Microbial Community Assessment in Wetlands for Water Pollution Control: Past, Present, and Future Outlook
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Phase One—1880 to 2012
2.2. Phase Two—2013 to 2016
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Past
3.1.1. Historical Perspective
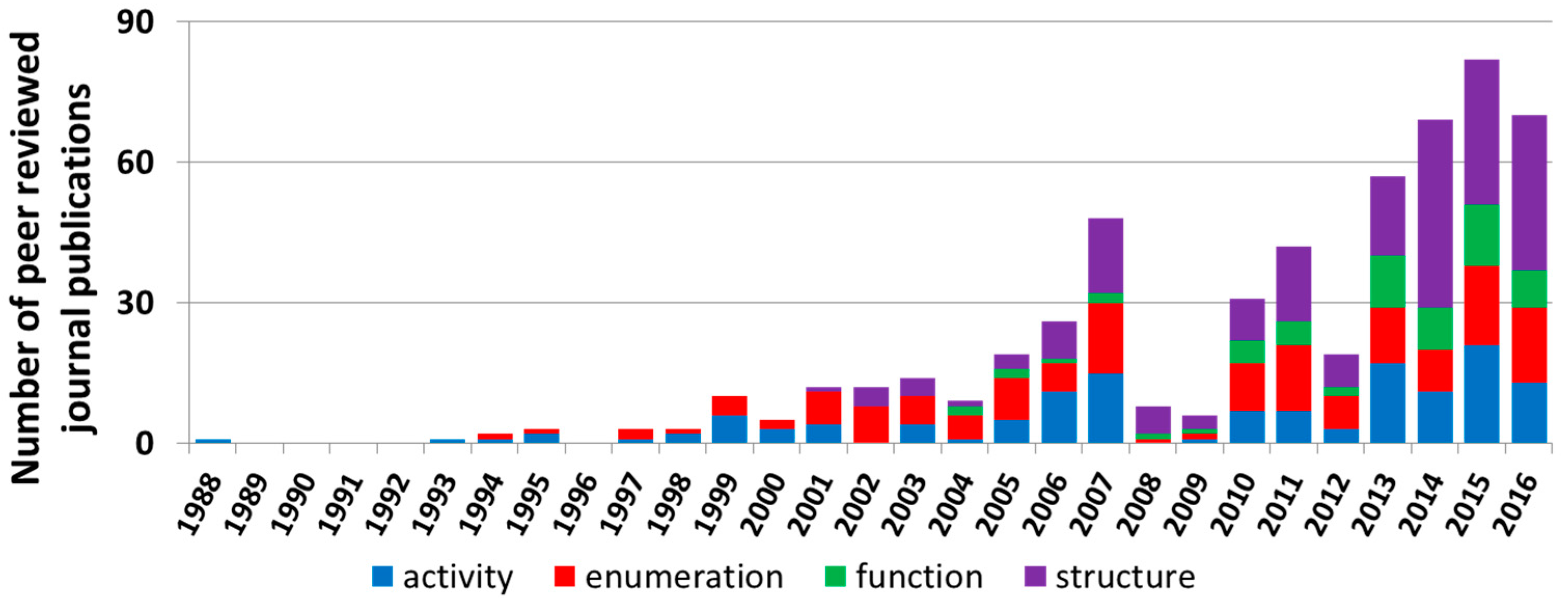
3.1.2. Microbial Community Assessment in Treatment Wetlands from 1988 to 2013
3.2. Present
3.2.1. Study Focus Areas
Functional Assessment
Structural Assessment
3.2.2. System Sizes
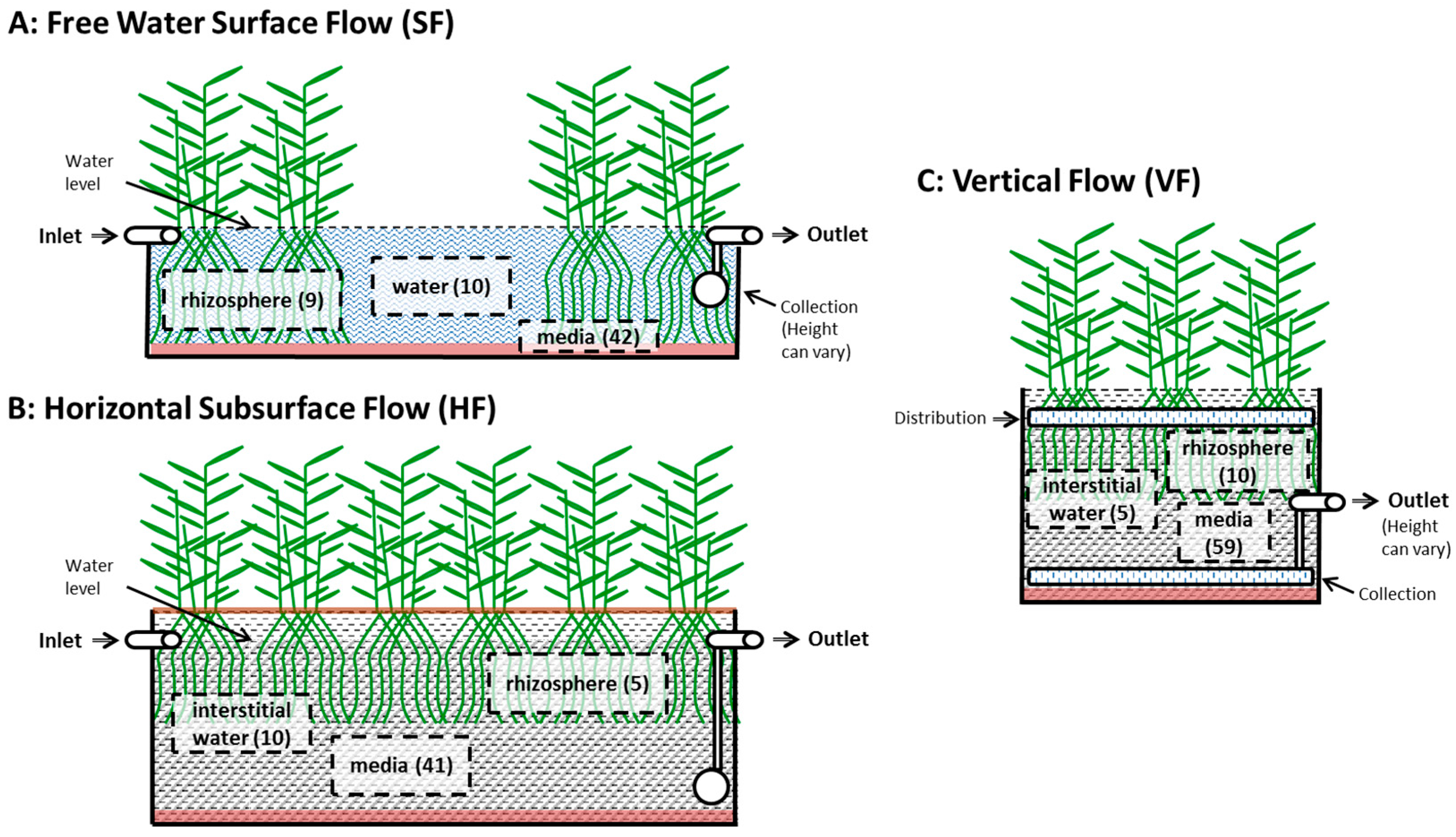
3.2.3. Internal Sampling Location
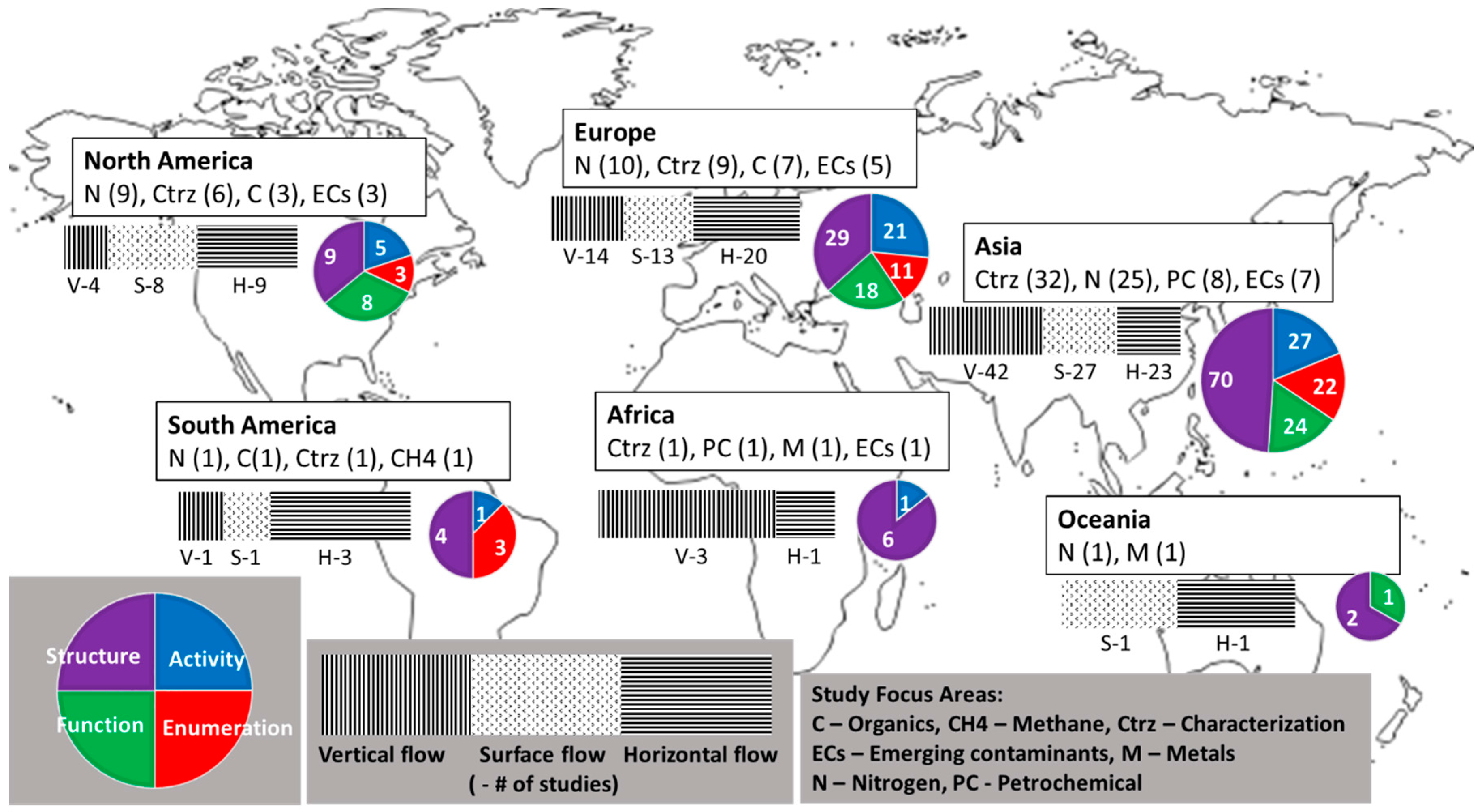
3.2.4. Regional Analysis
4. Conclusions and Future Horizons
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kadlec, R.; Wallace, S. Treatment Wetlands, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment. Water 2010, 2, 530–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment: Five Decades of Experience. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.; Rousseau, D.P.L.; Morato, J.; Lesage, E.; Matamoros, V.; Bayona, J.M. Contaminant Removal Processes in Subsurface-Flow Constructed Wetlands: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 561–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivala, J.; Murphy, C.; Troesch, S.; Wallace, S.; Esser, D. Intensified and Modified Wetland Designs. Sustain. Sanit. Pract. 2014, 18, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, K. Pflanzungen zwischen Gewassern und Land. Mitteilungen Max-Planck Gesselschaft 1953, 8, 17–20. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Fester, T.; Giebler, J.; Wick, L.Y.; Schlosser, D.; Kastner, M. Plant–microbe interactions as drivers of ecosystem functions relevant for the biodegradation of organic contaminants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, K.P.; Gagnon, V. Microbiology in Treatment Wetlands. Sustain. Sanit. Pract. 2014, 18, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Truu, J.; Truu, M.; Espenberg, M.; Nolvak, H.; Juhanson, J. Phytoremediation and Plant-Assisted Bioremediation in Soil and Treatment Wetlands: A Review. Open Biotechnol. J. 2015, 9, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truu, M.; Juhanson, J.; Truu, J. Microbial biomass, activity and community composition in constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3958–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsó, R.; Garcia, J. BIO_PORE, a mathematical model to simulate biofilm growth and water quality improvement in porous media: Application and calibration for constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 54, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivala, J.; Knowles, P.; Dotro, G.; Garcia, J.; Wallace, S. Clogging in subsurface flow treatment wetlands: Measurement, modeling and management. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1625–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, G.F.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zhu, W.; Shen, J.Q. An integrated model of substrate clogging in vertical flow constructed wetlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 119, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabzadeh, A.R.; Legge, R.; Weber, K.P. Multiphysics modelling of flow dynamics, biofilm development and wastewater treatment in a subsurface vertical flow constructed wetland mesocosm. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.; Chazarenc, F.; Claveau-Mallet, D.; Dittmer, U.; Forquet, N.; Molle, P.; Morvannou, A.; Pálfy, T.; Petitjean, A.; Anacleto, R.; et al. Modelling constructed wetlands: Scopes and aims—A comparative review. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 80, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulwetter, J.L.; Gagnon, V.; Sundberg, C.; Chazarenc, F.; Burr, M.D.; Brisson, J.; Campera, A.K.; Stein, O. Microbial processes influencing performance of treatment wetlands: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 987–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehle, S.; Elsaesser, D.; Gregoire, C.; Imfeld, G.; Niehaus, E.; Passeport, E.; Payraudeau, S.; Schäfer, R.B.; Tournebize, J.; Schulz, R. Pesticide risk mitigation by vegetated treatment systems: A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, A.; Matamoros, V.; Fontas, C.; Salvado, V. The ability of biologically based wastewater treatment systems to remove emerging organic contaminants—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 11708–11728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Button, M.; Nivala, J.; Weber, K.P.; Aubron, T.; Mueller, R.A. Microbial community metabolic function in subsurface flow constructed wetlands of different designs. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 80, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gest, H. The discovery of microorganisms by Robert Hooke and Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek, fellows of the Royal Society. Notes Rec. R. Soc. Lond. 2004, 58, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vymazal, J.; Sladecek, V.; Stach, J. Biota participating in wastewater treatment in a horizontal flow constructed wetland. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, D.C.; Davis, W.M.; Nickels, J.S.; King, J.D.; Bobbie, R.J. Determination of the sedimentary microbial biomass by extractable lipid phosphate. Oecologia 1979, 40, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, B.E.L.; Crable, B.R.; Suflita, J.M. On the contributions of David Cleaveland White, MD, PhD to microbial ecology: Celebrating the life of a pioneer. ISME J. 2008, 2, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlino, C.P. Bartolomeo Bizio’s Letter to the most Eminent Priest, Angelo Bellani, Concerning the Phenomenon of the Red Colored Polenta. J. Bacteriol. 1924, 9, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hatano, K.; Frederick, D.J.; Moore, J.A. Microbial Ecology of Constructed Wetlands Used for Treating Pulp Mill Wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 29, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Great Britain Royal Commission on Sewage Disposal. Final Report of the Commissioners Appointed to Inquire and Report What Methods of Treating and Disposing of Sewage (Including Any Liquid from Any Factory or Manufacturing Process) May Properly Be Adopted. General Summary of Conclusions and Recommendations; P.S. King and Son Ltd.: Orchard House, Westminster, London, UK, 1915. [Google Scholar]
- MacDougall, R.S. The Bacteria of the Soil, with Special Reference to Soil Inoculation. Trans. Bot. Soc. Edinb. 1897, 21, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, K.R.; Sexstone, A.J.; Bissonnette, G.K. Heterotrophic community-level physiological profiles of domestic wastewater following treatment by small constructed subsurface flow wetlands. Water Environ. Res. 2004, 76, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, J.L.; Mills, A.L. Classification and characterization of heterotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community-level sole-carbon-source utilization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Insam, H. A new set of substrates proposed for community characterization in environmental samples. In Microbial Communities: Functional Versus Structural Approaches; Insam, H., Rangger, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Brodrick, S.J.; Cullen, P.; Maher, W. Denitrification in a natural wetland receiving secondary treated effluent. Water Res. 1988, 22, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lünsmann, V.; Kappelmeyer, U.; Taubert, A.; Nijenhuis, I.; von Bergen, M.; Heipieper, H.J.; Müller, J.A.; Jehmlich, N. Aerobic toluene degraders in the rhizosphere of a constructed wetland model show diurnal polyhydroxyalkanoate metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4126–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, D.; Kuschk, P.; Mbwette, T.S.A.; Strange, F.; Muller, R.A.; Koser, H. New Aspects of Microbial Nitrogen Transformations in the Context of Wastewater Treatment—A Review. Eng. Life Sci. 2007, 7, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, J.D.C.; Donnelly, T.; Rayne, D.; Davenport, R.J. Microbial mechanisms of carbon removal in subsurface flow wetlands. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corbella, C.; Guivernau, M.; Vinas, M.; Puigagut, J. Operational, design and microbial aspects related to power production with microbial fuel cells implemented in constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2015, 84, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, M.W. Methyl-coenzyme M reductase genes: Unique functional markers for methanogenic and anaerobic methane-oxidizing Archaea. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 397, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhi, W.; Yuan, L.; Ji, G.; He, C. Enhanced Long-Term Nitrogen Removal and Its Quantitative Molecular Mechanism in Tidal Flow Constructed Wetlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4575–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Vymazal, J. Comment on “Enhanced Long-Term Nitrogen Removal and Its Quantitative Molecular Mechanism in Tidal Flow Constructed Wetlands”. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11241–11242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, W.; Yuan, L.; Ji, G.; He, C. Response to Comment on “Enhanced Long-Term Nitrogen Removal and Its Quantitative Molecular Mechanism in Tidal Flow Constructed Wetlands”. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11243–11244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Lavanchy, P.M.; Chen, Z.; Lünsmann, V.; Marin-Cevada, V.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Pieper, D.H.; Reiche, N.; Kappelmeyer, U.; Imparato, V.; Junca, H.; et al. Microbial toluene removal in hypoxic model constructed wetlands occurs predominantly via the ring monooxygenation pathway. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6241–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lünsmann, V.; Kappelmeyer, U.; Benndorf, R.; Martinez-Lavanchy, P.M.; Taubert, A.; Adrian, L.; Duarte, M.; Pieper, D.H.; von Bergen, M.; Müller, J.A.; et al. In situ protein-SIP highlights Burkholderiaceae as key players degrading toluene by para ring hydroxylation in a constructed wetland model. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hayatsu, M.; Fujii, T. Extraction of Bacterial RNA from Soil: Challenges and Solutions. Microbes Environ. 2012, 27, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, F.-A.; Lunsmann, V.; Kjeldal, H.; Jehmlich, N.; Tholey, A.; von Bergen, M.; Nielsen, J.L.; Hettich, R.L.; Seifert, J.; Nielsen, P.H. Enhancing metaproteomics—The value of models and defined environmental microbial systems. Proteomics 2016, 16, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, P.; Flood, J.A.; Ashbolt, N.J. The direct measurement of bacterial growth in biofilms of emergent plants (Schoenoplectus) of an artificial wetland. Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 32, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeckevelt, M.; Rokadia, H.; Imfeld, G.; Stelzer, N.; Paschke, H.; Kuschk, P.; Kastner, M.; Richnow, H.-H.; Weber, S. Assessment of in situ biodegradation of monochlorobenzene in contaminated groundwater treated in a constructed wetland. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 148, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligi, T.; Oopkaupa, K.; Truu, M.; Preema, J.-K.; Nolvaka, H.; Mitsch, W.J.; Mander, U.; Truu, J. Characterization of bacterial communities in soil and sediment of a created riverine wetland complex using high-throughput 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 72, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.P.; Legge, R.L. Comparison of the catabolic activity and catabolic profiles of rhizospheric, gravel-associated and interstitial microbial communities in treatment wetlands. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helt, C.D.; Weber, K.P.; Legge, R.L.; Slawson, R.M. Antibiotic resistance profiles of wetland bacteria and fecal indicators following ciprofloxacin exposure in lab-scale constructed mesocosms. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 39, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.P.; Mitzel, M.R.; Slawson, R.M.; Legge, R.L. Effect of ciprofloxacin on microbiological development in wetland mesocosms. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3185–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolvak, H.; Truu, M.; Tiirik, K.; Oopkaup, K.; Sildvee, T.; Kaasik, A.; Mander, U.; Truu, J. Dynamics of antibiotic resistance genes and their relationships with system treatment efficiency in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Button, M.; Auvinen, H.; Van Koetsem, F.; Hosseinkhani, B.; Rousseau, D.; Weber, K.P.; Du Laing, G. Susceptibility of constructed wetland microbial communities to silver nanoparticles: A microcosm study. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.P.; Legge, R.L. Method for the detachment of culturable bacteria from wetland gravel. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 80, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Button, M.; Weber, K.P.; Nivala, J.; Aubron, T.; Muller, R.A. Community-level physiological profiling of constructed wetland microbial communities: Effects of sample preparation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 178, 960–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Constructed Wetland | Treatment Wetland | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compendex | microbiology | 81 | Compendex | microbiology | 94 |
| microbiological | 81 | microbiological | 94 | ||
| microbial | 179 | microbial | 196 | ||
| Web of Science | microbiology | 7 | Web of Science | microbiology | 5 |
| microbiological | 25 | microbiological | 22 | ||
| microbial | 353 | microbial | 308 | ||
| Total | 726 | Total | 719 | ||
| Classification | Method | Crtz | N | C | ECs | CH4 | Petr | S | M | MFC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activity | Adenosine Triphosphate | 6 | ||||||||
| Amino Acid Assimilation | 3 | |||||||||
| O2 utilization | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| CO2 production | 10 | 6 | 4 | 3 | ||||||
| CH4 evolution | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| Enzyme Activity | 24 | 11 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Stable Isotope Probes | 6 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | |||||
| Ex-situ N Transformations | 2 | 28 | 2 | 4 | ||||||
| Other Transformations | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Function | CLPP | 19 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| qPCR (DNA–specific gene) | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||
| qPCR (DNA–N gene) | 1 | 21 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||
| FISH (specific gene) | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| qPCR (mRNA) | 1 | |||||||||
| Microarray | 1 | |||||||||
| Proteomics | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| Enumeration | Plate counting | 21 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | ||
| Most Probably Number | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Staining | 7 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Flow Cytometry | 2 | |||||||||
| qPCR (16S rRNA only) | 11 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Grid Counting | 8 | 1 | ||||||||
| FISH | 9 | 5 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Organic Mass/Fumigation | 8 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| EPS Components | 5 | |||||||||
| Stable Isotope Probes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Structure | FAME/PLFA | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| DGGE/TGGE/SSCP | 30 | 16 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 2 | |||
| TRFLP/ARDRA | 8 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| RISA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| DGGE Band Sequencing | 21 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| 454 Pyrosequencing | 9 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||
| ABI PRISM sequencing | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Sanger sequencing | 2 | |||||||||
| Illumina Miseq | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| Illumina Hiseq | 2 | |||||||||
| Unknown Sequencing | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||||
| Microscopy | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weber, K.P. Microbial Community Assessment in Wetlands for Water Pollution Control: Past, Present, and Future Outlook. Water 2016, 8, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110503
Weber KP. Microbial Community Assessment in Wetlands for Water Pollution Control: Past, Present, and Future Outlook. Water. 2016; 8(11):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110503
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeber, Kela P. 2016. "Microbial Community Assessment in Wetlands for Water Pollution Control: Past, Present, and Future Outlook" Water 8, no. 11: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110503
APA StyleWeber, K. P. (2016). Microbial Community Assessment in Wetlands for Water Pollution Control: Past, Present, and Future Outlook. Water, 8(11), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110503






