Multivariate Statistics and Hydrochemistry Combined to Reveal the Factors Affecting Shallow Groundwater Evolution in a Typical Area of the Huaibei Plain, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
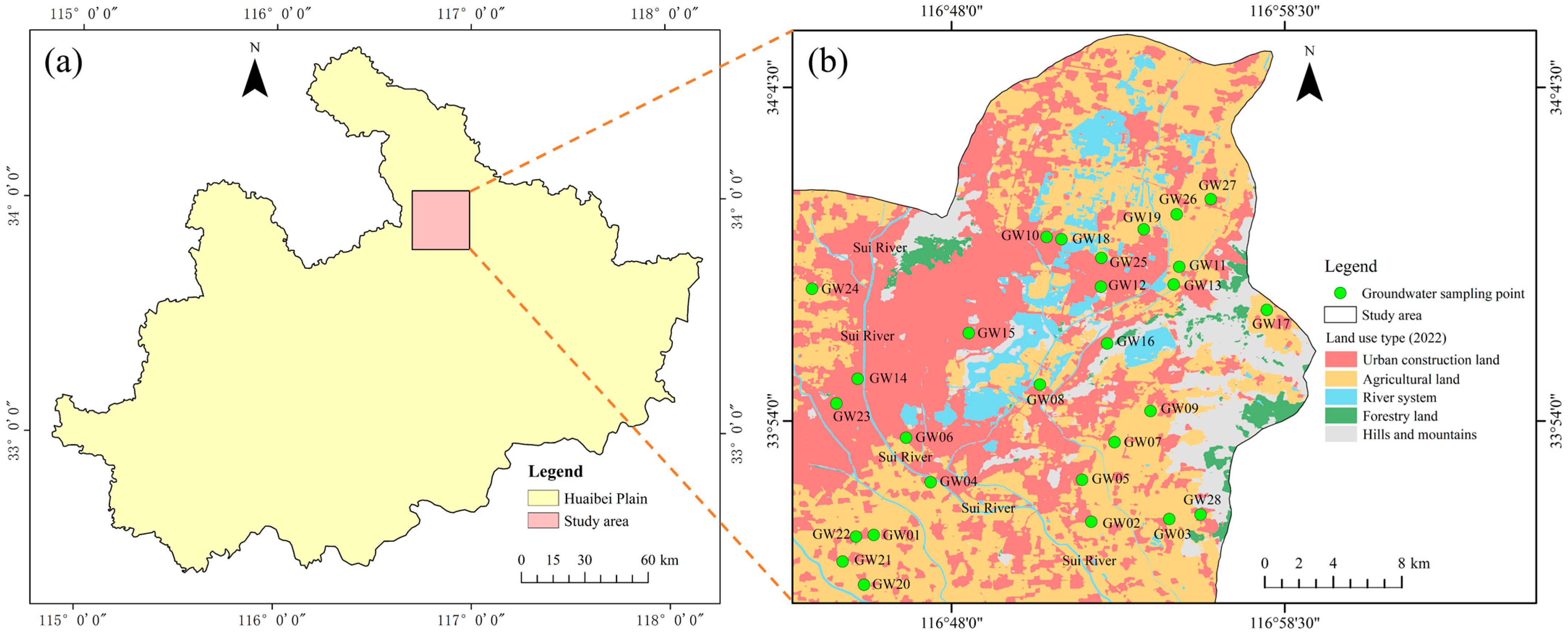
2. Study Area
3. Sample Collection and Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
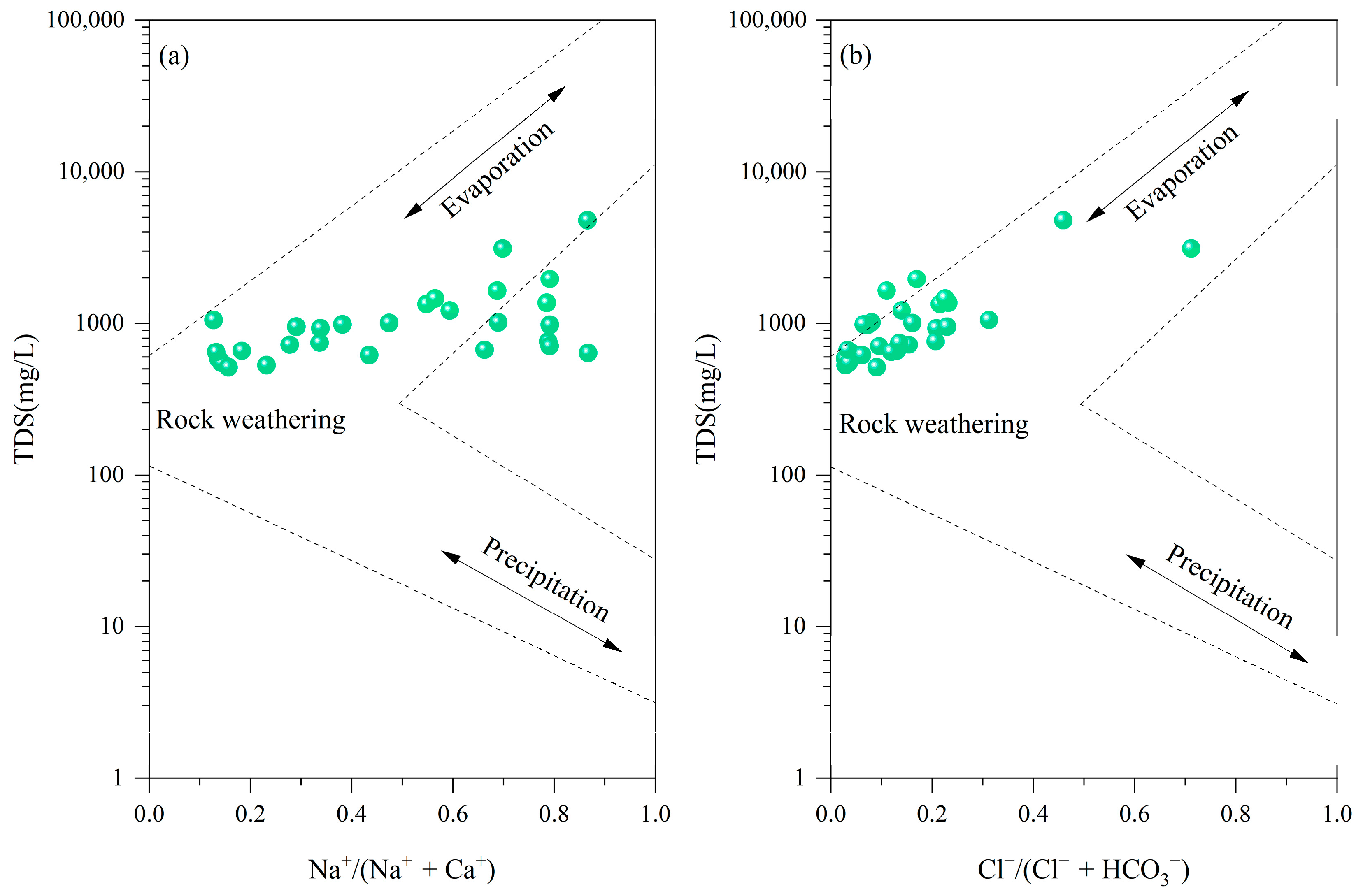
4.2. Hydrochemical Types and Controlling Factors
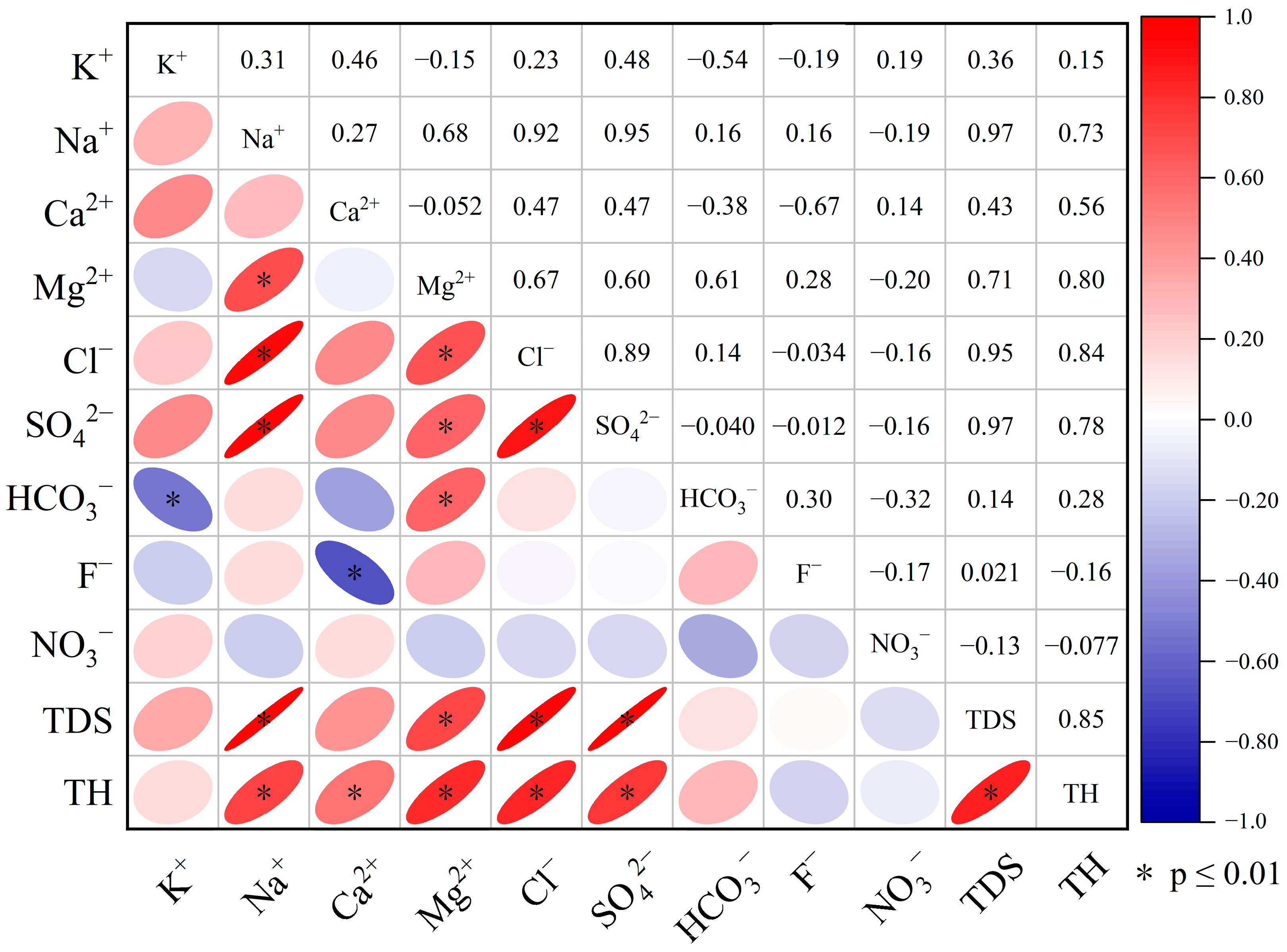
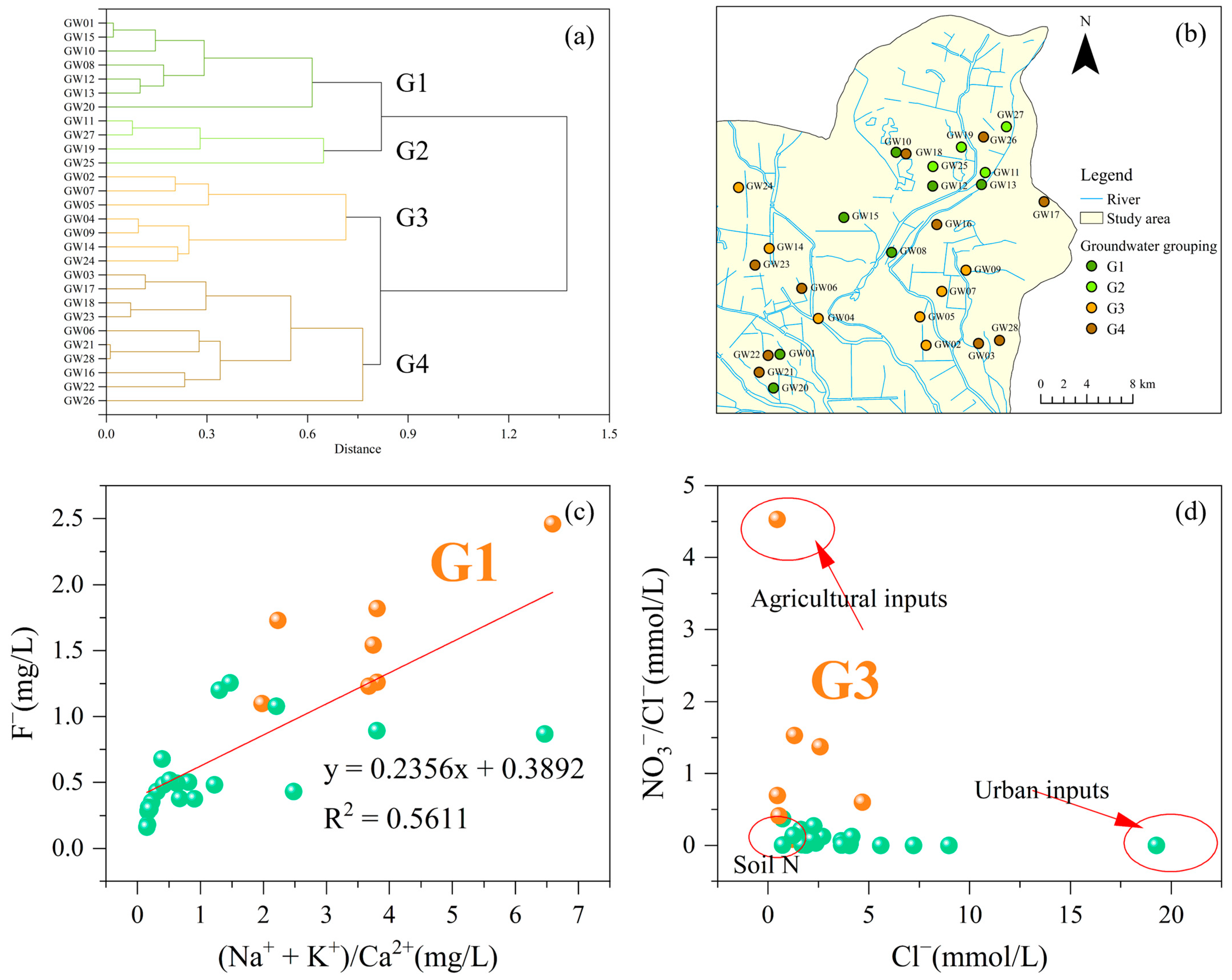
4.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, C.F.; Gong, J.S.; Tao, X.H.; Tan, M.J.; Zhou, K.E.; Wang, H.S.; Li, L.; Ye, Y.H. Comparison of the hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in the Huaihe river basin during a ten-year period and its significance to environmental change. East China Geol. 2023, 44, 282–291. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhou, K.E.; Li, J.; Gong, J.S.; Tan, M.J.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, Y.X.; Liu, L.; Ye, Y.H. Chemical influence factors and contribution rate in shallow groundwater of Wuxi City. East China Geol. 2024, 45, 440–451. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Xing, H.X.; Gong, J.S.; Wang, H.S.; Zhou, K.E.; Zhu, Y.X.; Deng, T.T. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in northern Tai lake basin. East China Geol. 2022, 43, 217–226. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.S.; Gong, J.S.; Tao, X.H.; Zhao, G.Z.; Guo, P.Z.; Zhou, K.E.; Jiao, T.L.; Tan, M.J.; Zhu, C.F.; Xu, N.Z.; et al. Analysis of multi-year rainfall variation and shallow groundwater flow field monitoring in Huaibei plain. Geol. China 2022, 49, 1778–1791. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, R.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, S.M.; Xia, M.; Wang, H.J. Spatiotemporal patterns of the shallow groundwater depth across the Huaibei plain. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2020, 59, 110–119. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Shu, L.; Wang, Z.; Lu, C.; Liu, B. Time-frequency analysis of groundwater depth variation based on the ICA-WTC composite method. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128914. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.; Mohapatra, G.; Arora, R. Spatio-temporal variation of depth to groundwater level and its driving factors in arid and semi-arid regions of India. Reg. Sustain. 2024, 5, 100143. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.M.; Wang, Z.L.; Du, F.G.; Hu, Y.S.; Lu, L. Study on the influence of groundwater depth on soil water change in shallow buried area of Huaibei plain. Water Sav. Irrig. 2019, 9, 6–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Lü, H.; Yagci, A.L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Pan, Y.; Su, J. Influence of groundwater on the propagation of meteorological drought to agricultural drought during crop growth periods: A case study in Huaibei plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 305, 109122. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Feng, S.; Qiu, H.; Liu, J. Interaction between the hydrochemical environment, dissolved organic matter, and microbial communities in groundwater: A case study of a vegetable cultivation area in Huaibei plain, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 895, 165166. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Hou, X.; Lin, M.; Ren, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, X. Multi-isotopes and hydrochemistry combined to reveal the major factors affecting Carboniferous groundwater evolution in the Huaibei coalfield, North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Gui, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, J. Spatial distributions of microbial diversity in the contaminated deep groundwater: A case study of the Huaibei coalfield. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120866. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, G.V.; Ghosh, P.K. Groundwater quality in high-sulfur coal mining region of India: Spatial distribution, source control, and health risk assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 368, 122281. [Google Scholar]
- Neogi, B.; Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, A.K. Groundwater geochemistry and risk assessment to human health in North Karanpura coalfield, India. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2023, 20, 100897. [Google Scholar]
- Kazapoe, R.W.; Addai, M.O.; Amuah, E.E.Y.; Dankwa, P. Characterization of groundwater in southwest Ghana: Implications for sustainable agriculture and safe water supply in a mining-dominated zone. Environ. Sustain. Ind. 2024, 22, 100341. [Google Scholar]
- Abu, M.; Zango, M.S.; Nunoo, S.; Anim-Gyampo, M. Groundwater characterization including prediction of the quality, fluoride, and nitrate occurrence in a typical artisanal mining area in Ghana: A hydrochemical and multivariate statistical approach. Groundwater Sust. Dev. 2023, 23, 101041. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Gui, H.; Xu, H.; Cui, L.; Yu, H. Occurrence, controlling factors and noncarcinogenic risk assessment based on Monte Carlo simulation of fluoride in mid-layer groundwater of Huaibei mining area, North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Gui, H.; Xu, H.; Cui, L.; Li, Z.; Yu, H. Quantifying nitrate pollution sources of shallow groundwater and related health risks based on deterministic and Monte Carlo models: A study in Huaibei mining area, Huaibei coalfield, China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2023, 249, 114434. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, H.X.; Li, L.; Ge, W.Y.; Ye, N.J.; Gong, J.S.; Zhou, K.E.; Zhu, C.F. Spatial distribution characteristics and origin of fluorine in groundwater of Huaibei city, Anhui province. Acta Geoscientica Sinica. 2014, 35, 163–168. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Ye, N.J.; Xing, H.X.; Zhu, C.F.; Gong, J.S. Distribution feature and influence factors analysis of high fluorine shallow groundwater of Suixi county, Anhui province. J. Nat. Sci. Hunan Norm. Univ. 2014, 37, 7–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Jia, C.; Yang, X.; Yang, H.; Chang, W. Probabilistic potential health risk quantification, hydrochemistry, driving forces of groundwater nitrate and fluoride in a typical irrigation district, northern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116171. [Google Scholar]
- Kom, K.P.; Gurugnanam, B.; Bairavi, S. Non-carcinogenic health risk assessment of nitrate and fluoride contamination in the groundwater of Noyyal basin, India. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 619–631. [Google Scholar]
- Jannat, J.N.; Khan, M.S.I.; Islam, H.M.T.; Islam, M.S.; Khan, R.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Varol, M.; Tokatli, C.; Pal, S.C.; Islam, A.; et al. Hydro-chemical assessment of fluoride and nitrate in groundwater from east and west coasts of Bangladesh and India. J. Cleaner Prod. 2022, 372, 133675. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Liu, Q.; Peng, W.; Liu, X. Source apportionment and natural background levels of major ions in shallow groundwater using multivariate statistical method: A case study in Huaibei plain, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113806. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Xi, B.; Lu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Hui, K.; Tan, W.; Wang, H.; Meng, F. Hydrochemistry characteristics and genesis of shallow groundwater in diverse industrial agglomeration areas in typical alluvial plain of the Yellow river. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 958, 177764. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Tang, C.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen plain, northeast China. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, K.; Wang, H.; Gong, J.; Zhu, C.; Qin, X. Occurrence and enrichment mechanism of arsenic-rich groundwater from eastern coastal China. Groundwater Sust. Dev. 2024, 27, 101385. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Liu, L.; Tang, M.J.; Tao, X.H.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Gong, J. Co-occurrence, sources and co-enrichment mechanism of arsenic, fluoride in groundwater from Huaihe river basin, China. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100276. [Google Scholar]
- Pasupuleti, S.; Singha, S.S.; Singha, S.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R.; Dhada, I. Groundwater characterization and non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic health risk assessment of nitrate exposure in the Mahanadi river basin of India. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Zhou, J. Hydrochemical evolution characteristics, controlling factors, and high nitrate hazards of shallow groundwater in a typical agricultural area of Nansi lake basin, north China. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115430. [Google Scholar]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H. Groundwater chemistry, distribution and potential health risk appraisal of nitrate enriched groundwater: A case study from the semi-urban region of south India. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111277. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S. Source identification and potential health risks of fluoride and nitrate in groundwater of a typical alluvial plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166920. [Google Scholar]
- Chorol, L.; Gupta, S.K. Hybrid analytic network process (ANP)-Entropy model, time series analysis for predicting nitrate and fluoride in groundwater and cumulative health risk assessment. J. Cleaner Prod. 2023, 428, 139316. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, D.; Meng, X.; Wen, X.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Wu, M.; Zhou, T. Hydrochemical characteristics, quality and health risk assessment of nitrate enriched coastal groundwater in northern China. J. Cleaner Prod. 2023, 403, 136872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Pei, Q. Hydrochemistry, quality and potential health risk appraisal of nitrate enriched groundwater in the Nanchong area, southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147186. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Sun, T.; Fan, H.; Wu, B.; Li, M.; Qian, L. Hydrochemical evaluation of groundwater quality and human health risk assessment of nitrate in the largest peninsula of China based on high-density sampling: A case study of Weifang. J. Cleaner Prod. 2021, 322, 129164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gong, J.S.; Wang, H.S.; Zhou, K.E.; Zhu, C.F.; Tao, X.H.; Ye, Y.H.; Tan, M.J.; Zhang, F. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in Bozhou city, Anhui province. East China Geol. 2023, 44, 345–356. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, S. Characterization of the hydrochemistry of water resources of the Weibei plain, northern China, as well as an assessment of the risk of high groundwater nitrate levels to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Jian, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jin, P.; Gao, S.; Wang, Q.; Ding, Z.; Wang, D.; Ma, Z. Distribution of groundwater hydrochemistry and quality assessment in Hutuo river drinking water source area of Shijiazhuang (North China Plain). Water 2024, 16, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Qi, Y.; Shao, G.; Ma, C. Geochemical characteristics and controlling factors of groundwater chemical composition in the Zihe river source area, Shandong, China. Water 2024, 16, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhou, P.; Wang, G.; Yu, X.; Fu, J.; Li, S.; Zhou, X. New insights into the controlling factors of nitrate spatiotemporal characteristics in groundwater of Dagu aquifer in Qingdao, China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Xiao, C.; Liang, X.; Wei, H. Response of groundwater chemical characteristics to land use types and health risk assessment of nitrate in semi-arid areas: A case study of Shuangliao city, northeast China. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113473. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Xiao, J.; Wang, W.; Li, Z. Nitrate dynamics in the streamwater-groundwater interaction system: Sources, fate, and controls. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y. Tracing nitrate origins and transformation processes in groundwater of the Hohhot basin’s piedmont strong runoff zone through dual isotopes and hydro-chemical analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, H. Traceability and biogeochemical process of nitrate in the Jinan karst spring catchment, north China. Water 2023, 15, 2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
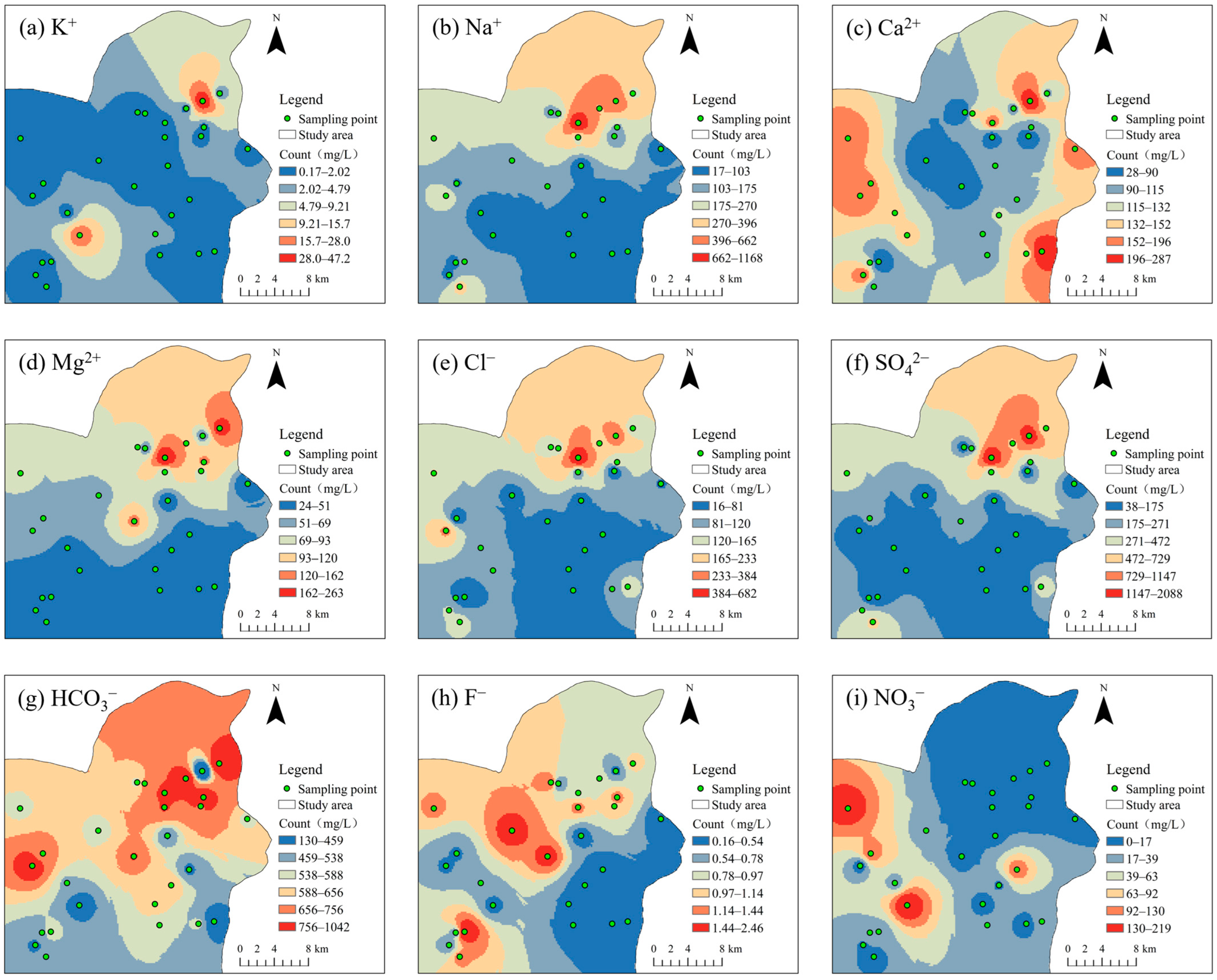
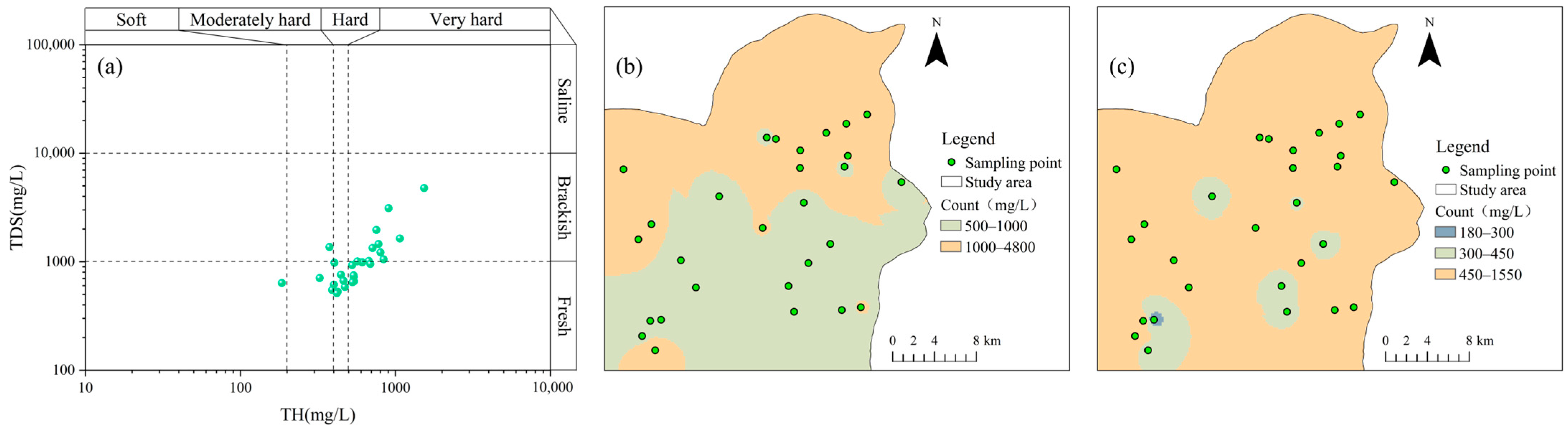
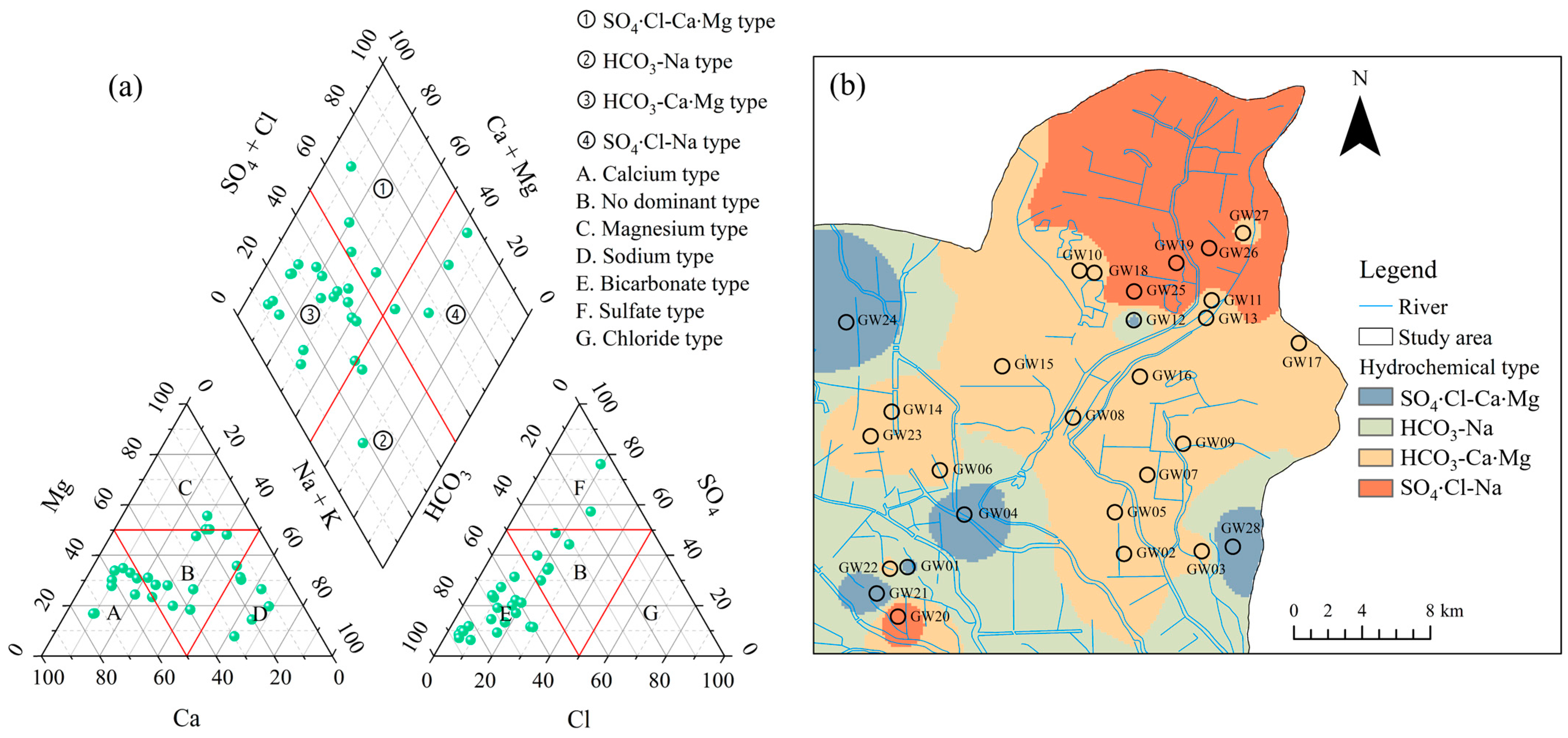

| Parameters | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | 0.1 | 47.3 | 3.3 | 9.6 | 2.9 |
| Na+ | 17.3 | 1170.0 | 180.7 | 238.7 | 1.3 |
| Ca2+ | 27.8 | 286.8 | 126.1 | 64.5 | 0.5 |
| Mg2+ | 24.1 | 262.7 | 69.9 | 54.0 | 0.8 |
| Cl− | 16.0 | 683.0 | 122.7 | 131.7 | 1.1 |
| SO42− | 38.1 | 2092.4 | 314.9 | 477.3 | 1.5 |
| HCO3− | 128.6 | 1043.1 | 610.7 | 204.9 | 0.3 |
| F− | 0.2 | 2.5 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
| NO3− | 0.0 | 219.0 | 30.9 | 57.0 | 1.8 |
| TDS | 512.8 | 4784.5 | 1149.0 | 898.6 | 0.8 |
| TH | 184.9 | 1533.8 | 604.0 | 267.3 | 0.4 |
| Variables | Component Matrix | Rotated Component Matrix | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | |
| K+ | 0.32 | −0.68 | 0.48 | −0.06 | 0.31 | 0.82 | 0.11 | 0.09 |
| Na+ | 0.94 | 0.09 | 0.24 | −0.02 | 0.96 | 0.10 | −0.11 | −0.11 |
| Ca2+ | 0.47 | −0.73 | −0.37 | −0.09 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.81 | 0.07 |
| Mg2+ | 0.75 | 0.55 | −0.12 | 0.22 | 0.79 | −0.52 | −0.19 | 0.02 |
| Cl− | 0.96 | 0.00 | −0.02 | −0.01 | 0.94 | 0.00 | 0.14 | −0.08 |
| SO42− | 0.96 | −0.14 | 0.20 | −0.07 | 0.95 | 0.26 | 0.07 | −0.10 |
| HCO3− | 0.18 | 0.82 | −0.36 | 0.08 | 0.21 | −0.85 | −0.22 | −0.15 |
| F− | −0.02 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.12 | 0.10 | −0.10 | −0.94 | −0.05 |
| NO3− | −0.17 | −0.43 | 0.04 | 0.88 | −0.11 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.97 |
| TDS | 0.99 | −0.01 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.99 | 0.08 | 0.06 | −0.04 |
| TH | 0.91 | 0.02 | −0.32 | 0.13 | 0.88 | −0.23 | 0.33 | 0.06 |
| Eigenvalues | 5.47 | 2.64 | 1.15 | 0.88 | 5.38 | 1.96 | 1.78 | 1.01 |
| Variance(%) | 49.72 | 23.98 | 10.49 | 7.98 | 48.93 | 17.84 | 16.19 | 9.21 |
| Cumulative(%) | 49.72 | 73.70 | 84.19 | 92.17 | 48.93 | 66.77 | 82.96 | 92.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, X.; Wang, H.; Gong, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, K.; Xu, N.; Li, L.; Li, J. Multivariate Statistics and Hydrochemistry Combined to Reveal the Factors Affecting Shallow Groundwater Evolution in a Typical Area of the Huaibei Plain, China. Water 2025, 17, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070962
Qin X, Wang H, Gong J, Ye Y, Zhou K, Xu N, Li L, Li J. Multivariate Statistics and Hydrochemistry Combined to Reveal the Factors Affecting Shallow Groundwater Evolution in a Typical Area of the Huaibei Plain, China. Water. 2025; 17(7):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070962
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Xi, Hesheng Wang, Jianshi Gong, Yonghong Ye, Kaie Zhou, Naizheng Xu, Liang Li, and Jie Li. 2025. "Multivariate Statistics and Hydrochemistry Combined to Reveal the Factors Affecting Shallow Groundwater Evolution in a Typical Area of the Huaibei Plain, China" Water 17, no. 7: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070962
APA StyleQin, X., Wang, H., Gong, J., Ye, Y., Zhou, K., Xu, N., Li, L., & Li, J. (2025). Multivariate Statistics and Hydrochemistry Combined to Reveal the Factors Affecting Shallow Groundwater Evolution in a Typical Area of the Huaibei Plain, China. Water, 17(7), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070962






