Influence of Key Physicochemical Factors on the Temporal Dynamics of Invasive and Native Ascidian Settlement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Assessment of Abiotic and Biotic Environmental Factors
2.3. Settlement Plate Placement
2.4. In Situ Species Assessment and Systematic Classification
2.5. Redundancy Analysis (RDA) and ANOVA Permutation Test on the Influence of Environmental Variables on Species Presence
3. Results
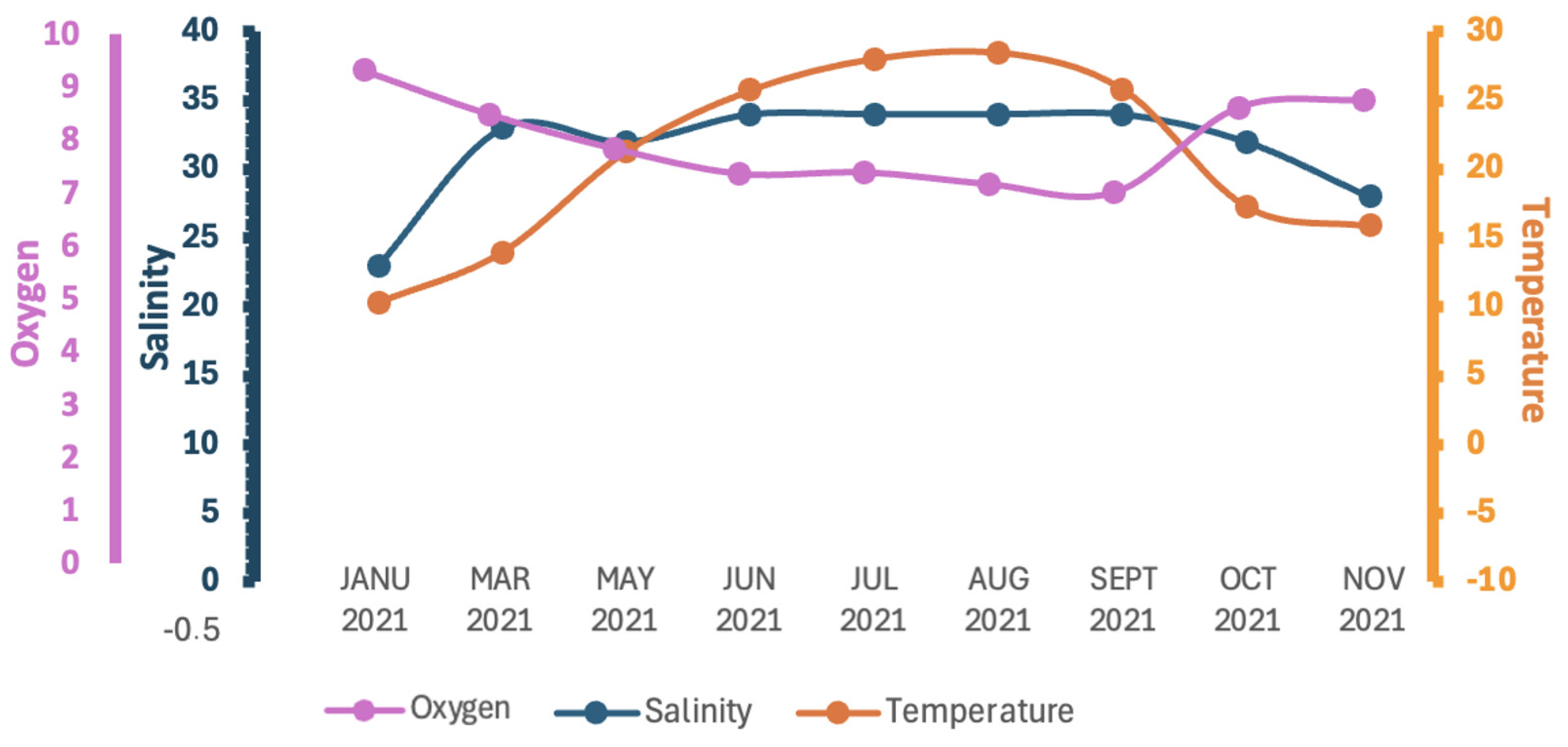
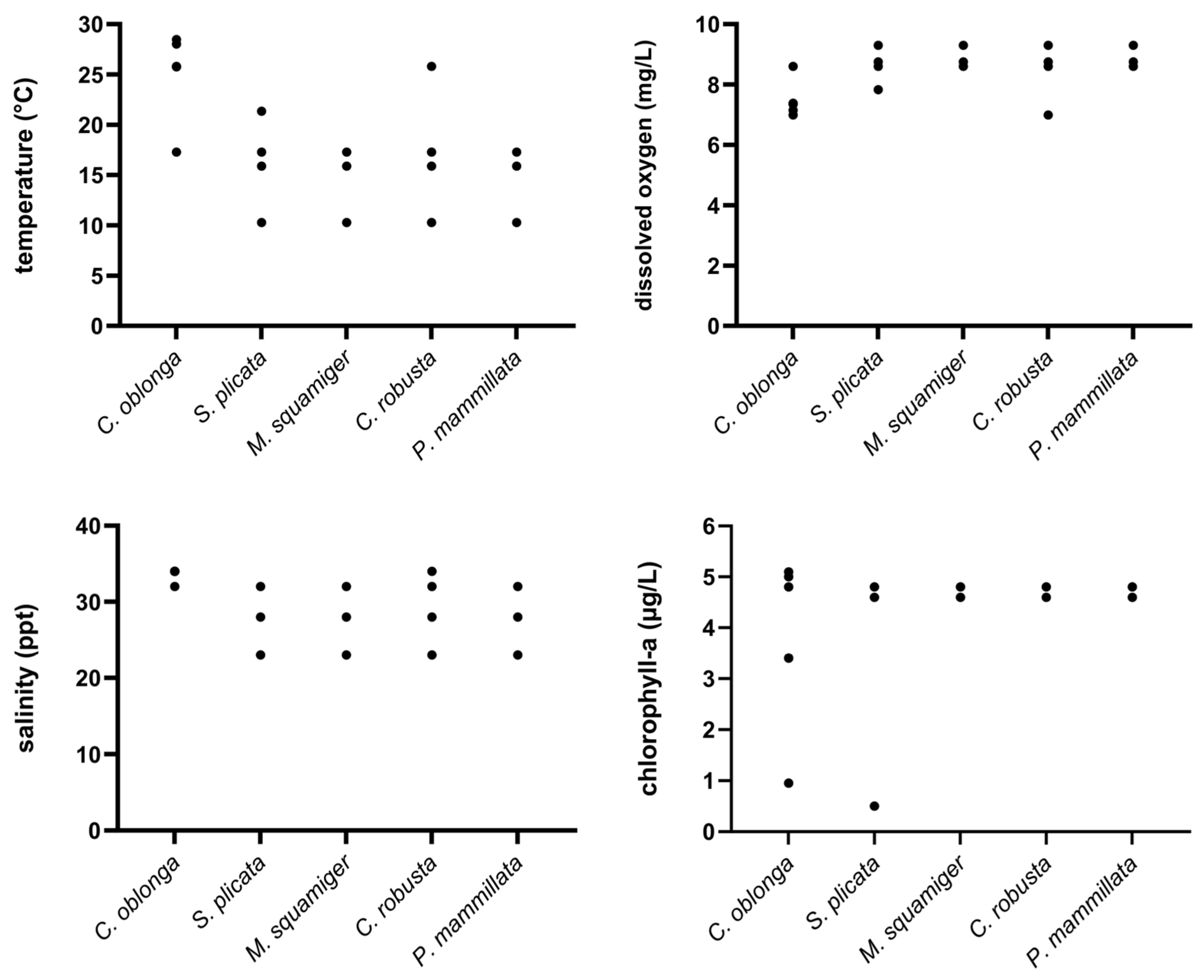
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters
3.2. Species Recruitment
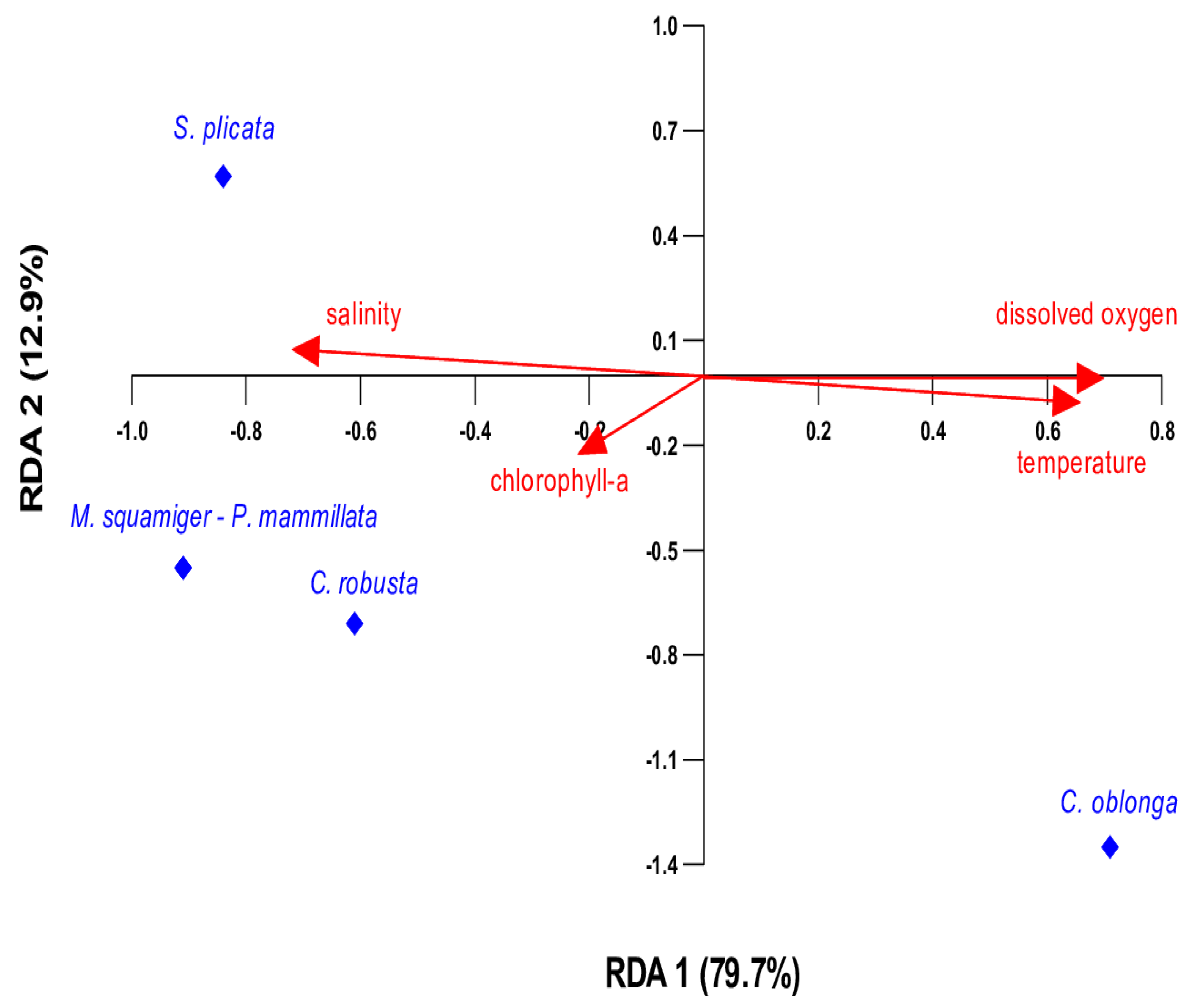
3.3. Influence of Environmental Variables on Species Presence/Absence: Insights from Redundancy Analysis (RDA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papadopoulos, D.K.; Lattos, A.; Giantsis, I.A.; Theodorou, J.A.; Michaelidis, B.; Feidantsis, K. The impact of ascidian biofouling on the farmed Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis physiology and welfare, revealed by stress biomarkers. Biofouling 2023, 39, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidantsis, K.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Lattos, A.; Theodorou, J.A.; Michaelidis, B.; Giantsis, I.A. Effects of biofouling by ascidians on cultured mussels: Apoptosis, autophagy, and antioxidant defense. J. Shellfish Res. 2023, 42, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvanou, M.; Feidantsis, K.; Papadopoulos, D.; Lattos, A.; Theodorou, J.; Michaelidis, B.; Giantsis, I. Major ascidian species with negative impacts on bivalve aquaculture: Current knowledge and future research aims. Open Geosci. 2024, 16, 20220660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, C.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Bailly, N. Ascidiacea (Chordata: Tunicata) of Greece: An updated checklist. Biodivers Data J. 2016, 4, e9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, W. Growth and survival of the bay scallop, Argopectenirradians, at various locations in the water column and at various densities. Proc. Natl. Shellfish. Ass. 1973, 63, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Leighton, D. A growth profile for the rock scallop Hinnitesmultirugosus held at several depths off La Jolla, California. Mar. Biol. 1978, 51, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, D. Control of sabellid infestation in green and pink abalones, Haliotis fulgens and H. corrugate, by exposure to elevated water temperatures. J. Shellfish Res. 1998, 17, 701–705. [Google Scholar]
- Côté, J.; Himmelman, J.H.; Claereboudt, M.; Bonardelli, J.C. Influence of density and depth in the growth of juvenile sea scallps (Placopectenmagellanicus) in suspended culture. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 1857–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, U.A.W. The Potential for Cultivation and Restocking of Pecten maximus (L.) and Aequipectenopercularis (L.) on Manx Inshore Fishing Grounds. Ph.D. Thesis, Port Erin Marine Laboratory, University of Liverpool, Isle of Man, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lodeiros, C.J.M.; Himmelman, J.H. Influence of fouling on the growth and survival of the tropical scallop, Euvola (Pecten) ziczac (L. 1758) in suspended culture. Aquacult. Res. 1996, 27, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsotsios, D.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Alvanou, M.V.; Georgoulis, I.; Lattos, A.; Michaelidis, B.; Feidantsis, K.; Giantsis, I.A.; Theodorou, J.A. Environmentally friendly and efficient methods for mitigating the density of ascidian fouling in mediterranean mussel farming. Fishes 2024, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claereboudt, M.R.; Bureau, D.; Côte, J.; Himmelman, J.H. Fouling development and its effect on the growth of juvenile giant scallops (Placopectenmagellanicus) in suspended culture. Aquaculture 1994, 121, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguenin, J.E.; Huguenin, S.S. Biofouling resistant shellfish trays. J. Shellfish Res. 1982, 2, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Enright, C. Control of biofouling in aquaculture. World Aquac. 1993, 24, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.T.; Blake, N.J. The culture of the southern bay scallop in Tampa bay, an urban Florida estuary. Aquac. Int. 1997, 5, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, E.R.; Cheshire, A.C.; Clarke, S.M.; Melville, A.J. An investigation into the composition, biomass and oxygen budget of the fouling community on a tuna aquaculture farm. Biofouling 1999, 13, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazouni, N.; Gaertner, J.C.; Deslou-Paoli, J.M. Composition of biofouling communities on suspended oyster cultures: An in situ study of their interactions with the water column. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2001, 214, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. Water Quality Management for Pond Fish Culture; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Laired, L.; Needham, T. Salmon and Trout Farming; Ellis Horwood Limited: Chichester, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Daigle, R.M.; Herbinger, C.M. Ecological interactions between the vase tunicate (Ciona intestinalis) and the farmed blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) in Nova Scotia, Canada. Aquat. Invasions 2009, 4, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, A.J.; Perdikaris, C.; Spinos, E. On the occurrence of rayed pearl oyster Pinctada imbricata radiata (Leach, 1814) in Western Greece (Ionian Sea) and its biofouling potential. Biharean Biol. 2019, 13, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tsotsios, D.; Moutopoulos, D.K.; Lattos, A.; Michaelidis, B.; Theodorou, J.A. Impacts of the Establishment of Biofoulants on Greek Aquaculture: Farmers’ Expert Knowledge. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, W.R. Environmental factors affecting reproduction and development in ascidians and other prochordates. Can. J. Zool. 2005, 83, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, G. Ecology and natural history of the protochordates. Can. J. Zool. 2005, 83, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, G. Invasive sea squirts: A growing global problem. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 1, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, R.; Ribes, M.; Gili, J.M.; Zabala, M. Seasonality in coastal benthic ecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2000, 15, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turon, X. The ascidians of Tossa de Mar (NE Spain) 2. Biological cycles of the colonial species. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1988, 29, 407–418. [Google Scholar]
- Turon, X. Periods of non-feeding in Polysyncratonlacazei (Ascidiacea: Didemnidae): A rejuvenative process? Mar. Biol. 1992, 112, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Portela, R.; Palacin, C.; Duran, S.; Turon, X. Biological traits of three closely related species of Pycnoclavella (Ascidiacea) in the Western Mediterranean. Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorson, G. Light as an ecological factor in the dispersal and settlement of larvae of marine bottom invertebrates. Ophelia 1964, 1, 167–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, K.M. Larval behavior, settlement preference, and induction of metamorphosis in the temperate solitary ascidian Molgulacitrina Alder & Hancock. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1991, 145, 175–187. [Google Scholar]
- Rius, M.; Branch, G.M.; Griffiths, C.L.; Turon, X. Larval settlement behaviour in six gregarious ascidians in relation to adult distribution. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 418, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R. Pheromones and the gregarious settlement of marine invertebrate larvae. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1986, 39, 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlik, J. Chemical ecology of the settlement of benthic marine-invertebrates. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 1992, 30, 273–335. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, A.; Beveridge, C.M.; Cowling, M.J.; Hodgkiess, T.; Parr, A.C.S.; Smith, M.J. Some physical factors affecting the accumulation of biofouling. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1999, 79, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavestrello, G.; Bianchi, C.N.; Calcinai, B.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Cerrano, C.; Morri, C.; Puce, S.; Sara, M. Bio-mineralogy as a structuring factor for marine epibenthic communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 193, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, A.; Davidson, J.; Bourque, D.; Stryhn, H. Recruitment patterns and population development of the invasive ascidian Ciona intestinalis in Prince Edward Island, Canada. Aquat. Invasions. 2009, 4, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, C.M.C.; Floerl, O.; Hayden, B.J. Biofouling on Greenshell™ mussel (Perna canaliculus) farms: A preliminary assessment and potential implications for sustainable aquaculture practices. Aquacult. Int. 2012, 20, 537–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katselis, G.N.; Moutopoulos, D.K.; Dimitriou, E.N.; Koutsikopoulos, C. Long-term changes of fisheries landings in enclosed gulf lagoons (Amvrakikos gulf, W Greece): Influences of fishing and other human impacts. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 131, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountoura, K.; Zacharias, I. Temporal and spatial distribution of hypoxic/seasonal anoxic zone in Amvrakikos gulf, Western Greece. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 94, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountoura, K.; Zacharias, I. Trophic state and oceanographic conditions of Amvrakikos Gulf: Evaluation and monitoring. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 2934–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaidou, A.; Moraitou-Apostolopoulou, M.; Ignatiades, L.A. Survey of estuarine benthic, zooplanktonic and phytoplanktonic communities of Amvrakikos Gulf, Ionian Sea. Mar. Ecol.-Pubbl. Stn. Zool. Napoli. 1983, 4, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayotidis, P.; Pancucci, M.A.; Balopoulos, E.; Gotsis-Skretas, O. Plankton distribution patterns in a Mediterranean dilution basin: Amvrakikos Gulf (Ionian Sea, Greece). Mar. Ecol.-Pubbl. Stn. Zool. Napoli 1994, 15, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friligos, N.; Balopoulos, E.T.; Psillidou-Giouranovits, R. Eutrophication and hydrography in the Amvrakikos Gulf, Ionian Sea. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 1997, 6, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ferentinos, G.; Papatheodorou, G.; Geraga, M.; Iatrou, M.; Fakiris, E.; Christodoulou, D.; Dimitriou, E.; Koutsikopoulos, C. Fjord water circulation patterns and dysoxic/anoxic conditions in a Mediterranean semi-enclosed embayment in the Amvrakikos Gulf, Greece. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 88, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehayias, G.; Aposporis, M. Zooplankton variation in relation to hydrology in an enclosed hypoxic bay (Amvrakikos Gulf, Greece). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2014, 15, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubek, J.P.; Campbell, K.L.; Doubek, K.M.; Hamre, K.D.; Lofton, M.E.; McClure, R.P.; Ward, N.K.; Carey, C.C. The effects of hypolimnetic anoxia on the diel vertical migration of freshwater crustacean zooplankton. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanam, P.; Perumal, P. Marine plankton in Indian waters. In Training Manual on GIS and Marine Biodiversity; John Milton, M.C., Ed.; Lyola College Pub: New Delhi, India, 2008; p. 492. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey, S.W.; Humphrey, G.F. New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Und Physiol. Der Pflanz. 1975, 167, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casso, M.; Navarro, M.; Ordóñez, V.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Pascual, M.; Turon, X. Seasonal patterns of settlement and growth of introduced and native ascidians in bivalve cultures in the Ebro Delta (NE Iberian Peninsula). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2018, 23, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, A.J.; Spinos, E.; Ramfos, A.; Tsamadias, E.I.; Bekiari, V.; Kamilari, M.; Ntouni, M.-M.; Tsotsios, D.; Feidantsis, K.; Lattos, A.; et al. Fan Mussel (Pinna nobilis L.) Spat Collection, Monitoring of Early Growth and Conservation Implications by Deploying Conventional Aquaculture Methodology. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukaras, K.; Nikolaidis, G. Dinophysis blooms in Greek coastal waters (Thermaikos Gulf, NW Aegean Sea). J. Plankton Res. 2004, 26, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladakis, G.; Kommata, V.; Kamilari, M.; Papaioannou, C.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Lattos, A.; Michaelidis, B.; Theodorou, I.A.; Batargias, C. Genetic identification of Ascidian species in mussel farm facilities of Greece. In Proceedings of the 18th Panhellenic Ichthyologist Conference, Messolonghi, Greece, 3–6 November 2022; pp. 436–439. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Rius, M.; Heasman, K.G.; McQuaid, C.D. Long-term coexistence of nonindigenous species in aquaculture facilities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2395–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitridge, I.; Dempster, T.; Guenther, J.; de Nys, R. The impact and control of biofouling in marine aquaculture: A review. Biofouling 2012, 28, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, J.R.; Levy, C.; Toft, J.D. Ecological implications of invasive tunicates associated with artificial structures in puget sound, Washington, USA. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 1303–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkanin, C.; Dower, J.F.; Filip, N.; Jamieson, G.; Therriault, T.W. Biotic resistance to the infiltration of natural benthic habitats: Examining the role of predation in the distribution of the invasive ascidian Botrylloides violaceus. J. Exp. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 439, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkanin, C.; Davidson, I.C.; Therriault, T.W.; Jamieson, G.; Dower, J.F. Manipulating propagule pressure to test the invasibility of subtidal marine habitats. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, L.P.; Rocha, R.M. The biotic resistance role of fish predation in fouling communities. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 3223–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.W.; Thiyagarajan, V.; Leung, A.W.Y.; Qian, P.Y. Development of a Marine Subtidal Epibiotic Community in Hong Kong: Implications for Deployment of Artificial Reefs. Biofouling 2003, 19, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezzi, M.; Del Pasqua, M.; Pierri, C.; Giangrande, A. Seasonal non-indigenous species succession in a marine macrofouling invertebrate community. Biol. Invasions 2017, 20, 937–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.M.D. Replacement of the compound ascidian species in a southeastern Brazilian fouling community. Bol. Do Inst.Ocean. 1991, 39, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, V.; Pascual, M.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Turon, X. When invasion biology meets taxonomy: Clavelina oblonga (Ascidiacea) is an old invader in the Mediterranean Sea. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagarajan, V.; Qian, P.-Y. Effect of temperature, salinity and delayed attachment on development of the solitary ascidian Styela plicata (Lesueur). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 290, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.T.; White, M.B.; Egan, A.E. The larval development and metamorphosis of the ascidians Pyurapraeputialis (Heller) and Pyurapachydermatina (Herdman) (Pleurogona, family Pyuridae). Linn. Soc. New South Wales 1976, 100, 205–217. [Google Scholar]
- Cloney, A.R. Ascidian Larvae and the Events of Metamorphosis. Am. Zoolog. 1982, 22, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, N. Embryogenesis: Developmental Biology of Ascidians; Developmental and Cell Biology Series; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; p. 234. [Google Scholar]
- Degnan, M.B.; Souter, D.; Degnan, M.S.; Long, C.S. Induction of metamorphosis with potassium ions requires development of competence and an anterior signallingcentre in the ascidian Herdmaniamomus. Dev. Genes Evol. 1996, 206, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chase, A.L.; Dijkstra, J.A.; Harris, L.G. The influence of substrate material on ascidian larval settlement. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2016, 106, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchemousse, S.; Bishop, J.D.D.; Viard, F. Contrasting global genetic patterns in two biologically similar, widespread and invasive Ciona species (Tunicata, Ascidiacea). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortic, A.; Mavric, B.; Pitacco, V.; Lipej, L. Temporal changes of a fouling community: Colonization patterns of the benthic epifauna in the shallow northern Adriatic Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 45, 101818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, D.M.; de Marco, P., Jr.; Andrade, A.F.; Rocha, R.M. Predicting global ascidian invasions. Divers. Distrib. 2018, 24, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, S. Life in Moving Fluids: The Physical Biology of Flow; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mullineaux, L.; Butman, C. Initial contact, exploration and attachment of barnacle (Balanus amphitrite) cyprids settling in flow. Mar. Biol. 1991, 110, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.R.; Boxshall, A.J. The influence of small-scale flow and chemical cues on the settlement of two congeneric barnacle species. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 183, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bologna, P.a.X.; Heck, K.L. Impacts of seagrass habitat architecture on bivalve settlement. Estuaries 2000, 23, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlbut, C. Community recruitment—Settlement and juvenile survival of 7 cooccurring species of sessile marine-invertebrates. Mar. Biol. 1991, 109, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, L.J.; Miron, G.; Bourget, E. Endoscopic observations of invertebrate larval substratum exploration and settlement. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 182, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, R.W.; Whitlatch, R.B. The influence of resident adults on recruitment: A comparison to settlement. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1995, 190, 169–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, R.W.; Whitlatch, R.B. The influence of resident adults on larval settlement: Experiments with four species of ascidians. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1995, 190, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, M.; Bourget, E. Substratum heterogeneity and complexity influence microhabitat selection of Balanus sp. and Tubulariacrocea larvae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 135, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesh, S.; Wesley, S.G. Influence of substratum colour on the recruitment of macrofouling communities. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2010, 90, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J.A.; Harris, L.G. Maintenance of diversity altered by a shift in dominant species: Implications for species coexistence. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 387, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, V.; Rius, M.; McQuaid, C.D.; Pineda, M.C.; Pascual, M.; Turon, X. Early biotic interactions among introduced and native species reveal cryptic predation and shifts in larval behaviour. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 488, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
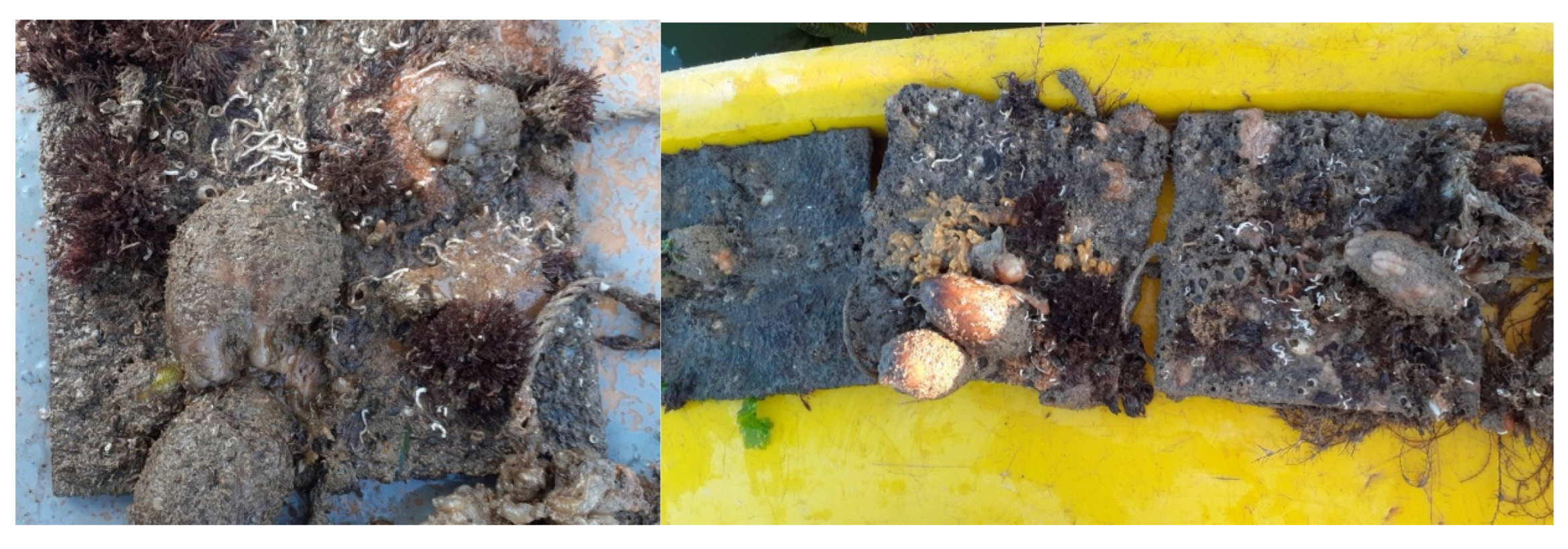

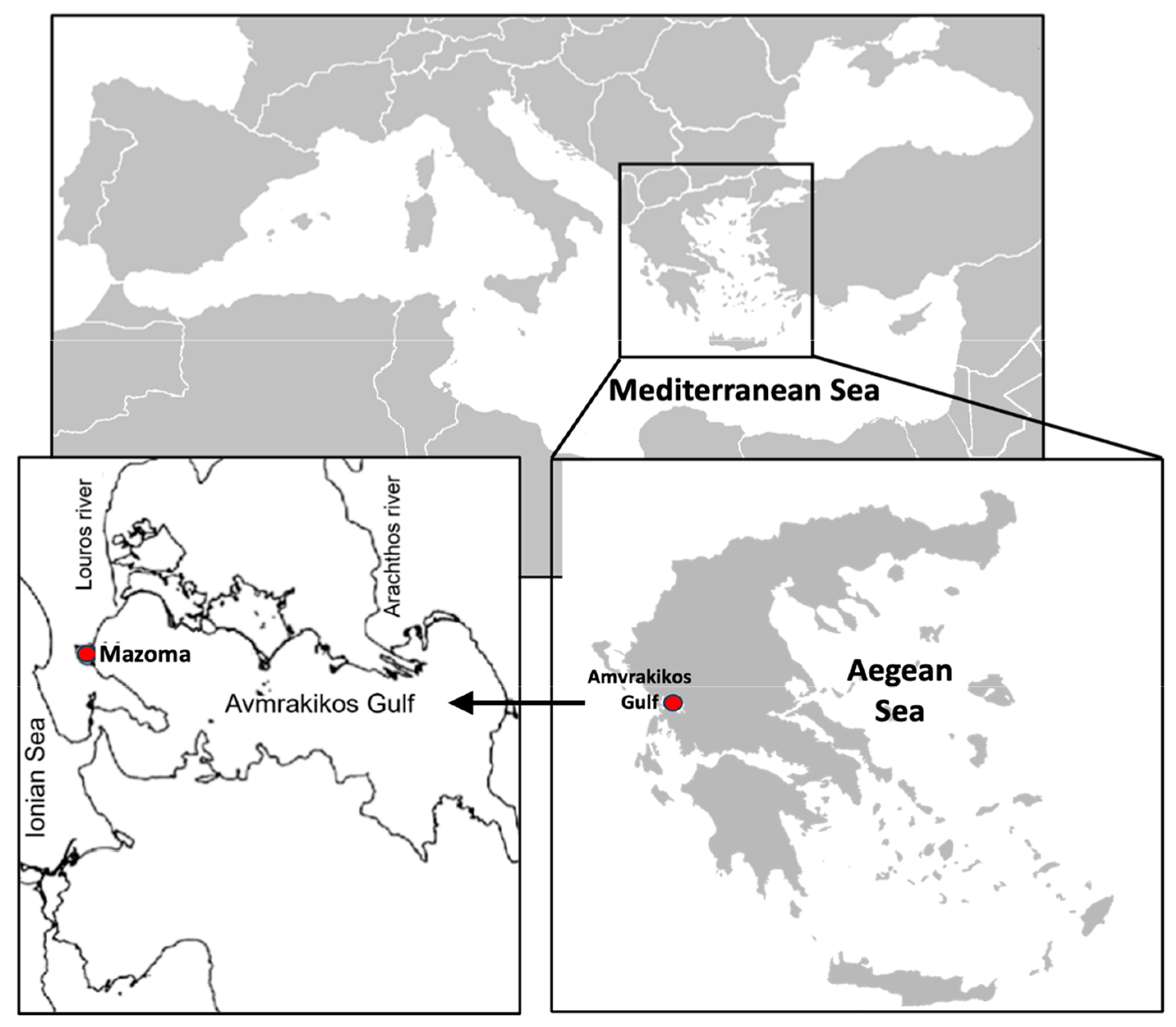

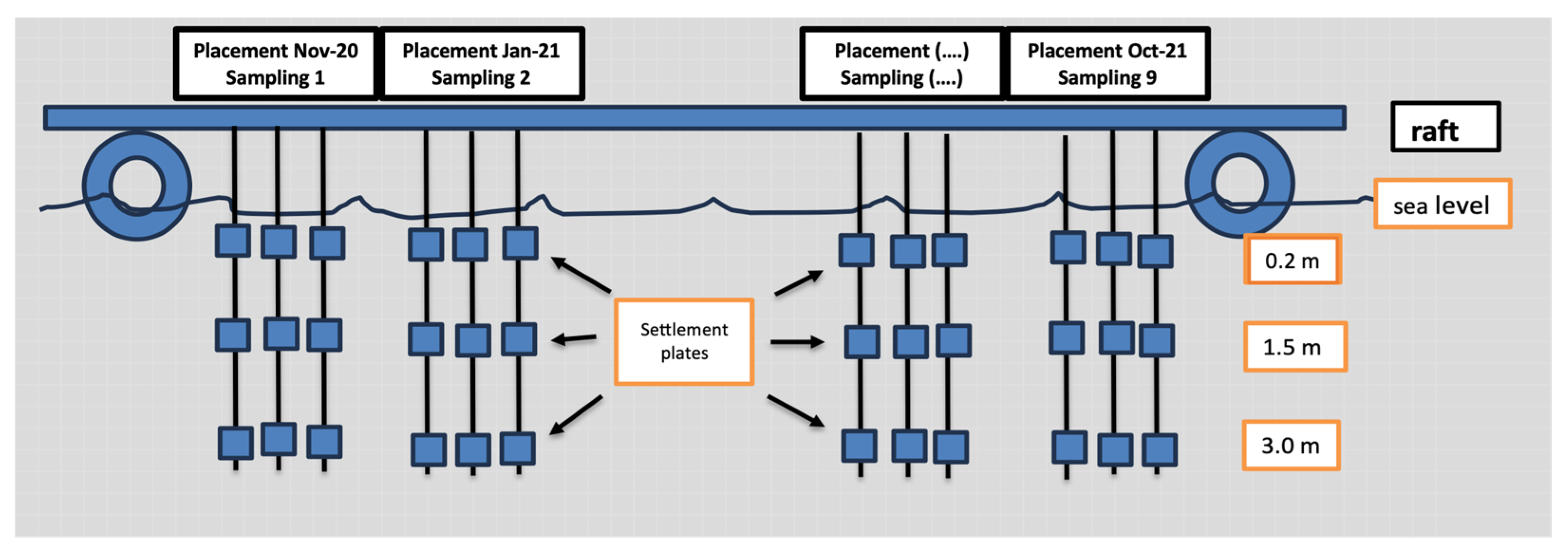



| Sampling Number | Placement | Sampling | Duration in the Sea (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 November | 21 January | 2 |
| 2 | 21 January | 21 March | 2 |
| 3 | 21 March | 21 May | 2 |
| 4 | 21 May | 21 Jun | 1 |
| 5 | 21 Jun | 21 July | 1 |
| 6 | 21 July | 21 August | 1 |
| 7 | 21 August | 21 September | 1 |
| 8 | 21 September | 21 October | 1 |
| 9 | 21 October | 21 November | 1 |
| Month | Salinity | Temperature | Oxygen |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21 January | 23.00 ± 0.74 | 10.28 ± 1.12 | 9.30 ± 0.51 |
| 21 March | 33.00 ± 1.04 | 13.93 ± 0.81 | 8.47 ± 0.73 |
| 21 May | 32.00 ± 0.68 | 21.33 ± 0.83 | 7.83 ± 0.57 |
| 21 Jun | 34.00 ± 0.55 | 25.75 ± 0.59 | 7.35 ± 0.39 |
| 21 July | 34.00 ± 0.73 | 28.02 ± 0.68 | 7.38 ± 0.33 |
| 21 August | 34.00 ± 0.77 | 28.47 ± 0.54 | 7.15 ± 0.42 |
| 21 September | 34.00 ± 0.61 | 25.80 ± 0.60 | 6.99 ± 0.27 |
| 21 October | 32.00 ± 1.12 | 17.28 ± 0.75 | 8.60 ± 0.46 |
| 21 November | 28.00 ± 1.28 | 15.88 ± 0.64 | 8.75 ± 0.32 |
| Month | TOC (mgL−1) | TN (mgL−1) | NH4+ (mgL−1) | NO3− (mgL−1) | NO2− (mgL−1) | PO43− (mgL−1) | Chl-a (mgm−3) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 January | 8.82 | 0.568 | <0.016 | 0.295 | 0.034 | 0.29 | 4.82 | 8.33 |
| 21 March | 4.50 | 0.695 | <0.015 | 0.415 | 0.043 | 0.38 | 5.26 | 8.34 |
| 21 May | 1.24 | 0.220 | <0.015 | 0.113 | <0.015 | <0.05 | 0.50 | 8.32 |
| 21 Jun | 2.01 | 0.223 | <0.015 | 0.126 | <0.015 | <0.05 | 0.95 | 8.32 |
| 21 July | 8.04 | 0.293 | <0.015 | 0.174 | <0.015 | 0.08 | 3.43 | 8.25 |
| 21 August | 8.93 | 0.387 | <0.015 | 0.299 | 0.019 | 0.19 | 4.98 | 8.21 |
| 21 September | 9.82 | 0.392 | <0.015 | 0.283 | 0.022 | 0.26 | 5.08 | 8.35 |
| 21 October | 10.68 | 0.453 | <0.015 | 0.374 | 0.029 | 0.28 | 4.76 | 8.36 |
| 21 November | 10.59 | 0.447 | <0.015 | 0.361 | 0.032 | 0.28 | 4.64 | 8.35 |
| Df | Variance | F | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| chlorophyll-a | 1 | 0.143 | 1.44 | 0.266 |
| temperature | 1 | 0.550 | 5.57 | 0.029 * |
| salinity | 1 | 0.050 | 0.51 | 0.645 |
| dissolved oxygen | 1 | 0. 194 | 1.97 | 0.178 |
| residual | 4 | 0.394 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsotsios, D.; Alvanou, M.V.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Bekiari, V.; Feidantsis, K.; Giantsis, I.A.; Theodorou, J.A. Influence of Key Physicochemical Factors on the Temporal Dynamics of Invasive and Native Ascidian Settlement. Water 2025, 17, 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081122
Tsotsios D, Alvanou MV, Papadopoulos DK, Bekiari V, Feidantsis K, Giantsis IA, Theodorou JA. Influence of Key Physicochemical Factors on the Temporal Dynamics of Invasive and Native Ascidian Settlement. Water. 2025; 17(8):1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081122
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsotsios, Dimitrios, Maria V. Alvanou, Dimitrios K. Papadopoulos, Vlasoula Bekiari, Konstantinos Feidantsis, Ioannis A. Giantsis, and John A. Theodorou. 2025. "Influence of Key Physicochemical Factors on the Temporal Dynamics of Invasive and Native Ascidian Settlement" Water 17, no. 8: 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081122
APA StyleTsotsios, D., Alvanou, M. V., Papadopoulos, D. K., Bekiari, V., Feidantsis, K., Giantsis, I. A., & Theodorou, J. A. (2025). Influence of Key Physicochemical Factors on the Temporal Dynamics of Invasive and Native Ascidian Settlement. Water, 17(8), 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081122











