Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Yangtze River, Poyang Lake and Its Tributaries: Spatial Distribution, Relationship Analysis and Source Apportionment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Preparation Methods
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Occurrence and Composition of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments
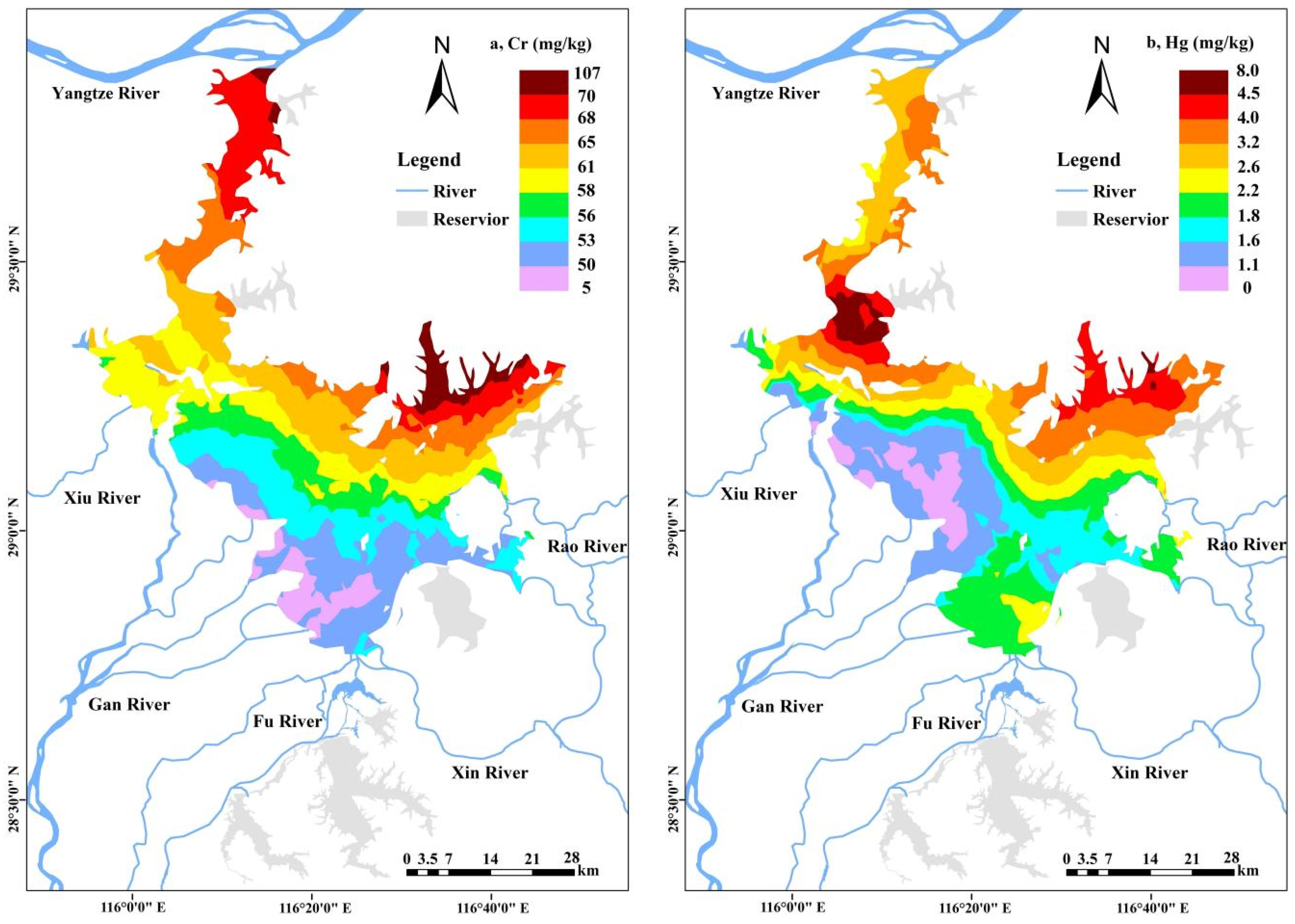
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments
3.3. Relationship Analysis
3.4. Source Apportionment of Sediment Heavy Metals
3.5. Environmental Evaluation of Heavy Metals
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, R.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, F.; Ding, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Yan, H.; Shao, W. Heavy metal pollution and assessment in the tidal flat sediments of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 74, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhamji, S.; Sbihi, K.; Lghoul, S.; Aziz, K.; El Maallem, A.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Aziz, F. Addressing the challenge of heavy metal contamination in aquatic environment: Harnessing the bioremediation potential of Navicula permitis diatom for wastewater treatment. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 197, 107776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Liang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Xing, B. Multivariate geostatistical analysis and source identification of heavy metals in the sediment of Poyang Lake in China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 621, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P.; Saravanan, V.; Rajeshkannan, R.; Arnica, G.; Rajasimman, M.; Baskar, G.; Pugazhendhi, A. Comprehensive review on toxic heavy metals in the aquatic system: Sources, identification, treatment strategies, and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Huang, J.; Zeng, G.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Bai, B. Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Dongting Lake, Middle China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 132, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redwan, M.; Elhaddad, E. Correction to: Heavy metal pollution in Manzala Lake sediments, Egypt: Sources, variability, and assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastami, K.; Neyestani, M.; Shemirani, F.; Soltani, F.; Haghparast, S.; Akbari, A. Heavy metal pollution assessment in relation to sediment properties in the coastal sediments of the southern Caspian Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, H.; Wu, Y.; Nahm, W.-K.; Liu, E. Accumulation of heavy metals in the lacustrine sediment of Longgan Lake, middle reaches of Yangtze River, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goretti, E.; Pallottini, M.; Ricciarini, M.; Selvaggi, R.; Cappelletti, D. Heavy metals bioaccumulation in selected tissues of red swamp crayfish: An easy tool for monitoring environmental contamination levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.-F.; Song, Y.-H.; Yuan, P.; Cui, X.-Y.; Qiu, G.-L. The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 161, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomons, W.; Förstner, U. Metals in the Hydrocycle; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Chen, L.; Tao, H.; Cao, M.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Shi, J. Pollution status and risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediment of a historically contaminated lake treated by oxidation pond in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 41794–41805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, M.; Shen, L.; Hu, L. Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, A. Lake sediment cores as indicators of historical metal(loid) accumulation. A case study in Mexico. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Keeler, B.; Polasky, S.; Poudel, R.; Rhude, K.; Rogers, M. Ecosystem services of earth’s largest freshwater lakes. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 41, 101046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyege, I.; Katwesigye, R.; Kiwanuka, M.; Mutanda, H.; Niyomukiza, J.; Kataraihya, D.; Kica, S.; Egor, M. Temporal trends of water quality parameters, heavy metals, microplastics, and emerging organic pollutants in Lake Victoria and its basin: Knowns, knowledge gaps, and future directions. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliu, D.; Bucse, A.; Lupascu, N.; Ispas, B.; Gheablau, C.; Stanescu, I. Assessment of the metal pollution in surface sediments of coastal Tasaul Lake (Romania). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, S.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ding, T. Heavy metals in sediments of the river-lake system in the Dianchi basin, China: Their pollution, sources, and risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Shi, X.; Sun, B.; Cui, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Distribution characteristics, risk assessment, and source analysis of heavy metals in typical lake sediments in Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Yu, H.; Jiang, X.; Guo, X.; Pang, Y.; Xu, X. Concentration distribution and toxicity of heavy metals in surface sediment of Poyang Lake, China. Wetlands 2019, 39, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, X.; Qi, W.; Peng, J.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. The influence of wet-to-dry season shifts on the microbial community stability and nitrogen cycle in the Poyang Lake sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Jin, G.; Tang, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.-G.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, S. Spatiotemporal variations of water levels and river-lake interaction in the Poyang Lake basin under the extreme drought. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J. Impact of lake inflow and the Yangtze River flow alterations on water levels in Poyang Lake, China. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2014, 30, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Guo, S.; Zeng, G.-M.; Li, F.; Gu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, W.; Peng, S. A new exploration of health risk assessment quantification from sources of soil heavy metals under different land use. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.-M.; Wen, H.-H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.-S.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Fang, T.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, G. Analysis of driving factors of spatial distribution of heavy metals in soil of non-ferrous metal smelting sites: Screening the geodetector calculation results combined with correlation analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, D.; Ingersoll, C.; Berger, T. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadov, M.; Humbatov, F.; Mammadzada, S.; Balayev, V.; Ibadov, N.; Ibrahimov, Q. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in coastal sediments of the western Caspian Sea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, R.; Nemati Mansour, S.; Ekrami, J.; Mosaferi, M. Health and ecological risks assessment of heavy metals and metalloids in surface sediments of Urmia Salt Lake, Northwest of Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, Z.; Haximu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Aji, R. An ecological risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of Bosten Lake, northwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2016, 8, 7255–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Che, F.; Fu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, W. Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Lake Qinghai. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 3037–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, D.; Yue, W.; Wang, B.; Huo, L.; Liu, K.; Zhang, B.-T. Heavy metals in sediments of Hulun Lake in Inner Mongolia: Spatial-temporal distributions, contamination assessment and source apportionment. Water 2023, 15, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Long, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Meng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S. Ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metal pollutions in sediments of the Chaohu Lake. Earth Environ. 2020, 48, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.S.; Friese, K.; Gao, Q.; Kimirei, I.; Kishe, M.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Yu, C.; Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Accumulation characteristics and ecological implications of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Mwanza Gulf, Lake Victoria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, L. Inputting history of heavy metals into the inland lake recorded in sediment profiles: Poyang Lake in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.; Wang, G.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X.; Xu, F.; Xu, Q.; Guo, L. Distributions, sources, and species of heavy metals/trace elements in shallow groundwater around the Poyang Lake, East China. Expo. Health 2018, 10, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, M.; Xie, Z. Level, source identification, and risk analysis of heavy metal in surface sediments from river-lake ecosystems in the Poyang Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21902–21916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Fan, D.; Yu, P.; Wang, J.; Tang, A. Distribution and accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in sediments in southern sea area of Huludao City, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Hu, C.; Yang, X.; Shui, B. Spatial variations and potential risks of heavy metals in sediments of Yueqing Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 112983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, C.; Bi, J.; Zhang, B.-T.; Liu, Y.; Shao, P.; Liu, T.; Wang, S.; Zhong, W. Spatial-temporal distribution and source analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments of Poyang Lake. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusunoki, K.; Sakata, M. Long-range transport of heavy metals from the Asian continent contributes to surface sediments in Lakes Shinji and Nakaumi in western Japan. Limnology 2018, 19, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.; Zhao, L.; Yang, S.; Struck, U.; Yin, D. Distribution and source of heavy metals in the sediments of the coastal East China sea: Geochemical controls and typhoon impact. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X. Multiphase spatial distribution characteristics of Cd morphology in typical intertidal. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-Q.; Ni, Z.-K.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Wang, S.-R.; Zeng, Q.-R. Influence of the river-lake relation change on the distribution of heavy metal and ecological risk assessment in the surface sediment of Poyang Lake. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Tian, Y.; Sen, P.; Wang, M. Effect of dissolved oxygen and nutrient levels on heavy metal contents and fractions in river surface sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-T.; Gao, Y.; Lin, C.; Yang, W.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Spatial distribution of phthalate acid esters in sediments of the Laizhou Bay and its relationship with anthropogenic activities and geochemical variables. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, S.; Li, N.; Luo, X. Source apportionment and risk assessment of metal pollution in natural biofilms and surface water along the Lancang River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Feng, X.; Tian, D.; Li, C.; Cheng, Q.; Yi, F. Evaluation and source apportionment on potentially toxic elements pollution of agricultural soil in mango planting areas in Panzhihua city, China. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2024, 34, 104–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, L.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J.; Liao, W.; Yu, Z. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants/plasticizers in coastal sediments from the Taiwan Strait in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-T.; Gao, Y.; Lin, C.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H. Spatial distribution of phthalate acid esters in sediments and its relationships with anthropogenic activities and environmental variables of the Jiaozhou Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 155, 111161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, X.; Duan, H.; Ruan, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Combination of UNMIX, PMF model and Pb-Zn-Cu isotopic compositions for quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in suburban agricultural soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2022, 234, 113369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Meng, L.; Liu, F.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Mao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, H. Distribution, source investigation, and risk assessment of topsoil heavy metals in areas with intensive anthropogenic activities using the positive matrix factorization (PMF) model coupled with self-organizing map (SOM). Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 6353–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, H.; Hu, C.; Wu, G.; Chen, M. Source analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments of Poyang Lake during the abundant water period by combining Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Positive Definite Matrix Factorization (PMF). Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lan, X.; Yu, F.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Du, L. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metals in soil-crop system based on PMF and evolutionary game theory. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Heavy Metals | Poyang Lake (mg/kg, d.w. n = 49) | Tributaries (mg/kg, d.w. n = 9) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | FOD | Min | Max | Mean | FOD | |
| Cu | ND | 115.0 | 37.1 | 95.9% | 14.0 | 39.0 | 24.0 | 100.0% |
| As | 2.0 | 28.0 | 16.7 | 100.0% | ND | 29.0 | 14.0 | 88.9% |
| Ni | ND | 71.0 | 37.2 | 98.0% | 10.0 | 61.0 | 32.3 | 100.0% |
| V | ND | 142.0 | 68.1 | 95.9% | 37.0 | 119.0 | 65.8 | 100.0% |
| Cr | 15.0 | 93.0 | 61.4 | 100.0% | 5.0 | 107.0 | 54.6 | 100.0% |
| Hg | ND | 8.0 | 2.7 | 73.5% | ND | 4.0 | 1.7 | 55.6% |
| Pb | 12.0 | 94.0 | 53.4 | 100.0% | 27.0 | 62.0 | 46.9 | 100.0% |
| Cd | ND | 8.0 | 1.7 | 59.2% | ND | 7.0 | 2.9 | 77.8% |
| ΣHMs | 80.0 | 492.0 | 278.4 | - | 150.0 | 412.0 | 231.1 | - |
| Heavy Metals | Upper Yangtze River (mg/kg, d.w. n = 3) | Lower Yangtze River (mg/kg, d.w. n = 3) | ||||||
| Min | Max | Mean | FOD | Min | Max | Mean | FOD | |
| Cu | 11.3 | 17.3 | 14.0 | 100.0% | 18.7 | 30.0 | 24.6 | 100.0% |
| As | 4.3 | 5.7 | 5.1 | 100.0% | 4.0 | 10.7 | 7.8 | 100.0% |
| Ni | 44.0 | 47.3 | 45.2 | 100.0% | 37.0 | 40.3 | 38.1 | 100.0% |
| V | 40.3 | 73.0 | 61.1 | 100.0% | 75.0 | 97.3 | 83.6 | 100.0% |
| Cr | 52.0 | 109.0 | 76.1 | 100.0% | 52.0 | 56.7 | 54.0 | 100.0% |
| Hg | 4.3 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 100.0% | ND | 4.7 | 2.1 | 66.7% |
| Pb | 25.0 | 31.3 | 27.7 | 100.0% | 28.0 | 45.0 | 36.3 | 100.0% |
| Cd | 8.0 | 9.3 | 8.7 | 100.0% | 5.0 | 12.7 | 8.3 | 100.0% |
| ΣHMs | 203.0 | 285.0 | 242.9 | - | 231.0 | 267.0 | 254.8 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, Y.; Wang, J.; Bi, J.; Liu, T.; Huang, M.; Li, G.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.-T. Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Yangtze River, Poyang Lake and Its Tributaries: Spatial Distribution, Relationship Analysis and Source Apportionment. Water 2025, 17, 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091295
Chi Y, Wang J, Bi J, Liu T, Huang M, Li G, Ma Y, Zhang B-T. Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Yangtze River, Poyang Lake and Its Tributaries: Spatial Distribution, Relationship Analysis and Source Apportionment. Water. 2025; 17(9):1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091295
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Yangyang, Jiayi Wang, Jiale Bi, Tong Liu, Meijing Huang, Gang Li, Yan Ma, and Bo-Tao Zhang. 2025. "Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Yangtze River, Poyang Lake and Its Tributaries: Spatial Distribution, Relationship Analysis and Source Apportionment" Water 17, no. 9: 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091295
APA StyleChi, Y., Wang, J., Bi, J., Liu, T., Huang, M., Li, G., Ma, Y., & Zhang, B.-T. (2025). Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Yangtze River, Poyang Lake and Its Tributaries: Spatial Distribution, Relationship Analysis and Source Apportionment. Water, 17(9), 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091295






