Multi-Decade Variations in Sediment and Nutrient Export in Cascading Developmental Rivers in Southwest China: Impacts of Land Use and Dams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Export Flux Calculation
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
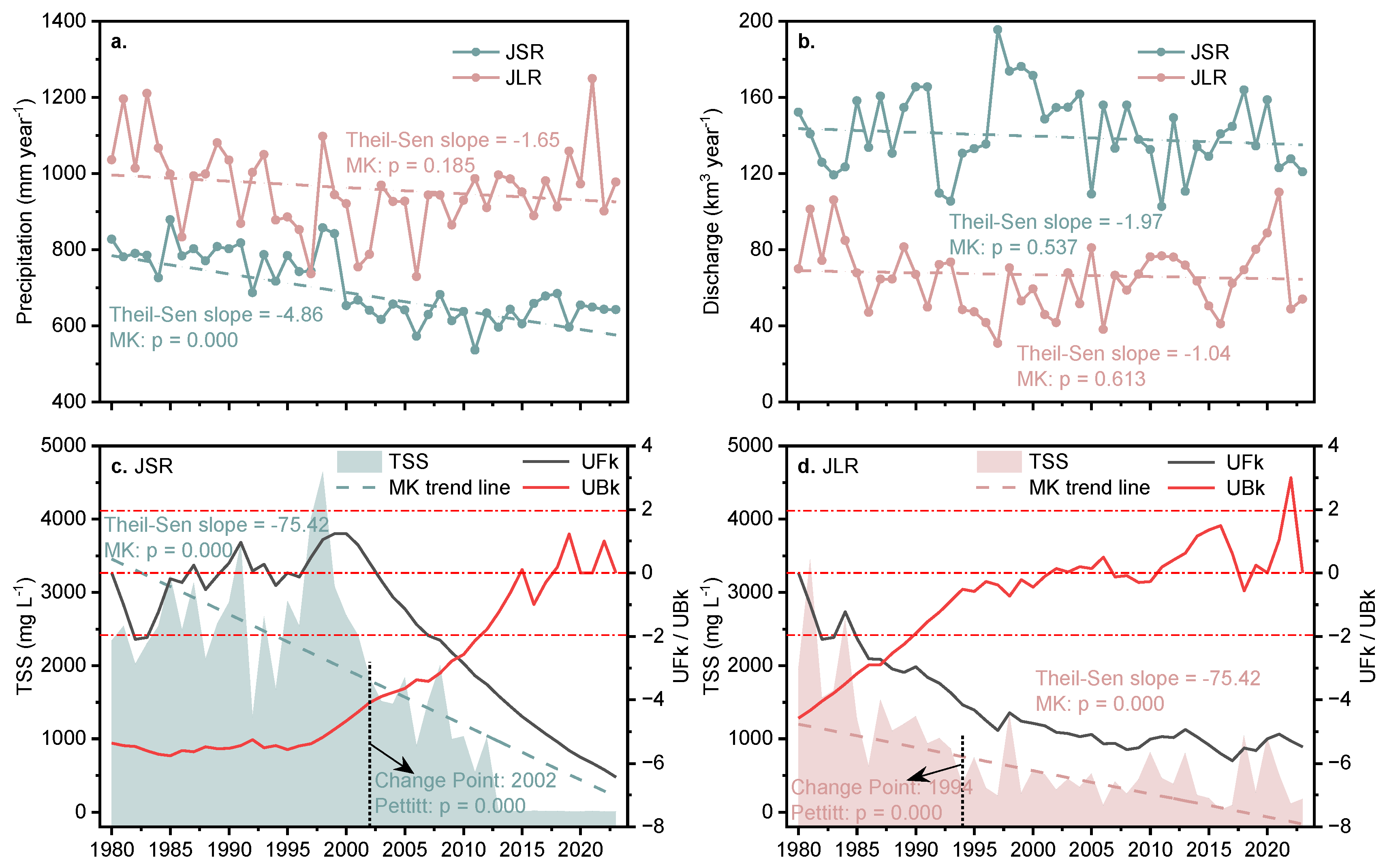
3.1. Precipitation, Flow Discharge, and Total Suspended Sediment Content
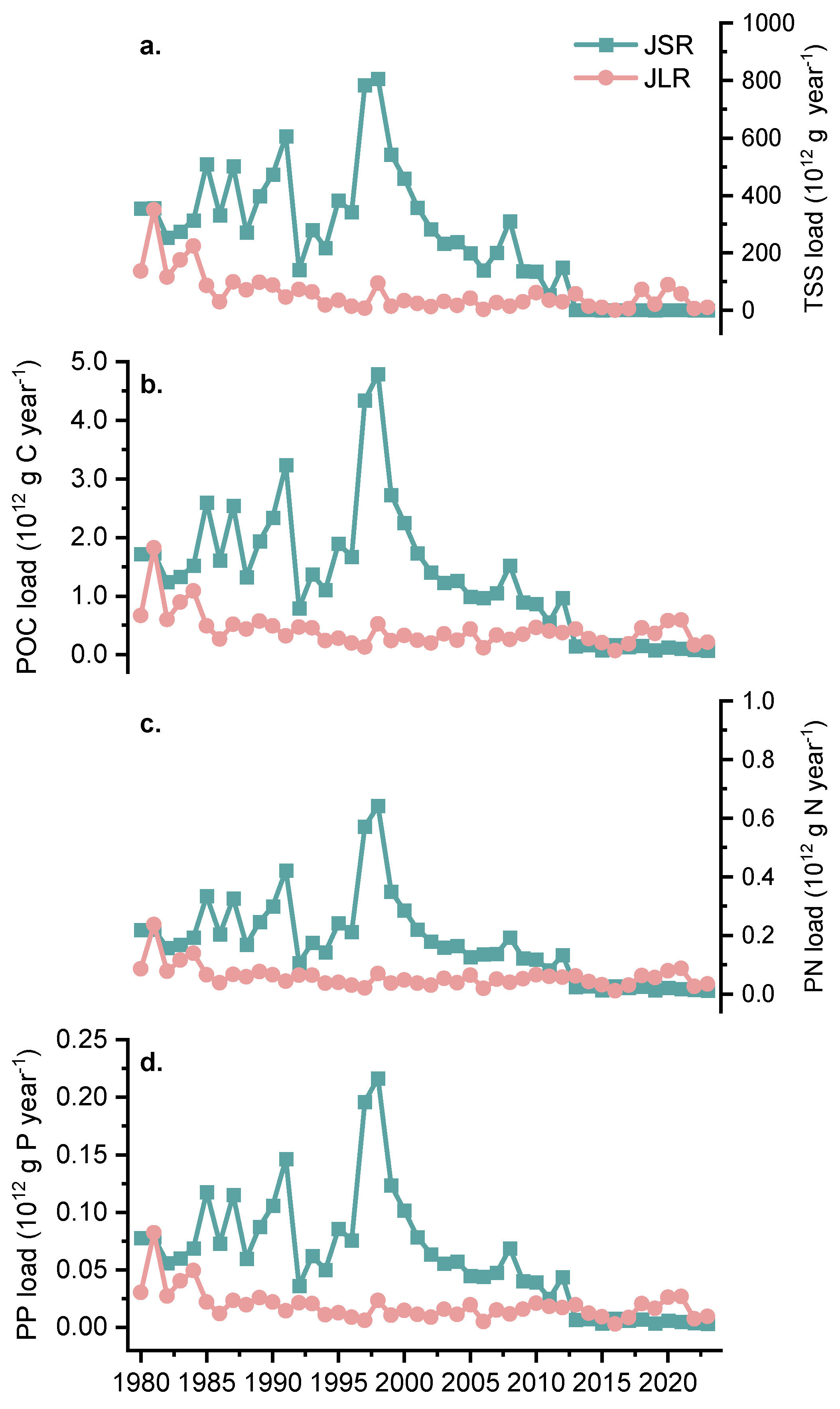
3.2. Downstream Fluxes of Sediment and Associated Particulate C, N, and P
4. Discussion
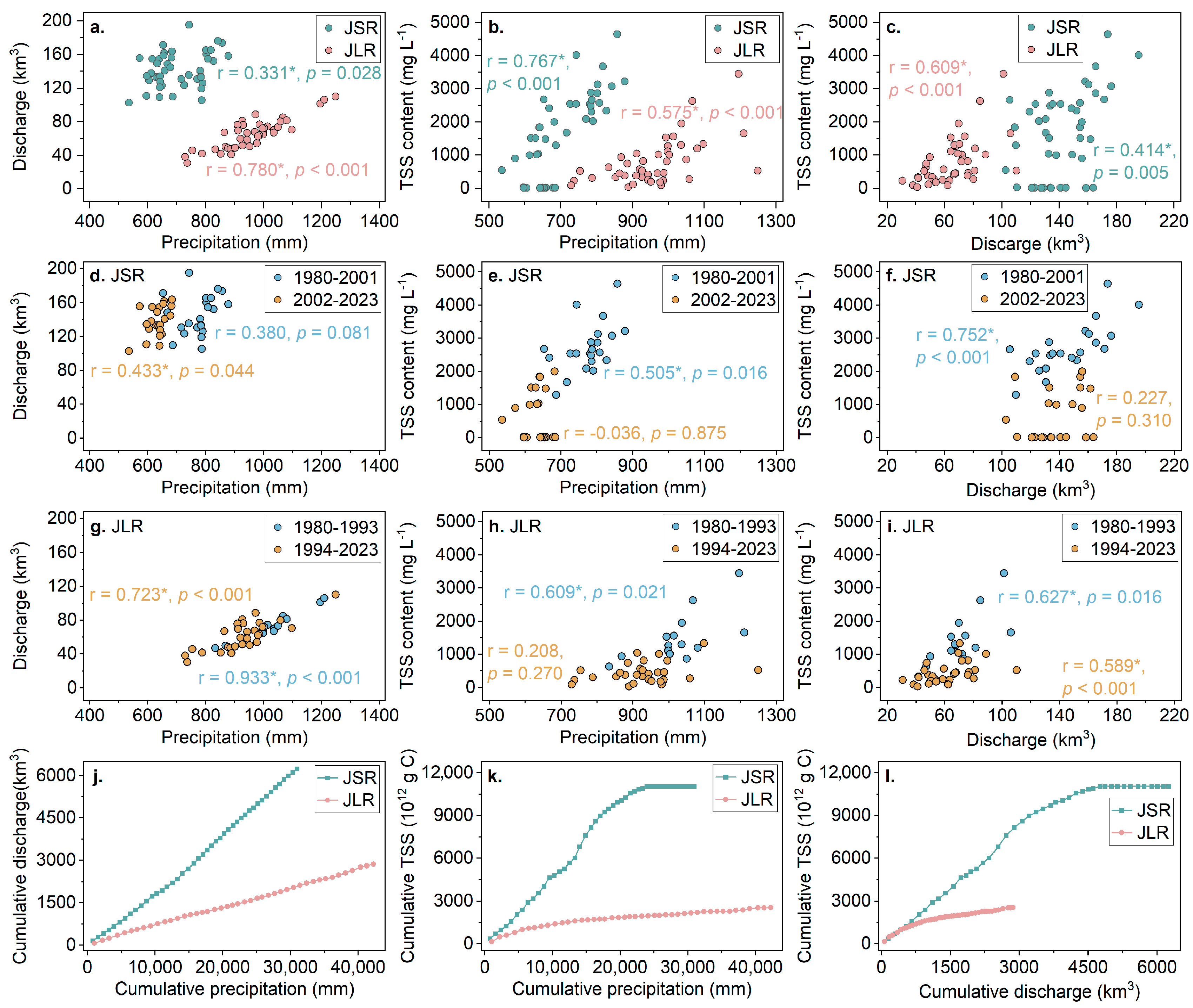
4.1. Changes in the Relationship Between Precipitation, Discharge, and Sediment Content
4.2. Anthropogenic Impacts on Riverine Sediment and Particulate C, N, and P Flux
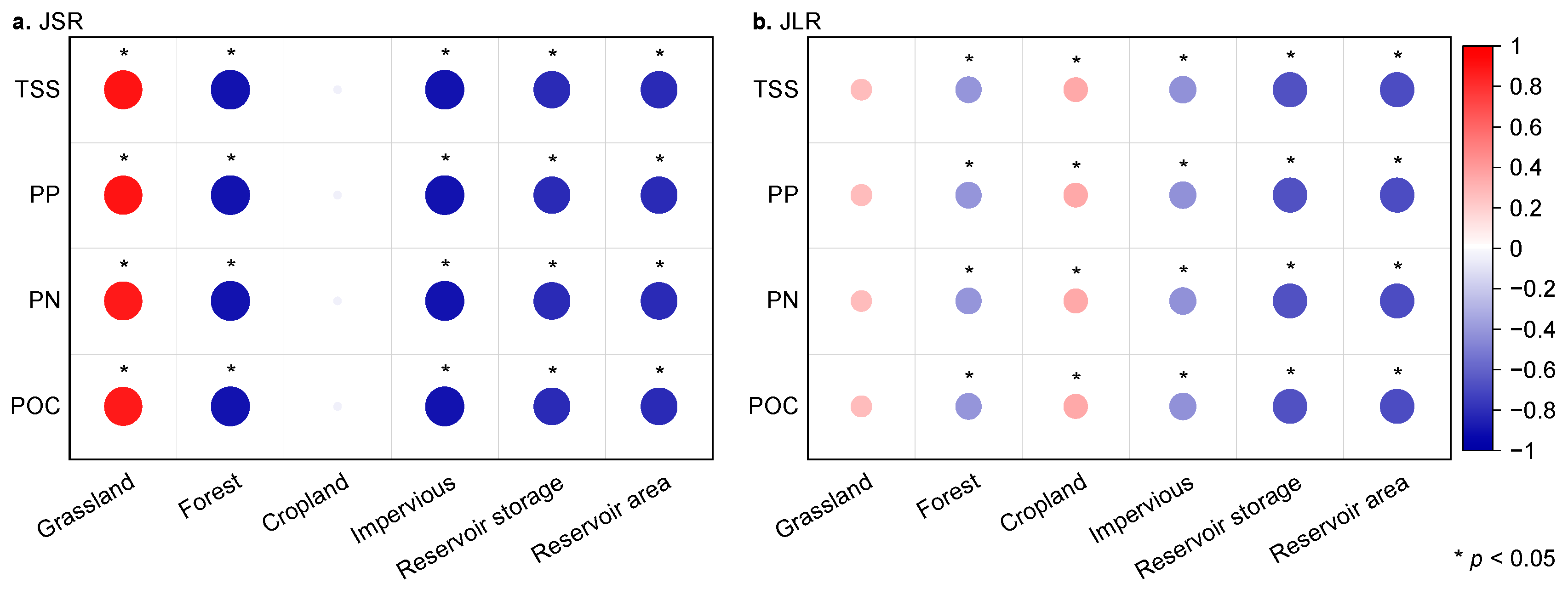
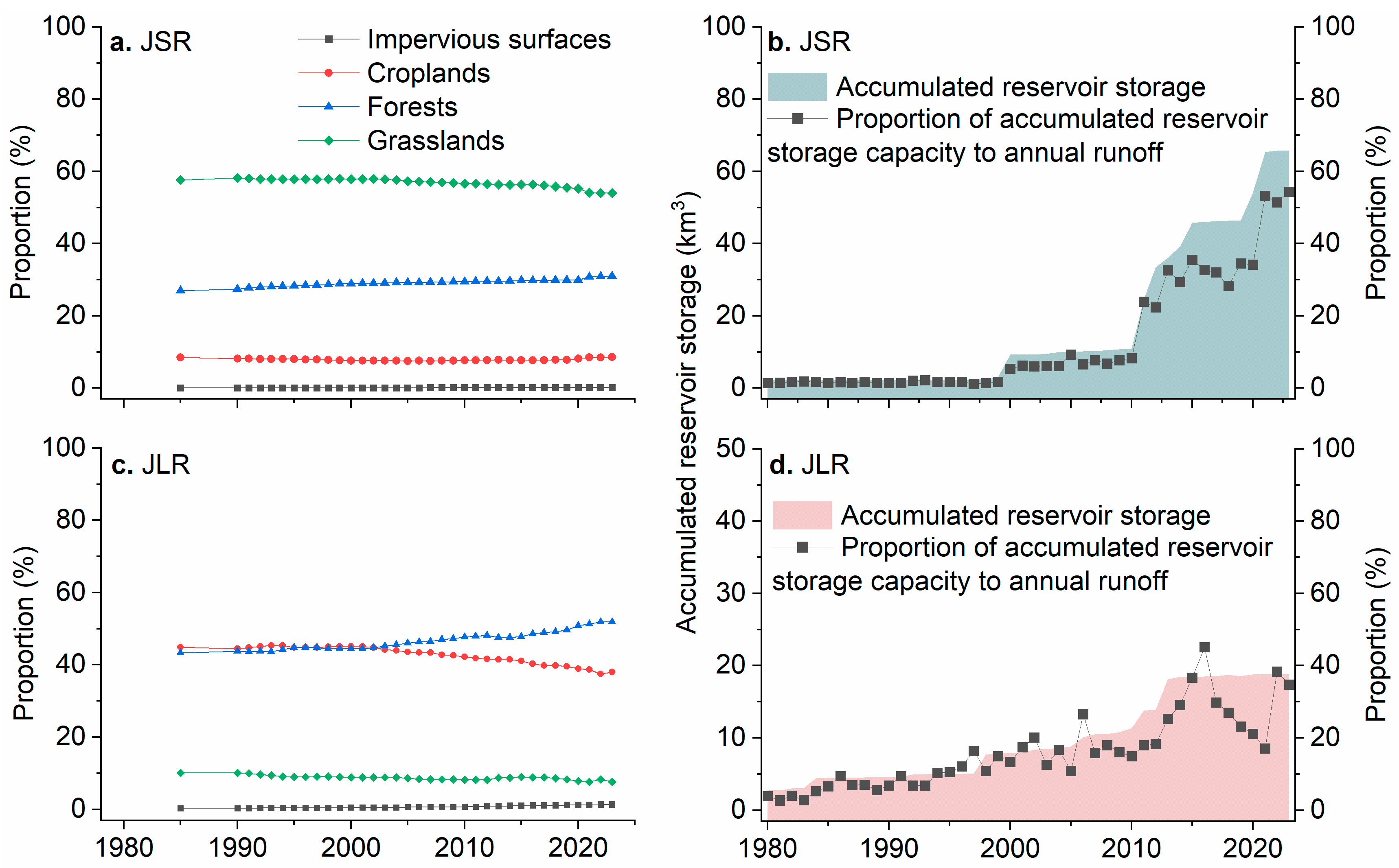
4.2.1. Impacts of Land Use Change
4.2.2. Impacts of Dams and Reservoirs
4.3. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, G.H.; Pavelsky, T.M. Global extent of rivers and streams. Science 2018, 361, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, J. Anthropogenic stresses on the world’s big rivers. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 12, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga, E.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Harrison, J.A.; Dumont, E.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Bouwman, A.F.; Fekete, B.M.; Kroeze, C.; Van Drecht, G. Global Nutrient Export from WaterSheds 2 (NEWS 2): Model development and implementation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefiore, L.R.; Kaplan, D.; Phlips, E.J.; Milbrandt, E.C.; Arias, M.E.; Morrison, E.; Nelson, N.G. Downstream Nutrient Concentrations Depend on Watershed Inputs More Than Reservoir Releases in a Highly Engineered Watershed. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR035590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbabazi, J.; Inoue, T.; Yokota, K.; Saga, M. Variability of particulate bioavailable phosphorus, particulate organic carbon and nitrogen in agricultural and urban rivers. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beusen, A.H.W.; Dekkers, A.L.M.; Bouwman, A.F.; Ludwig, W.; Harrison, J. Estimation of global river transport of sediments and associated particulate C, N, and P. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, GB4S05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, M.J.; Wüest, A.; Wehrli, B.; Landert, J.; Senn, D.B. Impact of a large tropical reservoir on riverine transport of sediment, carbon, and nutrients to downstream wetlands. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W12531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; He, G.; Huang, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, T.; Meng, J. Altered flow and sediment transport impacts on the ecosystems of Chinese major rivers: An urgent call for eco-fluvial dynamics. River 2024, 3, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethier, E.N.; Renshaw, C.E.; Magilligan, F.J. Rapid changes to global river suspended sediment flux by humans. Science 2022, 376, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repasch, M.; Scheingross, J.S.; Hovius, N.; Lupker, M.; Wittmann, H.; Haghipour, N.; Gröcke, D.R.; Orfeo, O.; Eglinton, T.I.; Sachse, D. Fluvial organic carbon cycling regulated by sediment transit time and mineral protection. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, T.S.; Mayer, L.M.; Amaral, J.H.F.; Arndt, S.; Galy, V.; Kemp, D.B.; Kuehl, S.A.; Murray, N.J.; Regnier, P. Anthropogenic impacts on mud and organic carbon cycling. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Meybeck, M.; Fekete, B.; Sharma, K.; Green, P.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Anthropogenic sediment retention: Major global impact from registered river impoundments. Glob. Planet. Change 2003, 39, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Hu, M.; Wu, X.; Wen, J.; Li, S.; Sun, M. Spatiotemporal variation characteristics of sediment nutrient load from the soil erosion of the Yangtze River Basin of China from 1901 to 2010. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.X.; Zhai, S.K.; Lu, X.X.; Liu, J.P.; Xu, J.X.; Xu, K.H. A quantitative assessment of human impacts on decrease in sediment flux from major Chinese rivers entering the western Pacific Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L19603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumwimba, M.N.; Bao, L.; Jie, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Su, J.; Muyembe, D.K.; Guide, A.; et al. Nutrients retention of a series of small dam-impacted urban rivers in northern China. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, R.H. River-Sediment Inputs to Major Deltas. In Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Subsidence; Milliman, J.D., Haq, B.U., Eds.; Coastal Systems and Continental Margins; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 63–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Tian, L.; Fang, H.; Walling, D.E.; Huang, L.; Park, E.; Li, D.; Zheng, C.; Feng, L. Changes in global fluvial sediment concentrations and fluxes between 1985 and 2020. Nat. Sustain. 2025, 8, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Junaid, M.; Deng, J.-Y.; Tang, Q.; Luo, L.; Xie, Z.; Pei, D. Effects of land-use patterns on seasonal water quality at multiple spatial scales in the Jialing River, Chongqing, China. Catena 2024, 234, 107646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, Z. Rainfall-induced nutrient losses from manure-fertilized farmland in an alluvial plain. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Lu, J.; Yao, S.; Yan, X.; Jin, Z.; Liu, L.; Lu, X.X. Distinguishing the multiple controls on the decreased sediment flux in the Jialing River basin of the Yangtze River, Southwestern China. Catena 2020, 193, 104593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquetti, N.B.; Beskow, S.; Guo, L.; Mello, C.R. Soil erosion assessment in the Amazon basin in the last 60 years of deforestation. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; He, X.; Gao, X.; Zhang, C.-E.; Tang, K. Effects of erosion patterns on nutrient loss following deforestation on the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 108, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirauda, D.; Caniani, D.; Colucci, M.T.; Ostoich, M. Assessing the fluvial system resilience of the river Bacchiglione to point sources of pollution in Northeast Italy: A novel Water Resilience Index (WRI) approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 36775–36792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cappellen, P.; Maavara, T. Rivers in the Anthropocene: Global scale modifications of riverine nutrient fluxes by damming. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2016, 16, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinti, R.A.; Condon, L.E.; Zhang, J. The evolution of dam induced river fragmentation in the United States. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Xu, K.H.; Dong, C.M.; Yang, S.L.; He, Y.J.; Shi, B.W. Declining Sediment Discharge in the Yangtze River from 1956 to 2017: Spatial and Temporal Changes and Their Causes. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.F.; Yang, S.L.; Xu, K.H.; Milliman, J.D.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.Y. Human impacts on sediment in the Yangtze River: A review and new perspectives. Glob. Planet. Change 2018, 162, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Jin, Z.; Guo, L.; Lu, J.; Ren, S.; Zhou, Y. On the cumulative dam impact in the upper Changjiang River: Streamflow and sediment load changes. Catena 2020, 184, 104250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalash, S. Effects of sedimentation on the storage capacity of the High Aswan Dam reservoir. Hydrobiologia 1982, 91–92, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E. Human impact on land–ocean sediment transfer by the world’s rivers. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 192–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ve, N.D.; Fan, D.; Van Vuong, B.; Lan, T.D. Sediment budget and morphological change in the Red River Delta under increasing human interferences. Mar. Geol. 2021, 431, 106379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.X.; Oeurng, C.; Le, T.P.Q.; Thuy, D.T. Sediment budget as affected by construction of a sequence of dams in the lower Red River, Viet Nam. Geomorphology 2015, 248, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, D.V.; Kantoush, S.; Sumi, T. Changes to long-term discharge and sediment loads in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta caused by upstream dams. Geomorphology 2020, 353, 107011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenlerkthawin, W.; Namsai, M.; Bidorn, K.; Rukvichai, C.; Panneerselvam, B.; Bidorn, B. Effects of Dam Construction in the Wang River on Sediment Regimes in the Chao Phraya River Basin. Water 2021, 13, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, X.Y.; Vericat, D.; Batalla, R.J.; Teo, F.Y.; Lee, K.S.P.; Gibbins, C.N. A review of the impacts of dams on the hydromorphology of tropical rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Syvitski, J.P.M.; Saito, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, M. Anthropogenic impacts on the decreasing sediment loads of nine major rivers in China, 1954–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Chen, M. Statistical studies of the characteristics and key influencing factors of sediment changes in the upper Yangtze River over the past 60 years. Geomorphology 2024, 466, 109414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Precipitation Dataset for China (1901–2023) [Data Set]; National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Online, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Peng, S. Spatiotemporal Trends and Attribution of Drought across China from 1901–2100. Sustainability 2020, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J. Spatiotemporal change and trend analysis of potential evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011–2100. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Gang, C.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Assessment of climate change trends over the Loess Plateau in China from 1901 to 2100. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 38, 2250–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Fan, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, K.; Chen, T.; Zhan, P.; Luo, S.; Yuan, C.; et al. A comprehensive geospatial database of nearly 100 000 reservoirs in China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4017–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover datasets and its dynamics in China from 1985 to 2023 [Data set]. Earth Syst. Sci. Data (1.0.3). Zenodo 2024, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitzinger, S.P.; Harrison, J.A.; Dumont, E.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Bouwman, A.F. Sources and delivery of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus to the coastal zone: An overview of Global Nutrient Export from Watersheds (NEWS) models and their application. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, GB4S01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Bai, X.; Tan, Q.; Ran, C.; Chen, H.; Xi, H.; Chen, F.; Wu, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; et al. Particulate organic carbon exports from the terrestrial biosphere controlled by erosion. Catena 2022, 209, 105815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.J.; Kroeze, C. Past and future trends in nutrients export by rivers to the coastal waters of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2075–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, K. Model-Based Evaluation of Hydroelectric Dam’s Impact on the Seasonal Variabilities of POC in Coastal Ocean: A Case Study of Three Gorges Project. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yu, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Q. Fluxes of particulate carbon from rivers to the ocean and their changing tendency in China. Prog. Geogr. 2012, 31, 118–122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: Oxford, UK, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Mahmud, I. pyMannKendall: A python package for non parametric Mann Kendall family of trend tests. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, A.N. A Non-Parametric Approach to the Change-Point Problem. Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Shen, H.; Zhanghua, W. Yangtze River of China: Historical analysis of discharge variability and sediment flux. Geomorphology 2001, 41, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Hou, L.; He, X. An assessment of human versus climatic impacts on large-sized basin erosion: The case of the upper Yangtze River. Nat. Hazard. 2014, 74, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhao, X.; Kang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Paerl, H.; Zhu, G.; Li, H.; Zhu, M.; Qin, B.; et al. Rainfall impacts on nonpoint nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in an agricultural river in subtropical montane reservoir region of southeast China. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 149, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Li, Z.; Duan, L.; Xu, X. Decoupling the influence of vegetation and climate on intra-annual variability in runoff in karst watersheds. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Chen, X.; Huang, R.; Smettem, K. Runoff change induced by vegetation recovery and climate change over carbonate and non-carbonate areas in the karst region of South-west China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brath, A.; Montanari, A.; Moretti, G. Assessing the effect on flood frequency of land use change via hydrological simulation (with uncertainty). J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; He, R.; Jiang, N.; Jing, X. Runoff reduction due to environmental changes in the Sanchuanhe river basin. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2008, 23, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, L. Estimation of soil erosion in some sections of Lower Jinsha River based on RUSLE. Nat. Hazard. 2015, 76, 1831–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Xiong, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, P.; Guo, S.; Xu, C.-Y. Separating the impacts of climate change and human activities on runoff using the Budyko-type equations with time-varying parameters. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Huang, S.; Wen, W.; Sun, X.; Tang, X.; Scholz, M. Nutrient distribution within and release from the contaminated sediment of Haihe River. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.; Feng, L.; Tang, J.; Park, E.; Ali, T.A.; Zheng, Y. Trends in River Total Suspended Sediments Driven by Dams and Soil Erosion: A Comparison Between the Yangtze and Mekong Rivers. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2022WR031979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xie, Y.; Guan, A.; Qi, W.; Cao, X.; Peng, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; et al. Dam construction reshapes sedimentary pollutant distribution along the Yangtze River by regulating sediment composition. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, X.T.; Yang, Z.; Mao, C.; West, A.J.; Ji, J. Dam-triggered organic carbon sequestration makes the Changjiang (Yangtze) river basin (China) a significant carbon sink. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 120, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lv, J.; Bao, Y.; Tang, Q.; Collins, A.L.; Khurram, D.; He, X. Linking soil erosion and sediment yield with landscape heterogeneity: Exploration using the lower Jinsha River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2024, 631, 130729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, Y.C.; Ghulam, A.; Chu, M.L. Assessing the Impacts of Future Urban Development Patterns and Climate Changes on Total Suspended Sediment Loading in Surface Waters Using Geoinformatics. J. Environ. Inf. 2014, 24, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Yan, S.; Chen, H. Estimating soil erosion response to land use/cover change in a catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kateb, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Mosandl, R. Soil erosion and surface runoff on different vegetation covers and slope gradients: A field experiment in Southern Shaanxi Province, China. Catena 2013, 105, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, S.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Liu, L. Multi-Decade Variations in Sediment and Nutrient Export in Cascading Developmental Rivers in Southwest China: Impacts of Land Use and Dams. Water 2025, 17, 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091333
Lyu S, Yu Q, Zhang L, Xu F, Wang Y, Dong Z, Liu L. Multi-Decade Variations in Sediment and Nutrient Export in Cascading Developmental Rivers in Southwest China: Impacts of Land Use and Dams. Water. 2025; 17(9):1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091333
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Shucong, Qibiao Yu, Liangjing Zhang, Fei Xu, Yu Wang, Zhaojun Dong, and Lusan Liu. 2025. "Multi-Decade Variations in Sediment and Nutrient Export in Cascading Developmental Rivers in Southwest China: Impacts of Land Use and Dams" Water 17, no. 9: 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091333
APA StyleLyu, S., Yu, Q., Zhang, L., Xu, F., Wang, Y., Dong, Z., & Liu, L. (2025). Multi-Decade Variations in Sediment and Nutrient Export in Cascading Developmental Rivers in Southwest China: Impacts of Land Use and Dams. Water, 17(9), 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091333





