Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Water Resources in the Songhua River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Overview of ArcSWAT Model
2.4. Calibration and Validation of ArcSWAT Model
3. Results
3.1. Model Performance
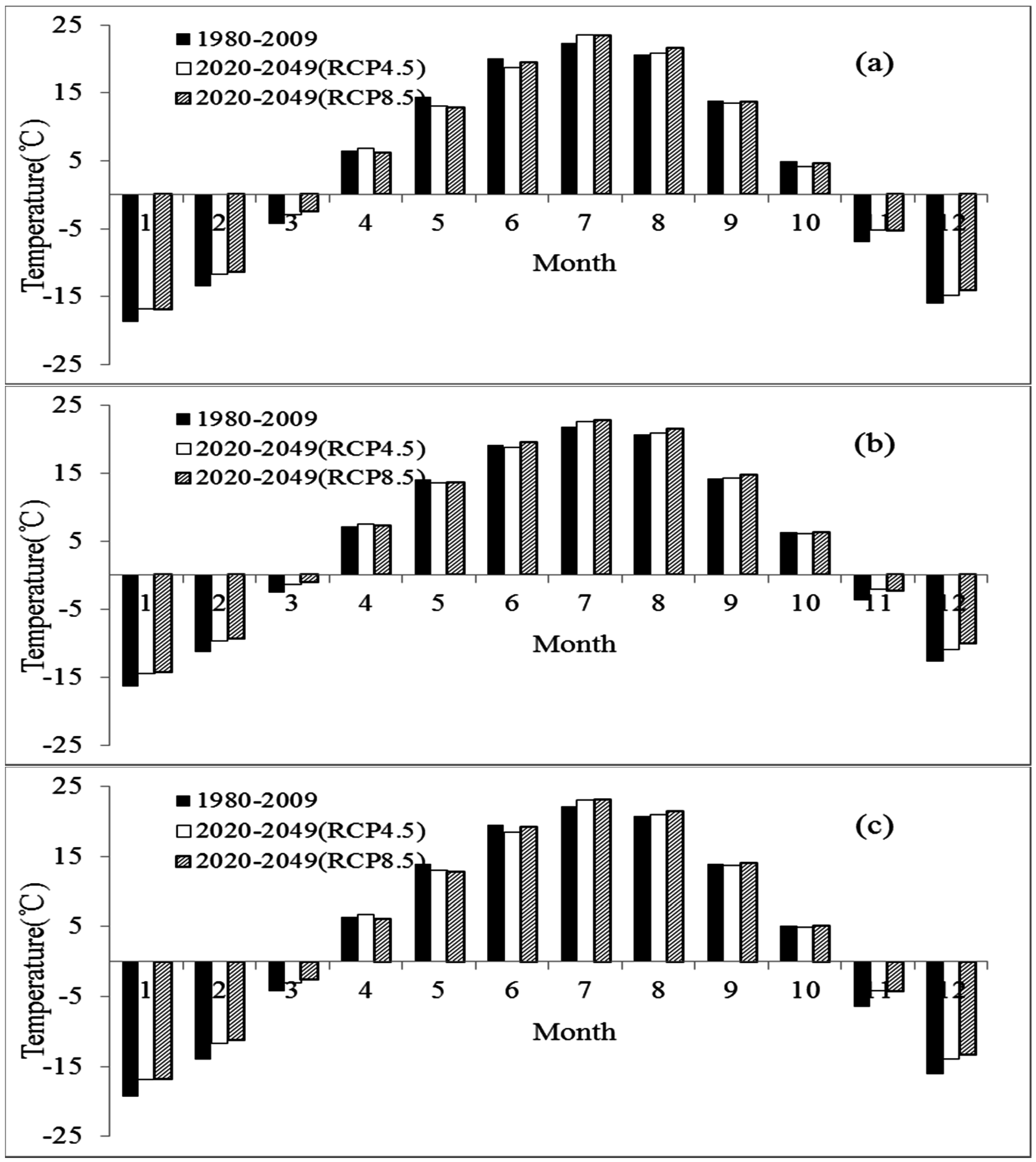
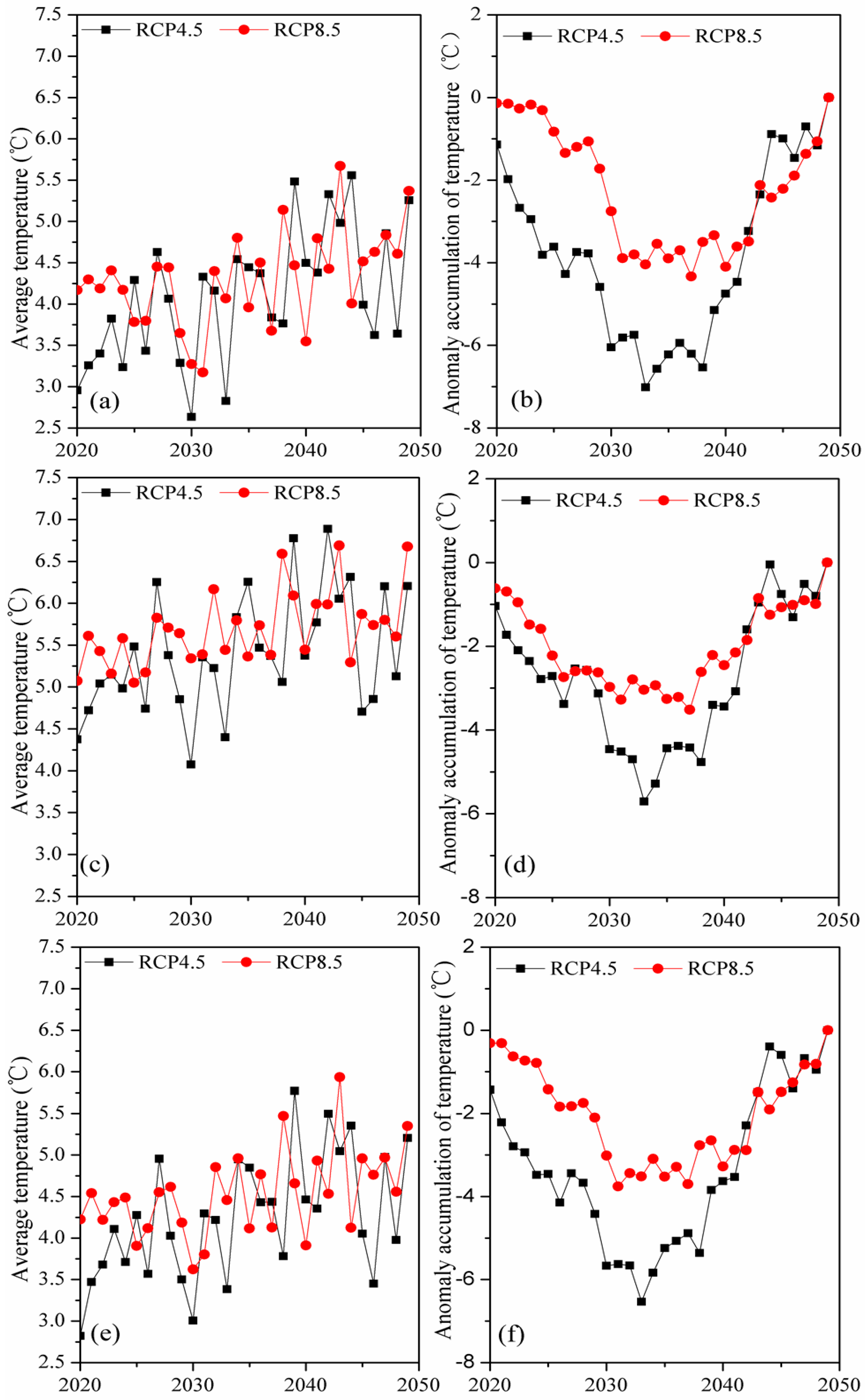
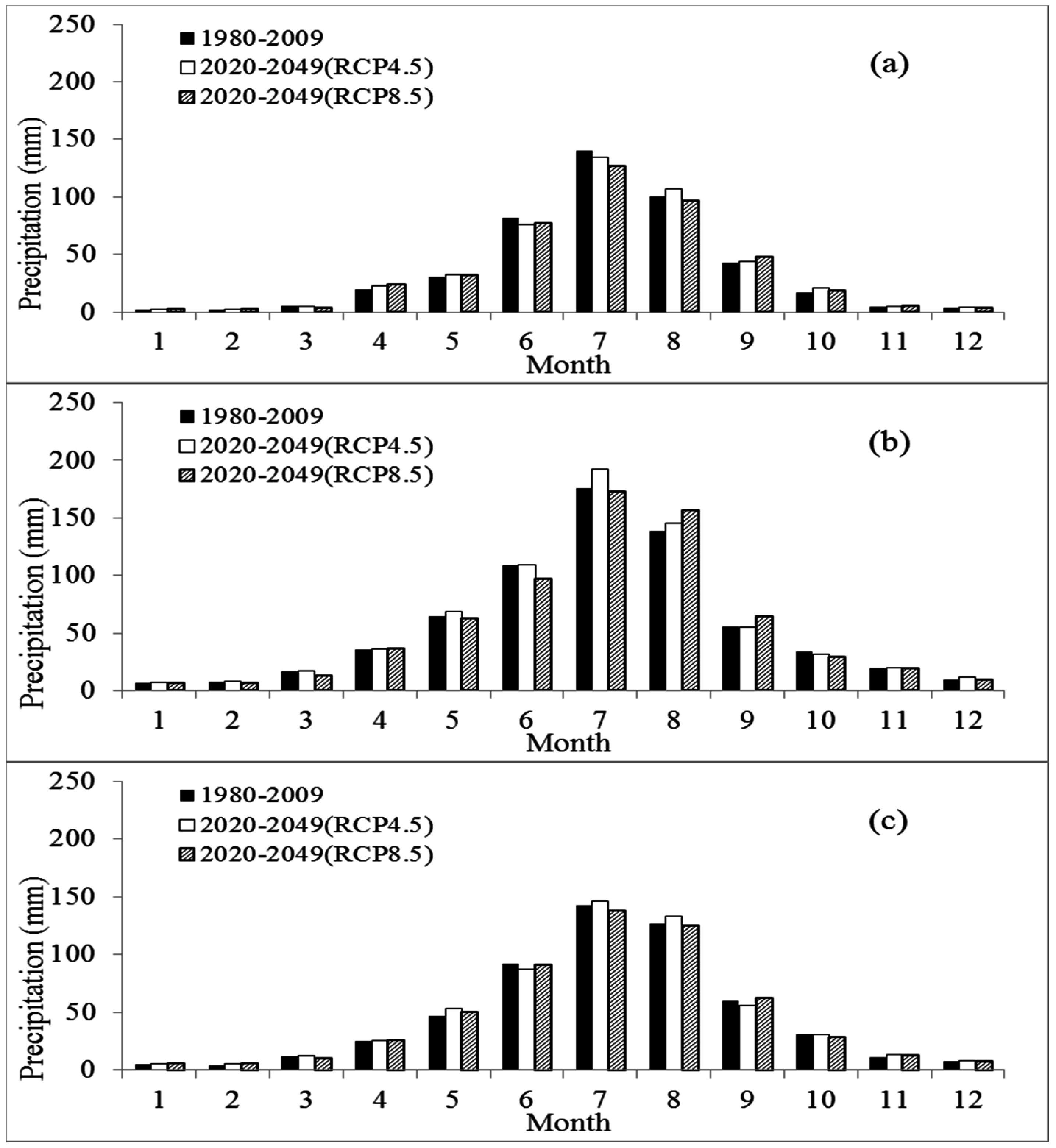
3.2. Changes of Projected Temperature and Precipitation
3.2.1. Changes of Projected Temperature
3.2.2. Changes of Projected Precipitation
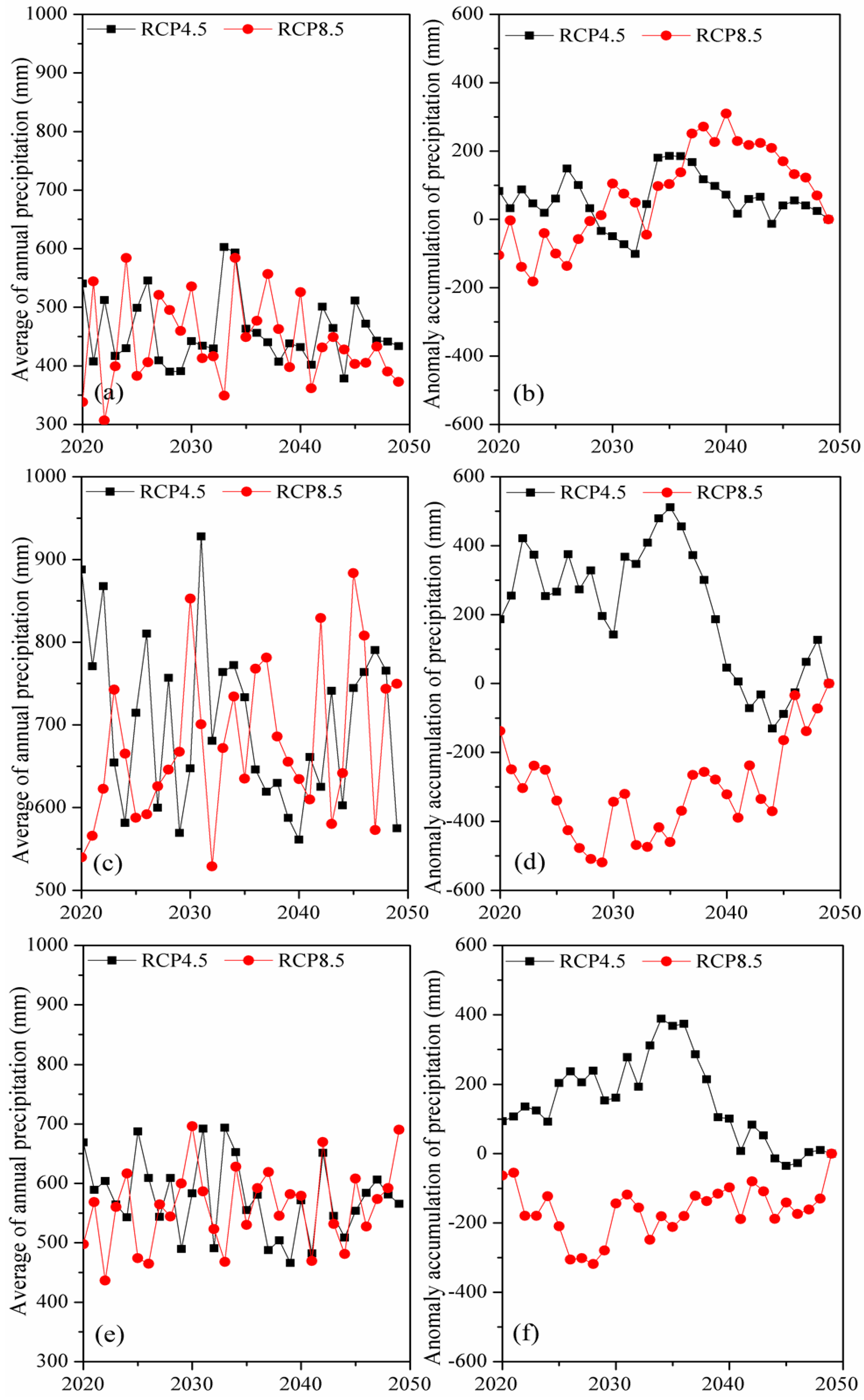
3.3. Changes in Water Resources During 2020–2049
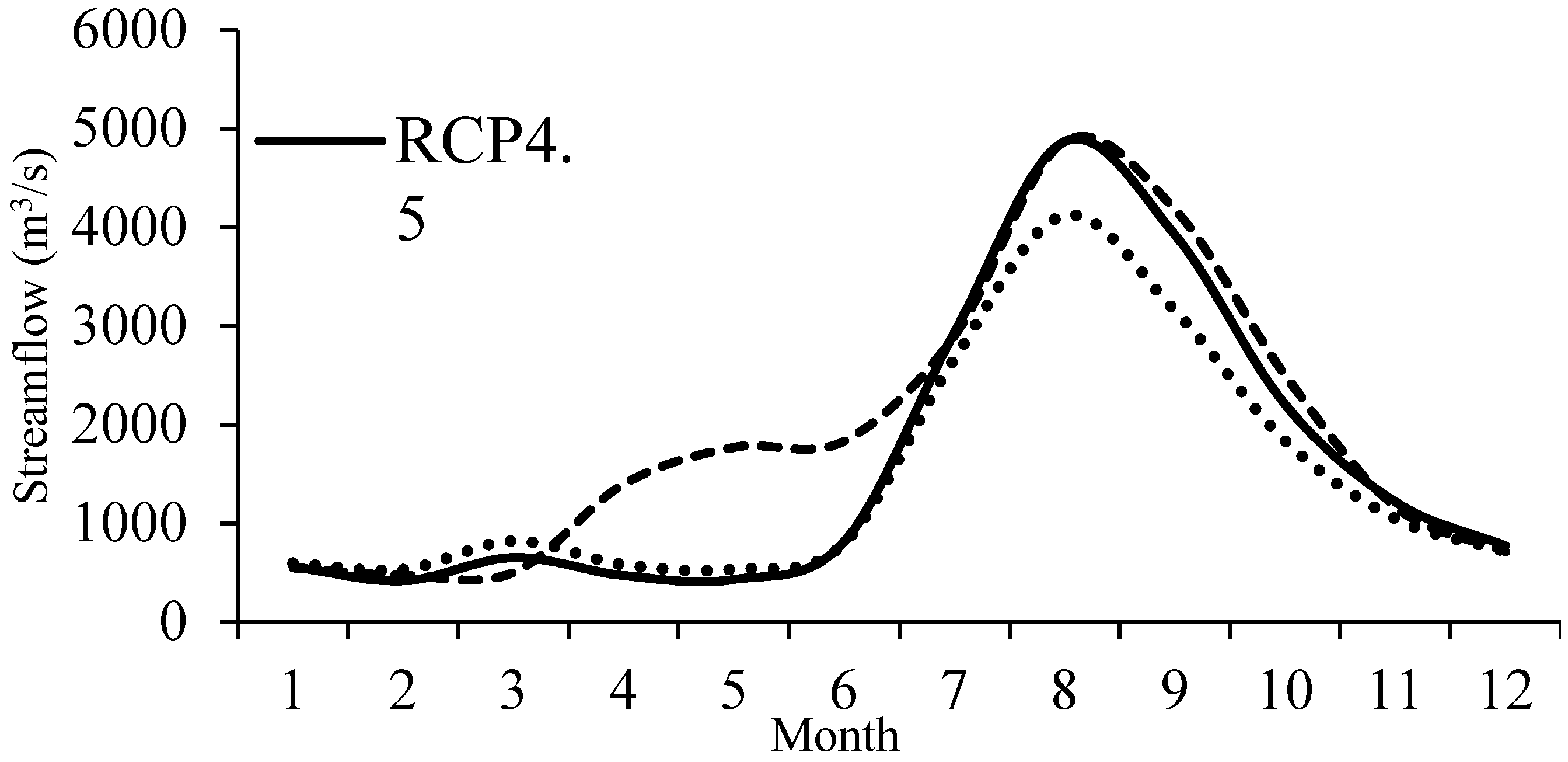
3.3.1. Intra-Annual and Inter-Annual Variations of Streamflow
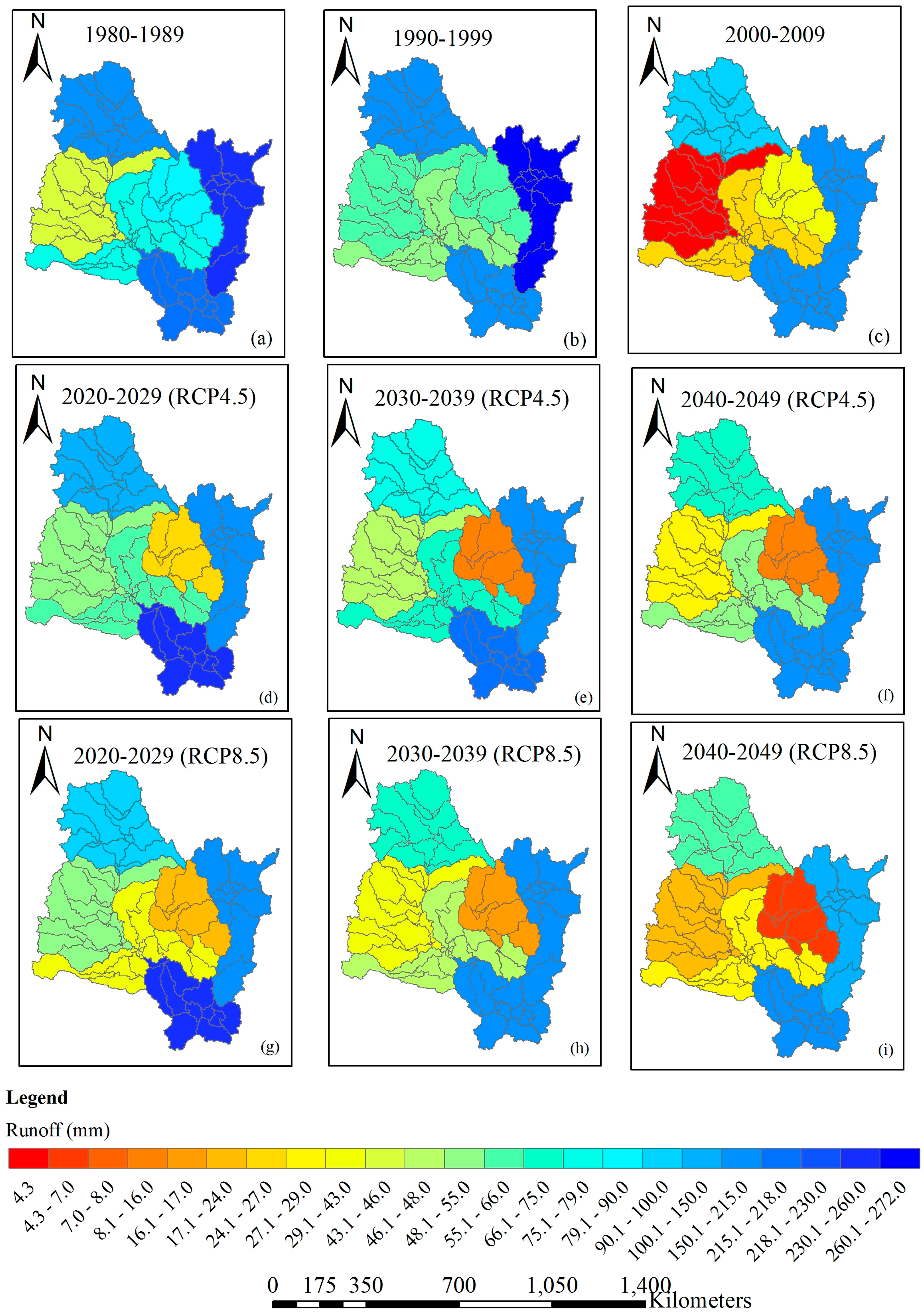
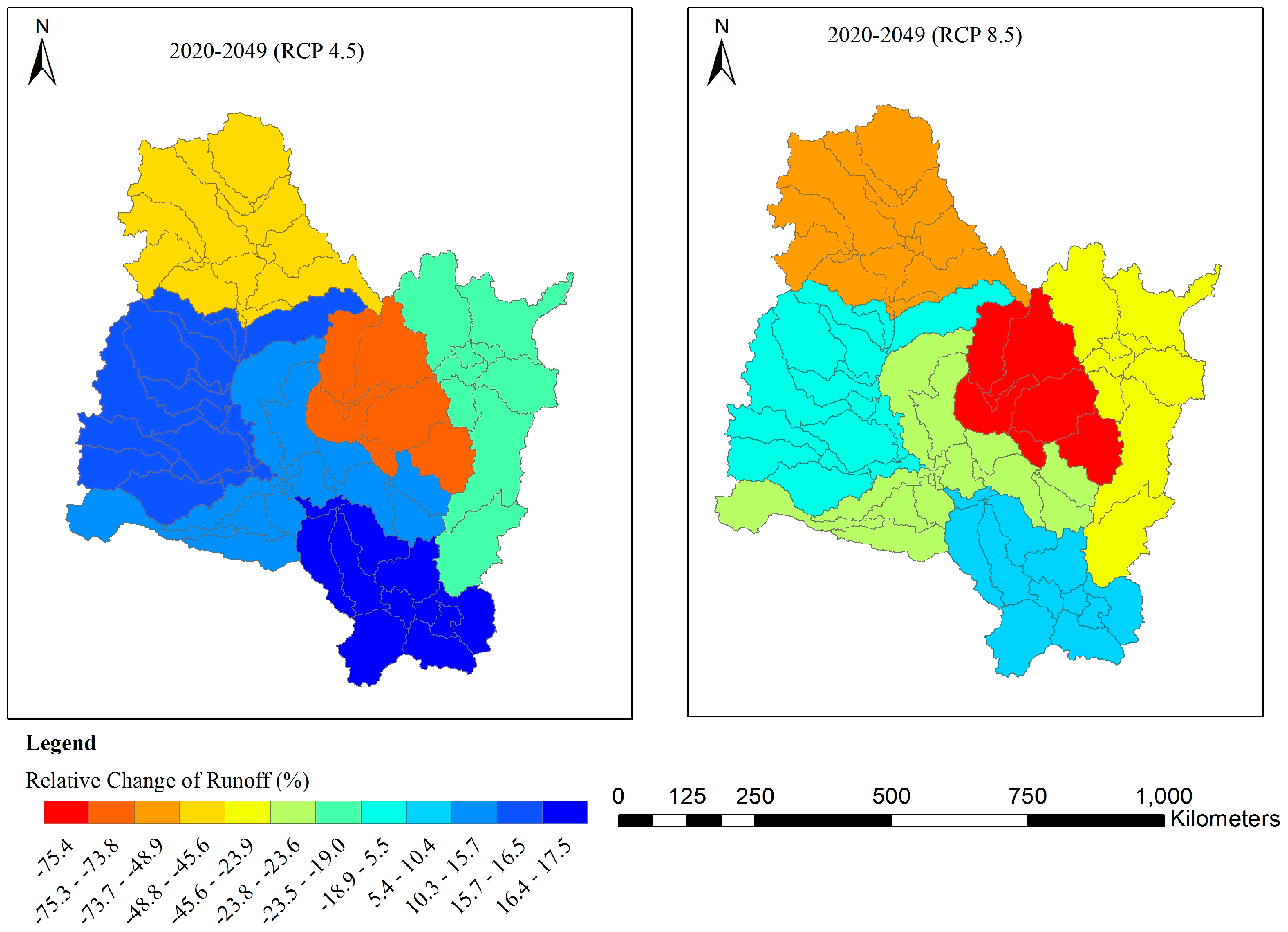
3.3.2. Spatial Variations of Predicted Water Resources
4. Discussion
4.1. Implication of This Study
4.2. Limitation of This Study
5. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.; Jung, I.W. Spatial and temporal changes in runoff caused by climate change in a complex large river basin in Oregon. J. Hydrol. 2010, 388, 186–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Sridhar, V. Impacts of Climate Change on Hydrology and Water Resources in the Boise and Spokane River Basins 1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2011, 48, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghefi, S.A.; Mousavi, S.J.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H. Analyses of the impact of climate change on water resources components, drought and wheat yield in semiarid regions: Karkheh River Basin in Iran. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 2018–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.E.; Funk, C.C. Food security under climate change. Science 2008, 319, 580–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.; Velde, M.V.D.; Lin, E.; Xiong, W.; Li, Y.C. The impacts of climate change on agricultural production systems in China. Clim. Chang. 2013, 120, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.H.; Peng, S.S.; Li, J.S.; Zhou, L.P.; Liu, H.Y.; Ma, Y.C.; Ding, Y.H.; et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, B. Global climate change and its impacts on water resources planning and management: Assessment and challenges. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2011, 25, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, B.; Harbor, J.; Engel, B.; Grove, M. Assessing Watershed-Scale, Long-Term Hydrologic Impacts of Land-Use Change Using a GIS-NPS Model. Environ. Manag. 2000, 26, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, M.G.R.; Young, A.R.; Goodwin, T.H.; Grew, R. A catchment-based water resource decision-support tool for the United Kingdom. Environ. Model. Softw. 2005, 20, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.H.; Shakya, N.M. Hydrological changes and its impact on water resources of Bagmati watershed, Nepal. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notter, B.; Macmillan, L.; Viviroli, D.; Weingartner, R.; Liniger, H.P. Impacts of environmental change on water resources in the Mt. Kenya region. J. Hydrol. 2007, 343, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J. Spatiotemporal variability of climate and streamflow in the Songhua River Basin, northeast China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 514, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, X.; Shao, W. A study on the annual runoff change and its relationship with water and soil conservation practices and climate change in the middle Yellow River basin. Catena 2013, 100, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, E.; Liu, D.L. Modelling the impacts of climate change on wheat yield and field water balance over the Murray—Darling Basin in Australia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 104, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, L.R. Assessing the effect of climate change on mean annual runoff. J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Liu, C.M.; Huang, W.C.; Lin, S.S.; Yen, T.H.; Wang, H.R.; Kuo, J.T.; Lee, Y.C. Developing a yearly warning index to assess the climatic impact on the water resources of Taiwan, a complex-terrain island. J. Hydrol. 2010, 390, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.K.; Sharma, N.; Pattnayak, K.C.; Gao, X.J.; Shi, Y. Temperature and precipitation changes in the north-east India and their future projections. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2012, 98–99, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawadi, S.; Ahmad, S. Changing climatic conditions in the Colorado River Basin: Implications for water resources management. J. Hydrol. 2012, 430–431, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Lasanta-Martínez, T.; Beguería, S. Mediterranean water resources in a global change scenario. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 105, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, L.; Wilk, J.; Todd, M.C.; Hughes, D.A.; Earle, A.; Kniveton, D.; Layberry, R.; Savenije, H.H. Impact of climate change and development scenarios on flow patterns in the Okavango River. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Xia, Z.Q.; Yu, L.L.; Wang, J.C. Temporal and spatial variation of characteristics of precipitation in Songhua River Basin during 1958–2009. J. Nat. Res. 2012, 27, 990–1000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Miao, C.Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.L. Streamflow changes and its influencing factors in the mainstream of the Songhua River basin, Northeast China over the past 50 years. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.Q.; Zhang, G.X. The dynamic evolvement and hydrological driving factors of marsh in Nenjiang River basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2013, 24, 177–183. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, G.; Yin, X. Hydrological Responses to Climate Change in Nenjiang River Basin, Northeastern China. Water Res. Manag. 2011, 25, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Analysis of Annual Runoff Variation Characteristics in Main Rivers of China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 2866–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, P.; Shao, H.; Wang, F. The Runoff Declining Process and Water Quality in Songhuajiang River Catchment, China under Global Climatic Change. CLEAN—Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Mo, X. Assessing the effect of climate change on mean annual runoff in the Songhua River basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Lin, Y.; Liu, B.; Gao, Y.; Li, S. Streamflow changes and its influencing factors in the mainstream of the Songhua River basin, Northeast China over the past 50 years. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiessen, A.H. Precipitation Averages for Large Areas. Mon. Weather Rev. 1911, 39, 1082–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setegn, S.G.; Rayner, D.; Melesse, A.M.; Dargahi, B.; Srinivasan, R. Impact of climate change on the hydroclimatology of Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, R.; Bao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Shen, Z. Uncertainty of SWAT model at different DEM resolutions in a large mountainous watershed. Water Res. 2014, 53, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, F.; Hao, Z.; Xu, C.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Tong, K. Impact of projected climate change on the hydrology in the headwaters of the Yellow River basin. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4379–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griensven, A.V.; Meixner, T.; Grunwald, S.; Bishop, T.; Diluzio, M.; Srinivasan, R. A global sensitivity analysis tool for the parameters of multi-variable catchment models. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Johnson, C.A.; Genuchten, M.T.V. Estimating Uncertain Flow and Transport Parameters Using a Sequential Uncertainty Fitting Procedure. Vadose Zone J. 2004, 3, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.L.; Ren, Z.Y.; Zhang, C. Statistical analysis on precipitation in Xi’an Region during the last 50 years. J. Northwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 44, 139–144. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Bu, R.C.; Xiong, Z.P.; Hu, Y.M. Characteristics of temperature and precipitation in Northeastern China from 1961 to 2005. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 519–531. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Yao, B.; Ni, G. Crop Water Demand in China under the SRA1B Emissions Scenario. Adv. Water Sci. 2011, 22, 38–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J.; Huang, Z. Influence of Irrigation Water Discharge Frequency on Soil Salt Removal and Rice Yield in a Semi-Arid and Saline-Sodic Area. Water 2013, 5, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y. Separating the Impacts of Climate Variation and Human Activities on Runoff in the Songhua River Basin, Northeast China. Water 2014, 6, 3320–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.H.; Jiang, W.G.; Luo, Z.L.; He, X.H.; Liu, Y.H. Analysis of wetland change in the Songhua River Basin from 1995 to 2008. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 17, 12125–12131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majone, B.; Bovolo, C.; Bellin, A.; blenkinsop, S.; Fowler, H.J. Modeling the impacts of future climate change on water resources for the Gállego river basin (Spain). Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, T.; Carambia, M.; Goergen, K.; Kotlarski, S.; Krahe, P.; Zappa, M.; Schär, C. Quantifying uncertainty sources in an ensemble of hydrological climate-impact projections. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Schaefli, B.; Mezghani, A.; Hingray, B.; Musy, A. Assessment of climate change impacts on alpine discharge regimes with climate model uncertainty. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2091–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Poulin, A.; Leconte, R. Overall uncertainty study of the hydrological impacts of climate change for a Canadian watershed. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Wetterhall, F.; Seibert, J. Evaluation of different downscaling techniques for hydrological climate-change impact studies at the catchment scale. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 37, 2087–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniyal, B.; Jha, M.K.; Verma, A.K. Assessing Climate Change Impact on Water Balance Components of a River Basin Using SWAT Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 4767–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, N.; Dietrich, J. Using SWAT for Strategic Planning of Basin Scale Irrigation Control Policies: A Case Study from a Humid Region in Northern Germany. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 3285–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
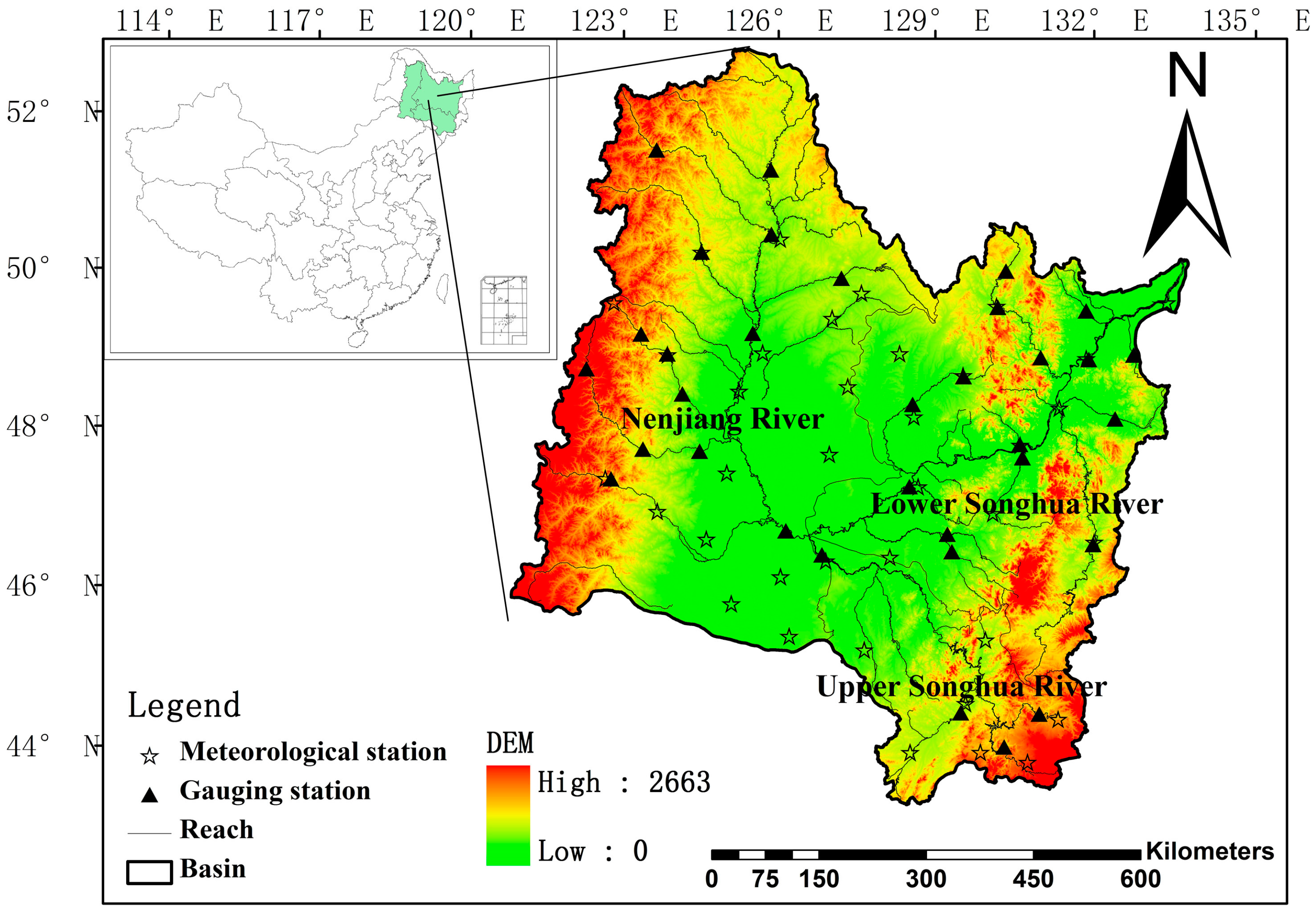

| Gauging Station | River | Basin | Drainage Area (km2) | Annual Runoff (108 m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiwen | Gan River | Nenjiang River Basin | 4879 | 10.83 |
| Liujiatun | 19,665 | 36.54 | ||
| Suolun | Taoer River | 5893 | 5.99 | |
| Balin | Yalu River | 2807 | 4.10 | |
| Zhalantun | 6891 | 9.97 | ||
| Nianzishan | 13,567 | 18.06 | ||
| Taerqi | Chuoer River | 1906 | 2.96 | |
| Wendegen | 12,447 | 17.58 | ||
| Liangjiazi | 15,544 | 18.86 | ||
| Xiaoergou | Nuomin River | 16,761 | 31.07 | |
| Dedu | Nemoer River | 7200 | 11.04 | |
| Shihuiyao | Mainstream | 17,205 | 27.66 | |
| Tongmeng | 108,029 | 150.65 | ||
| Dalai | 221,715 | 197.44 | ||
| Wudaogou | Huifa River | Upper Songhua River Basin | 12,391 | 23.05 |
| Gaolichengzi | Mainstream | 4728 | 23.29 | |
| Hanyangtun | 8532 | 29.92 | ||
| Fuyu | 71,783 | 141.82 | ||
| Tieli | Hulan River | Lower Songhua River Basin | 1838 | 5.10 |
| Qinjia | 9809 | 20.22 | ||
| Danianzigou | Lalin River | 5241 | 12.72 | |
| Wuchang | 5642 | 14.46 | ||
| Lianhua | Mayi River | 10,425 | 20.57 | |
| Mudanjiang | Mudan River | 22,194 | 50.69 | |
| Woken | Woken River | 4185 | 4.25 | |
| Baoquanling | Wutong River | 2750 | 8.09 | |
| Fulitun | Anbang River | 547 | 0.94 | |
| Wuying | Tangwang River | 4160 | 11.03 | |
| Yixin | 10,272 | 27.02 | ||
| Chenming | 19,186 | 51.35 | ||
| Haerbin | Mainstream | 389,769 | 393.44 | |
| Tonghe | 450,077 | 438.02 | ||
| Jiamusi | 528,277 | 612.70 |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| CN2 | Initial SCS runoff curve number for moisture condition II |
| ESCO | Soil evaporation compensation factor |
| CH_K2 (mm/h) | Effective hydraulic conductivity in main channel alluvium |
| SURLAG (day) | Surface runoff lag coefficient |
| GW_DELAY (day) | Delay time for aquifer recharge |
| ALPHA_BF (day) | Baseflow alpha factor |
| GWQMN (mm H2O) | Threshold depth of water in the shallow aquifer required for return flow to occur |
| GW_REVAP | Groundwater “revap” coefficient |
| REVAPMN (mm) | Threshold depth of water in the shallow aquifer for evaporation |
| SOL_AWC (mm H2O/mm soil) | Available water capacity of the soil layer |
| SOL_K (mm/h) | Saturated hydraulic conductivity |
| Model Evaluation | Ens | R2 | Er |
|---|---|---|---|
| Excellent | 0.75 < Ens ≤ 1.00 | 0.80 <R2 ≤ 1.00 | |Er| ≤ 10 |
| Good | 0.65 < Ens ≤ 0.75 | 0.70 < R2 ≤ 0.80 | 10 < |Er| ≤ 15 |
| Satisfactory | 0.54 < Ens ≤ 0.65 | 0.50 < R2 ≤ 0.70 | 15 < |Er| ≤ 25 |
| Unsatisfactory | 0 < Ens ≤ 0.54 | 0 < R2 ≤ 0.50 | |Er| > 25 |
| Simulation Periods | Ens | R2 | Er |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration (1980–1994) | 0.67 | 0.83 | −7.60 |
| Validation (1995–2009) | 0.72 | 0.74 | −9.63 |
| Climate Scenarios | Changing Rate (108 m3/a) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| NRB | USRB | LSRB | |
| RCP 4.5 | −3.62 | −2.02 | −3.60 |
| RCP 8.5 | −3.53 | −1.96 | −3.53 |
| 1980–2009 (108 m3) | RCP 4.5 | RCP 8.5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020–2049 (108 m3) | Relative Change (%) | 2020–2049 (108 m3) | Relative Change (%) | ||
| NRB | 202.8 | 135.9 | −33 | 126.1 | −37.8 |
| USRB | 138.8 | 163.3 | 17.7 | 152.2 | 9.68 |
| LSRB | 263.1 | 209.6 | −20.3 | 179.8 | −31.7 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J. Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Water Resources in the Songhua River Basin. Water 2016, 8, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8100420
Li F, Zhang G, Xu YJ. Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Water Resources in the Songhua River Basin. Water. 2016; 8(10):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8100420
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fengping, Guangxin Zhang, and Y. Jun Xu. 2016. "Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Water Resources in the Songhua River Basin" Water 8, no. 10: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8100420
APA StyleLi, F., Zhang, G., & Xu, Y. J. (2016). Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Water Resources in the Songhua River Basin. Water, 8(10), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8100420







