Green Regeneration and Resource Recovery of Nickel-Plating Waste Solution: A Synergistic Study of Electrodialysis and Advanced Oxidation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Composition of Wastewater
2.2. Experimental Steps
2.2.1. Regeneration of Wastewater by ED
2.2.2. Reuse of Regenerated Wastewater
2.2.3. PDS Oxidation Experiment
2.2.4. Calcium Salt Dosing Experiment
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ED Regeneration of Wastewater
3.2. Reuse of Regenerated Wastewater
3.3. Recovery of Phosphorus from Concentrated Wastewater
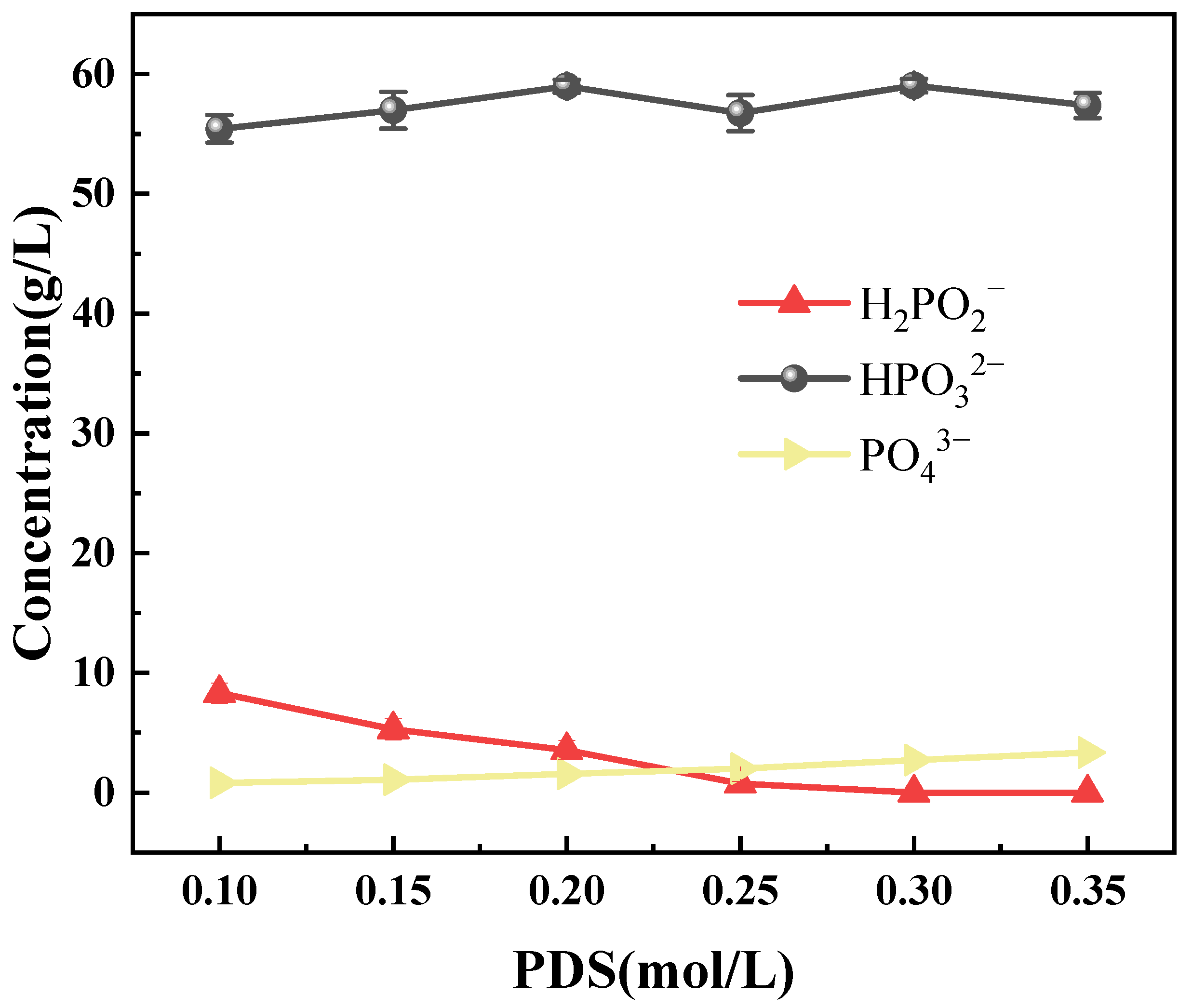
3.3.1. Phosphorus Speciation Changes During Oxidation
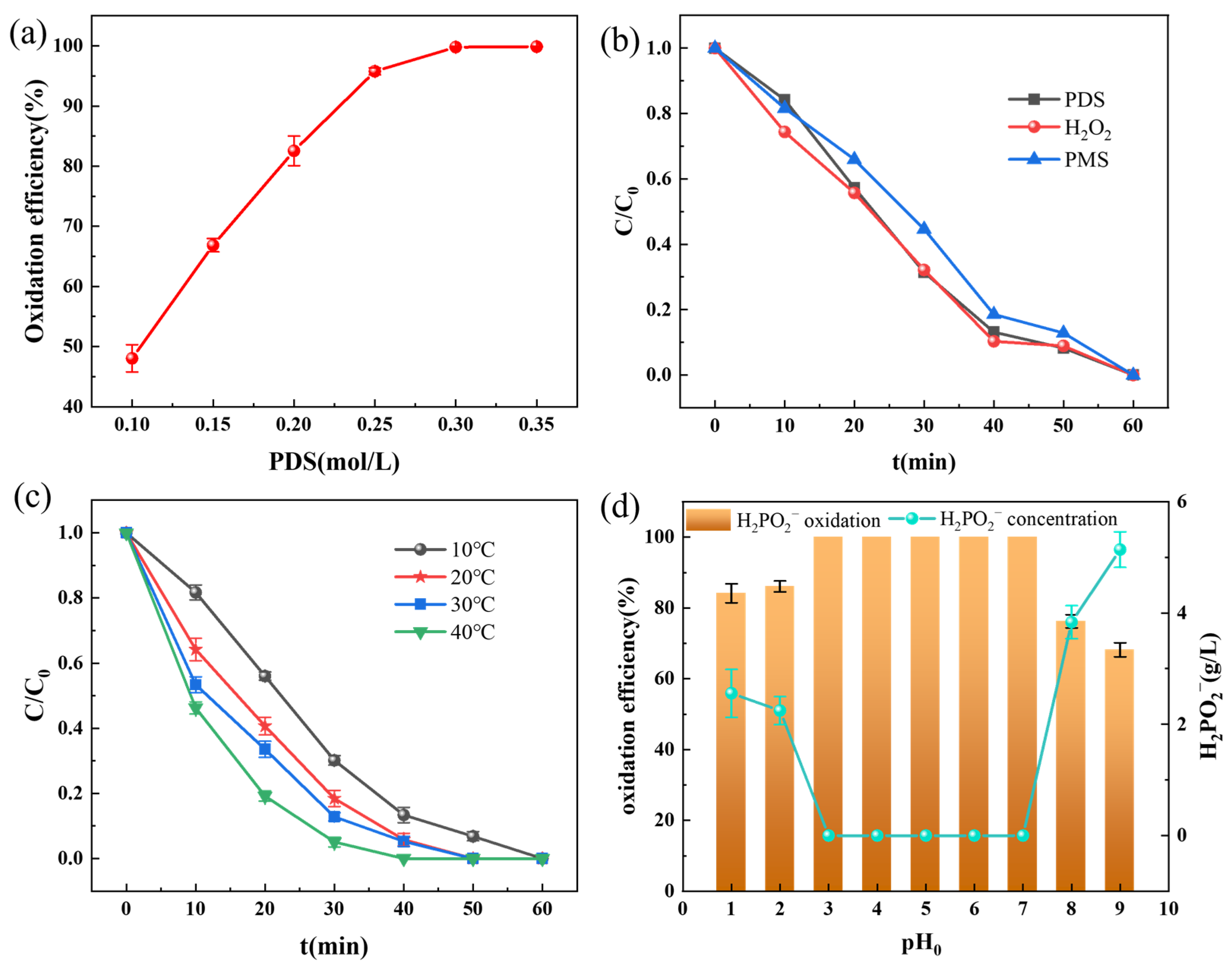
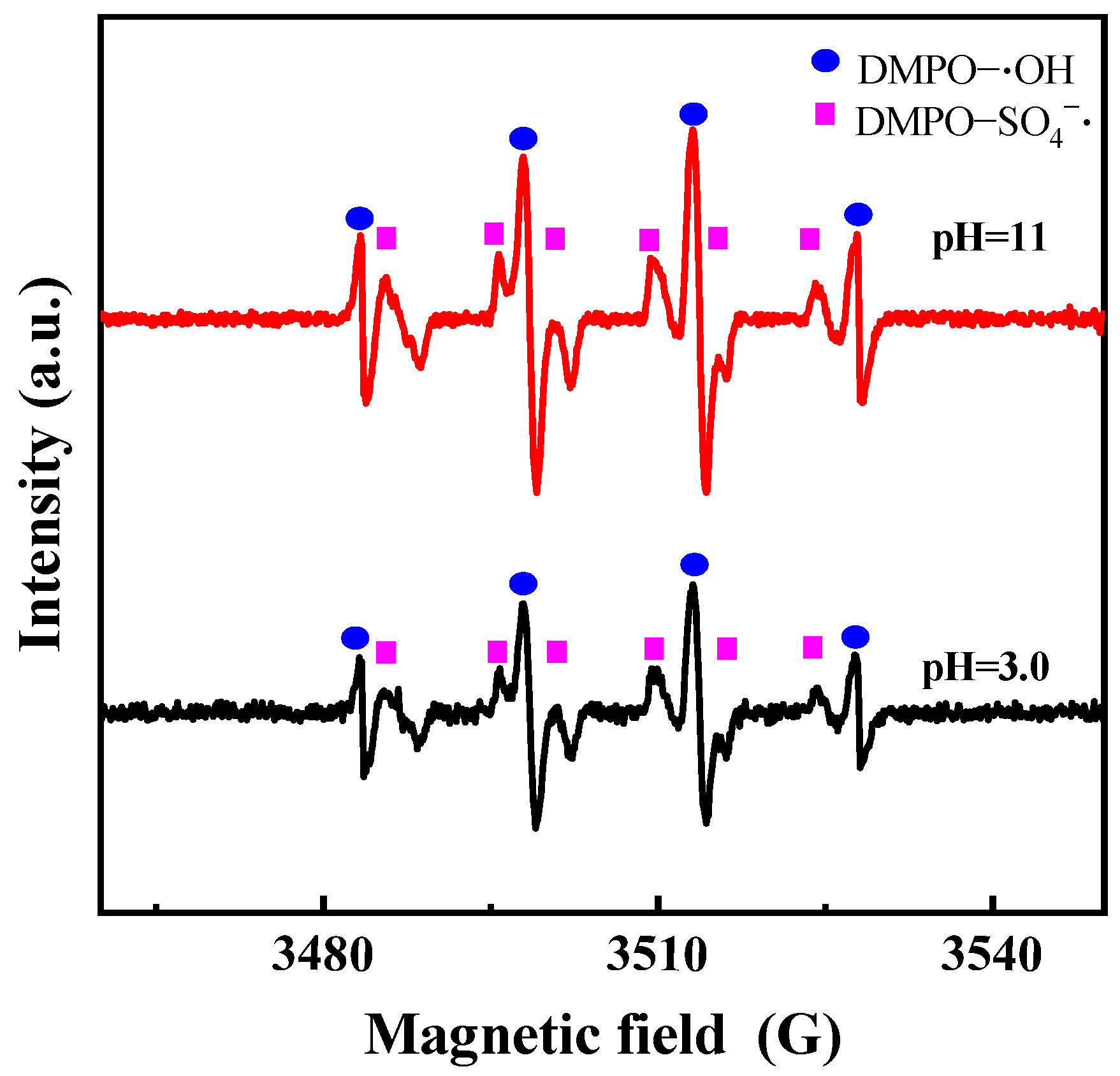
3.3.2. Effects of Reaction Parameters
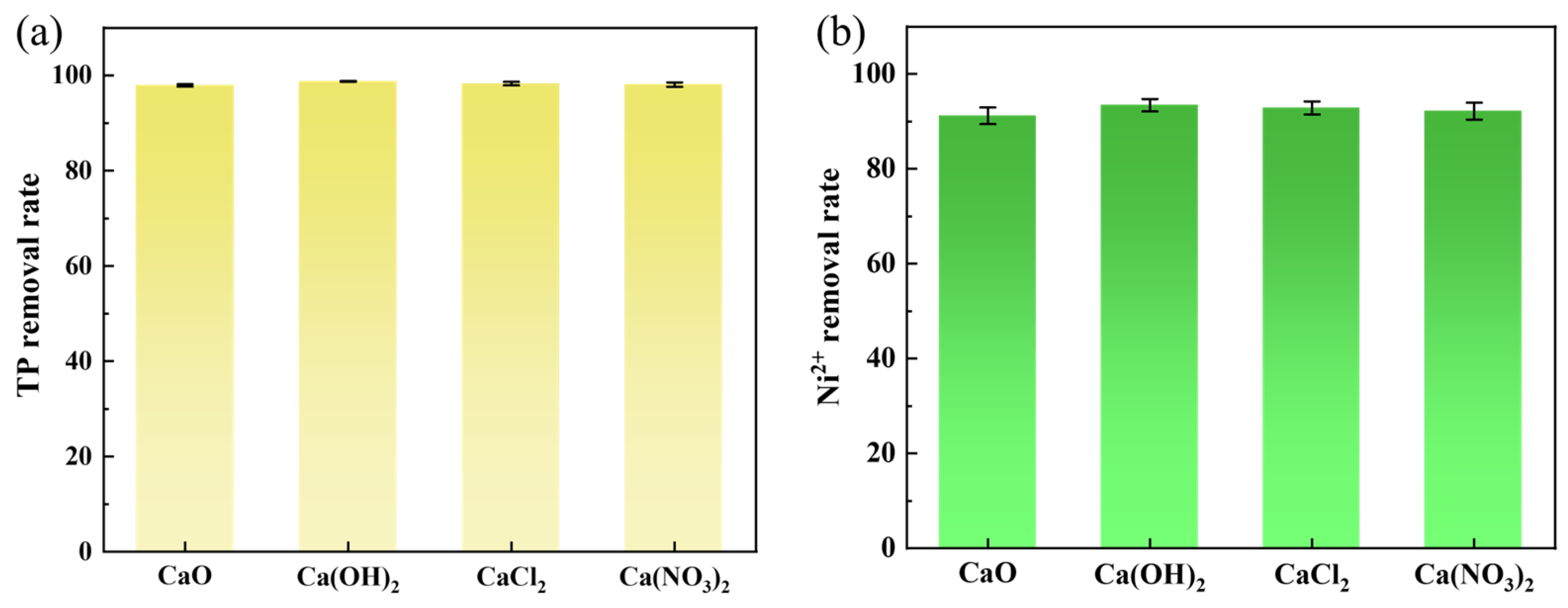
3.3.3. Effect of Calcium Dosage on Phosphorus Recovery
3.3.4. Analysis of Precipitated Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, K.; Qin, J.; Hu, M.; Hu, L.; Mao, M.; Li, X.; Lin, Z.; Liu, W. High-efficiency nickel recovery from spent electroless nickel plating solution: Effective degradation of high-concentration nickel complexes to form a nickel ferrite nanomaterial via Fe3O4 catalytic oxidation. Environ. Sci. Nano 2024, 11, 900–910. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Dai, M.; Ali, I.; Bian, H.; Peng, C. Recovery of nickel from actual electroplating wastewater by integrated electrodeposition with adsorption pretreatment technique. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 172, 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Zhong, J.; Feng, K.; Wu, Z.; Du, B.; He, J.; Li, Z.; He, L.; et al. Grave-to-cradle upcycling of Ni from electroplating wastewater to photothermal CO2 catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5305. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Hou, Y.; Ren, X.; Sun, C.; Wang, M. Research progress on the removal, recovery and direct high-value materialization of valuable metal elements in electroplating/electroless plating waste solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102577. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Shi, X.; Zeng, H. How far does the Copper/Nickle recovery from the practical application in the electroplating wastewater? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2023, 19, 200170. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Dai, M.; Wu, Y.; Fu, H.; Hou, X.; Peng, C.; Luo, H. Resource utilization of electroplating wastewater: Obstacles and solutions. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2022, 8, 484–509. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lian, R.; Wu, X.; Dai, L.; Ding, J.; Ye, X.; Chen, R.; Ding, R.; Liu, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. Nickel recovery from electroplating sludge via bipolar membrane electrodialysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 637, 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- Molaei, M.; Atapour, M. Nickel-based coatings as highly active electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction: A review on electroless plating cost-effective technique. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 40, e00991. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Takahashi, N.; Kaneko, K.; Shimizu, T.; Takarada, T. A novel method for nickel recovery and phosphorus removal from spent electroless nickel-plating solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Yang, B.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Z. Nickel speciation of spent electroless nickel plating effluent along the typical sequential treatment scheme. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, P.T.; Szlag, D.C. Current and emerging technologies for extending the lifetime of electroless nickel plating baths. Clean Prod. Process. 2001, 2, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagnaro, S.M.; Mesquida, C.; Zysler, R.; Stábile, F.; Yañez, R.A.; Soldati, A.; Ramos, S. Comparative study of Ni nanoparticles synthetized using electroless Ni plating waste and an analytical Ni reagent. Characterization and possible application in magnetic fluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2024, 611, 172594. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xu, N.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Fan, F.; Gao, W.; Zhao, Y. Electrocatalysis coupled super-stable mineralization for the efficient treatment of phosphorus containing plating wastewater. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 302, 120910. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, A.; Singh, B.K.; Purnendu, K.; Kumari, P.; Sankar, P.R.; Mundra, G.; Bohm, S. Utilization of the nickel hydroxide derived from a spent electroless nickel plating bath for energy storage applications. RSC Sustain. 2023, 1, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.H.; Chou, H.W.; Wu, Y.F. Removal of nickel from chemical plating waste solution through precipitation and production of microsized nickel hydroxide particles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Pan, S.; Sheng, J.; Ma, J.; Yan, Y.; Nie, Y.; Yuan, S. High-efficiency phosphorus recovery from hypophosphite and phosphite-containing wastewater via a new electrodialysis enrichment and hydrothermal oxidation coupling process. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154088. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, X.; Pan, Y.; Su, C.; Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Shao, Z. Superstructures with atomic-level arranged perovskite and oxide layers for advanced oxidation with an enhanced non-free radical pathway. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Shu, W.; Mao, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H. Efficient simultaneous removal of nickel, phosphorus and COD from electroless nickel plating wastewater by three dimensional electrodialytic system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 345, 127417. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Guan, W.; Fu, M. Recovery of nickel from electroless nickel plating wastewater based on the synergy of electrocatalytic oxidation and electrodeposition technology. Water Environ. Res. 2022, 94, e10741. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, A.; Yin, H.; Xie, X. Adsorption performance of tetratitanate nanowhiskers for Ni2+ from aqueous solution and removal of Ni2+ from actual electroplating wastewater via successive oxidation and adsorption processes. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103703. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K. Research on Metal Ion Recovery from Chemical Nickel Plating Waste Liquid Based on Membrane Separation Technology. Forum Res. Innov. Manag. 2025, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.Z.; Yang, Y.R.; Liu, T.; Guo, Z.Y.; Li, C.X.; Li, H.Y.; Cui, K.P.; Li, W.W. Biological upcycling of nickel and sulfate as electrocatalyst from electroplating wastewater. Water Res. 2024, 250, 121063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Xiao, K.; Wei, L.; Yang, B.; Yu, G.; Deng, S.; Duan, H.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Decomplexation removal of Ni (II)-citrate complexes through heterogeneous Fenton-like process using novel CuO-CeO2-CoOx composite nanocatalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 374, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarazzato, T.; Panossian, Z.; Tenório, J.A.S.; Pérez-Herranz, V.; Espinosa, D.C.R. A review of cleaner production in electroplating industries using electrodialysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 1590–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q. Study on Electrochemical Regeneration of Electroless Nickel Waste. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Li, C.; Liang, X.; Lu, G.; Xu, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, W.; Ji, F. Recovery of high purity ferric phosphate from a spent electroless nickel plating bath. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sheng, X.; Dong, Y.; Ma, Y. Removal of high-concentration phosphate by calcite: Effect of sulfate and pH. Desalination 2012, 289, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Bashan, L.E.; Bashan, Y. Recent advances in removing phosphorus from wastewater and its future use as fertilizer (1997–2003). Water Res. 2004, 38, 4222–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, F.; Xia, M. Integrating multi-method approaches for the green separation and retrieval of nickel and phosphorus from spent electroless nickel plating solutions. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 10576–10586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Jin, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Tan, Z.; Wang, L.; Cheng, X. Heterogeneous metal-activated persulfate and electrochemically activated persulfate: A review. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Guo, W.; Liu, Q.; Li, G.; Guo, S.; Chen, R. Cu2O/BiVO4 heterostructure controllably triggers radical and non-radical persulfate activation via light “on-off” for efficient organic contaminants degradation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2024, 344, 123606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jing, B.; Tang, Z.; Ao, Z.; Xia, D.; Zhu, M.; Wang, S. Experimental and DFT insights into the visible-light driving metal-free C3N5 activated persulfate system for efficient water purification. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 289, 120023. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C.; Huang, C.Y. Degradation of sulfamethazine in water in thermally activated persulfate process. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2024, 155, 105229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Xin, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Cai, C.; Wang, M. Erythromycin degradation and ERY-resistant gene inactivation in erythromycin mycelial dreg by heat-activated persulfate oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Han, Y.; Xiang, W.; Zhong, D.; Wang, C.; Zhou, T.; Wu, X.; Mao, J. In situ-formed phenoxyl radical on the CuO surface triggers efficient persulfate activation for phenol degradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15361–15370. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Fang, Y.; Peng, F.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, R. Efficient purification of tetracycline wastewater by activated persulfate with heterogeneous Co-V bimetallic oxides. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 619, 188–197. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, X.; Duan, X.; Sarmah, A.K.; Zhao, X. Remediation of environmentally persistent organic pollutants (POPs) by persulfates oxidation system (PS): A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Dong, H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, J.; Dong, Q.; Xiang, S.; Chu, D. Activation of persulfate by graphene/biochar composites for phenol degradation: Performance and nonradical dominated reaction mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109348. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Z.; Song, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, S.; He, F.; Yu, J. Deciphering CaO-induced peroxydisulfate activation for destruction of halogenated organic pollutants in a low energy vibrational mill. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134090. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Ye, G.; Yan, Z.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J. Overlooked role of void-nanoconfined effect in emerging pollutant degradation: Modulating the electronic structure of active sites to accelerate catalytic oxidation. Water Res. 2024, 249, 120950. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.T.; Du, W.Y.; Chen, J.L.; Zhang, J.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Hu, Y.Y. Removal of N-methyldiethanolamine in wastewater by using electro-activated persulfate: Mechanisms and applicability. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108008. [Google Scholar]
- Checa-Fernández, A.; Santos, A.; Romero, A.; Dominguez, C.M. Remediation of real soil polluted with hexachlorocyclohexanes (α-HCH and β-HCH) using combined thermal and alkaline activation of persulfate: Optimization of the operating conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 270, 118795. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Hu, Q.; Liu, W.; Qiao, Y.; Cai, D.; Zhu, P.; Wang, D.; Xu, H.; Shu, S.; et al. Accelerated spent coffee grounds humification by heat/base co-activated persulfate and products’ fertilization evaluation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, C.; Liang, X.; Xu, J.; Lu, G.; Ji, F. Advanced oxidation of hypophosphite and phosphite using a UV/H2O2 process. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 11893-1989; Water Quality—Determination of Total Phosphorus—Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Benvenuti, T.; Krapf, R.S.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Bernardes, A.M.; Zoppas-Ferreira, J. Recovery of nickel and water from nickel electroplating wastewater by electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 129, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wu, B. Sulfate radical-based oxidation for sludge treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Meng, X.; Luo, J.; Deng, L.; Shi, Z.; Crittenden, J. Oxidation of microcystin-LR via activation of peroxymonosulfate using ascorbic acid: Kinetic modeling and toxicity assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4305–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.; Tang, H. Fast and complete degradation of norfloxacin by using Fe/Fe3C@ NG as a bifunctional catalyst for activating peroxymonosulfate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 202, 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Ang, H.M.; Tadé, M.O.; Wang, S. Facile synthesis of hierarchically structured magnetic MnO2/ZnFe2O4 hybrid materials and their performance in heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 19914–19923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasahayam, S.K.; Guzman, L.; Gunawan, G.; Viswanathan, T. A comprehensive review of phosphorus removal technologies and processes. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2014, 51, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Shober, A.L.; Scheckel, K.G.; Penn, C.J.; Turner, K.C. Mechanisms of phosphorus removal by phosphorus sorbing materials. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar]




| Processing Technology | Key Achievements | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| chemical precipitation | Remarkable treatment effect; mature process; simple operation; wide range of applications | Produces large amounts of sludge; difficult to completely remove complexed nickel; stringent pH control requirements |
| advanced oxidation processes | Strong broad-spectrum degradation ability; highly efficient complex-breaking and destabilization; suitable for deep treatment | Higher operating costs; harsh reaction conditions; complex equipment and high maintenance requirements |
| electrochemical methods | High degree of automation control; green environmental protection; no secondary pollution; suitable for the recovery of valuable metals | Higher equipment and power costs; electrodes are susceptible to passivation or corrosion; pH- and conductivity-sensitive |
| ion exchange | Stable and clear effluent quality; resource recycling; easy to operate; can be automated | The resin easily becomes poisoned or clogged; the scope of application is limited; there are difficulties in the treatment of regeneration fluid. |
| adsorption | Highly efficient removal of nickel ions (free and complexed); high green potential; suitable for low concentrations of wastewater treatment | Limited adsorption capacity, which needs to be replaced or regenerated frequently; regeneration operation is complicated and may lead to secondary pollution; poor treatment of high concentrations of wastewater |
| membrane separation | Compact process with small footprint; no additives; no chemical reaction; adaptable and applicable to a variety of pollutants | Serious membrane contamination problems; high investment and operating costs; high requirements for influent water quality |
| biological treatments | Green environmental protection with no secondary pollution; produces a wide source of materials, making it renewable; low concentration of nickel has a good removal ability | Difficulty to achieve rapid industrialization and diffusion; stringent requirements for environmental conditions; regeneration and longevity of biomaterials |
| Items | pH | Ni2+ (g/L) | H2PO2− (g/L) | HPO32− (g/L) | PO43− (g/L) | TP (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 4.56 ± 0.2 | 5.82 ± 0.1 | 27.91 ± 2 | 124.96 ± 5 | 0.1687 ± 0.2 | 190.38 ± 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, X.; Cui, K.; Li, H.; Wu, W. Green Regeneration and Resource Recovery of Nickel-Plating Waste Solution: A Synergistic Study of Electrodialysis and Advanced Oxidation. Water 2025, 17, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071071
Xiong X, Cui K, Li H, Wu W. Green Regeneration and Resource Recovery of Nickel-Plating Waste Solution: A Synergistic Study of Electrodialysis and Advanced Oxidation. Water. 2025; 17(7):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071071
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Xiaolong, Kangping Cui, Haiyang Li, and Wenming Wu. 2025. "Green Regeneration and Resource Recovery of Nickel-Plating Waste Solution: A Synergistic Study of Electrodialysis and Advanced Oxidation" Water 17, no. 7: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071071
APA StyleXiong, X., Cui, K., Li, H., & Wu, W. (2025). Green Regeneration and Resource Recovery of Nickel-Plating Waste Solution: A Synergistic Study of Electrodialysis and Advanced Oxidation. Water, 17(7), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071071






