Investigating Sedimentation Patterns and Fluid Movement in Drip Irrigation Emitters in the Yellow River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Devices
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Evaluation Index and Determination Method
2.4.1. Performance Evaluation of Drip Irrigation Emitter Anti-Clogging
2.4.2. Collecting and Dry Weight Test of Sediment
2.4.3. Distribution and Mechanical Composition of Sediment Particle
2.5. Physical Model Structure and Simulation Parameter Design
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Dynamic Change in Anti-Clogging Characteristic Index of the Emitter
3.2. Correlation Analysis of Average Discharge Ratio Variation and Irrigation Uniformity Coefficient
3.3. Change in Capillary Sediment Quality in Different Types of Emitters
3.4. Change in the Quality of Clogging in the Channel of Different Emitters
3.5. Sediment Deposition Location and Particle Size Composition in Emitter Channel of Different Types
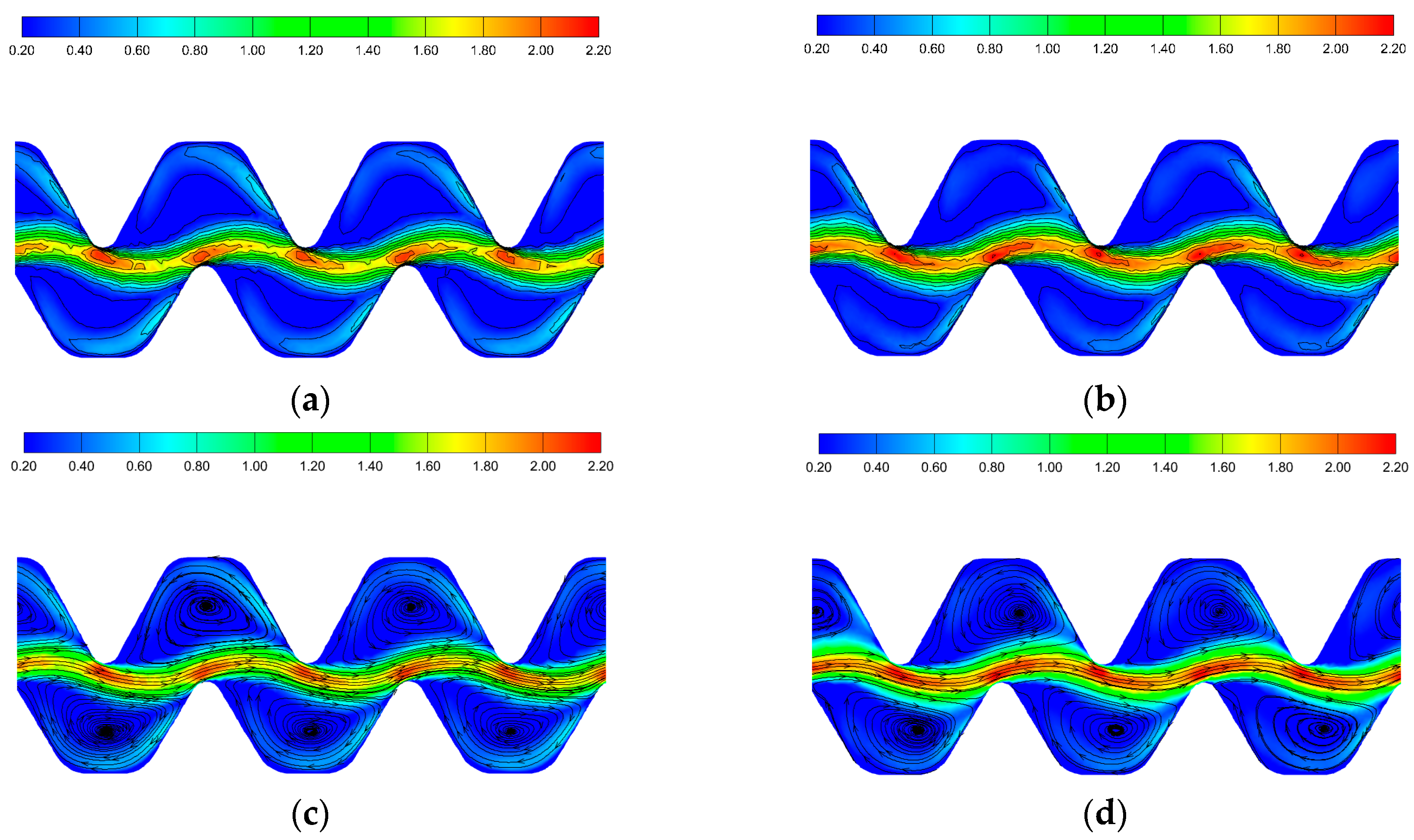
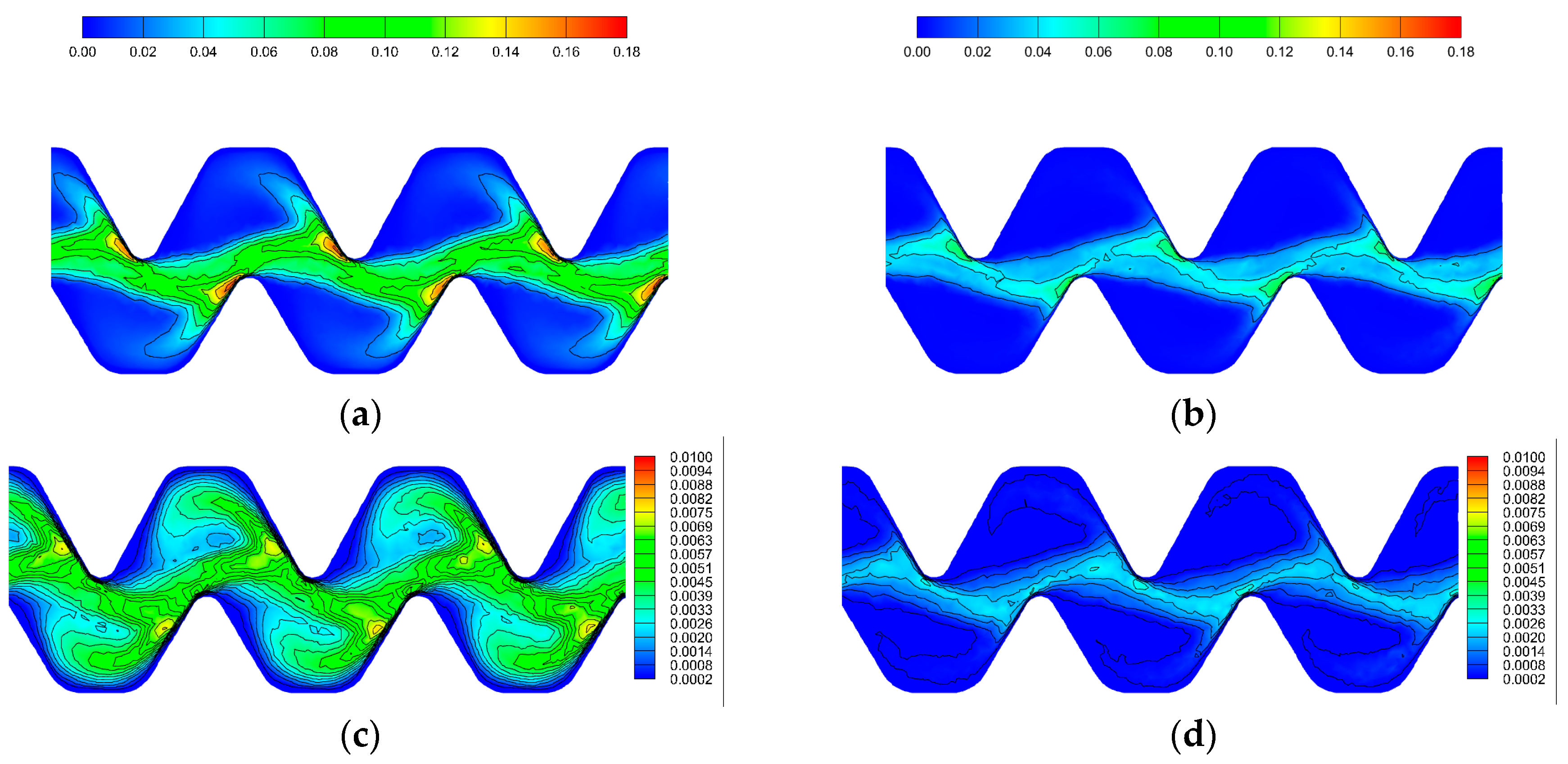
3.6. The Change in Flow Velocity and Turbulent Kinetic Energy in the Emitter
4. Discussion
4.1. The Impact of Sediment Characteristics on Emitter Clogging
4.2. The Impact of Flow Channel Structure on Emitter Clogging
4.3. The Coupling Effect Between Sediment Characteristics and Flow Channel Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DPIV | Digital particle image velocimetry |
| LIFV | Laser-induced fluorescence velocimetry |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| Dra | Discharge ratio variation |
| Cu | Christensen’s uniformity coefficient |
References
- Liu, M.; Zhou, X.; Huang, G.; Li, Y. The Increasing Water Stress Projected for China Could Shift the Agriculture and Manufacturing Industry Geographically. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Khan, S.U.; Swallow, B.; Liu, W.; Zhao, M. Coupling Coordination Analysis of China’s Water Resources Utilization Efficiency and Economic Development Level. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, J.; Sun, F. Spatiotemporal Differentiation of Coupling Coordination Degree between Economic Development and Water Environment and Its Influencing Factors Using GWR in China’s Province. Ecol. Model. 2021, 462, 109794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Shen, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Ditch Water and Yellow River Irrigation on Saline–Alkali Characteristics of Soil and Paddy. Water 2024, 16, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Feng, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Han, M. Sustainable Operation Mode of a Sand Filter in a Drip Irrigation System Using Yellow River Water in an Arid Area. Water Supply 2020, 20, 3636–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Shi, Z.; Jiang, Y. Eight Emitters Clogging Characteristics and Its Suitability under On-Site Reclaimed Water Drip Irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2014, 32, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, F.; Tian, L.; He, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ren, F. Soil Physicochemical Properties and Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Yield under Brackish Water Mulched Drip Irrigation. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Zhang, E.; Gan, H.; Niu, W.; Ali, S.; Dong, A.; Zhang, W.; Wu, M.; Sun, D. Aerated Drip Irrigation Increased the Emitter Clogging Risk of the Yellow River Water Drip Irrigation. Irrig. Drain. 2023, 72, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Lyu, D.; Liu, N.; Xing, S.; Wang, F. Anti-Clogging Performance Optimization for Shunt-Hedging Drip Irrigation Emitters Based on Water–Sand Motion Characteristics. Water 2022, 14, 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tian, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C. Water-Saving Potential of Different Agricultural Management Practices in an Arid River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wu, L.; Cheng, M.; Fan, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Qian, L. Review on Drip Irrigation: Impact on Crop Yield, Quality, and Water Productivity in China. Water 2023, 15, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wu, P.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, F.; Zhou, W. Microporous Ceramic Emitter: A Drip Irrigation Emitter Suitable for High-Sediment Water. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 67, 106169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yao, C. Hydraulic Performance and Parameter Optimisation of a Microporous Ceramic Emitter Using Computational Fluid Dynamics, Artificial Neural Network and Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 189, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Qiu, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, G. Characterization of Labyrinth Emitter-Clogging Substances in Biogas Slurry Drip Irrigation Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, T.; Zhou, B.; Puig-Bargu´es, J.; Ding, C.; Li, S.; Manan, I.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. Assessment of Emitter Clogging with Multiple Fouling and Root Intrusion in Sub-Surface Drip Irrigation during 5-Year Sugarcane Growth. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Puig-Bargués, J.; Li, M.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Y. Physical, Chemical and Biological Emitter Clogging Behaviors in Drip Irrigation Systems Using High-Sediment Loaded Water. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 270, 107738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, W. Review and Development Strategy of Irrigation with Unconventional Water Resources in China. Strateg. Study CAE 2018, 20, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Kong, J.; Yue, H.; Huang, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhangzhong, L. Magnetized Water Irrigation Alleviates Emitter Clogging of a Drip Fertigation System. Agronomy 2023, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Niu, W.; Du, Y.; Sun, J.; Dong, A.; Wu, M.; Mu, F.; Zhu, J.; Siddique, K.H.M. A Meta-Analysis of Labyrinth Channel Emitter Clogging Characteristics under Yellow River Water Drip Tape Irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 291, 108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, Y.S.; Wu, Y.; Jia, F.; Li, S.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y. Effects of Microorganisms on Clogging Process and Clogging Substances Accumulation of Drip Irrigation Emitters Using the High-Sediment Water Sources. Irrig. Sci. 2022, 40, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverenz, H.L.; Tchobanoglous, G.; Darby, J.L. Clogging in Intermittently Dosed Sand Filters Used for Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ling, G.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Gao, X. A Prediction Model of Labyrinth Emitter Service Duration (ESD) under Low-Quality (Sand-Laden Water) Irrigation. Water 2022, 14, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Xu, T.; Ren, S.; Lin, X.; Wei, R.; Xu, H. CFD and Digital Particle Tracking to Assess Flow Characteristics in the Labyrinth Flow Path of a Drip Irrigation Emitter. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 26, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, P.; Ren, S.; Wei, R.; Xu, H. Flow Characteristics in Energy Dissipation Units of Labyrinth Path in the Drip Irrigation Emitters with DPIV Technology. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 2010, 22, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Tang, Y.; Lu, B. Anti-Clogging Performance Evaluation and Parameterized Design of Emitters with Labyrinth Channels. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 74, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Xue, S. Effect of Optimization Forms of Flow Path on Emitter Hydraulic and Anti-Clogging Performance in Drip Irrigation System. Irrig. Sci. 2018, 36, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.; Niu, W.; Zhang, W.; Lv, C.; Wu, M. Influencing Factors and Characterization Methods of the Anti-Clogging Ability of Labyrinth Channel Emitters. Irrig. Drain. 2023, 72, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Luo, C.; Niu, W.; Yu, L. Influence of particle size and concentration of sediment on clogging of labyrinth channels emitters. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, P.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, N.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. Cascade relationship between the emitter structure-sedimentation-clogging behavior in drip irrigation systems with Yellow River water. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2020, 51, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Bao, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, E. The Study of Structural Optimization on Hydraulic Performance and Anti-Clogging Performance of Labyrinth Drip Irrigation Emitters. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ling, G.; Hu, M.; Wang, W.; Hu, X. Physical Clogging Characteristics of Labyrinth Emitters under Low-Quality (Sand-Laden Water) Irrigation. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 19812. 1–2017; Plastic Equipment for Water Saving Irrigation–Part 1: Drip Tape with Labyrinth on one Side. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China, SAC: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Bhattarai, R. Composite Fouling of Drip Emitters Applying Surface Water with High Sand Concentration: Dynamic Variation and Formation Mechanism. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 215, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Merkley, G.P. Relationships between Common Irrigation Application Uniformity Indicators. Irrig. Sci. 2012, 30, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, X. Influence of Fine Particle Size and Concentration on the Clogging of Labyrinth Emitters. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bai, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, X.; Wu, S.; Lei, J. Effect of Irrigation Commutative Flow Technology on Reducing Deposition and Improving Anti-clogging Performance of a Flat Labyrinth Drip Pipe. Water Supply 2022, 22, 7656–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, H. Study on Fluid Movement Characteristics inside the Emitter Flow Path of Drip Irrigation System Using the Yellow River Water. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Han, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, H. Analysis of Anti-Clogging Performance and Particle Transport Characteristics of a Stellate Irrig. Emitter. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 242, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Jiang, C.; Li, Y.; Shi, N.; Liu, S.; Hu, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Muhammad, T. Effect of Lateral Flushing on Emitter Clogging in Drip Irrigation Using High-Sediment Water. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 293, 108702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Puig-Bargués, J.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y. New Anti-Clogging Perspective by Discharging Sediment from Drip Irrigation Emitters with High-Sediment Loaded Water. Irrig. Sci. 2024, 42, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Qiu, X. Numerical Simulation and Optimisation of the Inlet Structure of Dentiform Emitters in Drip-Irrigation Systems. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 246, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Wu, P.; Zhu, D.; Niu, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J. Influence of Sediment Particle Size on Clogging of Large Labyrinth Channels Emitters. J. Irrig. Drain. 2016, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, N.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Long, J. Influence of Flushing Pressure, Flushing Frequency and Flushing Time on the Service Life of a Labyrinth-Channel Emitter. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 172, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Liu, L.; Tahir, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, N.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, Y. Effect of Fertilization on Emitter Clogging in Drip Irrigation Using High Sediment Water: Perspective of Sediment Discharge Capacity. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 294, 108723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Pan, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Hou, P.; Jiao, Y.; Sun, H.; Ma, C.; Ke, S. Optimal Structural Parameters of Drip Laminar Emitters Using High Sediment Irrigation Water. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2023, 39, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Mouheb, N.; Schillings, J.; Al-Muhammad, J.; Bendoula, R.; Tomas, S.; Amielh, M.; Anselmet, F. Impact of Hydrodynamics on Clay Particle Deposition and Biofilm Development in a Labyrinth-Channel Dripper. Irrig. Sci. 2019, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yuan, R.; Chen, Y.; Luo, W.; Yang, X.; Cao, Z. Characteristic analysis and structure optimization of labyrinth flow channels with different internal tooth structures. J. Chongqing Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2023, 37, 348–358. [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa Pereira, D.J.; Lavanholi, R.; de Araújo, A.C.S.; de Camargo, A.P.; Ait-Mouheb, N.; Frizzone, J.A.; Molle, B. Evaluating Sensitivity to Clogging by Solid Particles in Irrigation Emitters: Assessment of a Laboratory Protocol. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lv, C.; Zhao, X.; Dong, A.; Niu, W. The Influence Mechanism of the Main Suspended Particles of Yellow River Sand on the Emitter Clogging—An Attempt to Improve the Irrigation Water Utilization Efficiency in Yellow River Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 258, 107202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
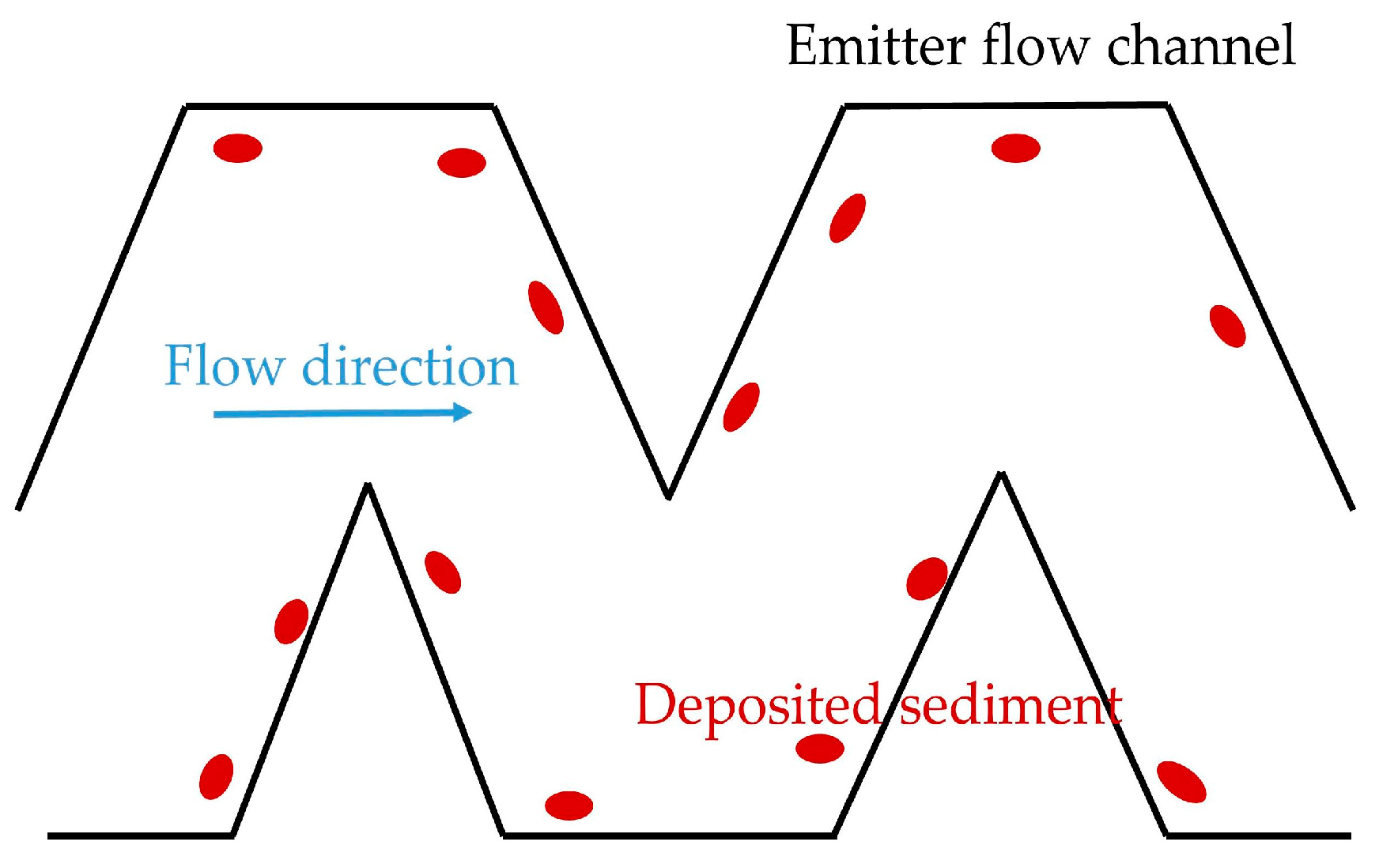
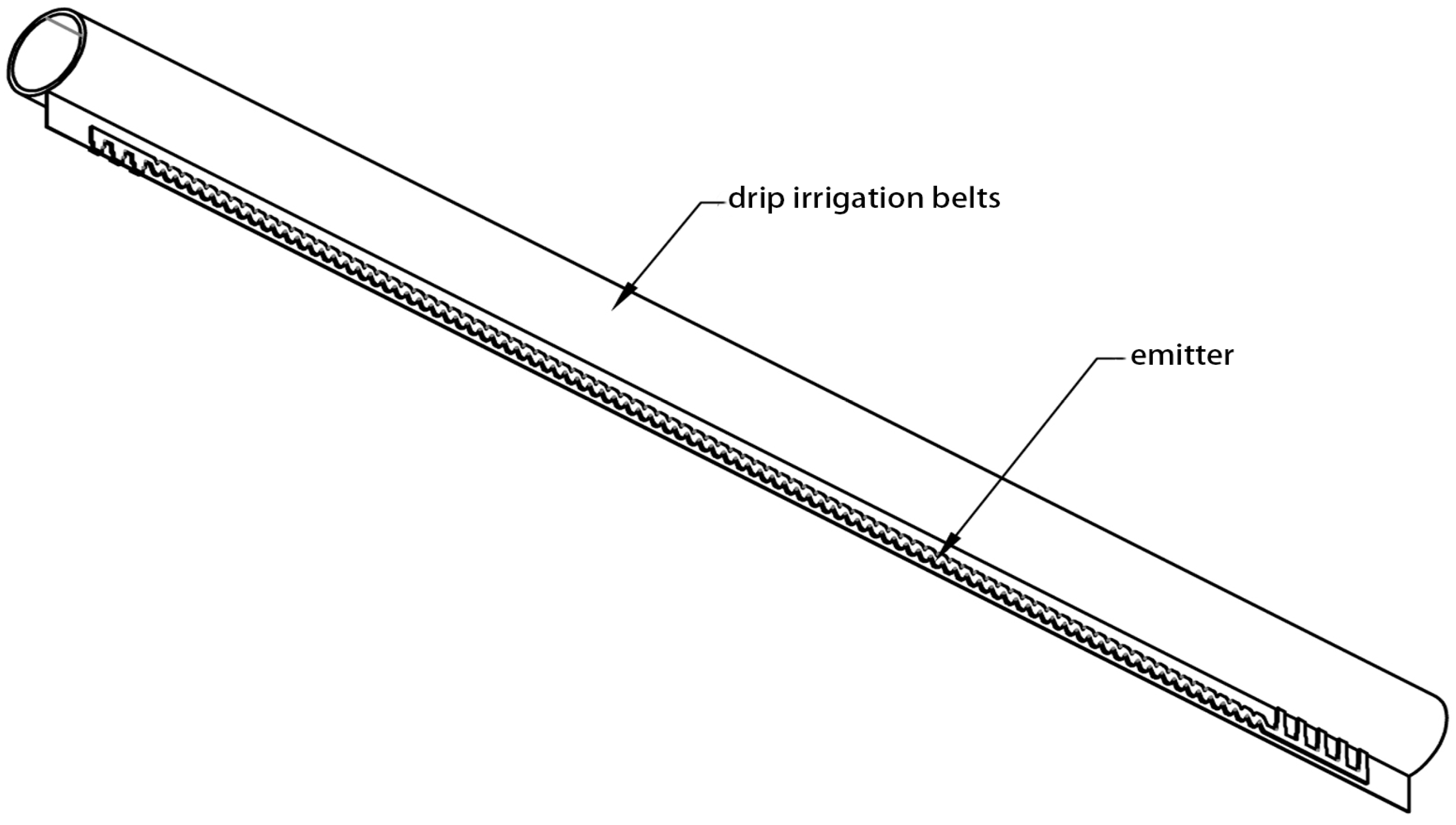

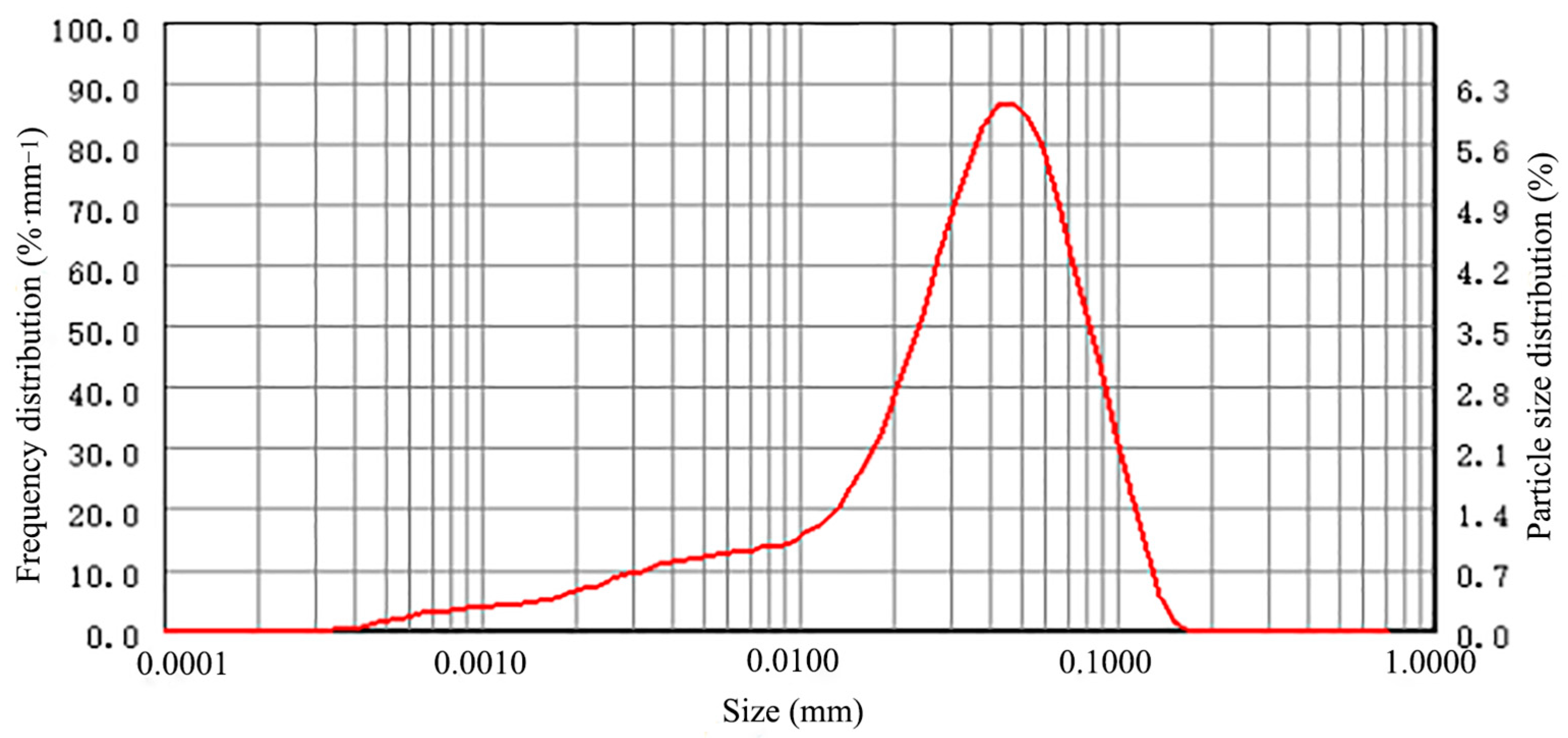
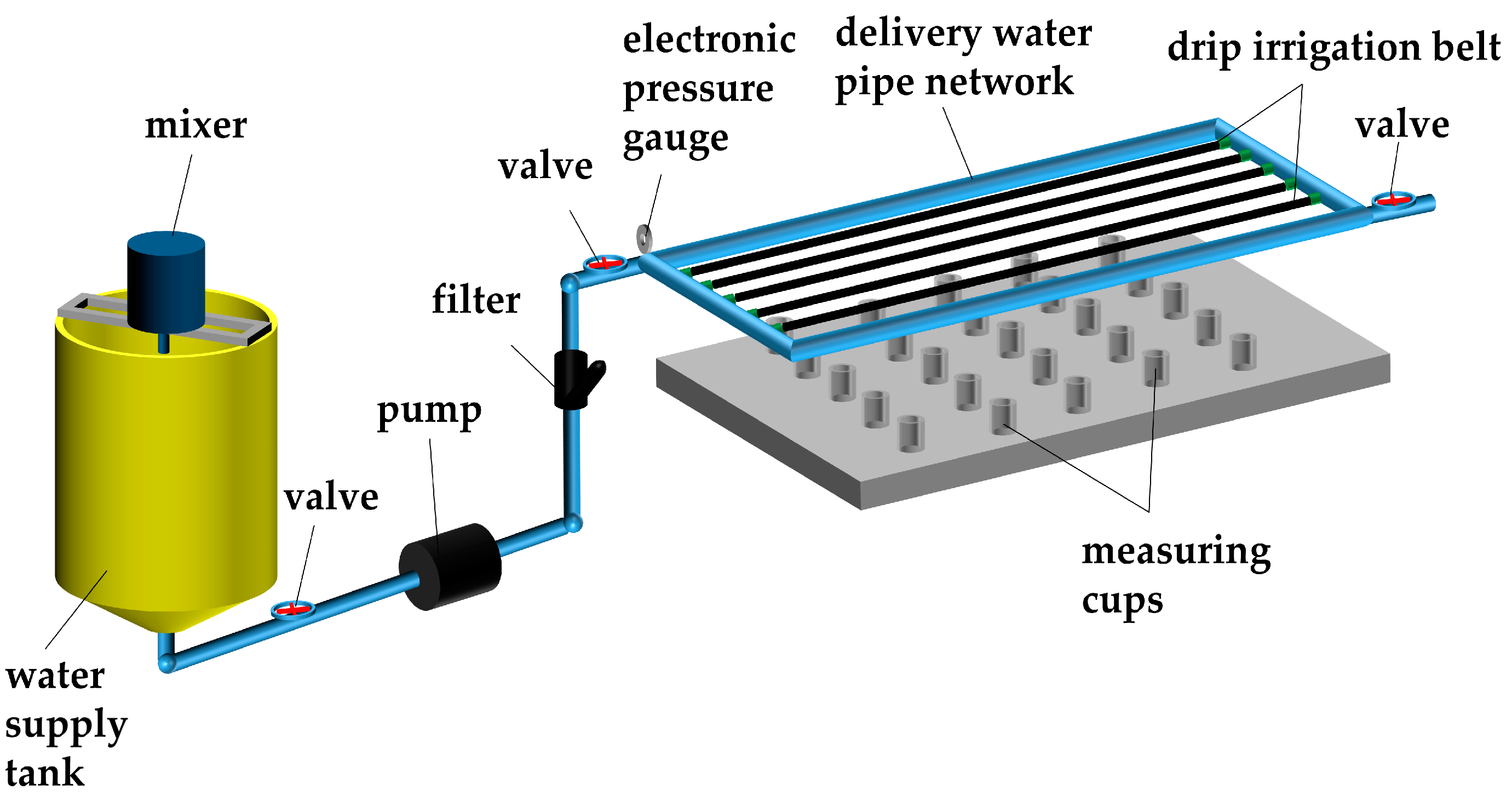
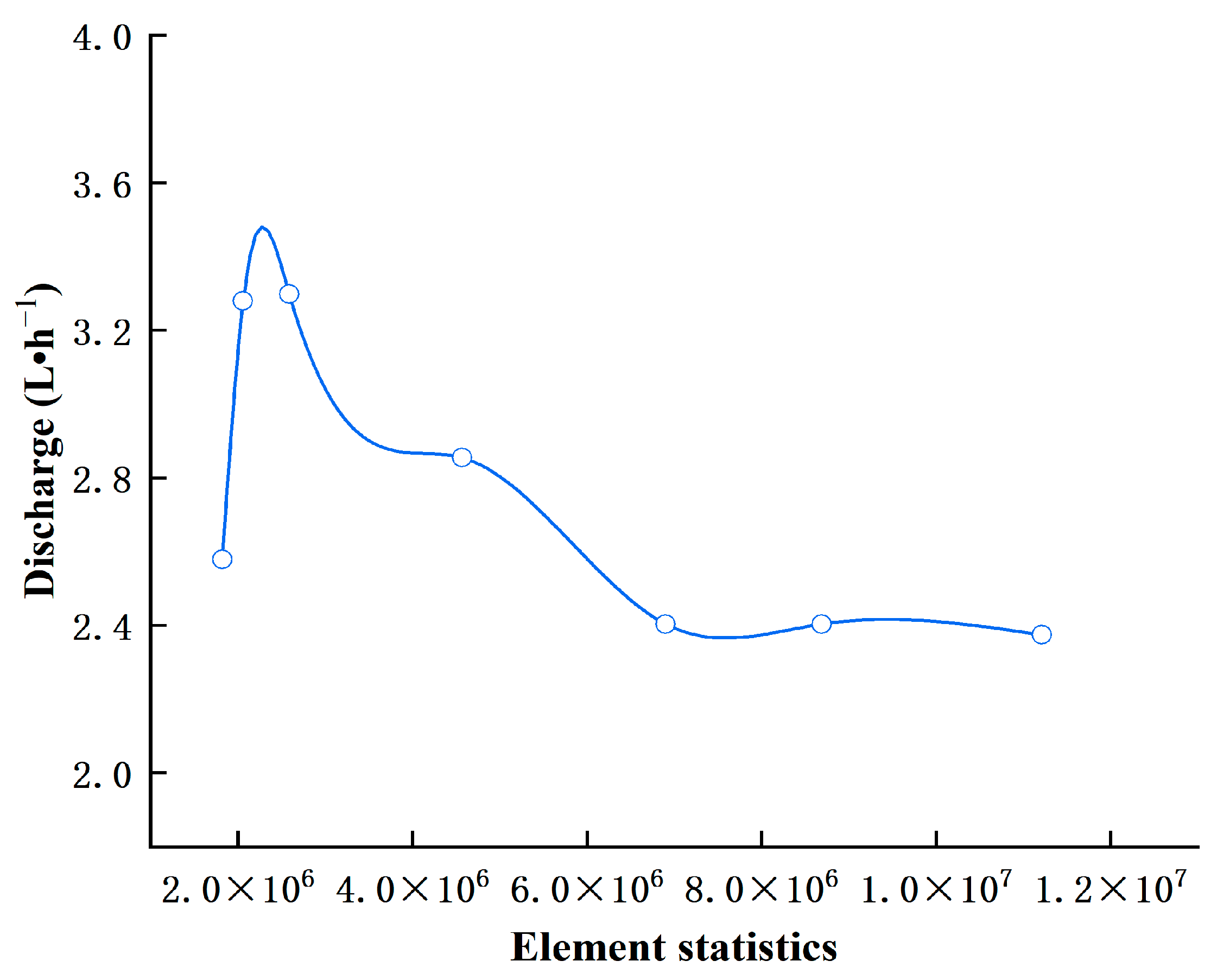
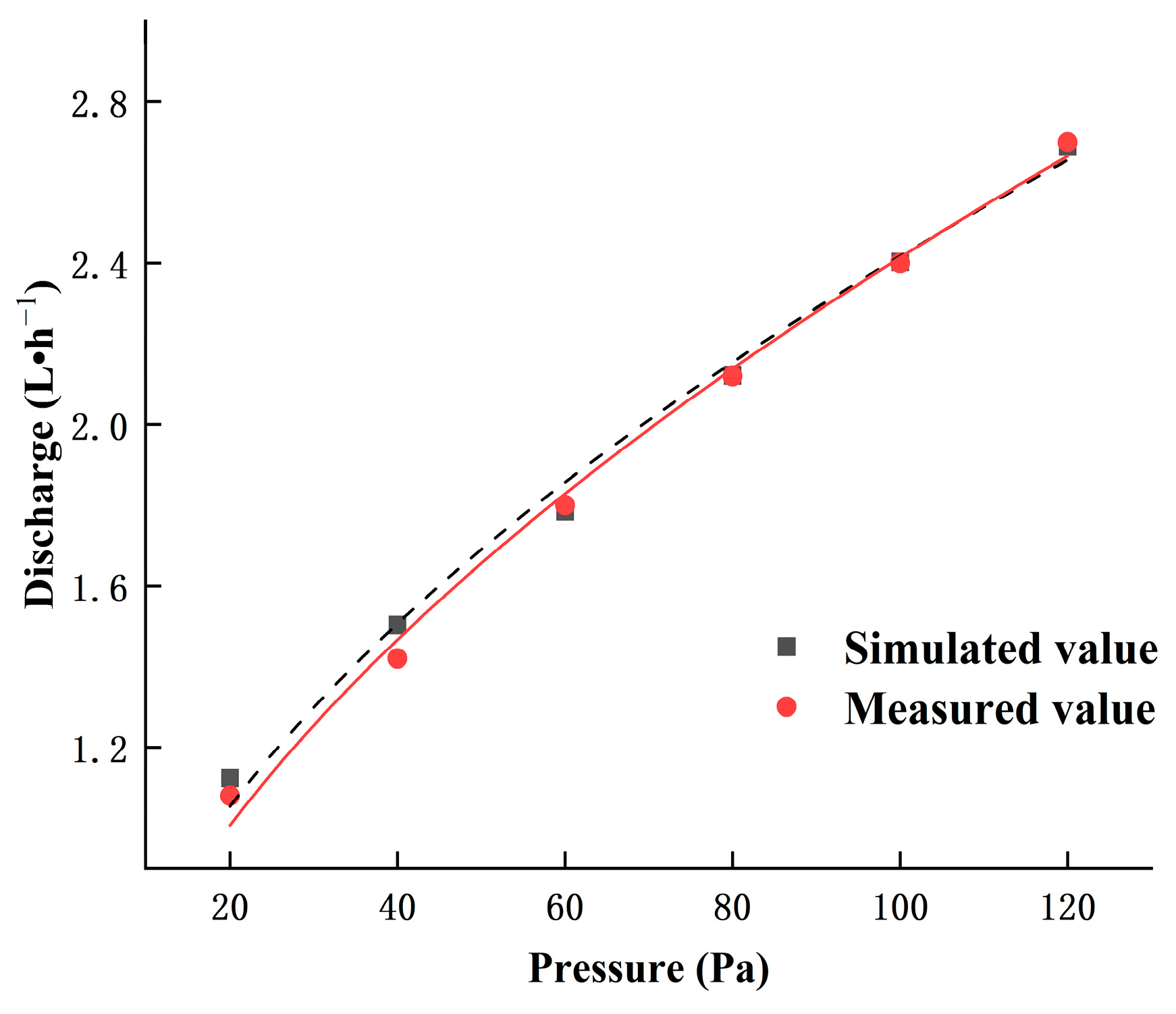


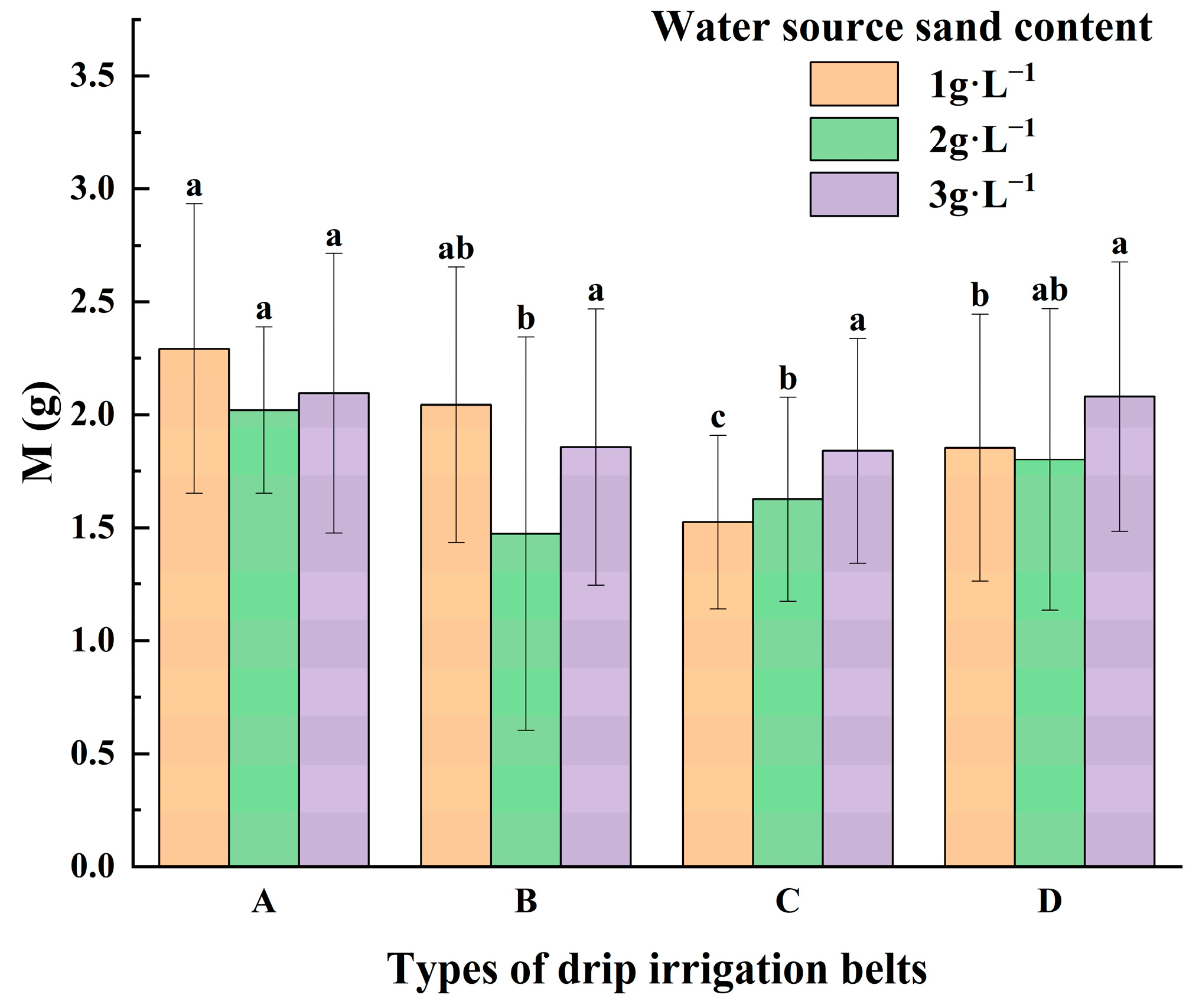

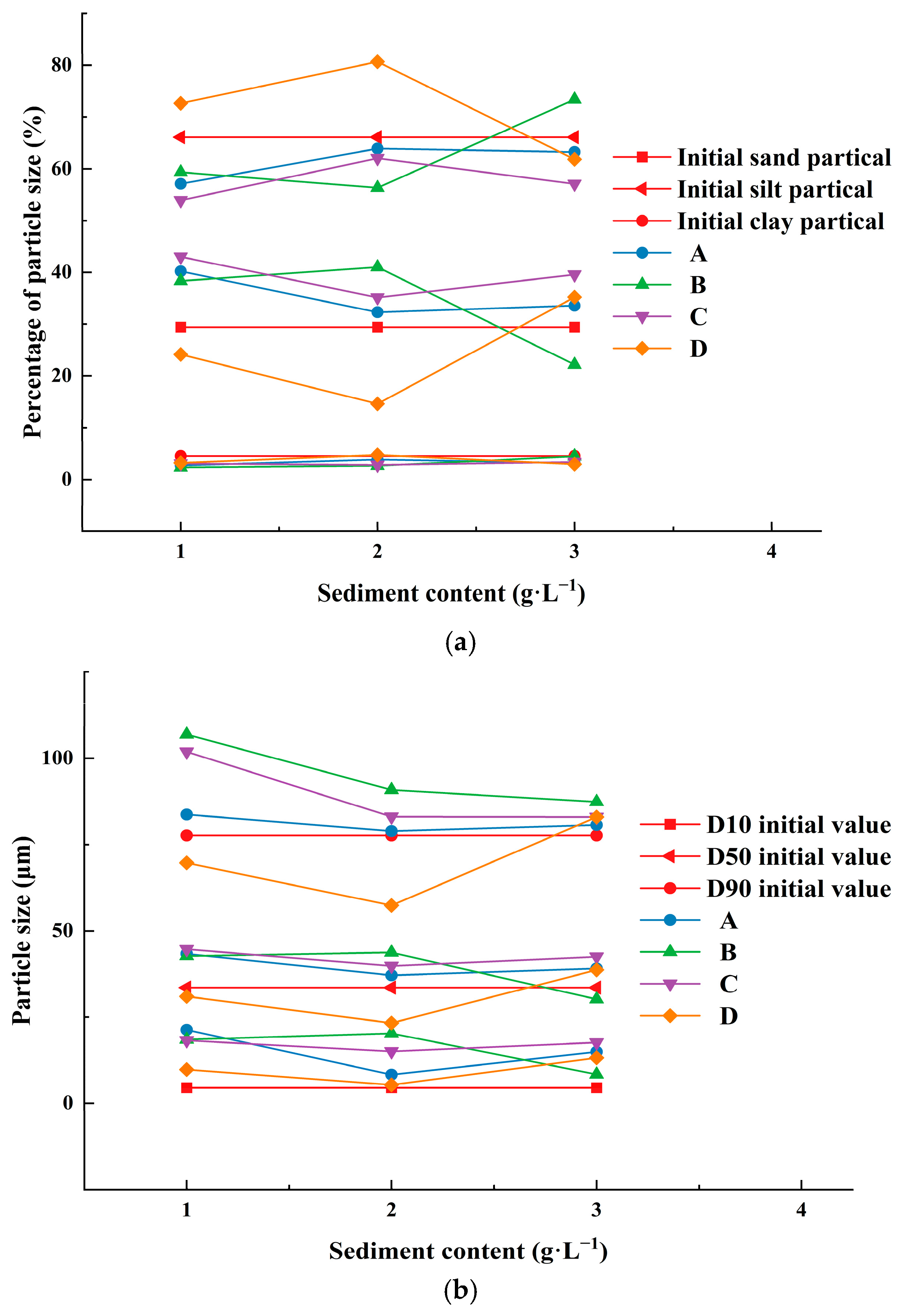

| Type | Inner Diameter (mm) | Pitch(cm) | Wall Thickness (mm) | Number of Outlets | Rated Flow Rate (L·h−1) | Flow Index (m) | Flow Coefficient (k) | Flow Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 17.5 | 20 | 0.14 | 5 | 3.43 | 0.52 | 0.310 | 3.4% |
| B | 16 | 30 | 0.20 | 3 | 2.40 | 0.52 | 0.218 | 5.2% |
| C | 16 | 20 | 0.16 | 5 | 4.54 | 0.55 | 0.367 | 7.1% |
| D | 16 | 30 | 0.20 | 5 | 3.20 | 0.55 | 0.251 | 3.4% |
| Particle Size (mm) | 0.0005 | 0.0010 | 0.0020 | 0.0050 | 0.0100 | 0.0200 | 0.0450 | 0.0750 | 0.1000 | 0.2000 |
| Cumulative Ratio (%) | 0.23 | 1.86 | 4.51 | 10.91 | 17.53 | 29.77 | 65.32 | 88.73 | 96.46 | 100.0 |
| Percentage of Particle Size | D10 | D50 | D90 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle size value (mm) | 0.00449 | 0.03353 | 0.07766 |
| Sediment Content | 1 g·L−1 | 2 g·L−1 | 3 g·L−1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Types | A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D |
| a | −0.62 | −0.74 | −0.60 | −1.01 | −0.85 | −1.00 | −0.76 | −0.91 | −0.87 | −0.87 | −0.62 | −0.97 |
| b | 1.70 | 1.78 | 1.62 | 2.01 | 1.84 | 1.97 | 1.73 | 1.92 | 1.88 | 1.84 | 1.57 | 1.94 |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.99 |
| Drip Irrigation Belt | Dra | Cu | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g·L−1 | 2 g·L−1 | 3 g·L−1 | 1 g·L−1 | 2 g·L−1 | 3 g·L−1 | |
| A | 93.28 a | 87.06 b | 85.76 b | 74.33 b | 75.74 b | 97.07 a |
| B | 91.05 a | 97.74 a | 97.76 a | 93.43 a | 92.28 a | 88.36 b |
| C | 88.24 b | 94.05 a | 99.01 a | 91.19 a | 87.21 a | 82.97 c |
| D | 91.52 a | 95.02 a | 98.04 a | 93.49 a | 91.91 a | 82.84 c |
| Sediment Content (g·L−1) | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.128 | 0.685 ** | 0.346 | 0.509 ** |
| 2 | 0.544 ** | 0.767 ** | 0.399 * | 0.075 |
| 3 | 0.410 * | 0.032 | 0.372 | 0.689 ** |
| Impact Factor | M | m | Q |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drip irrigation belt | 0.012 | 0.000 | 0.547 |
| Sediment content | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.822 |
| Drip irrigation belt × sediment content | 0.054 | 0.000 | 0.988 |
| Drip Irrigation Belt | Sediment Content (g·L−1) | >0.1 mm | 0.05~0.1 mm | 0.02~0.05 mm | 0.01~0.02 mm | 0.005~0.01 mm | 0~0.005 mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 5.55 | 34.66 | 51.25 | 5.17 | 0.05 | 3.32 |
| 2 | 3.65 | 28.62 | 44.59 | 11.51 | 4.40 | 7.23 | |
| 3 | 3.75 | 29.82 | 48.17 | 10.88 | 2.18 | 5.20 | |
| B | 1 | 9.74 | 28.60 | 44.72 | 11.75 | 2.00 | 3.19 |
| 2 | 4.70 | 36.33 | 48.58 | 6.14 | 0.16 | 4.09 | |
| 3 | 2.04 | 20.11 | 47.16 | 17.92 | 5.21 | 7.56 | |
| C | 1 | 10.42 | 32.61 | 45.01 | 6.52 | 0.35 | 5.09 |
| 2 | 4.94 | 30.20 | 47.80 | 10.02 | 2.16 | 4.88 | |
| 3 | 5.90 | 33.67 | 47.54 | 7.51 | 0.23 | 5.15 | |
| D | 1 | 2.29 | 21.86 | 49.26 | 17.21 | 3.76 | 5.62 |
| 2 | 0.55 | 14.04 | 42.89 | 24.06 | 9.01 | 9.45 | |
| 3 | 4.94 | 30.30 | 46.82 | 10.66 | 1.92 | 5.36 |
| Drip Irrigation Belt | Sediment Content (g·L−1) | D10 | D50 | D90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 0.02130 | 0.04333 | 0.08369 |
| 2 | 0.00834 | 0.03708 | 0.07891 | |
| 3 | 0.01491 | 0.03908 | 0.08066 | |
| B | 1 | 0.01847 | 0.04270 | 0.10690 |
| 2 | 0.02026 | 0.04372 | 0.09084 | |
| 3 | 0.00842 | 0.03014 | 0.08737 | |
| C | 1 | 0.01822 | 0.04465 | 0.10190 |
| 2 | 0.01505 | 0.03979 | 0.08303 | |
| 3 | 0.01762 | 0.04248 | 0.08295 | |
| D | 1 | 0.00982 | 0.03093 | 0.06971 |
| 2 | 0.00534 | 0.02329 | 0.05735 | |
| 3 | 0.01317 | 0.03867 | 0.08295 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Xue, M.; Sun, H.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Han, Q. Investigating Sedimentation Patterns and Fluid Movement in Drip Irrigation Emitters in the Yellow River Basin. Water 2025, 17, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070910
Wang M, Xue M, Sun H, Li H, Li R, Han Q. Investigating Sedimentation Patterns and Fluid Movement in Drip Irrigation Emitters in the Yellow River Basin. Water. 2025; 17(7):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070910
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mengyang, Mengyun Xue, Hao Sun, Hui Li, Rui Li, and Qibiao Han. 2025. "Investigating Sedimentation Patterns and Fluid Movement in Drip Irrigation Emitters in the Yellow River Basin" Water 17, no. 7: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070910
APA StyleWang, M., Xue, M., Sun, H., Li, H., Li, R., & Han, Q. (2025). Investigating Sedimentation Patterns and Fluid Movement in Drip Irrigation Emitters in the Yellow River Basin. Water, 17(7), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070910






