Abstract
The identification of the sources and fate of contaminants is important to protect the water quality of aquifer systems. In this study, contaminated groundwater from the drinking water wells in the Shijiazhuang area, China, was chemically (/Cl− ratio) and isotopically (δ15NNO3, δ18ONO3 and δ13CDOC; δ2HH2O, δ18OH2O) characterized to identify the sources of and address subsequent biogeochemical processes. The positive correlations between dominant anions and cations suggested that the dissolution of calcium carbonate and gypsum minerals was the most effective process in the groundwater. Elevated concentrations of , Cl− and Mg2+ could be related to the wastewater irrigation and usage of fertilizers. The natural water in the study area originated primarily from precipitation and experienced a limited extent of evaporation, as demonstrated by measurements of δ2HH2O and δ18OH2O. A cross-plot of δ15NNO3 vs. δ18ONO3 gave an enrichment of the 15N isotope relative to the 18O isotope by a factor of 2. A further insight into the denitrification process was obtained by the synergistic changes in δ13CDOC and δ15NNO3 values, confirming that a low extent of denitrification occurred. Nitrification processes were evaluated by means of δ18ONO3 and δ18OH2O. The initial δ15NNO3 value(s) of the source(s) were roughly estimated between 2‰ and 5‰. Based on the level of natural , anthropogenic activities were considered the main reason for the elevated concentration of the shallow groundwater. fertilizers were the major source of in the non-wastewater irrigated area, while wastewater was regarded as the primary source of in the wastewater-irrigated area. A low content of in deep groundwater might mainly be influenced by precipitation and soil organic N that was involved in denitrification reactions. Some of the deep groundwater samples could have been contaminated by wastewater. The mixing process of multiple sources was identified as another important factor affecting the concentration of the groundwater in the study area. The combined use of δ15NNO3, δ18ONO3 and δ13CDOC results and hydrochemical data (/Cl− ratios) gives an insight into the mixing effect of different sources and processes affecting concentration under conditions of intensive land-use activities.
1. Introduction
Shijiazhuang (SJZ) City is a representative area, which has been developed from a rural area to a metropolitan city in China. In most suburban and rural regions of SJZ, groundwater is the major source of drinking water due to the inadequate centralized water supply system. Nitrate contamination in groundwater caused by intensive land-use activities has become a major environmental concern in this area [1,2]. To prevent the deterioration of groundwater quality due to nitrate contamination, it is important to discern the major sources and fate of nitrate [3,4,5].
Some studies have been conducted to identify the nitrate contamination of groundwater using stable isotopes near the city of SJZ [6,7,8]. In the wastewater-irrigated area (the southern part of the study area), a stable N isotope of nitrate indicated that the nitrate in the groundwater originated from wastewater or a mixture of pig manure and wastewater [6,8]. However, the single isotope approach applied in these studies could not fully interpret the transformation of nitrogen in the groundwater. In the non-wastewater-irrigated area, a combination of δ15NNO3 and δ18ONO3 was used to trace sources in the shallow groundwater, suggesting that fertilizer and manure were the main sources of in the groundwater; nevertheless, denitrification seriously interfered with determining the source of nitrate [7].
In addition, previous studies drew different conclusions on whether microbial denitrification occurred. Chen et al., found a good linear relationship of δ15N and the logarithm of the residual that was consistent with denitrification of in groundwater in the southern part of the study area [6]. Similarly, Liu and Chen observed a linear relationship with a slope of 0.644 (ɛN/ɛO = 1.5) between δ15NNO3 and δ18ONO3 values (4.6‰–9.7‰ and 2.3‰–7.8‰, respectively) confirming the occurrence of denitrification [7]. Others, however, suggested the absence of denitrification based on constant /Cl− values, high DO values (1.20–5.97 mg/L) and a limited range of δ15NNO3 values [8]. In general, it is difficult to specify the varied sources and processes that affect the isotope composition of due to the isotope fractionation combined with similar isotopic values of various sources in SJZ area.
Similarly, isotopic composition of nitrate used to constrain the sources and fate of N also appears to have certain limitation in other study cases [4,5,9,10]. δ15NNO3 was not sufficient to estimate potential sources of nitrate contamination in rural regions in Korea since the concentration and δ15NNO3 of the unconfined groundwater nitrate exhibited seasonal variations due to seasonal changes in agricultural activities [11]. Later, the same author proposed that the impacts of various land-use activities on the nitrate contamination of groundwater could be more precisely inferred from long-term data on the concentration and δ15NNO3 of nitrate [12]. Since denitrification and mixing processes limited the identification of sources by δ15NNO3 in the groundwater, δ15NNO3 was combined with co-migrating isotopic tracers (δ11B and 87Sr/86Sr) to distinguish various sources under intensive agricultural activities in Brittany (France) [13]. In addition, based on the level of natural in the groundwater, anthropogenic contamination (inorganic fertilizer) can be discriminated from the soil organic N using δ15NNO3 and δ18ONO3 isotopic values in the Mt. Vulture area (Italy) [14]. These studies indicated that, for better understanding of the various sources and transformations of in groundwater, it is important to couple isotopic composition of with multiple lines of evidence.
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is ubiquitous in groundwater [15]. Changes in concentration and composition of DOC reflect biogeochemical sources and reaction processes that determine the chemical composition of groundwater [16,17,18]. Numerous studies have described the importance of organic carbon in controlling the occurrence of denitrification. Several studies relate denitrification activity to DOC concentration [19,20]. The availability of organic carbon limits the denitrification rate [17,21,22,23,24]. On the other hand, biogeochemical activities can be inferred from elevated δ13CDOC values [25,26]. Breukelen et al., found that dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentration decreased in association with increasing δ13CDOC values in a landfill leachate plume, supporting the occurrence of degradation and denitrification potentially being the dominated redox process at the top fringe [27]. It is hypothesized that the combination of δ13CDOC and δ15NNO3 isotopic values would provide a sensitive method for tracing denitrification process in groundwater.
The /Cl− method has been proven to be a valid and effective tool to distinguish the effect of N removal processes by dilution from denitrification [28,29]. In addition, the /Cl− in groundwater can be used as a source indicator because different sources of nitrate and chloride have different ratios in most cases [18,30]. Nishikawa et al., reported that the /Cl− ratios for the native groundwater, imported water, and septage collected in Warren ground-water basin were completely different. Based on the /Cl− ratios and concentrations, a three-part mixture of native ground water, imported water, and septage was identified [18]. Liu et al., showed the variation of the /Cl− molar ratios with Cl− concentrations in the surface and groundwater samples as well as sewage samples in both the summer and winter seasons [30]. Two source end members were distinguished as agricultural inputs with low-Cl/high-/Cl− ratios and municipal inputs with high-Cl/low-/Cl− ratios close to sewage.
In this study, the characteristics of δ15NNO3, δ18ONO3, and δ13CDOC were investigated in the unconfined Quaternary aquifers of SJZ, China. Traditional hydrochemical and isotopic parameters such as chemical composition (anion, cation, DOC concentrations and /Cl− ratio), δ2HH2O, and δ18OH2O of groundwater were also measured. The aim of this study is to combine δ15NNO3, δ18ONO3, and δ13CDOC data with the /Cl− ratio to understand biogeochemical processes in an alluvial aquifer where there are multiple potential sources, and to identify the mixing process of different sources in this region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
The Shijiazhuang (SJZ) area is located in the piedmont pluvial plain of Hutuo River (Figure 1). The region is middle-latitude continental semiarid monsoon climate with mean annual temperature of 12–13 °C, mean annual precipitation of 500–600 mm, and potential evaporation of 1100–1800 mm [31,32]. Historically, the Hutuo River played an important role in the formation of the alluvial fan at the front edge of the piedmont plain zone in the study area [33]. Today, the river is disconnected and severed due to drought and interception of water by the Huangbizhuang reservoir. The Shijin and Dongming canals are mainly used for agricultural irrigation. Xiao River is a seasonal stream originating from a mountainous area. Over the past few decades, a quantity of industrial and domestic wastewater flowed into Xiao River through Dongming Canal.
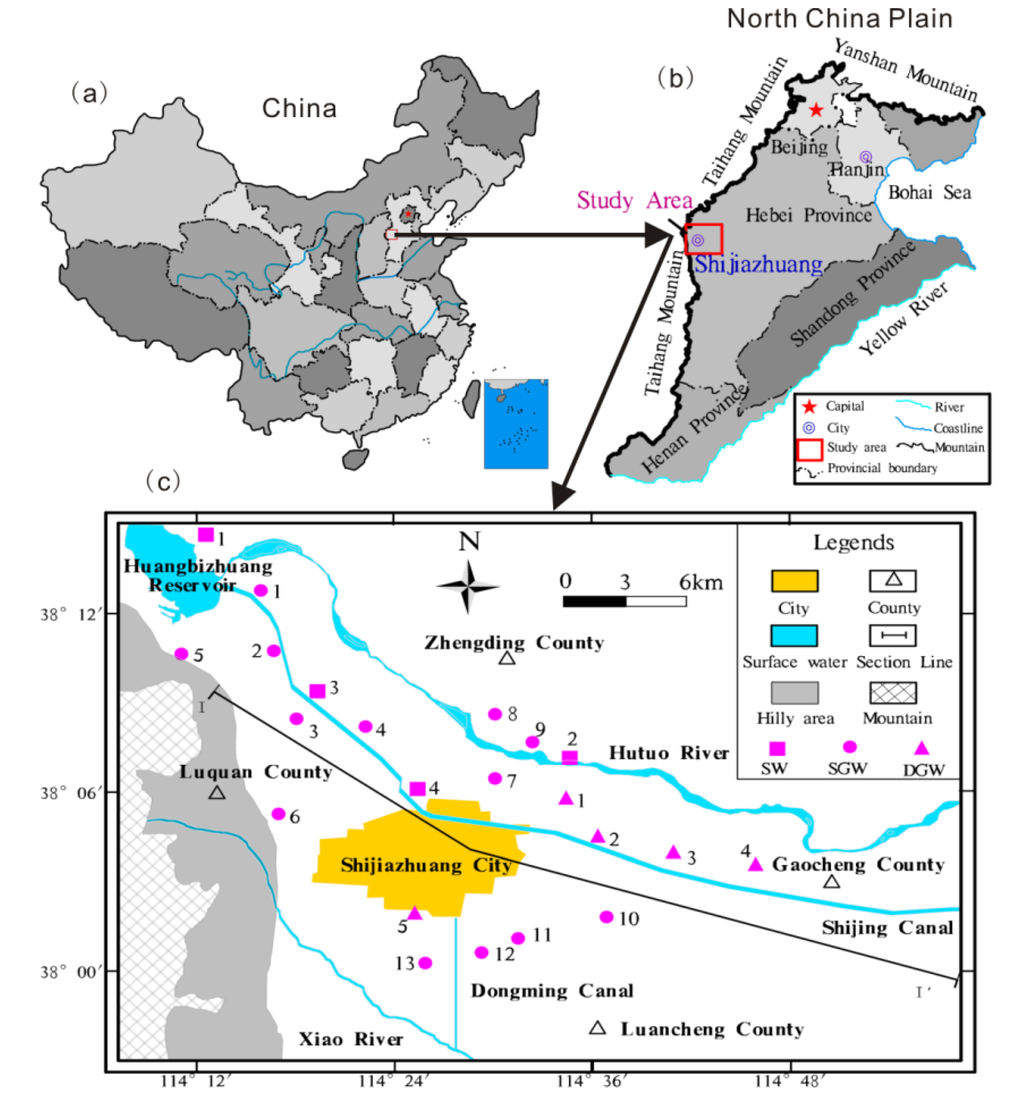
Figure 1.
Illustration of the study area and sampling points. (a,b) are location maps of the study area; and (c) sampling map. Line I–I' indicates location of hydrogeologic cross section in Figure 2. (SW: Surface water; SGW: Shallow groundwater; DGW: Deep groundwater).
The aquifers in this area are mainly composed of the multi-layer loose deposits of Quaternary with a depth of 350–450 m in the piedmont (Figure 2). The regional Quaternary aquifers can be divided into four groups: The Holocene formation (Q4), the late Pleistocene formation (Q3), the middle Pleistocene formation (Q2), and the early Pleistocene formation (Q1) [34]. Aquifer 1 (A1) is an unconfined shallow aquifer dominated by coarse-grained sand with the bottom boundary at 10–20 m deep, in which groundwater has been drained. Aquifer 2 (A2), a 50 m thick shallow confined aquifer (30–80 m depth), contains sandy gravel and medium to fine sand, and is the main source of groundwater for drinking water supplies. Aquifers 3 (A3) and 4 (A4) are both deep confined aquifers, consisting of 90 m thick sandy gravel (80–200 m depth) and 50–60 m thick cemented sandy gravel (300–370 m depth), respectively [1,34]. The shallow aquifers (A1 and A2) can be regarded as one system as a result of the natural hydraulic connection between them [31]. Aquifers 3 and 4 can be recognized as the deep unit. The shallow aquifers are over developed and contaminated, increasing the need to pump clean groundwater from the deep aquifers.
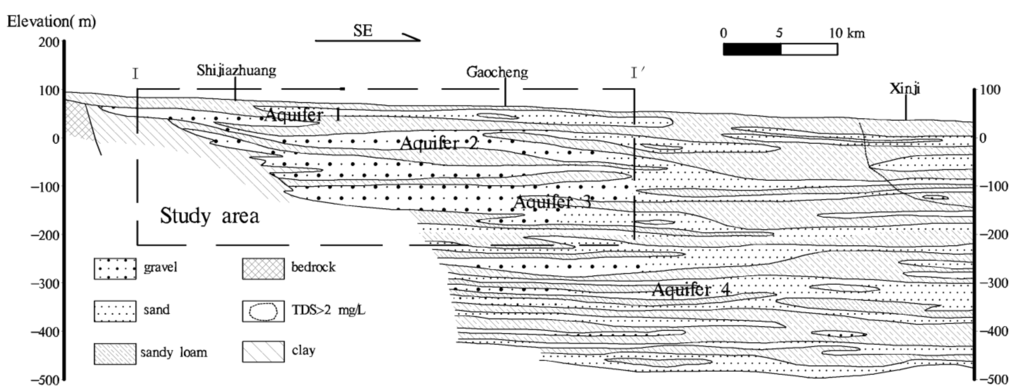
Figure 2.
The hydrogeologic cross section in Shijiazhuang. The range of study area is marked by rectangle with dashed lines. The Quaternary aquifers are divided into four groups named as Aquifers 1–4.
Several components make up groundwater recharge in the shallow groundwater aquifer unit: Precipitation, irrigation return flow, infiltration of surface water in rivers and canals, and lateral inflow from the Taihang Mountains [35]. The deep aquifer is mainly recharged by infiltration of paleo-precipitation under cold climatic conditions with modern vertical inflow from the shallow aquifer as another source.
Currently, groundwater discharge in the study area is mainly through intensive localized pumping in SJZ City and widespread pumping via small capacity wells for irrigation in the surrounding country areas [31,32,36]. Groundwater exploitation has resulted in serious water-level decline, forming a 400 km2 groundwater cone of depression in the shallow aquifer [37,38]. The water table is currently more than 10 m below ground surface; thus, evaporation of groundwater is generally considered negligible [39].
2.2. Sampling and Analytical Methods
Groundwater samples from domestic wells and surface water samples from the Huangbizhuang reservoir, Hutuo River and Shijin Canal were collected in September 2011 (Figure 1). Samples were collected unacidified for analysis of concentrations and values for anion, deuterium, and oxygen isotopes. Samples were acidified to pH <2 with concentrated HNO3 for cation analysis. To obtain sufficient dissolved for N and O isotope analyses, five liters of water were taken from each sampling site. For dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentration and C isotope analysis, 500 mL water samples were collected in amber glass bottles. All these samples were stored below 4 °C and transferred to the lab for chemical and isotopic analyses. The temperature, pH values and electrical conductivity (EC) were measured on site. Alkalinity was determined by titration within 24 h after sampling. Samples were filtered through 0.45 μm membrane filters prior to measurement of ion and DOC concentration, and C, N, O and H isotopic analyses. All these measurements were performed at China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), China.
The concentrations of major cations and anions were measured by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (ICAP6300, ICP-OES, Thermo Jarrell Ash Co., Franklin, MA, USA) and ion chromatography (Dionex ICS-1100, Dionex Co, Sunnyvale, CA, USA), respectively. DOC concentrations were determined using a TOC/TN analyzer (Analytik Jena AG, Jena, Germany).
All stable isotopic compositions are reported in per mil relative to their corresponding international standards (VPDB for 13C, V-SMOW for 2H and 18O, AIR for 15N), using the delta notation: δ(‰) = [(R − Rstd)/Rstd] × 1000, where R and Rstd are the isotope ratio of the sample and the standard, respectively.
O and H isotopic compositions were determined by a Thermal Conversion Elemental Analyzer (TC/EA, Thermo Finnigan, Bremen, Germany) coupled with the MAT 253 (Thermo Finnigan) [40], with a precision of ±0.1‰ and ±1‰ for δ18OH2O and δ2HH2O, respectively.
For analysis of N and O isotopes in nitrate, a modification of the procedure described by Silva (2000) was used for the conversion of dissolved to AgNO3 salt [41]. The water samples were filtered through 0.45 μm membrane filters in the laboratory. The Barium chloride was added to precipitate sulfate and phosphate in 5 L samples. Then the solution was filtered, agitated with activated carbon to remove dissolved organic matters, passed through a cation exchange column to remove all cations, neutralized with Ag2O, filtered to remove the AgCl precipitate, and freeze-dried to obtain solid AgNO3 [41]. About 0.5 mg AgNO3was transferred to silver capsules and loaded into the auto-sampler coupled to the EA (Flash 2000, Thermo Finnigan). N2 and CO generated after AgNO3 pyrosis at 1325 °C were separated in a chromatographic column at 60 °C, and then introduced into MAT 253 (Thermo Finnigan) where δ15NNO3 and δ18ONO3 were determined with a total uncertainty of ±0.3‰ for δ15NNO3 and of ±0.5‰ for δ18ONO3, respectively, for solutions of KNO3 standard processed through the entire column procedure.
To measure the C isotope of DOC, 200 mL water from each sample was concentrated to a volume of about 1 mL at 40 °C in a round-bottomed flask by rotary evaporation, and then acidified to pH 2 by adding 2–3 drops of 85% phosphoric acid to remove the dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) by agitation. Flask was rinsed with two 1.5 mL aliquots of ultra-pure deionized water, resulting in a final volume of 3.5–4.5 mL. One hundred μL of the concentrated sample was transferred to silver capsules (8 mm × 5 mm) and dried at 70 °C. More details about the procedure for preparation were described in a previous study [42]. The δ13CDOC analyses was carried out using a MAT 253 (Thermo Finnigan) after combustion in a Flash EA via open split at a temperature of 1020 °C, with a precision of ±0.25‰.
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition
The geochemical parameters and major ion composition of surface water (SW), shallow groundwater (SGW), and deep groundwater (DGW) samples are summarized in Table 1. Chemical data obtained are also plotted on a Piper diagram (Figure 3).
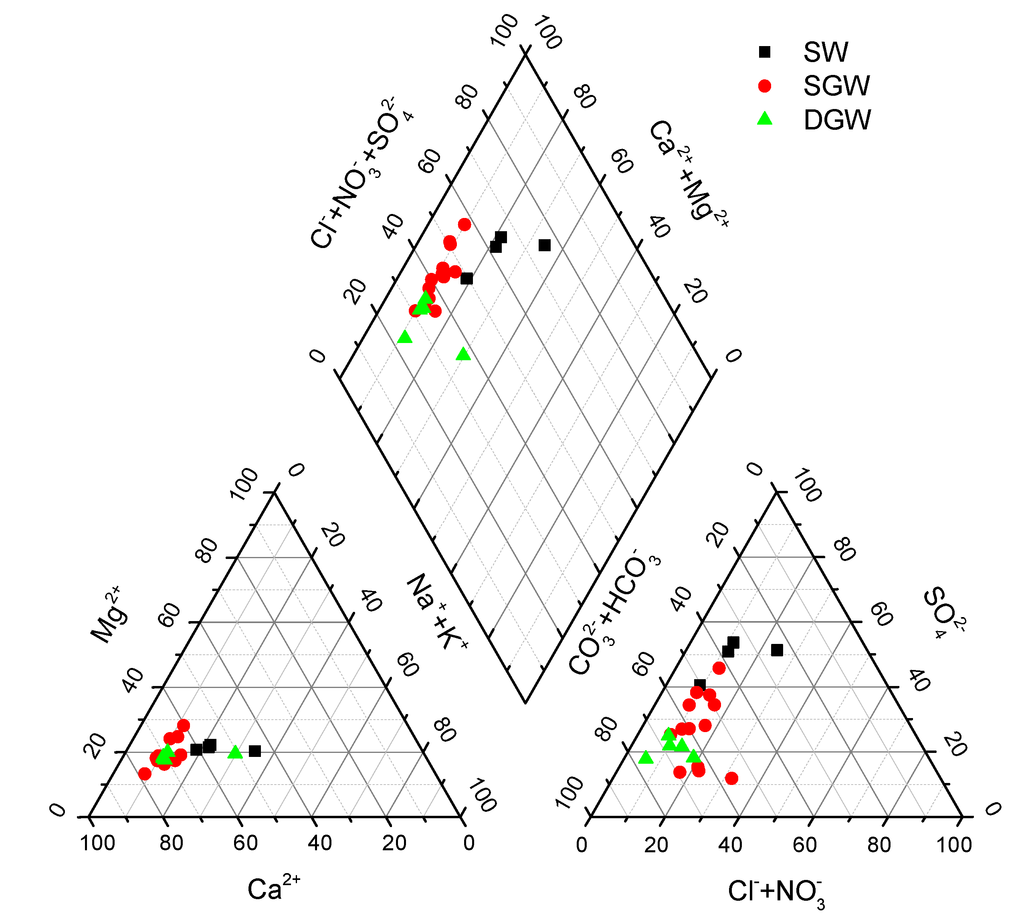
Figure 3.
Piper diagram of water samples. (SW: Surface water; SGW: Shallow groundwater; DGW: Deep groundwater).
The SW samples were alkaline with a pH of 8.1 to 9.2. Water temperatures ranged from 18 to 26 °C. Electrical conductivities (EC) varied from 577 to 717 μS/cm. Concentrations of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in the SW samples ranged from 4.1 to 22.1 mg C/L. The dissolved oxygen (DO) in SW01 and SW03 were 4.7 and 4.8 mg/L, respectively, while the DO concentration in SW02 was lower (2.3 mg/L). The concentrations of cations and anions in most SW samples followed the order: Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Na+ + K+ and > > Cl− + , except anions in the sample SW4 ( > > Cl− + ).

Table 1.
Chemical compositions and field data of the surface water and groundwater in Shijiazhuang.
| Sample | Site Description | Depth (m) | T (°C) | pH | EC (μS/cm) | DOC (mg C/L) | DO | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | Chemical Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg/L) | ||||||||||||||||
| Surface Water | ||||||||||||||||
| SW1 | HBZ Reserior | – | 18 | 8.4 | 689 | 4.1 | 4.7 | 4.3 | 22.7 | 69.6 | 27.6 | 57.2 | 263.3 | 2.6 | 194.7 | SO4-HCO3-Ca-Mg |
| SW2 | Hutuo River | – | 19 | 9.2 | 715 | 22.1 | 2.3 | 10.4 | 35.6 | 59.9 | 27.0 | 104.2 | 222.7 | 2.1 | 105.3 | SO4-HCO3-Ca-Mg |
| SW3 | Shijin Canal | – | 22 | 8.5 | 717 | 6.3 | 4.8 | 4.4 | 23.1 | 72.3 | 27.3 | 55.1 | 266.1 | 2.6 | 172.5 | SO4-HCO3-Ca-Mg |
| SW4 | Shijin Canal | – | 26 | 8.1 | 577 | 14.2 | n.d. | 4.6 | 17.5 | 71.4 | 24.4 | 37.6 | 178.2 | 2.3 | 221.2 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| Shallow Groundwater | ||||||||||||||||
| SGW1 | Yancun | 34 | 24 | 7.6 | 906 | 4.2 | 2.6 | 1.6 | 20.0 | 125.1 | 28.5 | 52.2 | 232.6 | 10.7 | 380.5 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| SGW2 | Baichigan | 40 | 20 | 7.4 | 928 | 3.9 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 16.8 | 133.3 | 31.9 | 65.6 | 192.6 | 13.3 | 442.4 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| SGW3 | Dahe | 40 | 19 | 7.2 | 1179 | 4.7 | 2.9 | 1.4 | 20.1 | 171.4 | 42.8 | 119.5 | 302.5 | 21.4 | 433.6 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| SGW4 | Houdubei | 45 | 26 | 7.6 | 808 | 4.6 | n.d. | 1.8 | 21.0 | 105.7 | 26.9 | 48.9 | 227.0 | 6.5 | 310.6 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| SGW5 | Shiqiyu | 60 | 17 | 7.3 | 970 | 20.2 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 20.1 | 162.5 | 38.7 | 68.6 | 332.7 | 16.2 | 309.7 | SO4-HCO3-Ca-Mg |
| SGW6 | Taitou | 15 | 16 | 7.1 | 1199 | 10.2 | 2.2 | 0.5 | 23.0 | 215.1 | 36.5 | 108.2 | 350.2 | 15.6 | 460.1 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| SGW7 | Beigaoying | 60 | 21 | 7.2 | 1005 | 4.8 | 2.0 | 2.2 | 16.4 | 140.5 | 36.9 | 65.3 | 192.1 | 26.2 | 424.7 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| SGW8 | Xiguan | 50 | 23 | 7.4 | 986 | 5.7 | 3.1 | 3.2 | 20.1 | 137.4 | 36.3 | 57.3 | 227.5 | 22.3 | 592.8 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| SGW9 | Taipingcun | 60 | 22 | 7.6 | 920 | 9.6 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 18.5 | 140.2 | 37.1 | 92.9 | 184.7 | 17.3 | 362.8 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| SGW10 | Bafang | 60 | 19 | 7.4 | 795 | 5.3 | 1.8 | 2.3 | 13.4 | 104.1 | 38.0 | 95.2 | 80.5 | 5.7 | 407.0 | HCO3-Cl-Ca-Mg |
| SGW11 | Dongxuying | 60 | 24 | 7.3 | 1007 | 9.9 | 1.1 | 2.2 | 20.6 | 123.7 | 48.0 | 142.9 | 108.8 | 7.7 | 451.2 | HCO3-Cl-Ca-Mg |
| SGW12 | Shaojiazhuang | 40 | 17 | 7.1 | 1189 | 15.8 | 2.8 | 2.0 | 24.9 | 140.7 | 65.6 | 254.0 | 102.2 | 23.2 | 486.6 | HCO3-Cl-Ca-Mg |
| SGW13 | Gaoqianbeijie | 60 | 17 | 7.0 | 1188 | 4.8 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 36.1 | 159.1 | 46.3 | 174.7 | 121.3 | 15.1 | 548.6 | HCO3-Cl-Ca-Mg |
| Deep Groundwater | ||||||||||||||||
| DGW1 | Xizhaotong | 100 | 23 | 7.9 | 589 | 3.9 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 13.5 | 90.2 | 22.5 | 33.5 | 112.5 | 4.8 | 300.8 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| DGW2 | Wujiaying | 100 | 17 | 7.6 | 537 | 4.3 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 11.6 | 82.1 | 21.0 | 42.8 | 97.0 | 3.1 | 300.8 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| DGW3 | Liangcun | 125 | 18 | 7.7 | 507 | 3.1 | 1.8 | 1.3 | 11.1 | 80.8 | 21.2 | 52.8 | 85.6 | 1.8 | 256.6 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| DGW4 | Nandun | 150 | 20 | 7.8 | 464 | 3.3 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 9.6 | 68.3 | 19.8 | 22.3 | 68.2 | 0.5 | 292.0 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
| DGW5 | Tatan | 180 | 20 | 7.5 | 994 | 5.5 | 2.6 | 1.2 | 49.8 | 87.0 | 33.5 | 121.7 | 125.1 | 5.9 | 433.6 | HCO3-SO4-Ca-Mg |
Notes: T, temperature; EC, electrical conductivity; DOC, dissolved organic carbon; DO, dissolved oxygen; n.d., not determined.
The pH values of SGW samples ranged from 7.0 to 7.6, and temperatures ranged from 16 to 26 °C. Conductivities varied from 795 to 1199 μS/cm. The DOC concentrations of most SGW samples varied in the range of 3.9 to 10.2 mg C/L, except for samples of SGW5 and SGW12 with values of 20.2 and 15.8 mg C/L, respectively. The DO concentration in SGW samples ranged from 1.1 to 3.1 mg/L. The orders of dominant cations and anions in SGW samples were Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Na+ + K+ and > > Cl− + , except the order of anion in sample SGW5 was > > Cl− + and in SGW10-13 was > Cl− + > . In particular, the HCO3.Cl-Ca.Mg type of groundwater was generally found in the southeastern part of the study area where the wastewater was used for irrigation during the1960s to 2000s [6].The DGW samples had pH values of 7.5 to 7.9 and temperatures between 17 and 23 °C. Most samples had low conductivities ranging from 464 to 589 μS/cm, whereas sample DGW5 had a high value of 994 μS/cm. The DGW samples had relatively low DOC concentrations in a narrow range of 3.1 to 5.5 mg C/L. The DO concentration in DGW samples ranged from 1.5 to 2.6 mg/L. The orders of dominance of cations and anions in DGW samples were Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Na+ + K+ and > > Cl− + .
concentrations of local surface water and groundwater varied significantly. Concentrations of in SW samples varied in a narrow range from 2.1 to 2.6 mg/L. The contents of in the SGW and DGW samples were determined in the range of 5.7 to 26.2 mg/L (average 15.5 mg/L) and 0.5 to 5.9 mg/L (average 3.2 mg/L), respectively. All samples had lower content than the statutory limit (50 mg/L for ) for drinking water (GB5749). However, the concentrations of most groundwater samples were significantly higher than the regional background value (4.4 mg/L in 1950s) in the groundwater.
3.2. Isotope Data
The isotopic compositions of , DOC and H2O in water samples from SJZ are presented in Table 2.
The δ15NNO3 and δ18ONO3 values in the SW samples were in the range of 9.4‰ to 12.6‰ and 10.9‰ to 20.2‰, respectively. The SGW samples had δ15NNO3 values ranging from 7.1‰ to 11.3‰ (average 8.8‰), and δ18ONO3 values ranging from 5.4‰ to 11.6‰ (average 8.4‰). δ15NNO3 values of DGW samples ranging from 9.4‰ to 11.9‰ (average 10.4‰), were higher than most of the SGW samples (except SGW6, SGW11 and SGW13). δ18ONO3 values of DGW samples ranged from 11.1‰ to 27.1‰ (average 20.1‰). The observed δ18ONO3 values in DGW samples were more enriched than that of SGW samples.
The δ13CDOC values of SW samples showing wide ranges varied from −31.7‰ to −24.7‰ (average −28.6‰). The δ13CDOC values in SGW samples were in the range of −32.4‰ to −25.5‰ (average −29.5‰). The deep groundwater had relatively positive δ13CDOC values in a narrow range of −27.1‰ to −25.7‰ (average −26.1‰).
The isotope ratios of the surface water showed a range of −58‰ to −51‰ for δ2HH2O and −6.5‰ to −4.6‰ for δ18OH2O, with negative d-excess values (d-excess = δ2HH2O-8δ18OH2O) of −15.2‰ to 0‰. The δ2HH2O and δ18OH2O values of the shallow groundwater ranged from −64‰ to −53‰ and −8.5‰ to −6.0‰, respectively, with d-excess values varying in a large range of −12‰ to 8.4‰. The isotope ratios of the deep groundwater were generally lower than that of surface water and shallow groundwater, ranging from −71‰ to −60‰ for δ2HH2O and from −9.8‰ to −8.0‰ for δ18OH2O. The d-excess values displayed considerable variability ranging from −6.2‰ to 14.8‰.

Table 2.
Environmental isotopes data of the field sampling.
| Sample | Site Description | δ15NNO3 (‰) | δ18ONO3 (‰) | δ13CDOC (‰) | δ2HH2O (‰) | δ18OH2O (‰) | d-excess (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Water | |||||||
| SW1 | HBZ Reserior | 12.6 | 20.2 | −31.7 | −58 | −5.8 | −11.6 |
| SW2 | Hutuo River | 9.4 | 11.1 | −26.6 | −52 | −4.6 | −15.2 |
| SW3 | Shijin Canal | 11.9 | 13.8 | −31.2 | −52 | −6.5 | 0 |
| SW4 | Shijin Canal | 11.7 | 10.9 | −24.7 | −51 | −6.1 | −2.2 |
| Shallow Groundwater | |||||||
| SGW1 | Yancun | 7.8 | 10.3 | −32.2 | −60 | −6.0 | −12 |
| SGW2 | Baichigan | 7.8 | 6.2 | −32.4 | −56 | −7.0 | 0 |
| SGW3 | Dahe | 8.0 | 8.6 | −32.2 | −53 | −7.1 | 3.8 |
| SGW4 | Houdubei | 9.5 | 9.6 | −30.9 | −54 | −6.9 | 1.2 |
| SGW5 | Shiqiyu | 7.1 | 7.7 | −32.3 | −61 | −8.5 | 7 |
| SGW6 | Taitou | 11.1 | 11.6 | −25.5 | −56 | −7.2 | 1.6 |
| SGW7 | Beigaoying | 8.2 | 5.6 | −28.1 | −56 | −7.0 | 0 |
| SGW8 | Xiguan | 7.2 | 5.4 | −27.3 | −55 | −7.3 | 3.4 |
| SGW9 | Taipingcun | 9.3 | 6.7 | −26.1 | −64 | −6.8 | −9.6 |
| SGW10 | Bafang | 9.1 | 11.5 | −30.6 | −58 | −8.1 | 6.8 |
| SGW11 | Dongxuying | 10.1 | 9.6 | −28.6 | −58 | −8.2 | 7.6 |
| SGW12 | Shaojiazhuang | 8.2 | 9.1 | −31.7 | −58 | −8.3 | 8.4 |
| SGW13 | Gaoqianbeijie | 11.3 | 7.4 | −25.9 | −59 | −8.4 | 8.2 |
| Deep Groundwater | |||||||
| DGW1 | Xizhaotong | 9.4 | 24.8 | −25.8 | −60 | −8.0 | 4 |
| DGW2 | Wujiaying | 9.9 | 24.9 | −27.1 | −62 | −9.6 | 14.8 |
| DGW3 | Liangcun | 11.2 | 12.7 | −25.9 | −61 | −8.1 | 3.8 |
| DGW4 | Nandun | 11.9 | 27.1 | −25.7 | −71 | −8.1 | −6.2 |
| DGW5 | Tatan | 9.6 | 11.1 | −26.1 | −69 | −9.8 | 9.4 |
4. Discussion
4.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Water
Dissolution is the most effective process in groundwater chemistry and could be considered the first step in the hydrochemical evolution. As shown in Figure 4a,b, the molar ratios of Ca2+/ are close to 0.5, while the molar ratios of (Ca2+ + Mg2+)/ are greater than 0.5. This indicates that the dissolution of calcium carbonate minerals is one of the most important hydrochemical processes [43]. The linear correlations between Ca2+ and , Na+ and suggest that in groundwater may be mainly derived from the dissolution of gypsum and mirabilite (Figure 4c,d). High concentration in the surface water might be the result of coal mining drainage from mountainous areas [36]. The shallow groundwater (HCO3.Cl-Ca.Mg type) with low concentration in the wastewater-irrigated area may be mainly affected by wastewater and precipitation (Figure 4c). The concentration of Mg2+ and Cl− showed a linear relationship indicating that Mg2+ and Cl− have a common source which could be attributed to the anthropogenic activities such as wastewater irrigation or usage of fertilizers (Figure 4e) [6,28,44]. The plot of Na+ and Cl− shows that the increased Cl− concentration is not closely related with the dissolution of halite or input of sea salt (Figure 4f).
In Figure 5a,b, concentrations show strong correlations with Mg2+ and Cl− concentrations indicating that they originate from the same sources. The Mg2+ and Cl− concentrations of the groundwater in the wastewater irrigation area were higher than those in the non-wastewater irrigated area, but the concentrations of groundwater in both areas fall within the similar range. This demonstrates that wastewater irrigation is not the only source of in groundwater. The concentrations of and are not correlated well with those of (Figure 5c,d), since the levels of and are controlled primarily by natural processes, and the concentration of is influenced mainly by anthropogenic inputs.
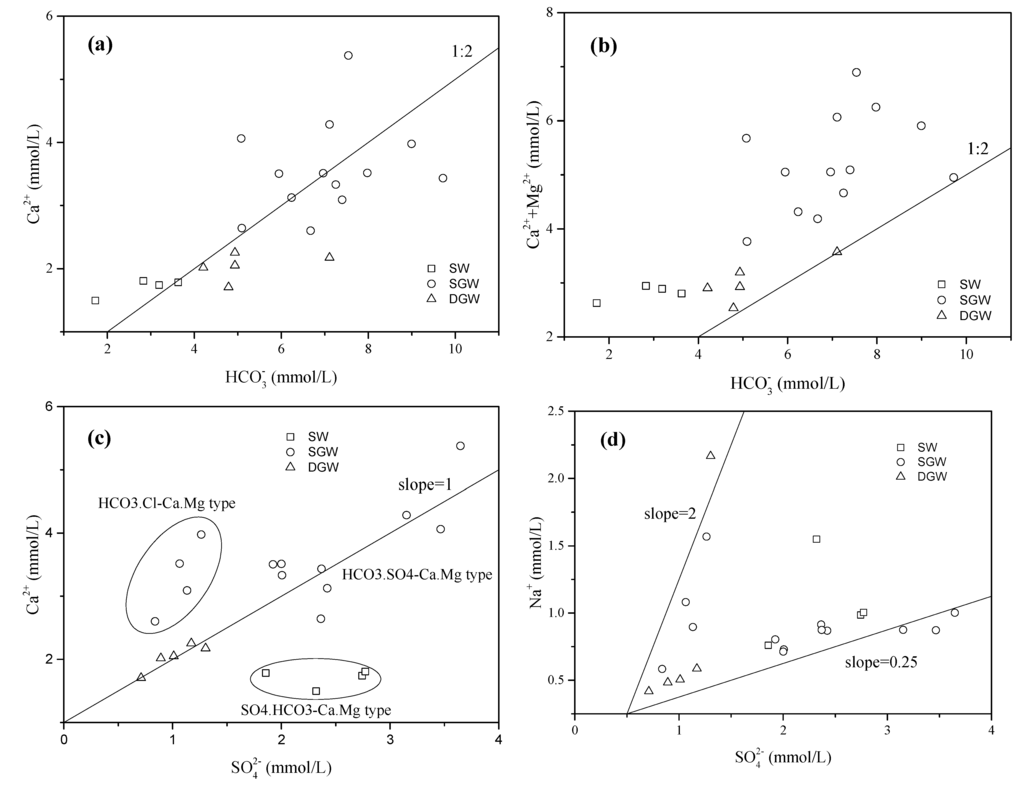
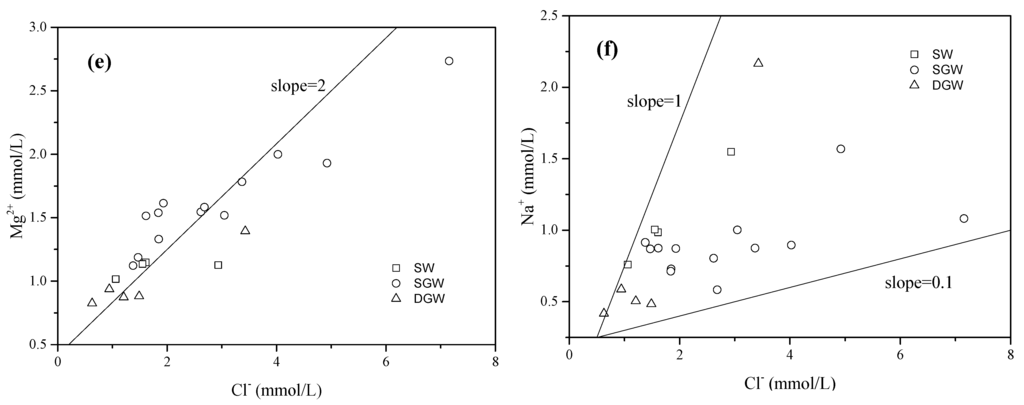
Figure 4.
Relationships between ion concentrations of the surface water and groundwater, including (a) Ca2+ vs. (b) Ca2++Mg2+ vs. (c). Ca2+ vs. (d) Na+ vs. (e) Mg2+ vs. Cl−; and (f) Na+ vs. Cl−. (SW: Surface water; SGW: Shallow groundwater; DGW: Deep groundwater).
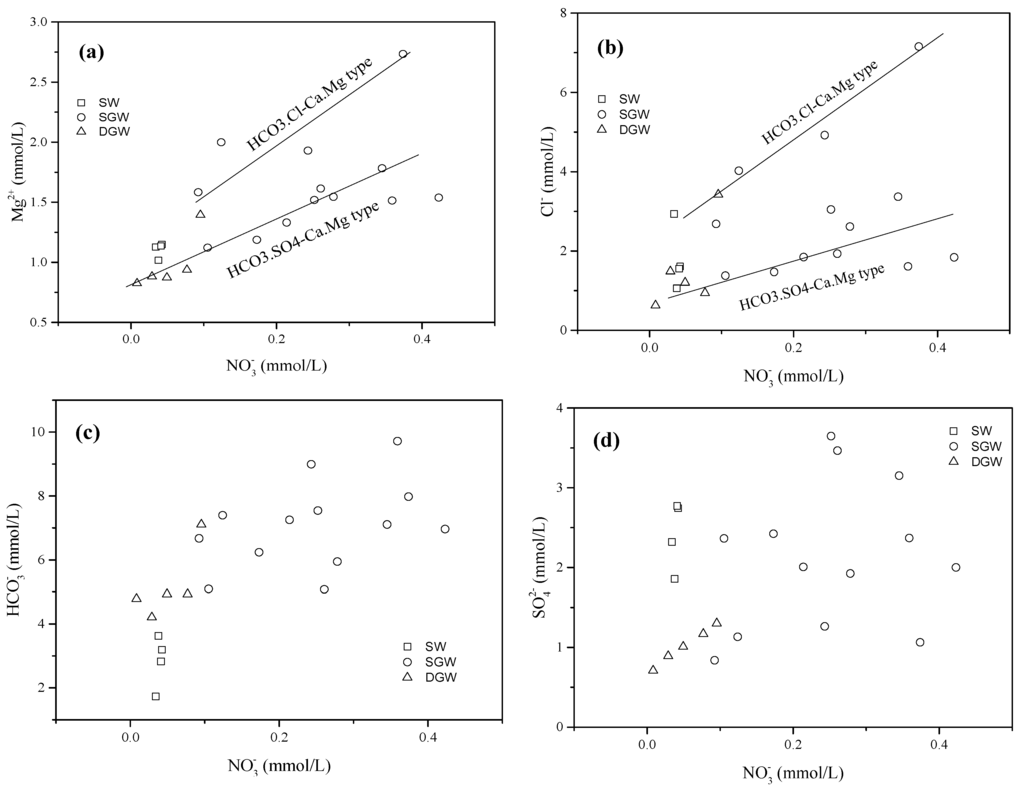
Figure 5.
Concentrations of cation (Mg2+) and anions (Cl−, and vs. that of concentrations in surface water and groundwater: (a) Mg2+ vs. ; (b) Cl− vs. ; (c) vs. ; (d) vs. . (SW: Surface water; SGW: Shallow groundwater; DGW: Deep groundwater).
The water samples all plot on or close to the local meteoric water line (LMWL) in Figure 6, suggesting that the surface water and groundwater originate from local precipitation. Most of the water samples have isotope compositions similar to the weighted mean isotope compositions (WMIC) of rain water in SJZ that has the composition of δ2HH2O = −55‰ and δ18OH2O = −7.8‰ (n = 142) calculated with data from 1985 to 2003 obtained from the Global Network for Isotopes in Precipitation (GNIP) dataset (available at http://isohis.iaea.org) (Figure 6). This isotopic similarity implies that the shallow groundwater was derived by direct inflow or infiltration of modern rainwater. The deep groundwater with relatively negative δ2HH2O and δ18OH2O reflects a paleorecharge effect under cold climatic conditions.
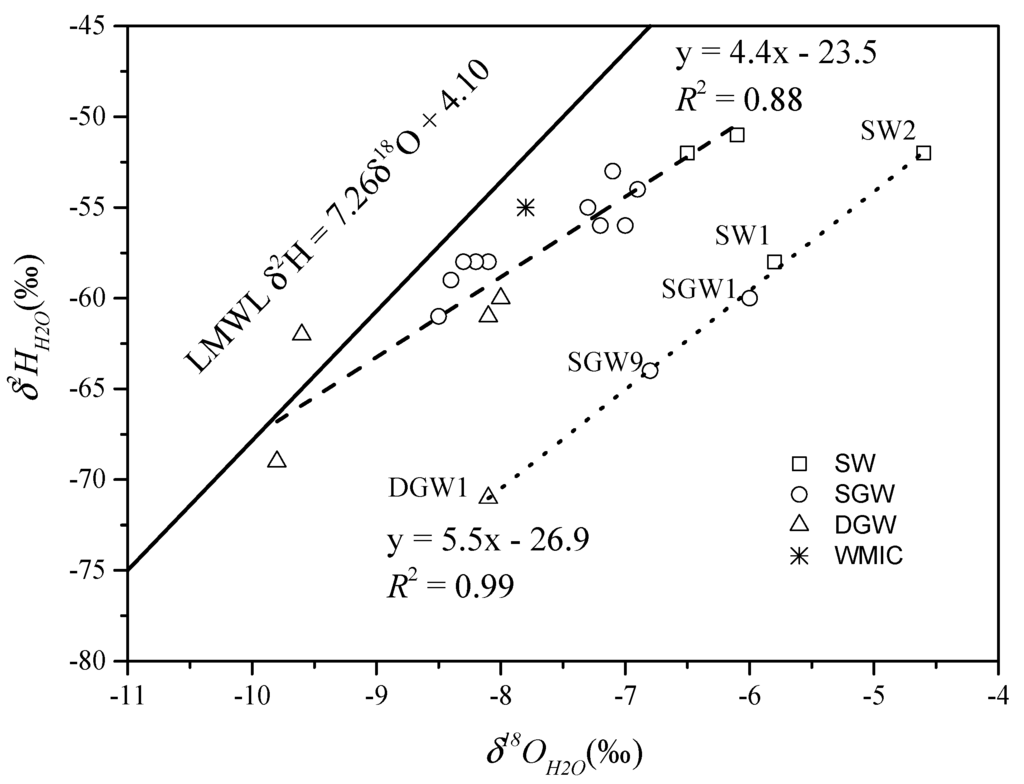
Figure 6.
Plot of δ2H against δ18OH2O for surface and ground water samples from the Shijiazhuang area. Local meteoric water line (LMWL, solid line) and evaporation lines (dashed line and dotted line) are shown for comparison. The LMWL is defined by Jia et al. [45]. (SW: Surface water; SGW: Shallow groundwater; DGW: Deep groundwater; WMIC: Weighted mean isotope composition).
The surface water and groundwater samples on the dashed line below LMWL, with d-excess values of −2.2‰ to +14.8‰, suggest these samples experienced minor evaporation. The two surface water samples from Huangbizhuang (SW1) and Hutuohe reservoirs (SW2), with d-excess values of −15.2‰ and −11.6‰, suggest long-term strong evaporation of Huangbizhuang and Hutuohe reservoirs under the semi-arid climate. The groundwater samples (SGW1 and SGW9) were collected near the Huangbizhuang and Hutuohe reservoirs, indicating the seepage from Huangbizhuang and Hutuohe reservoirs are the major source of this groundwater. The DGW1 could be recharged by Hutuo River in an old and cold period. As shown in Figure 7, some of the shallow groundwater samples have similar δ18OH2O values and Cl− concentrations with the surface waters, suggesting that these samples can be recharged by the surface water. In addition, wastewater contributes a considerable amount of Cl− to the shallow groundwater in the mixing process. Moreover, deep groundwater quality could be influenced by seepage from shallow groundwater. The surface water sample (SW2) might be subjected to intensive evaporation resulting in high Cl− concentration and δ18OH2O value.
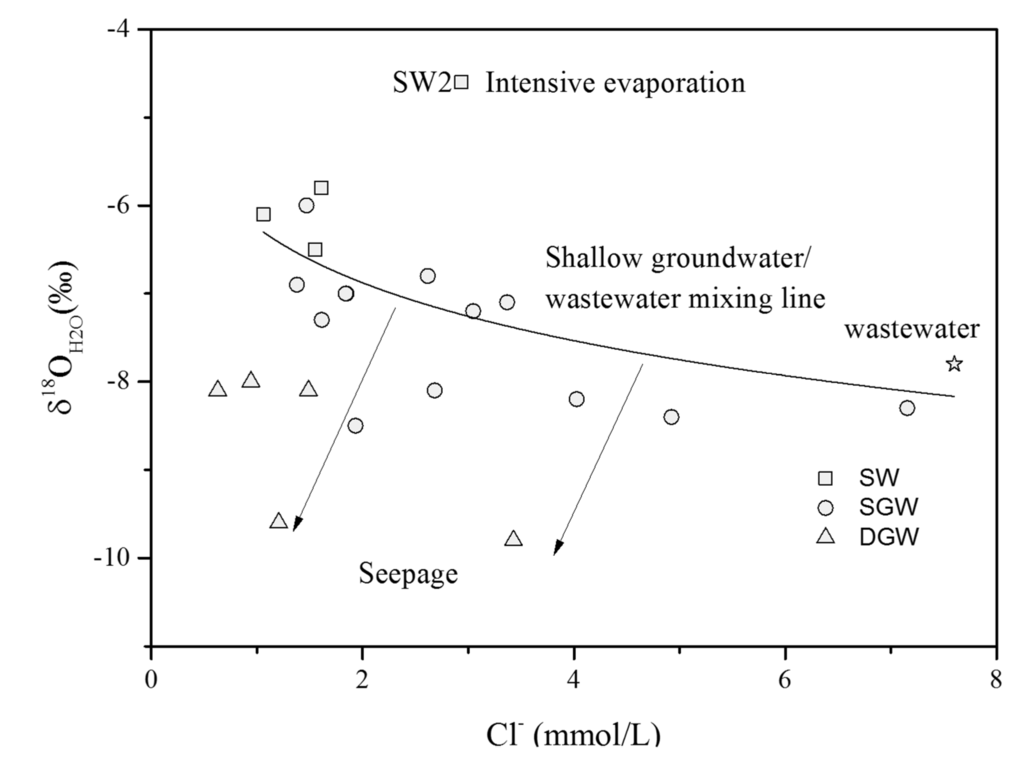
Figure 7.
Cl− concentrations vs. δ18OH2O values in the surface water and groundwater. (SW: Surface water; SGW: Shallow groundwater; DGW: Deep groundwater).
4.2. Source and Behavior of Nitrate
4.2.1. Evidence of Denitrification
Characterizing biogeochemical processes in groundwater is a key issue to understand the sources and behavior of . Microbial denitrification can decrease concentration and cause significant alterations of the isotopic composition of . Various studies have demonstrated that the heavy isotopes 15NNO3 and 18ONO3 become enriched with an ɛN/ɛO ratio that ranges from 1.3 to 2.1 in the residual pool during microbial denitrification [20,21,46,47]. Although the individual isotopic enrichment factors for δ15NNO3 and δ18ONO3 during denitrification may vary according to specific field conditions, the fractionation ratio (ɛN/ɛO) appears to remain constant. In this study, most of the samples show a positive trend in a δ15NNO3 and δ18ONO3 diagram (Figure 8) with an ɛN/ɛO ratio of proximately 2, suggesting microbial denitrification might occur. There were more positive δ15NNO3 and δ18ONO3 values and lower concentrations in deep groundwater than those in shallow groundwater (Figure 9a,b). This indicates that the higher extent of denitrification in the deep groundwater than that in the shallow groundwater.
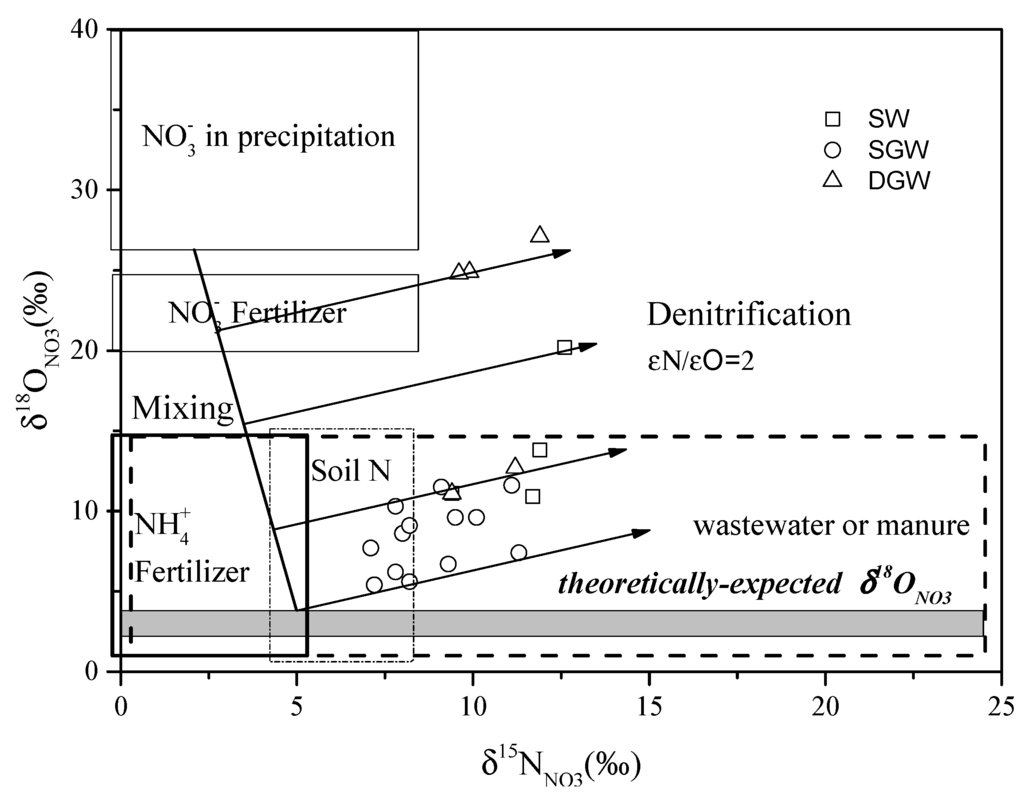
Figure 8.
Isotopic values of surface water and groundwater dissolved plotted with the ranges of the potential sources in the study area [4,9,48]. (SW: Surface water; SGW: Shallow groundwater; DGW: Deep groundwater).
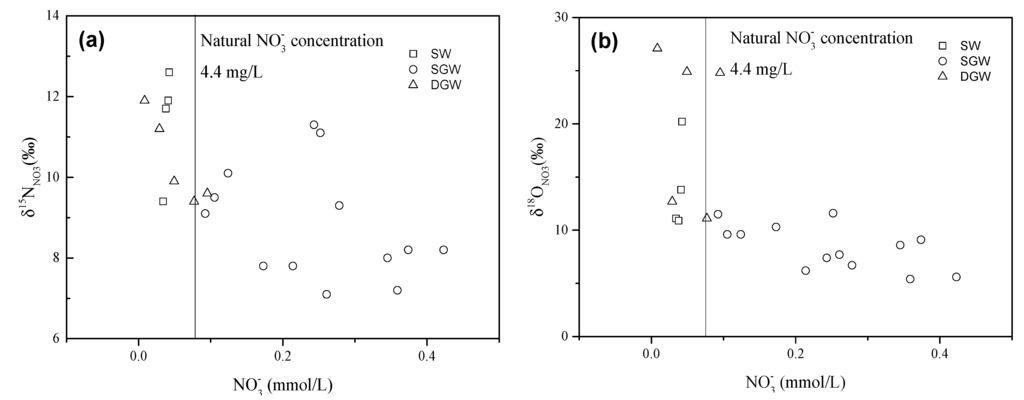
Figure 9.
Relationship between isotopic composition of and concentration in the surface water and groundwater: (a) δ15NNO3 vs. NO− 3; (b) δ18ONO3 vs. (SW: Surface water; SGW: Shallow groundwater; DGW: Deep groundwater).
Denitrification processes take place under reducing environments, usually in the saturated zone. This process is linked either to organic matter oxidation or sulfide oxidation [10,20,49]. It is believed that denitrification followed by sulfide oxidation cannot occur in carbonated aquifers where pH is over 7 [50]. Thus, DOC is the main energy source for microbial metabolism in the groundwater. The denitrification reaction involving carbon as electron donors can be described as follows:
For reaction (1), the residual DOC and will become increasingly enriched in the heavy isotopes (13C and 15N) rather than in the initial DOC and In the subsurface, a variety of biogeochemical reactions occur with DOC attenuation in the water infiltration and flow processes [22], while denitrification is the dominant attenuation process of in groundwater [10]. As shown in Figure 10, synergistic changes in δ13CDOC and δ15NNO3 values of the groundwater samples imply that variation of δ15NNO3 values are related to biogeochemical processes. It’s reasonable to propose denitrification as the most possible process. SGW7 and SGW8, deviating from the positive relationship between δ13CDOC and δ15NNO3 values, may be due to the import of manure (δ13CDOC = 27.3‰, [51]) in the Zhengding and Beigaoying areas where agricultural inputs could occur. Several samples (SGW9, DGW1, DGW5 and SW4) stray from the denitrification trend and approach SGW7 and SGW8, indicating these samples are concurrently influenced by the manure pollution and denitrification. The denitrification process occurs in the surface water (SW2) which has several favorable conditions such as low concentration of dissolved oxygen (2.3 mg/L) [23,28,52] and high concentration of DOC (22.1 mg C/L). The surface water with relatively high δ15NNO3 values and low δ13CDOC values may be the result of preferential uptake of light nitrogen isotopes by algae, leading to enrichment of heavy nitrogen isotope in the residual [53,54,55]. In general, the high δ13CDOC and δ15NNO3 values highlight that a limited extent of microbial denitrification occurred mainly in the deep groundwater and part of the shallow groundwater and surface water. The low concentration (typically < 5 mg C/L) and bioavailability of residual DOC may be one of the most important reasons for the low extent of denitrification in the study area [56].
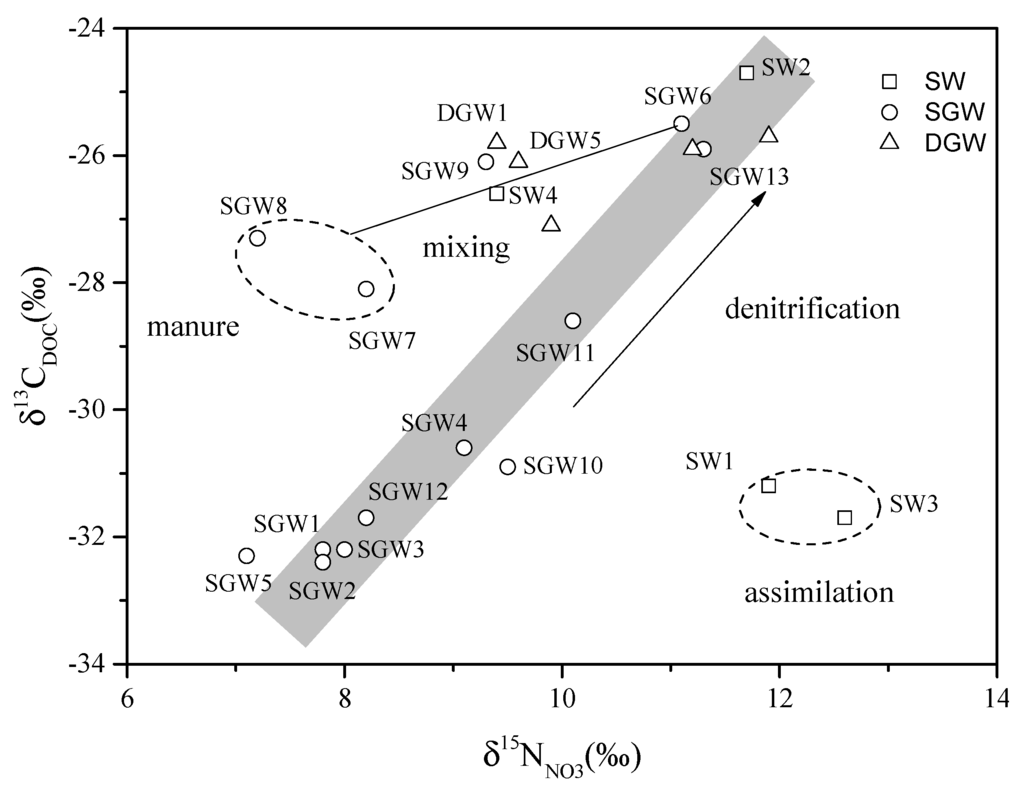
Figure 10.
Plot of δ13CDOC and δ15NNO3 in surface water and groundwater. The rectangle with gray shadow indicates the synergic trend between δ13CDOC and δ15NNO3. The two ellipses with dashed lines highlight the values deviating from the trend due to mixing with different sources and assimilation by microbial activities. (SW: Surface water; SGW: Shallow groundwater; DGW: Deep groundwater).
4.2.2. Sources of in Groundwater
The possible sources of nitrate in the groundwater in this area include agricultural input including fertilizer, fertilizer and manure, domestic and industrial wastewater, soil organic N, and atmospheric deposition. The characteristic N and O isotopic compositions of these possible nitrate sources are displayed in Figure 8.
In this study, denitrification poses the most difficulties for simple applications of nitrate isotopes. However, according to the mixing model reported in the previous study [9,57], combining the denitrification trend (ɛN/ɛO ratio) with the theoretically-expected δ18ONO3 value could preliminarily deduce the initial δ15NNO3 values of the in the water samples. In the case of the of groundwater originating from soil organic N, manure, fertilizer and wastewater, the dominant process related to throughout the hydrochemical profile is nitrification. Generally, generated via microbial nitrification incorporates two oxygen atoms from water and one from atmospheric O2 [58,59]. Therefore, the expected δ18O value of may be estimated as follows:
The δ18O signature of soil O2 is equivalent to that of atmospheric O2 which is about +23.5‰ [9]. The δ18OH2O of shallow groundwater in the investigated aquifer system ranges from −8.5‰ to −6.0‰ (Table 2). Consequently, the expected δ18ONO3 value for groundwater derived from nitrification of alternative sources in soils should be in the range of +2.2‰ to +3.8‰. The theoretically-expected value is less than the measured δ18ONO3 values (+5.4‰ to +9.1‰). Theoretically, both denitrification and contribution of in precipitation to natural water can lead to the increase in δ18ONO3 values. In this study, if denitrification is the only process for the elevated δ18ONO3 values, the initial δ15NNO3 values of DGW samples should be extremely depleted (less than −20‰) which are deviated from the common values −10‰ to +20‰) [4] (Figure 8). Thus, the relatively high δ18ONO3 values of DGW samples cannot be simply explained by the denitrification process, suggesting the existence of other process. As shown in Figure 8, denitrification, coupled with mixing processes between precipitation and surficial sources (soil organic N, wastewater, manure and fertilizer) can be responsible for the higher δ18ONO3 values of the water samples. In addition, the δ15NNO3 value(s) of possible surficial source(s) can be roughly estimated between 2‰ and 5‰ according to the mixing model. The typical δ15NNO3 values of soil N ranged from 0 to 8‰ and fertilizers from −6‰ and +6‰ [4]. In the SJZ area, the δ15NNO3 value of effluents N in the wastewater irrigated area was 2.5‰ [6], while the δ15NNO3 value of in the unsaturated zone was 5.7‰ [7]. The reported values of δ15NNO3 ranged between +8.7‰ and 14.4‰ for the compost-applied area and between +4.5‰ and +8.5‰ for the area where urea was applied with compost [12]. In general, soil N, fertilizer, wastewater, and the mix of fertilizer and manure could be possible sources.
For the shallow groundwater, soil organic N and precipitation cannot be the main origins of since concentrations of most samples are much higher than the natural concentration (4.4 mg/L [60]) (Figure 9a). Thus, in the shallow groundwater mainly derives from anthropogenic sources. In the non-wastewater-irrigated area, fertilizer could be the dominant source due to the initial δ15NNO3 values entirely falling in the range of fertilizer. In the wastewater-irrigated area, wastewater is the primary source. The relatively low /Cl− ratios of these samples collected from the wastewater-irrigated area can be another important piece of evidence for wastewater sources (Figure 11). For the deep groundwater, the samples with relatively low δ18ONO3 values might be contaminated by wastewater, while the samples with relatively high δ18ONO3 values could be attributed to a mixture of precipitation and soil organic N contribution (Figure 8).
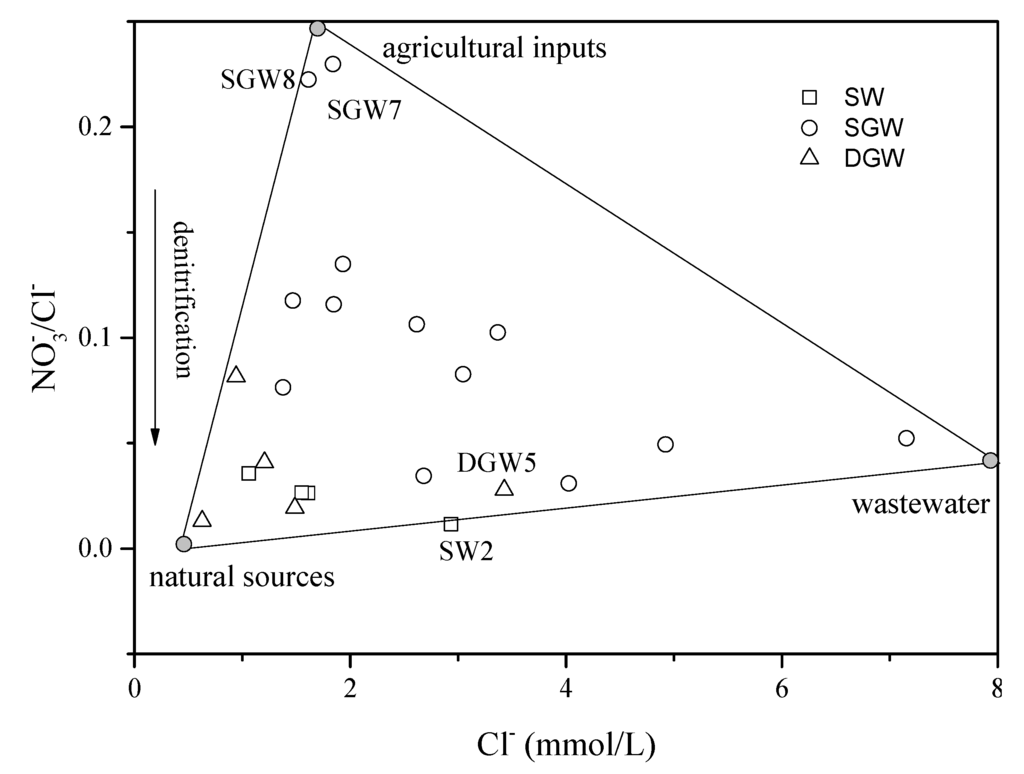
Figure 11.
Variations of /Cl− molar ratios with Cl− molar concentrations of surface water and groundwater. The solid lines represent the theoretical mixing lines constructed by using the manure, municipal wastewater, and precipitation as end members. (SW: Surface water; SGW: Shallow groundwater; DGW: Deep groundwater).
The mixing of different sources can be characterized by the pattern of /Cl− ratios and Cl concentrations (Figure 11). Agricultural inputs (high /Cl− ratios and low Cl concentration) are the dominant sources in the Zhengding and Beigaoying areas. The samples collected from the southern part of the study area are characterized by lower /Cl− ratios but high Cl− concentrations, confirming that long-term wastewater irrigation has a significant impact on the groundwater quality [6]. The surface water and deep groundwater are both primarily originated from natural sources (precipitation and soil organic nitrogen) with little influence of anthropogenic activities, and show low /Cl− ratios and Cl− concentrations. However, the samples SW2 and DGW5 are polluted by wastewater and show increased Cl− concentration. All data points are included in a mixing triangle, with end members represented by wastewater, natural sources, and agricultural inputs. Several points located in the middle of the mixing triangle, suggesting varied sources, can jointly aggravate the nitrate pollution.
5. Conclusions
This study focuses on the sources and fate of in the groundwater used as drinking water in the rural and suburban areas of SJZ, China.
The dissolution of the calcium carbonate and gypsum minerals was the most effective process in the groundwater chemistry. Hydrochemical data suggested that in the groundwater could be related to wastewater irrigation or usage of fertilizers. The isotopic data (δ18O and δ2H) indicated that the groundwater originated primarily from local precipitation and experiences different in extent of evaporation.
Denitrification affects the transformation of in the groundwater supported by the fractionation ratio (ɛN/ɛO) and the pattern of δ13CDOC and δ15NNO3. Our study clarifies that a low extent of denitrification could be ubiquitous in the groundwater, and the effect of denitrification in the deep groundwater is more significant than that in the shallow groundwater.
For the shallow groundwater, contamination is predominantly derived from fertilizers in non-wastewater irrigated areas; in contrast, the source can be mainly attributed to wastewater in wastewater irrigated area. For the deep groundwater samples, could primarily originate from precipitation and soil organic N. In addition, some of them were influenced by wastewater. In this study, the mixing processes of various sources are confirmed by dual isotopes (δ15NNO3, and δ18ONO3) and hydrochemistry (/Cl− ratio and Cl concentration) in the drinking water wells of SJZ.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for constructive comments that greatly improved this manuscript. We are grateful to Editor Jun Xu for his constructive comments. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC Grant Nos. 41002083, 40972157, and 41202169).
Author Contributions
Yanpeng Zhang participated in field sampling, experiments, design of the study, and writing the manuscript. Aiguo Zhou and Jianwei Zhou are co-supervisors of this research who guided the research and contributed to preparing the manuscript for publication. Cunfu Liu and Hesheng Cai modified the discussion section and made improvements to the English writing of the manuscript as well. Yunde Liu and Wen Xu participated in the field sampling and the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, Z.; Xue, Y.; Ren, F.; Shi, D.; Yin, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Sun, X. Evolution of Groundwater Environment in North China Plain; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zonggu, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Y. Investigation and Evaluation of Groundwater Sustainable Utilization in North China Plain; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, C.; Aravena, R. Nitrate isotopes in groundwater systems. In Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 261–297. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, D.; Botte, J.; de Baets, B.; Accoe, F.; Nestler, A.; Taylor, P.; van Cleemput, O.; Berglund, M.; Boeckx, P. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface- and groundwater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenech, C.; Rock, L.; Nolan, K.; Tobin, J.; Morrissey, A. The potential for a suite of isotope and chemical markers to differentiate sources of nitrate contamination: A review. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2023–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Yu, J.J. Use of 18O, 2H and 15N to identify nitrate contamination of groundwater in a wastewater irrigated field near the city of Shijiazhuang, China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 326, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Z.Y. Using stable isotope to trace the sources of nitrate in groundwater in Shijiazhuang. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 30, 1602–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, S.; Ma, L.N.; Yin, M. Nitrogen isotope tracing of sources of nitrate contamination in groundwater from wastewater irrigated area. Earth Sci. 2012, 37, 350–356. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, C.; MacDonnell, J.J. Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology; Access Online via Elsevier: Amsterdam, Noord-Holland, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rivett, M.O.; Buss, S.R.; Morgan, P.; Smith, J.W.; Bemment, C.D. Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: A review of biogeochemical controlling processes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4215–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.J.; Lee, S.M.; Ro, H.M. Evaluation of contamination sources of groundwater using nitrogen isotope data: A review. Geosci. J. 2003, 7, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.-J.; Han, G.-H.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, G.-T.; Yoon, K.-S.; Choi, S.-M.; Ro, H.-M. Impact of land-use types on nitrate concentration and δ15N in unconfined groundwater in rural areas of Korea. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 120, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widory, D.; Kloppmann, W.; Chery, L.; Bonnin, J.; Rochdi, H.; Guinamant, J.L. Nitrate in groundwater: An isotopic multi-tracer approach. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 72, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongelli, G.; Paternoster, M.; Sinisi, R. Assessing nitrate origin in a volcanic aquifer using a dual isotope approach. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, E.M. Organic Geochemistry of Natural Waters; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Hartland, A.; Fenwick, G.D.; Bury, S.J. Tracing sewage-derived organic matter into a shallow groundwater food web using stable isotope and fluorescence signatures. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2011, 62, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Starr, R.C.; Gillham, R.W. Denitrification and organic carbon availability in two aquifers. Ground Water 1993, 31, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T.; District, H.D.W. Evaluation of the Source and Transport of High Nitrate Concentrations in Ground Water, Warren Subbasin, California; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cannavo, P.; Richaume, A.; Lafolie, F. Fate of nitrogen and carbon in the vadose zone: In situ and laboratory measurements of seasonal variations in aerobic respiratory and denitrifying activities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukada, T.; Hiscock, K.M.; Dennis, P.F.; Grischek, T. A dual isotope approach to identify denitrification in groundwater at a river-bank infiltration site. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3070–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravena, R.; Robertson, W.D. Use of multiple isotope tracers to evaluate denitrification in ground water: Study of nitrate from a large—Flux septic system plume. Ground Water 1998, 36, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabich, W.J.; Valiela, I.; Hemond, H.F. Relationship between DOC concentration and vadose zone thickness and depth below water table in groundwater of Cape Cod, USA. Biogeochemistry 2001, 55, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desimone, L.A.; Howes, B.L. Nitrogen transport and transformations in a shallow aquifer receiving wastewater discharge: A mass balance approach. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, M.O.; Smith, J.W.N.; Buss, S.R.; Morgan, P. Nitrate occurrence and attenuation in the major aquifers of England and Wales. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2007, 40, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortelainen, N.M.; Karhu, J.A. Tracing the decomposition of dissolved organic carbon in artificial groundwater recharge using carbon isotope ratios. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, H.; Clark, I. Bioattenuation in groundwater impacted by landfill leachate traced with δ13C. Ground Water 2011, 49, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Breukelen, B.M.; Roling, W.F.M.; Groen, J.; Griffioen, J.; van Verseveld, H.W. Biogeochemistry and isotope geochemistry of a landfill leachate plume. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2003, 65, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengis, M.; Schiff, S.L.; Harris, M.; English, M.C.; Aravena, R.; Elgood, R.J.; MacLean, A. Multiple geochemical and isotopic approaches for assessing ground water elimination in a riparian zone. Ground Water 1999, 37, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widory, D.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Negrel, P.; Ladouche, B. Tracking the sources of nitrate in groundwater using coupled nitrogen and boron isotopes: A synthesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Q.; Li, S.L.; Lang, Y.C.; Xiao, H.Y. Using δ15N and δ18O values to identify nitrate sources in Karst ground water, Guiyang, southwest China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6928–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.H. Groundwater in Hebei; Seismological Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.T.; Tang, C.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Song, X.F.; Li, F.D.; Sakura, Y. Spatial characteristics of water quality, stable isotopes and tritium associated with groundwater flow in the hutuo river alluvial fan plain of the north China plain. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xu, Q.H.; Ma, Y.H.; Zhang, X.Q. Palaeochannels on the north China plain: Palaeoriver geomorphology. Geomorphology 1996, 18, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Nie, Z.L.; Zhang, Z.J.; Qi, J.X.; Nan, Y.J. Isotopes and sustainability of ground water resources, north China plain. Ground Water 2005, 43, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Sakura, Y.; Changyuan, T.; Hayashi, S. Groundwater-table and recharge changes in the piedmont region of Taihang mountain in gaocheng city and its relation to agricultural water use. WaterSA 2004, 28, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Research of Environment Evolution of Groundwater in Shijiazhuang. Master’s Thesis, Shijiazhuang University of Economics, Shijiazhuang, China, June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.M.; Yu, J.J.; Kendy, E. Groundwater exploitation and its impact on the environment in the north China plain. Water Int. 2001, 26, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Shen, Y.J.; Sakura, Y.; Kondoh, A.; Shimada, J. Use of water balance calculation and tritium to examine the dropdown of groundwater table in the piedmont of the north China plain (NCP). Environ. Geol. 2003, 44, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, C.; Zheng, L.; Lei, Y. Ground water sustainability: Methodology and application to the north China plain. Ground Water 2008, 46, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.D.; Gan, Y.Q.; Yu, T.T.; Liu, C.F.; Zhou, A.G. Online simultaneous determination of δD and δ18O in microliter water samples by thermal conversion/elemental analysis isotope ratio mass spectrometry. China Rock Min. Anal. 2010, 29, 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.; Kendall, C.; Wilkison, D.; Ziegler, A.; Chang, C.; Avanzino, R. A new method for collection of nitrate from fresh water and the analysis of nitrogen and oxygen isotope ratios. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, H.; Wiegner, T.N.; Ostrom, P.H.; Kaplan, L.A.; Ostrom, N.E. Isotopic (13C) analysis of dissolved organic carbon in stream water using an elemental analyzer coupled to a stable isotope ratio mass spectrometer. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dejwakh, N.R.; Meixner, T.; Michalski, G.; McIntosh, J. Using 17O to investigate nitrate sources and sinks in a semi-arid groundwater system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Yu, X.; Fan, D.; Zheng, J. Study on hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes in precipitation in both sides along Taihang mountain. Yellow River 2011, 7, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Böttcher, J.K.; Strebel, O.; Voerkelius, S.; Schmidt, H.L. Using isotope fractionation of nitrate-nitrogen and nitrate-oxygen for evaluation of microbial denitrification in a sandy aquifer. J. Hydrol. 1990, 114, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, L.I. Evaluation of the origin and fate of nitrate in the abbotsford aquifer using the isotopes of 15N and 18O in . Appl. Geochem. 1995, 10, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, T. Isotopic studies of nitrogen pollution in the hydrosphere and atmosphere: A review. Chem. Geol. 1986, 59, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitoria, L.; Soler, A.; Canals, A.; Otero, N. Environmental isotopes (N, S, C, O, D) to determine natural attenuation processes in nitrate contaminated waters: Example of Osona (NE Spain). Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3597–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, N.; Torrento, C.; Soler, A.; Mencio, A.; Mas-Pla, J. Monitoring groundwater nitrate attenuation in a regional system coupling hydrogeology with multi-isotopic methods: The case of Plana de Vic (Osona, Spain). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 133, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senbayram, M.; Dixon, L.; Goulding, K.W.; Bol, R. Long—Term influence of manure and mineral nitrogen applications on plant and soil 15N and 13C values from the Broadbalk Wheat Experiment. Rapid. Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beller, H.R.; Madrid, V.; Hudson, G.B.; McNab, W.W.; Carlsen, T. Biogeochemistry and natural attenuation of nitrate in groundwater at an explosives test facility. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, A.; Dähnke, K.; Emeis, K. Isotopic composition of nitrate in five German rivers discharging into the North Sea. Org. Geochem. 2008, 39, 1678–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglin, W.A.; Kendall, C.; Chang, C.C.; Silva, S.R.; Campbell, D. Chemical and isotopic evidence of nitrogen transformation in the mississippi river, 1997–98. Hydrol. Process 2001, 15, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertin, A.R.; Sickman, J.O.; Pinowska, A.; Stevenson, R.J. Identification of nitrogen sources and transformations within Karst springs using isotope tracers of nitrogen. Biogeochemistry 2012, 108, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.A.; Vervier, P. Hydrological variability, organic matter supply and denitrification in the Garonne river ecosystem. Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; Campbell, D.H.; Burns, D.A.; Shanley, J.B.; Silva, S.R.; Chang, C.C. Tracing sources of nitrate in snowmelt runoff using the oxygen and nitrogen isotopic compositions of nitrate. In International Symposium on Biogeochemistry of Seasonally Snow-Covered Catchments, Boulder, CO, USA, 1–14 July 1995; Tonnessen, K.A., Williams, M.W., Tranter, M., Eds.; International Association of Hydrological Sciences: Wallingford, UK; Volume 228, pp. 339–347.
- Andersson, K.K.; Hooper, A.B. O2 and H2O are each the source of one o in produced from NH3 by Nireosomonas 15N-NMR evidence. FEBS Lett. 1983, 164, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, D.M.; Spoelstra, J.; Schiff, S.L.; Venkiteswaran, J.J. Stable oxygen isotope ratios of nitrate produced from nitrification: 18O-Labeled water incubations of agricultural and temperate forest soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5358–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.H.; Wang, D.S. Impact of human activities on nitrate concentration in the shallow groundwater. Site Invest. Sci. Technol. 1999, 1, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).