Rice Fields and Aquatic Insect Biodiversity in Italy: State of Knowledge and Perspectives in the Context of Global Change
Abstract
1. Rice Fields as Ecosystem and Their Biodiversity
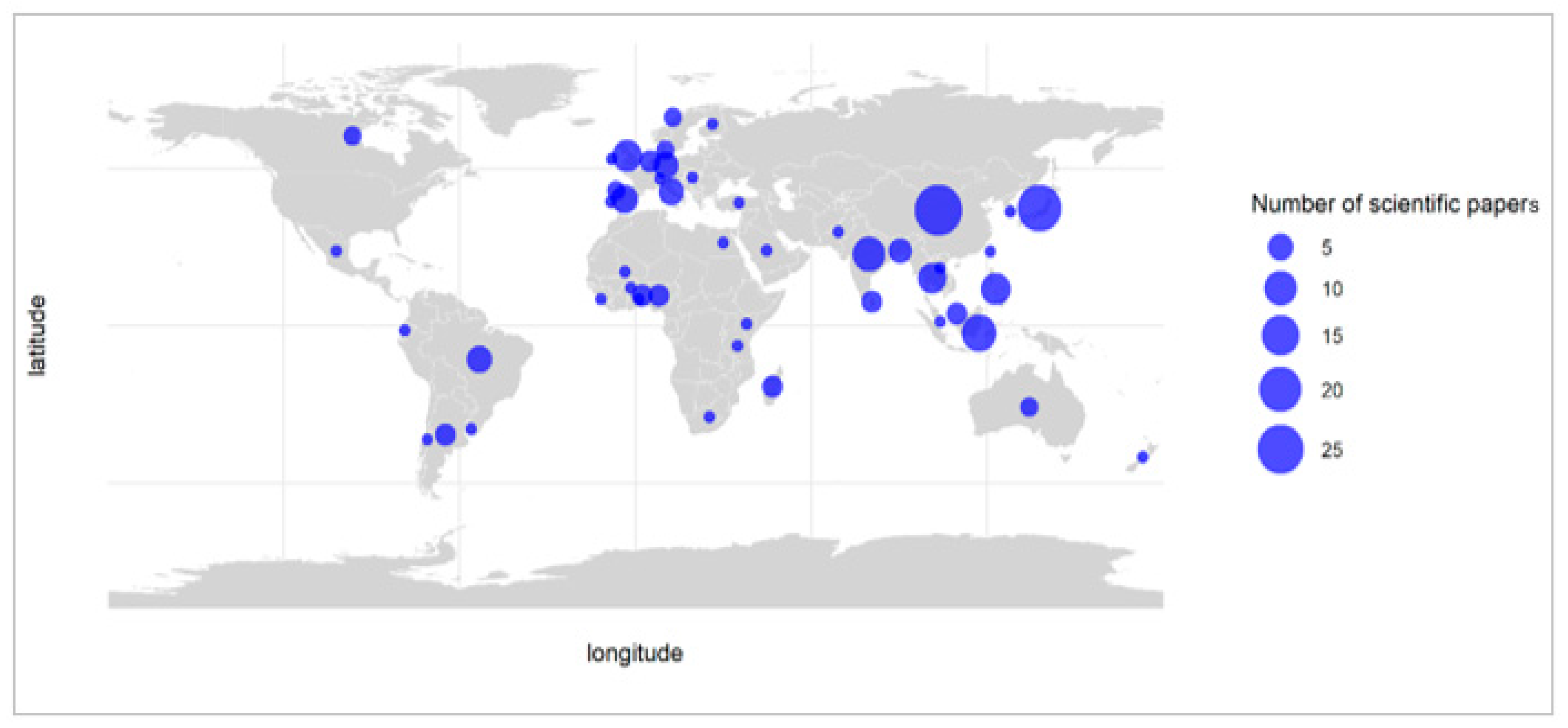
2. Insect Biodiversity of Italian Rice Fields
3. Rice Fields and Insect Biodiversity in the Current Global Change Scenario: Issues, Problems and New Agricultural Approaches
4. Rice Fields and Their Role in the Biological Invasion Context
5. Future Perspectives in Rice Field Entomological Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO—Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. OECD-FAO Agricul Outlook 2011–2030; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Chhokar, R.S.; Meena, R.P.; Kharub, A.S.; Gill, S.C.; Tripathi, S.C.; Gupta, O.P.; Mangrauthia, S.K.; Sundaram, R.M.; Sawant, C.P.; et al. Challenges and opportunities in productivity and sustainability of rice cultivation system: A critical review in Indian perspective. Cereal Res. Commun. 2021, 50, 573–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthayya, S.; Sugimoto, J.D.; Montgomery, S.; Maberly, G.F. An overview of global rice production, supply, trade, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1324, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, E.T.; Robson, B.J. Anthropogenic refuges for freshwater biodiversity: Their ecological characteristics and management. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 166, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoglio, S.; Bonada, N.; Guareschi, S.; López-Rodríguez, M.J.; Millán, A.; de Figueroa, J.M.T. Freshwater ecosystems and aquatic insects: A paradox in biological invasions. Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20151075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edirisinghe, J.P.; Bambaradeniya, C.N. Rice fields: An ecosystem rich in biodiversity. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2006, 34, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesler, L.S.; Grigarick, A.A.; Oraze, M.J.; Palrang, A.T. Arthropod fauna of conventional and organic rice fields in California. J. Econ. Entomol. 1993, 86, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlinda, S.; Karenina, T.; Irsan, C.; Pujiastuti, Y. Arthropods inhabiting flowering non-crop plants and adaptive vegetables planted around paddy fields of freshwater swamps of South Sumatra, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 2019, 20, 3328–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendawi, A.; Sherif, M.; Abada, A.; El-Abashi, M. Aquatic and semiaquatic insects occurring in Egyptian rice fields and hazardous effects of insecticides. Egypt. J. Agric. Res. 2005, 83, 493–501. [Google Scholar]
- Service, M.W. Mortalities of the immature stages of species B of the Anopheles gambiae complex in Kenya: Comparison between rice fields and temporary pools, identification of predators, and effects of insecticidal spraying. J. Med. Entomol. 1997, 13, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizzon, J.P.; Macedo, V.R.M.; Machado, V.; Fiuza, L.M. Microbiological and physical–chemical water quality of the rice fields in Sinos River’s basin, Southern Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2767–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhling, F.; Befeld, S.; Häusler, M.; Katzur, K.; Lepkojus, S.; Mesleard, F. Effects of insecticide applications on macroinvertebrate density and biomass in rice-fields in the Rhône-delta, France. Hydrobiologia 2000, 431, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasola, M.; Ruiz, X. The Value of Rice Fields as Substitutes for Natural Wetlands for Waterbirds in the Mediterranean Region. Col. Waterbirds 1996, 19, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longoni, V. Rice fields and waterbirds in the Mediterranean region and the Middle East. Waterbirds 2010, 33 (Suppl. S1), 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Guercio, G. I Friganeidi nuocciono al riso. I tafani del riso. Le larve delle tipule nocive al riso (In Italian). Redia 1911, 7, 466–467. [Google Scholar]
- Cavazza, F. Ricerche intorno alle specie dannose alla coltivazione del riso (Oryza sativa) e specialmente al Chironomus cavazzai Kieff. Boll. Lab. Zool. Gen. Agric. 1914, 6, 320–331. [Google Scholar]
- Moretti, G.P. Note sulla fauna entomologica delle risaie. Atti Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. 1932, 71, 61–85. [Google Scholar]
- Moretti, G.P. I tricotteri delle risaie. Atti Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. 1934, 73, 104–116. [Google Scholar]
- Cocchi, G. Ricerche sui Ditteri Chironomidi dannosi al riso nella bassa Bolognese. Boll. Oss. Mal. Piante Bologna 1966, 1, 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Goidanich, A. Contributi alla conoscenza dell’entomofauna di risaia. 1. Gli Straziomidi: Mancati nemici del riso. Risicoltura 1939, 29, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zangheri, S. Un dittero minatore del riso nel basso ferrarese (Hydrellia griseola Fallen, Dipt. Ephydridae). Boll. Soc. Entomol. Ital. 1956, 86, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Giugliano, L.; Hardersen, S.; Santini, G. Odonata communities in retrodunal ponds: A comparison of sampling methods. Int. J. Odonatol. 2012, 15, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golfieri, B.; Hardersen, S.; Maiolini, B.; Surian, N. Odonates as indicators of the ecological integrity of the river corridor: Development and application of the Odonate River Index (ORI) in northern Italy. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, D.; Bogliani, G. Odonata in rice agroecosystems: Testing good practices for their conservation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 275, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, D.; Savoldelli, S.; Rocco, A.; Rossaro, B. Italian rice agroecosystems: A threat to insect biodiversity? Landsc. Manag. Funct. Biodivers. IOBC Bull. 2012, 75, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Lupi, D.; Rocco, A.; Rossaro, B. Benthic macroinvertebrates in Italian rice fields. J. Limnol. 2013, 72, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, D.; Cardarelli, E.; Bogliani, G. Grass management intensity affects butterfly and orthopteran diversity on rice field banks. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 267, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianferoni, F.; Graziani, F.; Dioli, P.; Ceccolini, F. Review of the occurrence of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in Italy, with an update of its European and World distribution. Biologia 2018, 73, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AA.VV. “Il riso”, coordinamento scientifico di A. Ferrero. In Collana Coltura & Cultura; Bologna Script, Ed.; ideata e coordinata da R. Angelini; Bayer CropScience: Bologna, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bellini, R.; Pederzani, F.; Pilani, R.; Veronesi, R.; Maini, S. Hydroglyphus pusillus (Fabricius) (Coleoptera Dytiscidae): Its role as a mosquito larvae predator in rice fields. Boll. Dell’istituto Di Entomol. ‘G. Grandi’ Dell’ Univ. Di Bologna 2000, 54, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Toma, L.; Cipriani, M.; Goffredo, M.; Romi, R.; Lelli, R. First report on entomological field activities for the surveillance of West Nile disease in Italy. Vet. Ital 2008, 44, 499–512. [Google Scholar]
- Di Luca, M.; Boccolini, D.; Severini, F.; Toma, L.; Barbieri, F.M.; Massa, A.; Romi, R. A 2-year entomological study of potential malaria vectors in Central Italy. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009, 9, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccolini, D.; Toma, L.; Luca, M.D.; Severini, F.; Cocchi, M.; Bella, A.; Romi, R. Impact of environmental changes and human-related factors on the potential malaria vector, Anopheles labranchiae (Diptera: Culicidae), in Maremma, Central Italy. J. Med. Entomol. 2012, 49, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumpf, S.B.; Gravey, M.; Brönnimann, O.; Luoto, M.; Cianfrani, C.; Mariethoz, G.; Guisan, A. From white to green: Snow cover loss and increased vegetation productivity in the European Alps. Science 2022, 376, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosà, R.; Marini, G.; Bolzoni, L.; Neteler, M.; Metz, M.; Delucchi, L.; Rizzoli, A. Early warning of West Nile virus mosquito vector: Climate and land use models successfully explain phenology and abundance of Culex pipiens mosquitoes in north-western Italy. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzolari, M.; Mosca, A.; Montarsi, F.; Grisendi, A.; Scremin, M.; Roberto, P.; Albieri, A. Distribution and abundance of Aedes caspius (Pallas, 1771) and Aedes vexans (Meigen, 1830) in the Po Plain (northern Italy). Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.A.; Chaskopoulou, A.; Georgiou, L.; Frontera, E.; Cáceres, F.; Masia, M.; Figuerola, J. Mosquito management strategies in European rice fields: Environmental and public health perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, D.; Jucker, C.; Rocco, A. Rice fields as a hot spot of water beetles (Coleoptera Adephaga and Polyphaga). Redia 2014, 97, 95–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zanella, F. Biocenosi delle risaie con particolare riferimento ai Culicidi. Disinfest. Ig. Ambient. 2000, 17, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, T.; Fenoglio, S. Biodiversità e gestione delle risaie: Un caso di studio inerente alle comunità di invertebrati acquatici della Lomellina (PV). Pianura 2024, 44, 112–121. [Google Scholar]
- Bosi, G.; Bo, T.; Fenoglio, S. Alcune considerazioni sulla distribuzione di Noteridae e Dityscidae (Coleoptera) nella provincia di Alessandria. Riv. Piemont. Stor. Nat. 2009, 30, 79–93. [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli, G. Due abitatori dell’acqua: Hydrous piceus L. e Dytiscus marginalis L. Nat. Mont. 1982, 29, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Campaioli, S.; Ghetti, P.F.; Minelli, A.; Ruffo, S. Manuale per il Riconoscimento dei Macroinvertebrati Delle Acque Dolci Italiane (Vol. I); Provincia Autonoma di Trento: Trento, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Campaioli, S.; Ghetti, P.F.; Minelli, A.; Ruffo, S. Manuale per il Riconoscimento dei Macroinvertebrati Delle Acque Dolci Italiane (Vol. II); Provincia Autonoma di Trento: Trento, Italy, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Giudici, M.L.; Villa, B. The rice leaf bug, Trigonotylus caelestialium Kirkaldy, on rice in Italy. In Proceedings of the International Temperate Rice Conference, Novara, Italy, 25–28 June 2007; pp. 146–147. [Google Scholar]
- Gelosi, A. Punteruolo del riso (Sitophilus oryzae Linneus) [Biologia e lotta]. Inf. Fitopatol. 1982, 32, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lupi, D.; Cenghialta, C.; Giudici, M.L.; Villa, B.; Tabacchi, M. Prime acquisizioni sulla biologia e sul contenimento di Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus (punteruolo acquatico del riso) in Lombardia. In Atti Giornate Fitopatologiche; CLUEB: Bologna, Italy, 2008; pp. 245–246. [Google Scholar]
- Giudici, M.L.; Villa, B. The armyworm Mythimna unipuncta (Haworth) found on rice in Italy. In Proceedings of the Conference “Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Rice-Based Production Systems”, Turin, Italy, 13–15 September 2004; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Magagnoli, S.; Lanzoni, A.; Masetti, A.; Depalo, L.; Albertini, M.; Ferrari, R.; Burgio, G. Sustainability of strategies for Ostrinia nubilalis management in Northern Italy: Potential impact on beneficial arthropods and aflatoxin contamination in years with different meteorological conditions. Crop Prot. 2021, 142, 105529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supino, F. Note sulla fauna delle risaie. R. Ist. Lomb. Sci. Lett. 1932, 54, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Savini, D.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. Bad Moon Rising: Il gambero rosso della Louisiana, una minaccia per gli ecosistemi acquatici della Lombardia. Mem. Della Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Milano 2008, 36, 19–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kraehmer, H.; Thomas, C.; Vidotto, F. Rice production in Europe. In Rice Production Worldwide; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossaro, B.; Marziali, L.; Cortesi, P. The effects of tricyclazole treatment on aquatic invertebrates in a rice paddy field. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guareschi, S.; Laini, A.; Viaroli, P.; Bolpagni, R. Integrating habitat-and species-based perspectives for wetland conservation in lowland agricultural landscapes. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, E.; Doretto, A.; Falasco, E.; Fenoglio, S.; Gruppuso, L.; Nizzoli, D.; Viaroli, P.; Bona, F. If Alpine streams run dry: The drought memory of benthic communities. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 81, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruppuso, L.; Falasco, E.; Fenoglio, S.; Marino, A.; Nizzoli, D.; Piano, E.; Bona, F. Dataset of a flow intermittency study: Benthic communities of 13 alpine intermittent rivers. Data Brief 2024, 54, 110449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Bertolotti, S.; Macrì, M.; Bona, F.; Bonetta, S.; Falasco, E.; Fenoglio, S. Impact of wastewater treatment and drought in an Alpine region: A multidisciplinary case study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, A.; Moretti, B.; Lerda, C.; Said-Pullicino, D.; Celi, L.; Romani, M.; Fogliatto, S.; Vidotto, F. Conservation tillage in temperate rice cropping systems: Crop production and soil fertility. Field Crops Res. 2024, 308, 109–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, A.; Russo, F.; Moretti, B.; Romani, M.; Vidotto, F.; Fogliatto, S.; Celi, L.; Said-Pullicino, D. Interaction between water, crop residue and fertilization management on the source-differentiated nitrogen uptake by rice. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2024, 60, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, B.; Borzí, I. Drought in the Po Valley: Identification, Impacts and Strategies to Manage the Events. Water 2024, 16, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R.A.; Chadwick, M.A. Invasive alien species in freshwater ecosystems: A brief overview. In A Handbook of Global Freshwater Invasive Species; Francis, R.A., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2012; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Guareschi, S.; South, J. Biological invasions in intermittent rivers and streams: Current knowledge, and future frontiers. Ecosistemas 2024, 33, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, V.; Benassi, G.; Veneri, M.; Bellavere, C.; Menozzi, P.; Moroni, A.; Mckenzie, K.G. Ostracoda of the Italian ricefields thirty years on: New synthesis and hypothesis. J. Limnol. 2003, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valls, L.; Rueda, J.; Mesquita-Joanes, F. Rice fields as facilitators of freshwater invasions in protected wetlands: The case of Ostracoda (Crustacea) in the Albufera Natural Park (E Spain). Zool. Stud. 2014, 53, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterom, M.V.L.-V.; Casas-Ruiz, J.P.; Gampe, D.; López-Robles, M.A.; Ludwig, R.; Núñez-Marcé, A.; Muñoz, I. Responses of a native and a recent invader snail to warming and dry conditions: The case of the lower Ebro River. Aquat. Ecol. 2019, 53, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, M.; López, V.; Franch, N.; Pou-Rovira, Q.; Queral, J.M. Use of seasonally flooded rice fields by fish and crayfish in a Mediterranean wetland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 213, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, J.A.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. Structural damage caused by the invasive crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) in rice fields of the Iberian Peninsula: A study case. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2015, 186, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souty-Grosset, C.; Anastácio, P.M.; Aquiloni, L.; Banha, F.; Choquer, J.; Chucholl, C.; Tricarico, E. The red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii in Europe: Impacts on aquatic ecosystems and human well-being. Limnologica 2016, 58, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, D.; Colombo, M.; Giudici, M.L.; Villa, B.; Cenghialta, C.; Passoni, D. On the spatial spread of the rice water weevil, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel (Coleoptera: Erirhinidae), in Italy. J. Ent. Acar. Res. 2010, 42, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, D.; Jucker, C.; Rocco, A.; Giudici, M.L.; Boattin, S.; Colombo, M. Current status of the rice water weevil Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus in Italy: Eleven-year invasion. EPPO Bull. 2015, 45, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, D.; Viva, S. Stenopelmus rufinasus Gyllenhal 1836 (Coleoptera: Erirhinidae) naturalized in Spain. Coleopt. Bull. 2006, 60, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchi, S.; Malgioglio, A. Azolla-Anabaena as a biofertilizer for rice paddy fields in the Po Valley, a temperate rice area in Northern Italy. Int. J. Agron. 2010, 2010, 152158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, D.; Dioli, P.; Limonta, L. First evidence of Halyomorpha halys (Stål)(Hemiptera Heteroptera, Pentatomidae) feeding on rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Entomol. Res. 2017, 49, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, C.H.; Huig, N.; Van der Velde, G.; Van Alen, T.A.; Wagemaker, C.A.; Sherman, C.D.; Figuerola, J. How did this snail get here? Several dispersal vectors inferred for an aquatic invasive species. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preti, M.; Verheggen, F.; Angeli, S. Insect pest monitoring with camera-equipped traps: Strengths and limitations. J. Pest. Sci. 2021, 94, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laini, A.; Stubbington, R.; Beermann, A.J.; Burgazzi, G.; Datry, T.; Viaroli, P.; Wilkes, M.; Zizka VM, A.; Saccò, M.; Leese, F. Dissecting biodiversity: Assessing the taxonomic, functional and phylogenetic structure of an insect metacommunity in a river network using morphological and metabarcoding data. Eur. J. Biol. 2023, 90, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Pompanon, F.; Brochmann, C.; Willerslev, E. Towards next-generation biodiversity assessment using DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, M.; Konecny-Dupré, L.; Nguyen, A.; Elbrecht, V.; Datry, T.; Douady, C.; Lefébure, T. Enhancing DNA metabarcoding performance and applicability with bait capture enrichment and DNA from conservative ethanol. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.C. Taxonomic sufficiency: The influence of taxonomic resolution on freshwater bioassessments using benthic macroinvertebrates. Environ. Rev. 2008, 16, 45–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbrecht, V.; Vamos, E.E.; Steinke, D.; Leese, F. Estimating intraspecific genetic diversity from community DNA metabarcoding data. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turon, X.; Antich, A.; Palacín, C.; Præbel, K.; Wangensteen, O.S. From metabarcoding to metaphylogeography: Separating the wheat from the chaff. Ecol. Appl. 2020, 30, e02036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, R.; Nakao, R.; Ushimaru, A.; Minamoto, T. Development of environmental DNA detection assays for snakes in paddy fields in Japan. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 19, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kwon, S.; Jang, Y. Can eDNA Present in Aquatic Environments of Rural Areas Help Identify Species Diversity in the Order Anura? Water 2024, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Baba, Y.G.; Ito, K.; Yamasako, J. Complementary role of environmental DNA for line-transect bird surveys: A field test in a Japanese rice landscape. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, S.; Nishiwaki, A.; Yamazoe, K.; Sugai, K.; Takahara, T. Discovery of unknown new ponds occupied by the endangered giant water bug (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Belostomatidae) by combining environmental DNA and capture surveys. Entomol. Sci. 2023, 26, e12540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, H.; He, W.; Lai, G.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Q. Diversity of Parasitoid Wasps and Comparison of Sampling Strategies in Rice Fields Using Metabarcoding. Insects 2024, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kwon, S.; Noh, A. Detection of frog and aquatic insects by environmental DNA in paddy water ecology. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 50, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Lu, R.; Huang, W.; Liu, H.; Zou, Y.; Tao, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tang, K. Major diet of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) over different developmental stages in rice-field: Agroecological interactions between fishes and rice in Sichuan, China, based on DNA metabarcoding approach. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 56, e03298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbrecht, V.; Peinert, B.; Leese, F. Sorting things out: Assessing effects of unequal specimen biomass on DNA metabarcoding. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 6918–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, F.; Couton, M.; Altermatt, F. Navigating the seven challenges of taxonomic reference databases in metabarcoding analyses. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2023, 23, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigand, H.; Beermann, A.J.; Čiampor, F.; Costa, F.O.; Csabai, Z.; Duarte, S.; Geigerg, M.F.; Grabowski, M.; Rimet, F.; Rulik, B.; et al. DNA barcode reference libraries for the monitoring of aquatic biota in Europe: Gap-analysis and recommendations for future work. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J.; Virkkala, R.; Toivonen, H. Climate change and freshwater biodiversity: Detected patterns, future trends and adaptations in northern regions. Biol. Rev. 2009, 84, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenoglio, S.; Bo, T.; Cucco, M.; Mercalli, L.; Malacarne, G. Effects of global climate change on freshwater biota: A review with special emphasis on the Italian situation. Ital. J. Zool. 2010, 77, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Strayer, D.L. Bending the curve of global freshwater biodiversity loss: What are the prospects? Biol. Rev. 2025, 100, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobiet, A.; Kotlarski, S.; Beniston, M.; Heinrich, G.; Rajczak, J.; Stoffel, M. 21st century climate change in the European Alps—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 1138–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
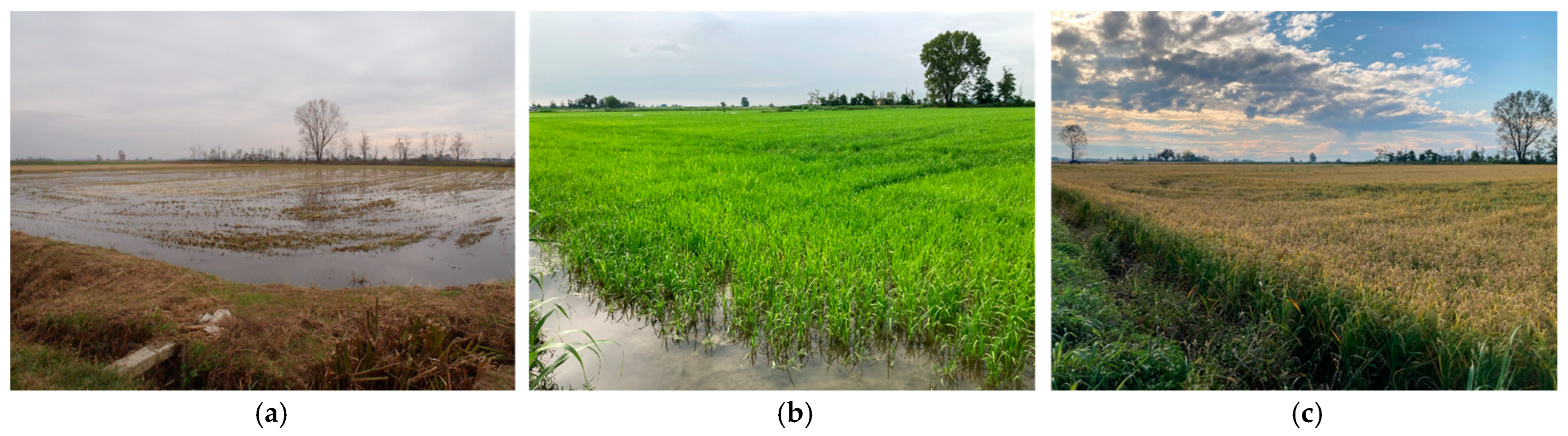



| Order | Families |
|---|---|
| Ephemeroptera | Baetidae, Caenidae, Ephemerellidae |
| Odonata-Zygoptera | Calopterygidae, Lestidae, Platycnemididae, Coenagrionidae |
| Odonata-Anisoptera | Gomphidae, Aeshnidae, Cordulegasteridae, Libellulidae, Corduliidae |
| Heteroptera | Gerridae, Nepidae, Corixidae, Notonectidae, Naucoridae, Pleidae, Veliidae, Hydrometridae, Ochteridae |
| Trichoptera | Leptoceridae, Hydropsychidae, Phryganeidae, Lepidostomatidae, Limnephilidae |
| Lepidoptera | Crambidae, Noctuidae |
| Diptera | Chironomidae, Ceratopogonidae, Culicidae, Chaoboridae, Psychodidae, Stratiomyidae, Limoniidae, Tipulidae, Tabanidae, Ephydridae, Syrphidae, Sciomyzidae, Empididae, Muscidae, Cordyluridae |
| Coleoptera | Gyrinidae, Dytiscidae, Haliplidae, Elmidae, Dryopidae, Helophoridae, Hydrophilidae, Limnebiidae |
| Keywords | N° Publications Worldwide | N° Publications Related to Italy |
|---|---|---|
| Rice + aquatic Insects | 197 | 2 |
| Rice fields + aquatic Insects | 152 | 3 |
| Rice fields + freshwater invertebrates | 17 | 1 |
| Rice fields + Diptera Culicidae | 202 | 3 |
| Rice fields + Coleoptera Curculionidae | 94 | 2 |
| Rice fields + Bacillus thuringensis | 258 | 4 |
| Rice fields + insecticides | 1260 | 12 |
| Rice fields + Diflubenzoron | 11 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bo, T.; Marino, A.; Guareschi, S.; Laini, A.; Fenoglio, S. Rice Fields and Aquatic Insect Biodiversity in Italy: State of Knowledge and Perspectives in the Context of Global Change. Water 2025, 17, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060845
Bo T, Marino A, Guareschi S, Laini A, Fenoglio S. Rice Fields and Aquatic Insect Biodiversity in Italy: State of Knowledge and Perspectives in the Context of Global Change. Water. 2025; 17(6):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060845
Chicago/Turabian StyleBo, Tiziano, Anna Marino, Simone Guareschi, Alex Laini, and Stefano Fenoglio. 2025. "Rice Fields and Aquatic Insect Biodiversity in Italy: State of Knowledge and Perspectives in the Context of Global Change" Water 17, no. 6: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060845
APA StyleBo, T., Marino, A., Guareschi, S., Laini, A., & Fenoglio, S. (2025). Rice Fields and Aquatic Insect Biodiversity in Italy: State of Knowledge and Perspectives in the Context of Global Change. Water, 17(6), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060845








