Utilizing the Google Earth Engine for an Efficient Spatial–Temporal Fusion Model of Grassland Evapotranspiration (OL-SS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Grassland Evapotranspiration
1.2. Spatiotemporal Fusion of Evapotranspiration
2. Materials and Methods
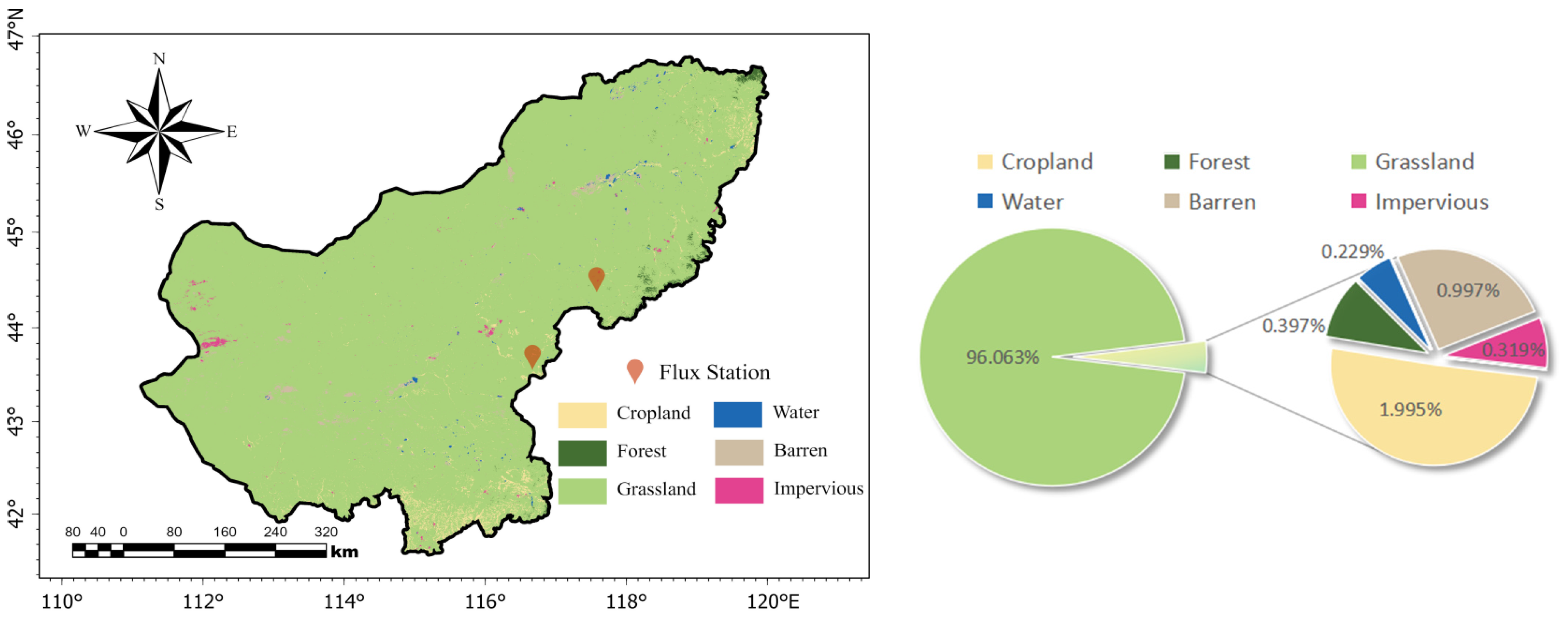
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. The Selection of Study Blocks
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Selection and Application of Datasets
3.1.1. Datasets for Image Fusion
3.1.2. Datasets for Evapotranspiration Calculation
3.2. Model Referenced for OL-SS Construction
3.2.1. OL-STARFM
3.2.2. SEBS Model
4. Results
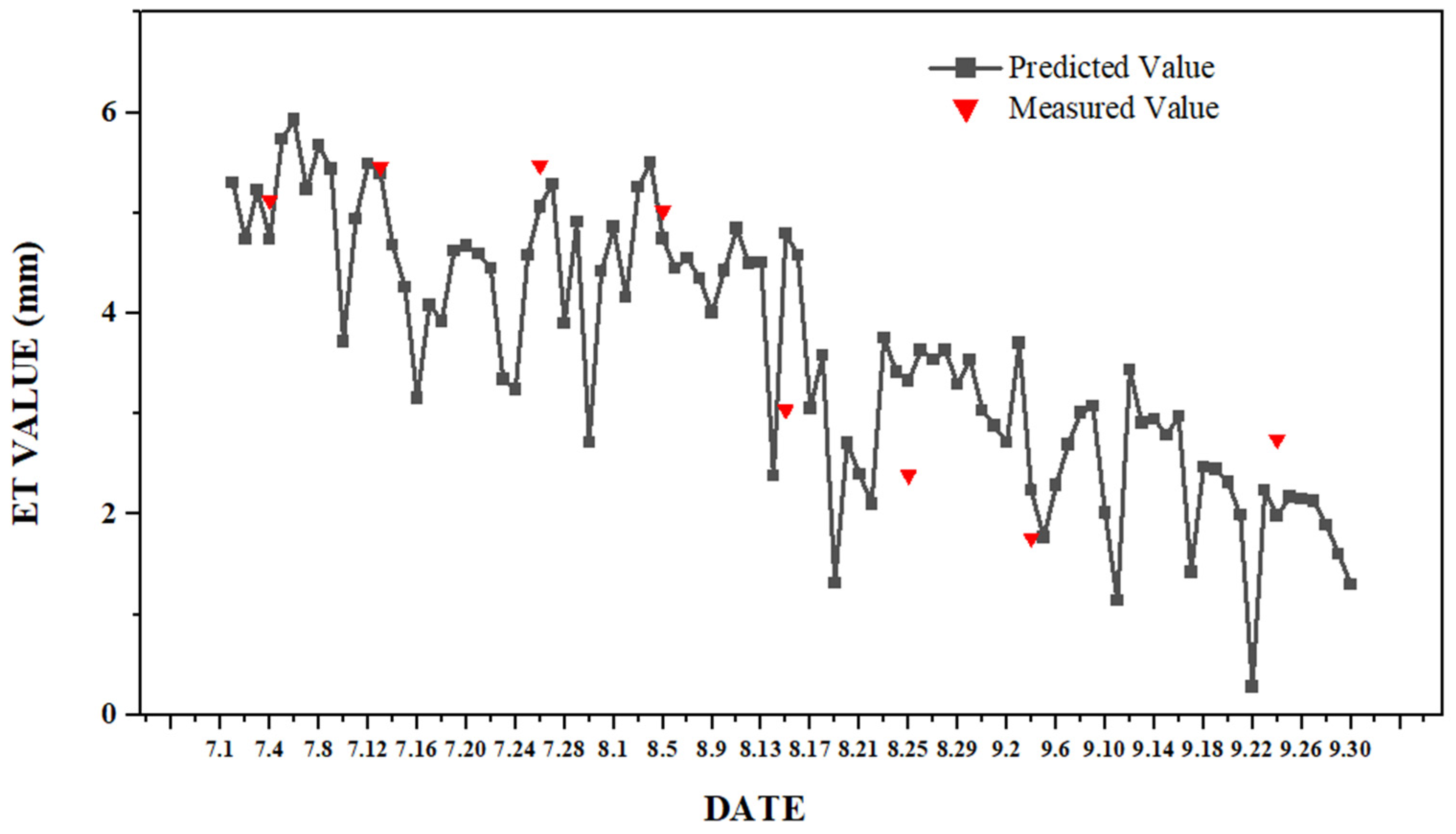
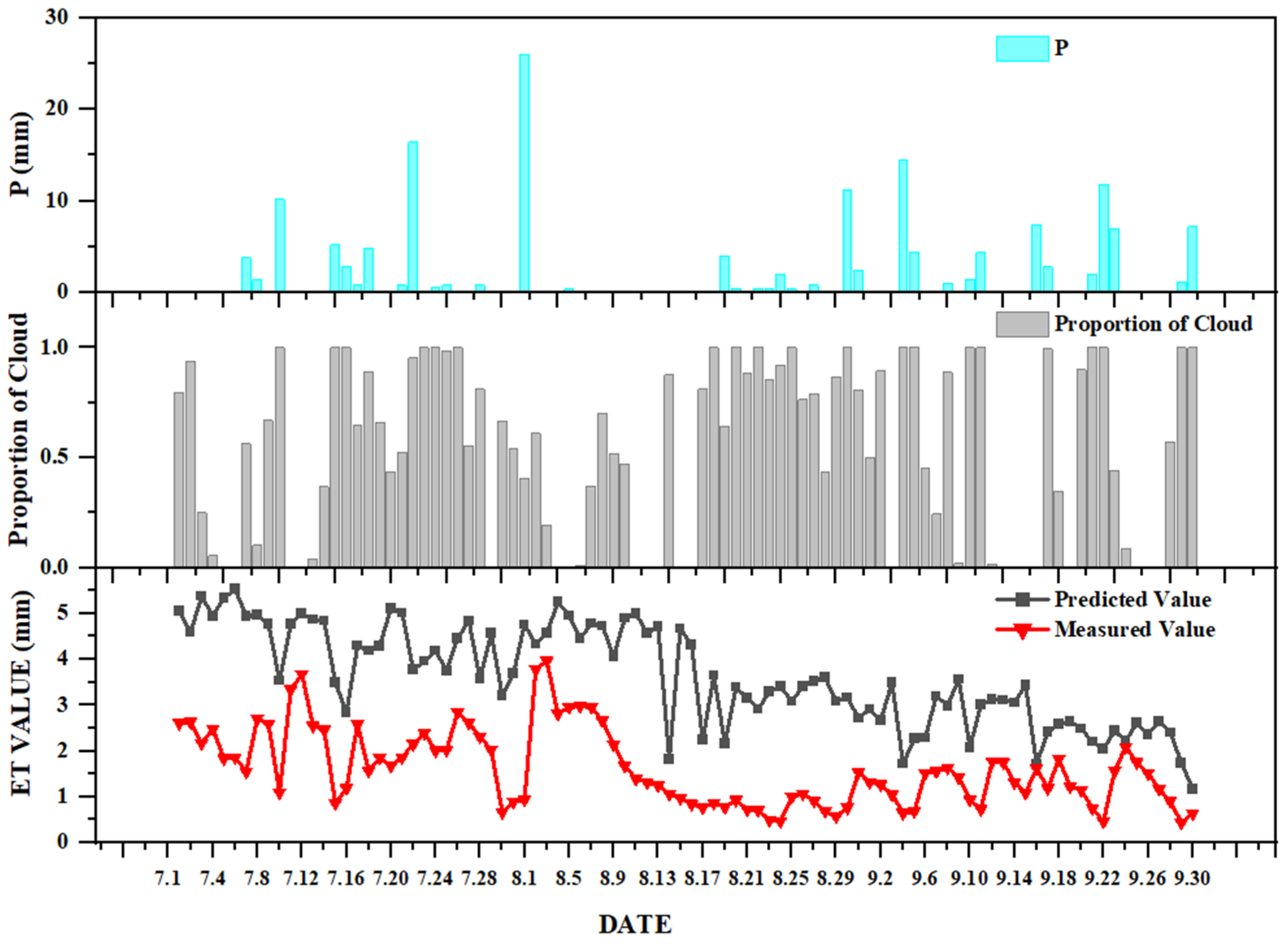
4.1. Fusion Result Evaluation
4.2. Fusion Result Verification
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bardgett, R.D.; Bullock, J.M.; Lavorel, S.; Manning, P.; Schaffner, U.; Ostle, N.; Chomel, M.; Durigan, G.; Fry, E.L.; Johnson, D.; et al. Combatting global grassland degradation. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.D.; Wang, J.P.; Wei, W.; Fu, B.J.; Wu, D.P. Effects of landscape restoration on soil water storage and water use in the Loess Plateau Region, China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.G.; Yu, X.X.; Jia, G.D.; Liu, Z.Q.; Sun, L.B.; Zheng, P.F.; Zhu, X.H. Grassland soil moisture fluctuation and its relationship with evapotranspiration. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinglan, A.; Wang, G.Q.; Liu, T.X.; Xue, B.L.; Kuczera, G. Spatial variation of correlations between vertical soil water and evapotranspiration and their controlling factors in a semi-arid region. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laipelt, L.; Kayser, R.H.B.; Fleischmann, A.S.; Ruhoff, A.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Erickson, T.A.; Melton, F. Long-term monitoring of evapotranspiration using the SEBAL algorithm and Google Earth Engine cloud computing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkiaka, E.; Bryant, R.G.; Dembélé, M.; Yonaba, R.; Imuwahen Priscilla, A.; Karambiri, H. Quantifying the effects of climate and environmental changes on evapotranspiration variability in the Sahel. J. Hydrol. 2024, 642, 131874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.Z.; Zhao, M.S.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Bohms, S.; Singh, R.K.; Gowda, P.H.; Velpuri, N.M.; Alemu, H.; Verdin, J.P. Operational Evapotranspiration Mapping Using Remote Sensing and Weather Datasets: A New Parameterization for the SSEB Approach. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.L.; Jia, L.; Hu, G.C. Global land surface evapotranspiration monitoring by ETMonitor model driven by multi-source satellite earth observations. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, D.G.; Holmes, T.R.H.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Gash, J.H.; Meesters, A.; Dolman, A.J. Global land-surface evaporation estimated from satellite-based observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, W.; Zhu, X.L.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.H.; Yang, L.Q.; Helmer, E.H. An Improved Flexible Spatiotemporal DAta Fusion (IFSDAF) method for producing high spatiotemporal resolution normalized difference vegetation index time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 227, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Stein, A. Spatiotemporal Image Fusion in Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.G.; Schwaller, M.R.; Hall, F.G. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Terzopoulos, D.; Waters, K. Constructing Physics-Based Facial Models of Individuals. Graph. Interface 1993, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, B. A Rigorously-Weighted Spatiotemporal Fusion Model with Uncertainty Analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Atkinson, P.M. Spatio-temporal fusion for daily Sentinel-2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.Z.; Shi, W.Z.; Zhang, H.; Hao, M. A Flexible Object-Level Processing Strategy to Enhance the Weight Function-Based Spatiotemporal Fusion Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, S. A dataset of observational key parameters in carbon and water fluxes in a semi-arid steppe, Inner Mongolia (2012–2020): Based on a long-term manipulative experiment of precipitation pattern. China Sci. Data 2023, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. A dataset of carbon and water fluxes of the typical grasslands in Duolun County, Inner Mongolia during 2006–2015. China Sci. Data 2023, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.H.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Gong, H.L. Downscaling of MODIS One Kilometer Evapotranspiration Using Landsat-8 Data and Machine Learning Approaches. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W.; Glassy, J.M. An operational remote sensing algorithm of land surface evaporation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Smith, M.; Perrier, A.; Pereira, L.S. An update for the definition of reference evapotranspiration. ICID Bull. 1994, 43, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth, W.; Gurney, R.; Hsu, A.; Ormsby, J. FIFE: The variation in energy partition at surface flux sites. IAHS Publ. 1989, 186, 523–534. [Google Scholar]
- Guven, A.; Aytek, A.; Yuce, M.I.; Aksoy, H. Genetic programming-based empirical model for daily reference evapotranspiration estimation. Clean–Soil Air Water 2008, 36, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, J.; Kişi, Ö.; Landeras, G.; López, J.J.; Nazemi, A.H.; Stuyt, L.C. Daily reference evapotranspiration modeling by using genetic programming approach in the Basque Country (Northern Spain). J. Hydrol. 2012, 414, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M.; Khoshkam, H.; Bateni, S.M.; Jun, C.; Band, S.S. Hybrid machine learning and deep learning models for multi-step-ahead daily reference evapotranspiration forecasting in different climate regions across the contiguous United States. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 108311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Product | GEE ID | Bands | Scale | Offset | Time Coverage | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LANDSAT 8 OLI/TIRS | LANDSAT/LC08/C02/T1_L2 | SR_B2 | 0.0000275 | −0.2 | 2013-03-18T15:58:14–Present | 30 m |
| SR_B3 | ||||||
| SR_B4 | ||||||
| SR_B5 | ||||||
| SR_B6 | ||||||
| SR_B7 | ||||||
| ST_EMIS | 0.0001 | - | ||||
| QA_PIXEL | - | - | ||||
| MCD43A4 V6.1 NBAR product | MODIS/061/MCD43A4 | Nadir_Reflectance_Band2 | 0.0001 | 0 | 2000-02-24T00:00:00–Present | 500 m |
| Nadir_Reflectance_Band3 | ||||||
| Nadir_Reflectance_Band4 | ||||||
| Nadir_Reflectance_Band5 | ||||||
| Nadir_Reflectance_Band6 | ||||||
| Nadir_Reflectance_Band7 |
| SITE | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PATH | 28 | 28 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
| ROW | 124 | 124 | 126 | 125 | 124 | 124 | 124 | 124 |
| July Date | 7.12 | 7.12 | 7.10 * | 7.19 * | 7.12 | 7.12 | 7.12 | 7.12 |
| August Date | 8.13 | 8.13 | 8.11 | 8.04 * | 8.13 | 8.13 | 8.13 | 8.13 |
| September Date | 9.14 | 9.14 | 9.12 | 9.21 | 9.14 | 9.14 | 9.14 | 9.14 |
| Product | GEE ID | Bands | Scale | Offset | Time Coverage | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERA5-Land Hourly | ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/HOURLY | skin_temperature | 1 | 0 | 1950-01-01T01:00:00–Present | 0.1° |
| surface_solar_radiation_downwards_hourly | ||||||
| surface_thermal_radiation_downwards_hourly | ||||||
| temperature_2m | ||||||
| u_component_of_wind_10m | ||||||
| v_component_of_wind_10m | ||||||
| ERA5-Land Daily | ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/DAILY_AGGR | surface_net_solar_radiation_sum | 1 | 0 | 1950-01-02T00:00:00–Present | 0.1° |
| surface_net_thermal_radiation_sum |
| Sites | Time | Indexes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | AAD | RMSPE | ||
| a | 7→8 | 0.0363 | 0.0252 | 0.2443 |
| 8→9 | 0.0367 | 0.0260 | 0.2340 | |
| 7→9 | 0.0347 | 0.0221 | 0.2501 | |
| b | 7→8 | 0.0295 | 0.0204 | 0.1466 |
| 8→9 | 0.0278 | 0.0187 | 0.1495 | |
| 7→9 | 0.0351 | 0.0218 | 0.1934 | |
| c | 7→8 | 0.1168 | 0.0909 | 0.4107 |
| 8→9 | 0.0377 | 0.0221 | 0.1340 | |
| 7→9 | 0.1272 | 0.0975 | 0.4815 | |
| d | 7→8 | 0.1427 | 0.0819 | 0.5945 |
| 8→9 | 0.1017 | 0.0724 | 0.5127 | |
| 7→9 | 0.1600 | 0.1127 | 0.6962 | |
| e | 7→8 | 0.0141 | 0.0099 | 0.0988 |
| 8→9 | 0.0174 | 0.0124 | 0.1113 | |
| 7→9 | 0.0212 | 0.0148 | 0.1409 | |
| f | 7→8 | 0.0549 | 0.0374 | 0.3145 |
| 8→9 | 0.0530 | 0.0363 | 0.3429 | |
| 7→9 | 0.0326 | 0.0188 | 0.1966 | |
| g | 7→8 | 0.0188 | 0.0136 | 0.1157 |
| 8→9 | 0.0322 | 0.0214 | 0.2023 | |
| 7→9 | 0.0197 | 0.0135 | 0.1231 | |
| h | 7→8 | 0.0248 | 0.0155 | 0.1701 |
| 8→9 | 0.0258 | 0.0156 | 0.1801 | |
| 7→9 | 0.0296 | 0.0185 | 0.2163 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; An, C.; Dong, Z. Utilizing the Google Earth Engine for an Efficient Spatial–Temporal Fusion Model of Grassland Evapotranspiration (OL-SS). Water 2025, 17, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071034
Yu H, An C, Dong Z. Utilizing the Google Earth Engine for an Efficient Spatial–Temporal Fusion Model of Grassland Evapotranspiration (OL-SS). Water. 2025; 17(7):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071034
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Hao, Chunchun An, and Zhi Dong. 2025. "Utilizing the Google Earth Engine for an Efficient Spatial–Temporal Fusion Model of Grassland Evapotranspiration (OL-SS)" Water 17, no. 7: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071034
APA StyleYu, H., An, C., & Dong, Z. (2025). Utilizing the Google Earth Engine for an Efficient Spatial–Temporal Fusion Model of Grassland Evapotranspiration (OL-SS). Water, 17(7), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071034







