An Experimental Study on the Behavior of Fish in Response to Turbidity Changes—A Case Study of Korean Fishes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fish Behavior Experiment
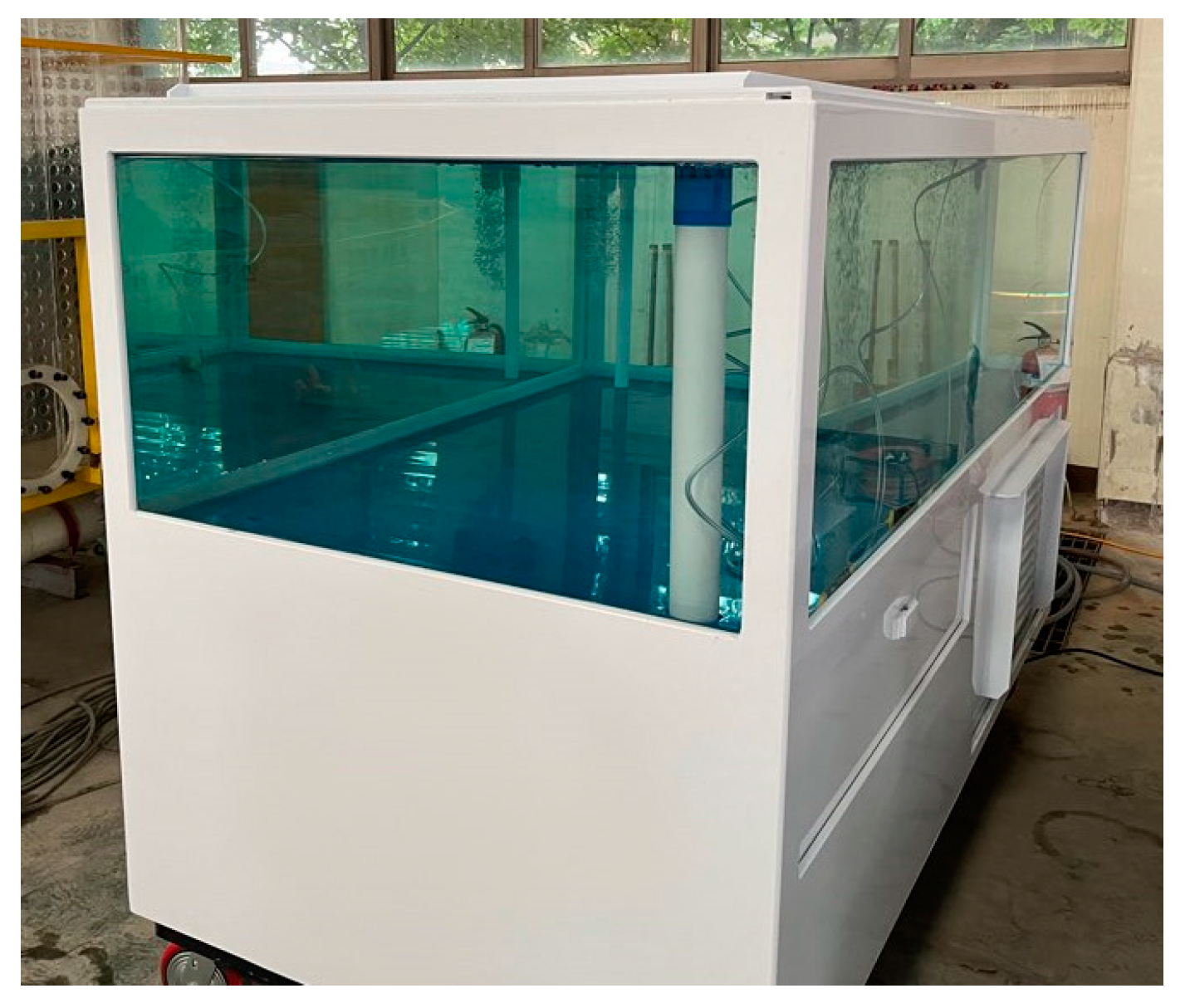
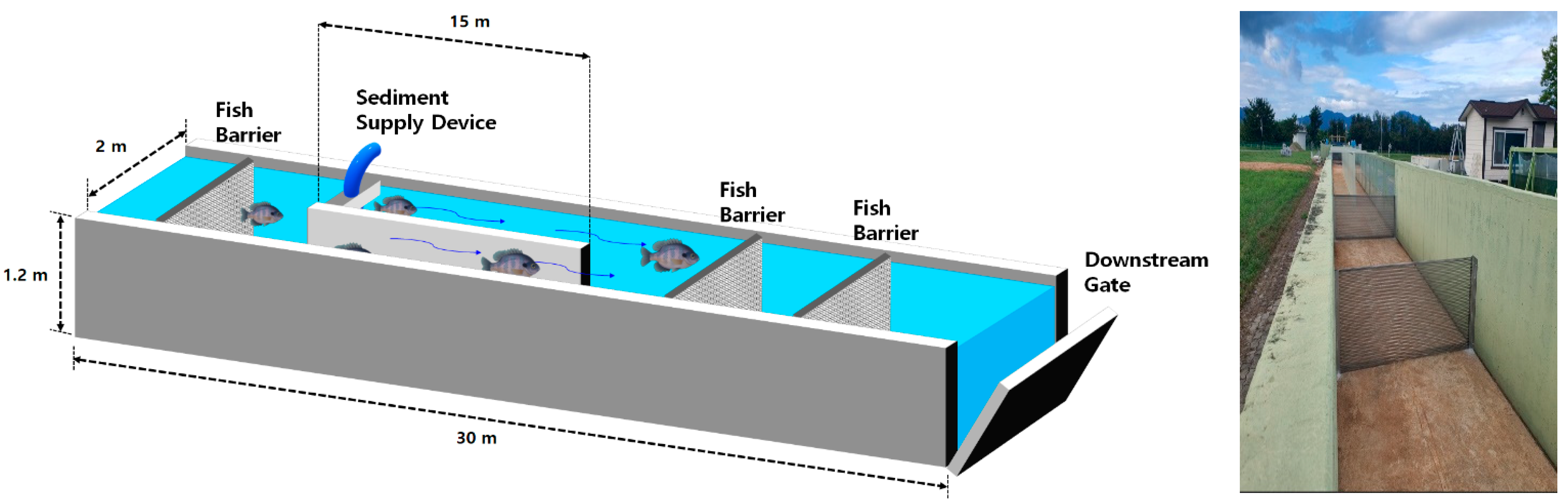
2.1. Fish Behavior Experiment Setup
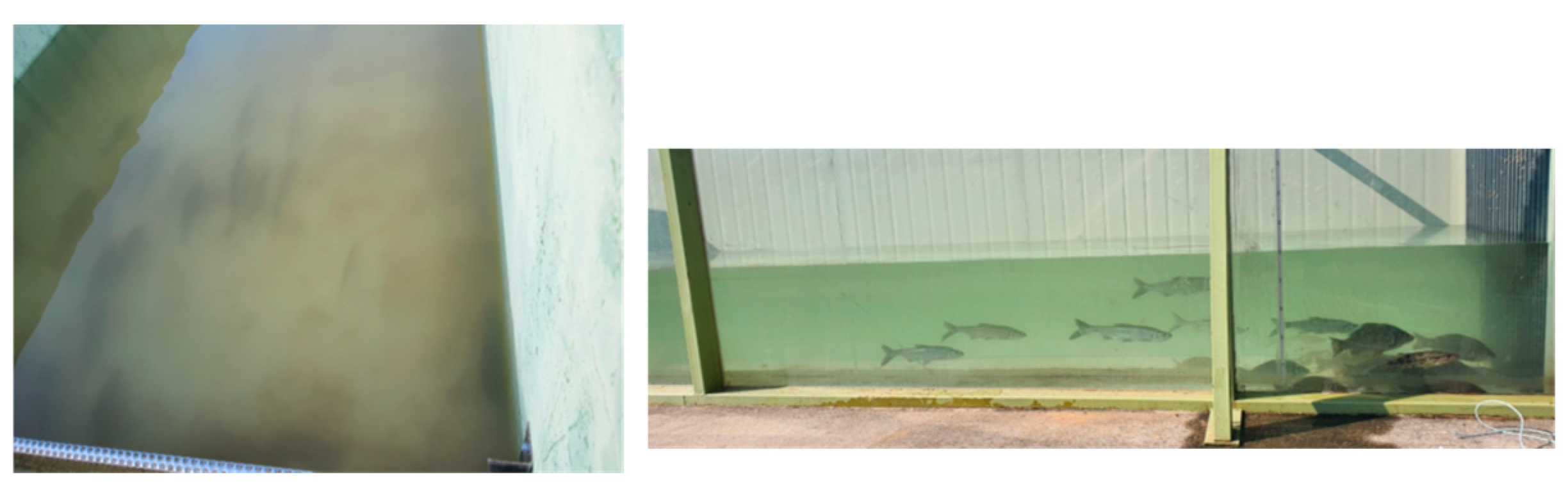
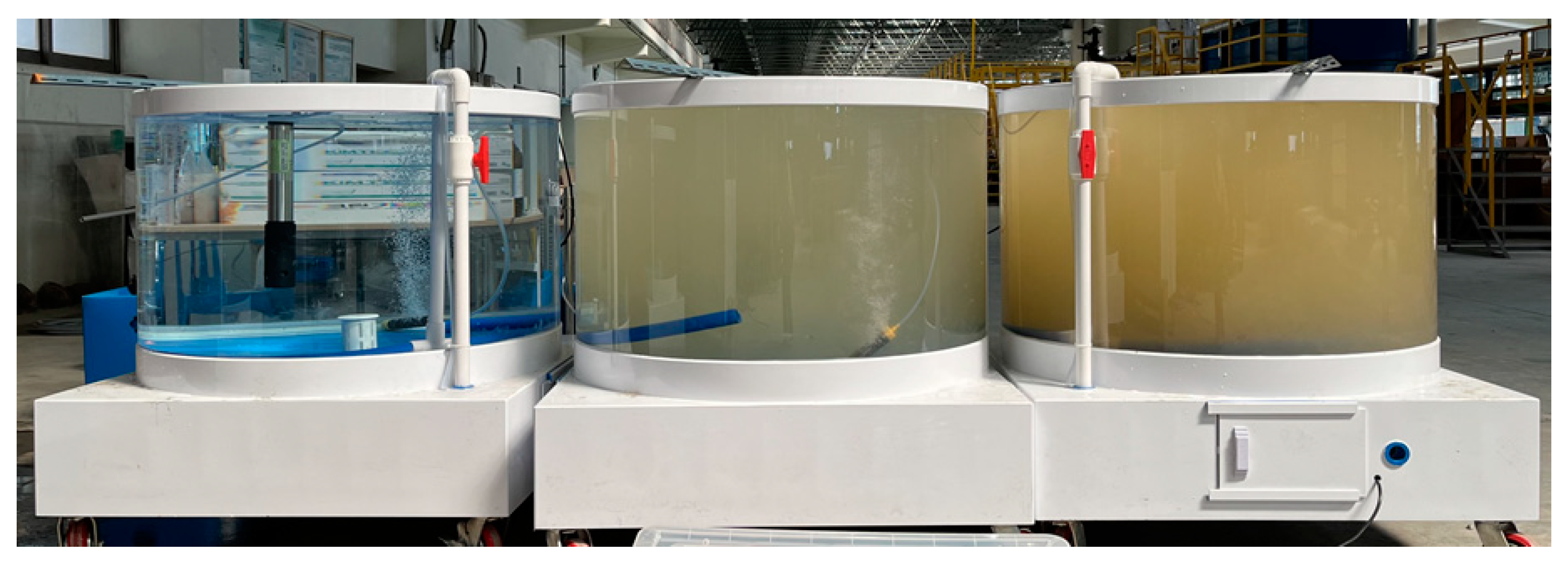
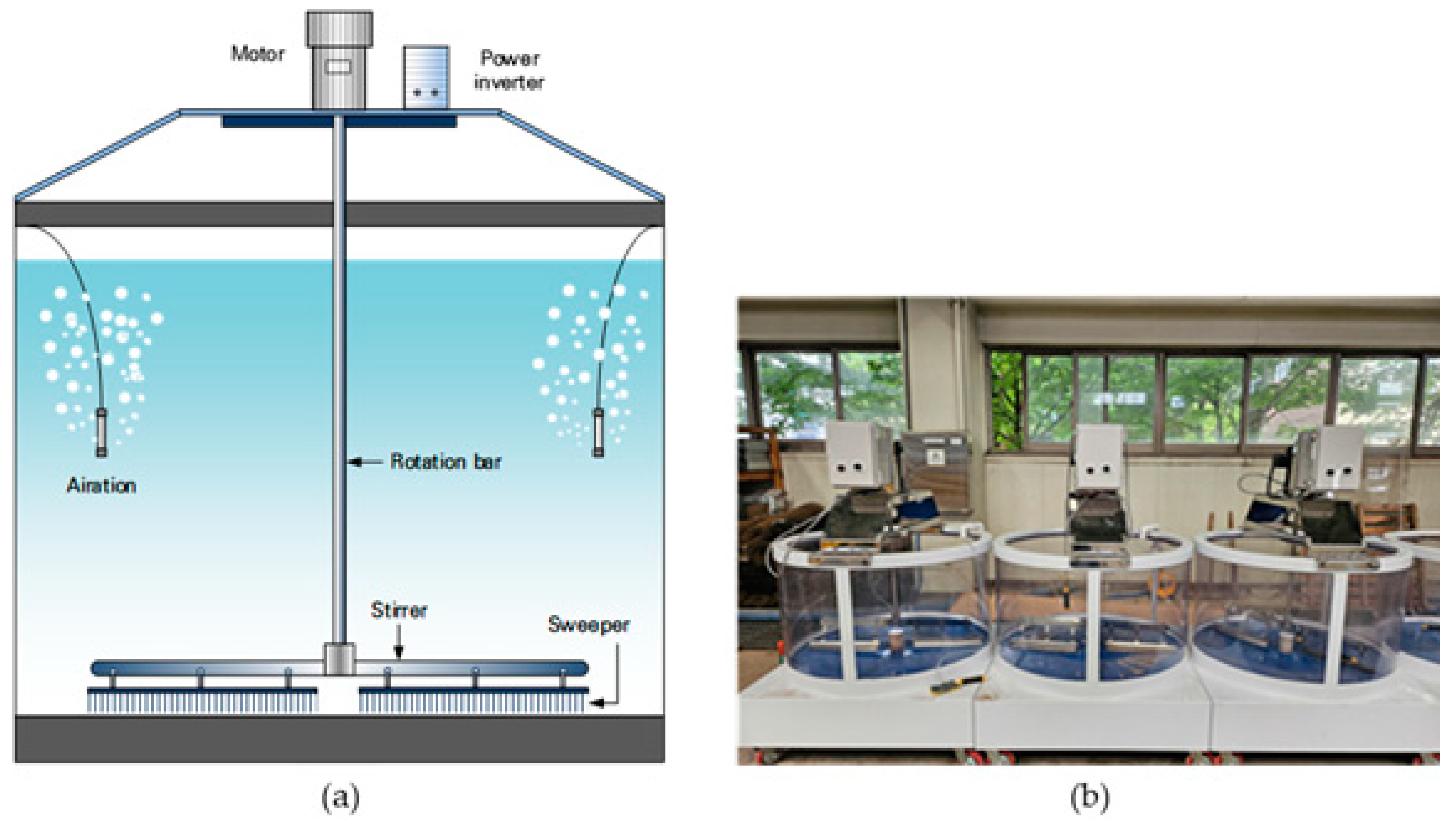
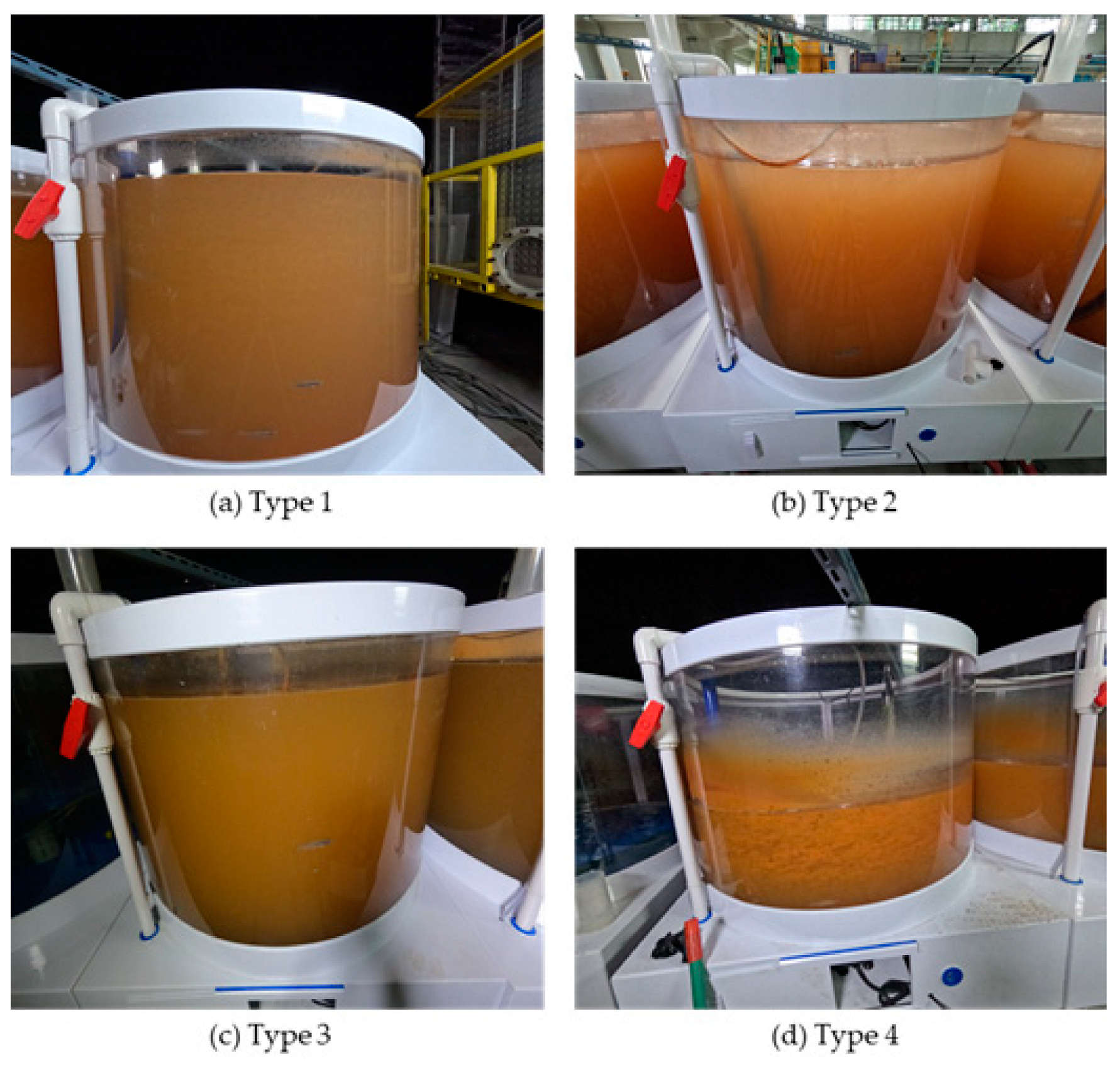
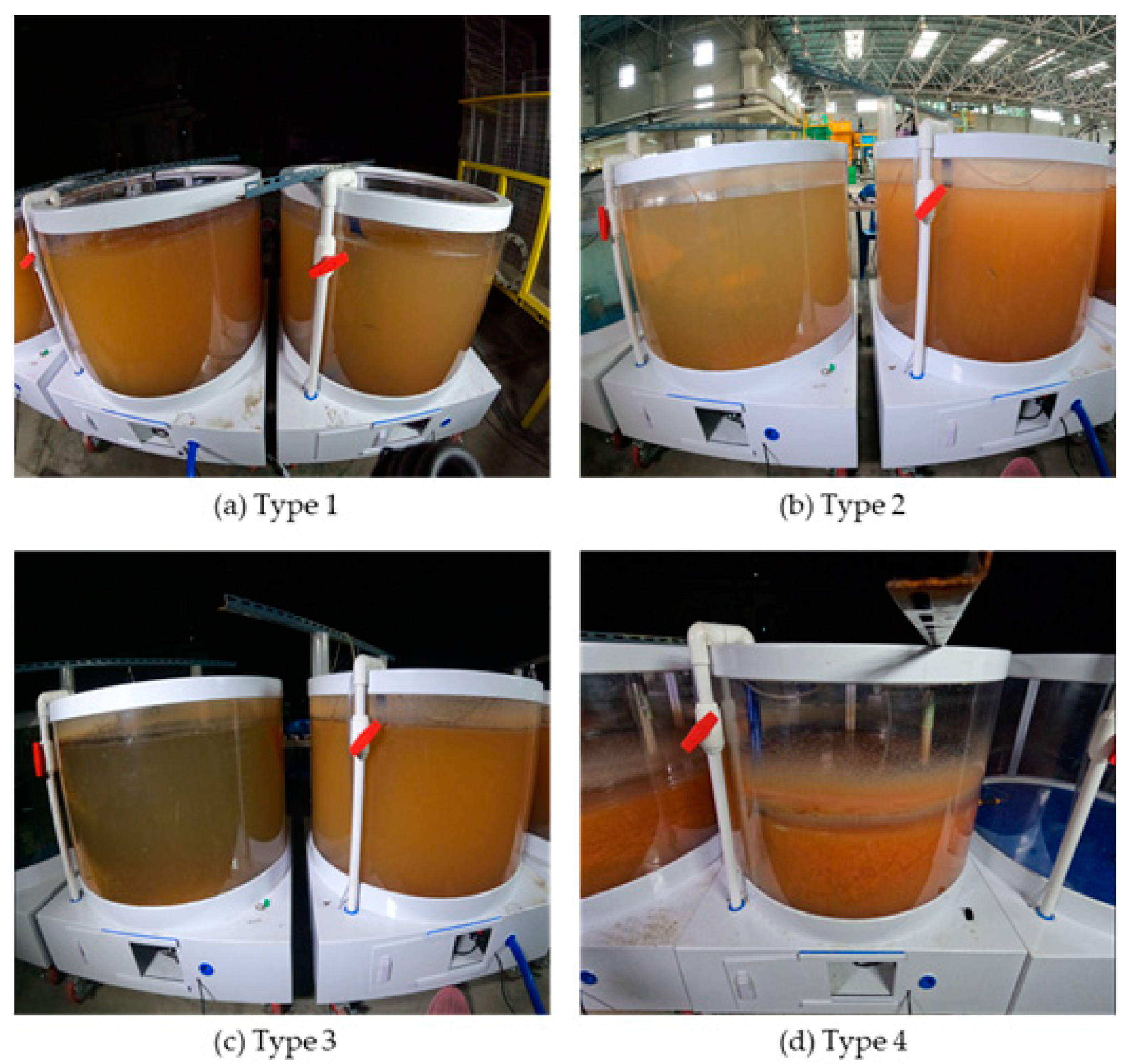
2.2. Experiment on Fish Behavior Under Turbidity Conditions (Aquarium Systems)
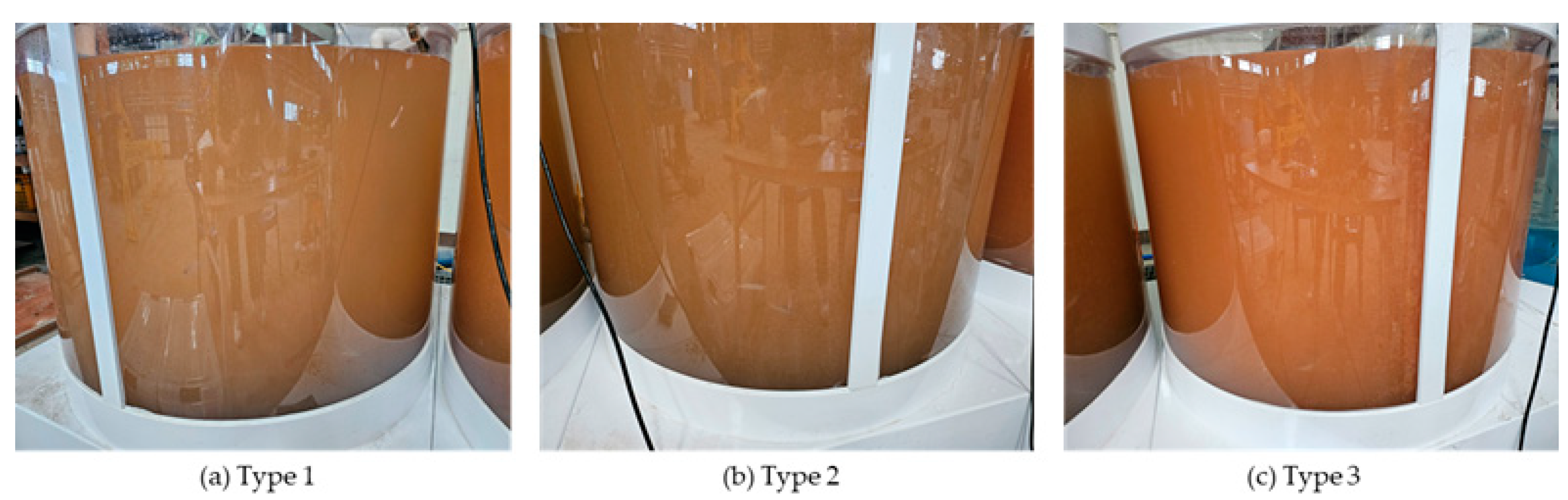
3. Experiment on Fish Conditions at Different Levels of Suspended Solids Concentration
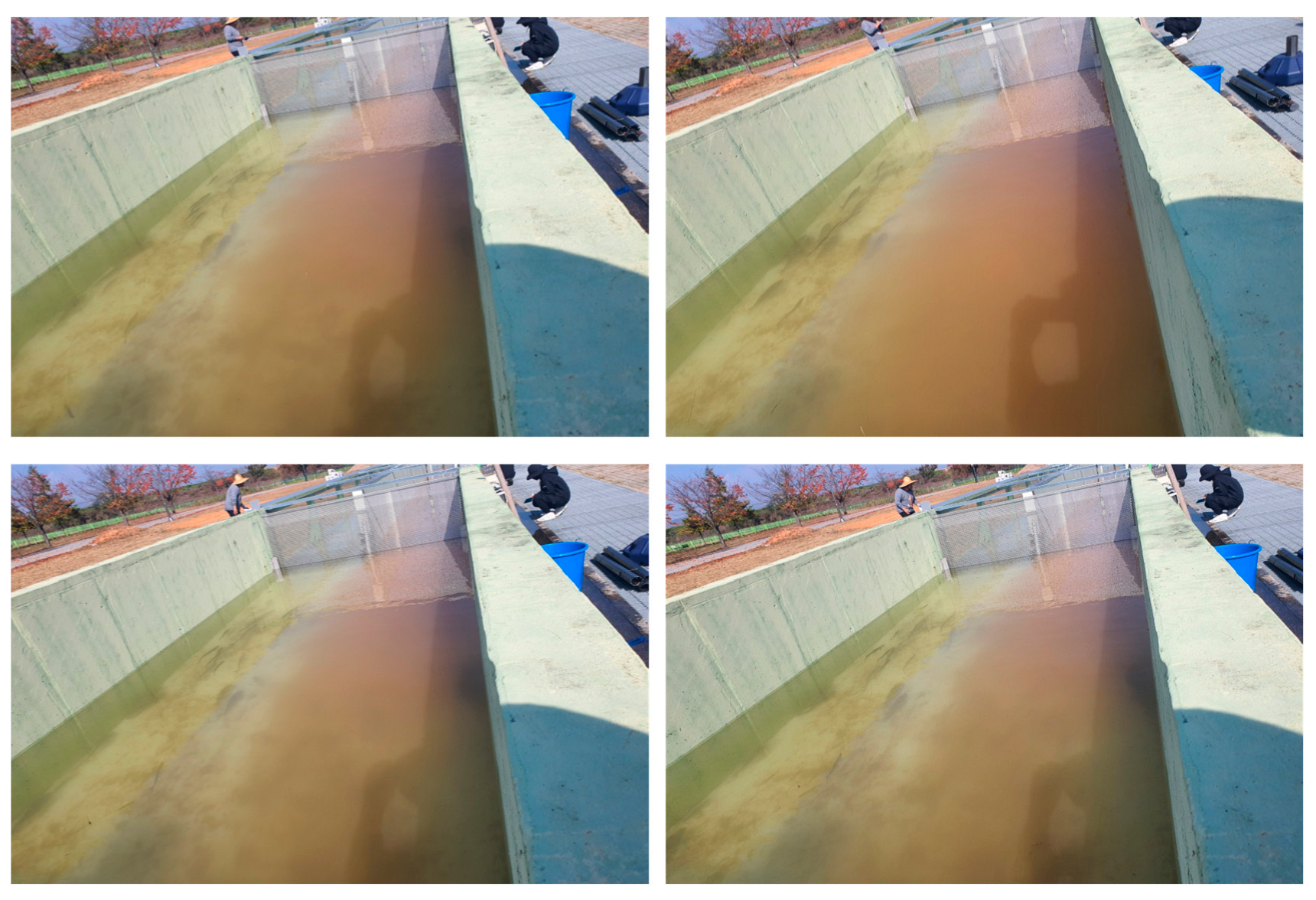
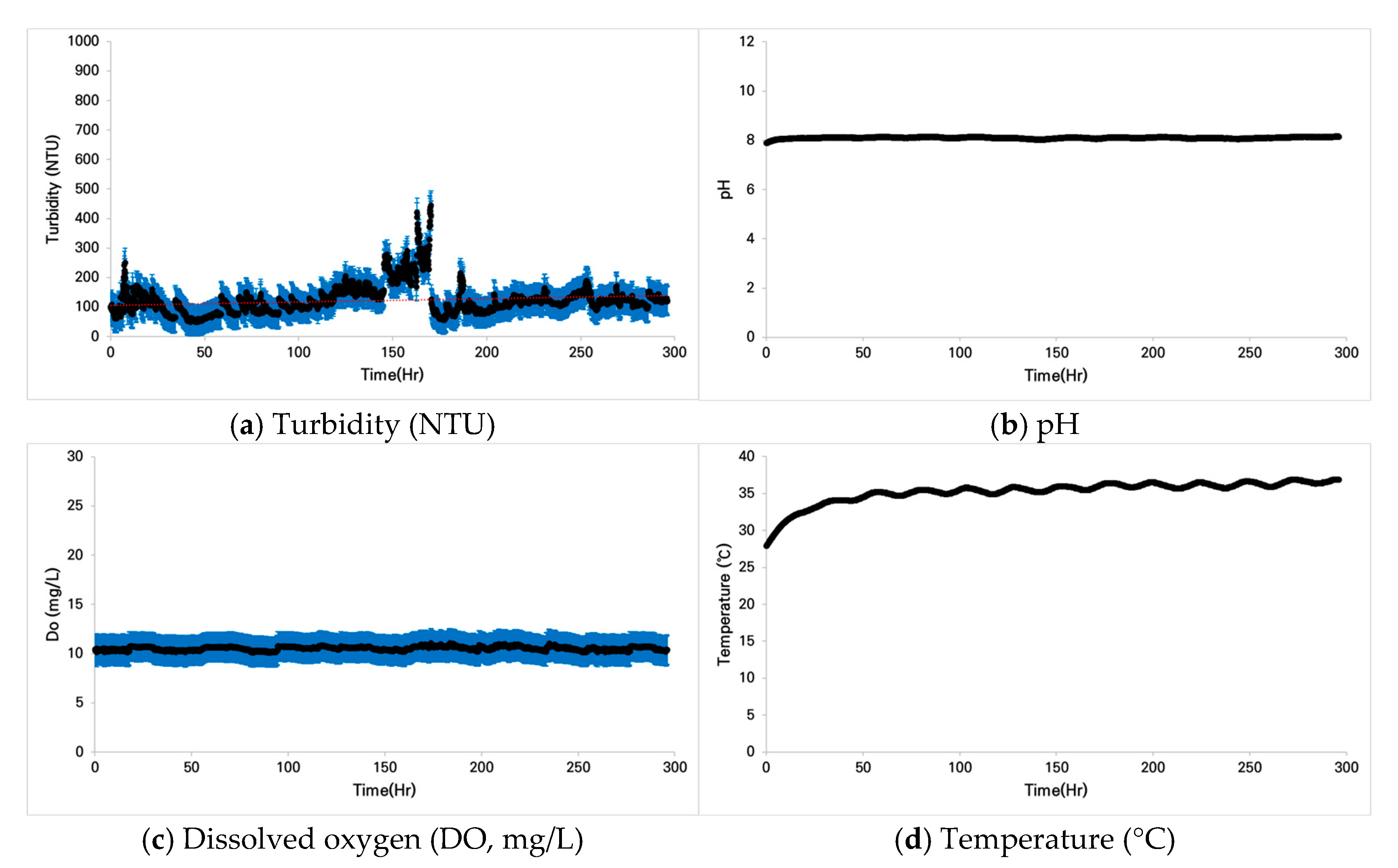
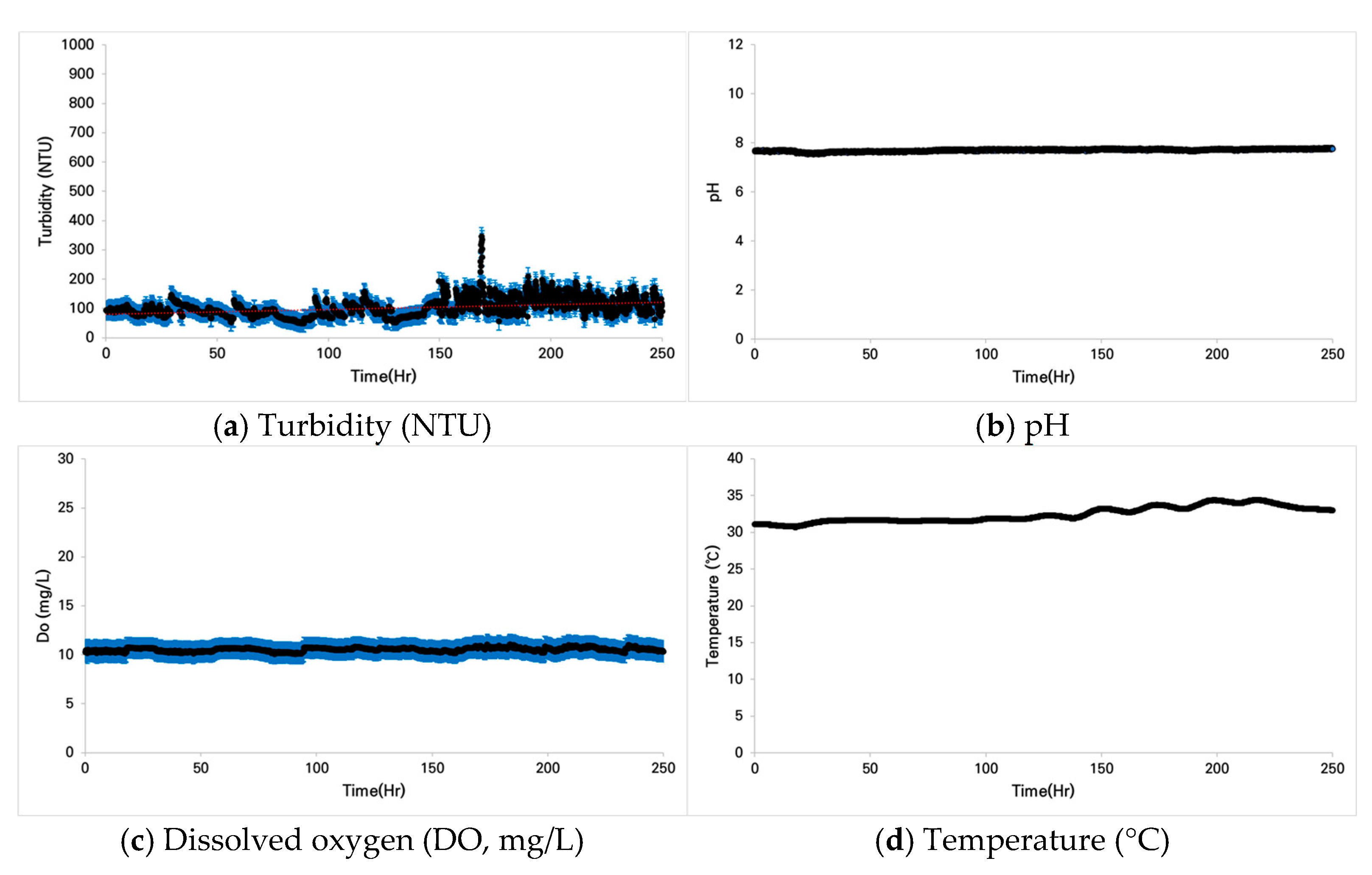
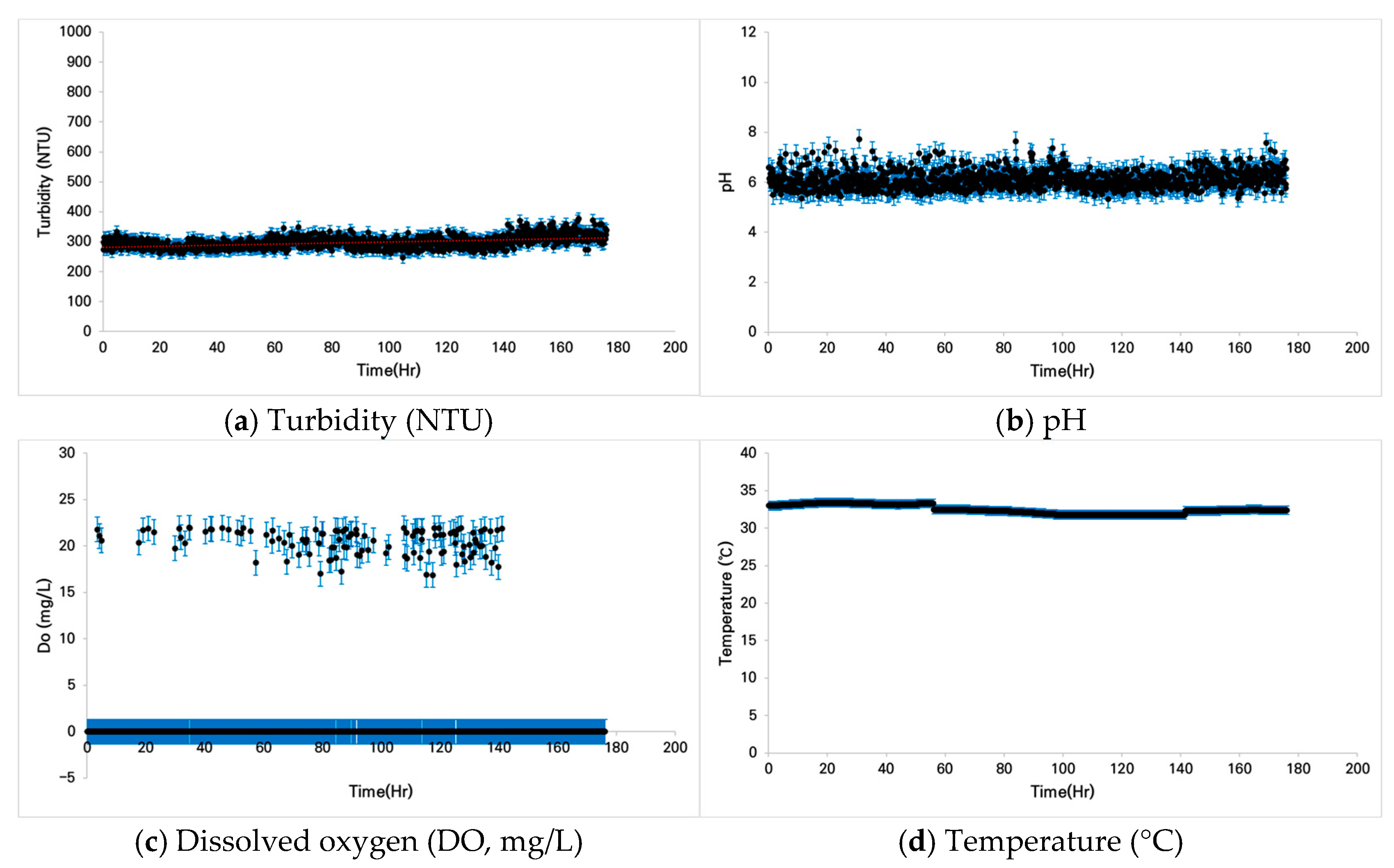
3.1. Analysis of Water Quality Changes
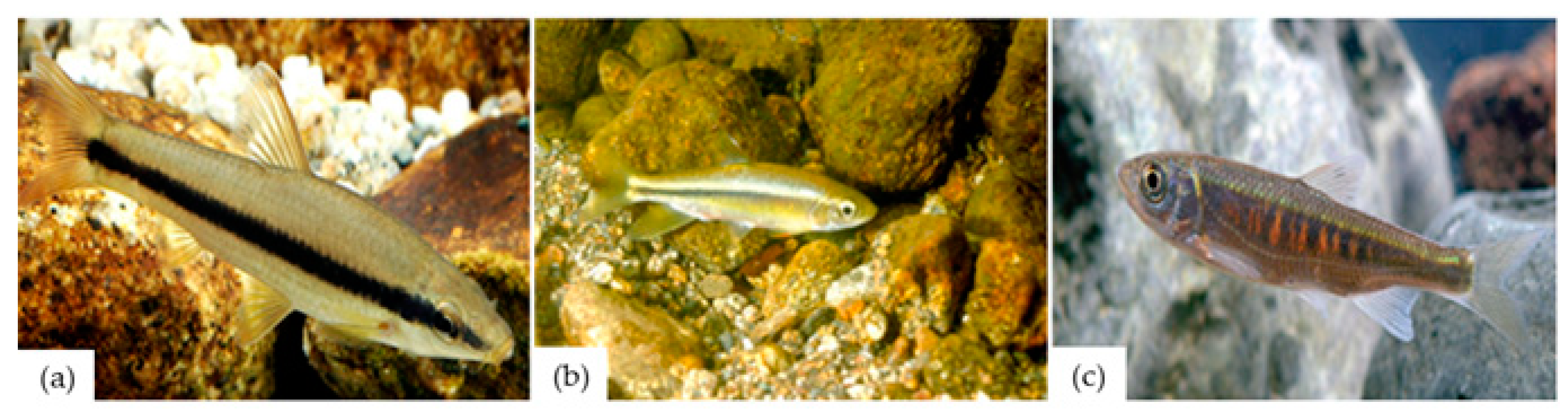
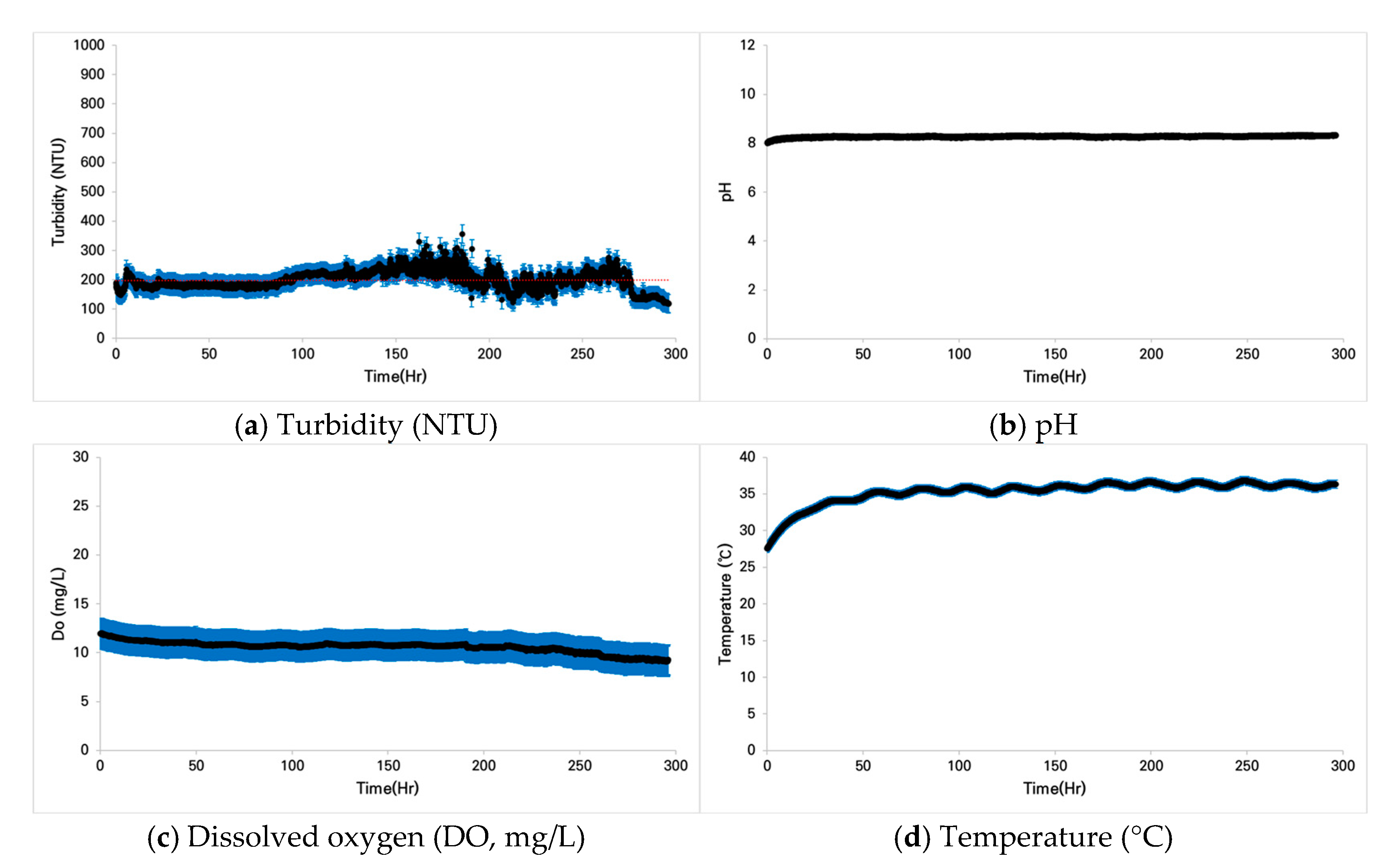
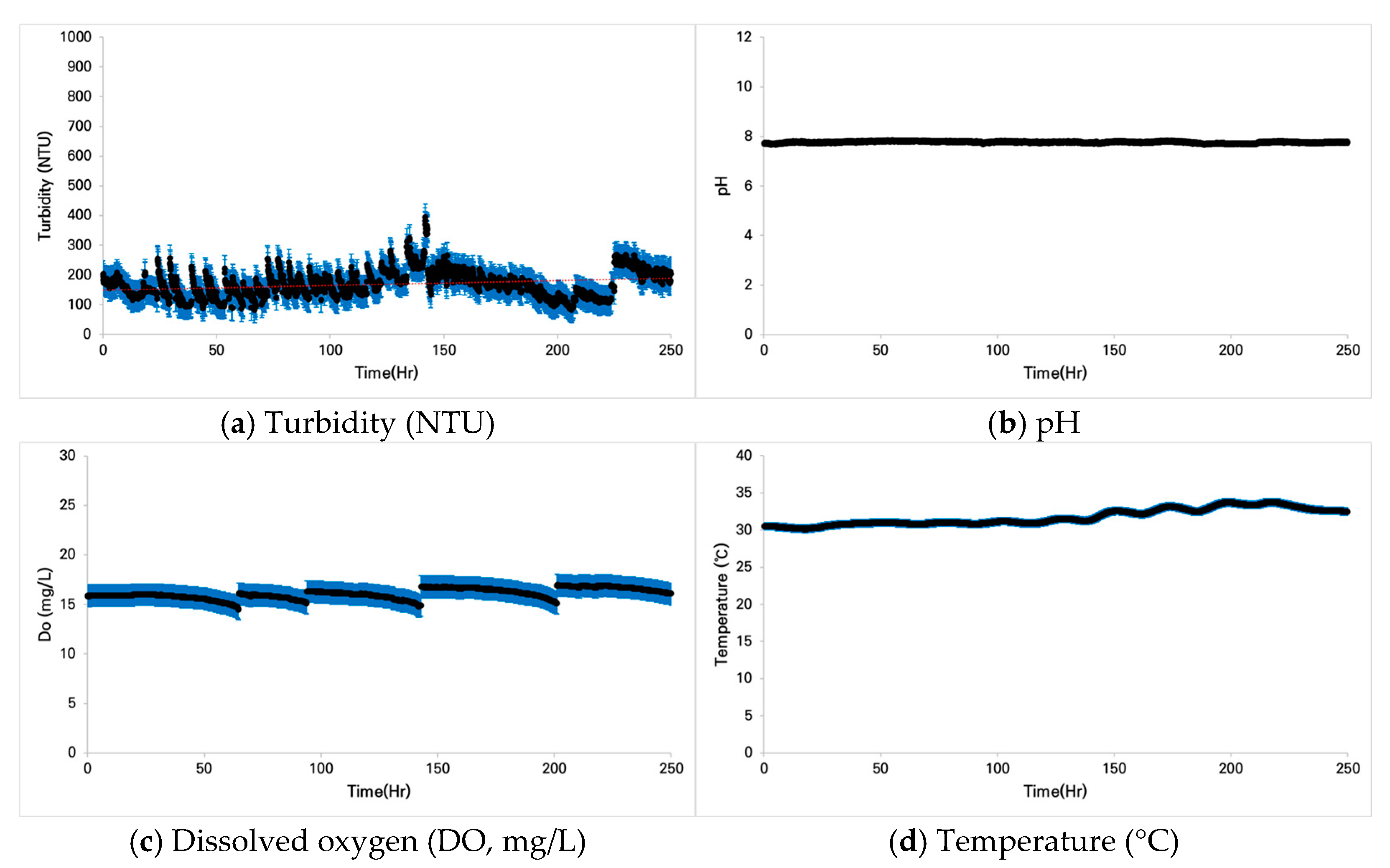
3.1.1. Case 1: Zacco platypus
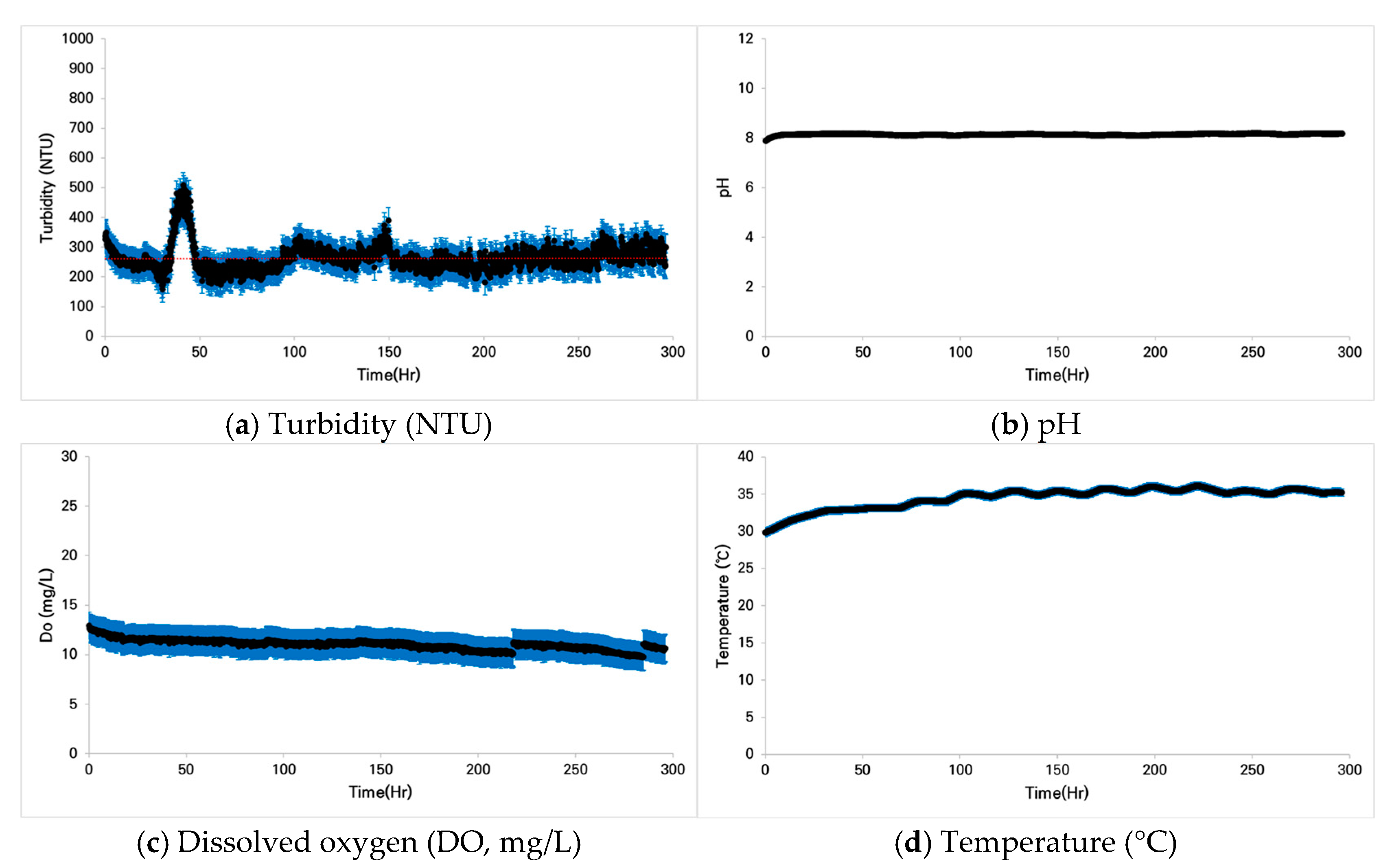
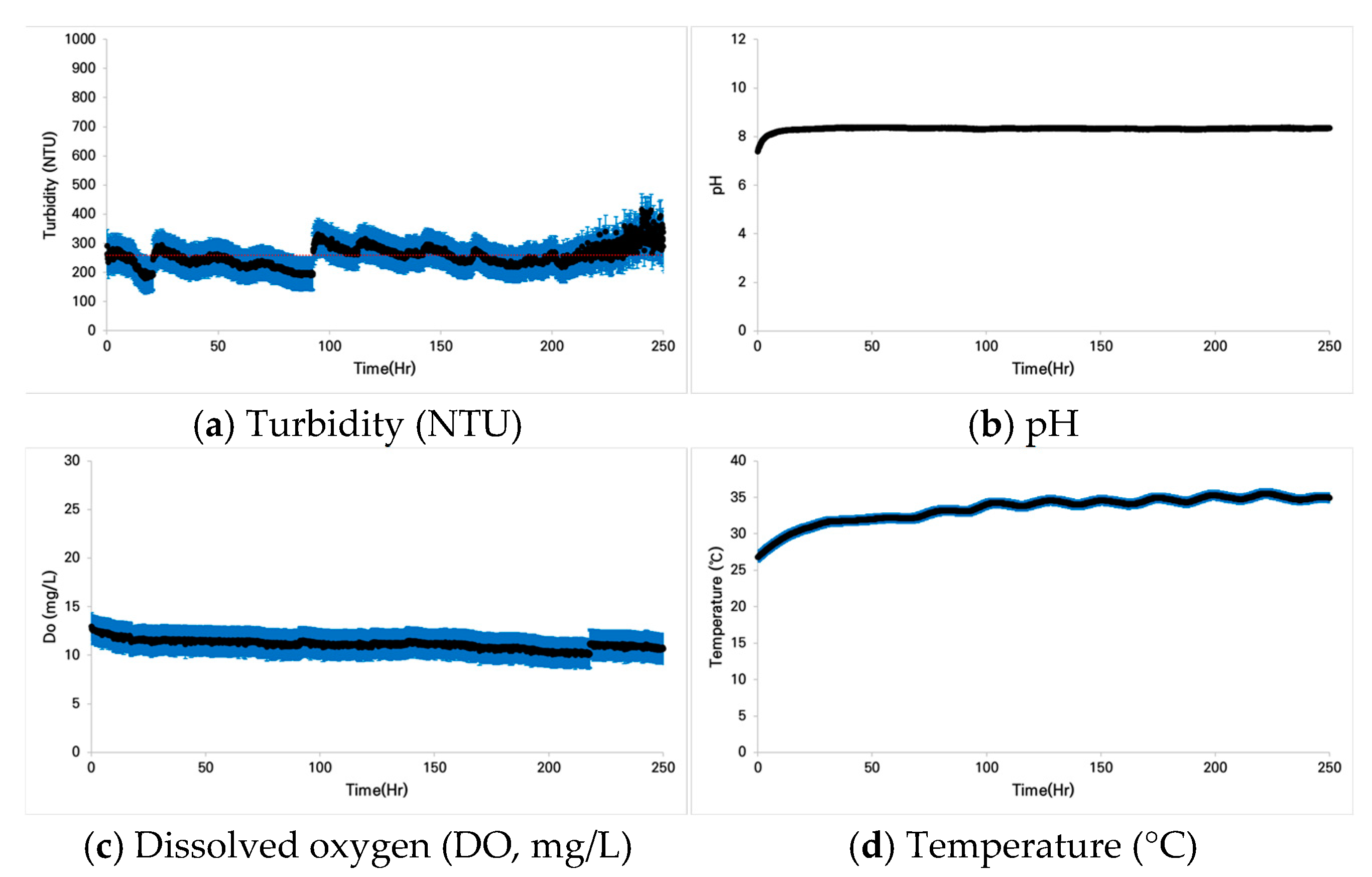
3.1.2. Case 2: Pseudopungtungia nigra
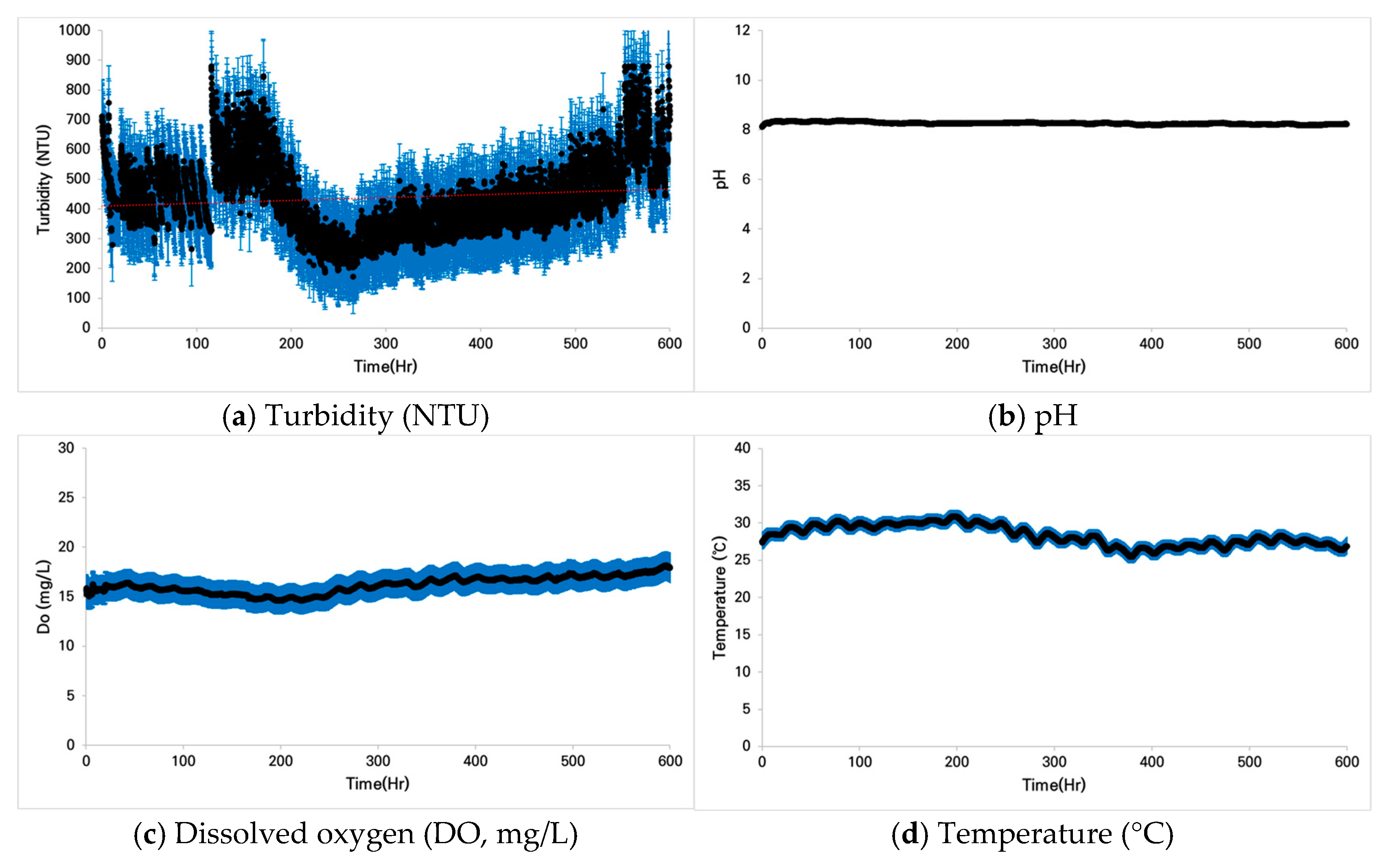
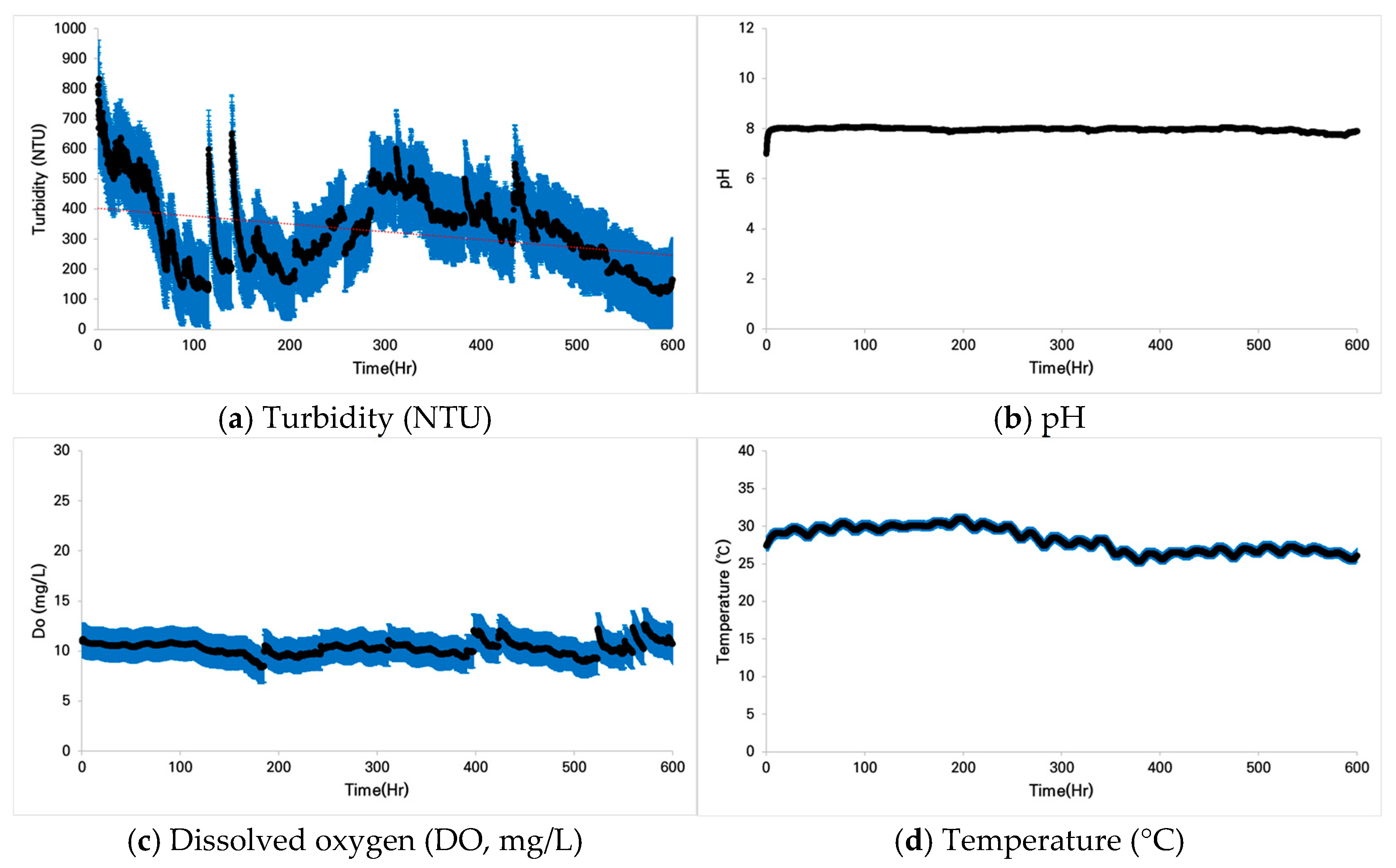
3.1.3. Case 3: Zacco koreanus
3.2. Fish Conditions Under Prolonged Turbidity
3.2.1. Case 1: Zacco platypus
3.2.2. Case 2: Pseudopungtungia nigra
3.2.3. Case 3: Zacco koreanus
4. Experiment Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, J.-K.; Lee, N.-J.; Nam, D.-H. Monitoring of the Mobility of Fish on Turbidity Changes. Korean. J. Ecol. Environ. 2023, 10, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bash, J.; Berman, C.; Bolton, S. Effects of Turbidity and Suspended Solids on Salmonids. Available online: https://www.wsdot.wa.gov/research/reports/fullreports/526.1.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Park, J.-K.; Park, J.-H.; Na, S.-I.; Beak, S.-C. Estimation of suspended solid concentration variation in Daechung Reservoir using satellite imagery. In Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference, Republic of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 19–20 May 2011; Volume 5, p. 203. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, T.-H.; Kim, Y.-P.; Kim, J.-K.; An, K.-G. Analysis of ecological health using a water quality and fish in Bocheong stream. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 43, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-K.; Choi, J.-S.; Jang, Y.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, B.C. Effects of turbid water on fish community: Case studies of the Daegi stream and Bong-san stream. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 40, 459–467. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.-S.; Kim, J.-K. Ichthyofauna and fish community in Hongcheon river, Korea. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2004, 22, 446–455. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahams, M.V.; Kattenfeld, M.G. The role of turbidity as a constraint on predator-prey interactions in aquatic environments. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1997, 40, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utne-Palm, A.C. The effect of prey mobility, prey contrast, turbidity and spectral composition on the reaction distance of Gobiusculus flavescens to its planktonic prey. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 54, 1244–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.-D.; Kang, S.-K.; Lee, C.-H.; Sung, C.-G.; An, K.-G.; Choi, T.S. Effect on early life stage of three freshwater fish (Carassius auratus, Cyprinus carpio, Oryzias latipes) exposed to suspended solids. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 47, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S. The effects of suspended solids on the mortality and the glycogen content of abalone, Haliotis discus hannai. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Saf. 2008, 14, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kjelland, M.E.; Woodley, C.M.; Swannack, T.M.; Smith, D.L. A review of the potential effects of suspended sediment on fishes: Potential dredging-related physiological, behavioral, and transgenerational implications. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2015, 35, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, X.C.; Thompson, W.A.; Smith, C.M.; Wilson, J.M.; Vijayan, M.M. Exposure to total suspended solids (TSS) impacts gill structure and function in adult zebrafish. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 113, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Yang, J.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, S. The source, distribution, and environmental effects of suspended particulate matter in the Yangtze River System. Water 2023, 15, 3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Environmental Research. Ministry of Environment’s Guidelines on the Investigation and Evaluation of Aquatic Ecosystem Continuity. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/LSW/admRulInfoP.do?admRulSeq=2100000220502 (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Boubee, J.A.T.; Dean, T.L.; West, D.W.; Barrier, R.F.G. Avoidance of suspended sediment by the juvenile migratory stage of six New Zealand native fish species. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1997, 31, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S. Fish fauna and community in Cheongpyeong reservoir. Korean J. Limnol. 2005, 38, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Débora, M.S.S.; Mércia Regina, S.M.; Denise Carla, S.M.; Iolanda Karoline, B.S.R.; Jakeline Priscila, L.S.; Sildiane, M.C.; Paulo, C.M. Histological Changes in Gills of Two Fish Species as Indicators of Water Quality in Jansen Lagoon (São Luís, Maranhão State, Brazil). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 12927–12937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banasiak, R.; Verhoeven, R. Quantification of the erosion resistance of undisturbed and remoulded cohesive sediments. In The Interactions Between Sediments and Water; Kronvang, B., Faganeli, J., Ogrinc, N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 17–27. ISBN 978-1-4020-5477-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-C.; Lee, H.-Y.; Seo, E.-W.; Shim, J.-H.; Lee, J.-E. The influence of muddy water in Imha Reservoir on the ichthyofauna and fish growth. J. Life Sci. 2007, 17, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, C.P.; MacDonald, D.D. Effects of suspended sediments on aquatic ecosystems. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1991, 11, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












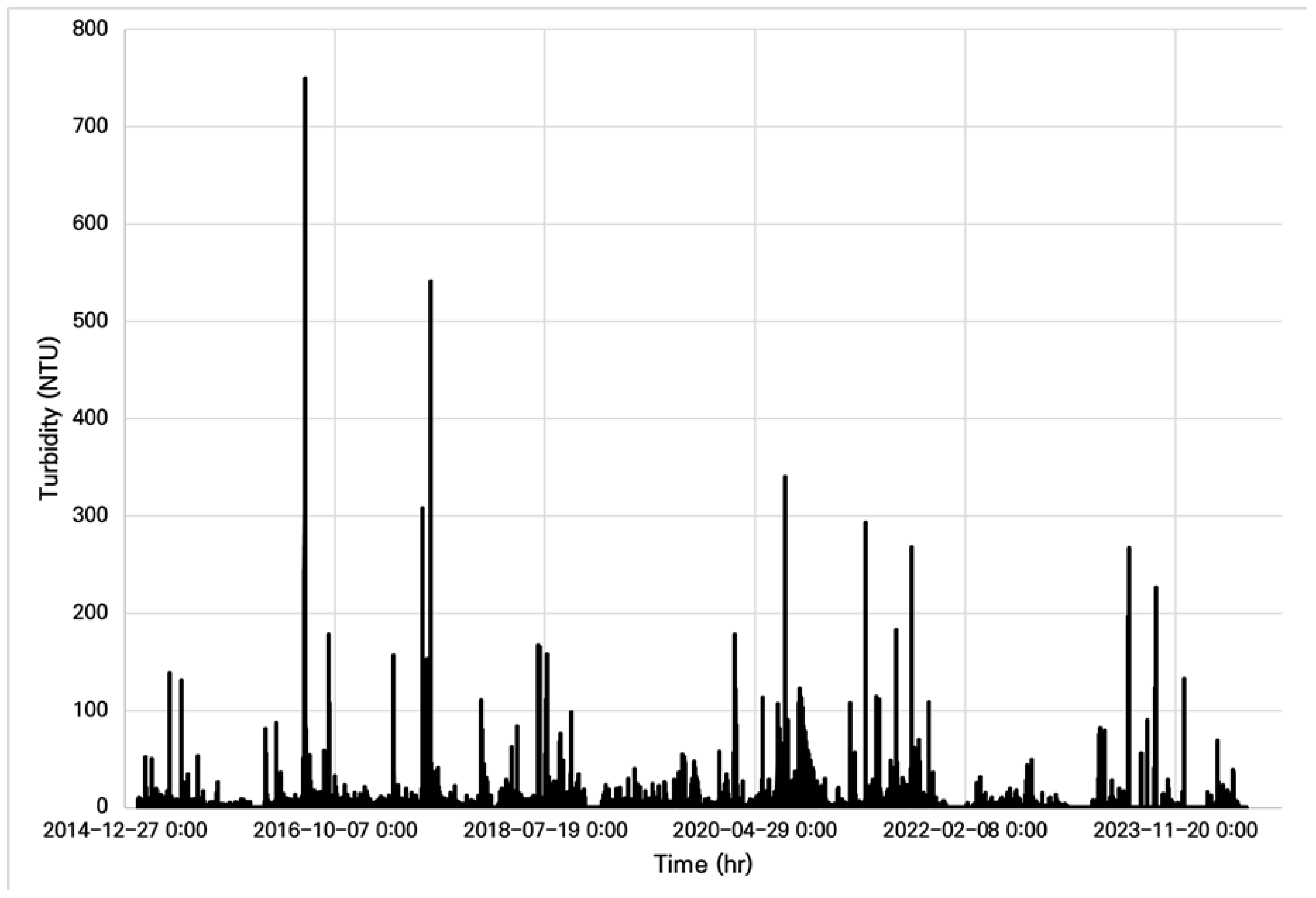
| Turbidity | Andong 1 | Andong 2 | Andong 3 | Andong 4 | Andong 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Value | 9.2 | 23.5 | 23.2 | 26.4 | 47.1 |
| Mean | 2.3 | 5.7 | 7.0 | 7.8 | 9.5 |
| Minimum Value | 0.4 | 1.3 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 2.7 |
| Classification | Waterway Conditions | Turbidity Conditions in the Waterway | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| CASE 1 | Water depth (55 cm) Flow velocity (0.25 m/s) Flow rate (0.35 cm/s) | 0–5 NTU (no sediment supply, Blank), ~25 NTU, ~50 NTU ~75 NTU, ~100 NTU, 120 NTU (river during rainfall), ≥120 NTU | Fish behavior confirmation Low concentration confirmation required first (turbidity conditions that fish respond to) If high concentration is required |
| CASE 2 | Flow velocity change | - | Considering sediment travel time |
| Time (s) | Turbidity (NTU) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | |||||||||||||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | |
| 0 | 7.0 | 7.7 | 15.3 | 9.4 | 10.6 | 7.0 | 7.7 | 15.3 | 9.4 | 15.3 | 7.0 | 7.7 | 15.3 | 9.4 | 10.6 |
| 20 | 7.4 | 8.1 | 19.2 | 10.4 | 10.4 | 6.5 | 8.2 | 16.6 | 9.3 | 16.6 | |||||
| 40 | 17.5 | 22 | 43.1 | 11.2 | 23.8 | 7.2 | 7.6 | 17.2 | 8.9 | 17.2 | |||||
| 60 | 54.8 | 22.3 | 50.1 | 41.0 | 44.8 | 5.7 | 6.7 | 30.3 | 9.6 | 30.3 | |||||
| 80 | 44.9 | 35.6 | 56.4 | 48.9 | 52.9 | 6.8 | 9.6 | 32.0 | 9.3 | 32.0 | 15.3 | 10.6 | |||
| 100 | 39.0 | 26.5 | 45.7 | 63.0 | 51.1 | 51.0 | 52.8 | 34.8 | 8.6 | 34.8 | 7.7 | 17.0 | 13.3 | ||
| 120 | 23.9 | 24.9 | 47.3 | 63.5 | 53.9 | 69.6 | 50.7 | 31.6 | 8.8 | 31.6 | 9.6 | 16.6 | 9.5 | ||
| 140 | 27.3 | 18.6 | 49.0 | 62.6 | 55.8 | 56.4 | 49.8 | 31.3 | 9.4 | 31.3 | 3.8 | 6.7 | 16.8 | 1.2 | |
| 160 | 24.6 | 20.5 | 53.5 | 65.4 | 52.8 | 49.5 | 45.9 | 32.8 | 23.3 | 32.8 | 4.1 | 6.6 | 14.9 | 1.5 | |
| 180 | 17.5 | 20.5 | 50.8 | 62.5 | 54.3 | 46.5 | 42.1 | 34.8 | 40.7 | 34.8 | 4.5 | 7.9 | 14.6 | 1.7 | |
| 200 | 16.4 | 23.2 | 18.0 | 66.2 | 50.0 | 42.8 | 45.9 | 30.0 | 61.5 | 30.0 | 3.7 | 7 | 17.0 | 9.4 | 1.8 |
| 220 | 5.6 | 9.2 | 17.2 | 60.9 | 35.7 | 44.1 | 43.1 | 16.7 | 84.2 | 16.7 | 3.8 | 6.8 | 16.3 | 10.3 | 2.0 |
| 240 | 6.1 | 7.5 | 16.2 | 28.6 | 24.0 | 38.3 | 39.8 | 16.8 | 88.2 | 16.8 | 3.5 | 8.2 | 20.7 | 9.5 | 2.3 |
| 260 | 5.0 | 7.2 | 17.7 | 19.1 | 18.5 | 9.6 | 9.9 | 16.8 | 85.2 | 16.8 | 3.5 | 6.7 | 15.6 | 10.5 | 2.4 |
| 280 | 4.1 | 7.6 | 17.7 | 10.8 | 16.7 | 5.0 | 7.1 | 15.5 | 86.2 | 15.5 | 3.0 | 6.9 | 17.2 | 8.1 | 2.5 |
| 300 | 10.7 | 16.8 | 84.2 | 7.7 | 2.6 | ||||||||||
| 320 | 10.3 | 11.9 | 67.1 | 9.5 | 2.8 | ||||||||||
| 340 | 10.1 | 9.4 | 46.4 | 8.4 | 3.0 | ||||||||||
| 360 | 10.0 | 30.8 | 8.3 | ||||||||||||
| 380 | 9.5 | 16.4 | 7.5 | ||||||||||||
| 400 | 10.2 | 11.7 | 6.1 | ||||||||||||
| 420 | 9.8 | 9.9 | 6.7 | ||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.-G.; Lee, N.-J.; Kim, S.-J.; Nam, D.-H. An Experimental Study on the Behavior of Fish in Response to Turbidity Changes—A Case Study of Korean Fishes. Water 2025, 17, 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091340
Kang J-G, Lee N-J, Kim S-J, Nam D-H. An Experimental Study on the Behavior of Fish in Response to Turbidity Changes—A Case Study of Korean Fishes. Water. 2025; 17(9):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091340
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Joon-Gu, Nam-Joo Lee, Sung-Jung Kim, and Dong-Ho Nam. 2025. "An Experimental Study on the Behavior of Fish in Response to Turbidity Changes—A Case Study of Korean Fishes" Water 17, no. 9: 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091340
APA StyleKang, J.-G., Lee, N.-J., Kim, S.-J., & Nam, D.-H. (2025). An Experimental Study on the Behavior of Fish in Response to Turbidity Changes—A Case Study of Korean Fishes. Water, 17(9), 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091340







