Ecological Impact of Spartina alterniflora Control Methods on Tiaozini Wetland Against the Background of Carbon Neutrality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Determination of Physical and Chemical Properties
2.4. Computation of Soil Organic Carbon Density
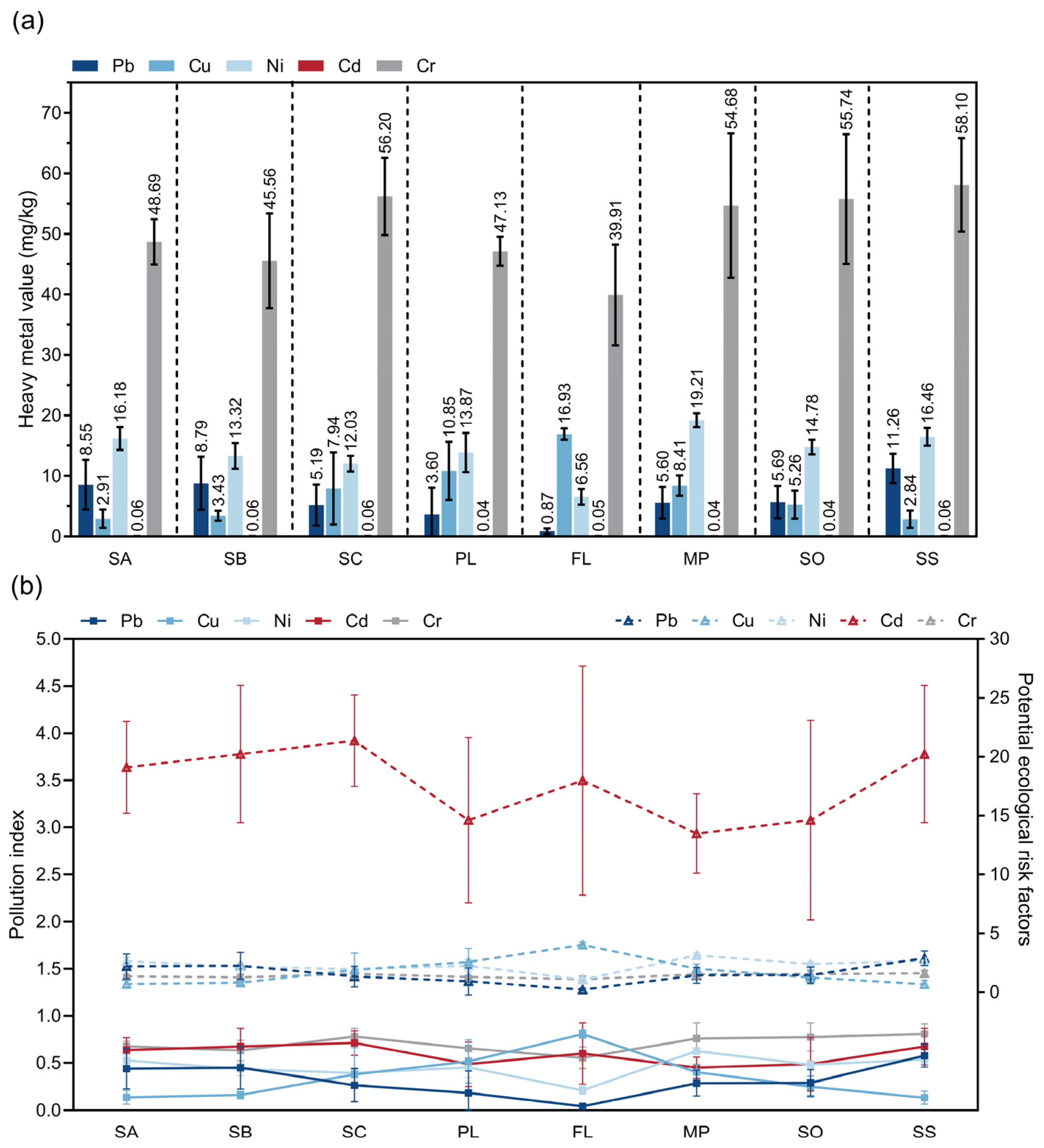
2.5. Detection and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals
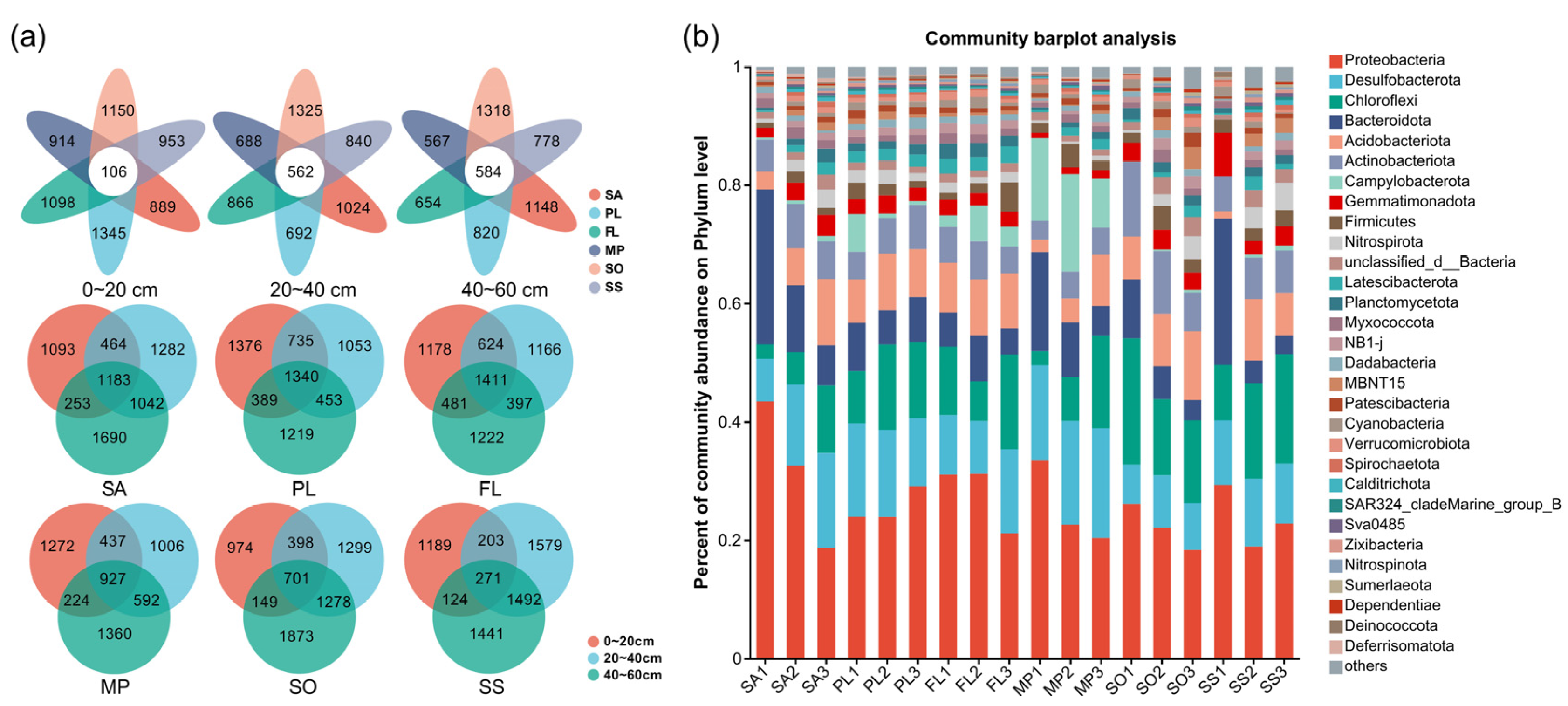
2.6. Soil Microbial Determination
2.7. Soil Enzyme Activity Assay
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
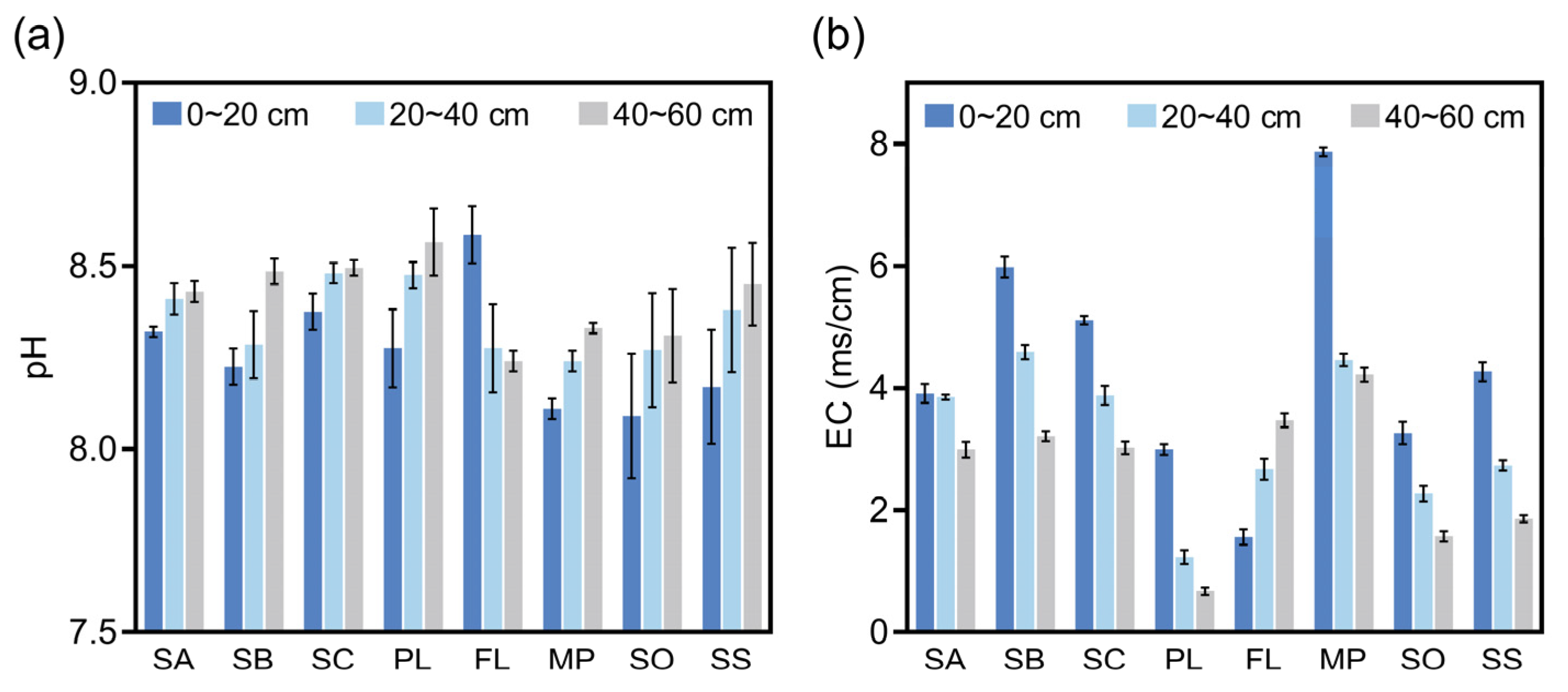
3.1. pH and Conductivity of Soil at Different Sampling Sites
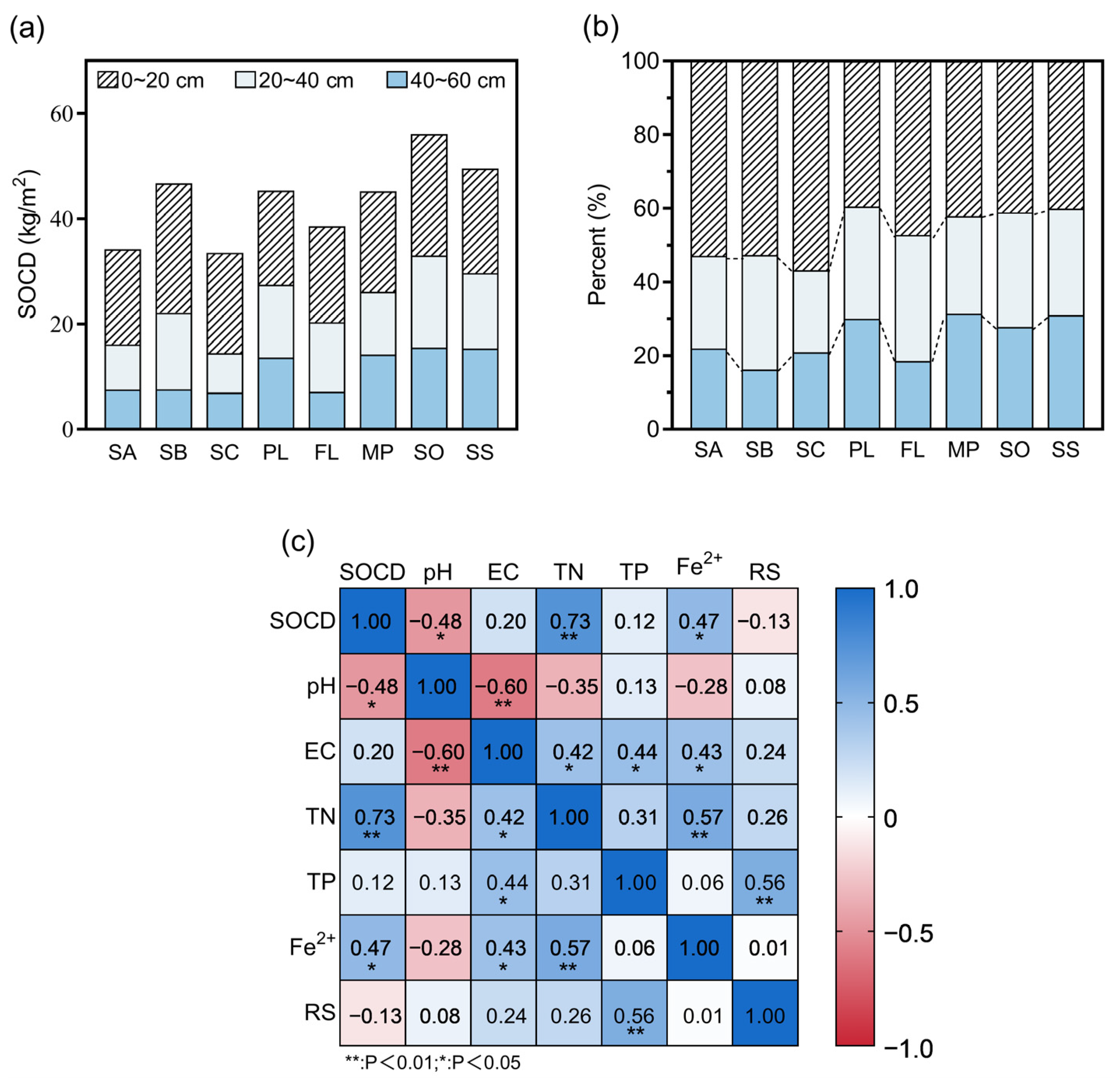
3.2. Organic Carbon Density of Soil at Different Sampling Sites
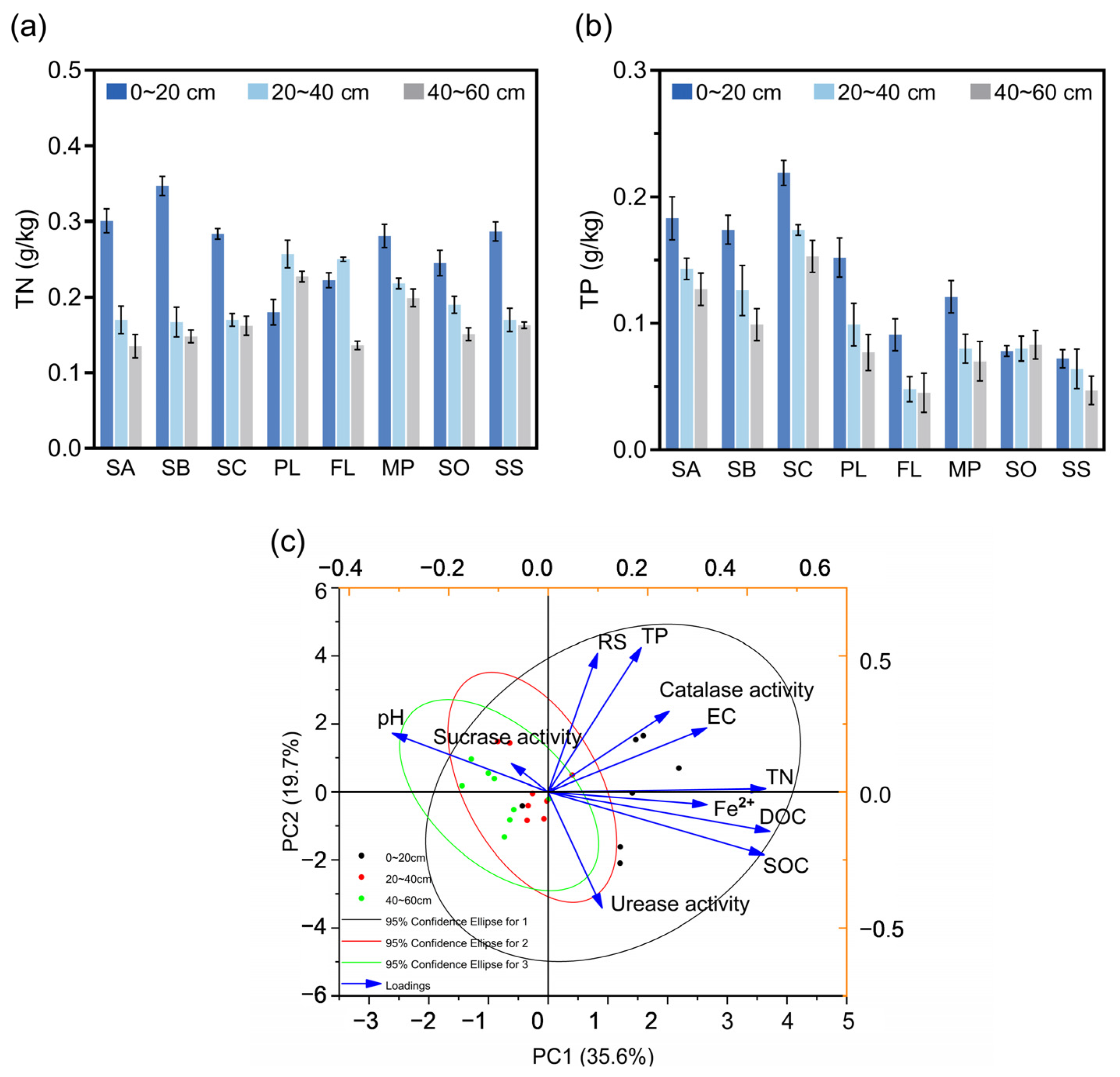
3.3. Total Nitrogen and Total Phosphorus in Soil at Different Sampling Sites
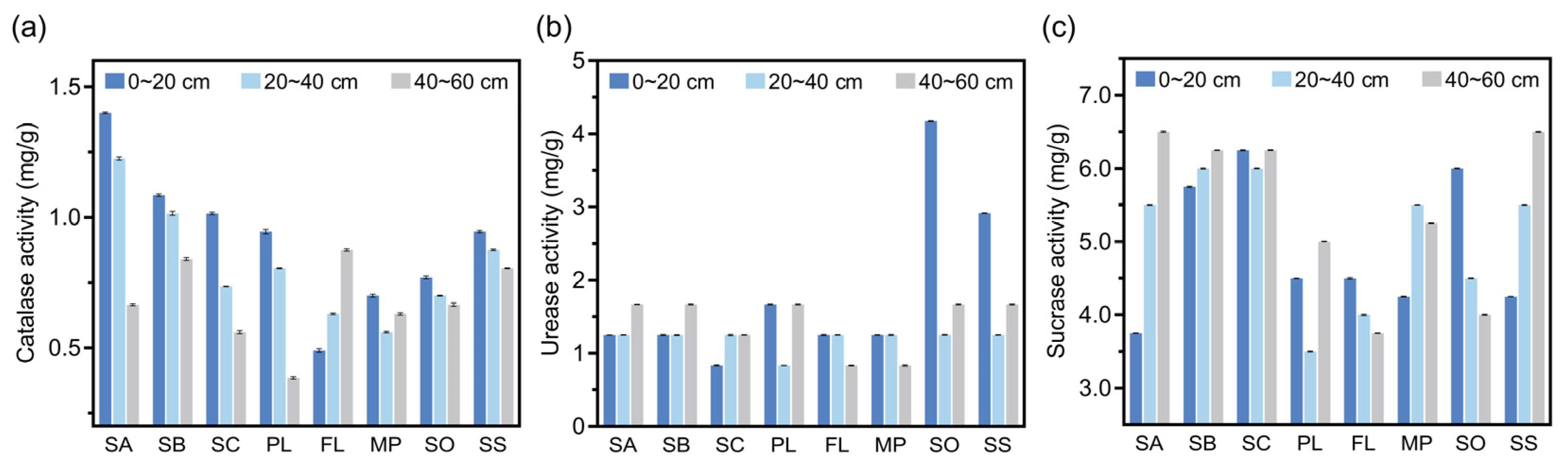
3.4. Enzyme Activity in Soil at Different Sampling Sites
3.5. Comparison of Soil Microbial Communities at Different Sampling Sites
3.6. Heavy Metal Values of the Soil at Different Sampling Sites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, Y.; Tian, X.; Bai, J.; Zhou, H.; Wen, L. Assessing the Carbon Neutrality Capacity of Wetland and Non-Wetland Ecosystems in a Typical Coastal Region. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2025, 53, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Hauck, J.; Olsen, A.; Peters, G.P.; Peters, W.; Pongratz, J.; Sitch, S.; et al. Global Carbon Budget 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3269–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. Habitat suitability and potential biological corridors for waterbirds in Yancheng coastal wetland of China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawei, W.; Zhenqi, W.; Wei, H.; Changhu, L.; Pan, C. The Native Reed-specific Bird, Reed Parrotbill, Has Been Detected in Exotic Smooth Cordgrass. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Martin, P.A.; Hao, Y.; Sutherland, W.J.; Shackelford, G.E.; Wu, J.; Ju, R.; Zhou, W.; Li, B. A global synthesis of the effectiveness and ecological impacts of management interventions for Spartina species. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 17, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, B.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M. Inhibition of Spartina alterniflora Growth Alters Soil Bacteria and Their Regulation of Carbon Metabolism. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabet Aghlidi, P.; Cheraghi, M.; Lorestani, B.; Sobhanardakani, S.; Merrikhpour, H. Analysis, spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of arsenic and some heavy metals of agricultural soils, case study: South of Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grevstad, F.S.; Strong, D.R.; Garcia-Rossi, D.; Switzer, R.W.; Wecker, M.S. Biological control of Spartina alterniflora in Willapa Bay, Washington using the planthopper Prokelisia marginata: Agent specificity and early results. Biol. Control 2003, 27, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chi, Y.; Lu, H.; Sun, G.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Luo, Y. Effects of the Comprehensive Elimination of Spartina alterniflora along China’s Coast on Blue Carbon and Scenario Prediction after Ecological Restoration. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Ge, C. Wind-Driven Mechanisms for Allometric Growth of Spartina alterniflora Leaves: Implications for Adaptive Management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2025, 262, 107556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Li, G.; Guang, Z.; Wang, S. Content and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Tiaozini migratory bird habitat and its adjacent intertidal zone in Dongtai. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2023, 42, 656–666. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Liu, M. Characteristics of soil microbial diversity in the embankment area of Tiaozini wetland. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci. 2023, 64, 1283–1291. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Senge, M.; Ito, K.; Onishi, T.; Yoshiyama, K. Experimental Evaluation of Irrigation Methods for Soil Desalinization. Paddy Water Environ. 2015, 13, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Sediment-Water Interface Process of Lakes: Nitrogen and Phosphorus Biogeochemistry; China Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 60–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qian, B.; Liu, L.; Xiao, X. Comparative tests on different methods for content of soil organic matter. J. Hohai Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2011, 39, 34–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Zhou, L. Colorimetric determination of dissolved organic carbon in soil solution and water environment. China Environ. Sci. 2002, 22, 433–437. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y. Optimizing Conditions for Soil Available Iron Determination with Method of Phenanthroline Colorimetry. Soils 2013, 45, 718–721. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. Methods of Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; 79p. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Wan, Z.; Guo, Y.; Song, C.; Jin, S.; Zuo, Y. Estimation of Soil Organic Carbon Storage in Palustrine Wetlands, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Leng, Z.; Jia, H.; Wei, L.; Yuguda, T.K.; Du, D. Effect of Seawall Embankment Reclamation on the Distribution of Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn Pollution in Invasive Spartina alterniflora and Native Phragmites Australis Coastal Saltmarshes of East China. Biology 2023, 12, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control. A Sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S. Soil Enzymes and Their Research Methods; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 294–297. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Sheuermann, A.; Xin, P.; Li, L.; Lockington, D.A. Salt Transport Under Tide and Evaporation in a Subtropical Wetland: Field Monitoring and Numerical Simulation. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR031530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xong, X.; Zhang, H.; Araya, K.; Teramoto, C.; Ohmiya, K.; Zhu, B.; Sun, Q.; Wang, W. Improvement of Salt-Affected Soils by Deep Ploughing—Part 1: Plot Field Tests in a Saline Soil (Solonchak) Region. Eng. Agric. Environ. Food 2011, 4, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, J.C.; Borgnis, E.L.; Turner, R.E.; Milan, C.S. Carbon Sequestration and Sediment Accretion in San Francisco Bay Tidal Wetlands. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 1163–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcleod, E.; Chmura, G.L.; Bouillon, S.; Salm, R.; Björk, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Lovelock, C.E.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Silliman, B.R. A Blueprint for Blue Carbon: Toward an Improved Understanding of the Role of Vegetated Coastal Habitats in Sequestering CO2. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Ye, S.; Yuan, H.; Yu, C.; Ding, X.; Zhao, G.; Pei, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Yu, X.; et al. Enhanced Sequestration of Carbon in Ocean Sediments as a Means to Reduce Global Emissions: A Case Study from a Coastal Wetland Restoration Project in the Liaohe Delta, Northeast China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2024, 648, 112286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Liu, D.; Yuan, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Miao, Y.; Chen, Z.; He, T.; Ding, W. Wetland Restoration after Agricultural Abandonment Enhances Soil Organic Carbon Efficiently by Stimulating Plant- Rather than Microbial-Derived Carbon Accumulation in Northeast China. CATENA 2024, 241, 108077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Song, Z.; Zhang, X.; He, D.; Guo, L.; van Zwieten, L.; Yu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Fang, Y.; et al. Organic Blue Carbon Sequestration in Vegetated Coastal Wetlands: Processes and Influencing Factors. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 255, 104853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wei, S.; Chen, H.; Li, B.; Nie, M. Effects of Spartina Invasion on the Soil Organic Carbon Content in Salt Marsh and Mangrove Ecosystems in China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Song, J.; Cao, L.; Li, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, N. Distribution and Storage of Soil Organic Carbon in a Coastal Wetland under the Pressure of Human Activities. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Tong, C.; Zhang, Y. Changes of Soil Organic Carbon Density and Stock in the Minjiang River Estuarine Wetland under Natural Salinity Gradient. Wetl. Sci. 2024, 22, 218–226. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Fu, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, R.; Li, S. Distribution and Storage of Soil Organic Carbon in Hainan lsland. Trop. Geogr. 2011, 31, 554–558. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Bian, H. Effects of Exogenous Fe Addition on Soil Respiration Rate and Dissolved Organic Carbon Structure in Temperate Forest Swamps of Northeastern China. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spohn, M.; Stendahl, J. Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Contents in Forest Soils Are Related to Soil Texture in Interaction with pH and Metal Cations. Geoderma 2024, 441, 116746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahm, B.D.; Harrison, R.B. Controls on the Sorption, Desorption and Mineralization of Low-Molecular-Weight Organic Acids in Variable-Charge Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendooven, L.; Alcántara-Hernández, R.J.; Valenzuela-Encinas, C.; Luna-Guido, M.; Perez-Guevara, F.; Marsch, R. Dynamics of Carbon and Nitrogen in an Extreme Alkaline Saline Soil: A Review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, N.R.; VanZomeren, C.M.; Berkowitz, J.F. Temperature, Redox, and Amendments Alter Wetland Soil Inorganic Phosphorus Retention Dynamics in a Laurentian Great Lakes Priority Watershed. J. Great Lakes Res. 2022, 48, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Huang, C.; Bai, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Q.; Wen, X. Effects of Drought and Salt Stresses on Growth Characteristics of Euhalophyte Suaeda Salsa in Coastal Wetlands. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2018, 103, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Yang, J.; Gao, S.; Yao, R.; Wang, X. The Effect and Influence Mechanism of Soil Salinity on Phosphorus Availability in Coastal Salt-Affected Soils. Water 2022, 14, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hamel, C.; Lu, P.; Wang, J.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Gan, G.Y. Using enzyme activities as an indicator of soil fertility in grassland—An academic dilemma. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1175946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guwy, A.J.; Martin, S.R.; Hawkes, F.R.; Hawkes, D.L. Catalase Activity Measurements in Suspended Aerobic Biomass and Soil Samples. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1999, 25, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Jing, X.; Wang, X.-F.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, G.-F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Oxidative Post-Translational Modification of Catalase Confers Salt Stress Acclimatization by Regulating H2O2 Homeostasis in Malus hupehensis. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 287, 154037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Shi, L.; Lu, W.; Bao, L.; Meng, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, N.; et al. Differences in the Activities of Six Soil Enzymes in Response to Cadmium Contamination of Paddy Soils in High Geological Background Areas. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Geng, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Z. Restoration via the Aggregate Spray-Seeding Technique Affected the Soil Proteobacteria on an Uninhabited Island: Community Structure, Metabolic Function, Nutritional Type, and Life Strategy. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 53, e03009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón-Tomás, B.; Lanzén, A.; Sánchez, P.; Estupiñán, M.; Sanz-Sáez, I.; Bilbao, M.E.; Rojo, D.; Mendibil, I.; Pérez-Cruz, C.; Ferri, M.; et al. Revisiting the Mercury Cycle in Marine Sediments: A Potential Multifaceted Role for Desulfobacterota. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Liu, F.; Fang, W.; Yang, T.; Chen, G.-H.; He, Z.; Wang, S. Microbial Sulfur Metabolism and Environmental Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsing Rao, M.P.; Luo, Z.-H.; Dong, Z.-Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, B.-B.; Guo, S.-X.; Nie, G.-X.; Li, W.-J. Metagenomic Analysis Further Extends the Role of Chloroflexi in Fundamental Biogeochemical Cycles. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.-H.; Wu, Y.-H. Genomic Characteristics of Nine Nitrospirota Metagenome-Assembled Genomes in Deep-Sea Sediments from East Pacific Polymetallic Nodules Zone. Mar. Genom. 2024, 75, 101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, O.S.; Fernandes, A.S.; Tupy, S.M.; Ferreira, T.G.; Almeida, L.N.; Creevey, C.J.; Santana, M.F. Insights into Plant Interactions and the Biogeochemical Role of the Globally Widespread Acidobacteriota Phylum. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; Wu, J. Benthic Bacterial Communities and Bacteria–Environment Interactions after Kandelia obovata Introduction and Spartina alterniflora Invasion in Yueqing Bay, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 58, 102787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, X. Mowing plus Shading as an Effective Method to Control the Invasive Plant Spartina alterniflora. Flora 2019, 257, 151408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Wang, M.; Tian, W.; Hui, H. The Content and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Coastal Wetlands around the Bohai Sea. Plant Soil Environ. 2024, 70, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Lin, H.; Lin, C. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in the Surface Sediments: A Reexamination into the Offshore Environment in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Bai, J.; Zhang, G.; Wu, J. Effects of Coastal Reclamation History on Heavy Metals in Different Types of Wetland Soils in the Pearl River Delta: Levels, Sources and Ecological Risks. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åsa, M.M. Berglund Evaluating Blood and Excrement as Bioindicators for Metal Accumulation in Birds. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Lin, J.; Liang, K.; Xia, Z. Selected Trace Metals (As, Cd and Hg) Distribution and Contamination in the Coastal Wetland Sediment of the Northern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 66, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, L. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in Tianjin Lingang Coastal Wetland Park. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2021, 11, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, N.; Hintemann, T.; Kramarewa, T.; Katayama, A.; Yasuta, T.; Marschner, P.; Kandeler, E. Response of Microbial Activity and Microbial Community Composition in Soils to Long-Term Arsenic and Cadmium Exposure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; He, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Cao, X. Ecological Impact of Spartina alterniflora Control Methods on Tiaozini Wetland Against the Background of Carbon Neutrality. Water 2025, 17, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060877
Wang X, He Q, Chen X, Zhang X, Song X, Li X, Cao X. Ecological Impact of Spartina alterniflora Control Methods on Tiaozini Wetland Against the Background of Carbon Neutrality. Water. 2025; 17(6):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060877
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinyi, Qingyi He, Xiao Chen, Xueshi Zhang, Xinshan Song, Xiang Li, and Xin Cao. 2025. "Ecological Impact of Spartina alterniflora Control Methods on Tiaozini Wetland Against the Background of Carbon Neutrality" Water 17, no. 6: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060877
APA StyleWang, X., He, Q., Chen, X., Zhang, X., Song, X., Li, X., & Cao, X. (2025). Ecological Impact of Spartina alterniflora Control Methods on Tiaozini Wetland Against the Background of Carbon Neutrality. Water, 17(6), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060877





