Hydrological Conditions and Dominant Phytoplankton Species in the Middle and Upper Reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River, Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Points
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
2.3.1. Biodiversity Indices
2.3.2. Dominant Species
2.3.3. Niche Width
2.3.4. Niche Overlap and Relative Resource Occupancy
2.3.5. Data Processing
3. Results
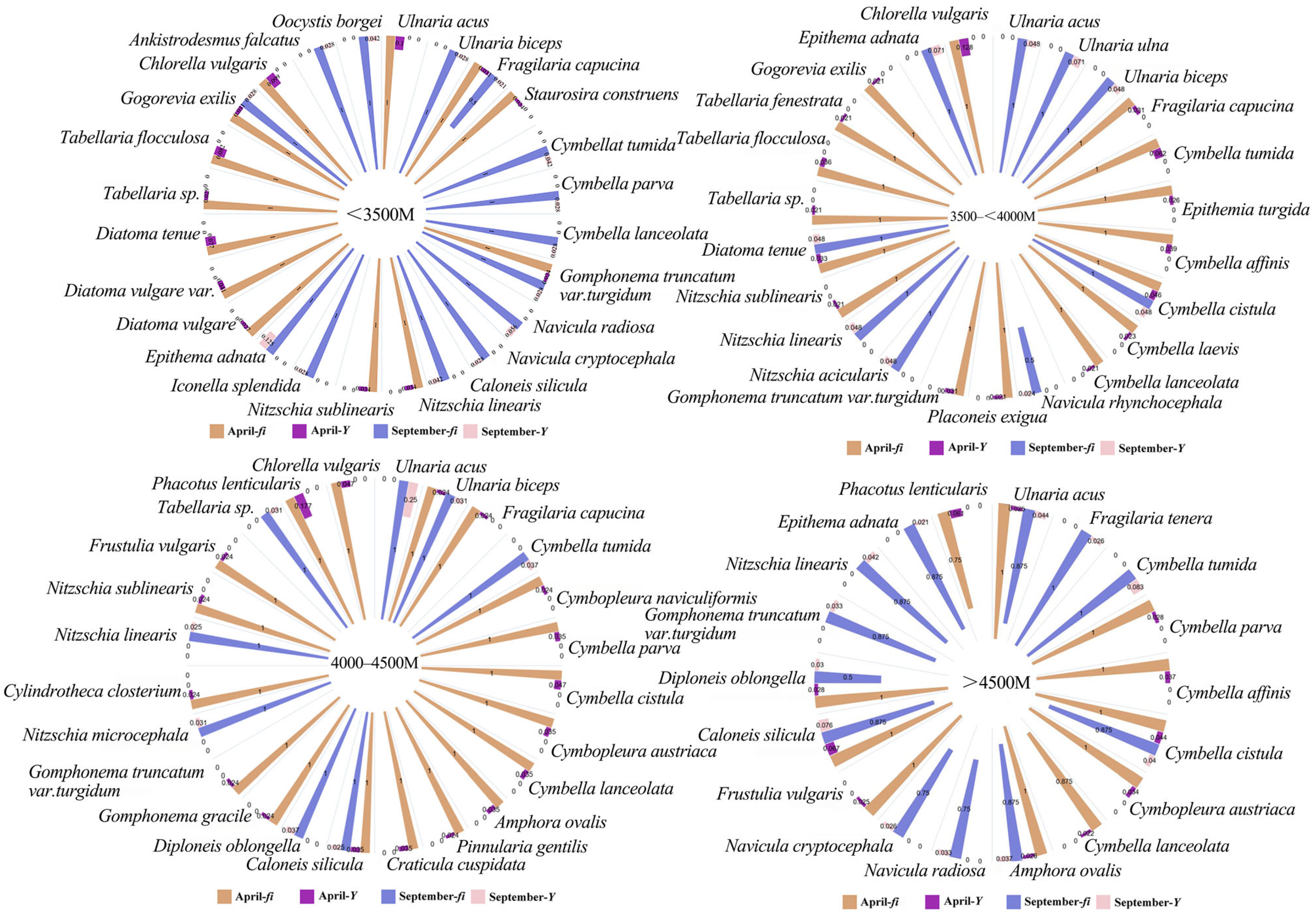
3.1. Dominant Species
3.2. Niche Width
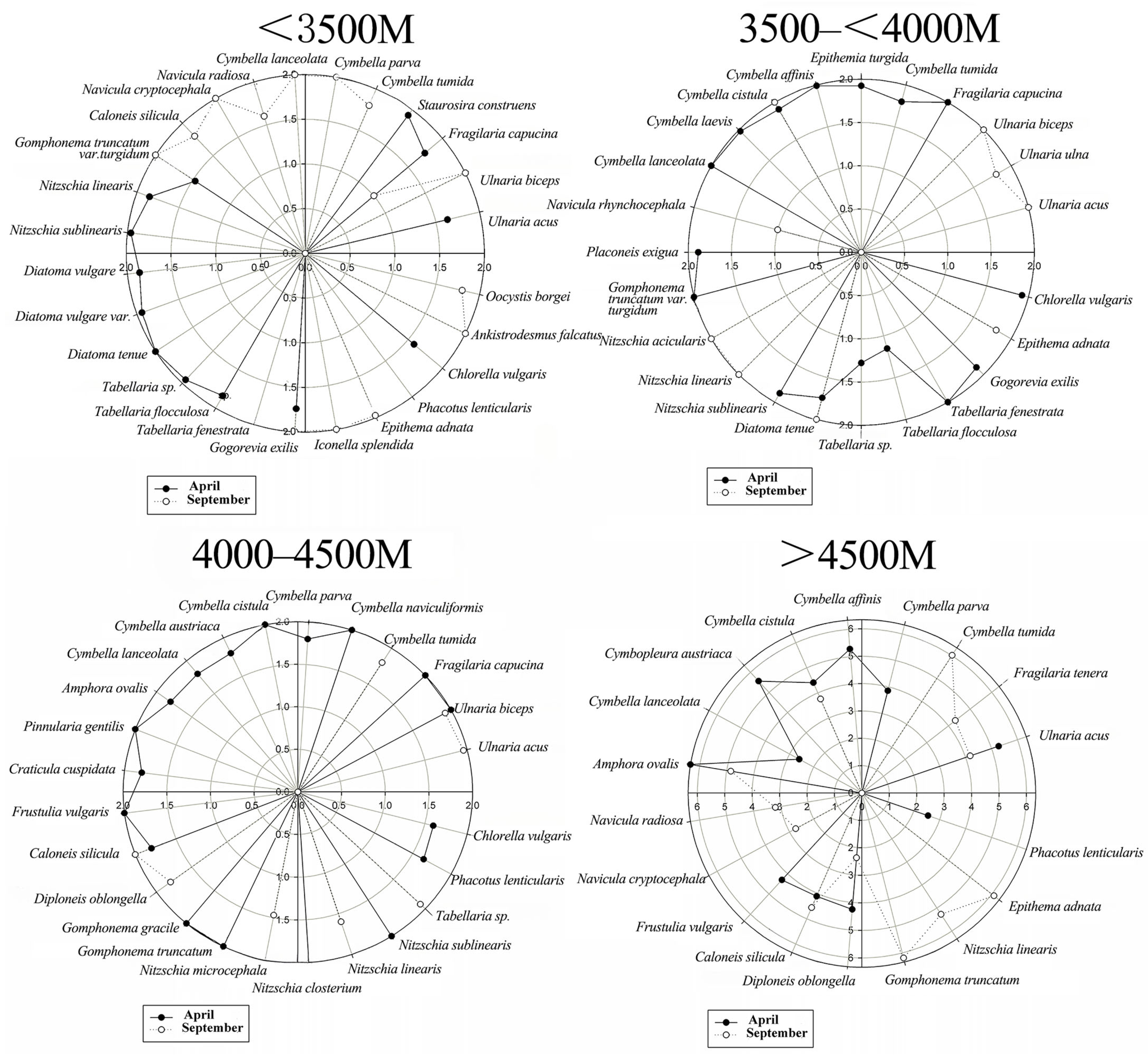
3.2.1. Seasonal Variation in Niche Width
3.2.2. Niche Width Relative to Elevation
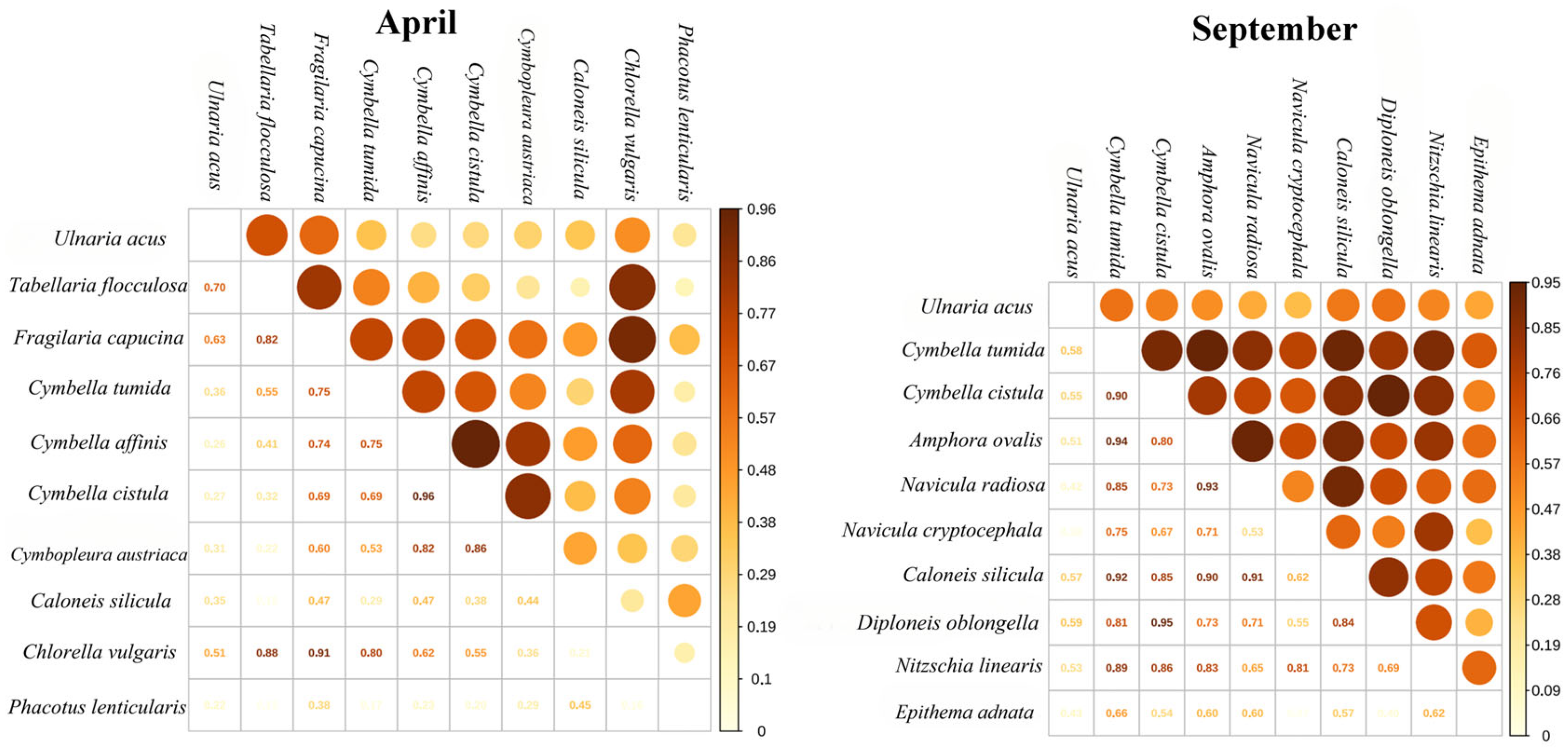
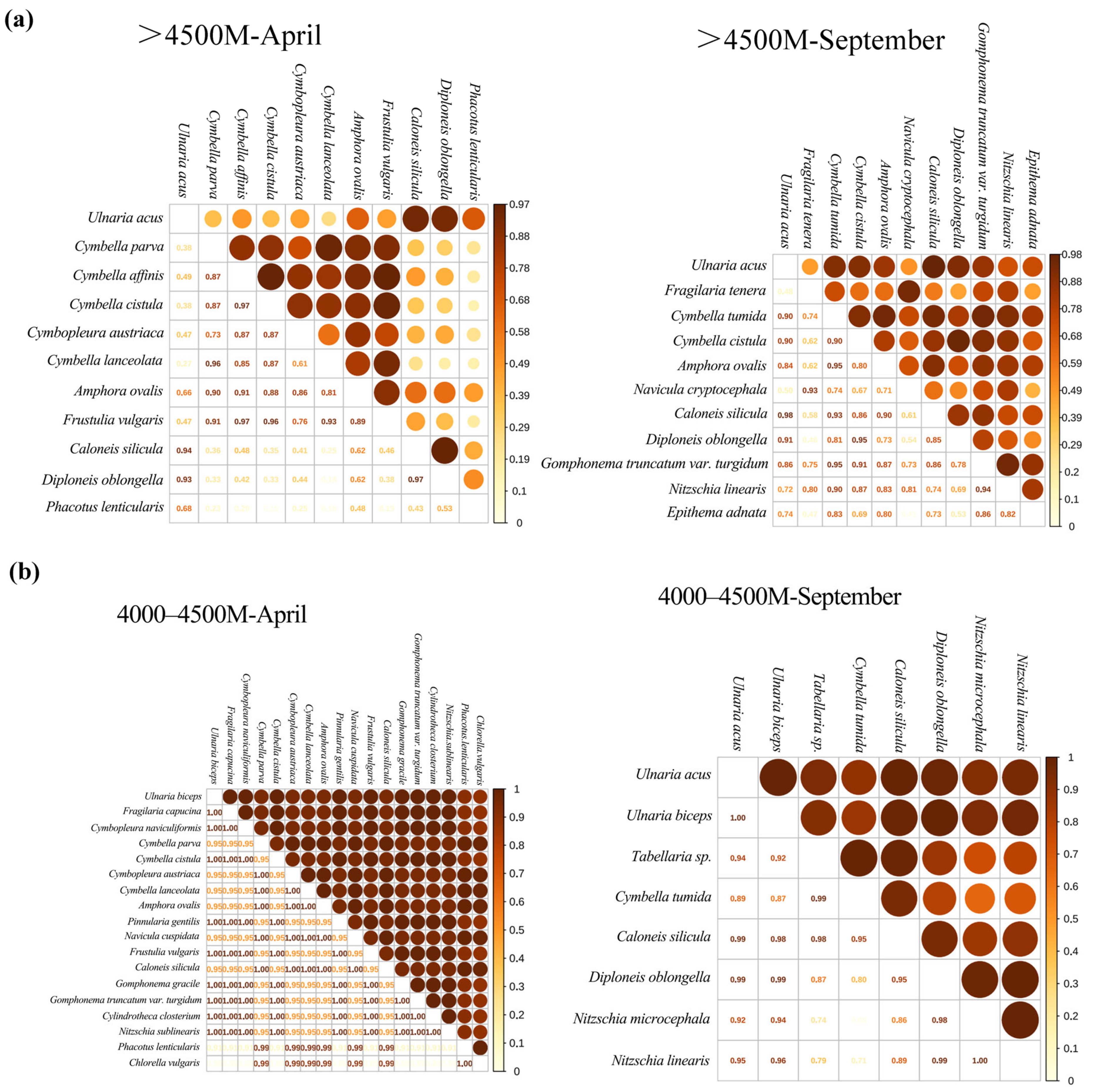
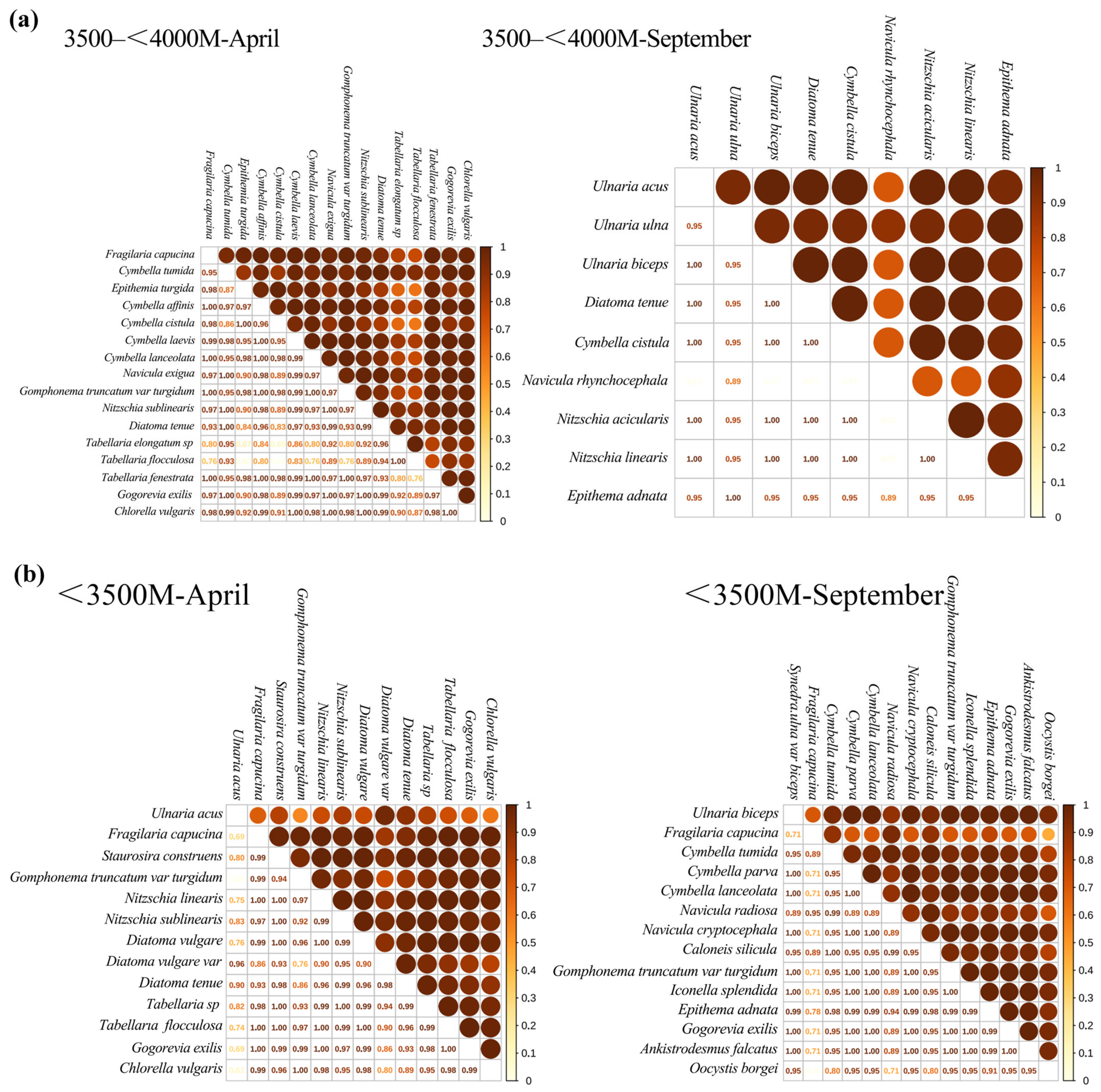
3.2.3. Niche Overlap Relative to Season
3.2.4. Niche Overlap Relative to Elevation Asl
3.2.5. Seasonal Relative Resource Occupancy
3.3. Ecological Niche Differentiation
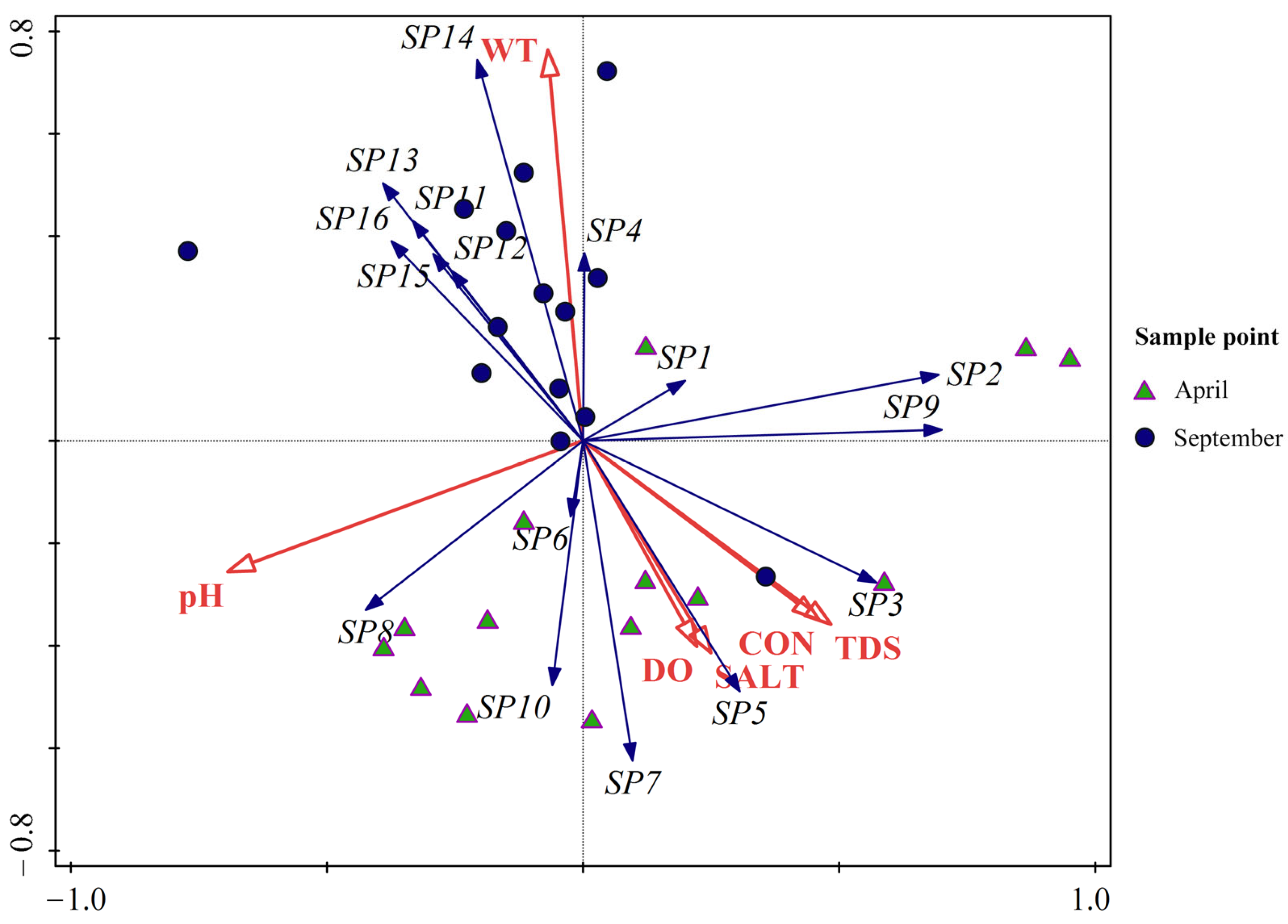
3.3.1. Environmental Factors
3.3.2. Redundancy Analysis and Ordination Plot
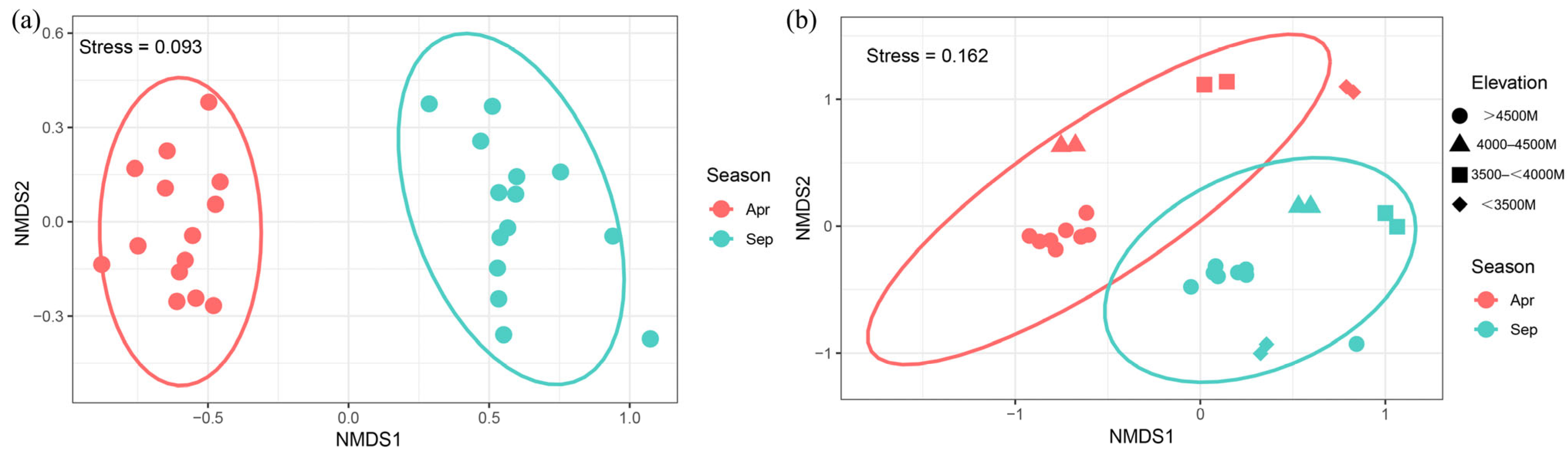
3.3.3. NMDS Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Phytoplankton Community Characteristics and Dominant Species
4.2. Niche Width and Overlap of Dominant Species
4.3. Factors Influencing Phytoplankton Community Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, T.D.; Chen, F.H.; Cui, P.; Ma, Y.M.; Xu, B.Q.; Zhu, L.P.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.C.; Ai, L.K.; Yang, X.X. From the Tibetan Plateau to the third pole and the extended third pole. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 924–931. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Q.; Liu, H.; Chao, X.; Yang, S.; Ba, S. Distribution patterns and driving factors of the phytoplankton community in the middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.B.; Hu, G.Y.; Qian, G.Q.; Lu, J.F.; Zhang, Z.C.; Luo, W.Y.; Lv, P. High-altitude aeolian research on the Tibetan Plateau. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 864–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.L.; Zhu, M.Z. Use of planktonic protists for assessing water quality in Jiaozhou Bay, northern China. Protistology 2012, 7, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Filker, S.; Sommaruga, R.; Vila, I.; Stoeck, T. Microbial eukaryote plankton communities of high-mountain lakes from three continents exhibit strong biogeographic patterns. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 2286–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Interlandi, S.J.; Kilham, S.S. Limiting Resources and the Regulation of Diversity in Phytoplankton Communities. Ecology 2001, 82, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X. Spatial-Temporal Evolutional Laws of the Key Hydrological Elements in Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.Y.; Li, W. Spatial-Temporal Change Trends and Driving Factors of NDVI in the Riparian Vegetation at Different Altitudinal Gradients in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. Biodivers. Sci. 2024, 32, 23432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Wan, Y.; Wu, P.; Wang, J. Effects of Environmental Factors on Phytoplankton Growth and Community Structure. Adv. Environ. Prot. 2024, 14, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pan, C.; An, R.; Ba, S. Niche and interspecific association of dominant phytoplankton species in different hydrological periods in the middle and lower reaches of Lhasa River, Tibet, China. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 118–130. [Google Scholar]
- Pastore, A.I.; Allesina, S.; Kraft, N.J.B. The evolution of niche overlap and competitive differences. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodchikoff, C.N.; Schulz, W.C. Measures of niche overlap. Ecology 1980, 61, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, G.E. Concluding remarks. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1957, 22, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R.K.; Futuyma, D.J. On the measurement of niche breadth and overlap. Ecology 1971, 52, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.F.; Cao, J.X.; Liu, G.X. Diversity of phytoplankton community in different reaches of Niyang River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2012, 21, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.P.; Ye, S.W.; Yang, X.F.; Zhang, L.S.; Zhong, G.H.; Li, Z.J. Spatial-temporal dynamics of aquatic organism community and their relationships to environment in Niyang River, Tibet: 1. Phytoplankton. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 695–706. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, J.J.; Qu, X.; Zhu, D.J.; Yuan, Z.; Tang, Y.Z. Impacts of Climate Change on Blue and Green Water Resources in the Middle and Upper Yarlung Zangbo River, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jin, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.P.; Wu, S.; Wang, N.M.; Jin, X.; Ma, B. Distribution and Feeding Habit Difference of Oxygymnocypris stewarti in the Yarlung Zangbo River System. Wetl. Sci. 2022, 20, 704–708. [Google Scholar]
- Comprehensive Scientific Expedition to the Tibetan Plateau, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Rivers and Lakes of Tibet; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Lin, B.; Sun, J.; Luozhu, N.; Da, P.; Dawa, J. Suspended Sediment Transport Responses to Increasing Human Activities in a High-Altitude River: A Case Study in a Typical Sub-Catchment of the Yarlung Tsangpo River. Water 2020, 12, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z. Driving Forces of Nitrogen Cycling and the Climate Feedback Loops in the Yarlung Tsangpo River Basin, the Highest-Altitude Large River Basin in the World. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.G. Exploring the distribution patterns and conservation approaches of biodiversity on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Biodivers. Sci. 2018, 26, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, S.; Yang, X.L.; Huang, X.; Gui, Q. Phytoplankton community characteristics and water quality evaluation in the lower reaches of Lhasa River in spring and summer. Res. Plateau Sci. 2017, 1, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, S.; Wang, D.B.; Zhou, J.H.; Bai, X.Y.; Bai, K. Community structures of phytoplankton and its relationship with environmental factors in the Lhasa River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 787–798. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.X.; Liu, X.W.; Liu, J.T.; Bai, J.R. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Land Use/Cover Change for the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin from 1980 to 2015. China Rural Water Hydropower 2019, 3, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Z.H.; Chen, C.Y. Tibetan Rivers and Lakes; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Huang, X.F. Research Methods of Freshwater Plankton; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, I.; O’Farrell, I.; Unrein, F.; Sinistro, R.; Afonso, M.D.; Tell, G. Algal Assemblages Across a Wetland, from a Shallow Lake to Relictual Oxbow Lakes (Lower Paraná River, South America). Hydrobiologia 2004, 511, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.Y.; Wang, K.; Huang, S.J.; Jiao, N.Z.; Chen, F. Distinct patterns of picocyanobacterial communities in winter and summer in the Chesapeake Bay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2955–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, P.; Azeiteiro, M.U.; Gonçalves, F.; Pereira, J.M. Distribution and ecological preferences of diatoms and dinoflagellates in the west Iberian Coastal zone (North Portugal). Acta Oecologica 2007, 32, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, S.J. Relationships among Functional Properties of Californian Grassland. Nature 1967, 216, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianka, E.R. The structure of Lizard communities. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capblancq, T.; Forester, B. Redundancy Analysis (RDA): A Swiss Army knife for landscape genomics. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, 2298–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; An, R.Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Chen, J.L.; Ma, W.Q.; Ba, S. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics and driving factors of phytoplankton community in Lhalu Wetland, Tibet, China. J. Lake Sci. 2024, 36, 403–417. [Google Scholar]
- Ta, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.L. Periphytic Algal Community Structure and Relationship to Environmental Factors in the Lower Reaches of Lhasa River. Hydroecol. Aquat. Biol. 2023, 47, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, D.D.; Liu, D.F.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, Z.J.; Zhu, X.M.; Tan, Q.R. Influence of Periodic Temperature Disturbance on the Succession of Algal Community Structure. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.X.; Yang, S.Q.; Ye, Q.Y.; Wan, K.M.; Deng, Y.T.; Zhao, T.; Dong, P.C.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.N.; Wu, Z.X. Characteristics of Phytoplankton Community Structure in Lakes of Wetlands Dominated by Different Aquatic Plants and Its Driving Factors. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 5811–5821. [Google Scholar]
- Feinsinger, P.; Spears, E.E.; Poole, R.W. A Simple Measure of Niche Breadth. Ecology 1981, 62, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Merino, S.M.; Reyes-Bonilla, H.; Lira-Noriega, A. Ecological Niche Models and Species Distribution Models in Marine Environments: A Literature Review and Spatial Analysis of Evidence. Ecol. Model. 2020, 415, 108837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Thangaraj, S.; Sun, J. Water Quality Shifts the Dominant Phytoplankton Group from Diatoms to Dinoflagellates in the Coastal Ecosystem of the Bohai Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 183, 114078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, J.D.; Lee, M.D.; Xu, F.; Phan, M.D.; Wang, X.; Qu, P. Transient Exposure to Novel High Temperatures Reshapes Coastal Phytoplankton Communities. ISME J. 2020, 14, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.T.; Zhao, W.; He, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.L.; Yu, H.X.; Chai, F.Y.; Wang, H.C. Correlation Analysis of Water Ecological Environment Factors in Sturgeon Intensive Culture. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, Q.S.; Sun, J.; Song, S.Q.; Shen, Z.L.; Yu, Z.M. Canonical Correspondence Analysis of Summer Phytoplankton Community and Its Environment in the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2007, 31, 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- De Baar, H.J.W.; Boyd, P.W.; Coale, K.H.; Landry, M.R.; Tsuda, A.; Assmy, P.; Bakker, D.C.E.; Bozec, Y.; Barber, R.T.; Brzezinski, M.A.; et al. Synthesis of iron fertilization experiments: From the Iron Age in the Age of Enlightenment. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2005, 110, C09S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, N.; Deng, J.M.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, Y.J.; Gong, Z.J.; Li, M. Community Structure of Phytoplankton and Environmental Impact Factors in Lake Hongze from 2015 to 2020. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 3097–3105. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Chai, Y.; Luo, J.; Guo, K.; Tan, F.; Yang, D.; He, Y. Long Lake Phytoplankton Dominant Species Seasonal Succession and Ecological Niche Analysis. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 44, 612–621. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.; Li, Z.; Zhao, M.M.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, R.; Rong, J.; Li, L. Combined effects of light and nutrient supply on primary producers in subtropical shallow lakes: A microcosm study. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 10639–10649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| April % | September % | |
|---|---|---|
| Bacillariophyta | 87.06 | 93.80 |
| Chlorophyta | 11.72 | 3.96 |
| Cyanobacteria | 1.22 | 1.60 |
| Euglenophyta | - | 0.32 |
| Cryptophyta | - | 0.32 |
| Dominant Species | April | September | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fi | Y | fi | Y | |
| Ulnaria acus | 0.857 | 0.034 | 0.786 | 0.063 |
| Tabellaria flocculosa | 0.714 | 0.021 | / | / |
| Fragilaria capucina | 1 | 0.025 | / | / |
| Cymbella tumida | 0.929 | 0.023 | 0.929 | 0.065 |
| Cymbella affinis | 0.857 | 0.026 | / | / |
| Cymbella cistula | 1 | 0.037 | 0.857 | 0.033 |
| Cymbopleura austriaca | 1 | 0.024 | / | / |
| Amphora ovalis | / | / | 0.786 | 0.027 |
| Diploneis oblongella | / | / | 0.5 | 0.025 |
| Caloneis silicula | 1 | 0.041 | 0.857 | 0.06 |
| Navicula radiosa | / | / | 0.571 | 0.02 |
| Navicula cryptocephala | / | / | 0.714 | 0.021 |
| Nitzschia linearis | / | / | 0.857 | 0.036 |
| Epithema adnata | / | / | 0.929 | 0.031 |
| Chlorella vulgaris | 1 | 0.059 | / | / |
| Phacotus lenticularis | 0.786 | 0.043 | / | / |
| Dominant Species | Bi | |
|---|---|---|
| April | September | |
| Ulnaria acus | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Tabellaria flocculosa | 3.226 | / |
| Fragilaria capucina | 1.000 | / |
| Cymbella tumida | 1.000 | 2.000 |
| Cymbella affinis | 4.907 | / |
| Cymbella cistula | 8.346 | 2.000 |
| Cymbopleura austriaca | 1.000 | / |
| Amphora ovalis | / | 5.765 |
| Diploneis oblongella | / | 1.000 |
| Caloneis silicula | 3.240 | 1.000 |
| Navicula radiosa | / | 1.000 |
| Navicula cryptocephala | / | 7.000 |
| Nitzschia linearis | / | 1.000 |
| Epithema adnata | / | 1.000 |
| Chlorella vulgaris | 2.000 | / |
| Phacotus lenticularis | 1.000 | / |
| Dominant Species | April | September |
|---|---|---|
| Ulnaria acus | −0.173 | −0.266 |
| Tabellaria flocculosa | −0.046 | - |
| Fragilaria capucina | 0.369 | - |
| Cymbella tumida | 0.120 | 0.152 |
| Cymbella cistula | 0.127 | 0.106 |
| Cymbella affinis | 0.167 | - |
| Cymbopleura austriaca | 0.014 | - |
| Amphora ovalis | - | 0.120 |
| Navicula radiosa | - | 0.023 |
| Navicula cryptocephala | - | −0.130 |
| Caloneis silicula | −0.362 | 0.116 |
| Diploneis oblongella | - | 0.013 |
| Nitzschia acicularis | - | 0.065 |
| Epithema adnata | - | −0.227 |
| Chlorella vulgaris | 0.126 | - |
| Phacotus lenticularis | −0.956 | - |
| Species | >4500 m | 4000–4500 m | 3500–<4000 m | <3500 m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| April | September | April | September | April | September | April | Autumn | |
| Ulnaria acus | −0.059 | 0.016 | / | 0.048 | / | 0.024 | −0.184 | / |
| Fragilaria tenera | / | −0.161 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Ulnaria ulna | / | / | / | / | / | 0.022 | / | / |
| Ulnaria biceps | / | / | 0.004 | 0.047 | / | 0.024 | / | 0.030 |
| Fragilaria capucina | / | / | 0.004 | / | 0.019 | / | 0.020 | −0.204 |
| Staurosira construens | / | / | / | / | / | / | 0.037 | / |
| Cymbella tumida | / | 0.124 | / | −0.022 | 0.022 | / | / | 0.014 |
| Epithemia turgida | / | / | / | / | −0.039 | / | / | / |
| Cymbopleura naviculiformis | / | / | 0.004 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Cymbella parva | 0.087 | / | 0.003 | / | / | / | / | 0.030 |
| Cymbella affinis | 0.165 | / | / | / | 0.029 | / | / | / |
| Cymbella cistula | 0.102 | 0.063 | 0.004 | / | −0.048 | 0.024 | / | / |
| Cymbopleura austriaca | 0.040 | / | 0.003 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Cymbella laevis | / | / | / | / | 0.032 | / | / | / |
| Cymbella lanceolata | −0.023 | / | 0.003 | / | 0.019 | / | / | 0.030 |
| Amphora ovalis | 0.266 | 0.047 | 0.003 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Pinnularia gentilis | / | / | 0.004 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Navicula rhynchocephala | / | / | / | / | / | −0.188 | / | / |
| Navicula radiosa | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | −0.029 |
| Navicula cryptocephala | / | −0.132 | / | / | / | / | / | 0.030 |
| Placoneis exigua | / | / | / | / | 0.031 | / | / | / |
| Craticula cuspidata | / | / | 0.003 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Frustulia vulgaris | 0.149 | / | 0.004 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Caloneis silicula | −0.124 | 0.044 | 0.003 | 0.036 | / | / | / | 0.014 |
| Diploneis oblongella | −0.150 | −0.057 | / | 0.029 | / | / | / | / |
| Gomphonema gracile | / | / | 0.004 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Gomphonema truncatum var. turgidum | / | 0.106 | 0.004 | / | 0.019 | / | −0.031 | 0.030 |
| Nitzschia microcephala | / | / | / | −0.045 | / | / | / | / |
| Cylindrotheca closterium | / | / | 0.004 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Nitzschia acicularis | / | / | / | / | / | 0.024 | / | / |
| Nitzschia linearis | / | 0.056 | / | −0.012 | / | 0.024 | 0.033 | / |
| Nitzschia sublinearis | / | / | 0.004 | / | 0.031 | / | 0.035 | / |
| Diatoma vulgare | / | / | / | / | / | 0.034 | / | |
| Diatoma vulgare var. | / | / | / | / | / | / | −0.038 | / |
| Diatoma tenue | / | / | / | / | 0.013 | 0.024 | 0.016 | / |
| Tabellaria sp. | / | / | / | −0.022 | −0.088 | / | 0.036 | / |
| Tabellaria flocculosa | / | / | / | / | −0.123 | / | 0.032 | / |
| Tabellaria fenestrata | / | / | / | / | 0.019 | / | / | / |
| Gogorevia exilis | / | / | / | / | 0.031 | / | 0.020 | 0.030 |
| Iconella splendida | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 0.030 |
| Epithema adnata | / | −0.106 | / | / | / | 0.022 | / | 0.037 |
| Phacotus lenticularis | −0.452 | / | −0.025 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Chlorella vulgaris | / | / | −0.033 | / | 0.034 | / | −0.007 | / |
| Ankistrodesmus falcatus | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 0.030 |
| Oocystis borgei | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | −0.069 |
| Sampling Period | Water Temperature (°C) | pH | Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) | Conductivity (μs/cm) | Salinity (ppt) | Total Dissolved Solids (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| April | 8.58 ± 0.74 a | 8.40 ± 0.13 | 7.66 ± 0.27 | 291.96 ± 19.99 a | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 144.26 ± 9.79 a |
| September | 13.71 ± 0.78 b | 8.42 ± 0.05 | 7.09 ± 0.53 | 232.36 ± 18.89 b | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 113.86 ± 9.20 b |
| >4500 m | 4000–4500 m | 3500–<4000 m | <3500 m | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| April | September | April | September | April | September | April | September | |
| WT (°C) | 6.92 ± 0.85 e | 11.91 ± 0.82 de | 9.55 ± 1.05 bcd | 15.25 ± 0.15 cd | 11.60 ± 0.70 bcd | 15.60 ± 1.50 abc | 11.20 ± 0.60 ab | 17.50 ± 0.80 a |
| pH | 8.69 ± 0.09 a | 8.47 ± 0.07 bc | 8.01 ± 0.40 ab | 8.41 ± 0.01 c | 8.44 ± 0.11 ab | 8.38 ± 0.15 ab | 7.62 ± 0.13 ab | 8.30 ± 0.07 ab |
| DO (mg/L) | 7.83 ± 0.43 ab | 6.43 ± 0.11 b | 6.95 ± 0.15 ab | 10.15 ± 3.75 ab | 7.65 ± 0.55 b | 6.80 ± 0.30 a | 7.75 ± 0.85 b | 6.95 ± 0.15 b |
| CON (μs/cm) | 253.47 ± 20.96 cd | 194.29 ± 8.56 a | 405.00 ± 1.00 a | 340.00 ± 2.00 bcd | 360.00 ± 2.00 d | 326.00 ± 43.00 ab | 265.00 ± 0.05 abc | 183.35 ± 0.15 d |
| SALT (ppt) | 0.01 ± 0.01 bc | 0.09 ± 0.003 a | 0.19 ± 0.01 b | 0.15 ± 0.001 bc | 0.15 ± 0.02 c | 0.16 ± 0.02 ab | 0.12 ± 0.01 ab | 0.09 ± 0.01 c |
| TDS (mg/L) | 125.21 ± 10.09 cde | 94.63 ± 3.75 a | 198.50 ± 3.50 a | 165.00 ± 1.00 bcd | 180.00 ± 1.00 de | 162.00 ± 20.00 ab | 130.50 ± 1.50 abc | 91.55 ± 0.45 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Li, S.; Jin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, L.; Li, L. Hydrological Conditions and Dominant Phytoplankton Species in the Middle and Upper Reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River, Tibetan Plateau. Water 2025, 17, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091346
Xu W, Li S, Jin H, Zhang Z, Lu W, Zhao Y, Pan L, Li L. Hydrological Conditions and Dominant Phytoplankton Species in the Middle and Upper Reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River, Tibetan Plateau. Water. 2025; 17(9):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091346
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wenyan, Shenhui Li, Hongyu Jin, Zepeng Zhang, Wanqiao Lu, Yanzhe Zhao, Lianghan Pan, and Lei Li. 2025. "Hydrological Conditions and Dominant Phytoplankton Species in the Middle and Upper Reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River, Tibetan Plateau" Water 17, no. 9: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091346
APA StyleXu, W., Li, S., Jin, H., Zhang, Z., Lu, W., Zhao, Y., Pan, L., & Li, L. (2025). Hydrological Conditions and Dominant Phytoplankton Species in the Middle and Upper Reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River, Tibetan Plateau. Water, 17(9), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091346






