Study on Spatio-Temporal Changes and Driving Factors of Soil and Water Conservation Ecosystem Services in the Source Region of the Yellow River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Date and Methods
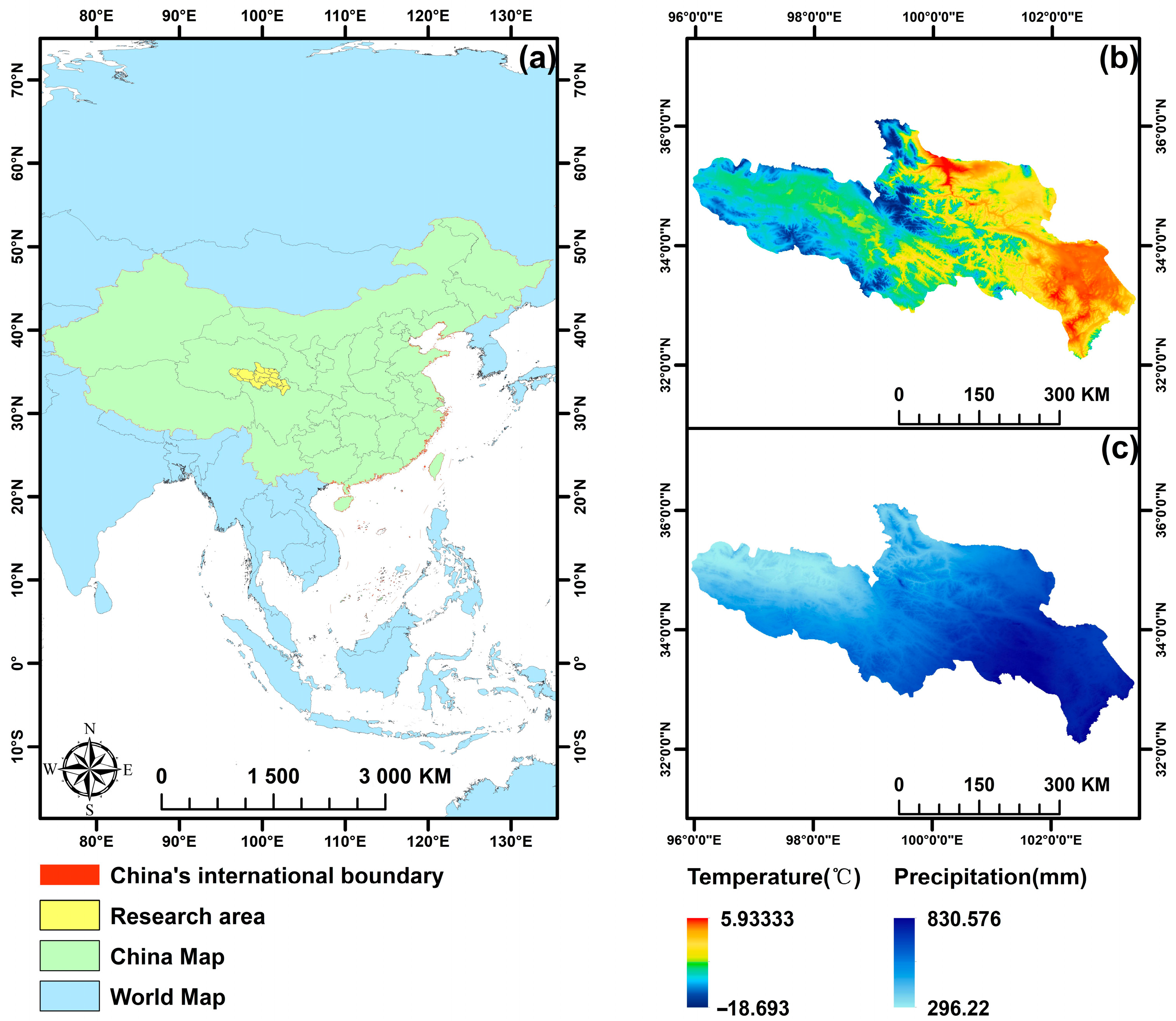
2.1. Research Area Overview
2.2. Data
2.2.1. NPP Data
2.2.2. Digital Elevation Data (DEM)
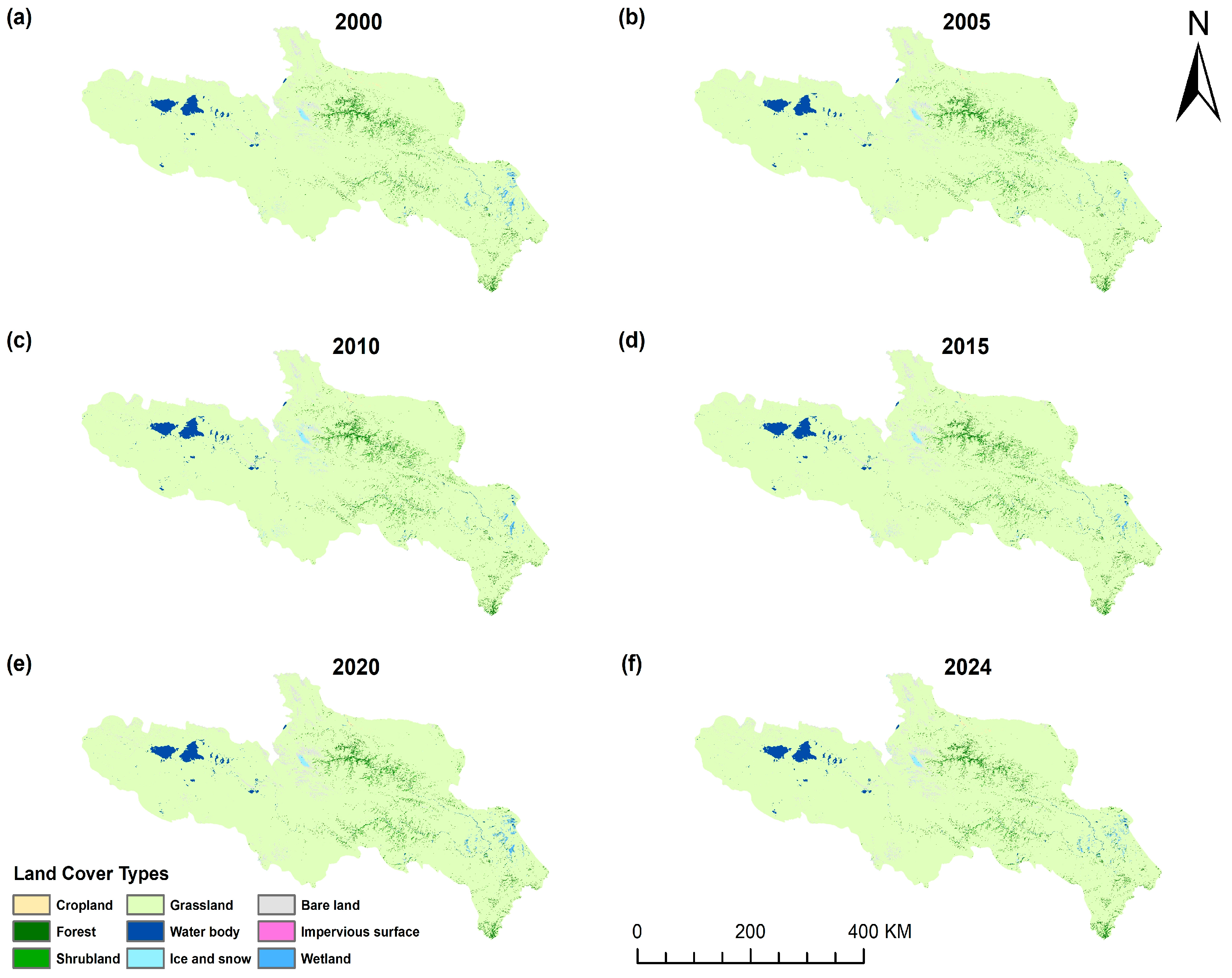
2.2.3. Land Use Data
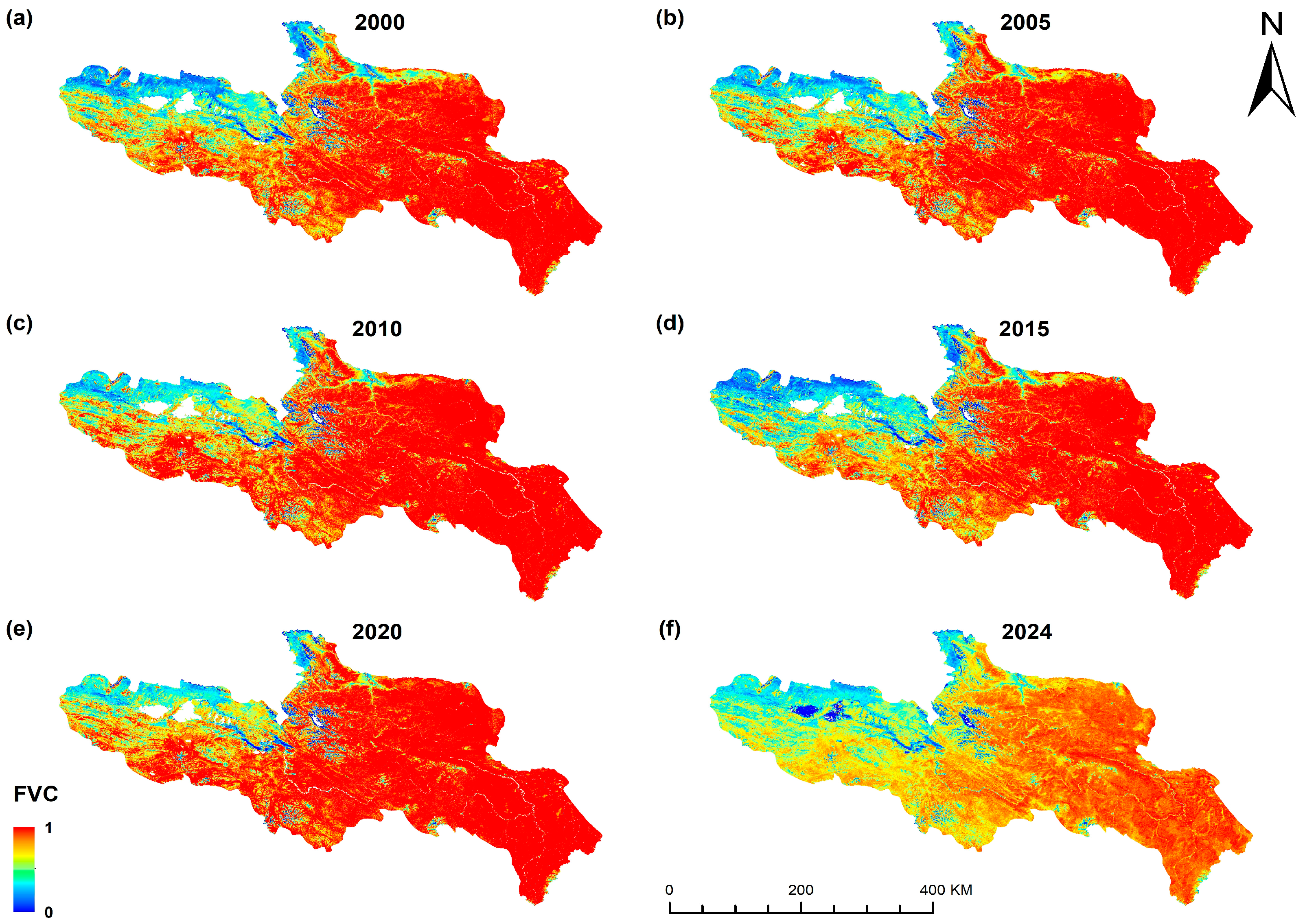
2.2.4. NDVI Data
2.2.5. Soil Properties Data
2.2.6. Soil Moisture Data
2.2.7. GDP per Capita
2.2.8. Meteorological Data
2.2.9. Grazing Intensity Data
2.2.10. Population Density
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Soil and Water Conservation Service Index
Evaluation Model
Se, NPPmean, K Factor Normalization Processing
Calculation of Soil Erodibility Factor
Calculation of Slope Factor
2.3.2. Standard Deviation Ellipse and Barycenter Model
2.3.3. Optimal Geodetector Model
2.3.4. Driving Factors
Vegetation Coverage
Intensity of Human Activity
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Land Use and Vegetation Coverage in the Source Region of the Yellow River
3.1.1. Spatio-Temporal Variation Characteristics of Land Use
3.1.2. Spatio-Temporal Variation Characteristics of Vegetation Coverage
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Variation Characteristics of Soil and Water Conservation Service Capacity in the Source Region of the Yellow River Temporal and Spatial Variation of Soil and Water Conservation Service Capacity in the Source Region of the Yellow River
3.2.1. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Soil and Water Conservation Service Capacity
3.2.2. Center of Gravity Migration of Soil and Water Conservation Service Capacity
3.3. Analysis of Driving Factors of Soil and Water Conservation Service Capacity in the Source Region of the Yellow River Driving Factors of Soil and Water Conservation Service Capacity in the Source Region of the Yellow River
3.3.1. Factor Detector Detection
3.3.2. Interactive Detector Detection
3.3.3. Risk Detector Detection
3.3.4. Ecological Detector Detection
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatio-Temporal Pattern of Land Use and Vegetation Cover Change and Its Impact on Soil and Water Conservation Services
4.2. Spatial and Temporal Heterogeneity Changes in Soil and Water Conservation Service Capacity
4.3. Dominance and Interaction of Climate Factors
4.4. Soil and Water Conservation Service Management Strategies and Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
5.1. Spatio-Temporal Variation Characteristics of Land Use and Vegetation Coverage in the Source Region of the Yellow River
5.2. Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics of Soil and Water Conservation Service Capacity in the Source Region of the Yellow River
5.3. Driving Factors Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Service Capacity in the Source Region of the Yellow River
5.4. Adaptation Strategies to Climate and Human Challenges in the Source Region of the Yellow River
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, T.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Gou, J.J.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhao, X. Hydrological response to climate change and human activities in the Three-River Source Region. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2022, 2022, 1477–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhong, J.; Xu, S. Simulation of Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Water Yield Function in the Source Area of the Yellow River and an Analysis of Influencing Factors. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, W.; Ma, K.; Hao, T.; Zhao, J.; Tang, R.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Mujtaba, K.G.; et al. Ecological–economic assessment and managerial significance of water conservation in the Headwaters of the Yellow River. Water 2022, 14, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; He, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Tan, S.; He, H. Spatial and temporal characteristics of soil conservation service in the area of the upper and middle of the Yellow River, China. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpeh, H.S. Assessing the Effect of Land Degradation on Farmer’s Livelihood: A Case of Muhanga District, Rwanda. Glob. Acad. Sci. J. Multidiscip. Stud. (GASJMS) 2025, 3, 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Joorabian Shooshtari, S.; Ardakani, T.; Beik Khormizi, H. Modeling future sediment retention service in the Bagh-e-Shadi Forest protected area using InVEST and the ACCESS-ESM1-5 climate model. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Z.; He, R. Impacts of climate change on hydrology in the Yellow River source region, China. J. Water Clim. Change 2020, 11, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, T.; Yong, B.; Krysanova, V.; Shi, P.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X. Impacts of climate change on flow regime and sequential threats to riverine ecosystem in the source region of the Yellow River. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Song, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S. Prediction and evaluation of ecosystem service value based on land use of the Yellow River source area. Sustainability 2022, 15, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, H.; Salahou, M.K. Watershed-level spatial pattern of degraded alpine meadow and its key influencing factors in the Yellow River Source Zone of West China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Lyu, J.; Zheng, F.; Xu, W.; Gan, X. Variations of runoff and sediment and their response to human activities in the source region of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, B.; Zhu, L.; Cruse, R.; Li, D.; Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Kuzyakov, Y.; An, S. Call for joint international actions to improve scientific understanding and address soil erosion and riverine sediment issues in mountainous regions. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2023, 11, 586–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xi, J. Multi-Objective optimization of the spatial structure and layout of the protected area based on ecosystem services: A case study of the Yellow River’s headwaters region in the three-river-source national park. Chin. J. Urban Environ. Stud. 2021, 9, 2150016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yao, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Fan, Z.; Guo, J. Spatial scale effects on the trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem services in China’s Huaihe river basin. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, G.; Pagano, L.; Vergamini, D.; Bartolini, F. Soils and ecosystem services: Policy narratives and instruments for soil health in the EU. Bio-Based Appl. Econ. (BAE) 2025, 14, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Li, Z.; Feng, Q.; Gui, J.; Zhang, B. Spatiotemporal variations of water conservation and its influencing factors in ecological barrier region, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Evaluation of soil and water conservation function in Dingxi City, Upper Yellow River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Qin, T.; Xu, S.; Lu, J.; Liu, H.; Gao, H. Evolution and influencing factors of water yield and water conservation services in the yellow river source area from 2000 to 2020. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2023, 21, 4195–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, Q.; Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Lu, Z.; Wang, S. Application of the New Assessment Framework in the Identification of Key Areas for Ecological Protection: A Case Study of the Yellow River Source Area on the Tibetan Plateau. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2292748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Kurban, A.; Voorde, T.; Maeyer, P.; Zhang, C. Coupled SSPs-RCPs scenarios to project the future dynamic variations of water-soil-carbon-biodiversity services in Central Asia. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, J.; Chen, G.; Lin, Y.; Yang, A.; Cheng, J. Coupling PLUS–InVEST model for ecosystem service research in Yunnan Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 15, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, F.; Yang, G.; Jiang, L. Improved method of freeze–thaw erosion for the Three-River Source Region in the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 1678–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhai, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, X. Soil water erosion and its hydrodynamic characteristics in degraded bald patches of alpine meadows in the Yellow River Source Area, western China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jia, D.; Zhai, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Bank erosion under the impacts of fluvial erosion, frost heaving/freeze-thaw process of rivers in seasonal frozen regions. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Tang, R.; Lin, H. Simulation and Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Soil Erosion in the Source Region of the Yellow River Using Machine Learning Method. Land 2024, 13, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.Q.; Xiao, T.; Liu, J.Y.; Qi, Y. Soil erosion rates and characteristics of typical alpine meadow using 137Cs technique in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhao, Y. Soil erosion assessment of alpine grassland in the source park of the yellow river on the qinghai-Tibetan plateau, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 9, 771439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bai, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, K. Quantitative Assessment of Habitat Quality and Analysis of its Drivers in the Yellow River Basin. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhu, M.; Liang, Y.; Qin, G.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Land use/land cover change and their driving factors in the Yellow River Basin of Shandong Province based on google earth Engine from 2000 to 2020. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, R.; Clarke, K.C.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J.; Jia, X.; Li, J. Spatial correlations among ecosystem services and their socio-ecological driving factors: A case study in the city belt along the Yellow River in Ningxia, China. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 108, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Hu, A.; Gan, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, Y. Spatial and temporal characteristics of ecosystem service trade-off and synergy relationships in the Western Sichuan Plateau, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Ma, S.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal variation in ecosystem services and their drivers among different landscape heterogeneity units and terrain gradients in the southern hill and mountain belt, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Zhou, Z.; Zou, Y.; Pulatov, B.; Biswas, A. Analysis of spatial and temporal characteristics and spatial flow process of soil conservation service in Jinghe Basin of China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.; Chen, J.; Lan, Y.; Chen, Z.; You, H.; Han, X.; Zhou, G. Exploring the drivers of soil conservation variation in the source of Yellow River under diverse development scenarios from a geospatial perspective. Sustainability 2024, 16, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Yang, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, J. Distinguishing the Multifactorial Impacts on Ecosystem Services under the Long-Term Ecological Restoration in the Gonghe Basin of China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Sheng, S.; Gong, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, H. Analyzing Coupling Coordination and Driving Factors of Social–Ecological Resilience: A Case Study of the Lower Yellow River. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, B.; Tao, W.; Zhang, D. Ecosystem services assessment, trade-off, and bundles in the Yellow River Basin, China. Diversity 2021, 13, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, M. Dynamics and interactions of water-related ecosystem services in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 1681–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qiao, J.; Li, M.; Huang, M. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their drivers at different spatial scales in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Tang, R.; Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z. Synergistic estimates of global 4-day 500 m gross primary production, evapotranspiration, and ecosystem water use efficiency from satellite data. J. Hydrol. 2025, 660, 133506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daldegan, G.A.; Noon, M.; Zvoleff, A.; Gonzalez-Roglich, M. A Review of Publicly Available Geospatial Datasets and Indicators in Support of Land Degradation Monitoring; Global Environment Facility (GEF): Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, M.; Tsu, H.; Hulley, G.; Iwao, K.; Pieri, D.; Cudahy, T.; Kargel, J. The advanced spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer (ASTER) after fifteen years: Review of global products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 38, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesch, D.; Oimoen, M.; Danielson, J.; Meyer, D. Validation of the ASTER global digital elevation model version 3 over the conterminous United States. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgelman, J.C.; Pascu, C.; Szkuta, K.; Von Schomberg, R.; Karalopoulos, A.; Repanas, K.; Schouppe, M. Open science, open data, and open scholarship: European policies to make science fit for the twenty-first century. Front. Big Data 2019, 2, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, G.; Schwingshackl, C.; Gasser, T.; Houghton, R.A.; Sitch, S.; Canadell, J.G.; Cescatti, A.; Ciais, P.; Federici, S.; Friedlingstein, P.; et al. Harmonising the land-use flux estimates of global models and national inventories for 2000–2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 1093–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses-Tovar, C.L. NDVI as indicator of degradation. Unasylva 2011, 62, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Balik, G.; Aktaş, E.; Önaç, A.K.; Birişçi, T. Vegetation Cover Change of Çeşme Alaçatı Wind Power Plant Using Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI). J. Int. Environ. Appl. Sci. 2017, 12, 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- FAO; IIASA. Harmonized World Soil Database Version 2.0.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations location: Rome, Italy; Laxenburg, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, A.; Arsenault, K.; Kumar, S.; Shukla, S.; Peterson, P.; Wang, S.; Funk, C.; Peters-Lidard, C.D. A land data assimilation system for sub-Saharan Africa food and water security applications. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, A.; McCartney, S.; Ruane, A.C.; Mladenova, I.E.; Whitcraft, A.K.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Bolten, J.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Rosenzweig, C.; Uz, S.S. Hydrologic and agricultural earth observations and modeling for the water-food nexus. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, A.; McNally, A.; Slinski, K.; Arsenault, K.R.; Shukla, S.; Getirana, A.; Koster, R.D. NASA’s NMME-based S2S hydrologic forecast system for food insecurity early warning in Southern Africa. J. Hydrology 2023, 617, 129005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, C.A. OECD-China Governance Project: The Institutional Arrangements for the Production of Statistics; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Kou, X.; Niu, L.; Xia, X.; Xiao, W.; Zhu, J. Spatiotemporal variations and its driving factors of soil conservation services in the Three Gorges Reservoir area in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1266169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Y.; Wang, N.; Peng, F.; Wang, Q. Spatial–temporal variations of water ecosystem services value and its influencing factors: A case in typical regions of the Central Loess Plateau. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Sun, K.; Lü, S.; Li, M.; Wan, Y.; Yu, G.; Gao, Y. Determining whether Qinghai–Tibet Plateau waterbodies have acted like carbon sinks or sources over the past 20 years. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Peng, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Xia, X.; Qin, Z.; Ren, P.; Liang, S.; Yuan, W. A long-term high-resolution dataset of grasslands grazing intensity in China. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ciais, P.; Yang, H.; Smith, P.; Grassi, G.; Schwingshackl, C.; Panagos, P.; Bar-On, Y.; Sitch, S.; Chevallier, F.; et al. Land use-induced soil carbon loss in the dry tropics nearly offsets gains in northern lands. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J.E.; Bright, E.A.; Coleman, P.R.; Durfee, R.C.; Worley, B.A. LandScan: A global population database for estimating populations at risk. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 849–857. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, P.; Zhang, H. Surface water changes in China’s Yangtze River Delta over the past forty years. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, J.; Du, F.; Zhang, Y. Separating the effects of two dimensions on ecosystem services: Environmental variables and net trade-offs. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 845–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Lü, Y.; He, C.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B. Assessing the soil erosion control service of ecosystems change in the Loess Plateau of China. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Mao, Z.Y.; Bin, X.; Yu, X.W. Analysis of changes in ecosystem capacity index and driving factors in the Loess Plateau under ecological engineering orientation. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 12, 1404424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; BORŮVKA, L.; Saberioon, M.M.; Kozák, J.; Vašát, R.; Němeček, K. Comparing different data preprocessing methods for monitoring soil heavy metals based on soil spectral features. Soil Water Res. 2015, 10, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perović, V.; Čakmak, D.; Pavlović, D.; Matić, M.; Kostić, O.; Mitrović, M.; Pavlović, P. From prediction to ecological insight: Exploring soil erodibility through integrated spatial modelling. Landsc. Ecol. 2025, 40, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zheng, F.; Römkens, M.J.M. Comparison of soil erodibility factors in USLE, RUSLE2, EPIC and Dg models based on a Chinese soil erodibility database. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B–Soil Plant Sci. 2013, 63, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Williams, J.R. Epic-Erosion/Productivity Impact Calculator: 1. Model Determination; U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA): Madison, WI, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.L.; Shu, A.P.; Xu, X.L.; Yang, Q.K.; Yu, B. Soil erodibility and its estimation for agricultural soils in China. J. Arid. Environ. 2008, 72, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A. A single, continuous function for slope steepness influence on soil loss. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value and Its Tradeoffs and Synergies in the Liaoning Coastal Economic Belt. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Ma, L.; Liu, Y. Comparing the driving mechanisms of different types of urban construction land expansion: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 722–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y. Application of ecosystem service flows model in water security assessment: A case study in Weihe River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, L.; Yang, W.; Xu, K. Driving Force Exploration for Flash Flood Based on Mann–Kendall Test and Geographical Detector: A Case Study of Hainan Island, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Li, G.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity analysis of water conservation in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration based on the geodetector and spatial elastic coefficient trajectory models. GeoHealth 2020, 4, e2020GH000248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Hao, Y.; Xia, A.; Liu, W.; Hu, R.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y. Quantitative assessment of the impact of physical and anthropogenic factors on vegetation spatial-temporal variation in Northern Tibet. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Cao, M.; Xue, B. Space-time characteristics of vegetation cover and distribution: Case of the Henan Province in China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 11967–11979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ah, R.; Yu, T.; Dong, Z.; Tong, B. Spatiotemporal variations in the intensity of human activity in Inner Mongolia and the identification of influencing forces. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Huang, G.; Zheng, G.; Wang, Y. Correlation between spatio-temporal evolution of habitat quality and human activity intensity in typical mountain cities: A case study of Guiyang city, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, W. Land Use/Cover-Related Ecosystem Service Value in Fragile Ecological Environments: A Case Study in Hexi Region, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, M.; Ye, L.; Liao, C.; Yao, L.; Tu, Z.; Xing, Q.; Ding, Z. Long-term dynamics of ecosystem services and their influencing factors in ecologically fragile southwest China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bao, S.; Han, M.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L. Dynamic Spatio-Temporal Simulation of Land Use and Ecosystem Service Value Assessment in Agro-Pastoral Ecotone, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Song, W.; Deng, X.; Xu, X. Grassland ecosystem responses to climate change and human activities within the Three-River Headwaters region of China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, J. The 30m-NDVI-based alpine grassland changes and climate impacts in the Three-River headwaters region on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from 1990 to 2018. J. Resour. Ecol. 2022, 13, 186–195. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, G.; Shao, J.; Guo, Y.; Dang, Y. Effects of Forest Resource Changes on Ecosystem Function: A Case Study of Xichuan County, the Main Source of Water for South-to-North Water Transfer in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 6973–6985. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, L.; Sun, J.; Tian, G.; Wang, D. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Forecasting of Ecosystem Service Value in Zhengzhou Using Land-Use Scenario Simulation. Land 2025, 14, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Fu, Q.; Ma, F. Ecological Function Zoning Framework for Small Watershed Ecosystem Services Based on Multivariate Analysis from a Scale Perspective. Land 2024, 13, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.; Mendoza, G.; Regetz, J.; Polasky, S.; Tallis, H.; Cameron, D.; Shaw, M. Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, S.; Proutsos, N.; Alexandridis, V.; Mallinis, G. Ecosystem services supply from Peri-Urban watersheds in Greece: Soil conservation and water retention. Land 2024, 13, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, N.; Huang, C.; Zhang, K.; Qiao, B.; Wen, P. Trade-off and synergy relationships and spatial bundle analysis of ecosystem services in the qilian mountains. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreti, E.; Striker, G.G. Plant responses to hypoxia: Signaling and adaptation. Plants 2020, 9, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X. Green-up dates in the Tibetan Plateau have continuously advanced from 1982 to 2011. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4309–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, B.; Ma, B. Mechanism and modeling of different plant root effects on soil detachment rate. Catena 2022, 212, 106109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Determining the mechanism of the root effect on soil detachment under mixed modes of different plant species using flume simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremen, C. Managing ecosystem services: What do we need to know about their ecology? Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.S.; Wilson, M.A.; Boumans, R.M.J. A typology for the classification, description and valuation of ecosystem functions, goods and services. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.Y.; Fang, Q.; Yu, W.Y.; Fan, C.H.; Zi, R.Y.; Zhao, L.S. RUSLE model evaluation of the soil and water conservation ratio of the guizhou province in china between 2000 and 2019. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Ji, H.; Hao, L. Quantitative assessment of climate change, land conversion, and management measures on key ecosystem services in arid and semi-arid regions: A case study of Inner Mongolia, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.Q.; Su, Z.H.; Zhang, K.X.; Bai, Y.M. Impact of Extreme Weather Events on Ecosystem Services. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2024, 22, 3577–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhao, X.Y.; Xu, X.C.; Ma, P.; Du, Y. Spatial-temporal evolution, tradeoffs and synergies of ecosystem services in the middle Yellow River. Earth Env. 2022, 13, 477–490. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Mu, X.M.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.J.; Li, Z.X. Estimation of soil erosion and evaluation of soil and water conservation benefit in terraces under extreme precipitation. Water 2022, 14, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Yang, C.; Wu, T.; Zhai, Y.F.; Tian, S.X.; Feng, Y.Q. Analysis of vegetation coverage changes and driving forces in the source region of the yellow river. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Song, X.N.; Leng, P.; Ji, Y.S.; Hong, W. Spatiotemporal variation of drought conditions based on MODIS data over the source area of Yellow River. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 36, 178. [Google Scholar]
- Peitian, Z.H.U.; Yonghuan, M.A.; Peixian, C.H.E.N.; Lei, L.I.; Ruixue, G.U.O. Migration characteristics of cultivated land gravity center and climate suitability evaluation in China. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2024, 60, 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.Y.; Shen, Q.Y.; Fan, W.D.; Dong, S.K.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xu, Y.D.; Ma, T.X.; Cao, Y. Nature-based solutions vs. human-induced approaches for alpine grassland ecosystem: “climate-help” overwhelms “human act” to promote ecological restoration in the Three-River-Source Region of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W. Three-River-Source National Park System Pilot Area’s steps toward cohesive conservation and management. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2020, 8, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batabyal, A.A.; Kahn, J.R.; O’Neill, R.V. On the scarcity value of ecosystem services. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2003, 46, 334–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela, A.P. Freshwater ecosystem services resilience in a changing world. Limnetica 2025, 45, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breshears, D.D.; López-Hoffman, L.; Graumlich, L.J. When ecosystem services crash: Preparing for big, fast, patchy climate change. Ambio 2011, 40, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderegg, W.R.L.; Kane, J.M.; Anderegg, L.D.L. Consequences of widespread tree mortality triggered by drought and temperature stress. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, R.; Schlüter, M.; Biggs, D.; Bohensky, E.L.; BurnSilver, S.; Cundill, G.; West, P.C. Toward principles for enhancing the resilience of ecosystem services. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 421–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zeng, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; You, Y.; Wang, L.; Su, K. Assessing the impact of climate and human activities on ecosystem services in the loess plateau ecological screen, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Qin, T.; Liu, S.S.; Wang, J.W.; Dong, B.; Yan, S.J.; Nie, H. Analysis and prediction of ecosystem service values based on land use/cover change in the Yiluo River Basin. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollinger, B.; Alewell, C.; Kneisel, C.; Meusburger, K.; Brandová, D.; Kubik, P.; Schaller, M.; Ketterer, M.; Egli, M. The effect of permafrost on time-split soil erosion using radionuclides (137Cs, 239+ 240Pu, meteoric 10Be) and stable isotopes (δ 13C) in the eastern Swiss Alps. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 1400–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yang, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X. The influence of permafrost degradation on the change of suprapermafrost water: A case study in the source areaof the Yellow River. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2023, 50, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- GGuo, Z.G.; Niu, F.J.; Zhan, H.; Wu, Q.B. Changes of grassland ecosystem due to degradation of permafrost frozen soil in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 3294–3301. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Fang, S.; Zhuo, W. Revealing the driving mechanisms of land surface temperature spatial heterogeneity and its sensitive regions in China based on GeoDetector. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Wu, W.B.; Hu, X.Y. Analysis of the driving role and impact of road construction on carbon stock. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 67131–67149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, L.; Dan, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, R.D.; Fu, G.; Yuan, Y.X.; Zheng, Z.H. Spatiotemporal patterns and driving factors of soil protection in the wind-water erosion area of Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Arid Land 2024, 16, 1522–1540. [Google Scholar]
- Le Goff, N.; Ottorini, J.M.; Ningre, F. Dynamics of a mixed beech (Fagus silvatica L.) and hornbeam (Carpinus betulus L.) natural regeneration in North-East France: Evolution of stand density and species composition with an insight into tree mortality factors. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liang, X.; Lin, J.S. Plant transpiration and groundwater dynamics in water-limited climates: Impacts of hydraulic redistribution. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 4416–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rule, A.; Dill, S.E.; Sun, G.; Chen, A.; Khawaja, S.; Li, I.; Rozelle, S. Challenges and opportunities in aligning conservation with development in China’s national parks: A narrative literature review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, X.U.; Chuansheng, W. Ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin: Framework, path, and countermeasure. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. (Chin. Version) 2020, 35, 875–883. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Q.; Cao, W.; Fan, J.; Huang, L.; Xu, X.L. Effects of an ecological conservation and restoration project in the Three-River Source Region, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wu, D.; Huang, L.; Lu, L. Spatial and temporal variations and significance identification of ecosystem services in the Sanjiangyuan National Park, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Bai, Y. Ecological Vulnerability Assessment of the Sanjiangyuan Region Based on” Pressure-State-Response-Management” Model. World Sci. Res. J. 2024, 10, 22–39. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, X.Y.; Yang, X.C.; Guo, J.; Chen, A.; Zhang, M.; Yang, D.; Hou, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, X.H. Identifying ecological governance zones for the Beijing-Tianjin Sandstorm Source Control Project by integrating ecosystem services and dust flow trajectories and its driving forces analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.H.; Xie, T.T.; Yang, Y.J.; Chen, S.Q.; Chen, F.; Huang, W.; Chen, J. Discussion of the “warming and wetting” trend and its future variation in the drylands of Northwest China under global warming. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 1241–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Tang, H. Evidence of warming and wetting climate over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2010, 42, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.C. A study on the rationale and consequences of ecological migration in the Sanjiangyuan of the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau. Can. Divers. 2011, 8, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Gao, J.; Xie, G.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, B. Identifying important ecological areas for potential rainwater harvesting in the semi-arid area of Chifeng, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Xue, X.; Michael, A.U. Moving towards a systematic marine eco-compensation mechanism in China: Policy, practice and strategy. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 169, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börner, J.; Baylis, K.; Corbera, E.; Ezzine-de-Blas, D.; Honey-Rosés, J.; Persson, U.M.; Wunder, S. The effectiveness of payments for environmental services. World Dev. 2017, 96, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Judgment Standard | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Nonlinear weakening | |
| Single-factor nonlinear weakening | |
| Double-factor strengthening | |
| Independence | |
| Nonlinear enhancement |
| Influencing Factors | Explanatory Variables | Code | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical factor | Climate factors | Annual average temperature/°C | X1 |
| Annual mean precipitation/mm | X2 | ||
| Vegetation factor | Vegetation coverage/% | X3 | |
| Orographic factor | DEM/m | X4 | |
| Slope/(°) | X5 | ||
| Soil factors | Soil moisture/% | X6 | |
| Human factors | Economic factors | Average GDP/(yuan·km−2) | X7 |
| Demographic factors | Population density/(person·km−2) | X8 | |
| Human activities | Grazing capacity | X9 | |
| Factor | Year | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2024 | |
| X1 | 0.5748 ± 0.0106 | 0.5997 ± 0.0070 | 0.549 ± 0.0288 | 0.6310 ± 0.0291 | 0.5633 ± 0.0187 | 0.6209 ± 0.0220 |
| X2 | 0.4577 ± 0.0124 | 0.4313 ± 0.0062 | 0.4305 ± 0.0068 | 0.4653 ± 0.0178 | 0.4345 ± 0.0040 | 0.4214 ± 0.0132 |
| X3 | 0.4595 ± 0.0538 | 0.5373 ± 0.0012 | 0.5949 ± 0.0419 | 0.4689 ± 0.0472 | 0.6022 ± 0.0471 | 0.5508 ± 0.0107 |
| X4 | 0.015 ± 0.0015 | 0.0123 ± 0.0004 | 0.0122 ± 0.0005 | 0.0145 ± 0.0011 | 0.01 ± 0.0020 | 0.0136 ± 0.0005 |
| X5 | 0.0032 ± 0.0000 | 0.0028 ± 0.0002 | 0.0027 ± 0.0003 | 0.0034 ± 0.0002 | 0.0026 ± 0.0003 | 0.0037 ± 0.0004 |
| X6 | 0.053 ± 0.0120 | 0.0391 ± 0.0021 | 0.0353 ± 0.0005 | 0.0387 ± 0.0018 | 0.0253 ± 0.0076 | 0.025 ± 0.0078 |
| X7 | 0.3733 ± 0.0091 | 0.3636 ± 0.0160 | 0.3337 ± 0.0371 | 0.4101 ± 0.0168 | 0.4225 ± 0.0256 | 0.4143 ± 0.0198 |
| X8 | 0.261 ± 0.0436 | 0.2279 ± 0.0202 | 0.1869 ± 0.0087 | 0.2355 ± 0.0256 | 0.168 ± 0.0221 | 0.1164 ± 0.0586 |
| X9 | 0.0141 ± 0.0005 | 0.0172 ± 0.0017 | 0.0125 ± 0.0016 | 0.012 ± 0.0019 | 0.0106 ± 0.0029 | 0.0222 ± 0.0052 |
| Factor | Optimal Range | Q Value |
|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.71~3.47/°C | 0.3473 |
| X2 | 682~730/mm | 0.3244 |
| X3 | 81.7~100/% | 0.2604 |
| X4 | 3390~3740/m | 0.2538 |
| X5 | 18.3~24.3/(°) | 0.2488 |
| X6 | 26.7~29.4/% | 0.2768 |
| X7 | 11,900~14,100/(yuan·km−2) | 0.3496 |
| X8 | 7~9(person·km−2) | 0.3552 |
| X9 | 0.352~0.652 | 0.2583 |
| Year | Factor | Optimal Range | Q Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | X1 | 0.821~2.320/°C | 0.3474 |
| X2 | 637~701/mm | 0.3233 | |
| X3 | 81.1~100/% | 0.2409 | |
| X4 | 3390~3740/m | 0.2386 | |
| X5 | 18.3~24.3 (°) | 0.2338 | |
| X6 | 25.9~29.1/% | 0.2631 | |
| X7 | 3710~4290/(yuan·km−2) | 0.3575 | |
| X8 | 6.3~13.2 (person·km−2) | 0.3133 | |
| X9 | 0.140~0.221 | 0.3184 | |
| 2005 | X1 | 1.62~3.23/°C | 0.3526 |
| X2 | 712~768/mm | 0.3174 | |
| X3 | 81.1~100/% | 0.2427 | |
| X4 | 3390~3740/m | 0.2404 | |
| X5 | 18.3~24.3 (°) | 0.2353 | |
| X6 | 24.2~24.9/% | 0.2685 | |
| X7 | 7000~8490/(yuan·km−2) | 0.3515 | |
| X8 | 7~9 (person·km−2) | 0.3519 | |
| X9 | 0.305~0.592 | 0.2497 | |
| 2010 | X1 | 1.71~3.47/°C | 0.3473 |
| X2 | 682~730/mm | 0.3244 | |
| X3 | 81.1–100/% | 0.2604 | |
| X4 | 3390~3740/m | 0.2538 | |
| X5 | 18.3~24.3 (°) | 0.2488 | |
| X6 | 26.7~29.4/% | 0.2768 | |
| X7 | 11,900~14,100/(yuan·km−2) | 0.3496 | |
| X8 | 7~9 (person·km−2) | 0.3552 | |
| X9 | 0.352~0.652 | 0.2583 | |
| 2015 | X1 | 2~5.54/°C | 0.3223 |
| X2 | 592~640/mm | 0.2915 | |
| X3 | 81.1~100/% | 0.2262 | |
| X4 | 3390~3740/m | 0.2193 | |
| X5 | 15.2~19.3 (°) | 0.2142 | |
| X6 | 25.1~29.0/% | 0.2388 | |
| X7 | 27,200~28,600/(yuan·km−2) | 0.3335 | |
| X8 | 7~8 (person·km−2) | 0.3141 | |
| X9 | 0.671~0.815 | 0.2197 | |
| 2020 | X1 | 1.92~5.55/°C | 0.3266 |
| X2 | 783~843/mm | 0.3094 | |
| X3 | 85.2~100/% | 0.2452 | |
| X4 | 3390~3740/m | 0.2406 | |
| X5 | 15.2~19.3 (°) | 0.2369 | |
| X6 | 28.9~31.3/% | 0.2497 | |
| X7 | 1.57~2.3/(yuan·km−2) | 0.3315 | |
| X8 | 5~6 (person·km−2) | 0.3234 | |
| X9 | 0.512~0.946 | 0.2378 | |
| 2024 | X1 | 2.28~5.84/°C | 0.3270 |
| X2 | 686~783/mm | 0.2990 | |
| X3 | 81.1~100/% | 0.2288 | |
| X4 | 3390~3740/m | 0.2276 | |
| X5 | 15.2~19.3 (°) | 0.2231 | |
| X6 | 27.6~28.3/% | 0.2686 | |
| X7 | 44,600~61,100/(yuan·km−2) | 0.3400 | |
| X8 | 7~9 (person·km−2) | 0.3152 | |
| X9 | 0.374~0.662 | 0.2371 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, K.; Zhang, F.; Chen, T.; Yan, B. Study on Spatio-Temporal Changes and Driving Factors of Soil and Water Conservation Ecosystem Services in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Water 2026, 18, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010128
Li X, Zhang X, Sheng K, Zhang F, Chen T, Yan B. Study on Spatio-Temporal Changes and Driving Factors of Soil and Water Conservation Ecosystem Services in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Water. 2026; 18(1):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010128
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaoqing, Xingnian Zhang, Keding Sheng, Fengqiuli Zhang, Tongde Chen, and Binzu Yan. 2026. "Study on Spatio-Temporal Changes and Driving Factors of Soil and Water Conservation Ecosystem Services in the Source Region of the Yellow River" Water 18, no. 1: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010128
APA StyleLi, X., Zhang, X., Sheng, K., Zhang, F., Chen, T., & Yan, B. (2026). Study on Spatio-Temporal Changes and Driving Factors of Soil and Water Conservation Ecosystem Services in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Water, 18(1), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010128






