The Efficacy of a Novel Selection of Bacillus spp. on Reducing Off-Flavor Compounds and Improving Flesh Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethic Statement
2.2. Screening and Identification of Bacillus Probiotic for the Inhibition of Actinomycete
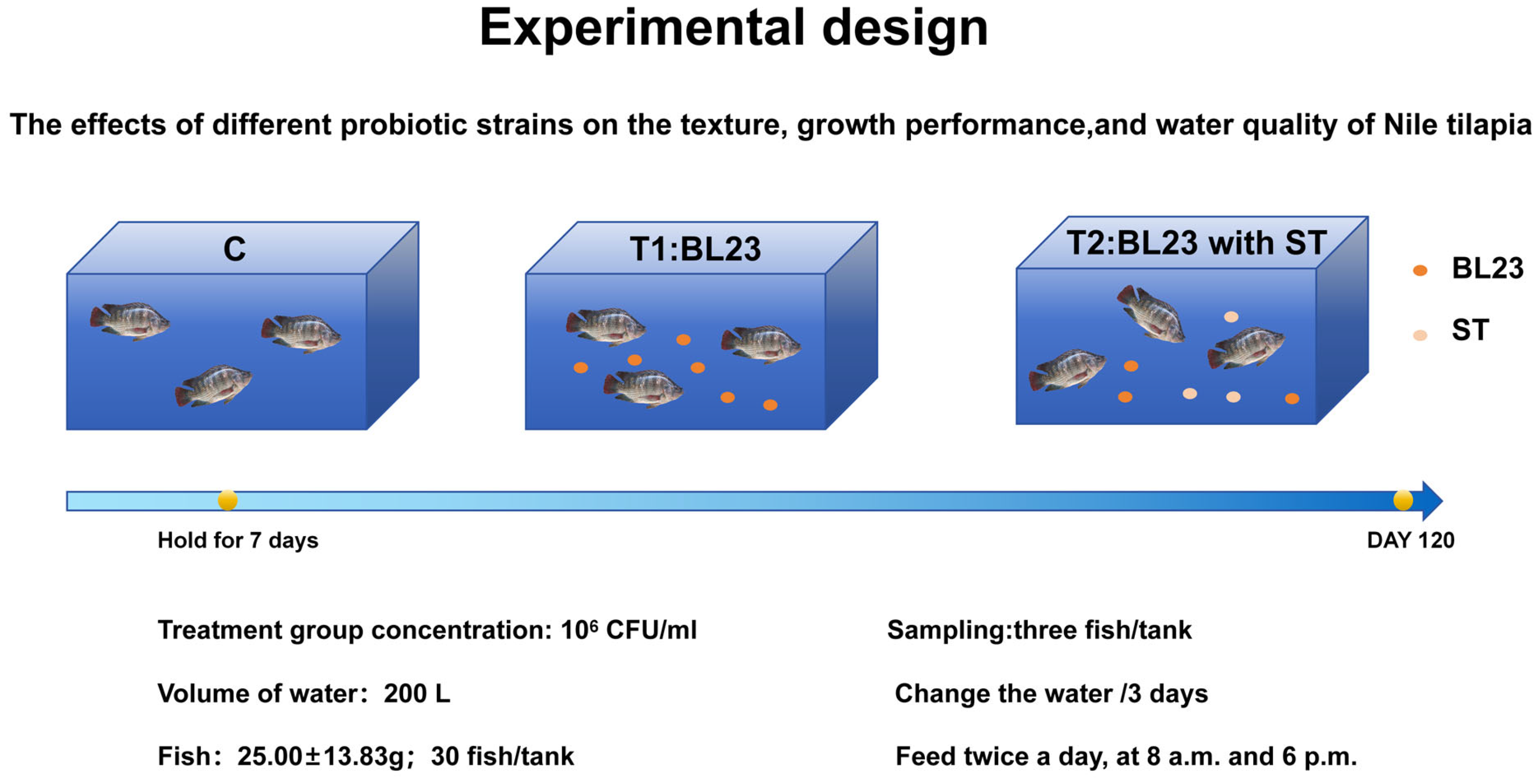
2.3. Fish Culture Experiment
- (1)
- Specific growth rate (SGR) = 100 × In (Final weight) − In (Initial weight)/Culturing days.
- (2)
- Feed conversion ratio (FCR) = Total feed given (g)/Total weight gained (g).
- (3)
- Average daily gain (ADG) = Weight gain (g)/Culturing days.
- (4)
- Weight gain (WG) = Final weight (g) − Initial weight (g).
- (5)
- Survival rate (SR) (%) = 100 × (Number of fish harvested/Number of fish stocked).
2.4. Water Quality Determination
2.5. Texture Measurement of Fish Flesh
2.6. Extraction and Determination of GSM and 2-MIB Concentration
2.6.1. Sample Preparation
2.6.2. Purge and Trap (P&T)
2.6.3. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MC)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Confirmation of Streptomyces spp.
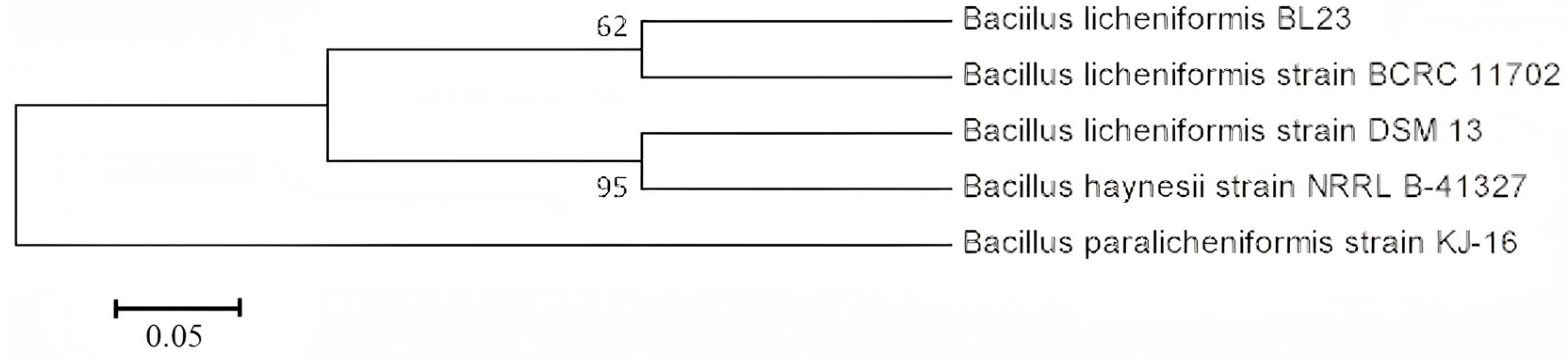
3.2. Selection and Characterization of Probiotics
3.3. Growth Performance of Tilapia
3.4. Texture of Fish Flesh
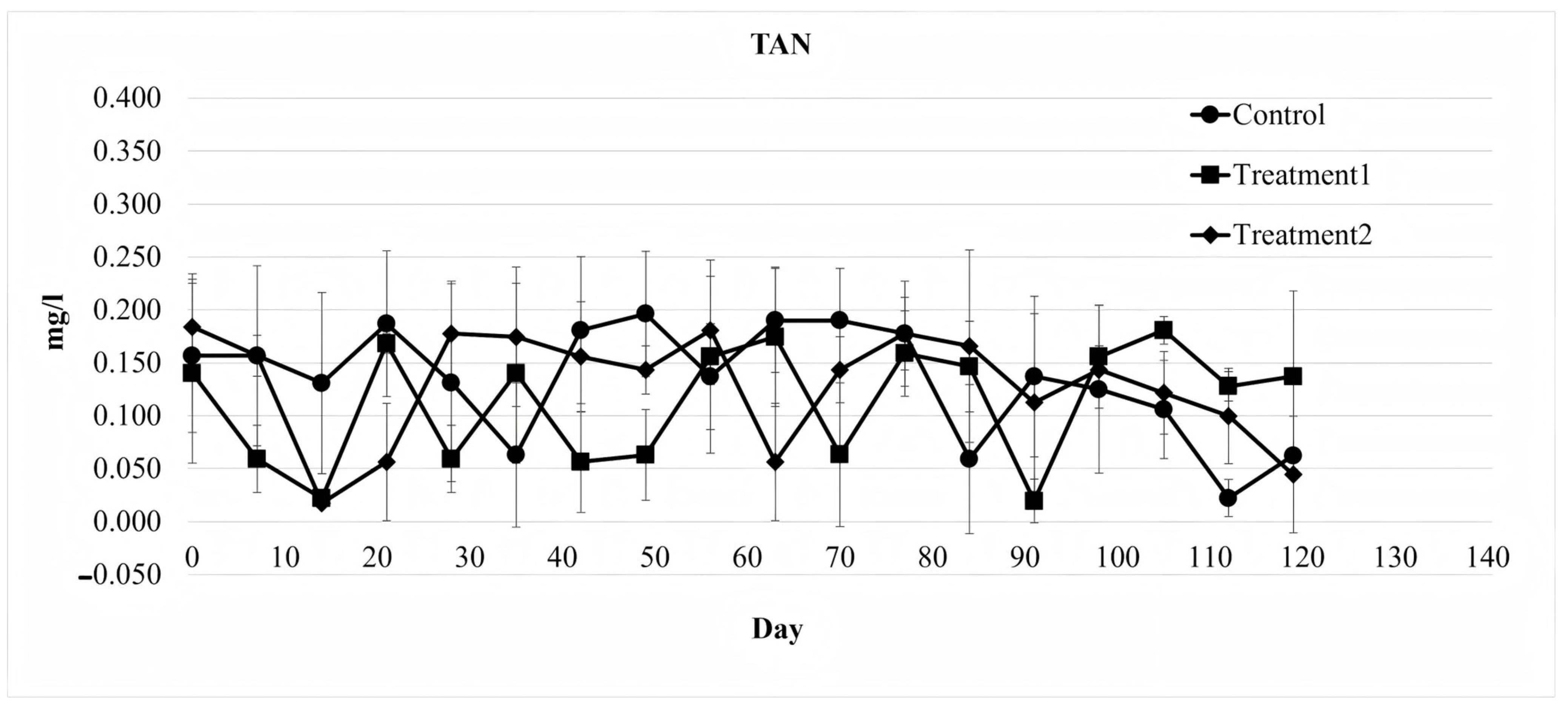
3.5. Water Quality
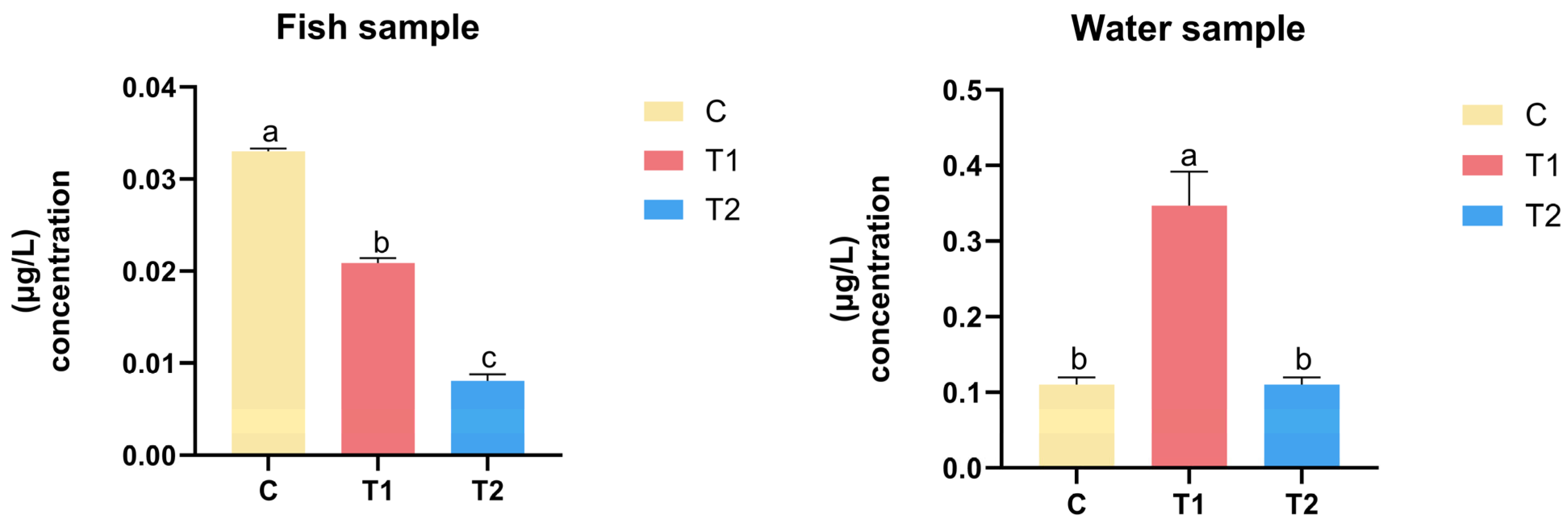
3.6. GSM and 2-MIB Concentration in Fish and Water
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindholm-Lehto, P.C.; Vielma, J.; Pakkanen, H.; Alén, R. Depuration of geosmin- and 2-methylisoborneol-induced off-flavors in recirculating aquaculture system (RAS) farmed European whitefish Coregonus lavaretus. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4585–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Leung, P. Unlocking the potential of aquatic foods in global food security and nutrition: A missing piece under the lens of seafood liking index. Glob. Food Secur. 2022, 33, 100641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarin, S.A. Convergence of aquatic products consumption: A disaggregated analysis in European countries. Mar. Policy 2024, 165, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liato, V.; Aïder, M. Geosmin as a source of the earthy-musty smell in fruits, vegetables and water: Origins, impact on foods and water, and review of the removing techniques. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm-Lehto, P.C.; Vielma, J. Controlling of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol induced off-flavours in recirculating aquaculture system farmed fish—A review. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioni, A.; Cau, A.; Addis, P. Gas Chromatographic Mass Spectrometry Determination of Geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol Off-Flavor in Mugil cephalus Roe. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam-Koong, H.; Schroeder, J.P.; Petrick, G.; Schulz, C. Removal of the off-flavor compounds geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol from recirculating aquaculture system water by ultrasonically induced cavitation. Aquac. Eng. 2016, 70, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Xu, D.; Li, F.; Fu, M.-L. Removal efficiency and possible pathway of odor compounds (2-methylisoborneol and geosmin) by ozonation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 117, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zhang, J.-M.; Ji, S.; Zeng, X.-B.; Jin, X.-C.; Shen, Z.-Q.; Xie, B.; Luo, X.-N.; Li, K.; Liu, L.-P. Histology and transcriptomic analysis reveal the inflammation and affected pathways under 2-methylisoborneol (2-MIB) exposure on grass carp. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 938, 173233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.; Newcombe, G.; Sztajnbok, P. The application of powdered activated carbon for mib and geosmin removal: Predicting pac doses in four raw waters. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xue, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, C.; Chen, N.; Lei, X.; Shen, Z.; Sugiura, N. Removal of geosmin (trans-1,10-dimethyl-trans-9-decalol) from aqueous solution using an indirect electrochemical method. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6979–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, K.K.; Davidson, J.W.; Rimando, A.M.; Summerfelt, S.T. Evaluation of ozonation on levels of the off-flavor compounds geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in water and rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss from recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2010, 43, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, J.; Acosta, M.; Mendoza, G.; Pitones, V. Bacillus subtilis, an ideal probiotic bacterium to shrimp and fish aquaculture that increase feed digestibility, prevent microbial diseases, and avoid water pollution. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.Z.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Z. Probiotics as Means of Diseases Control in Aquaculture, a Review of Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y. A review on the application of Bacillus as probiotics in aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doan, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Ringø, E.; Ángeles Esteban, M.; Dadar, M.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Faggio, C. Host-Associated Probiotics: A Key Factor in Sustainable Aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 16–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, N.V. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaj-Fyzul, A.; Austin, B. Probiotics, immunostimulants, plant products and oral vaccines, and their role as feed supplements in the control of bacterial fish diseases. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 937–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuere, L.; Rombaut, G.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W. Probiotic Bacteria as Biological Control Agents in Aquaculture. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugaban, J.I.I.; Vazquez Bucheli, J.E.; Park, Y.J.; Suh, D.H.; Jung, E.S.; Franco, B.D.G.d.M.; Ivanova, I.V.; Holzapfel, W.H.; Todorov, S.D. Antimicrobial properties of Pediococcus acidilactici and Pediococcus pentosaceus isolated from silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standen, B.T.; Rodiles, A.; Peggs, D.L.; Davies, S.J.; Santos, G.A.; Merrifield, D.L. Modulation of the intestinal microbiota and morphology of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, following the application of a multi-species probiotic. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8403–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaraj, K.; Samayanpaulraj, V.; Narayanadoss, V.; Uthandakalaipandian, R. Isolation of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Intestine of Freshwater Fishes and Elucidation of Probiotic Potential for Aquaculture Application. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1598–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorriehzahra, M.J.; Delshad, S.T.; Adel, M.; Tiwari, R.; Karthik, K.; Dhama, K.; Lazado, C.C. Probiotics as beneficial microbes in aquaculture: An update on their multiple modes of action: A review. Vet. Q. 2016, 36, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoghi, A.; Khosravi-Darani, K.; Sohrabvandi, S. Surface binding of toxins and heavy metals by probiotics. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, W.A.; Mendonça, C.M.N.; Urquiza, A.V.; Marteinsson, V.Þ.; LeBlanc, J.G.; Cotter, P.D.; Villalobos, E.F.; Romero, J.; Oliveira, R.P.S. Use of Probiotic Bacteria and Bacteriocins as an Alternative to Antibiotics in Aquaculture. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurangwa, E.; Verdegem, M.C.J. Microorganisms in recirculating aquaculture systems and their management. Rev. Aquac. 2015, 7, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharti, K.; Yan, L.; Li, K.; Boonpeng, N.; Liu, L. Growth and Muscle Quality of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) in In-Pond Raceway Aquaculture and Traditional Pond Culture. Water 2023, 15, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, E.C.; Públio, M.R.; Santarosa, P.R.; Freitas, F.Z. Antilisterial activity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from vacuum-packaged Brazilian meat and meat products. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2001, 32, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Islam, M.Z.; Islam, M.A.U. Antibacterial Activities of Actinomycete Isolates Collected from Soils of Rajshahi, Bangladesh. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 857925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kishino, H.; Yano, T.-a. Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molayemraftar, T.; Peyghan, R.; Razi Jalali, M.; Shahriari, A. Single and combined effects of ammonia and nitrite on common carp, Cyprinus carpio: Toxicity, hematological parameters, antioxidant defenses, acetylcholinesterase, and acid phosphatase activities. Aquaculture 2022, 548, 737676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Shao, J.; Wang, J.; Li, R. Genes associated with 2-methylisoborneol biosynthesis in cyanobacteria: Isolation, characterization, and expression in response to light. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.S.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, W.J.; Bin Lee, S.; Joo, S.J.; Gupta, S.K.; Park, S.C. Probiotics in addressing heavy metal toxicities in fish farming: Current progress and perspective. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 282, 116755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Shadnoush, M.; Sohrabvandi, S.; Yousefi, M.; Khorshidian, N.; Mortazavian, A.M. Probiotics as potential detoxification tools for mitigation of pesticides: A mini review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 2078–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qin, M.; Huang, Y.; Liao, X.; Liu, Y.; Ren, H.; Sun, J. Designing a reengineered probiotic yeast to spontaneously degrade residual antibiotics in gut during antimicrobial therapy. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 483, 144177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Shimizu, K.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Utsumi, M.; Cao, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N. Geosmin degradation by seasonal biofilm from a biological treatment facility. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yuan, R.; Shi, C.; Yu, L.; Gu, J.; Zhang, C.J.J.o.E.S. Biodegradation of geosmin in drinking water by novel bacteria isolated from biologically active carbon. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauderdale, C.V.; Aldrich, H.C.; Lindner, A.S. Isolation and characterization of a bacterium capable of removing taste- and odor-causing 2-methylisoborneol from water. Water Res. 2004, 38, 4135–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Luo, G.; Tang, H.; Yao, M.; Wang, X. Kinetic Characteristics of Degradation of Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol by Bacillus subtilis (in Chinese with English abstract). Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, S.C.; Lin, T.F.; Tseng, I.C.; Lin, H.M. Identification of 2-MIB and geosmin producers in Feng-Shen reservoir in south Taiwan. Water Supply 2006, 6, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butakova, E.A. Specific features of odor-causing compounds (geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol) as secondary metabolites of cyanobacteria. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 60, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, E.A.; Evans, C.A.; Geary, P.M.; Dunstan, R.H.; Cole, B. The role of Actinobacteria in taste and odour episodes involving geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in aquatic environments. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-Aqua 2013, 62, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattheis, J.P.; Roberts, R.G. Identification of geosmin as a volatile metabolite of Penicillium expansum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3170–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Zhou, B.; Yuan, R. Biodegradation of 2-methylisoborneol by Bacillus idriensis isolated from biological activated carbon. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 76, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganegoda, S.S.; Manage, P.M. Isolation and identification of novel, native geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol degrading bacteria. Water Pract. Technol. 2025, 20, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, A.A.; Magouz, F.I.; Mahmoud, S.A.; Abdel-Rahim, M.M. The effects of some commercial probiotics as water additive on water quality, fish performance, blood biochemical parameters, expression of growth and immune-related genes, and histology of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiel, M.A.E.; Abdelghany, M.F.; Khames, D.K.; Abd El-hameed, S.A.A.; Mansour, E.M.G.; El-Nadi, A.S.M.; Shoukry, A.A. Administration of some probiotic strains in the rearing water enhances the water quality, performance, body chemical analysis, antioxidant and immune responses of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdomanov, A.; Sirakov, I.; Stoyanova, S.; Velichkova, K.; Nedeva, I.; Staykov, Y. The effect of diet supplemented with Proviotic® on growth, blood biochemical parameters and meat quality in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cultivated in recirculation system. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2019, 12, 404–412. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/effect-diet-supplemented-with-proviotic®-on/docview/2211915689/se-2?accountid=28625 (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Hai, N.V. Research findings from the use of probiotics in tilapia aquaculture: A review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suphoronski, S.A.; de Souza, F.P.; Chideroli, R.T.; Mantovani Favero, L.; Ferrari, N.A.; Ziemniczak, H.M.; Gonçalves, D.D.; Lopera Barrero, N.M.; Pereira, U.P. Effect of Enterococcus faecium as a Water and/or Feed Additive on the Gut Microbiota, Hematologic and Immunological Parameters, and Resistance Against Francisellosis and Streptococcosis in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 743957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Jian, S.; Wen, C.; Kajbaf, K.; Kumar, V.; Yang, G. Effects of dietary supplementation with β-glucan and Bacillus subtilis on growth, fillet quality, immune capacity, and antioxidant status of Pengze crucian carp (Carassius auratus var. Pengze). Aquaculture 2019, 508, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.J.F.p.; biochemistry. Effect of treatment with probiotics as water additives on tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) growth performance and immune response. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 36, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa, N.; Wang, H.-P.; Yao, H.; Abou-ElGheit, E. Mixed Bacillus species enhance the innate immune response and stress tolerance in yellow perch subjected to hypoxia and air-exposure stress. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, L.; Telli, G.S.; Dias, D.d.C.; Gonçalves, G.S.; Guimarães, M.C.; Ishikawa, C.M.; Cavalcante, R.B.; Natori, M.M.; Fernandez Alarcon, M.F.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.; et al. Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis in diets for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Effects on growth performance, gut microbiota modulation and innate immunology. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo, R.V.; Braga, L.G.T. Use of probiotics in aquaculture. In Probiotic in Animals; InTech Publishers: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Mian, S.; Rashid, A.; Rahmatullah, S. Effects of stocking density on growth and production of GIFT (Oreochromis niloticus). Bangladesh J. Fish 2010, 14, 45–53. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281823113_Effects_of_stocking_density_on_growth_and_production_of_GIFT_Oreochromis_niloticus (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Huang, W.B.; Chiu, T.S. Effects of stocking density on survival, growth, size variation, and production of Tilapia fry. Aquac. Res. 1997, 28, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opiyo, M.A.; Jumbe, J.; Ngugi, C.C.; Charo-Karisa, H. Different levels of probiotics affect growth, survival and body composition of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultured in low input ponds. Sci. Afr. 2019, 4, e00103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assan, D.; Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Hlordzi, V.; Chen, H.; Mraz, J.; Mustapha, U.F.; Abarike, E.D. Effects of probiotics on digestive enzymes of fish (finfish and shellfish); status and prospects: A mini review. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 257, 110653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Han, L.; Chen, X.; Xie, M.; Kong, W.; Wu, Z. Dietary Supplementation of Probiotic Bacillus subtilis Affects Antioxidant Defenses and Immune Response in Grass Carp Under Aeromonas hydrophila Challenge. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobi, N.; Vaseeharan, B.; Chen, J.-C.; Rekha, R.; Vijayakumar, S.; Anjugam, M.; Iswarya, A. Dietary supplementation of probiotic Bacillus licheniformis Dahb1 improves growth performance, mucus and serum immune parameters, antioxidant enzyme activity as well as resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 74, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Target Gene | Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | Amplicon Size (Base Pairs) | Annealing Temp. (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16S rRNA | 27-F 1492-R | AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG CGGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT | 1500 | 50 |
| geoA | geoA-F geoA-R | CTCCTCAACGAGTCCCTGTG GCTGGTAGGAGAAGAGGTCG | 238 | 59 |
| tpc | AMmib-F AMmib-R | TGGACGACTGCTACTGCGAG AAGGCGTGCTGTAGTTCGTTGTG | 592 | 58 |
| Actinomycetes | Olfaction Test | GC-MS | PCR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geosmin | 2-MIB | geoA | tpc | ||
| S. roseoflavus | + | + | + | + | + |
| S.thermocarboxydus | + | + | − | + | − |
| S. cyaneofuscatus | + | + | − | + | − |
| Group | Control | Treatment1 | Treatment2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (ST) | (ST and BL23) | ||
| Initial weight (g) | 25.00 ± 13.83 a | 22.17 ± 12.01 a | 23.50 ± 10.35 a |
| Final weight (g) | 88.50 ± 27.79 ab | 78.33 ± 23.19 a | 111.11 ± 28.26 b |
| Specific growth rate (SGR) (%) | 1.09 ± 0.04 ab | 1.08 ± 0.23 a | 1.32 ± 0.07 b |
| Feed conversation ratio (FCR) | 1.78 ± 1.02 a | 2.06 ± 0.93 a | 1.86 ± 0.98 a |
| Average daily gain (ADG) (g/day) | 0.57 ± 0.14 ab | 0.47 ± 0.06 a | 0.76 ± 0.12 b |
| Weight gain (WG) (g) | 68.33 ± 16.67 ab | 56.17 ± 7.32 a | 90.81 ± 14.47 b |
| Survival rate (SR) (%) | 93.33 ± 11.55 a | 96.67 ± 5.77 a | 90.00 ± 10.00 a |
| Group | Control | Treatment1 | Treatment2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (ST) | (ST and BL23) | ||
| Hardness (g) | 280 ± 27.78 ab | 230.00 ± 47.29 a | 323.33 ± 17.01 b |
| Springiness (mm) | 0.64 ± 0.14 a | 1.29 ± 1.11 a | 0.64 ± 0.17 a |
| Cohesiveness | 0.84 ± 0.06 a | 0.68 ± 0.06 a | 0.81 ± 0.12 a |
| Stickiness (g) | 163.73 ± 21.38 b | 79.95 ± 8.59 a | 176.38 ± 63.79 b |
| Chewiness (g × mm) | 233.99 ± 27.64 b | 153.57 ± 21 d.16 a | 261.56 ± 39.86 b |
| Resilience | 0.90 ± 0.81 a | 1.34 ± 0.24 a | 0.81 ± 0.12 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Boonpeng, N.; Li, K.; Yan, L.; Amankwah, J.F.; Satapornvanit, K.; Borski, R.; Liu, L. The Efficacy of a Novel Selection of Bacillus spp. on Reducing Off-Flavor Compounds and Improving Flesh Quality. Water 2025, 17, 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091357
Liu T, Boonpeng N, Li K, Yan L, Amankwah JF, Satapornvanit K, Borski R, Liu L. The Efficacy of a Novel Selection of Bacillus spp. on Reducing Off-Flavor Compounds and Improving Flesh Quality. Water. 2025; 17(9):1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091357
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tianyu, Nattida Boonpeng, Kang Li, Li Yan, Justice Frimpong Amankwah, Kriengkrai Satapornvanit, Russell Borski, and Liping Liu. 2025. "The Efficacy of a Novel Selection of Bacillus spp. on Reducing Off-Flavor Compounds and Improving Flesh Quality" Water 17, no. 9: 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091357
APA StyleLiu, T., Boonpeng, N., Li, K., Yan, L., Amankwah, J. F., Satapornvanit, K., Borski, R., & Liu, L. (2025). The Efficacy of a Novel Selection of Bacillus spp. on Reducing Off-Flavor Compounds and Improving Flesh Quality. Water, 17(9), 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091357






