Synergistic Regulation of Soil Salinity and Ion Transport in Arid Agroecosystems: A Field Study on Drip Irrigation and Subsurface Drainage in Xinjiang, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Characterization
2.2. Subsurface Drainage System Configuration
- Drainage lateral depths (D = 1.4, 1.6 m);
- Lateral spacing (S = 20, 30, 40 m).
- Perforated laterals: Corrugated single-wall design (Ø90 mm);
- Slot geometry: Opening width ≤ 1 mm, effective porosity > 25% (≥250 cm2/m2);
- Hydraulic gradient: 0.1% slope (DB15/T 2567—2022 compliant [13]);
- Collector main: Non-perforated PVC pipe (Ø110 mm) with 0.2% slope.
2.3. Crop Cultivation and Irrigation Materials
- Plastic mulching: 1.45 m width (PE film, 0.008 mm thickness);
- Row spacing: Narrow rows 25 cm (intra-bed), wide rows 60 cm (inter-bed);
- Drip line layout: 85 cm spacing with pressure-compensating emitters (1.6 L·h−1 flow rate);
- Irrigation network: 0.8·dS m−1 groundwater source (ECw).
- Pre-sowing leaching: 180 mm application (10 May 2023) with 16-day continuous drainage monitoring (ECdw 3.2–4.1 dS·m−1);
- Growth-stage irrigation: 6 events synchronized with critical phenological stages (V4–R6) using 80% ETc replacement.
- Basal application: 150 kg·ha−1 urea (46-0-0);
- Side-dressing: 120 kg·ha−1 MKP (0-52-34) + 90 kg·ha−1 SOP (0-0-50);
- Fertigation frequency: Split into 5 applications through drip system.
2.4. Soil Sampling and Analytical Methodology
- Normality verification via Shapiro–Wilk tests (W = 0.96, p > 0.05);
- Descriptive profiling with 95% confidence intervals;
- Multivariate collinearity diagnostics (VIF < 5 threshold).
3. Results and Analysis
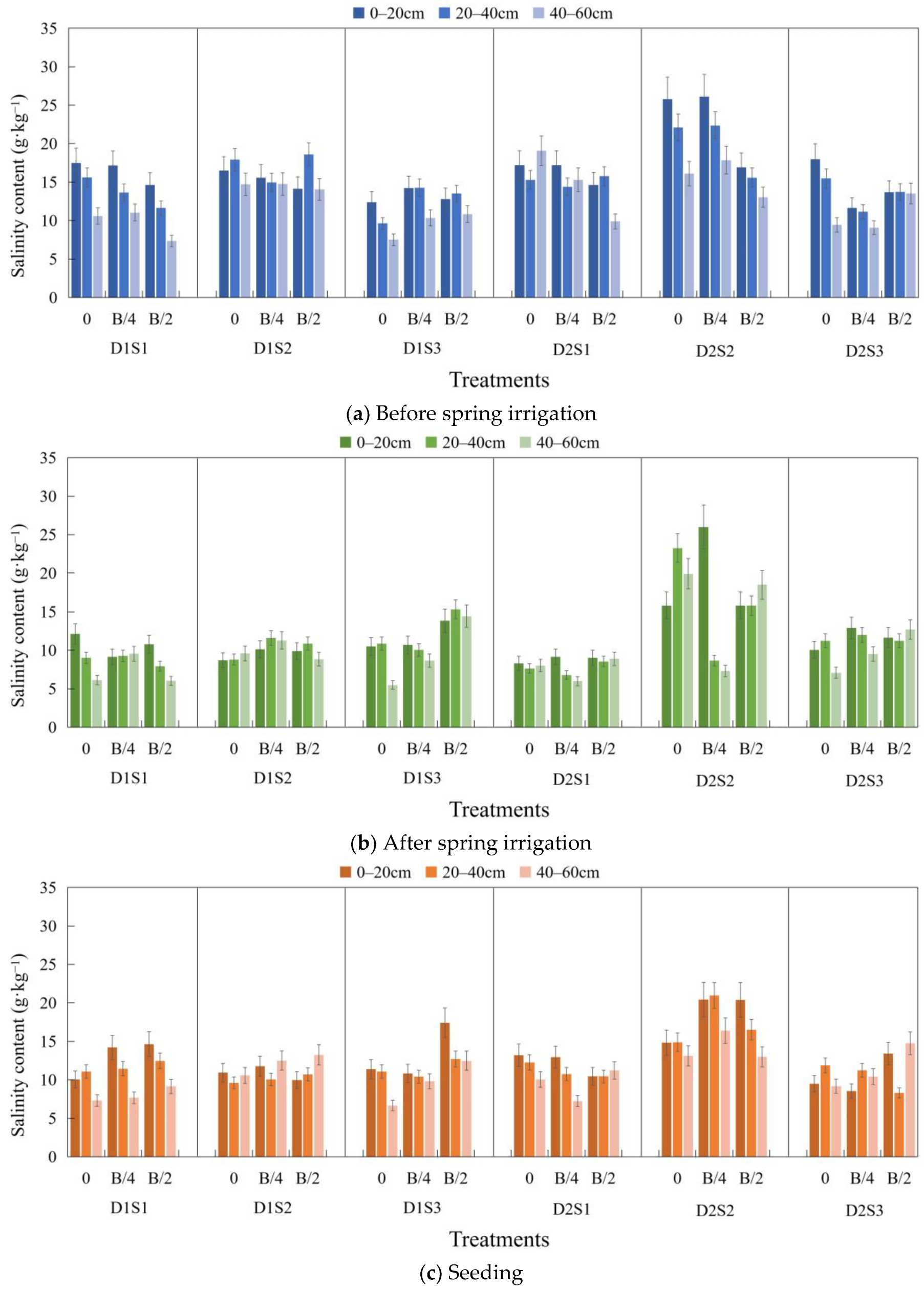
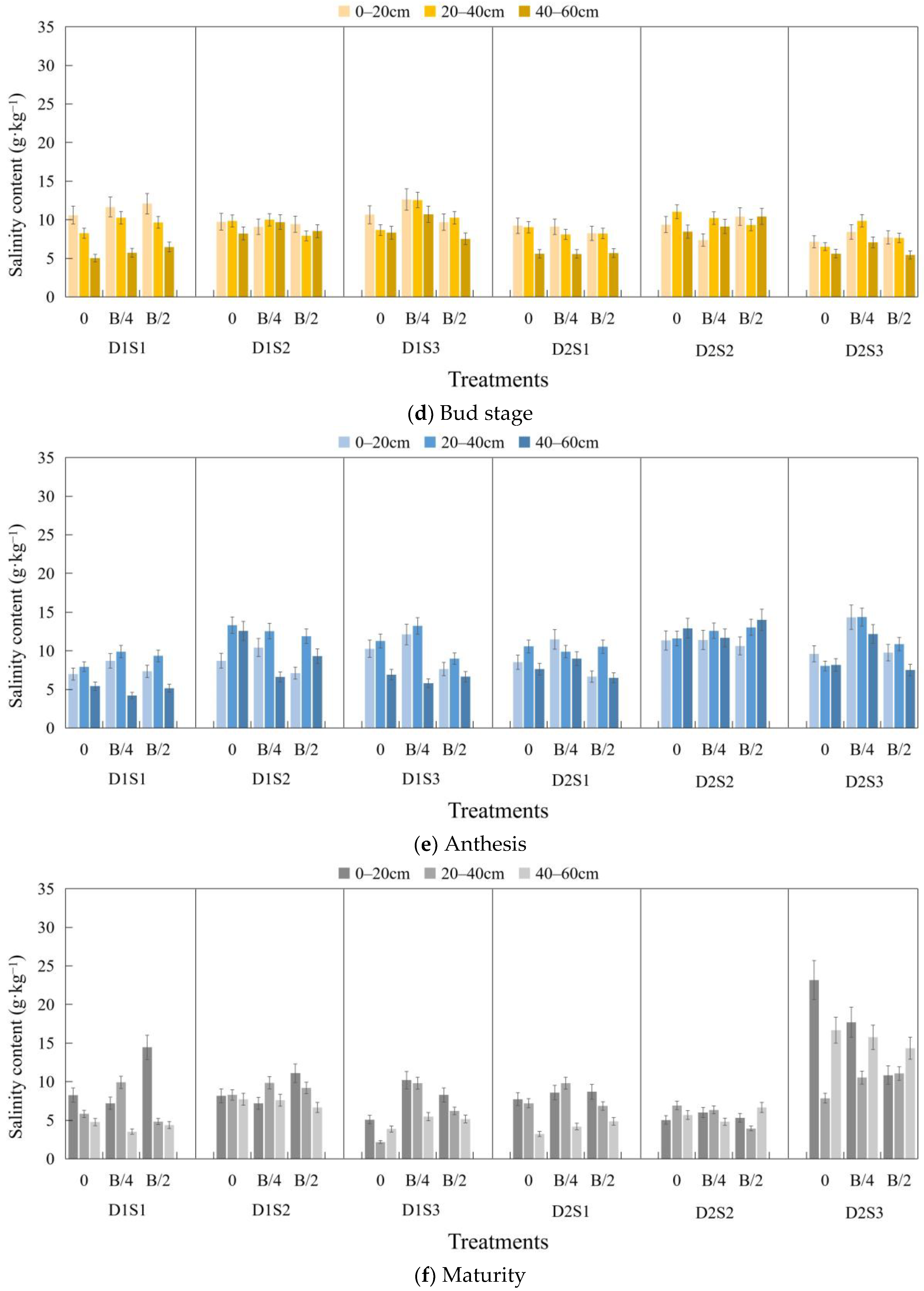
3.1. Soil Salinity Content at Various Periods of the Crop
3.2. Desalinization Rate
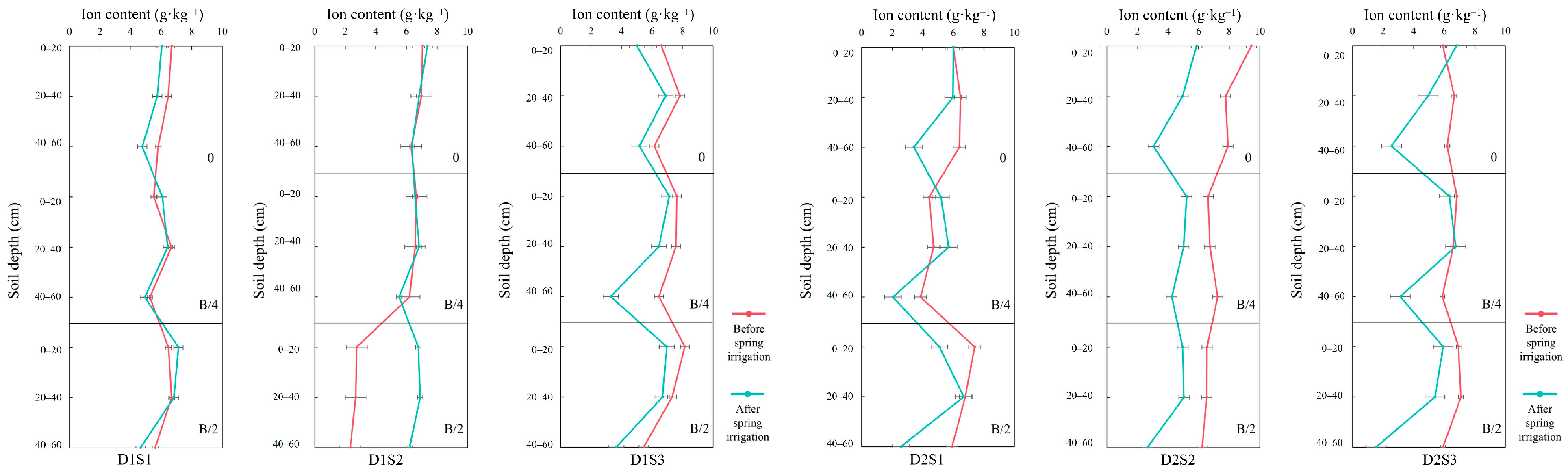
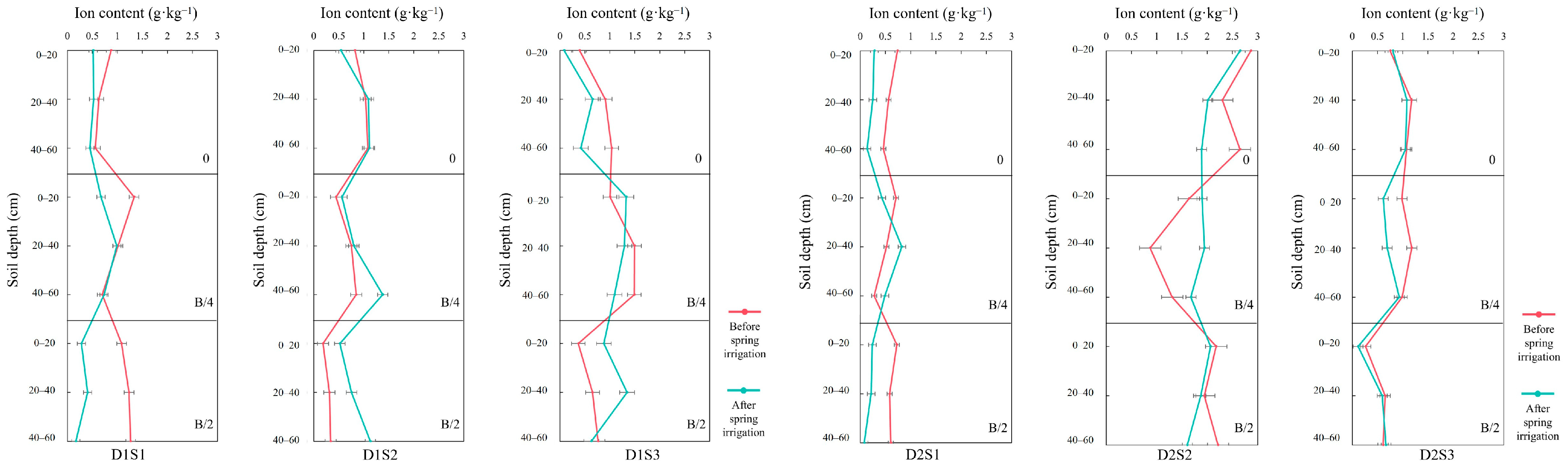
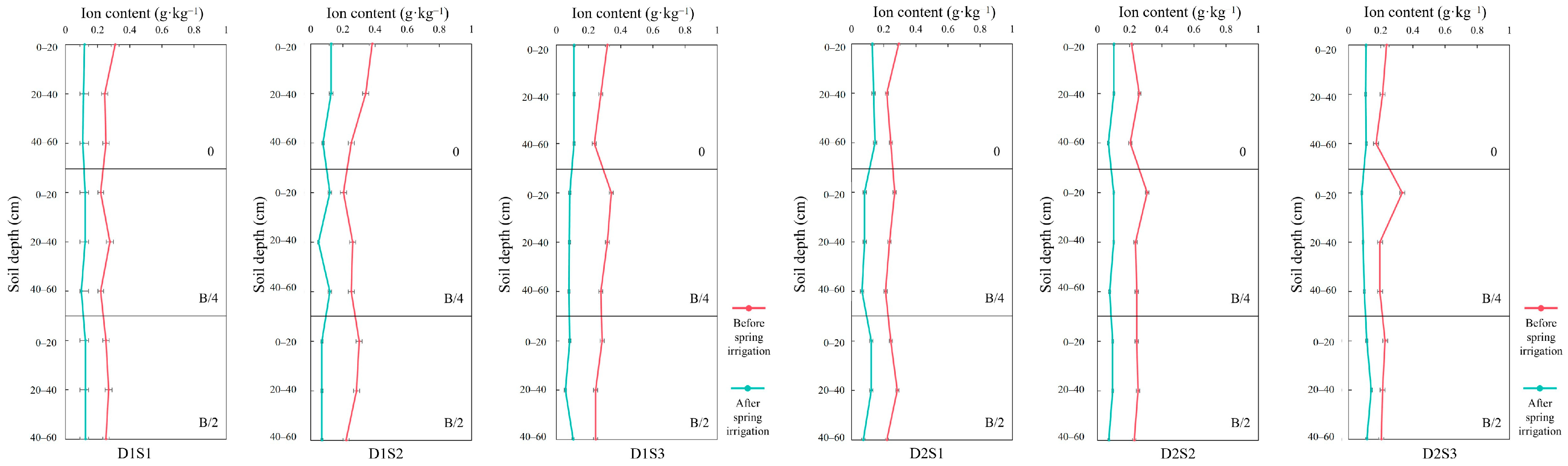
3.3. Salt Ions in Soil Before and After Spring Irrigation
- (1)
- SO42−
- (2)
- Ca2+
- (3)
- Cl−
- (4)
- Na+
- (5)
- HCO3−
- (6)
- Mg2+
- (7)
- K+
3.4. Soil Water Chemistry Before and After Spring Irrigation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaushal, S.S.; Mayer, P.; Shatkay, R.R.; Maas, C.M.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Hintz, W.D.; Wessel, B.M.; Tully, K.; Rippy, M.A.; Grant, S. Salinization of inland waters. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 3rd ed.; Anbar, A., Weis, D., Anbar, A., Weis, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2025; pp. 151–191. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Han, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, M. Optimizing cotton yield and soil salinity management: Integrating brackish water leaching and freshwater drip irrigation with subsurface drainage. Field Crops Res. 2024, 314, 109454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, S.; Hartman, S.; Chiarelli, D.D.; Rulli, M.C.; D’Odorico, P. The tradeoff between water savings and salinization prevention in dryland irrigation. Adv. Water Resour. 2024, 183, 104604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Rong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Huo, Z. A novel conceptual model coupling crop growth and soil water-heat-salt processes in arid area. J. Hydrol. 2025, 647, 132284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Guo, C.; Wu, J.; Qiang, W.; Qin, S.; Yang, H.; Li, H. Evaluation of combined open ditch and subsurface drainage: Experimental data and optimization of specifications in arid Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 306, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yao, C.; Wu, J.; Qin, S.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Mao, J. Field and numerical experiments of subsurface drainage systems in saline and low-permeability interlayered fields in arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 300, 108898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Wu, H.; Zeng, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, X. Numerical study on water and salt transport of electroosmosis in saline soil. J. Electrost. 2024, 132, 103992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, H.; Gong, P.; Li, P.; Li, L. Electrolysis characterization of saline wastewater discharged from a subsurface pipe in saline-alkali land. J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 55, 104265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Modeling strategies to balance salt leaching and nitrogen loss for drip irrigation with saline water in arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolomio, M.; Borin, M. Controlled drainage and crop production in a long-term experiment in North-Eastern Italy. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 222, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Ma, X.; Ding, F.; Xu, W.; Fu, Y.; Bian, Q.; Kade, M. Optimizing Subsurface Drainage Spacing for Salinity Control in Arid Agroecosystems. Agronomy 2025, 15, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. Guidelines for Treated Wastewater Use for Irrigation—Part 2: Design of Irrigation Projects. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- DB15/T 2567-2022; Technical Code for Concealed Pipe Drainage, Salt Discharge and Supporting Improvement Measures in Moderately to Severely Saline-alkali Land. Market Supervision and Administration Bureau of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region: Inner Mongolia, China, 2022.
- Mao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Ye, M.; Yang, J. Evaluation of effects of limited irrigation on regional-scale water movement and salt accumulation in arid agricultural areas. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 262, 107398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Kang, Y.; Wang, X. Salt leaching and response of Dianthus chinensis L. to saline water drip-irrigation in two coastal saline soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 218, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Luo, W.; Xie, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, S.; Liu, W. Salinity dynamics of wetland ditches receiving drainage from irrigated agricultural land in arid and semi-arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 100, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Chen, X.; Mu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Xue, Q.; Sun, C.; Li, J. Microscopic analysis of deformation and water–salt transport in chlorine saline soils under unidirectional freezing in cold and arid zones. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 17, 2445–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.H.; Eissa, M.; Mohamed, E.A.; Ramadan, H.S.; Czuppon, G.; Kovács, A.; Szűcs, P. Application of stable isotopes, mixing models, and K-means cluster analysis to detect recharge and salinity origins in Siwa Oasis, Egypt. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, H.; Li, P.; Gong, P.; Yu, X.; Ye, F.; Guo, Y.; Wu, Z. Effects of salt content and particle size on spectral reflectance and model accuracy: Estimating soil salt content in arid, saline-alkali lands. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 111666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wang, G.; Gou, Q. Dynamics of soil water, temperature, and salt and their coupled effects in Haloxylon ammodendron forests of different ages in an arid desert oasis ecotone. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 55, 101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumaia, M.; Lotfi, D.; Yann, L.; Gerhard, S.; Mohamed, H.; Rajouene, M. Identifying the origin of groundwater salinisation in the Sidi El Hani basin (central-eastern Tunisia). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 147, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Fagodiya, R.K.; Prajapat, K.; Narjary, B.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R.K.; Bundela, D.S.; Barman, A. Sub-surface drainage: A win-win technology for achieving carbon neutrality and land amelioration in salt-affected Vertisols of India. Geoderma Reg. 2023, 35, e00708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J. Characterization of Soil Water and Salt Transport Under Shallow Buried Underground Drainpipe Drainage Conditions in Yinbei Irrigation District. Master’s Thesis, Ningxia University, Yinchuan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K. Effect of Irrigation Water Volume and Underground Drainpipe Burial Depth on Drainage and Salt Discharge Pattern with Numerical Simulation. Master’s Thesis, Shihezi University, Shihezi, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Wei, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F. A wireless sensor network-based salt drainage monitoring system for modified alkali underground drainpipe. J. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Bello, S.K.; Alayafi, A.H.; AL-Solaimani, S.G.; Abo-Elyousr, K.A.M. Mitigating Soil Salinity Stress with Gypsum and Bio-Organic Amendments: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Naz, A.; Sharma, S.B.; Dasgupta, R. Changes in Salinity, Mangrove Community Ecology, and Organic Blue Carbon Stock in Response to Cyclones at Indian Sundarbans. Life 2023, 13, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Q.; Wang, H.; Ma, H.; Ding, F.; Xu, W.; Ma, X.; Fu, Y. Synergistic Regulation of Soil Salinity and Ion Transport in Arid Agroecosystems: A Field Study on Drip Irrigation and Subsurface Drainage in Xinjiang, China. Water 2025, 17, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091388
Zhu Q, Wang H, Ma H, Ding F, Xu W, Ma X, Fu Y. Synergistic Regulation of Soil Salinity and Ion Transport in Arid Agroecosystems: A Field Study on Drip Irrigation and Subsurface Drainage in Xinjiang, China. Water. 2025; 17(9):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091388
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Qianqian, Hui Wang, Honghong Ma, Feng Ding, Wanli Xu, Xiaopeng Ma, and Yanbo Fu. 2025. "Synergistic Regulation of Soil Salinity and Ion Transport in Arid Agroecosystems: A Field Study on Drip Irrigation and Subsurface Drainage in Xinjiang, China" Water 17, no. 9: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091388
APA StyleZhu, Q., Wang, H., Ma, H., Ding, F., Xu, W., Ma, X., & Fu, Y. (2025). Synergistic Regulation of Soil Salinity and Ion Transport in Arid Agroecosystems: A Field Study on Drip Irrigation and Subsurface Drainage in Xinjiang, China. Water, 17(9), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091388





