Satellite Retrieval and Spatiotemporal Variability in Chlorophyll-a for Marine Ranching: An Example from Daya Bay, Guangdong Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Preprocessing of Satellite Data
2.4. Physically Based Retrieval Model
| Band 2 | Band 3 | Band 4 | Band 8 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| central wavelength (nm) | 490 | 560 | 665 | 842 | |
| a (m-1) | water | 0.0196 | 0.0844 | 0.4221 | 3.7938 |
| Chl-a | 0.9310 | 0.6308 | 0.9394 | 0.5348 | |
| suspended sediment | 0.1202 | 0.0463 | 0.0321 | 0.1144 | |
| aerobic organic matter | 0.1961 | 0.1404 | 0.1293 | 0.1001 | |
| b (m-1) | water | 0.0031 | 0.0017 | 0.0008 | 0.0003 |
| Chl-a | 0.0906 | 0.1721 | 0.0905 | 0.1418 | |
| suspended sediment | 0.0523 | 0.0589 | 0.0529 | ||
| aerobic organic matter | 0.0078 | 0.0098 | 0.0047 | ||
2.5. Accuracy Assessment
2.6. Spatiotemporal Evolution Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Model Performance
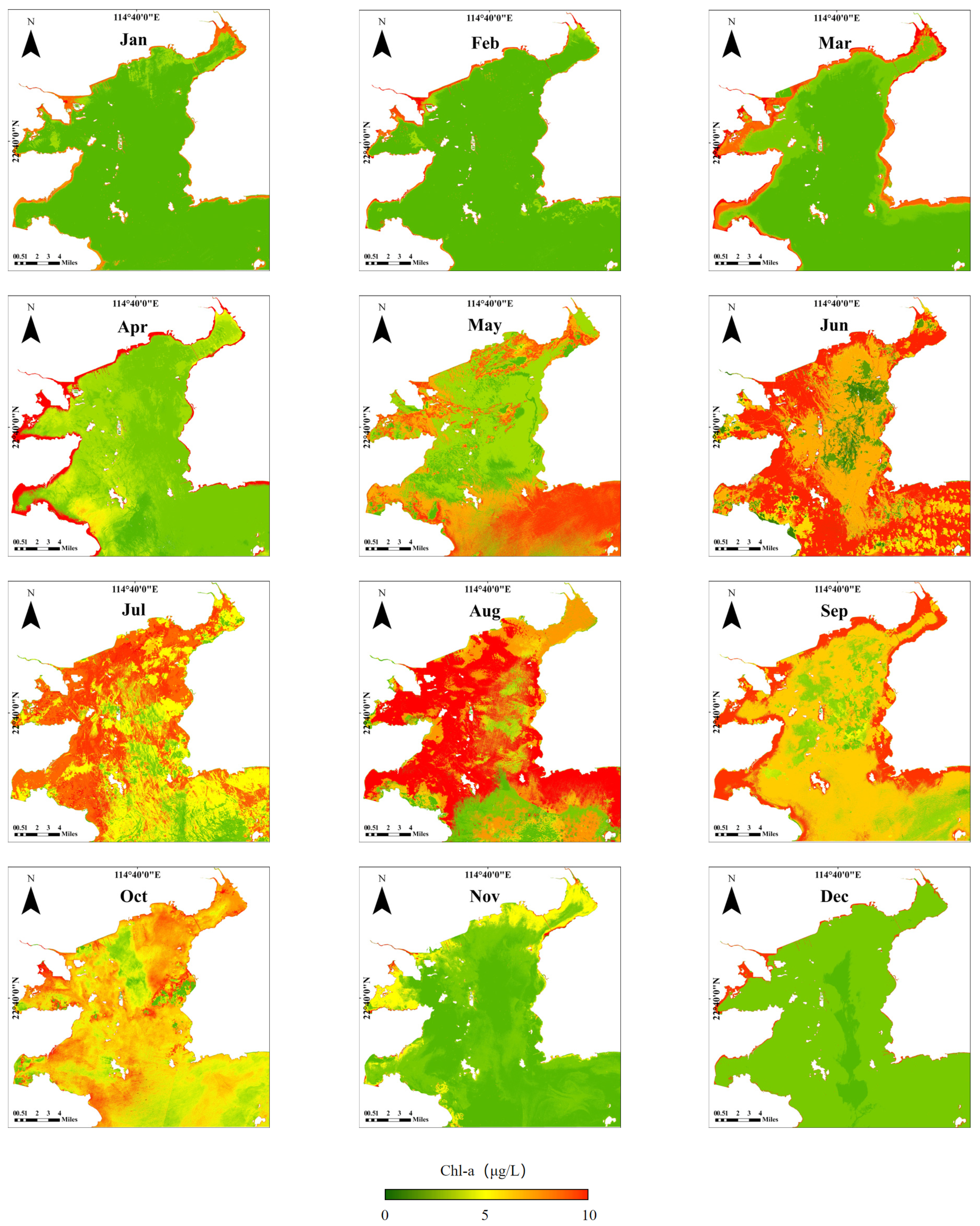
3.2. Intra-Annual Spatiotemporal Distribution Pattern of Chl-a
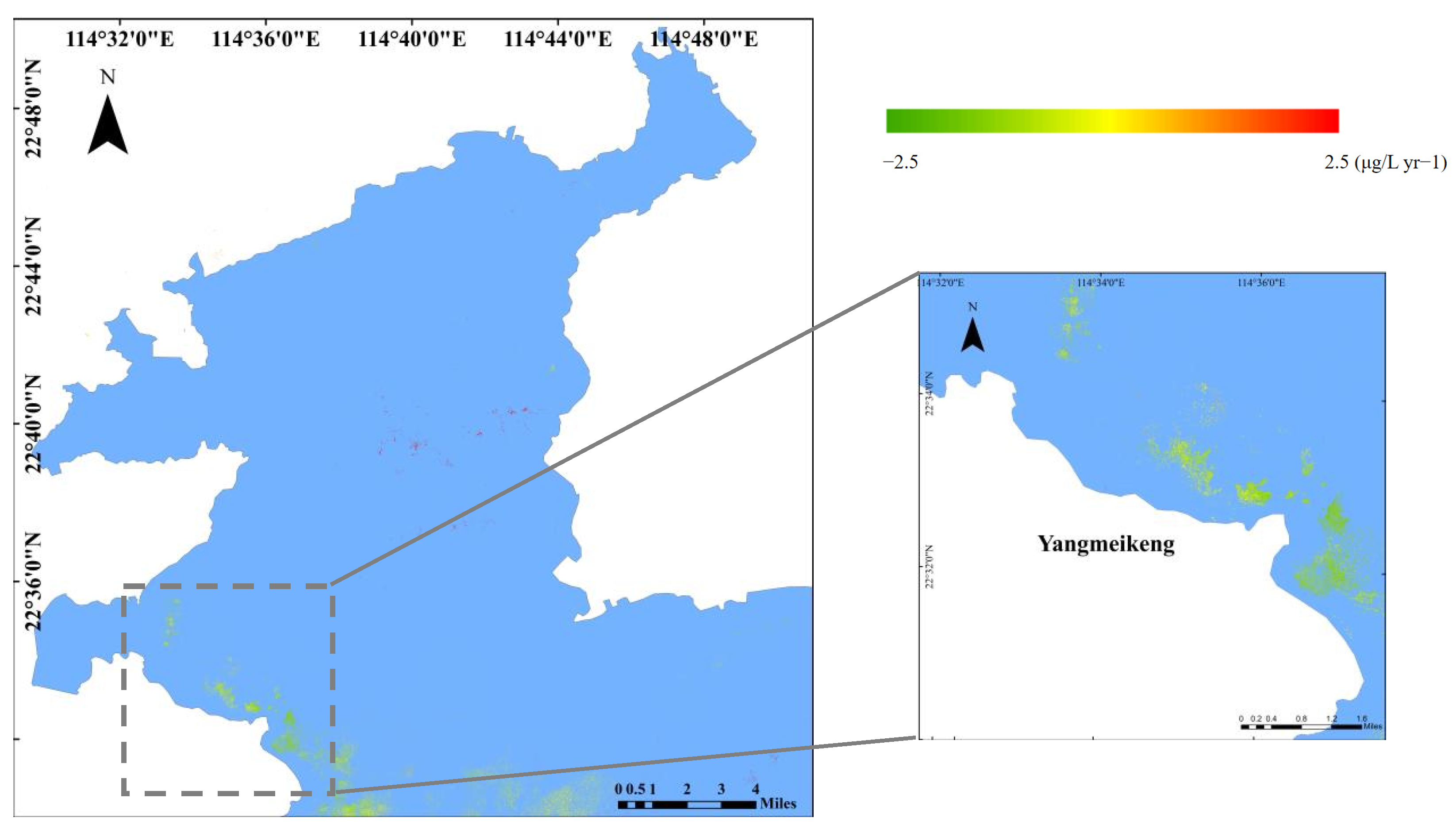
3.3. Interannual Variation Trend of Chl-a
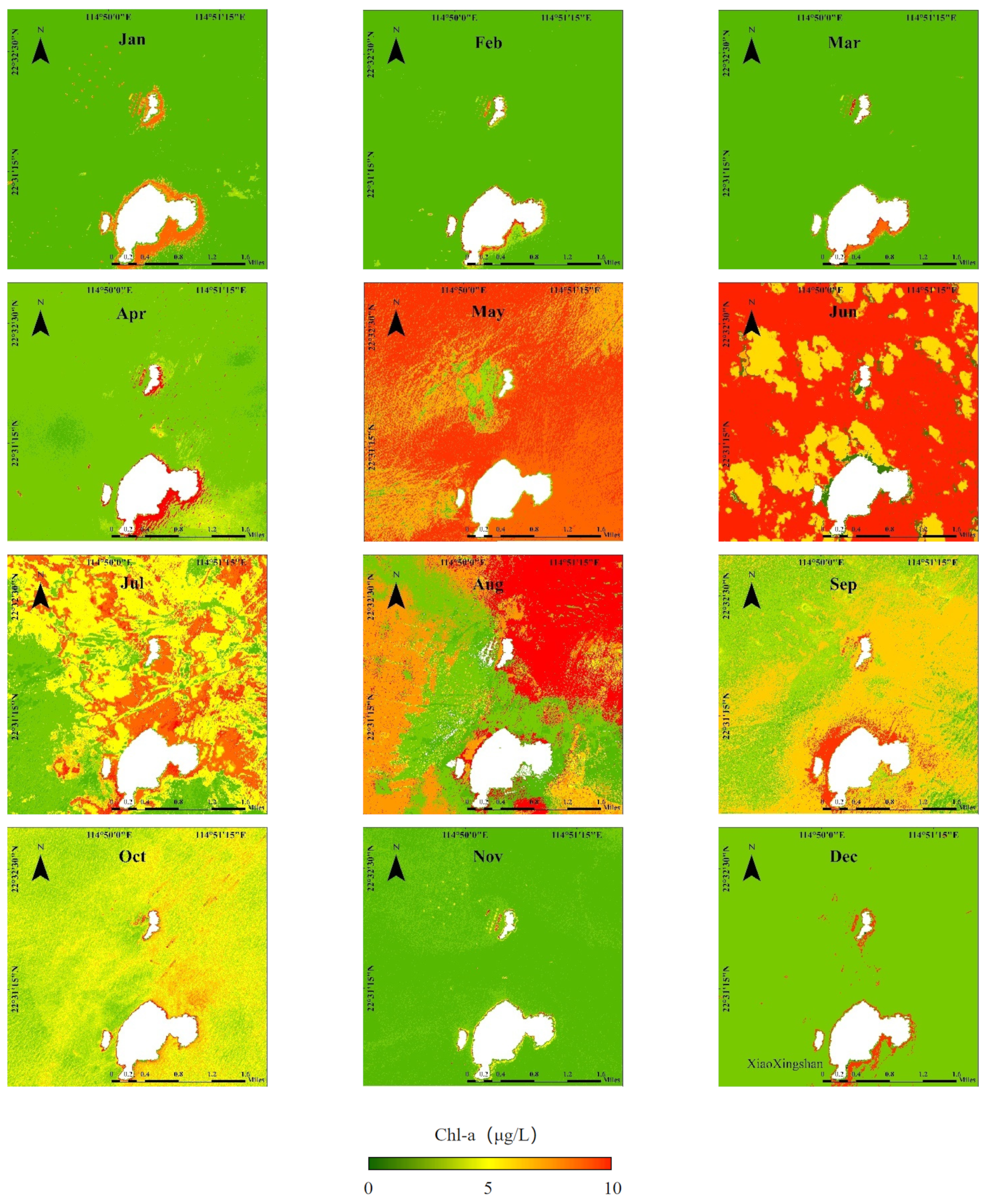
3.4. Comparison Between Nearshore and Offshore Marine Ranching
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Chl-a
4.2. Pollution Source Analysis
4.3. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; He, X.; Wu, X. Geological Evolution of Offshore Pollution and Its Long-Term Potential Impacts on Marine Ecosystems. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häder, D.P.; Banaszak, A.T.; Villafañe, V.E.; Narvarte, M.A.; González, R.A.; Helbling, E.W. Anthropogenic Pollution of Aquatic Ecosystems: Emerging Problems with Global Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugère, C.; Aguilar-Manjarrez, J.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Soto, D. The Ecosystem Approach to Aquaculture 10 Years on—A Critical Review and Consideration of Its Future Role in Blue Growth. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 493–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikeset, A.M.; Mazzarella, A.B.; Davíðsdóttir, B.; Klinger, D.H.; Levin, S.A.; Rovenskaya, E.; Stenseth, N.C. What Is Blue Growth? The Semantics of “Sustainable Development” of Marine Environments. Mar. Policy 2018, 87, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Lin, J. Marine Ranching Construction and Management in East China Sea: Programs for Sustainable Fishery and Aquaculture. Water 2019, 11, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Wan, X. Influencing Factors of Spatial Variation of National Marine Ranching in China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 199, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yin, W.; Li, D. Policy Network Analysis of China’s Ocean Ranching Policy: Network Structure, Actors and Interaction. Mar. Policy 2022, 140, 105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.R.; Webber, J.; Zonneveld, S.; Carless, D.; Jackson, B.; Artioli, Y.; Miller, P.I.; Holmyard, J.; Baker-Austin, C.; Kershaw, S.; et al. Stakeholder Perspectives on the Importance of Water Quality and Other Constraints for Sustainable Mariculture. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 114, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambin, A.F.; Angelats, E.; Gonzalez, J.S.; Miozzo, M.; DIni, P. Sustainable Marine Ecosystems: Deep Learning for Water Quality Assessment and Forecasting. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 121344–121365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, A.; Bruen, M.; Cocchiglia, L.; Kelly-Quinn, M. Water Quality Monitoring during the Construction of the M3 Motorway in Ireland. Water Environ. J. 2012, 26, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neposhyvailenko, N.; Omelych, I.; Dziuba, N. Assessment of Environmental Impact of Road Construction Based on Results of Remote Sensing Monitoring. Agrology 2024, 7, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidic, R.D.; Brantley, S.L.; Vandenbossche, J.M.; Yoxtheimer, D.; Abad, J.D. Impact of Shale Gas Development on Regional Water Quality. Science 2013, 340, 1235009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, M.; Su, Y.; Shahzad, M.I.; Ayub, G.; Rahman, S.U.; Ijaz, J. A Review on Monitoring, Forecasting, and Early Warning of Harmful Algal Bloom. Aquaculture 2024, 593, 741351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, J.; Kirchner, J.S.; Jewell, K.S.; Schluesener, M.P.; Wick, A.; Ternes, T.A.; Duester, L. Making Waves: Time for Chemical Surface Water Quality Monitoring to Catch up with Its Technical Potential. Water Res. 2022, 213, 118168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau-Patissier, D.; Gower, J.F.R.; Dekker, A.G.; Phinn, S.R.; Brando, V.E. A Review of Ocean Color Remote Sensing Methods and Statistical Techniques for the Detection, Mapping and Analysis of Phytoplankton Blooms in Coastal and Open Oceans. Prog. Oceanogr. 2014, 123, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Yu, G.; Sun, S.; Dou, Y.; Li, H.; Qiao, Z. Monitoring Water Quality of the Haihe River Based on Ground-Based Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Water 2022, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Wen, W.; Zhuang, F.; Yu, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, Y. Universal High-Frequency Monitoring Methods of River Water Quality in China Based on Machine Learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Driscol, J.; Sarigai, S.; Wu, Q.; Lippitt, C.D.; Morgan, M. Towards Synoptic Water Monitoring Systems: A Review of AI Methods for Automating Water Body Detection and Water Quality Monitoring Using Remote Sensing. Sensors 2022, 22, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjovu, G.E.; Stephen, H.; James, D.; Ahmad, S. Overview of the Application of Remote Sensing in Effective Monitoring of Water Quality Parameters. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yue, X.; Wang, H.; Ling, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hong, J.; Pen, W.; Song, H. Dynamic Inversion of Inland Aquaculture Water Quality Based on UAVs-WSN Spectral Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Z. Multispectral Remote Sensing for Estimating Water Quality Parameters: A Comparative Study of Inversion Methods Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Sustainability 2023, 15, 10298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kong, J.; Hu, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, F. A Review of Remote Sensing for Water Quality Retrieval: Progress and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yin, Y.; Chen, X.; Jin, J.; Wu, S. Long-Term Spatiotemporal Mapping in Lacustrine Environment by Remote Sensing:Review with Case Study, Challenges, and Future Directions. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Wang, L.; McCabe, M.F. Multi-Sensor Remote Sensing for Drought Characterization: Current Status, Opportunities and a Roadmap for the Future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, D. Spatio-Temporal-Spectral Observation Model for Urban Remote Sensing. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 24, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sishodia, R.P.; Ray, R.L.; Singh, S.K. Applications of Remote Sensing in Precision Agriculture: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.; Kushal, K.C.; Fulton, J.P.; Shearer, S.; Ozkan, E. Remote Sensing in Agriculture—Accomplishments, Limitations, and Opportunities. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainurin, S.N.; Wan Ismail, W.Z.; Mahamud, S.N.I.; Ismail, I.; Jamaludin, J.; Ariffin, K.N.Z.; Wan Ahmad Kamil, W.M. Advancements in Monitoring Water Quality Based on Various Sensing Methods: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 14080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Fu, R.; Li, D.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y.; Jia, K.; Hicks, B.J. Remote Sensing Big Data for Water Environment Monitoring: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Earths Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Xiong, B. Inversion of Water Quality by Remote-Sensing Monitoring Based on Machine Learning in Complex Freshwater Environments. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 291, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjovu, G.E.; Stephen, H.; James, D.; Ahmad, S. Measurement of Total Dissolved Solids and Total Suspended Solids in Water Systems: A Review of the Issues, Conventional, and Remote Sensing Techniques. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.S. A Comprehensive Approach to Assessing Eutrophication for the Guangdong Coastal Waters in China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1280821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Liu, P.; Hu, X.; Zhu, S. Harmful Algal Blooms in Eutrophic Marine Environments: Causes, Monitoring, and Treatment. Water 2024, 16, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, R.; Deng, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Sea Surface Chlorophyll-a in Coral Reefs of the South China Sea over the Past Decade Based on Landsat-8 Operational Land Images. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, N.; Luo, M.; Jiang, T.; Chan, T.O.; Yau, C.S.T.; Sun, Y. Downscaling Sentinel-3 Chlorophyll-a Concentration for Inland Lakes Based on Multivariate Analysis and Gradient Boosting Decision Trees Regression. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 7850–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, P.; Domenikiotis, C.; Neofitou, N.; Vafidis, D. Study of the Spatiotemporal Variability of Oceanographic Parameters and Their Relationship to Holothuria Species Abundance in a Marine Protected Area of the Mediterranean Using Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, N.H.; Nguyen, M.N.; Paget, M.; Anstee, J.; Viet, N.D.; Nones, M.; Tuan, V.A. Assessment of Human-Induced Effects on Sea/Brackish Water Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Ha Long Bay of Vietnam with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, H.; Jiang, J.; Han, G.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Jia, X.; Ji, Q.; Li, B. Applying Deep Learning in the Prediction of Chlorophyll-a in the East China Sea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharvogel, D.; Brandmeier, M.; Weis, M. A Deep Learning Approach for Calamity Assessment Using Sentinel-2 Data. Forests 2020, 11, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Taberner, M.; García-Haro, F.J.; Martínez, B.; Izquierdo-Verdiguier, E.; Atzberger, C.; Camps-Valls, G.; Gilabert, M.A. Understanding Deep Learning in Land Use Classification Based on Sentinel-2 Time Series. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaponara, R.; Tucci, B.; Ghermandi, L. On the Use of Satellite Sentinel 2 Data for Automatic Mapping of Burnt Areas and Burn Severity. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, F.; Delgado Blasco, J.M.; Ivanescu, C. Improving Rapid Flood Impact Assessment: An Enhanced Multi-Sensor Approach Including a New Flood Mapping Method Based on Sentinel-2 Data. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phiri, D.; Simwanda, M.; Salekin, S.; Nyirenda, V.R.; Murayama, Y.; Ranagalage, M. Sentinel-2 Data for Land Cover/Use Mapping: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseev, A.; Chernikhovskii, D. Assessment of the Health Status of Tree Stands Based on Sentinel-2B Remote Sensing Materials and the Short-Wave Vegetation Index SWVI. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 876. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Li, D. Development of in Situ Sensors for Chlorophyll Concentration Measurement. J. Sens. 2015, 2015, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liqiong, J.H.; Chen, C.X.; Tian, L.; Feng, L.; Yesou, H.; Li, F.; Huang, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, X. Modification and Validation of a Quasi-Analytical Algorithm for Inherent Optical Properties in the Turbid Waters of Poyang Lake, China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083643. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhellemont, Q. Adaptation of the Dark Spectrum Fitting Atmospheric Correction for Aquatic Applications of the Landsat and Sentinel-2 Archives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Deng, R.; Lu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Shen, X.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Y. The Study of Spatial-Temporal Characteristics for CODMn in Shenzhen Reservoir Based on GF-1 WFV. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 26, 1562–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Deng, R.; Liang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Ai, X.; Qin, Y. Remote Sensing Retrieval of Total Phosphorus in the Pearl River Channels Based on the GF-1 Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruru, D.; Yingqing, H.; Yan, Q.; Qidong, C.; Lei, C. Measuring Pure Water Absorption Coefficient in the Near-Infrared Spectrum (900–2500 nm). J. Remote Sens. 2012, 16, 192–206. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Tong, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, C.; Tang, J. Satellite-Observed Decreases in Water Turbidity in the Pearl River Estuary: Potential Linkage with Sea-Level Rise. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2020JC016842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Schurgers, G.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, J. Eutrophication changes in fifty large lakes on the Yangtze Plain of China derived from MERIS and OLCI observations. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Loiselle, S.A.; Yang, D.; Ma, R.; Su, W.; Gao, C. Remote estimation of chlorophyll a concentrations over a wide range of optical conditions based on water classification from VIIRS observations. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, R.; Han, D.; Scholz, M. Response of Eutrophication Development to Variations in Nutrients and Hydrological Regime: A Case Study in the Changjiang River (Yangtze) Basin. Water 2020, 12, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Yin, Y.; Cai, Y. Confounding effects of seasonality and anthropogenic river regulation on suspended particulate matter-driven mercury transport to coastal seas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z. Suspended particulate matter affects the distribution and migration of heavy metals in the Yellow River. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 912, 169537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Ahmed, M.K.; Chen, K.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Chen, B.; et al. Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in suspended particles in the Sundarban mangrove river, Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, X.-Z. Eutrophication control strategies for highly anthropogenic influenced coastal waters. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 705, 135760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Quan, F.; Lu, H.; Zeng, H. Impact of climate change on coastal water quality and its interaction with pollution prevention efforts. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, W.; Sun, X.; Hou, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; et al. Seasonal and spatial variations in nutrients under the influence of natural and anthropogenic factors in coastal waters of the northern Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, X.; Yu, Z.; Chiang, P. Temperature and nutrients are significant drivers of seasonal shift in phytoplankton community from a drinking water reservoir, subtropical China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5917–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, C.G.; Diehl, S.; Schmidt, G.M. Influence of water-column depth and mixing on phytoplankton biomass, community composition, and nutrients. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 2361–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausmeier, C.A.; Litchman, E. Algal games: The vertical distribution of phytoplankton in poorly mixed water columns. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Z. Contrasting chlorophyll-a seasonal patterns between nearshore and offshore waters in the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China: A new analysis using improved satellite data. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 203, 104173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Mo, L.; Bao, M.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, X. Diversity and distribution of culturable fouling bacteria in typical mariculture zones in Daya Bay, South China. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Wan, L.; Song, C.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, X. Nitrogen and phosphorus turnover and coupling in ponds with different aquaculture species. Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsen, S.; Kortet, R.; Skov, P.V.; Ytteborg, E.; Gitlesen, S.; Kleinegris, D.; Mydland, L.; Hansen, J.Ø.; Lock, E.; Mørkøre, T.; et al. Future feed resources in sustainable salmonid production: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1790–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, S.; Bhat, S.U.; Gani, A.; Bhat, F.A. Perspectives on utilization of macrophytes as feed ingredient for fish in future aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Jia, J.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Shi, K.; Gao, Y. Changes in chlorophyll a and its response to nitrogen and phosphorus characteristics over the past three decades in Poyang Lake, China. Ecohydrology 2021, 14, e2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Wei, J.; Li, R. Distribution, relationship, and environmental driving factors of chlorophyll-a and algal cell density: A national view of China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 54, e03084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapaksha, R.P.; Wu, M.-L.; Wang, Y.-T.; Bandara, G.; Atapaththu, K.S.S.; Wang, Y.-S. Long-term alterations of nutrient dynamics and phytoplankton communities in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 208, 116955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Xi, B.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, X.; Macreadie, P.I. Nutrient input estimation and reduction strategies related to land use and landscape pattern (LULP) in a near-eutrophic coastal bay with a small watershed in the South China sea. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 206, 105573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Li, H.; Peng, X.; Zhang, W.; Lou, Q.; Gong, J.; Ye, J. Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Seawater and Sediments from Daya Bay (South China): Environmental Fates, Source Apportionment and Ecological Risks. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Gordon, H.R.; Nakajima, T.; Lenoble, J.; Frouin, R.; Grassl, H.; Herman, B.M.; King, M.D.; Teillet, P.M. Passive remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol and atmospheric correction for the aerosol effect. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16815–16830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Jiang, J.H.; Diner, D.J.; Su, H.; Gu, Y.; Liou, K.-N.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, L.; Takano, Y.; Fan, X.; et al. Intra-annual variations of regional aerosol optical depth, vertical distribution, and particle types from multiple satellite and ground-based observational datasets. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11247–11260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Wang, Z.F.; Du, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.Q.; Fu, P.Q.; Pan, X.L.; Li, J.; Jayne, J.; Worsnop, D.R. Long-term real-time measurements of aerosol particle composition in Beijing, China: Seasonal variations, meteorological effects, and source analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10149–10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| No. | Date | Measured Value (μg/L) | Inversion Value (μg/L) | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 October 2020 | 4.5 | 5.68 | 26.22% |
| 2 | 21 October 2020 | 1.9 | 2.31 | 21.58% |
| 3 | 21 October 2020 | 2 | 1.32 | 34.00% |
| 4 | 22 October 2020 | 1.4 | 2.60 | 85.71% |
| 5 | 22 October 2020 | 1.35 | 1.31 | 2.96% |
| 6 | 22 October 2020 | 1.3 | 0.81 | 37.69% |
| 7 | 31 October 2020 | 4.49 | 5.31 | 18.35% |
| 8 | 1 November 2020 | 0.33 | 0.83 | 151.52% |
| 9 | 30 October 2020 | 1.05 | 1.78 | 69.52% |
| 10 | 22 October 2020 | 3.5 | 3.12 | 10.86% |
| 11 | 1 November 2020 | 0.6 | 1.44 | 140.00% |
| 12 | 16 August 2019 | 6.04 | 4.35 | 27.98% |
| 13 | 16 August 2019 | 6.82 | 5.77 | 15.40% |
| 14 | 16 August 2019 | 1.53 | 1.82 | 18.95% |
| 15 | 16 August 2019 | 1.75 | 3.15 | 80.00% |
| 16 | 17 August 2019 | 9.48 | 5.33 | 43.78% |
| 17 | 17 August 2019 | 5.68 | 7.62 | 34.15% |
| 18 | 16 August 2019 | 3.51 | 4.22 | 20.23% |
| 19 | 17 August 2019 | 4.85 | 4.77 | 1.63% |
| 20 | 17 August 2019 | 4.94 | 6.21 | 25.71% |
| 21 | 17 August 2019 | 9.83 | 12.54 | 27.57% |
| 22 | 17 August 2019 | 9.98 | 13.61 | 36.37% |
| 23 | 18 August 2019 | 9.9 | 8.66 | 12.48% |
| 24 | 16 August 2019 | 2.06 | 4.51 | 118.93% |
| 25 | 17 August 2019 | 1.61 | 0.48 | 70.19% |
| 26 | 17 August 2019 | 2.61 | 3.27 | 25.29% |
| 27 | 18 August 2019 | 4.5 | 2.78 | 38.22% |
| 28 | 18 August 2019 | 2.46 | 6.48 | 163.41% |
| 29 | 18 August 2019 | 2.55 | 3.66 | 43.53% |
| 30 | 17 August 2019 | 1.6 | 1.53 | 4.38% |
| 31 | 18 August 2019 | 1.57 | 2.34 | 49.04% |
| 32 | 18 August 2019 | 1.53 | 2.19 | 43.14% |
| 33 | 15 August 2019 | 1.46 | 1.28 | 12.33% |
| 34 | 18 August 2019 | 4.47 | 4.69 | 4.92% |
| 35 | 15 August 2019 | 1.36 | 0.72 | 47.06% |
| 36 | 15 August 2019 | 0.18 | 0.33 | 83.33% |
| 37 | 15 August 2019 | 1.66 | 1.54 | 7.23% |
| 38 | 16 August 2019 | 3.54 | 4.52 | 27.68% |
| Min | - | 0.18 | 0.33 | 1.63% |
| Max | - | 9.98 | 13.61 | 163.41% |
| Average | - | 3.42 | 3.81 | 44.25% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Deng, R.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Lei, C. Satellite Retrieval and Spatiotemporal Variability in Chlorophyll-a for Marine Ranching: An Example from Daya Bay, Guangdong Province, China. Water 2025, 17, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060780
Yang J, Deng R, Ma Y, Li J, Guo Y, Lei C. Satellite Retrieval and Spatiotemporal Variability in Chlorophyll-a for Marine Ranching: An Example from Daya Bay, Guangdong Province, China. Water. 2025; 17(6):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060780
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Junying, Ruru Deng, Yiwei Ma, Jiayi Li, Yu Guo, and Cong Lei. 2025. "Satellite Retrieval and Spatiotemporal Variability in Chlorophyll-a for Marine Ranching: An Example from Daya Bay, Guangdong Province, China" Water 17, no. 6: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060780
APA StyleYang, J., Deng, R., Ma, Y., Li, J., Guo, Y., & Lei, C. (2025). Satellite Retrieval and Spatiotemporal Variability in Chlorophyll-a for Marine Ranching: An Example from Daya Bay, Guangdong Province, China. Water, 17(6), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060780






