The Effects of Three Bean Shell Biochars Under Different Pyrolysis Temperatures on the Adsorption of Cd and Pb in Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biochar Preparation
2.2. Characterization and Physicochemical Properties of the Biochar
2.3. Pb or Cd Adsorption by Biochar
2.4. Models to Fit the Adsorption Capacity of Biochar for Pb or Cd
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
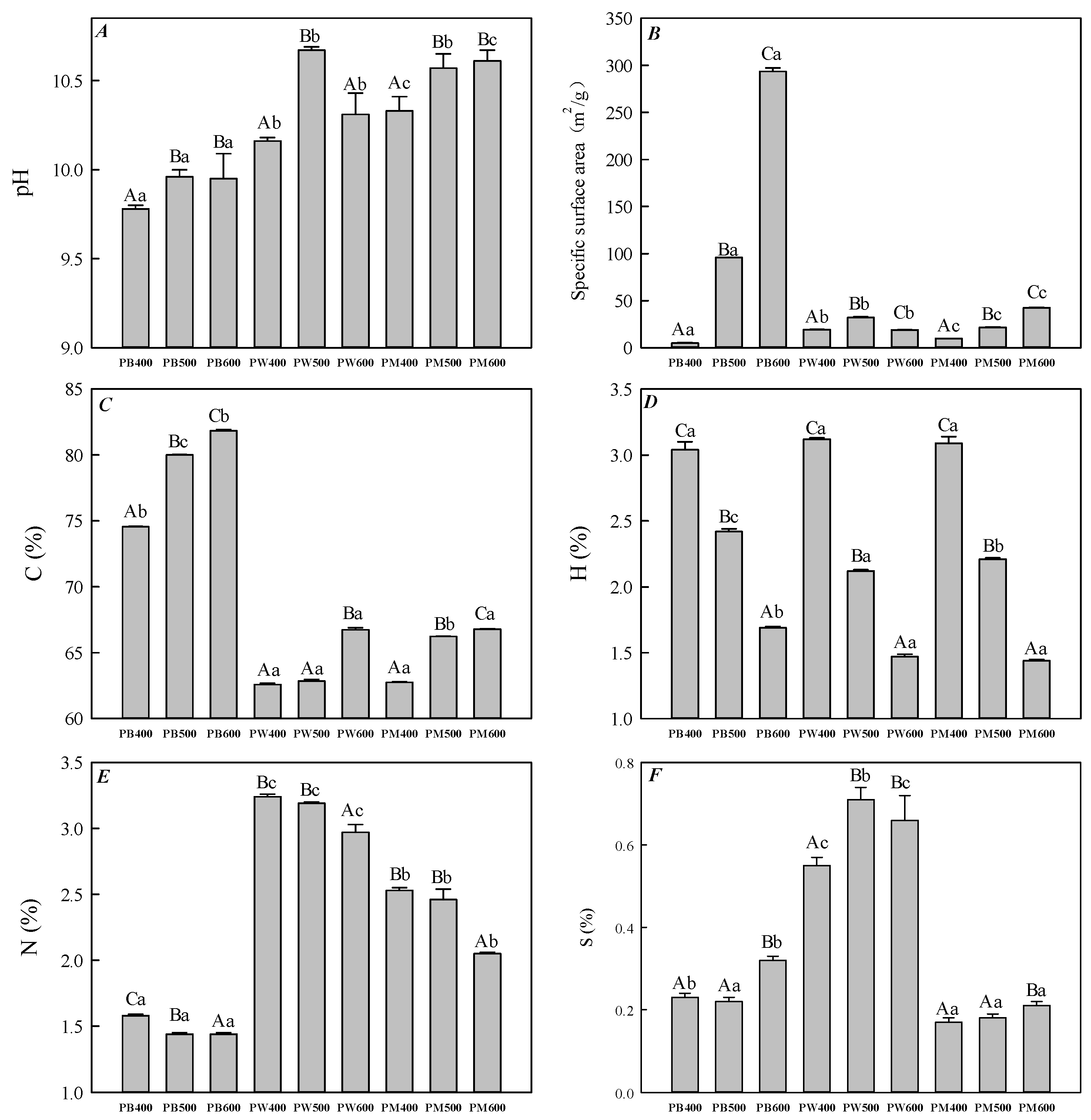
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of the Three Kinds of Biochar
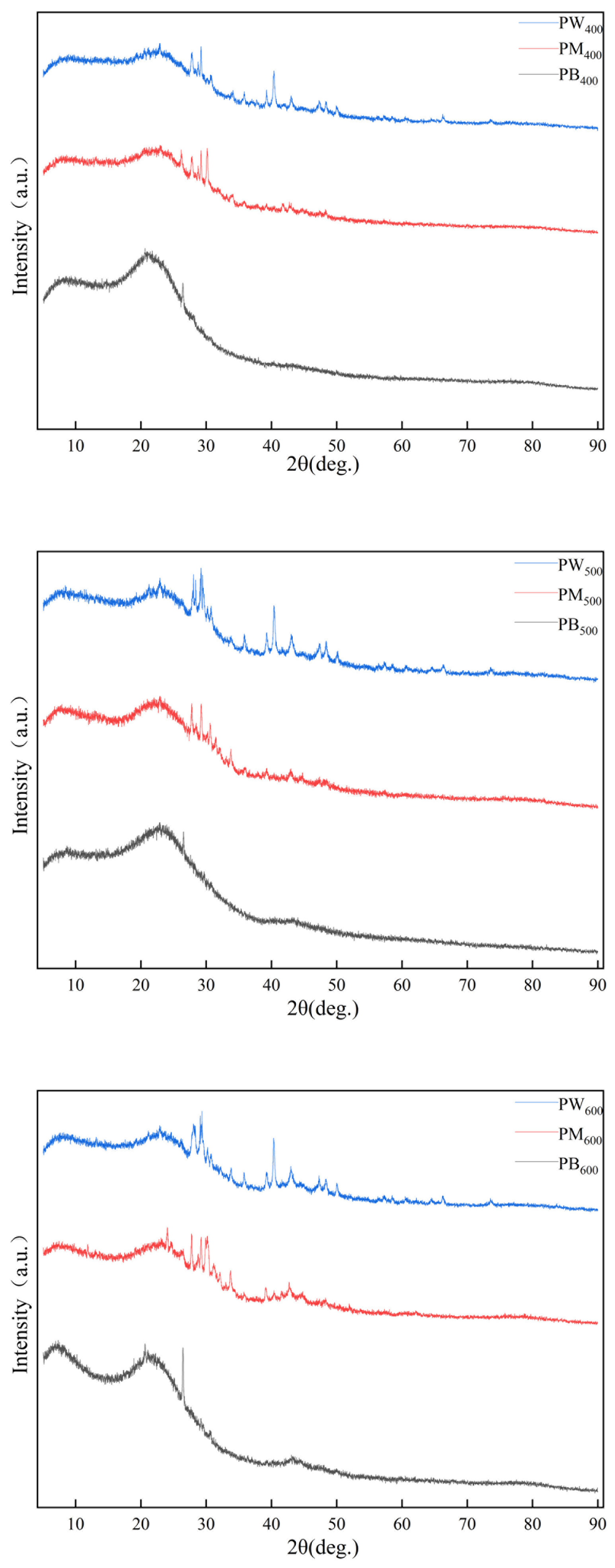
3.2. Structural Characterization of the Three Biochar Materials
3.2.1. SEM Analysis
3.2.2. XRD Analysis
3.3. Pb Adsorption by the Three Types of Biochar
3.4. Cd Adsorption by the Three Types of Biochar
3.5. Biochar Adsorption Isotherm Models for Pb and Cd
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, X.; Huang, D.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zeng, G.; Xu, P.; Wan, J. Remediation of contaminated soils by biotechnology with nanomaterials: Bio-behavior, applications, and perspectives. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kula, I.; Uğurlu, M.; Karaoğlu, H.; Celik, A. Adsorption of Cd (II) ions from aqueous solutions using activated carbon prepared from olive stone by ZnCl2 activation. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, B.; Tao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Ding, X.; Chu, H. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105081. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, G.; Niu, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Xiang, P. Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effects, sources and removing technology. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129205. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, D.; Sarswat, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent—A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 191–202. [Google Scholar]
- Inyang, M.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Cao, X. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by biochars derived from anaerobically digested biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, O.R.; Herbert, B.E.; Rhue, R.D.; Kuo, L.J. Metal interactions at the biochar-water interface: Energetics and structure-sorption relationships elucidated by flow adsorption microcalorimetry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5550–5556. [Google Scholar]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braida, W.J.; Pignatello, J.J.; Lu, Y.; Ravikovitch, P.I.; Neimark, A.V.; Xing, B. Sorption hysteresis of benzene in charcoal particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Song, B.; Chen, M.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.; Cao, X. Physicochemical property and colloidal stability of micron-and nano-particle biochar derived from a variety of feedstock sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 685–695. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Bian, R.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Pan, G. Effect of pyrolysis temperature of biochar on Cd, Pb and as bioavailability and bacterial community composition in contaminated paddy soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 247, 114237. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, S.; Bhattacharya, J. Influence of temperature and duration of pyrolysis on the property heterogeneity of rice straw biochar and optimization of pyrolysis conditions for its application in soils. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Han, L.; Gao, W.; Liu, R.; Chen, M. Effective removal of heavy metal by biochar colloids under different pyrolysis temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Chen, B. Interaction mechanisms of organic contaminants with burned straw ash charcoal. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Bhattacharya, T. Biochar: A sustainable solution. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 6642–6680. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lu, B.; Xian, J.; Tsang, E.P.; Cheng, W.; Fang, J.; Fang, Z. Magnetic biochar for environmental remediation: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122468. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, M.; Hu, X. Removal of heavy metals from soil with biochar composite: A critical review of the mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105830. [Google Scholar]
- Mansoor, S.; Kour, N.; Manhas, S.; Zahid, S.; Wani, O.A.; Sharma, V.; Wijaya, L.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Alsahli, A.A.; El-Serehy, H.A.; et al. Biochar as a tool for effective management of drought and heavy metal toxicity. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129458. [Google Scholar]
- Uchimiya, M.; Chang, S.; Klasson, K.T. Screening biochars for heavy metal retention in soil: Role of oxygen functional groups. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 432–441. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, L. Adsorption of Cu2+ in water by activated carbon made from peanut shell. Yunnan Chem. Technol. 2022, 33–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L. Modification of Peanut Shell Biochar and Its Adsorption Properties of Pb2+. Biomass Chem. Eng. 2022, 56, 43–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Polo, M.; Rivera-Utrilla, J. Adsorbent-adsorbate interactions in the adsorption of Cd(II) and Hg(II) on ozonized activated carbons. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3850–3854. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.H.; Xu, R.K.; Zhang, H. The forms of alkalis in the biochar produced from crop residues at different temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3488–3497. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, C.E.; Chuang, V.J.; Masiello, C.A.; Gonnermann, H.; Gao, X.; Dugan, B.; Driver, L.E.; Panzacchi, P.; Zygourakis, K.; Davies, C.A. New approaches to measuring biochar density and porosity. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 66, 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Kwon, S.; Lu, Y. Effect of natural organic substances on the surface and adsorptive properties of environmental black carbon (char): Attenuation of surface activity by humic and fulvic acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7757–7763. [Google Scholar]
- Onay, O. Influence of pyrolysis temperature and heating rate on the production of bio-oil and char from safflower seed by pyrolysis, using a well-swept fixed-bed reactor. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 523–531. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, H. The structure evolution of biochar from biomass pyrolysis and its correlation with gas pollutant adsorption performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Khater, E.S.; Bahnasawy, A.; Hamouda, R.; Sabahy, A.; Abbas, W.; Morsy, O.M. Biochar production under different pyrolysis temperatures with different types of agricultural wastes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2625. [Google Scholar]
- Uchimiya, M.; Wartelle, L.H.; Klasson, K.T.; Fortier, C.A.; Lima, I.M. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on biochar property and function as a heavy metal sorbent in soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2501–2510. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, M.; Shi, L.; Wu, C.; Li, W.; An, W.; Liu, Z.; Xue, S. Effect of sulfur and sulfur-iron modified biochar on cadmium availability and transfer in the soil–rice system. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 314–322. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, Y.; Sheng, G.; Chiou, C.T.; Xing, B. Compositions and sorptive properties of crop residue-derived chars. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4649–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, O.R.; Kuo, L.J.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Louchouarn, P.; Amonette, J.E.; Herbert, B.E. An index-based approach to assessing recalcitrance and soil carbon sequestration potential of engineered black carbons (biochars). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujre, N.; Mitra, S.; Agnihotri, R.; Sharma, M.P.; Gupta, D. Novel agrotechnological intervention for soil amendment through areca nut husk biochar in conjunction with vetiver grass. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Shi, S.; Liu, J.; Su, S.; Liang, Q.; Zeng, X.; Li, T. Study of the effect of pyrolysis temperature on the Cd2+ adsorption characteristics of biochar. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazini, R.; Soleimani, M.; Mirghaffari, N. Characterization of barley straw biochar produced in various temperatures and its effect on lead and cadmium removal from aqueous solutions. Water Environ. J. 2018, 32, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, D.H.K.; Lee, S.M.; Seshaiah, K. Biosorption of toxic heavy metal ions from water environment using honeycomb biomass—An industrial waste material. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 5967–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, D.; Li, L.; Pan, G.; Chen, J.; Guo, H. Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in aqueous solution by biochars derived from different crop residues. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 1001–1008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Ma, L.; Gao, B.; Harris, W. Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3285–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.J.; Liang, X.F.; Lin, D.S.; Xu, Y.M.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.B.; Qin, X. Adsorption of Cd2+ on biochar from aqueous solution. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2013, 34, 3716–3721. [Google Scholar]
- Saadi, R.; Saadi, Z.; Fazaeli, R.; Fard, N.E. Monolayer and multilayer adsorption isotherm models for sorption from aqueous media. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, A.B.; Arbestain, M.C.; Sevilla, M.; Maciá-Agulló, J.A.; Fiol, S.; López, R.; Smernik, R.J.; Aitkenhead, W.P.; Arce, F.; Macías, F. Chemical and structural properties of carbonaceous products obtained by pyrolysis and hydrothermal carbonization of corn stover. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2010, 48, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number | Pb Solution Concentrations (mg/L) | Cd Solution Concentrations (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 5 | 4 |
| 4 | 10 | 10 |
| 5 | 20 | 20 |
| 6 | 40 | 40 |
| 7 | 50 | 50 |
| 8 | 100 | 100 |
| 9 | 200 | 200 |
| 10 | 300 | 300 |
| 11 | 400 | 400 |
| 12 | 500 | not set |
| Equation | Adsorption Isotherm Model | Adsorption Isotherm Formulas |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | Henry | G = k1c |
| (2) | Freundlich | G = k2c1/n |
| (3) | Langmuir | G = G0c/(A + c) |
| Biochar Material | Fitting Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henry Type | Freundlich Type | Langmuir Type | ||||
| R | p Value | R | p Value | R | p Value | |
| PB400 | 0.9334 | <0.0001 | 0.9358 | <0.0001 | 0.9364 | <0.0001 |
| PB500 | 0.9862 | <0.0001 | 0.9949 | <0.0001 | 0.9970 | <0.0001 |
| PB600 | 0.9997 | <0.0001 | 0.9998 | <0.0001 | 0.9999 | <0.0001 |
| PW400 | 0.9664 | <0.0001 | 0.9853 | <0.0001 | 0.9898 | <0.0001 |
| PW500 | 0.9914 | <0.0001 | 0.9972 | <0.0001 | 0.9968 | <0.0001 |
| PW600 | 0.9999 | <0.0001 | 0.9999 | <0.0001 | 0.9999 | <0.0001 |
| PM400 | 0.9401 | <0.0001 | 0.9397 | <0.0001 | 0.9299 | <0.0001 |
| PM500 | 0.9787 | <0.0001 | 0.9877 | <0.0001 | 0.9885 | <0.0001 |
| PM600 | 0.9999 | <0.0001 | 0.9999 | <0.0001 | 0.9999 | <0.0001 |
| Biochar Material | Fitting Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henry Type | Freundlich Type | Langmuir Type | ||||
| R | p Value | R | p Value | R | p Value | |
| PB400 | 0.9969 | <0.0001 | 0.9983 | <0.0001 | 0.9960 | <0.0001 |
| PB500 | 0.9572 | <0.0001 | 0.9878 | <0.0001 | 0.9519 | <0.0001 |
| PB600 | 0.9964 | <0.0001 | 0.9994 | <0.0001 | 0.9937 | <0.0001 |
| PW400 | 0.9953 | <0.0001 | 0.9952 | <0.0001 | 0.9951 | <0.0001 |
| PW500 | 0.9869 | <0.0001 | 0.9947 | <0.0001 | 0.9850 | <0.0001 |
| PW600 | 0.9809 | <0.0001 | 0.9840 | <0.0001 | 0.9798 | <0.0001 |
| PM400 | 0.9961 | <0.0001 | 0.9980 | <0.0001 | 0.9958 | <0.0001 |
| PM500 | 0.9622 | <0.0001 | 0.9912 | <0.0001 | 0.9573 | <0.0001 |
| PM600 | 0.9949 | <0.0001 | 0.9956 | <0.0001 | 0.9940 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, T.; Xia, H.; Zhang, H.; Guang, S.; Hu, W.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, K.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, A. The Effects of Three Bean Shell Biochars Under Different Pyrolysis Temperatures on the Adsorption of Cd and Pb in Aqueous Solutions. Water 2025, 17, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070918
Shen T, Xia H, Zhang H, Guang S, Hu W, Zhao W, Zhao K, Xiao X, Zhang S, Xu A. The Effects of Three Bean Shell Biochars Under Different Pyrolysis Temperatures on the Adsorption of Cd and Pb in Aqueous Solutions. Water. 2025; 17(7):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070918
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Tao, Hongyu Xia, Heyi Zhang, Song Guang, Wenwen Hu, Wenrui Zhao, Kuan Zhao, Xin Xiao, Shiwen Zhang, and Aiai Xu. 2025. "The Effects of Three Bean Shell Biochars Under Different Pyrolysis Temperatures on the Adsorption of Cd and Pb in Aqueous Solutions" Water 17, no. 7: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070918
APA StyleShen, T., Xia, H., Zhang, H., Guang, S., Hu, W., Zhao, W., Zhao, K., Xiao, X., Zhang, S., & Xu, A. (2025). The Effects of Three Bean Shell Biochars Under Different Pyrolysis Temperatures on the Adsorption of Cd and Pb in Aqueous Solutions. Water, 17(7), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070918




