Ponding Water Quality of Rice Paddies Fertilized with Anaerobically Digested Liquid Pig Manure as Affected by Fly Ash and Zeolite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Soil Characteristics
2.2. Liquid Pig Manure
2.3. Fly Ash and Zeolite
2.4. Plot Experiment Setting and Rice Cultivation
2.5. Sampling and Analyses of the Ponding Water
2.6. Calculations and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ponding Water Chemistry
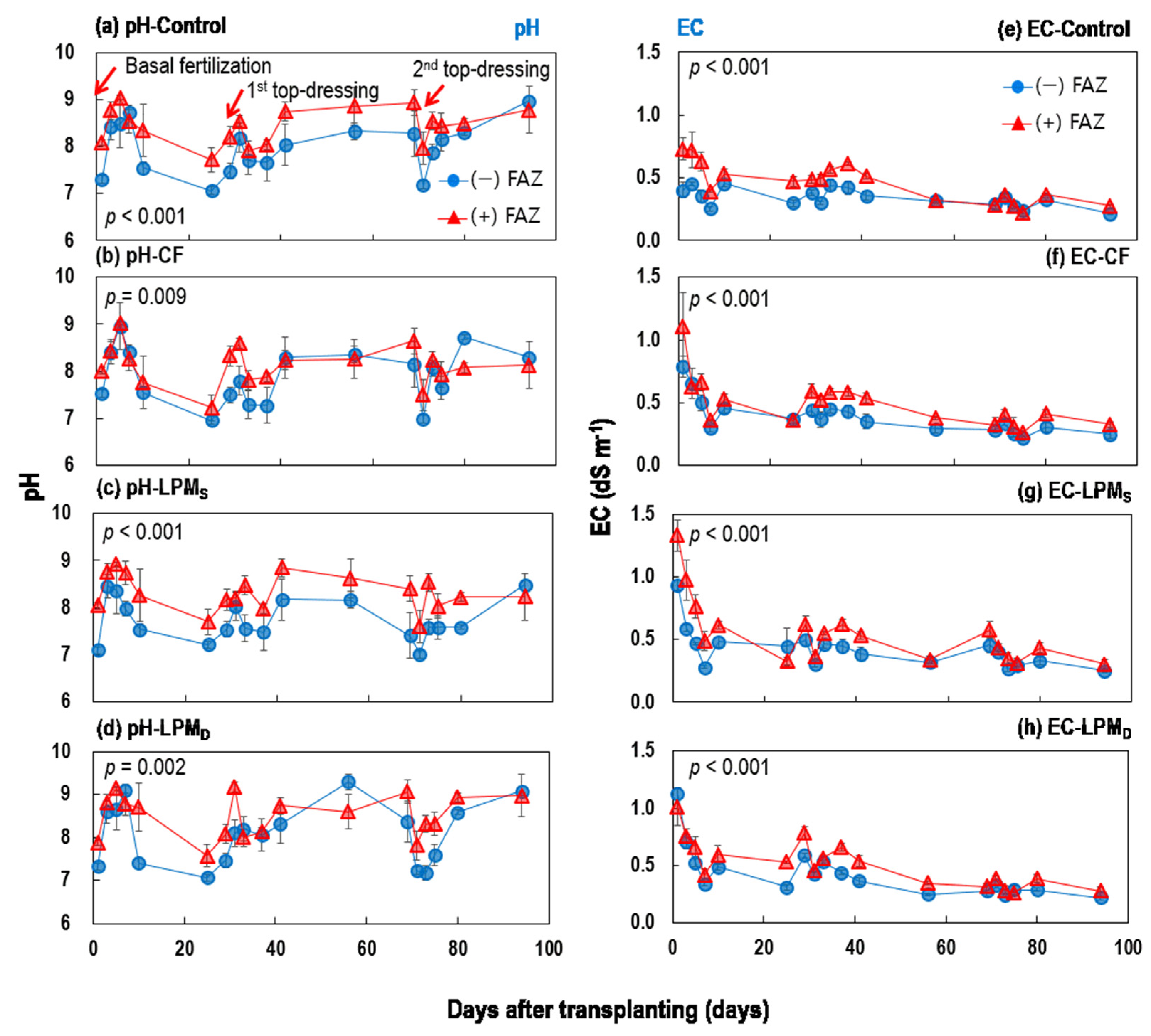
3.1.1. Temporal Changes in the pH and EC of Ponding Water
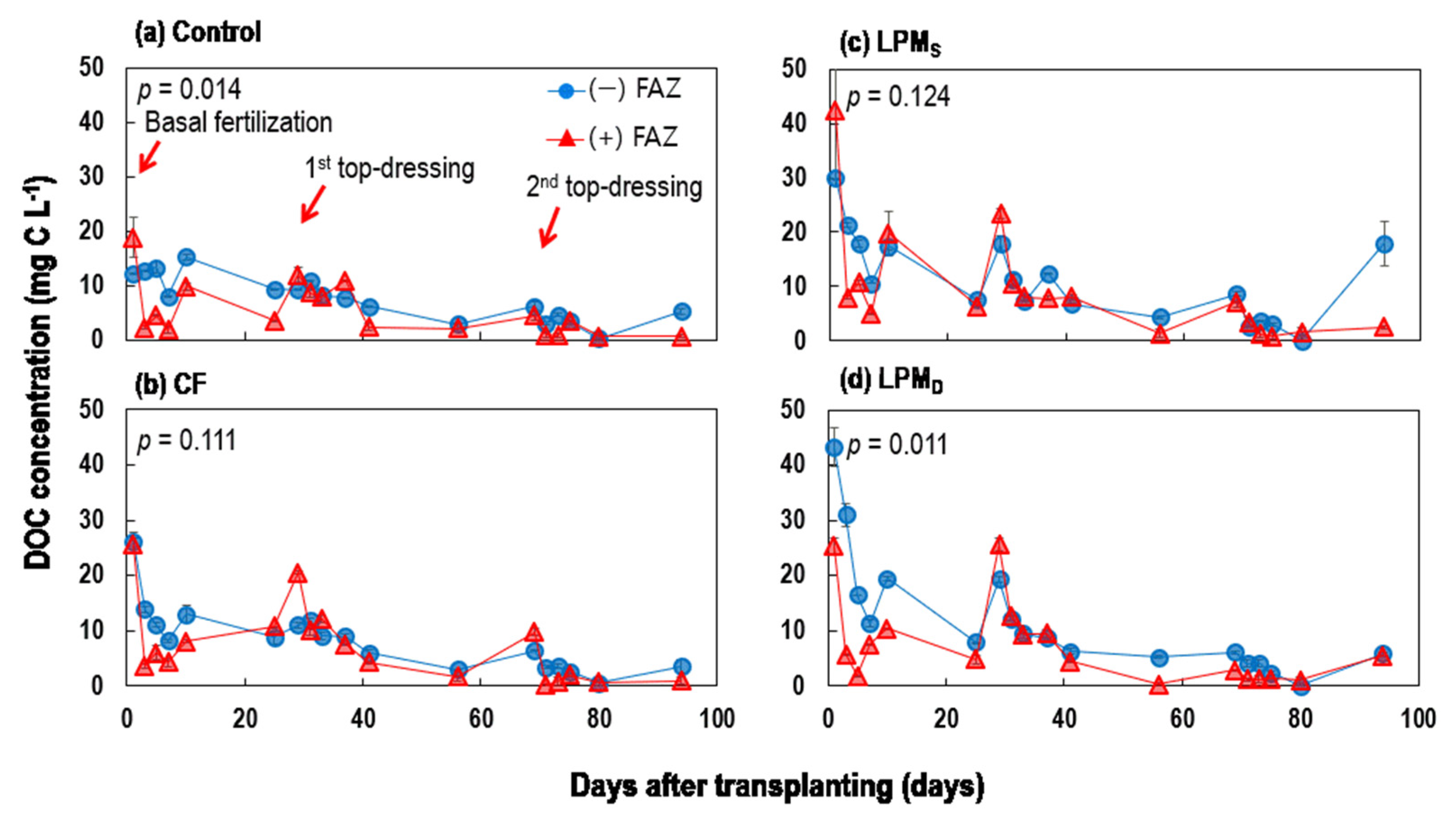
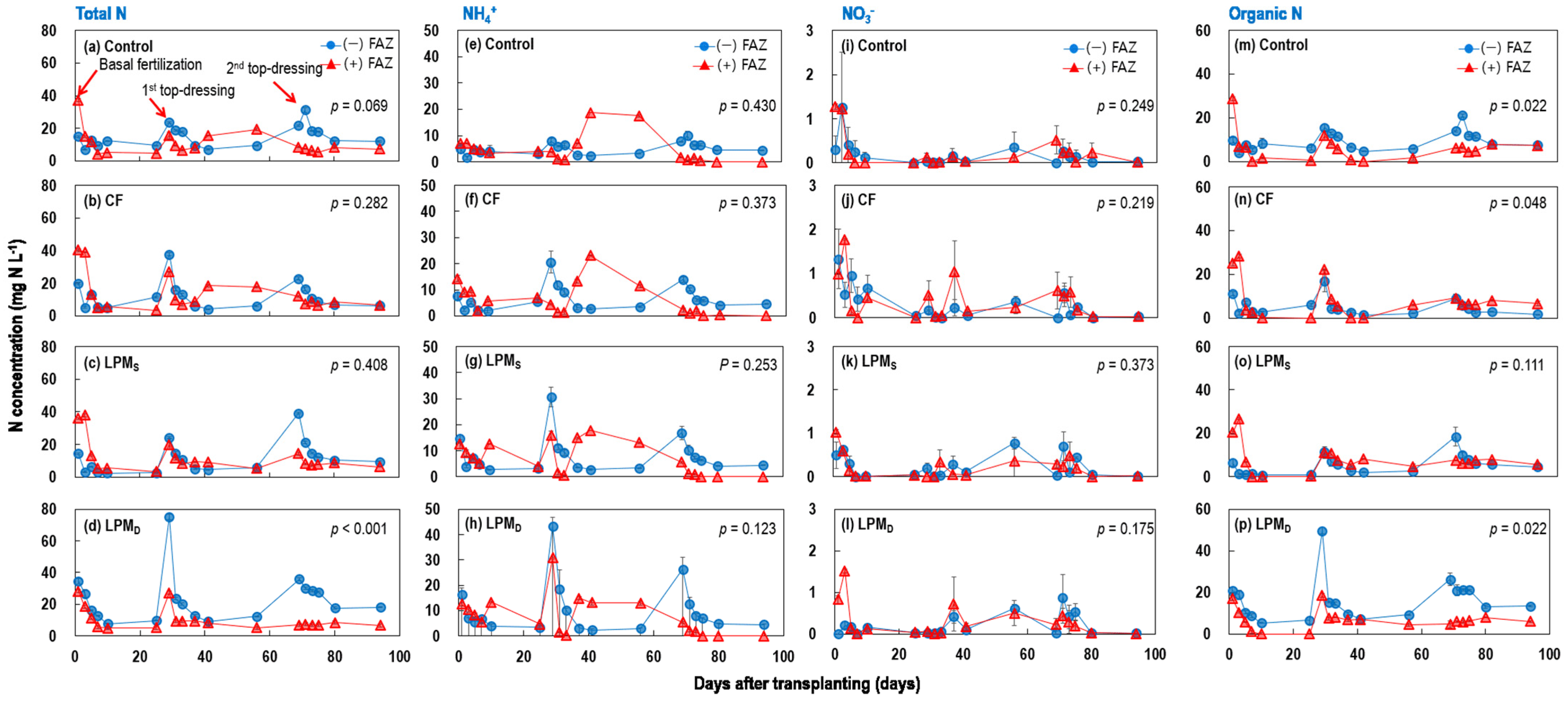
3.1.2. Temporal Changes in DOC, Total N, and Total P of Ponding Water
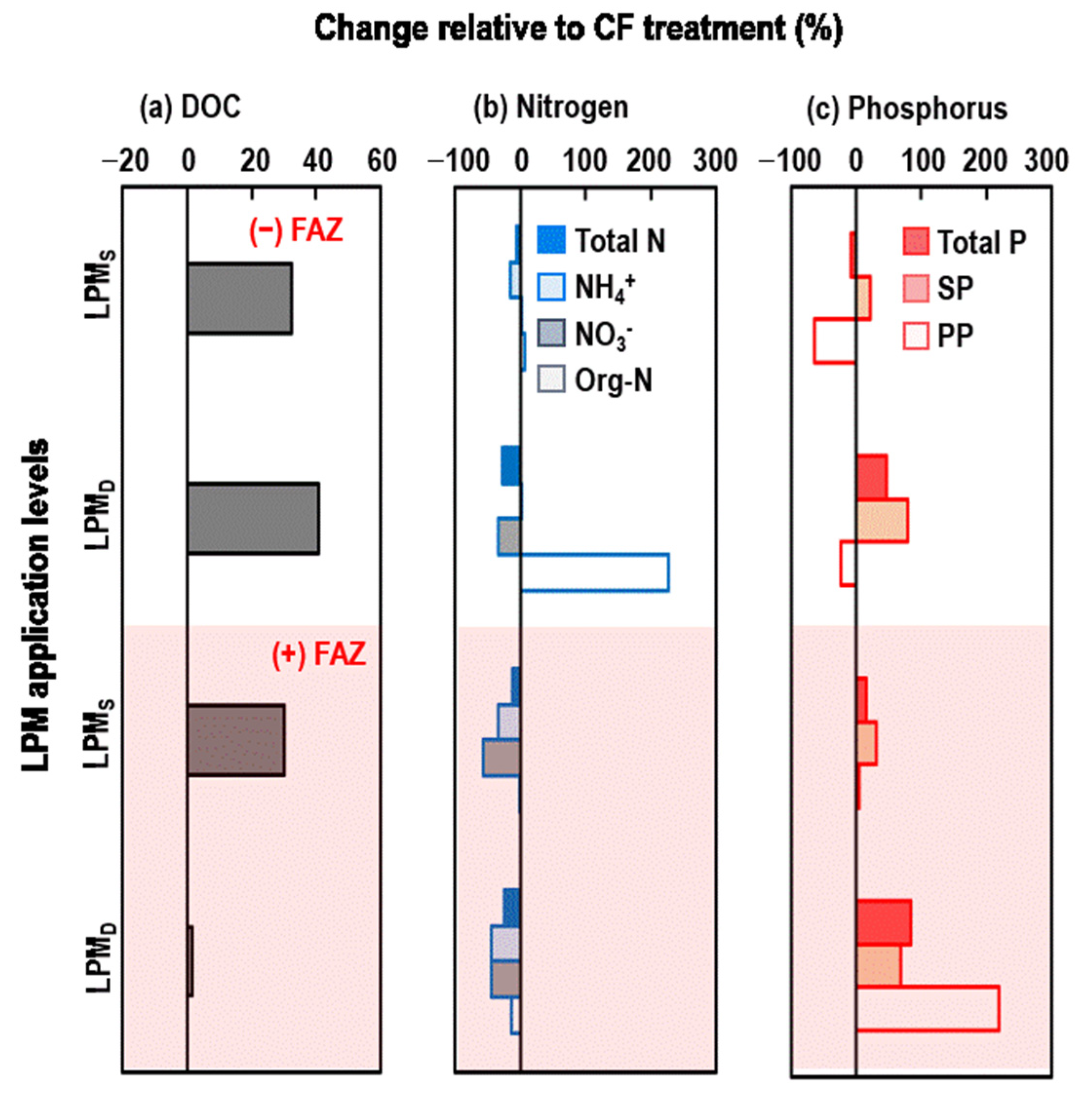
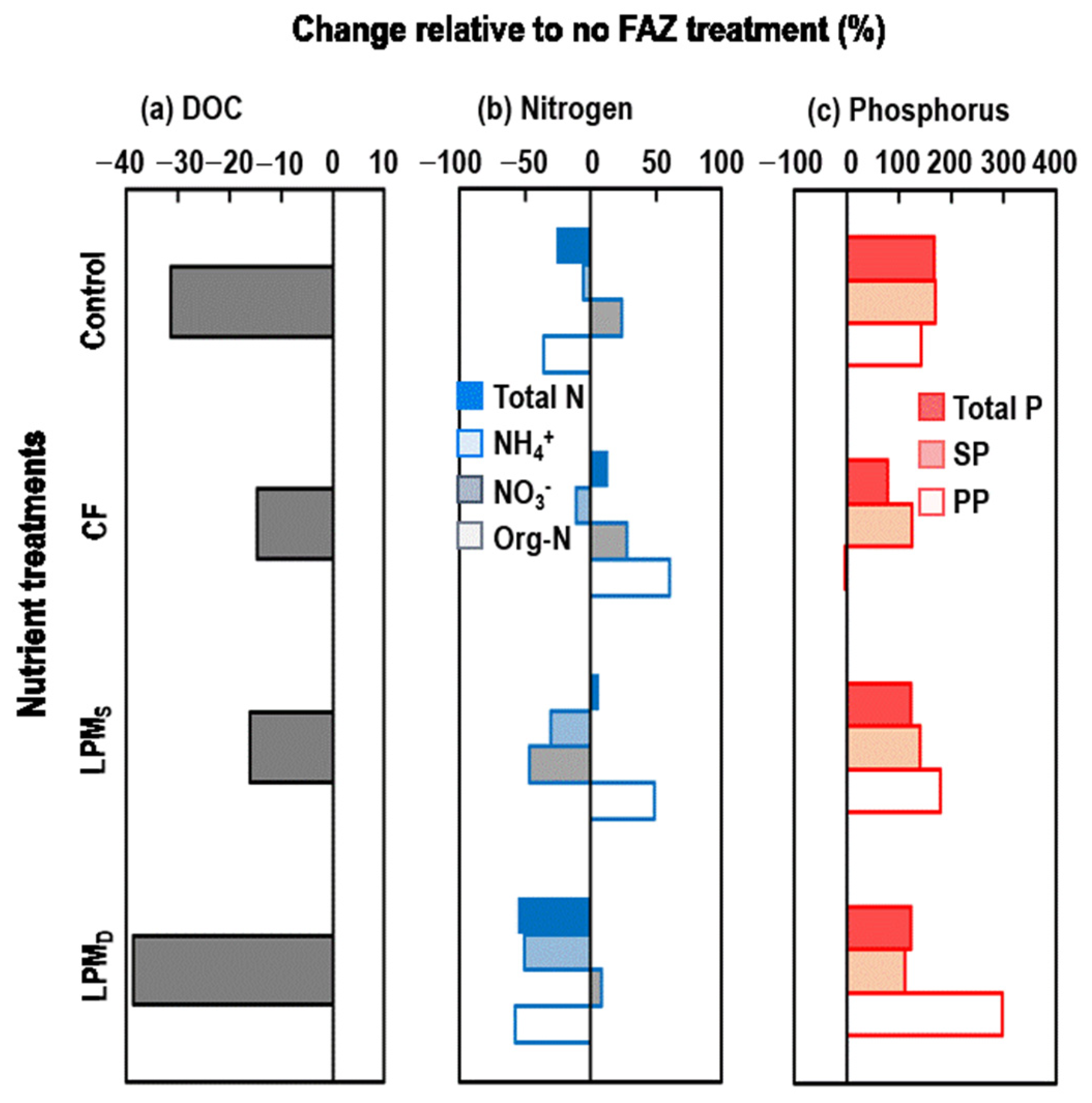
3.1.3. Changes in DOC, N, and P of Ponding Water Due to Different Nutrient Sources and FAZ Amendments
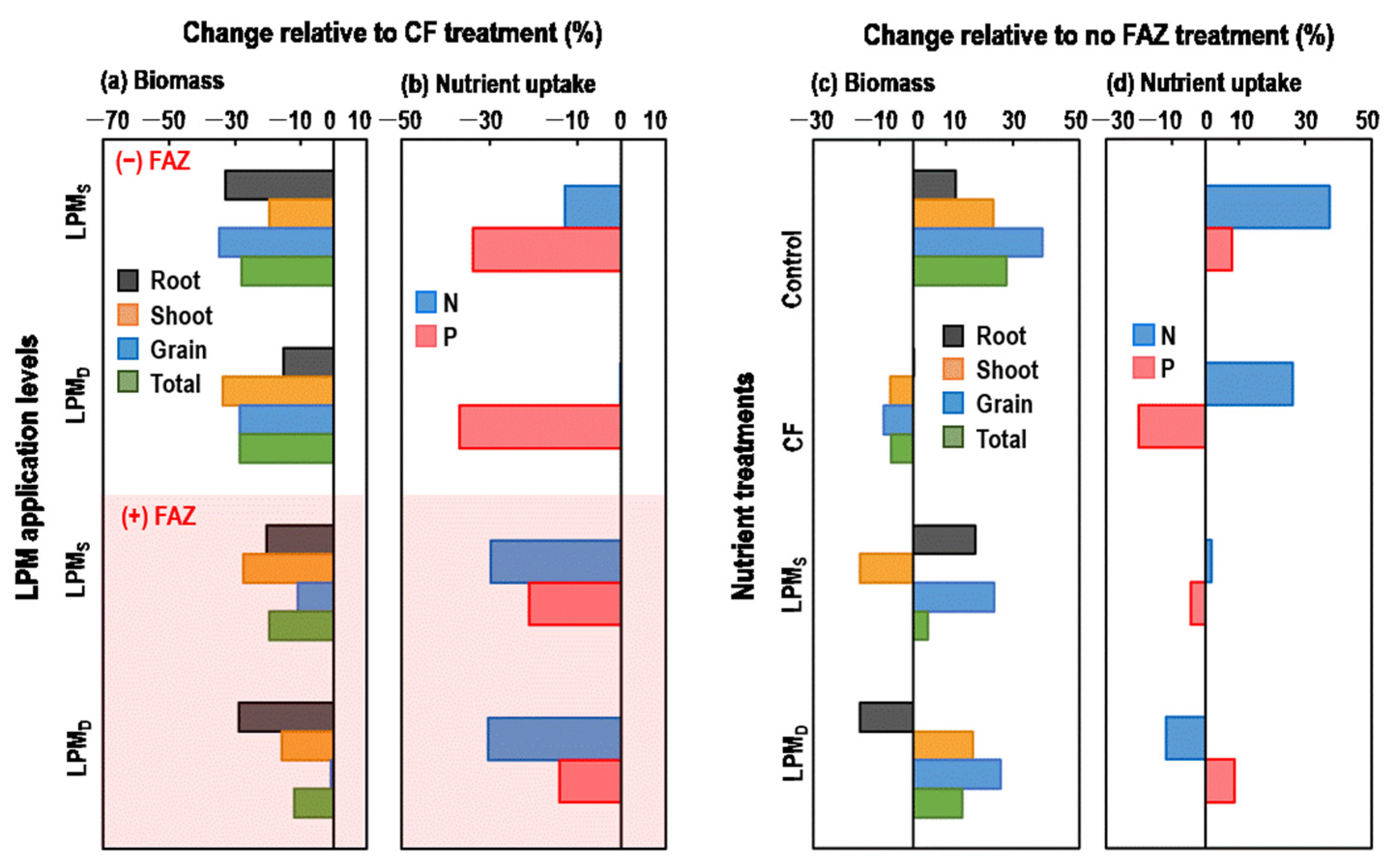
3.2. Rice Biomass and Nutrient Uptake
4. Discussion
4.1. FAZ Consistently Decreased DOC and NH4+ but Increased P in the Ponding Water
4.2. Rice Growth and Nutrient Uptake as Affected by FAZ Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPM | Liquid pig manure |
| FA | Fly ash |
| Z | Zeolite |
| FAZ | Fly ash + zeolite |
| CF | Chemical fertilizer |
| N | Nitrogen |
| P | Phosphorus |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
References
- Jeong, Y.J.; Park, H.J.; Baek, N.; Seo, B.S.; Lee, K.S.; Kwak, J.H.; Choi, S.K.; Lee, S.M.; Yoon, K.S.; Lim, S.S.; et al. Assessment of sources variability of riverine particulate organic matter with land use and rainfall changes using a three-indicator (δ13C, δ15N, and C/N) Bayesian mixing model. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, J.; Ribeiro, H.; Alvarenga, P.; Fangueiro, D. A step towards the production of manure based fertilizers: Disclosing the effects of animal species and slurry treatment on their nutrients content and availability. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.I.; Ham, J.H.; Baek, N.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, W.J. Co-application of fly ash and zeolites increases N uptake but decreases P uptake and biomass of rice fertilized with fermented liquid manure. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.W.; Seo, D.C.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, J.S. Utilization of liquid pig manure for resource cycling agriculture in rice-green manure crop rotation in South Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.Z.; Inamura, T.; Umeda, M. Growth and Nitrogen Uptake of Paddy Rice as Influenced by Fermented Manure Liquid and Squeezed Manure Liquid. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2003, 49, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Liang, P.; Wu, S.; Leung, A.O.W.; Christie, P. Replacement of mineral fertilizers with anaerobically digested pig slurry in paddy fields: Assessment of plant growth and grain quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8916–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Shen, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hong, Z. Effect of swine liquid manure application in paddy field on water quality, soil fertility and crop yields. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 16, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Lim, S.S.; Park, H.J.; Yang, H.I.; Park, S.I.; Kwak, J.H.; Choi, W.J. Fly ash and zeolite decrease metal uptake but do not improve rice growth in paddy soils contaminated with Cu and Zu. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, M.; Pande, M.; Bhadoria, P.B.S.; Mahapatra, S.C. Potential Fly-Ash Utilization in Agriculture: A Global Review. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2009, 19, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.I.; Lim, S.S.; Lee, K.S.; Park, W.K.; Shin, J.D.; Yoon, K.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, W.J. Coal fly ash enhanced planted-floating bed performance in phosphorus-contaminated water treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Hwang, S.W.; Lee, S.L.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, D.C. Sorption behavior of phosphate by fly ash discharged from biomass thermal power plant. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Haraquchi, K.; Gacho, C.C.; Salinas, L.S.; Silverio, C.M.; Wongsiri, B.P. Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution by Crystallization Using Coal Fly Ash. In Proceedings of the International Ash Utilization Symposium, Lexington, KY, USA, 22–24 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Englert, A.H.; Rubio, J. Characterization and Environmental Application of a Chilean Natural Zeolite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2005, 75, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural Zeolites as Effective Adsorbents in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.S.; Lee, D.S.; Kwak, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, W.J. Fly ash and zeolite amendments increase soil nutrient retention but decrease paddy rice growth in a low fertility soils. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortone, G. Integrated anaerobic/aerobic biological treatment for intensive swine production. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5424–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelme-Ayala, P.; El-Din, M.G.; Smith, R.; Code, K.R.; Leonard, J. Advanced treatment of liquid swine manure using physico-chemical treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, A.; Guo, H.; Li, N.; Zhang, N.; Cheng, S.; Guan, J.; Li, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z. Scaling sustainable pig manure treatment: Life cycle assessments for small to large piggeries in China. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 52, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, M.; Huang, Q.; Khan, S.; Nawab, J.; Khan, M.A.; Ali, A.; Ullah, R.; Kubar, A.A.; Guo, G.; Yaseen, M.; et al. Methods for the removal and recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients from animal waste: A critical review. Ecol. Front. 2024, 44, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RDA (Rural Development Administration). Taxonomical Classifications of Korean Soils; RDA: Suwon, Republic of Korea, 2000.
- APHA-AWWA-WEF (American Public Health Association-American Water Work Association-Water Environment Federation). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Xie, S.; Huang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, G. Effects and mechanisms of Cd remediation with zeolite in brown rice (Oryza sativa). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, H.; Mihara, C.; KaKuda, K.; Wada, G. The Fate of Ammonium Nitrogen Applied to Flooded Rice as Affected by Zeolite Addition. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1996, 42, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Sun, N.; Kuang, R.; Wang, C.; Zhan, A.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Q.; et al. Progress in Adsorptive Removal of Volatile Organic Compounds by Zeolites. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2023, 23, 220442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, H.; Leng, S.; Yu, J.; Feng, K.; Cao, L.; Huang, J. Regulation of hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of aluminosilicate zeolites: A review. Crit. Rev. Solid. State 2020, 46, 330–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Hubadilah, S.K.; Aziz, M.H.A.; Jamalludin, M.R. Application of natural zeolite clinoptilolite for the removal of ammonia in wastewater. Mater. Today-Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.T.; Petrovic, A.M. Clinoptilolite Zeolite Influence on Nitrate leaching and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in simulated Sand Based Golf Greens. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 1190–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepaskhah, A.R.; Yousefi, F. Effects of Zeolite Application on Nitrate and Ammonium Retention of a Loamy Soil under Saturated Conditions. Soil Res. 2007, 45, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, A.; Daroub, S.H.; Ognevich, I. Addition of Clinoptilolite Zeolite to a Simulated Sandy Medium to Reduce Nitrogen Leaching. Soil Crop Sci. Soc. Fla. 2004, 63, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Tarkalson, D.D.; Ippolito, J.A. Clinoptilolite Zeolite Influence on Inorganic Nitrogen in Silt Loam and Sandy Agricultural Soils. Soil Sci. 2010, 175, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Li, X. Mechanisms of Irrigation Water Levels on Nitrogen Transformation and Microbial Activity in Paddy Fields. Water 2024, 16, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lim, S.S.; Kwak, J.H.; Baek, W.J.; Yoon, K.S.; Choi, S.M.; Choi, W.J. Nitrogen inputs with different substrate quality modified pH, Eh, and N dynamics of a paddy soil incubated under waterlogged conditions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 2234–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.A.; Sulman, B.N.; Mayes, M.A.; Patterson, C.M.; Classen, A.T. Plant roots stimulate the decomposition of complex, but not simple, soil carbon. Funct. Ecol. 2020, 34, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kong, H.; Wu, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Z. Phosphate immobilization from aqueous solution by fly ashes in relation to their composition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Luan, Z.; Peng, X.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, J.; Jia, Z. Phosphate removal from aqueous solutions using raw and activated red mud and fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.G.; Bai, S.Q.; Zhu, L.; Shan, H.D. Removal Mechanism of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution by Fly Ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husson, O. Redox potential (Eh) and pH as drivers of soil/plant/microorganism systems: A transdisciplinary overview pointing to integrative opportunities for agronomy. Plant Soil 2013, 362, 389–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Gruau, G.; Dupas, R.; Petitjean, P.; Li, Q.; Pinay, G. Respective roles of Fe- oxyhydroxide dissolution, pH changes and sediment inputs in dissolved phosphorus release from wetland soils under anoxic conditions. Geoderma 2019, 338, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Fahad, S.; Wu, L.; Zhou, W.; Xu, P.; Sun, Z.; Salam, A.; Imran, M.; Jiang, M.; Kuzyakov, Y.; et al. Labile Organic Matter Intensifies Phosphorous Mobilization in Paddy Soils by Microbial Iron (III) Reduction. Geoderma 2019, 352, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Hsu, L.C.; Liu, Y.T.; Wang, S.L.; White, J.R.; Shaheen, S.M.; Chen, Q.; Rinklebe, J. Soil acidification enhances the mobilization of phosphorus under anoxic conditions in an agricultural soil: Investigating the potential for loss of phosphorus to water and the associated environmental risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Ha, H.S.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, Y.B.; Kim, P.J. Fly Ash Effect on Improving Soil Properties and Rice Productivity in Korean Paddy Soils. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Sahu, R.K.; Padhy, R.N. Growth, Yield and Elemental Status of Rice (Oryza sativa) Grown in Fly Ash Amended Soils. Ecotoxicology 2007, 16, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautaray, S.K.; Ghosh, B.C.; Mittra, B.N. Effect of Fly Ash, Organic Wastes and Chemical Fertilizers on Yield, Nutrient Uptake, Heavy Metal Content and Residual Fertility in a Rice-Mustard Cropping Sequence under Acid Lateritic Soils. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 90, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.P.; Siddiqui, Z.A. Effects of fly ash and Helminthosporium oryzae on growth and yield of three cultivars of rice. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 86, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aref, F. Effect of saline irrigation water on yield and yield components of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 3503–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, F.; Rad, H.E. Physiological characterization of rice under salinity stress during vegetative and reproductive stages. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xia, G.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, J.; Jin, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, S.; Chi, D. The influence of zeolite amendment on yield performance, quality characteristics, and nitrogen use efficiency of paddy rice. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 2777–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavoosi, M. Effects of Zeolite Application on Rice Yield, Nitrogen Recovery, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2007, 38, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepaskhah, A.R.; Barzegar, M. Yield, water and nitrogen-use response of rice to zeolite and nitrogen fertilization in a semi-arid environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Núñez, J.E.; Barahona-Amores, L.A.; Castillo-Ortiz, O.A. Effect of zeolite on the nitrogen fertilizer efficiency in rice crop. Agron. Mesoam. 2015, 26, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lim, S.S.; Kwak, J.H.; Lee, S.I.; Lee, D.S.; Hao, X.; Yoon, K.S.; Choi, W.J. Soil and compost type affect phosphorus leaching from Inceptisol, Ultisol, and Andisol in a column experiment. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2007, 42, 2188–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 9.3 (0.0) |
| EC (dS m−1) | 19.3 (0.0) |
| Total organic C (mg C L−1) | 1.73 (0.01) |
| Nitrogen (g N L−1) | Total N, 3.18 (0.20); NH4+, 0.73 (0.02); NO3−, 0.02 (0.00); organic N, 2.43 (0.19) |
| Total P (g P L−1) | 0.113 (0.01) |
| Cations (mg L−1) | Ca, 37.4 (0.2); K, 2252.3 (8.4); Mg, 2.1 (0.0); Na, 410.3 (3.6) |
| Variable | Fly Ash | Zeolite | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH (1:5) | 11.7 (0.1) | 6.9 (0.1) | |
| EC1:5 (dS m−1) | 1.55 (0.02) | 0.17 (0.01) | |
| T-C (g C kg−1) | 24.2 (0.1) | 0.29 (0.02) | |
| T-N (g N kg−1) | 0.60 (0.01) | 0.07 (0.00) | |
| T-P (g P kg−1) | 1.58 (0.01) | 0.11 (0.01) | |
| Cation exchange capacity (cmolc kg−1) | 1.8 (0.0) | 107.0 (0.0) | |
| Particle-size distribution (%) | Clay | 1.8 (0.8) | 53.1 (0.8) |
| Silt | 75.4 (0.6) | 31.0 (0.7) | |
| Sand | 1.9 (0.8) | 15.9 (0.0) | |
| Specific surface area (m2 g−1) | 1.8 (0.1) | 53.2 (2.2) | |
| Treatment Code a | Nutrient Inputs (g m−2) b | Soil Amendments (FAZ) (kg m−2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Source | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| Control | No input | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ControlFAZ | No input | 0 | 0 | 0 | 26 |
| CF | CF | 11 | 1.97 | 5.56 | 0 |
| CFFAZ | CF | 11 | 1.97 | 5.56 | 26 |
| LPMS | LPMS | 11 | 2.36 | 7.8 | 0 |
| LPMS+FAZ | LPMS | 11 | 2.36 | 7.8 | 26 |
| LPMD | LPMD | 22 | 2.75 | 15.6 | 0 |
| LPMD+FAZ | LPMD | 22 | 2.75 | 15.6 | 26 |
| Treatment Code a | DOC (mg C L−1) | Nitrogen (mg N L−1) | Phosphorus (mg P L−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T–N | NH4+ | NO3− | Organic N | T–P | Soluble P | Particulate P | ||
| Control | 7.7 (0.3) b | 14.8 (0.4) e | 5.0 (0.7) cd | 0.20 (0.1) a | 9.6 (0.8) e | 0.10 (0.0) a | 0.08 (0.0) a | 0.02 (0.02) a |
| ControlFAZ | 5.3 (0.7) a | 10.9 (0.5) ab | 4.7 (0.2) bc | 0.24 (0.1) ab | 6.1 (0.5) bc | 0.27 (0.0) ab | 0.22 (0.0) ab | 0.06 (0.03) a |
| CF | 8.4 (0.6) bc | 12.0 (0.5) c | 6.7 (0.9) f | 0.32 (0.2) ab | 5.0 (1.0) a | 0.22 (0.1) ab | 0.15 (0.0) a | 0.09 (0.08) a |
| CFFAZ | 7.2 (0.6) b | 13.6 (0.4) d | 6.0 (0.5) ef | 0.41 (0.1) b | 8.0 (0.4) d | 0.39 (0.1) bcd | 0.33 (0.1) bc | 0.08 (0.04) a |
| LPMS | 11.1 (0.6) d | 11.4 (0.4) b | 5.7 (0.7) de | 0.32 (0.1) ab | 5.3 (0.9) ab | 0.21 (0.1) a | 0.18 (0.1) ab | 0.03 (0.02) a |
| LPMS+FAZ | 9.4 (1.5) cd | 12.1 (0.7) c | 4.0 (0.3) ab | 0.17 (0.1) a | 7.9 (0.5) d | 0.46 (0.1) cd | 0.43 (0.1) cd | 0.09 (0.05) a |
| LPMD | 11.9 (0.6) d | 23.2 (0.8) f | 6.8 (0.8) f | 0.21 (0.1) a | 16.3 (1.0) f | 0.33 (0.1) abc | 0.26 (0.1) abc | 0.07 (0.04) a |
| LPMD+FAZ | 7.3 (0.4) b | 10.3 (0.6) a | 3.3 (0.3) a | 0.22 (0.0) ab | 6.7 (0.6) c | 0.72 (0.1) d | 0.56 (0.2) d | 0.27 (0.21) b |
| Effects | Probability > F | |||||||
| Nutrient source (N) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.045 | <0.001 | 0.014 | 0.003 | <0.001 |
| FAZ | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.931 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| N × FAZ | 0.014 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.205 | <0.001 | 0.406 | 0.545 | 0.003 |
| Treatment Code a | Dry Matter (g m −2) | Nutrient Uptake (g m−2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root | Shoot | Grain | Total | N | P | |
| Control | 125.8 (8.2) a | 277.8 (16.7) a | 287.5 (29.0) a | 691.0 (50.1) a | 2.8 (0.4) a | 3.1 (0.4) a |
| ControlFAZ | 141.9 (14.7) a | 344.9 (20.0) ab | 399.1 (17.3) ab | 885.9 (38.6) ab | 3.8 (0.2) ab | 3.4 (0.3) a |
| CF | 230.5 (19.1) b | 594.2 (55.2) c | 574.7 (35.4) b | 1399.4 (88.2) d | 5.8 (0.8) c | 6.3 (0.4) c |
| CFFAZ | 230.8 (13.1) b | 553.8 (23.3) c | 523.5 (81.8) ab | 1308.1 (83.6) cd | 7.3 (0.6) d | 5.0 (0.7) bc |
| LPMS | 154.7 (12.7) a | 478.3 (30.8) bc | 374.9 (28.0) ab | 1007.9 (32.0) abc | 5.1 (0.5) bc | 4.1 (0.3) ab |
| LPMS+FAZ | 183.6 (10.8) ab | 402.4 (14.4) ab | 466.1 (36.9) ab | 1052.1 (46.7) bc | 5.2 (0.4) bc | 4.0 (0.4) ab |
| LPMD | 195.3 (14.1) ab | 394.6 (14.5) ab | 410.6 (15.8) ab | 1000.4 (32.4) abc | 5.8 (0.6) c | 4.0 (0.2) ab |
| LPMD+FAZ | 164.3 (13.4) ab | 466.0 (25.2) bc | 519.1 (35.4) ab | 1149.3 (70.0) bcd | 5.1 (0.1) bc | 4.3 (0.6) ab |
| Effects | Probability > F | |||||
| Nutrient source (N) | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.087 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FAZ | 0.815 | 0.862 | 0.240 | 0.322 | 0.175 | 0.507 |
| N × FAZ | 0.536 | 0.273 | 0.664 | 0.529 | 0.135 | 0.249 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-I.; Baek, N.; Park, S.-W.; Shin, E.-S.; Lee, J.; Ham, J.-H.; Choi, W.-J. Ponding Water Quality of Rice Paddies Fertilized with Anaerobically Digested Liquid Pig Manure as Affected by Fly Ash and Zeolite. Water 2025, 17, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081189
Lee S-I, Baek N, Park S-W, Shin E-S, Lee J, Ham J-H, Choi W-J. Ponding Water Quality of Rice Paddies Fertilized with Anaerobically Digested Liquid Pig Manure as Affected by Fly Ash and Zeolite. Water. 2025; 17(8):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081189
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Se-In, Nuri Baek, Seo-Woo Park, Eun-Seo Shin, Jiyu Lee, Jong-Hyun Ham, and Woo-Jung Choi. 2025. "Ponding Water Quality of Rice Paddies Fertilized with Anaerobically Digested Liquid Pig Manure as Affected by Fly Ash and Zeolite" Water 17, no. 8: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081189
APA StyleLee, S.-I., Baek, N., Park, S.-W., Shin, E.-S., Lee, J., Ham, J.-H., & Choi, W.-J. (2025). Ponding Water Quality of Rice Paddies Fertilized with Anaerobically Digested Liquid Pig Manure as Affected by Fly Ash and Zeolite. Water, 17(8), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081189






