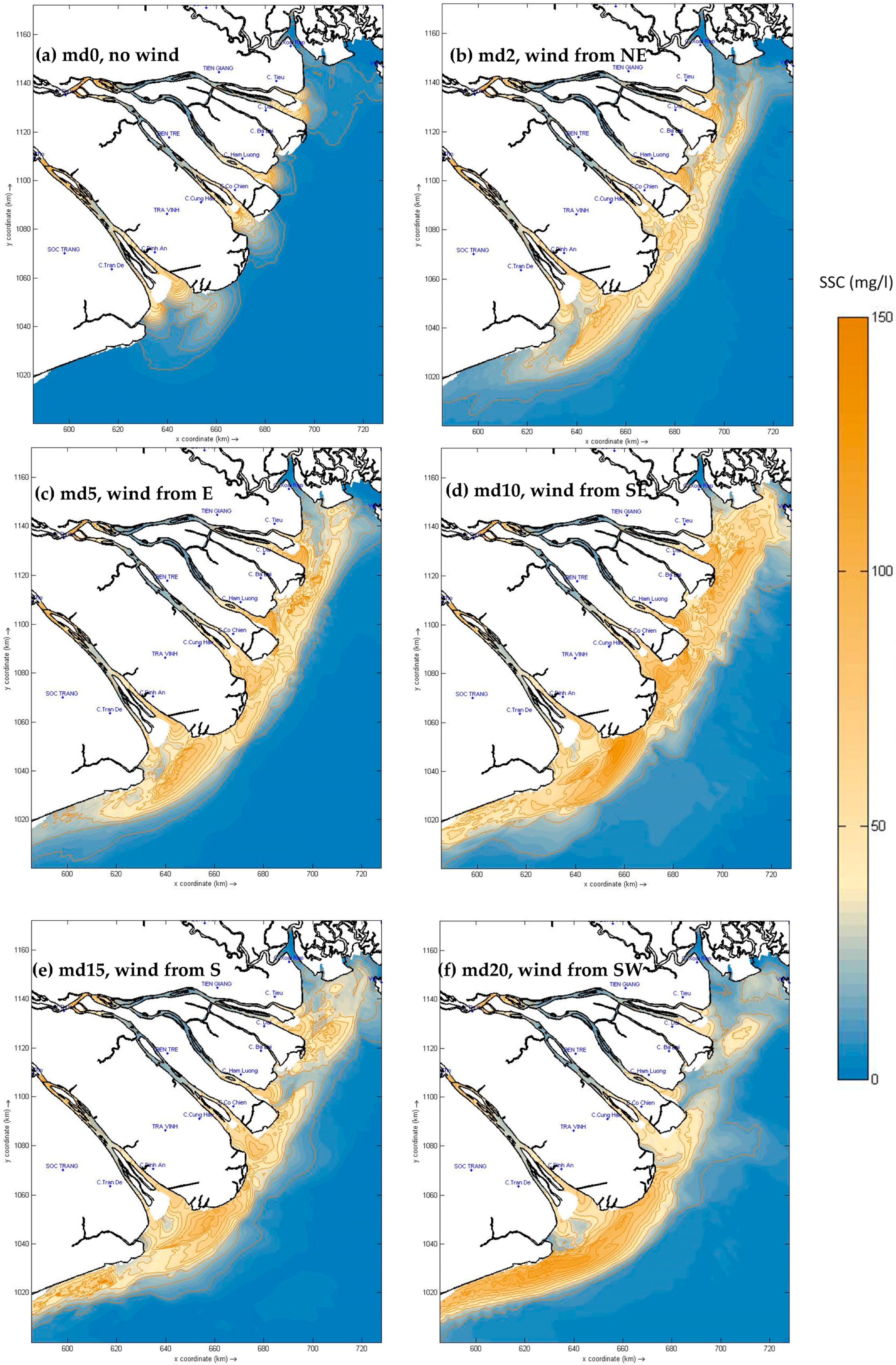
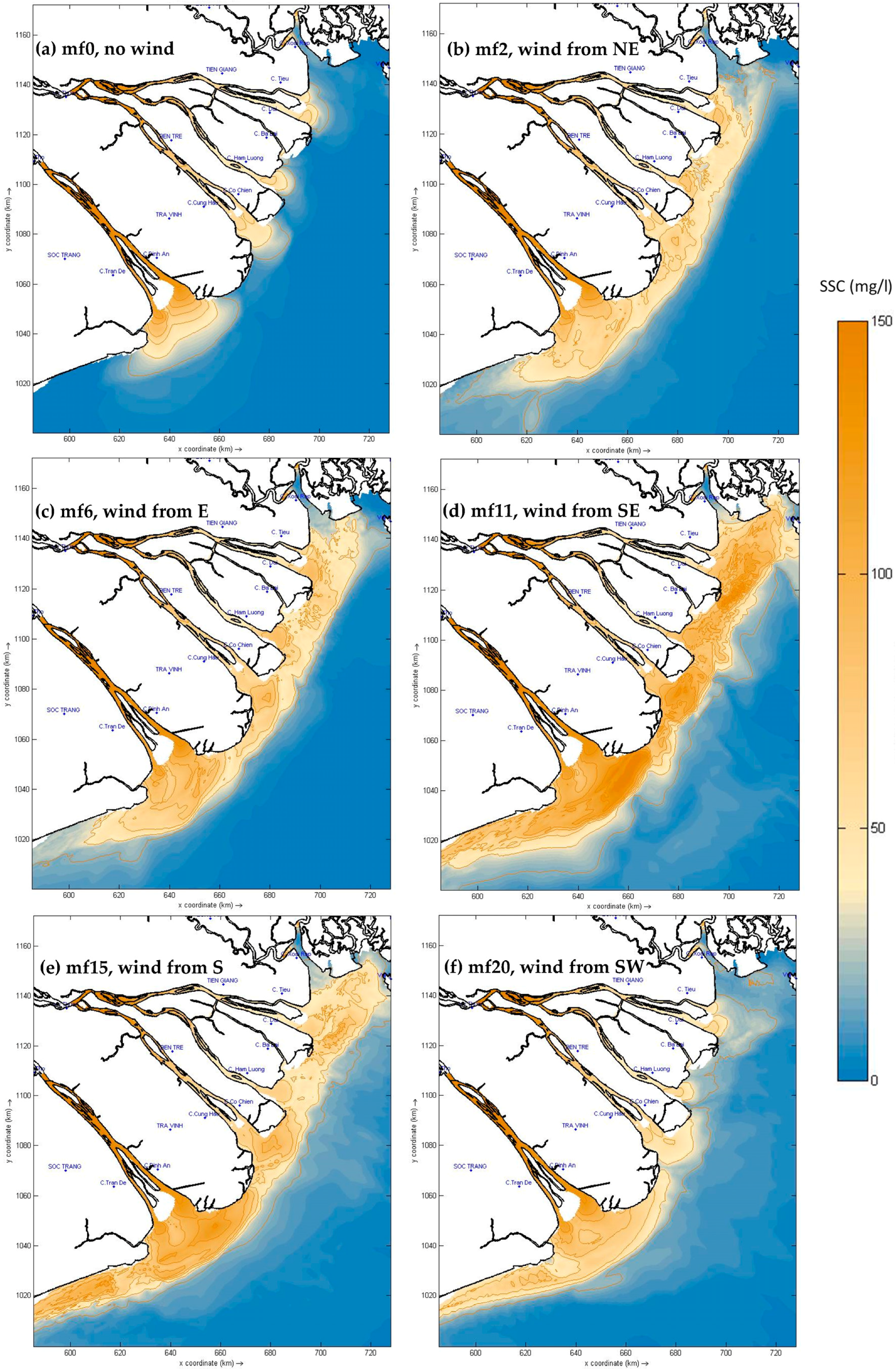
3.2. Spatial Distribution of SSC with or without Waves
3.2.1. Without Waves
3.2.2. With Waves
3.3. Temporal Variation of SSC
3.4. Alongshore Sediment Transport
3.4.1. Without Waves
3.4.2. Sensitivity to Wave Height and Direction
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.P.; Xue, Z.; Ross, K.; Wang, H.J.; Yang, Z.S.; Li, A.C.; Gao, S. Fate of sediments delivered to the sea by Asian large rivers: Long-distance transport and formation of remote alongshore clinothems. Sediment. Rec. 2009, 7, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, Y.; Chaimanee, N.; Jarupongsakul, T.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Shrinking megadeltas in Asia: Sea-level rise and sediment reduction impacts from case study of the Chao Phraya delta. Newsl. IGBP/IHDP Land Ocean Interact. Coast. Zone 2007, 2, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Meybeck, M.; Fekete, B.; Sharma, K.; Green, P.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Anthropogenic sediment retention: Major global impact from registered river impoundments. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2003, 39, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Saito, Y. Morphodynamics of Deltas under the Influence of Humans. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2007, 57, 261–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Yang, Z.S.; Saito, Y.; Liu, J.P.; Sun, X. Interannual and seasonal variation of the Huanghe (Yellow River) water discharge over the past 50 years: Connections to impacts from ENSO events and dams. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 50, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Yang, Z.S.; Wang, Y.; Saito, Y.; Liu, J.P. Reconstruction of sediment flux from the Changjiang (Yangtze River) to the sea since the 1860s. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinh, V.D.; Ouillon, S.; Tanh, T.D.; Chu, L.V. Impact of the Hoa Binh dam (Vietnam) on water and sediment budgets in the Red River basin and delta. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3987–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlünz, B.; Schneider, R.R. Transport of terrestrial organic carbon to the oceans by rivers: Re-estimating flux- and burial rates. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2000, 88, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viers, J.; Dupré, B.; Gaillardet, J. Chemical composition of suspended sediments in World Rivers: New insights from a new database. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochelle-Newall, E.J.; Chu, V.T.; Pringault, O.; Amouroux, D.; Arfi, R.; Bettarel, Y.; Bouvier, T.; Bouvier, C.; Got, P.; Nguyen, T.M.; et al. Phytoplankton diversity and productivity in a highly turbid, tropical coastal system (Bach Dang Estuary, Vietnam). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2317–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mari, X.; Torréton, J.P.; Chu, V.T.; Lefebvre, J.P.; Ouillon, S. Seasonal aggregation dynamics along a salinity gradient in the Bach Dang estuary, North Vietnam. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 96, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.; Amouroux, D.; Duong, T.N.; Rochelle-Newall, E.; Ouillon, S.; Arfi, R.; Chu, V.T.; Mari, X.; Torréton, J.P. Butyltin and mercury compounds fate and tidal transport in waters of the tropical Bach Dang estuary (Haiphong, Vietnam). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Kettner, A.J.; Green, P. Impact of Humans on the Flux of Terrestrial Sediment to the Global Coastal Ocean. Science 2005, 308, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouillon, S. Erosion and sediment transport: Width and stakes. Houille Blanche 1998, 53, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, P.D.; Plumb, R.A. The Asian Monsoon: Causes, History and Effects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; p. 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Horaguchi, K.; Saito, Y.; Nguyen, V.L.; Tateishi, M.; Ta, T.K.O.; Nanayama, F.; Watanabe, K. Monsoon-influenced variations in morphology and sediment of a mesotidal beach on the Mekong River Delta coast. Geomorphology 2010, 116, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastham, J.; Mpelasoka, F.; Mainuddin, M.; Ticehurst, C.; Dyce, P.; Hodgson, G.; Ali, R.; Kirby, M. Mekong River Basin Water Resources Assessment: Impacts of Climate Change; CSIRO National Research Flagship, Water for a Healthy Country: Canberra, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.L.; Ta, T.K.O.; Tateishi, M. Late Holocene depositional environments and coastal evolution of the Mekong River Delta, Southern Vietnam. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2000, 18, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E. The changing sediment load of the Mekong River. AMBIO 2008, 37, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Liu, J.P.; Ge, Q. Changes in hydrology and sediment delivery of the Mekong River in the last 50 years: Connection to damming, monsoon, and ENSO. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.V.H.; Nguyen, H.N.; Wolanski, E.; Tran, T.C.; Haruyama, S. The combined impact on the flooding in Vietnam’s Mekong River Delta of local man-made structures, sea level rise, and dams upstream in the river catchment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Lu, X.X.; Kummu, M. Sediment load estimates and variations in the lower Mekong River. River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manh, N.V.; Dung, N.V.; Hung, N.N.; Merz, B.; Apel, H. Large-scale suspended sediment transport and sediment deposition in the Mekong delta. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3033–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; He, R.; Liu, J.P.; Warner, J.C. Modeling transport and deposition of the Mekong River sediment. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 37, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisel, H.; Mangin, A.; Vantrepotte, V.; Dessailly, D.; Dinh, N.D.; Garnesson, P.; Ouillon, S.; Lefebvre, J.P.; Mériaux, X.; Phan, M.T. Analysis of the suspended particulate matter concentration variability of the coastal waters under the Mekong’s influence: A remote sensing approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczuciński, W.; Jagodziński, R.; Hanebuth, T.J.J.; Stattegger, K.; Wetzel, A.; Mitręga, M.; Unverricht, D.; Phach, P.V. Modern sedimentation and sediment dispersal pattern on the continental shelf off the Mekong River delta, South China Sea. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 110, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolanski, E.; Ngoc Huan, N.; Trong Dao, L.; Huu Nhan, N.; Ngoc Thuy, N. Fine sediment dynamics in the Mekong River Estuary, Vietnam. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1996, 43, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolanski, E.; Nhan, N.H.; Spagnol, S. Sediment dynamics during low flow conditions in the Mekong River Estuary, Vietnam. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 472–482. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, H.; Hein, B.; Pohlmann, T. Recent dynamics in the region of Mekong water influence. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 110, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission (MRC). State of the Basin Report: 2003; MRC: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Milliman, J.D.; Meade, R.H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans. J. Hydrol. 1983, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, K.T.O.; Nguyen, V.L.; Tateishio, M.; Kobayashi, I.; Tanabe, S.; Saito, Y. Holocene delta evolution and sediment discharge of the Mekong River, southern Vietnam. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2002, 21, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hordoir, R.; Nguyen, K.D.; Polcher, J. Simulating tropical river plumes, a set of parametrizations based on macroscale data: A test case in the Mekong Delta region. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, C09036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snidvongs, A.; Teng, S.K. Global International Waters Assessment, Mekong River GIWA Regional Assessment 55; University of Kalmar: Kalmar, Sweden, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Unverricht, D.; Szczuciński, W.; Stattegger, K.; Jagodziński, R.; Le, X.T.; Kwong, L.L.W. Modern sedimentation and morphology of the subaqueous Mekong delta, Southern Vietnam. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 110, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltares. Mekong Delta Water Resources Assessment Studies; Report of the Vietnam-Netherlands Mekong Delta Masterplan Project; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands.
- Vietnamese National Centre for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasts. Statistics on Typhoon Occurrence in Vietnam. 2016. Available online: http://ttnh.vnea.org (accessed on 20 April 2016).
- Tri, V.K. Hydrology and hydraulic infrastructure systems in the Mekong delta, Vietnam. In The Mekong Delta System; Renaud, F.G., Kuenzer, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2012; pp. 49–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.X.; Siew, R.Y. Water discharge and sediment flux changes over the past decades in the Lower Mekong River: Possible impacts of the Chinese dams. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicki, A. Large and very large subaqueous delta dunes on the continental shelf off southern Vietnam, South China Sea. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2008, 28, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T. Processes and Factors Controlling and Affecting the Retreat of Mangrove Shorelines in South Vietnam. Ph.D. Thesis, Kiel University, Kiel, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, G.P.; Salomon, J.C.; Bassoulet, P.; du Penhoat, Y.; de Grandpre, C. Effects of tides on mixing and suspended sediment transport in macrotidal estuaries. Sediment. Geol. 1980, 26, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, K.R. Coastal and Estuarine Sediment Dynamics; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1986; p. 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronkers, J. Tide-induced residual transport of fine sediment. In Physics of Shallow Estuaries and Bays; van de Kreeke, J., Ed.; Lecture Notes Coastal Estuarine Studies, Volome 16; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1986; pp. 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottolichio, A.; Le Hir, P.; Castaing, P. Modeling mechanisms for the turbidity maximum stability in the Gironde estuary, France. Proc. Mar. Sci. 2001, 3, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, J.P.; Ouillon, S.; Vinh, V.D.; Arfi, R.; Panche, J.Y.; Mari, X.; Van Thuoc, C.; Torréton, J.P. Seasonal variability of cohesive sediment aggregation in the Bach Dang-Cam Estuary, Haiphong (Vietnam). Geo-Mar. Lett. 2012, 32, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherall, P.; Marks, K.M.; Jakobsson, M.; Schmitt, T.; Tani, S.; Arndt, J.E.; Rovere, M.; Chayes, D.; Ferrini, V.; Wigley, R. A new digital bathymetric model of the world’s oceans. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanh, D.T. Integrated Water Resources Management and Sustainable Use for the Dong Nai River System; Technical Report of the Project KC.08.18/06-10; The Southern Institute of Water Resources Research: Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2010. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar]
- Groenewoud, P. Overview of the Service and Validation of the Database; Reference: RP_A870; BMT ARGOSS: Marknesse, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lefevre, F.; Lyard, F.; Le Provost, C.; Schrama, E.J.O. FES99: A global tide finite element solution assimilating tide gauge and altimetric information. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyard, F.; Lefevre, F.; Letellier, T.; Francis, O. Modelling the global ocean tides: Modern insights from FES2004. Ocean Dyn. 2006, 56, 394–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Ocean Atlas 2013 Version 2 (WOA13 V2). Available online: https://www.nodc.noaa.gov/OC5/woa13/ (accessed on 20 April 2016).
- Deltares Systems. Delft3D-FLOW User Manual: Simulation of Multi-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Flows and Transport Phenomena, including Sediments; Technical Report; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Booij, N.; Ris, R.C.; Holthuijsen, L.H. A third-generation wave model for coastal regions: 1. Model description and validation. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 7649–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ris, R.C.; Holthuijsen, L.H.; Booij, N. A third-generation wave model for coastal regions: 2. Verification. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 7667–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltares Systems. Delft3D-WAVE User Manual: Simulation of Short-Crested Waves with SWAN; Technical Report; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jouon, A.; Lefebvre, J.P.; Douillet, P.; Ouillon, S.; Schmied, L. Wind wave measurements and modelling in a fetch-limited semi-enclosed lagoon. Coast. Eng. 2009, 56, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K.; Barnett, T.P.; Bouws, E.; Carlson, H.; Cartwright, D.E.; Enke, K.; Ewing, J.; Gienapp, H.; Hasselmann, D.E.; Kruseman, P.; et al. Measurements of Wind Wave Growth and Swell Decay during the Joint North Sea Wave Project (JONSWAP). Deutsche Hydrographische Zeitschrift 8 (12); Deutsches Hydrographisches Institut: Hamburg, Germany, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Bouws, E.; Komen, G. On the balance between growth and dissipation in an extreme, depth-limited wind-sea in the southern North Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1983, 13, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battjes, J.; Janssen, J. Energy loss and set-up due to breaking of random waves. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference Coastal Engineering, ASCE, Hamburg, Germany, 26 August–6 September 1978; pp. 569–587.
- Arcement, G.J., Jr.; Schneider, V.R. Guide for Selecting Manning’s Roughness Coefficients for Natural Channels and Flood Plains. U.S. Geological Survey Water Supply Paper 2339; 1989. Available online: http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/bridge/wsp2339.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Simons, D.B.; Senturk, F. Sediment Transport Technology—Water and Sediment Dynamics; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Uittenbogaard, R.E. Model for Eddy Diffusivity and Viscosity Related to Sub-Grid Velocity and Bed Topography; Technical Report; WL Delft Hydraulics: Delft, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vossen, B. Horizontal Large Eddy Simulations; Evaluation of Computations with DELFT3D-FLOW; Report MEAH-197; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Unified view of sediment transport by currents and waves, Part II: Suspended transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 668–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partheniades, E. Erosion and deposition of cohesive soils. J. Hydraul. Div. 1965, 91, 105–139. [Google Scholar]
- Krone, R.B. Flume Studies of the Transport of Sediment in Estuarial Shoaling Processes; Hydraulic Engineering Laboratory and Sanitary Engineering Research Laboratory, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Douillet, P.; Ouillon, S.; Cordier, E. A numerical model for fine suspended sediment transport in the south-west lagoon of New-Caledonia. Coral Reefs 2001, 20, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterwerp, J.C.; van Kesteren, W.G.M. Introduction to the Physics of Cohesive Sediment in the Marine Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 1–466. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, N.N.; Delgado, J.M.; Güntner, A.; Merz, B.; Bárdossy, A.; Apel, H. Sedimentation in the floodplains of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam Part II: Deposition and erosion. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 28, 3145–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela, L.I.; Ramos, S.; Rexeira, A.T. Effect of salinity on the settling velocity of fine sediments of a harbour basin. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 2, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Mathematical modeling of suspended sediment in non-uniform flows. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1986, 112, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouillon, S.; Le Guennec, B. Modelling non-cohesive suspended sediment transport in 2D vertical free surface flows. J. Hydraul. Res. 1996, 34, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L. Principles of Sediment Transport in Rivers, Estuaries and Coastal Seas; Aqua Publications: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, O.S. Spectral wave–current bottom boundary layer flows. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Coastal Engineering Research Council, Kobe, Japan, 23–28 October 1994; pp. 384–398. [CrossRef]
- Walstra, D.J.R.; Roelvink, J.A. 3D Calculation of Wave Driven Cross-shore Currents. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Sydney, Australia, 16–21 July 2000; pp. 1050–1063. [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models, Part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Boyle, D.P.; Bäse, F. Comparison of different efficiency criteria for hydrological model assessment. Adv. Geosci. 2005, 5, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvale, E.P.; Archer, A.W.; Johnson, H.R. Daily, monthly, and yearly tidal cycles within laminated siltstones of the Mansfield Formation (Pennsylvanian) of Indiana. Geology 1989, 17, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinh, V.D.; Lan, T.D.; Tu, T.A.; Anh, N.K.; Tien, N.N. Influence of dynamic processes on morphological change in the coastal area of Mekong river mouth. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2016, 16, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y. Deltas in Southeast and East Asia: Their evolution and current problems. In APN/SURVAS/LOICZ Joint Conference on Coastal Impact of Climate Change and Adaption in the Asia-Pacific Region; Mimura, N., Yokoki, H., Eds.; APN: Kobe, Japan, 2000; pp. 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, N.; Fiandrino, A.; Fraunie, P.; Ouillon, S.; Forget, P.; Naudin, J.J. Suspended matter dispersion in the Ebro ROFI: An integrated approach. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouillon, S.; Douillet, P.; Andréfouët, S. Coupling satellite data with in situ measurements and numerical modeling to study fine suspended sediment transport: A study for the lagoon of New Caledonia. Coral Reefs 2004, 23, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroud, J.R.; Lesht, B.M.; Schwab, D.J.; Beletsky, D.; Stein, M.L. Assimilation of satellite images into a sediment transport of Lake Michigan. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W02419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carniello, L.; Silvestri, S.; Marani, M.; D’Alpaos, A.; Volpe, V.; Defina, A. Sediment dynamics in shallow tidal basins: In situ observations, satellite retrievals, and numerical modeling in the Venice Lagoon. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 802–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mao, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhu, Q. Using GOCI retrieval data to initialize and validate a sediment transport model for monitoring diurnal variation of SSC in Hangzhou Bay, China. Water 2016, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Scenario | Wave Direction | Duration (Days) | Wave | Wind Velocity (m·s−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hs (m) | Tp (s) | ||||
| md0 | 29.87 | ||||
| md1 | NE | 0.27 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 |
| md2 | 5.48 | 2 | 8.5 | 7.5 | |
| md3 | 1.10 | 4 | 10.5 | 10.5 | |
| md4 | E | 1.64 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 |
| md5 | 23.29 | 2 | 8.5 | 8 | |
| md6 | 11.78 | 4 | 10.5 | 12.5 | |
| md7 | 4.38 | 6 | 11.5 | 14.5 | |
| md8 | 0.55 | 8 | 12.5 | 16.5 | |
| md9 | SE | 1.64 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 |
| md10 | 18.36 | 2 | 8.5 | 7.5 | |
| md11 | 9.59 | 4 | 10.5 | 10.5 | |
| md12 | 3.29 | 6 | 11.5 | 12.5 | |
| md13 | 0.27 | 8 | 12.5 | 14.5 | |
| md14 | S | 2.47 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 |
| md15 | 25.21 | 2 | 8.5 | 6.5 | |
| md16 | 14.80 | 4 | 10.5 | 9.5 | |
| md17 | 7.67 | 6 | 11.5 | 12.5 | |
| md18 | 1.10 | 8 | 12.5 | 14.5 | |
| md19 | SW | 3.29 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 |
| md20 | 45.76 | 2 | 8.5 | 7.5 | |
| md21 | 31.51 | 4 | 10.5 | 10.5 | |
| md22 | 21.65 | 6 | 11.5 | 12.5 | |
| md23 | 6.30 | 8 | 12.5 | 14.5 | |
| md24 | 2.74 | 10.5 | 13.5 | 16.5 | |
| Scenario | Wave Direction | Duration (Days) | Wave | Wind Velocity (m·s−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hs (m) | Tp (s) | ||||
| mf0 | 13.01 | ||||
| mf1 | NE | 0.09 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 |
| mf2 | 2.82 | 2 | 9 | 7.5 | |
| mf3 | 0.55 | 4 | 10.5 | 9.5 | |
| mf4 | 0.09 | 6 | 11.5 | 12.5 | |
| mf5 | E | 0.46 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 |
| mf6 | 7.74 | 2 | 9 | 7.5 | |
| mf7 | 4.64 | 4 | 10.5 | 10.5 | |
| mf8 | 2.00 | 6 | 11.5 | 12.5 | |
| mf9 | 0.09 | 8 | 12.5 | 14.5 | |
| mf10 | SE | 0.09 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 |
| mf11 | 6.19 | 2 | 9 | 7.5 | |
| mf12 | 4.55 | 4 | 10.5 | 11 | |
| mf13 | 1.00 | 6 | 11.5 | 12.5 | |
| mf14 | S | 0.18 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 |
| mf15 | 7.46 | 2 | 9 | 7.5 | |
| mf16 | 5.92 | 4 | 10.5 | 11.5 | |
| mf17 | 2.09 | 6 | 11.5 | 13 | |
| mf18 | 0.46 | 8 | 12.5 | 15 | |
| mf19 | SW | 0.27 | 0.5 | 6.5 | 4.5 |
| mf20 | 12.56 | 2 | 9 | 7.5 | |
| mf21 | 11.01 | 4 | 10.5 | 11.5 | |
| mf22 | 6.28 | 6 | 11.5 | 13 | |
| mf23 | 1.18 | 8 | 12.5 | 15 | |
| mf24 | 0.27 | 10.5 | 13.5 | 17 | |
| Low Flow Season | Flood Season | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario | Wave Direction | Cross Section | Scenario | Wave Direction | Cross Section | ||||
| m1 | m2 | m3 | m1 | m2 | m3 | ||||
| md0 | −2.32 | −0.65 | −0.15 | mf0 | −5.04 | −0.37 | 0.71 | ||
| md1 | NE | −0.05 | −0.02 | −0.01 | mf1 | NE | −0.07 | −0.01 | 0.00 |
| md2 | −7.02 | −4.44 | −1.52 | mf2 | −7.28 | −3.04 | −0.89 | ||
| md3 | −6.38 | −4.43 | −1.23 | mf3 | −3.65 | −2.19 | −0.49 | ||
| md4 | E | −0.30 | −0.10 | −0.06 | mf4 | −1.50 | −1.00 | −0.21 | |
| md5 | −39.60 | −15.97 | −5.49 | mf5 | E | −0.31 | −0.04 | 0.01 | |
| md6 | −117.58 | −51.71 | −5.98 | mf6 | −21.38 | −6.11 | −1.54 | ||
| md7 | −81.66 | −37.03 | −3.30 | mf7 | −38.83 | −15.98 | −1.35 | ||
| md8 | −16.91 | −7.61 | −0.80 | mf8 | −29.81 | −13.39 | 0.26 | ||
| md9 | SE | −0.39 | −0.07 | −0.07 | mf9 | −0.02 | −1.08 | 0.02 | |
| md10 | −24.16 | 2.63 | 11.12 | mf10 | SE | −0.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| md11 | −53.18 | 17.96 | 37.14 | mf11 | −19.14 | 1.47 | 6.24 | ||
| md12 | −36.69 | 15.49 | 26.06 | mf12 | −41.88 | 13.45 | 27.64 | ||
| md13 | −5.53 | 2.12 | 3.23 | mf13 | −15.00 | 5.97 | 10.29 | ||
| md14 | S | −0.23 | 0.02 | 0.01 | mf14 | S | −0.07 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| md15 | 2.02 | 9.39 | 3.83 | mf15 | 1.89 | 0.29 | 3.79 | ||
| md16 | 30.21 | 47.87 | 32.25 | mf16 | 38.13 | 6.13 | 41.94 | ||
| md17 | 62.96 | 80.14 | 67.92 | mf17 | 23.29 | 22.69 | 25.24 | ||
| md18 | 38.93 | 44.46 | 36.71 | mf18 | 10.61 | 12.48 | 9.27 | ||
| md19 | SW | −0.13 | 0.02 | 0.05 | mf19 | SW | −0.06 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| md20 | 67.09 | 23.05 | 6.33 | mf20 | 10.42 | 6.02 | 2.51 | ||
| md21 | 229.37 | 125.38 | 51.66 | mf21 | 85.28 | 55.33 | 19.94 | ||
| md22 | 361.55 | 201.51 | 95.72 | mf22 | 95.57 | 58.32 | 21.96 | ||
| md23 | 234.97 | 128.43 | 63.25 | mf23 | 37.57 | 20.87 | 8.62 | ||
| md24 | 187.43 | 104.88 | 54.69 | mf24 | 15.46 | 8.40 | 3.65 | ||
| Wave Direction | Low Flow Season | Flood Season | Total Year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross Section | Cross Section | Cross Section | |||||||
| m1 | m2 | m3 | m1 | m2 | m3 | m1 | m2 | m3 | |
| calm | −2.32 | −0.65 | −0.15 | −5.04 | −0.37 | 0.71 | −7.356 | −1.013 | 0.555 |
| NE | −13.45 | −8.89 | −2.76 | −12.51 | −6.24 | −1.59 | −25.95 | −15.12 | −4.35 |
| E | −256.06 | −112.43 | −15.64 | −90.35 | −36.59 | −2.59 | −346.41 | −149.02 | −18.24 |
| SE | −119.95 | 38.13 | 77.48 | −76.11 | 20.90 | 44.18 | −196.06 | 59.03 | 121.66 |
| S | 133.88 | 181.88 | 140.72 | 73.84 | 41.61 | 80.26 | 207.73 | 223.49 | 220.98 |
| SW | 1080.28 | 583.25 | 271.69 | 244.25 | 148.95 | 56.70 | 1324.53 | 732.20 | 328.39 |
| NEward | 1214.52 | 803.34 | 489.96 | 318.22 | 211.45 | 182.13 | 1532.26 | 1014.72 | 671.59 |
| SWward | −392.13 | −122.03 | −18.62 | −184.14 | −43.20 | −4.47 | −575.78 | −165.15 | −22.58 |
| Net transport | 822.39 | 681.31 | 471.34 | 134.08 | 168.25 | 177.66 | 956.48 | 849.57 | 649.01 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duy Vinh, V.; Ouillon, S.; Van Thao, N.; Ngoc Tien, N. Numerical Simulations of Suspended Sediment Dynamics Due to Seasonal Forcing in the Mekong Coastal Area. Water 2016, 8, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060255
Duy Vinh V, Ouillon S, Van Thao N, Ngoc Tien N. Numerical Simulations of Suspended Sediment Dynamics Due to Seasonal Forcing in the Mekong Coastal Area. Water. 2016; 8(6):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060255
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuy Vinh, Vu, Sylvain Ouillon, Nguyen Van Thao, and Nguyen Ngoc Tien. 2016. "Numerical Simulations of Suspended Sediment Dynamics Due to Seasonal Forcing in the Mekong Coastal Area" Water 8, no. 6: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060255
APA StyleDuy Vinh, V., Ouillon, S., Van Thao, N., & Ngoc Tien, N. (2016). Numerical Simulations of Suspended Sediment Dynamics Due to Seasonal Forcing in the Mekong Coastal Area. Water, 8(6), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060255








