Study of Bacterial Growth in Drinking Water Distribution Pipes as a Function of the Water Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
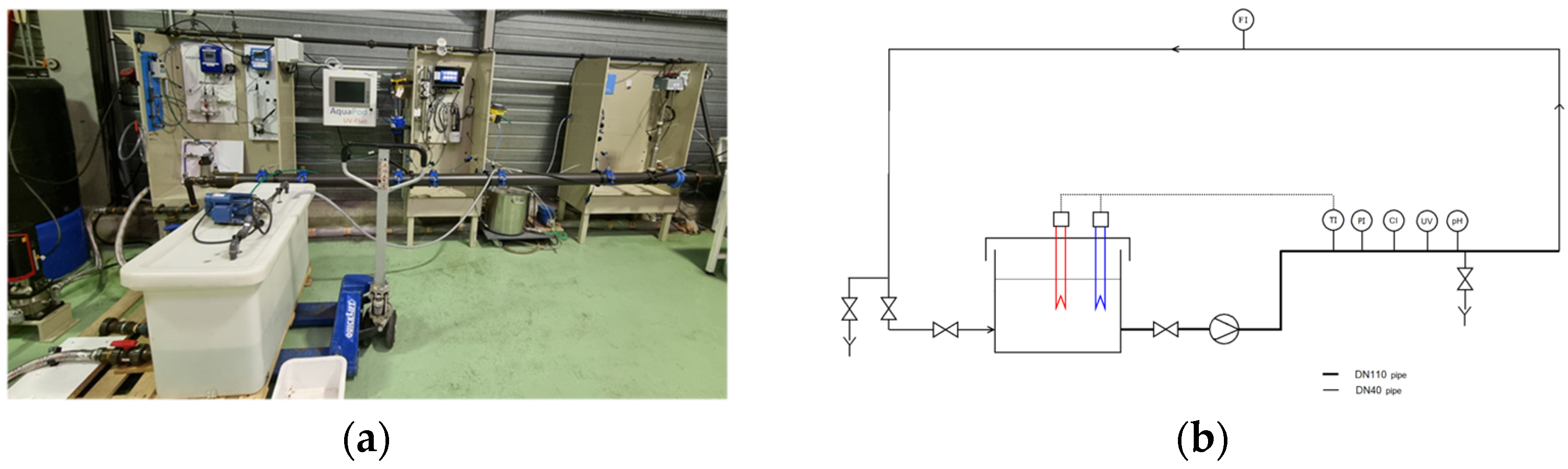
2.1. Experimental Pilot-Plant and Protocol
2.1.1. Pilot-Plant
2.1.2. Protocol
2.2. Microbiological and Physico-Chemical Parameters
2.2.1. Microbiological Parameters
2.2.2. Physico-Chemical Parameters
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
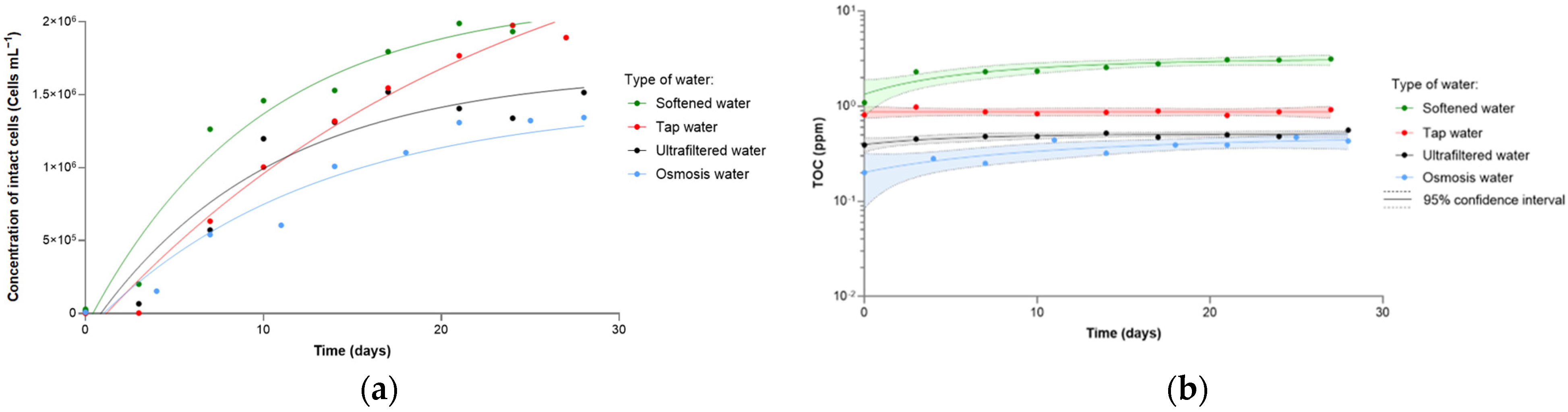
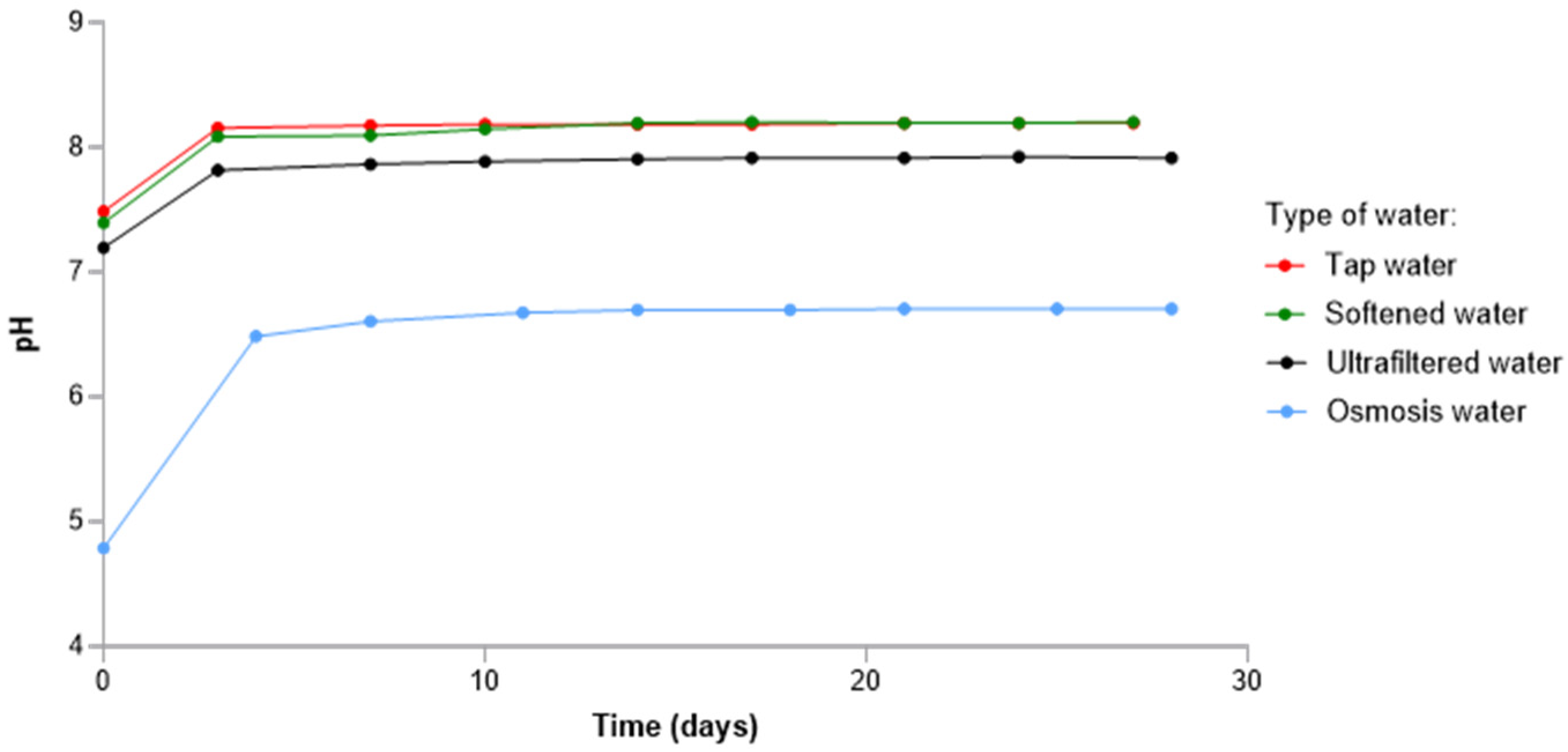
3.1. Effect of the Type of Water
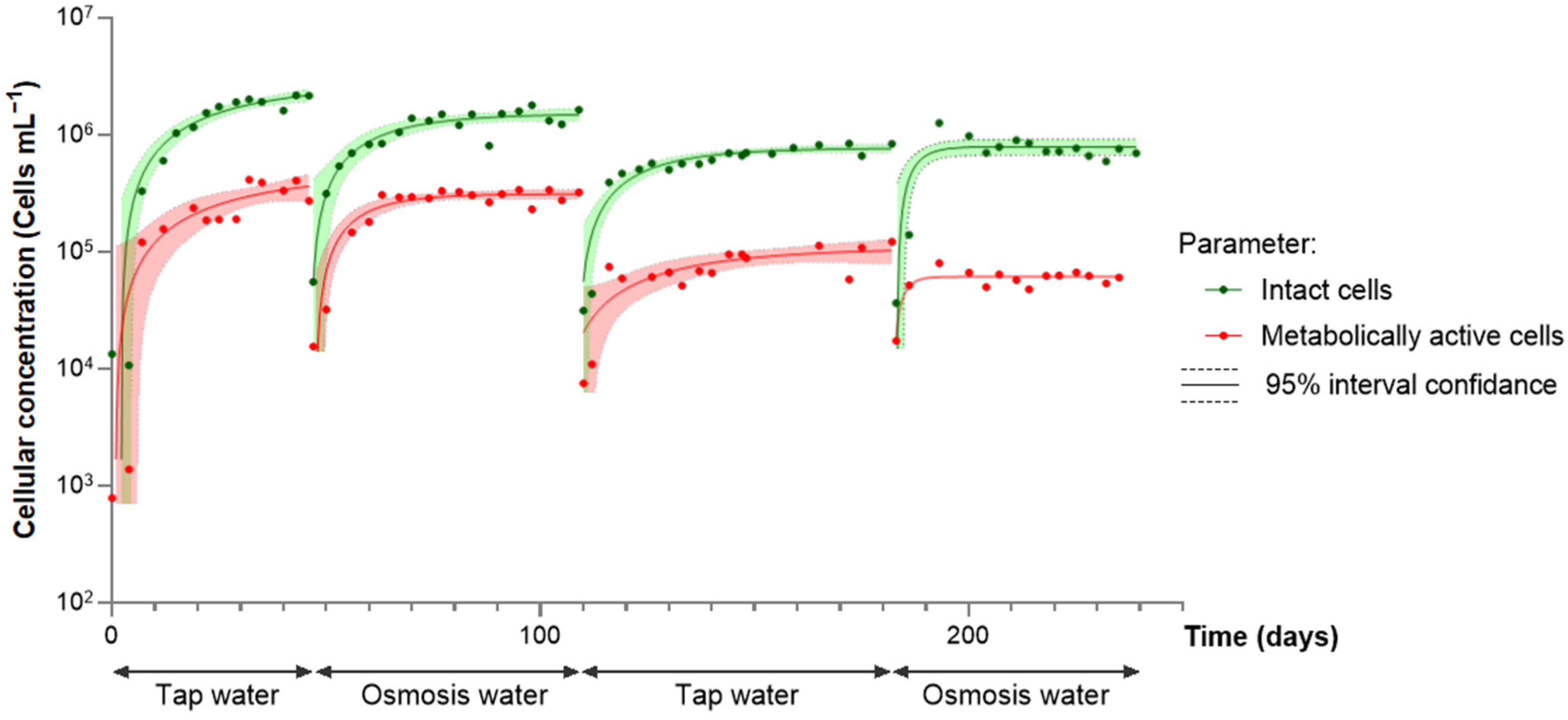
3.2. Behavior of Water Containing a Previously Developed Biofilm
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDOC | Biodegradable dissolved organic carbon |
| CFU | Colony forming units |
| DL | Detection limit |
| GAC | Granular activated carbon |
| LPRO | Low-pressure reverse osmosis |
| QL | Quantification limit |
| RO | Reverse osmosis |
| T | Temperature |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| UF | Ultrafiltration |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Hammes, F.; Berney, M.; Wang, Y.; Vital, M.; Köster, O.; Egli, T. Flow-Cytometric Total Bacterial Cell Counts as a Descriptive Microbiological Parameter for Drinking Water Treatment Processes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kooij, D.; van der Wielen, P.W.J.J. Microbial Growth in Drinking-Water Supplies: Problems, Causes, Control and Research Needs; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2013; Volume 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prest, E.I.; Hammes, F.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Biological Stability of Drinking Water: Controlling Factors, Methods, and Challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, C.R.; Hammes, F. Drinking Water Microbiology—From Measurement to Management. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Verberk, J.Q.J.C.; Van Dijk, J.C. Bacteriology of Drinking Water Distribution Systems: An Integral and Multidimensional Review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9265–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenschlager, K.; Hwang, C.; Liu, W.-T.; Boon, N.; Köster, O.; Vrouwenvelder, H.; Egli, T.; Hammes, F. A Microbiology-Based Multi-Parametric Approach towards Assessing Biological Stability in Drinking Water Distribution Networks. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Bakker, G.L.; Li, S.; Vreeburg, J.H.G.; Verberk, J.Q.J.C.; Medema, G.J.; Liu, W.T.; Van Dijk, J.C. Pyrosequencing Reveals Bacterial Communities in Unchlorinated Drinking Water Distribution System: An Integral Study of Bulk Water, Suspended Solids, Loose Deposits, and Pipe Wall Biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5467–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fass, S.; Dincher, M.L.; Reasoner, D.J.; Gatel, D.; Block, J.-C. Fate of Escherichia coli Experimentally Injected in a Drinking Water Distribution Pilot System. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkinen, J.; Kaunisto, T.; Pursiainen, A.; Miettinen, I.T.; Kusnetsov, J.; Riihinen, K.; Keinänen-Toivola, M.M. Drinking Water Quality and Formation of Biofilms in an Office Building during Its First Year of Operation, a Full Scale Study. Water Res. 2014, 49, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtola, M.J.; Laxander, M.; Miettinen, I.T.; Hirvonen, A.; Vartiainen, T.; Martikainen, P.J. The Effects of Changing Water Flow Velocity on the Formation of Biofilms and Water Quality in Pilot Distribution System Consisting of Copper or Polyethylene Pipes. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2151–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, G.M.; Malaeb, L. Impact of Intermittent Water Supply on Water Quality in Lebanon. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 26, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Whitaker, R.; LeChevallier, M.W.; Liu, W.-T. Drinking Water Microbiome Assembly Induced by Water Stagnation. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Kim, H.-C.; Meyer, A.S.; Kim, S.; Maeng, S.K. Influences of NOM Composition and Bacteriological Characteristics on Biological Stability in a Full-Scale Drinking Water Treatment Plant. Chemosphere 2016, 160, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.; Pullerits, K.; Keucken, A.; Persson, K.M.; Paul, C.J.; Rådström, P. Bacterial Release from Pipe Biofilm in a Full-Scale Drinking Water Distribution System. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatanović, L.; Van Der Hoek, J.P.; Vreeburg, J.H.G. An Experimental Study on the Influence of Water Stagnation and Temperature Change on Water Quality in a Full-Scale Domestic Drinking Water System. Water Res. 2017, 123, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payment, P.; Siemiatycki, J.; Richardson, L.; Renaud, G.; Franco, E.; Prevost, M. A Prospective Epidemiological Study of Gastrointestinal Health Effects Due to the Consumption of Drinking Water. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 1997, 7, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoehn, R. Biological Causes of Tastes and Odors in Drinking Water Supplies. Water Qual. Bull. 1988, 13, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Taligrot, H.; Wurtzer, S.; Monnot, M.; Geslin, J.; Moulin, L.; Moulin, P. Effect of Volumetric Concentration Factor on Virus Removal for Low-Pressure Reverse Osmosis Membrane in Drinking Water Production: A Study on Different Scales. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladeia Ramos, R.; Rodrigues Dos Santos, C.; Pinheiro Drumond, G.; Valéria De Souza Santos, L.; Cristina Santos Amaral, M. Critical Review of Microplastic in Membrane Treatment Plant: Removal Efficiency, Environmental Risk Assessment, Membrane Fouling, and MP Release. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diawara, C.K.; Diop, S.N.; Diallo, M.A.; Farcy, M.; Deratani, A. Performance of Nanofiltration (NF) and Low Pressure Reverse Osmosis (LPRO) Membranes in the Removal of Fluorine and Salinity from Brackish Drinking Water. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2011, 3, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6222; Water Quality—Enumeration of Culturable Micro-organisms—Colony Count by Inoculation in a Nutrient Agar Culture Medium. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- ISO 8199; Water Quality—General Requirements and Guidance for Microbiological Examinations by Culture. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- The dMIQE Group; Whale, A.S.; De Spiegelaere, W.; Trypsteen, W.; Nour, A.A.; Bae, Y.-K.; Benes, V.; Burke, D.; Cleveland, M.; Corbisier, P.; et al. The Digital MIQE Guidelines Update: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Digital PCR Experiments for 2020. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1012–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomski, N.; Roguet, A.; Lucas, F.S.; Veyrier, F.J.; Cambau, E.; Accrombessi, H.; Moilleron, R.; Behr, M.A.; Moulin, L. atpE Gene as a New Useful Specific Molecular Target to Quantify Mycobacterium in Environmental Samples. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuj, S.N.; Whiley, D.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Bell, S.C.; Wainwright, C.E.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P. Identification of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa by a Duplex Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay Targeting the ecfX and the gyrB Genes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 63, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarian, E.J.; Bopp, D.J.; Saylors, A.; Limberger, R.J.; Musser, K.A. Design and Implementation of a Protocol for the Detection of Legionella in Clinical and Environmental Samples. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 62, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlemann, D.P.R.; Labrenz, M.; Jürgens, K.; Bertilsson, S.; Waniek, J.J.; Andersson, A.F. Transitions in Bacterial Communities along the 2000 Km Salinity Gradient of the Baltic Sea. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 15923-1; Water Quality—Determination of Selected Parameters by Discrete Analysis Systems. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- NF EN 1484; Water Analysis—Guidelines for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) and Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC). Association Française de Normalisation: Saint-Denis, France, 1997.
- NF EN 27888; Water Quality—Determination of Electrical Conductivity. Association Française de Normalisation: Saint-Denis, France, 1994.
- García-Timermans, C.; Malfroot, B.; Dierendonck, C.; Mol, Z.; Pluym, T.; Waegenaar, F.; Arends, J.B.A.; Demeestere, K.; Walgraeve, C.; Boon, N.; et al. Pilot-Scale Drinking Water Distribution System to Study Water Quality Changes during Transport. npj Clean Water 2023, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; LePuil, M.; Taylor, J.S.; Randall, A.A. Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Biostability Relative to Alternative Methods of Water Treatment. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-Aqua 2007, 56, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, I.C.; Hong, S.; Randall, A.A. Removal of Assimilable Organic Carbon and Biodegradable Dissolved Organic Carbon by Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 175, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Hu, J.Y. Assessment of the Extent of Bacterial Growth in Reverse Osmosis System for Improving Drinking Water Quality. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2010, 45, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckes, M.C.; Haught, R.C.; Kelty, K.; Blannon, J.C.; Cmehil, D. Impact on Water Distribution System Biofilm Densities from Reverse Osmosis Membrane Treatment of Supply Water. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2007, 6, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, K.E.; Osborn, A.M.; Boxall, J. Characterising and Understanding the Impact of Microbial Biofilms and the Extracellular Polymeric Substance (EPS) Matrix in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 614–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Qi, W.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y. Impact of Biofilm Formation and Detachment on the Transmission of Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velten, S.; Boller, M.; Köster, O.; Helbing, J.; Weilenmann, H.-U.; Hammes, F. Development of Biomass in a Drinking Water Granular Active Carbon (GAC) Filter. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6347–6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Chen, W.; Wang, L. Particle Properties in Granular Activated Carbon Filter during Drinking Water Treatment. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallon, K. The Release of Particles from GAC Filter-Adsorbers and Their Effect on Disinfection. Master’s Thesis, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Frias, J.; Ribas, F.; Lucena, F. Effects of Different Nutrients on Bacterial Growth in a Pilot Distribution System. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2001, 80, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bott, T.L.; Kaplan, L.A. Bacterial Biomass, Metabolic State, and Activity in Stream Sediments: Relation to Environmental Variables and Multiple Assay Comparisons. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 50, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, C.; Joret, J.C.C. Paramètres prédictifs de l’apparition des coliformes dans les réseaux de distribution d’eau d’alimentation. Rev. Sci. Eau 2005, 7, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Becerra-Castro, C.; Macedo, G.; Silva, A.M.T.; Manaia, C.M.; Nunes, O.C. Proteobacteria Become Predominant during Regrowth after Water Disinfection. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, A.; Su, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Gao, S. Effects of Carbon Sources on Phosphorus Speciation Transformation Process, Characteristics of Extracellular Polymeric Substances, and Microecology in Anaerobic Systems. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, B.; Peng, Y. Long-Term Effect of pH on Short-Chain Fatty Acids Accumulation and Microbial Community in Sludge Fermentation Systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, Y.; Bouchon, D.; Héchard, Y.; Moulin, L. Spatio-Temporal Survey of Opportunistic Premise Plumbing Pathogens in the Paris Drinking Water Distribution System. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbeau, B.; Julienne, K.; Carriere, A.; Gauthier, V. Dead-End Flushing of a Distribution System: Short and Long-Term Effects on Water Quality. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-Aqua 2005, 54, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, P.; Billen, G.; Laurent, P.; Levi, Y.; Randon, G. Studies of BDOC and Bacterial Dynamics in the Drinking Water Distribution System of the Northern Parisian Suburbs. Rev. Sci. Eau 2005, 5, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, V.; Gérard, B.; Portal, J.-M.; Block, J.-C.; Gatel, D. Organic Matter as Loose Deposits in a Drinking Water Distribution System. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sade, Z.; Hegyi, S.; Halevy, I. Equilibration Times of Dissolved Inorganic Carbon During pH Transitions. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 9, 792858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Wende, E.; Characklis, W.G.; Smith, D.B. Biofilms and Bacterial Drinking Water Quality. Water Res. 1989, 23, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial Biofilms: From the Natural Environment to Infectious Diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Water Works Association. Water Quality & Treatment: A Handbook on Drinking Water, 6th ed.; Edzwald, J.K., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-07-163011-5. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, P.S.; Franklin, M.J. Physiological Heterogeneity in Biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingender, J.; Neu, T.R.; Flemming, H.-C. What Are Bacterial Extracellular Polymeric Substances? In Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances; Wingender, J., Neu, T.R., Flemming, H.-C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 1–19. ISBN 978-3-642-64277-7. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E. Water Quality: An Introduction; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-23334-1. [Google Scholar]
- Røder, H.L.; Sørensen, S.J.; Burmølle, M. Studying Bacterial Multispecies Biofilms: Where to Start? Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delafont, V.; Perrin, Y.; Bouchon, D.; Moulin, L.; Héchard, Y. Targeted Metagenomics of Microbial Diversity in Free-Living Amoebae and Water Samples. In Legionella; Buchrieser, C., Hilbi, H., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1921, pp. 421–428. ISBN 978-1-4939-9047-4. [Google Scholar]


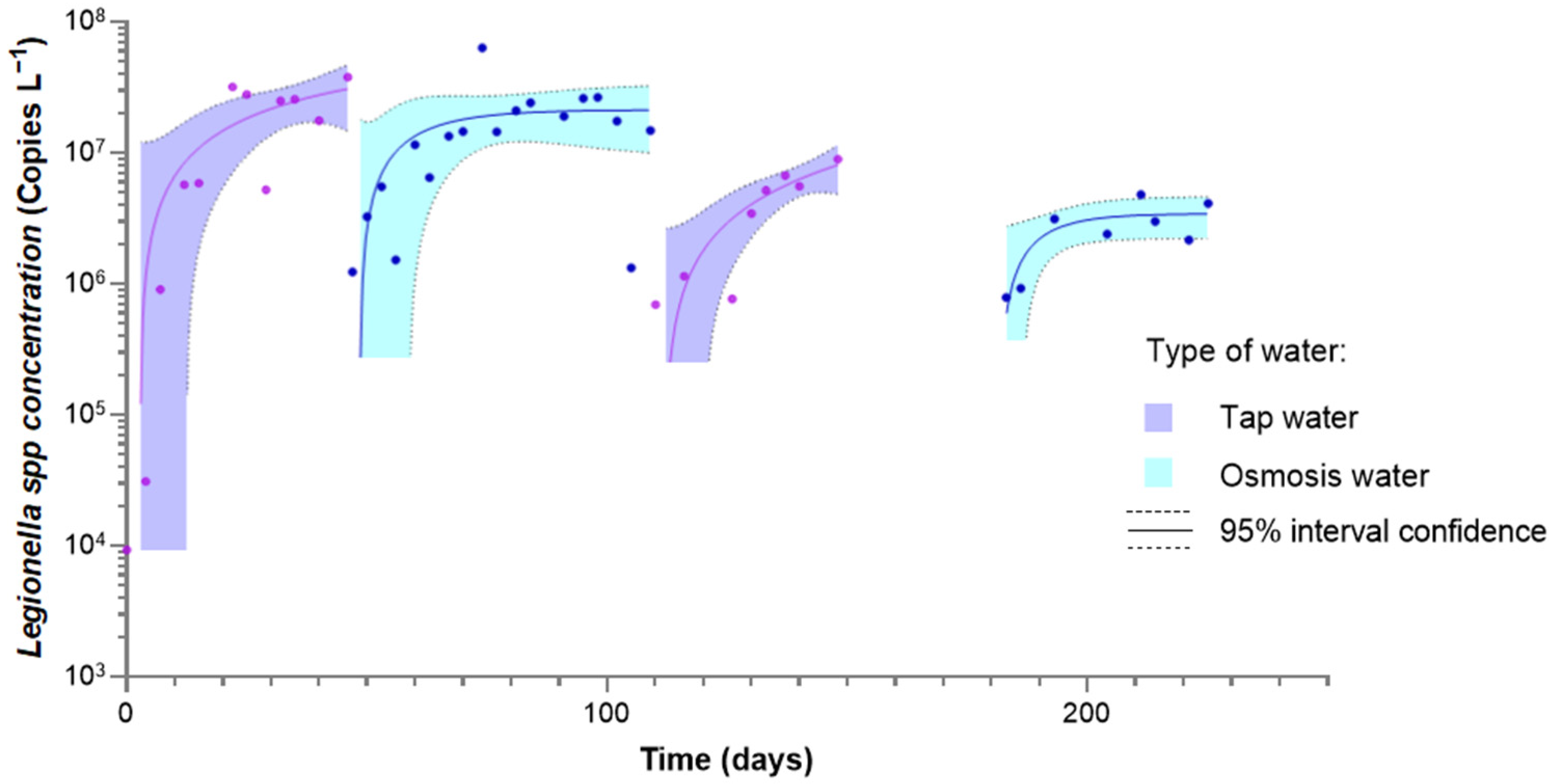
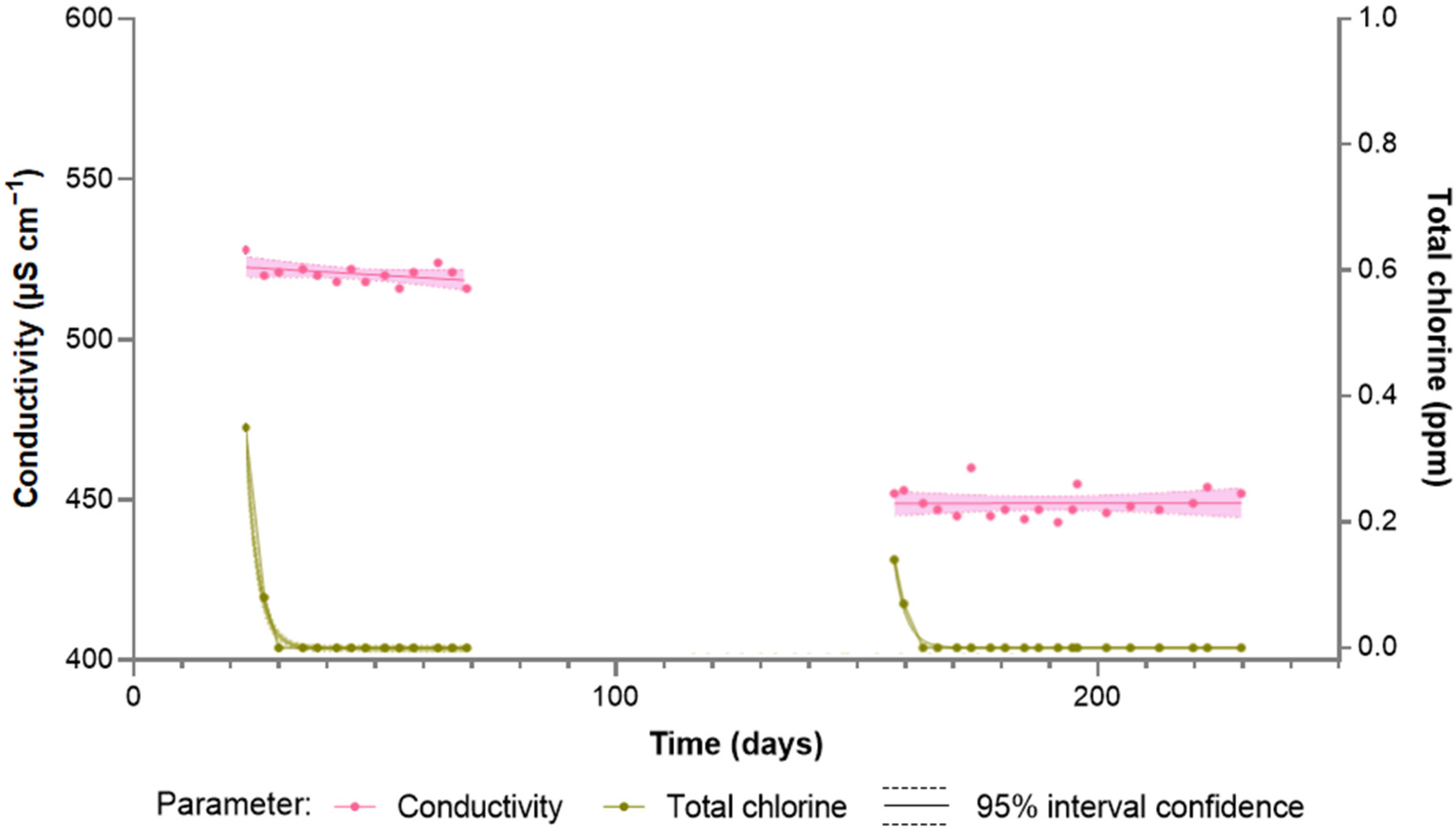


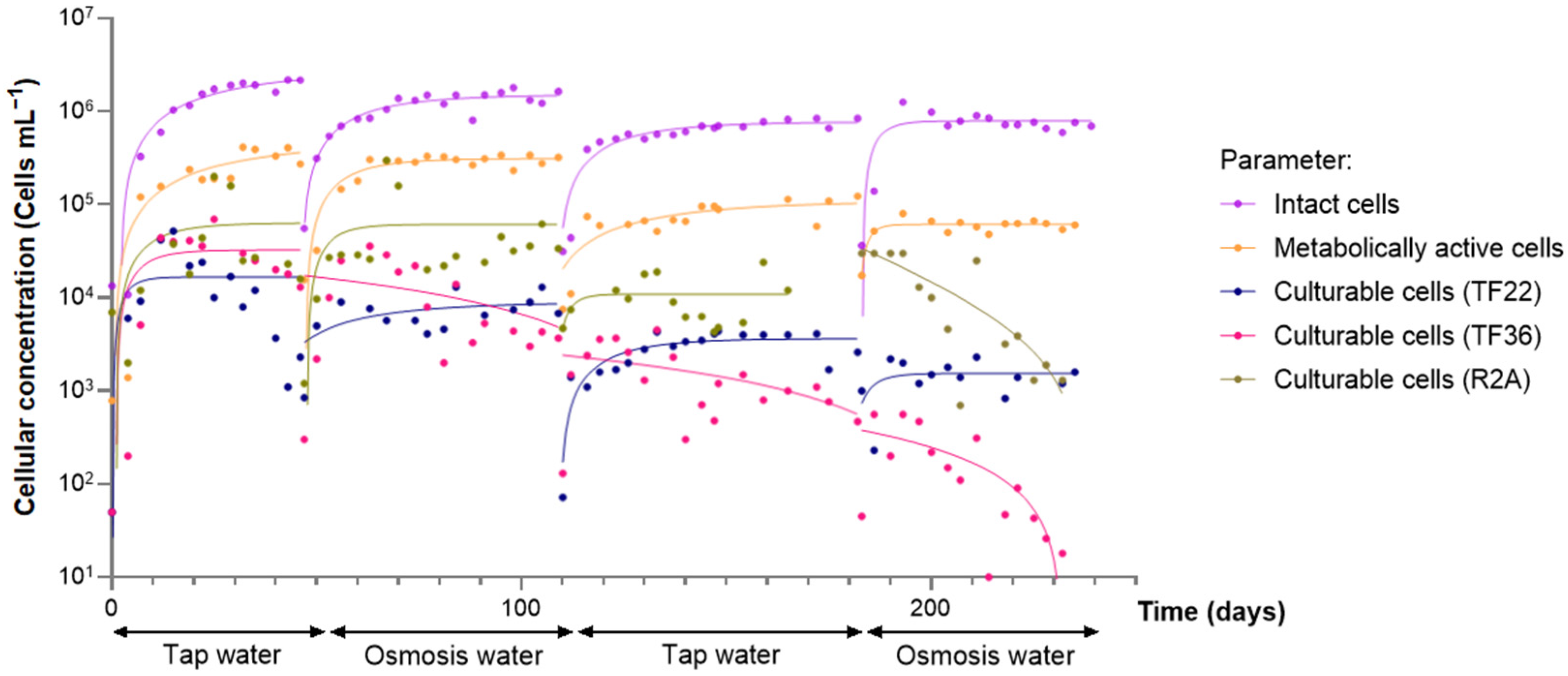

| Parameter | Tap Water | Softened Water | Ultrafiltered Water | LPRO Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.49 | 7.40 | 7.20 | 4.79 |
| Conductivity (µS cm−1) | 488 | 501 | 513 | <50 |
| TOC (mgC L−1) | 0.81 | 1.09 | 0.39 | <0.20 |
| Nitrate (mg L−1) | 19.6 | 22.4 | 28.4 | <2.0 |
| Ammonium (mg L−1) | <0.03 | <0.03 | <0.03 | <0.03 |
| Orthophosphate (mg L−1) | 0.67 | 0.84 | 0.12 | 0.09 |
| Total Chlorine (mg L−1) | 0.22 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Active Chlorine (mg L−1) | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Parameter | Method | Unit | Detection Limit (DL) | Quantification Limit (QL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total cells and intact cells | Flow cytometry | Cells mL−1 | 200 | 100 |
| Metabolically active cells | Solid phase cytometry | Cells mL−1 | 1 | 10 |
| Total Flora on PCA medium | NF EN ISO 6222 [21] | CFU mL−1 | 3 | 5 |
| Total flora on R2A medium | NF EN ISO 8199 [22] | CFU 150 µL−1 | 3 | 4 |
| Specific bacteria | Digital PCR | Copies L−1 | 20 | 60 |
| ATPE-F | CGGYGCCGGTATCGGYGA | atpE | Mycobacteria | [24] |
| ATPE-R | CGAAGACGAACARSGCCAT | |||
| ATPE-P | ROX-ACSGTGATGAAGAACGGBGTRAA-QXL610 | |||
| ecfX-F | CGCATGCCTATCAGGCGTT | ecfX | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [25] |
| ecfX-R | GAACTGCCCAGGTGCTTGC | |||
| ecfX-P | TAMRA-ATGGCGAGTTGCTGCGCTTCCT-BHQ2 | |||
| Leg23SF forward | CCCATGAAGCCCGTTGAA | 23S rRNA | Legionella | [26] |
| Leg23SR reverse | ACAATCAGCCAATTAGTACGAGTTAGC | |||
| Lsp23SP | FAM-TCCACACCTCGCCTATCAACGTCGTAGT-BHQ1 | |||
| LmipF forward | AAAGGCATGCAAGACGCTATG | mip | ||
| LmipR reverse | GAAACTTGTTAAGAACGTCTTTCATTTG | |||
| LmipP | HEX-TGGCGCTCAATTGGCTTTAACCGA-BHQ1 |
| Parameter | Apparatus | Method | Unit | Quantification Limit (QL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonium (NH4+) | Gallery plus, Thermo (Waltham, USA) | NF EN ISO 15923-1 [28] | mg L−1 | 0.03 |
| Nitrates (NO3−) | 2 | |||
| Orthophosphates (PO43−) | Smartchem 450 (Rome, Italy), AMS | 0.05 | ||
| TOC | Analytikjena 3100 (Jean, Germany) | NF EN 1484 [29] | mgC L−1 | 0.2 |
| Conductivity | 855 robotic titrosampler, Metrohm (Herisau, Switzerland) | NF EN 27888 [30] | µS cm−1 | 50 |
| Active Chlorine | DR300, Hach (Loveland, CO, USA) | USEPA DPD Method | mg L−1 | 0.01 |
| Total Chlorine | 0.01 |
| Parameter | Tap Water | Softened Water | Ultrafiltered Water | LPRO Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial concentration at stationary phase (cells mL−1) | >2 × 106 | 2 × 106 | 1.5 × 106 | 1.1 × 106 |
| Time to stationary phase (days) | >30 | 21 | 17 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taligrot, H.; Wurtzer, S.; Monnot, M.; Geslin, J.; Belkebir, C.; Moulin, L.; Moulin, P. Study of Bacterial Growth in Drinking Water Distribution Pipes as a Function of the Water Quality. Water 2025, 17, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060835
Taligrot H, Wurtzer S, Monnot M, Geslin J, Belkebir C, Moulin L, Moulin P. Study of Bacterial Growth in Drinking Water Distribution Pipes as a Function of the Water Quality. Water. 2025; 17(6):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060835
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaligrot, Hugo, Sébastien Wurtzer, Mathias Monnot, Jacques Geslin, Chaimaa Belkebir, Laurent Moulin, and Philippe Moulin. 2025. "Study of Bacterial Growth in Drinking Water Distribution Pipes as a Function of the Water Quality" Water 17, no. 6: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060835
APA StyleTaligrot, H., Wurtzer, S., Monnot, M., Geslin, J., Belkebir, C., Moulin, L., & Moulin, P. (2025). Study of Bacterial Growth in Drinking Water Distribution Pipes as a Function of the Water Quality. Water, 17(6), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060835







