Snapshot of the Bacterial Composition of Two Invertebrates, Peltodoris atromaculata and Petrosia ficiformis, from a Shallow Hydrothermal Spring on the West Coast of Sicily
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3. Raw Data Processing and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing Output and Analysis
3.2. The Bacterial Composition of P. atromaculata and P. ficiformis Collected at the Phylum Level
3.3. The Bacterial Composition of P. atromaculata and P. ficiformis at the Class Level
3.4. The Bacterial Composition of P. atromaculata and P. ficiformis at the Family Level
3.5. The Bacterial Composition of P. atromaculata and P. ficiformis at the Genus Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Price, R.E.; Giovannelli, D. A Review of the Geochemistry and Microbiology of Marine Shallow-Water Hydrothermal Vents. In Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollner, S.; Colaço, A.; Gebruk, A.; Halpin, P.N.; Higgs, N.; Menini, E.; Mestre, N.C.; Qian, P.Y.; Sarrazin, J.; Szafranski, K.; et al. Application of Scientific Criteria for Identifying Hydrothermal Ecosystems in Need of Protection. Mar. Policy 2021, 132, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubilier, N.; Bergin, C.; Lott, C. Symbiotic Diversity in Marine Animals: The Art of Harnessing Chemosynthesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Juniper, S.K.; Perez, M.; Ju, S.J.; Kim, S.J. Diversity and Characterization of Bacterial Communities of Five Co-Occurring Species at a Hydrothermal Vent on the Tonga Arc. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 4481–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dover, C.L.; Arnaud-Haond, S.; Gianni, M.; Helmreich, S.; Huber, J.A.; Jaeckel, A.L.; Metaxas, A.; Pendleton, L.H.; Petersen, S.; Ramirez-Llodra, E.; et al. Scientific Rationale And International Obligations For Protection of Active Hydrothermal Vent Ecosystems from Deep-Sea Mining. Mar. Policy 2018, 90, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duperron, S.; Halary, S.; Lorion, J.; Sibuet, M.; Gaill, F. Unexpected Co-occurrence of Six Bacterial Symbionts in the Gills of the Cold Seep Mussel Idas Sp. (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.S.; Soon, N.; Chang, Y.; Wainwright, B.J. Bacterial and Fungal Co-Occurrence in the Nudibranch, Pteraeolidia semperi. Life 2022, 12, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, N.V.; Eliseikina, M.G.; Balakirev, E.S.; Ayala, F.J. Multiple Bacterial Partners in Symbiosis with the Nudibranch Mollusk Rostanga alisae. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanvicente-Añorve, L.; Hermoso-Salazar, M.; Ortigosa, J.; Solís-Weiss, V.; Lemus-Santana, E. Opisthobranch Assemblages from a Coral Reef System: The Role of Habitat Type and Food Availability. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2012, 88, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wägele, H.; Willan, R.C. Phylogeny of the Nudibranchia. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2000, 130, 83–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.R.; Sanders, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Amir, A.; Ladau, J.; Locey, K.J.; Prill, R.J.; Tripathi, A.; Gibbons, S.M.; Ackermann, G.; et al. A Communal Catalogue Reveals Earth’s Multiscale Microbial Diversity. Nature 2017, 551, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, M.; Betti, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Canese, S.; Cau, A.; Andaloro, F.; Greco, S.; Bo, M. Diversity and Abundance of Heterobranchs (Mollusca, Gastropoda) from the Mesophotic and Bathyal Zone of the Mediterranean Sea. Eur. Zool. J. 2022, 89, 160–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, C. The Growth of Peltodoris atromaculata Bergh, 1880 (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia) in the Laboratory. J. Molluscan Stud. 1996, 62, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemballa, S.; Schermutzki, F. Cytotoxic Haplosclerid Sponges Preferred: A Field Study on the Diet of the Dotted Sea Slug Peltodoris atromaculata (Doridoidea: Nudibranchia). Mar. Biol. 2004, 144, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, A.; Marletta, G. Observations on the Dorid Peltodoris atromaculata Bergh, 1880 (Gastropoda Nudibranchia) along the Central-Eastern Coast of Sicily, Ionian Sea. Biodivers. J. 2021, 12, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M.; Ribes, M.; van Duyl, F.C. Nutrient fluxes through sponges: Biology, budgets, and ecological implications. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2012, 62, 113–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M.; Aguilar, R.; Bannister, R.; Bell, J.; Conway, J.; Dayton, P.; Díaz, C.; Gutt, J.; Kelly, M.; Kenchington, E.; et al. Sponge Grounds as Key Marine Habitats: A Synthetic Review of Types, Structure, Functional Roles, and Conservation Concerns. In Marine Animal Forests: The Ecology of Benthic Biodiversity Hotspots; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 145–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, N.E.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Kelly, M.; Raleigh, J.; Travers, S.A.A.; McCormack, G.P. Reassessment of the Classification of the Order Haplosclerida (Class Demospongiae, Phylum Porifera) Using 18S RRNA Gene Sequence Data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 43, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Giovine, M.; Steindler, L. Petrosia ficiformis (Poiret, 1789): An excellent model for holobiont and biotechnological studies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 74, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, N.S.; Taylor, M.W. Marine sponges and their microbial symbionts: Love and other relationships. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, M.N.; Taboada, S.; Riesgo, A.; Díez-Vives, C.; De Leo, F.C.; Jeffreys, R.M.; Copley, J.T.; Little, C.T.S.; Ríos, P.; Cristobo, J.; et al. Evidence of Vent-Adaptation in Sponges Living at the Periphery of Hydrothermal Vent Environments: Ecological and Evolutionary Implications. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzella, V.; Dell’Anno, A.; Etxebarría, N.; González-Gaya, B.; Nuzzo, G.; Fontana, A.; Núñez-Pons, L. High Microbiome and Metabolome Diversification in Coexisting Sponges with Different Bio-Ecological Traits. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, s42003–s42024. [Google Scholar]
- Pagliara, P.; Barca, A.; Verri, T.; Caroppo, C. The Marine Sponge Petrosia ficiformis Harbors Different Cyanobacteria Strains with Potential Biotechnological Application. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, S.; Hentschel, U.; Taylor, M.W. Deep Sequencing Reveals Diversity and Community Structure of Complex Microbiota in Five Mediterranean Sponges. In Ancient Animals, New Challenges; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher, K.M.; Kuo, J.; Fromont, J.; Sutton, D.C. Vertical transmission of Cyanobacterial symbionts in the marine sponge Chondrilla australiensis (Demospongiae). Hydrobiologia 2001, 461, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.H.; Jiang, A.J.; Li, X.G.; Wu, S.J.; Chen, J.W.; Qu, M.J.; Qi, X.Q.; Dai, J.; Zhao, R.; et al. Metagenomic Analysis Reveals Wide Distribution of Phototrophic Bacteria in Hydrothermal Vents on the Ultraslow-Spreading Southwest Indian Ridge. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast Length Adjustment of Short Reads to Improve Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, C.; Scalabrin, S.; Morgante, M.; Giorgi, F.M. An Extensive Evaluation of Read Trimming Effects on Illumina NGS Data Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A Versatile Open Source Tool for Metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Bi, H.-Y.; Chen, H.-G.; Zheng, P.-F.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Li, J.-T. Metagenomics Reveals Dominant Unusual Sulfur Oxidizers Inhabiting Active Hydrothermal Chimneys from the Southwest Indian Ridge. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 861795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, G.J. The Microbiomes of Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents: Distributed Globally, Shaped Locally. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Most, N.; Qian, P.Y.; Gao, Y.; Gollner, S. Active hydrothermal vent ecosystems in the Indian Ocean are in need of protection. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1067912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, S.P.; Pelletreau, K.N.; Rumpho, M.E. 16S rDNA-based metagenomic analysis of bacterial diversity associated with two populations of the kleptoplastic sea slug Elysia chlorotica and its algal prey Vaucheria litorea. Biol. Bull. 2012, 223, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersters, K.; De Vos, P.; Gillis, M.; Swings, J.; Vandamme, P.; Stackebrandt, E. Introduction to the Proteobacteria. In The Prokaryotes; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucato, A.; Vecchioni, L.; Savoca, D.; Presentato, A.; Arculeo, M.; Alduina, R. A Comparative Analysis of Aquatic and Polyethylene-Associated Antibiotic-Resistant Microbiota in the Mediterranean Sea. Biology 2021, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.S.; Shin, N.R.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, M.S.; Whon, T.W.; Hyun, D.W.; Yun, J.H.; Jung, M.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Bae, J.W. Host Habitat Is the Major Determinant of the Gut Microbiome of Fish. Microbiome 2021, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leto, Y.; Capri, F.C.; Mineo, A.; Cosenza, A.; Gallo, G.; Alduina, R.; Mannina, G. Initial PH Conditions Shape the Microbial Community Structure of Sewage Sludge in Batch Fermentations for the Improvement of Volatile Fatty Acid Production. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capri, F.C.; Prazzi, E.; Casamento, G.; Gambino, D.; Cassata, G.; Alduina, R. Correlation Between Microbial Community and Hatching Failure in Loggerhead Sea Turtle Caretta Caretta. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuij, T.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Putchakarn, S.; Pires, A.C.C.; Gomes, N.C.M.; de Voogd, N.J. Exploring Prokaryotic Communities in the Guts and Mucus of Nudibranchs, and Their Similarity to Sediment and Seawater Microbiomes. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Vives, C.; Taboada, S.; Leiva, C.; Busch, K.; Hentschel, U.; Riesgo, A. On the Way to Specificity-Microbiome Reflects Sponge Genetic Cluster Primarily in Highly Structured Populations. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 4412–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrshad, M.; Rodriguez-Valera, F.; Amoozegar, M.A.; López-García, P.; Ghai, R. The Enigmatic SAR202 Cluster up Close: Shedding Light on a Globally Distributed Dark Ocean Lineage Involved in Sulfur Cycling. ISME J. 2018, 12, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, D.F.R.; Polónia, A.R.M. Bacterial and Archaeal Communities Inhabiting Mussels, Sediment and Water in Indonesian Anchialine Lakes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.S.; Chander, P.; George, S. Phylogenetic Framework and Molecular Signatures for the Class Chloroflexi and Its Different Clades; Proposal for Division of the Class Chloroflexi Class. Nov. into the Suborder Chloroflexineae Subord. Nov., Consisting of the Emended Family Oscillochloridaceae and the Family Chloroflexaceae Fam. Nov., and the Suborder Roseiflexineae Subord. Nov., Containing the Family Roseiflexaceae Fam. Nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 103, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Moitinho-Silva, L.; Lurgi, M.; Björk, J.R.; Easson, C.; Astudillo-García, C.; Olson, J.B.; Erwin, P.M.; López-Legentil, S.; Luter, H.; et al. Diversity, Structure and Convergent Evolution of the Global Sponge Microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, M.; Adams, J.; Swain, M.; Hegarty, M.; Huws, S.; Gallagher, J. Metaphylogenomic and Potential Functionality of the Limpet Patella Pellucida’s Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18819–18839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pita, L.; Rix, L.; Slaby, B.M.; Franke, A.; Hentschel, U. The Sponge Holobiont in a Changing Ocean: From Microbes to Ecosystems. Microbiome 2018, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, D.F.R.; Swierts, T.; Coelho, F.J.R.C.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Huang, Y.M.; Ferreira, M.R.S.; Putchakarn, S.; Carvalheiro, L.; van der Ent, E.; Ueng, J.P.; et al. The Sponge Microbiome within the Greater Coral Reef Microbial Metacommunity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, P.A.; Robbins, S.J.; Tan, S.; Rix, L.; Miller, D.J.; Webster, N.S.; Zhang, G.; Bourne, D.G. Comparative Genomics Identifies Key Adaptive Traits of Sponge-Associated Microbial Symbionts. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 26, e16690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgsdorf, I.; Handley, K.M.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Erwin, P.M.; Steindler, L. Life at Home and on the Roam: Genomic Adaptions Reflect the Dual Lifestyle of an Intracellular, Facultative Symbiont. mSystems 2019, 4, e00057-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, S.; Jóhannsson, R.; Marteinsson, V. Bacterial Diversity in the Marine Sponge Halichondria panicea from Icelandic Waters and Host-Specificity of Its Dominant Symbiont “Candidatus Halichondribacter Symbioticus”. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 95, fiy220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipkema, D.; de Caralt, S.; Morillo, J.A.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Sørensen, S.J.; Smidt, H.; Uriz, M.J. Similar Sponge-Associated Bacteria Can Be Acquired via Both Vertical and Horizontal Transmission. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3807–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arillo, A.; Bavestrello, G.; Burlando, B.; Sarfi, M. Metabolic Integration between Symbiotic Cyanobacteria and Sponges: A Possible Mechanism. Mar. Biol. 1993, 117, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgsdorf, I.; Erwin, P.M.; López-Legentil, S.; Cerrano, C.; Haber, M.; Frenk, S.; Steindler, L. Biogeography Rather than Association with Cyanobacteria Structures Symbiotic Microbial Communities in the Marine Sponge Petrosia ficiformis. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafi, F.F.; Fuerst, J.A.; Fieseler, L.; Engels, C.; Goh, W.W.L.; Hentschel, U. Widespread Distribution of Poribacteria in Demospongiae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5695–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, C.; Galani, A.; Gavriilidou, A.; Chaib de Mares, M.; van der Oost, J.; Medema, M.H.; Sipkema, D. Comparative Metagenomic Analysis of Biosynthetic Diversity across Sponge Microbiomes Highlights Metabolic Novelty, Conservation, and Diversification. mSystems 2022, 7, e0035722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.-S.; Gao, Z.-M.; Gong, L.; Li, Q.-M.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Chen, H.-G.; He, L.-S.; Wang, Y. Genome-Centric View of the Microbiome in a New Deep-Sea Glass Sponge Species Bathydorus sp. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1078171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sickinger, C.; Brackwehr, S.M.; Melo Clavijo, J.; Gasperoni, G.; Tierling, S.; Preisfeld, A.; Christa, G. Microbiome Origin and Stress-Related Changes in Bacterial Abundance of the Photosymbiotic Sea Slug Berghia stephanieae (Á. Valdés, 2005). Symbiosis 2024, 93, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yang, S.; Ka, W.; Gao, P.; Li, Y.; Long, R.; Wang, J. Association of Gut Microbiota with Metabolism in Rainbow Trout Under Acute Heat Stress. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 846336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neave, M.J.; Michell, C.T.; Apprill, A.; Voolstra, C.R. Endozoicomonas Genomes Reveal Functional Adaptation and Plasticity in Bacterial Strains Symbiotically Associated with Diverse Marine Hosts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pérez, M.; Rodriguez-Valera, F. The Family Alteromonadaceae. In The Prokaryotes; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 69–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, E.P.; Mikhailov, V.V. New Family, Alteromonadaceae Fam. Nov., Including Marine Proteobacteria of the Genera Alteromonas, Pseudoalteromonas, Idiomarina, and Colwellia. Microbiology 2001, 70, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Jin, C.; Jin, A.; Lou, Z. Characterization of Fe(III)-Reducing Enrichment Cultures and Isolation of Enterobacter sp. Nan-1 from the Deep-Sea Sediment, South China Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 2020, 19, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Lu, J.; Sun, Z.; Xie, J.; Huang, J.; Su, M.; Wu, N. Characterization of Tissue-Associated Bacterial Community of Two Bathymodiolus Species from the Adjacent Cold Seep and Hydrothermal Vent Environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 149046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilidou, A.; Gutleben, J.; Versluis, D.; Forgiarini, F.; van Passel, M.W.J.; Ingham, C.J.; Smidt, H.; Sipkema, D. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Flavobacteriaceae: Insights into Carbohydrate Metabolism, Gliding Motility and Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 569. [Google Scholar]
- de Voogd, N.J.; Gauvin-bialecki, A.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Cleary, D.F.R. Assessing the Bacterial Communities of Sponges Inhabiting the Remote Western Indian Ocean Island of Mayotte. Mar. Ecol. 2018, 39, e12517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.; Yang, Y.T.; Lu, M.C.; Wong, T.Y.; Sung, P.J.; Huang, Y. Sen Antimicrobial Activity and Diversity of Bacteria Associated with Taiwanese Marine Sponge Theonella swinhoei. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turon, M.; Cáliz, J.; Triadó-Margarit, X.; Casamayor, E.O.; Uriz, M.J. Sponges and Their Microbiomes Show Similar Community Metrics across Impacted and Well-Preserved Reefs. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedysh, S.N.; Dunfield, P.F. B Eijerinckiaceae. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Gusmão, A.C.B.; Peres, F.V.; Paula, F.S.; Pellizari, V.H.; Kolm, H.E.; Signori, C.N. Microbial Communities in the Deep-Sea Sediments of the South São Paulo Plateau, Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Int. Microbiol. 2023, 26, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Thu, C.A.; Win, T.N.; Aung, N.L.; Win, H.S.; Naing, S.; Li, H.; et al. Microbial Community Structures and Important Taxa across Oxygen Gradients in the Andaman Sea and Eastern Bay of Bengal Epipelagic Waters. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1041521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, E.; Hanora, A.; Abdalla, S.; Abdelrahman Ahmed, A.A.; Zakeer, S. Shotgun Metagenomic Analysis of Bacterial Symbionts Associated with “Chromodoris quadricolor” Mantle. Mar. Genom. 2023, 69, 101030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelossi, E.; Milanese, M.; Milano, A.; Pronzato, R.; Riccardi, G. Characterisation and Antimicrobial Activity of Epibiotic Bacteria from Petrosia Ficiformis (Porifera, Demospongiae). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 309, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Hara, K.; Kasai, H.; Teramura, T.; Sunamura, M.; Ishibashi, J.; Kakegawa, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Kimura, H.; Marumo, K.; et al. Spatial Distribution, Diversity and Composition of Bacterial Communities in Sub-Seafloor Fluids at a Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Field of the Suiyo Seamount. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2009, 56, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.P.; McDonald, I.R.; Wood, A.P. The Family Methylobacteriaceae. In The Prokaryotes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



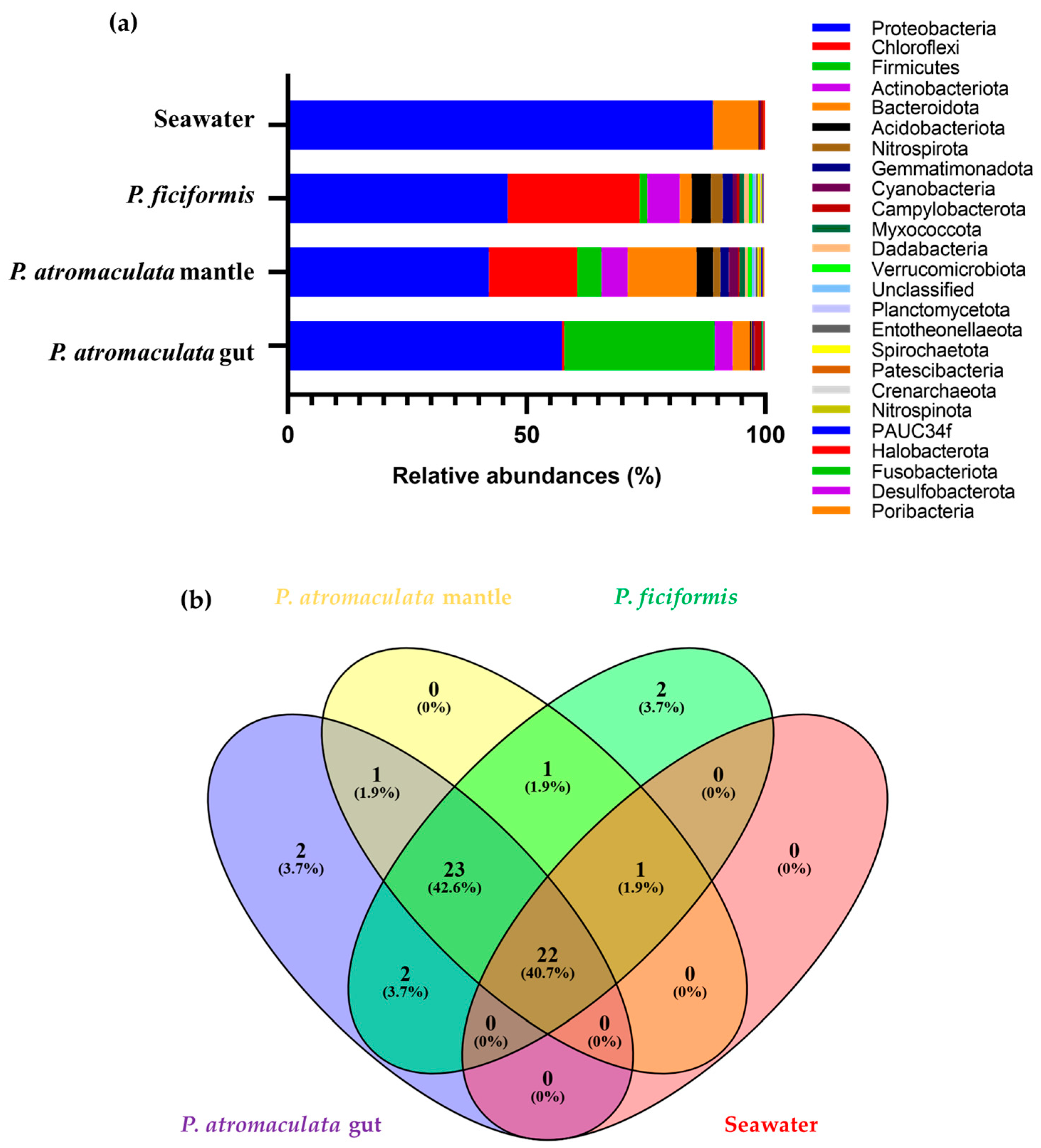


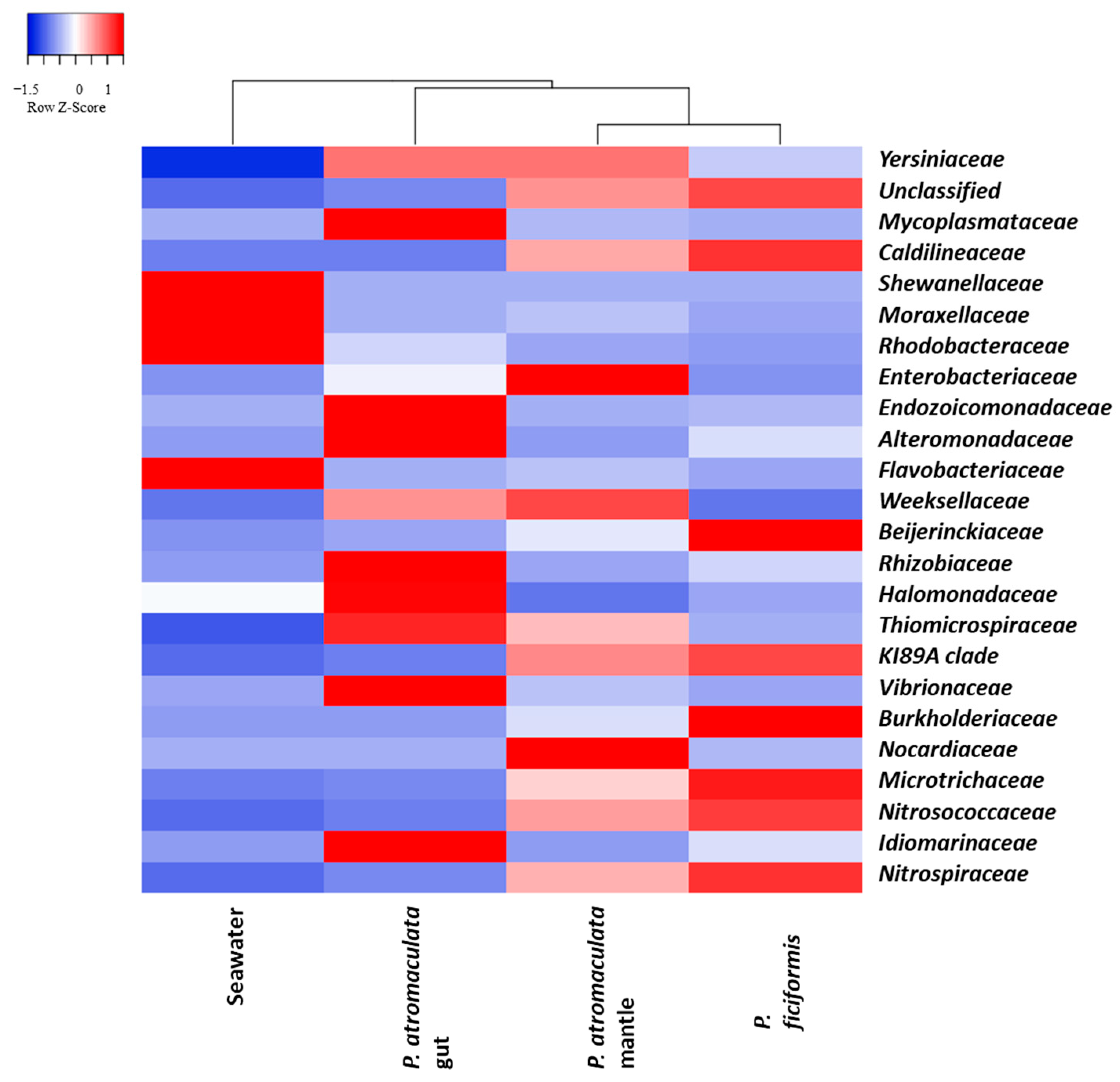

| Sample | Families | Good’s Coverage | Simpson’s Index | Shannon–Wiener Index | Evenness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. atromaculata gut (n = 3) | 134 (±66.7) | 0.98 (±0.01) | 0.40 (±0.3) | 1.77 (±1.35) | 0.35 (±0.24) |
| P. atromaculata mantle (n = 3) | 181 (±57.3) | 0.95 (±0.02) | 0.23 (±0.12) | 2.42 (±0.72) | 0.46 (±0.11) |
| P. ficiformis (n = 3) | 180 (±35.2) | 0.96 (±0.02) | 0.19 (±0.09) | 2.32 (±1.01) | 0.44 (±0.18) |
| Seawater | 126 | 0.98 | 0.27 | 1.6 | 0.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallo, A.; Villanova, V.; Vecchioni, L.; Grancagnolo, D.; Arculeo, M.; Alduina, R. Snapshot of the Bacterial Composition of Two Invertebrates, Peltodoris atromaculata and Petrosia ficiformis, from a Shallow Hydrothermal Spring on the West Coast of Sicily. Water 2025, 17, 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071036
Gallo A, Villanova V, Vecchioni L, Grancagnolo D, Arculeo M, Alduina R. Snapshot of the Bacterial Composition of Two Invertebrates, Peltodoris atromaculata and Petrosia ficiformis, from a Shallow Hydrothermal Spring on the West Coast of Sicily. Water. 2025; 17(7):1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071036
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallo, Annamaria, Valeria Villanova, Luca Vecchioni, Desiree Grancagnolo, Marco Arculeo, and Rosa Alduina. 2025. "Snapshot of the Bacterial Composition of Two Invertebrates, Peltodoris atromaculata and Petrosia ficiformis, from a Shallow Hydrothermal Spring on the West Coast of Sicily" Water 17, no. 7: 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071036
APA StyleGallo, A., Villanova, V., Vecchioni, L., Grancagnolo, D., Arculeo, M., & Alduina, R. (2025). Snapshot of the Bacterial Composition of Two Invertebrates, Peltodoris atromaculata and Petrosia ficiformis, from a Shallow Hydrothermal Spring on the West Coast of Sicily. Water, 17(7), 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071036







