Anaerobic Enrichment and Succession of Microcystin-Degrading Bacterial Communities from Shrimp Pond Sediment and Shrimp Intestine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MC Accumulation in Pond and Shrimp
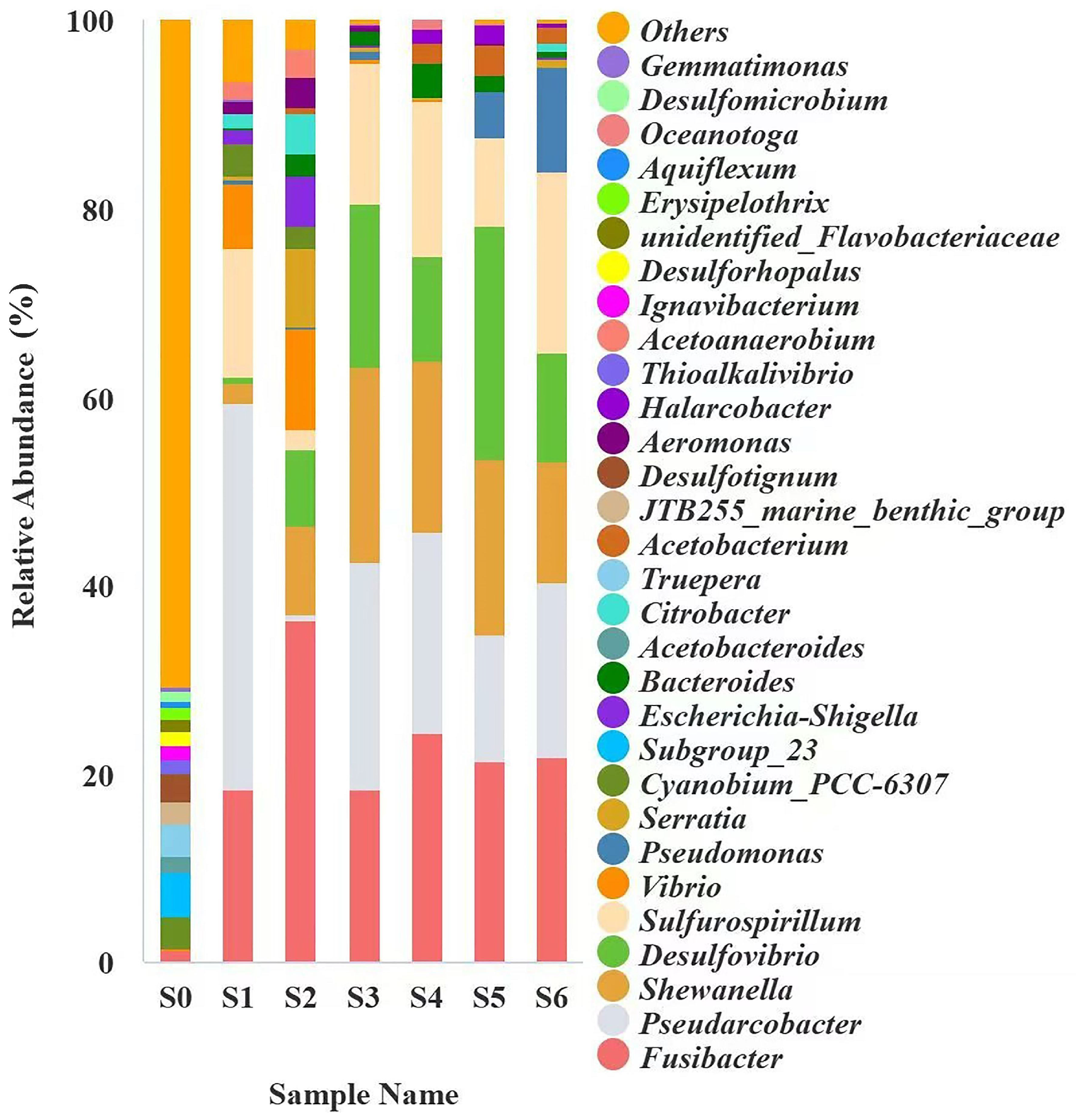
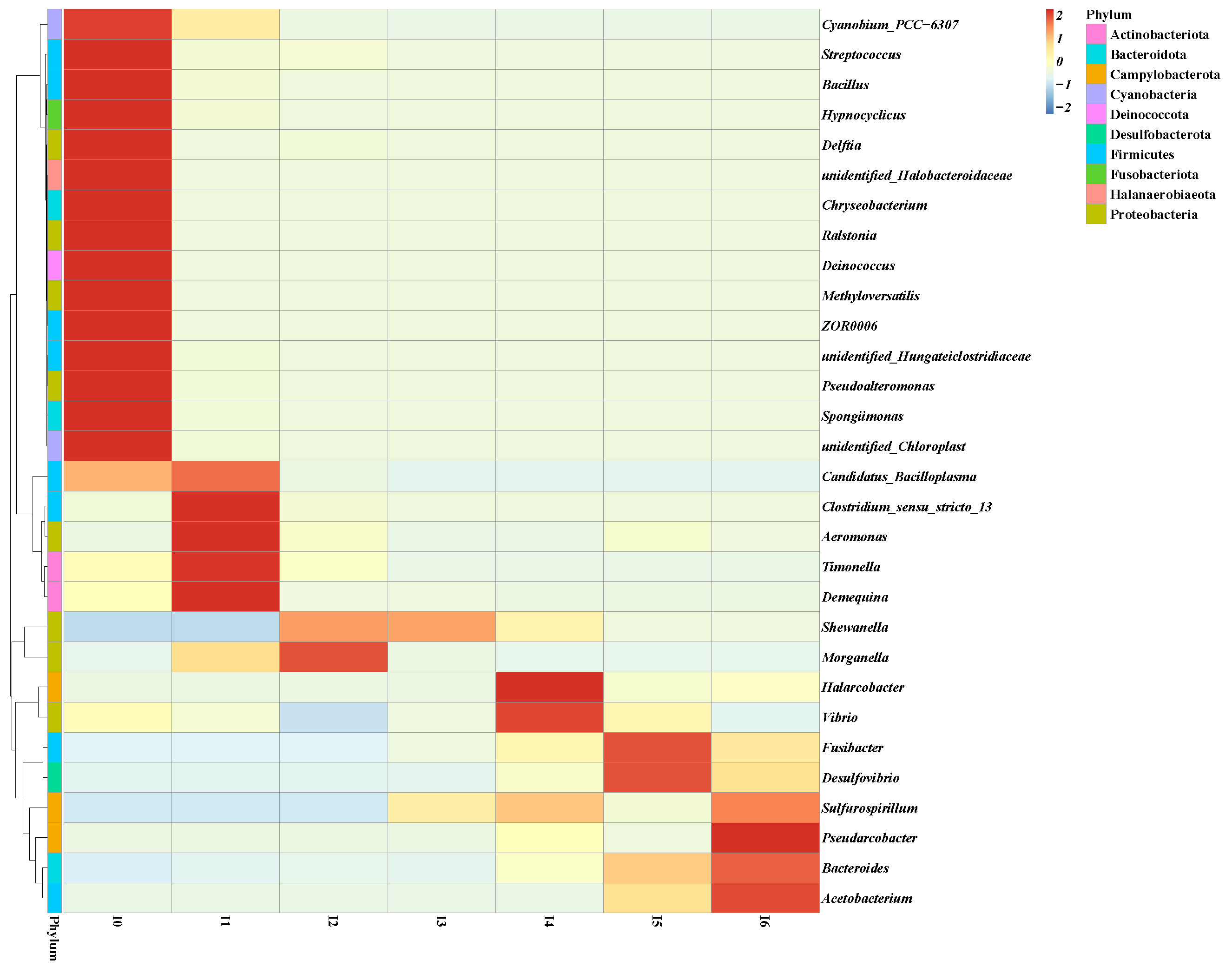
2.2. Bacterial Community Structure Enriched in Pond Sediment and Shrimp Intestine
2.3. Degradation Performance of MCs in Bacterial Communities from Pond Sediment and Shrimp Intestine Under Anaerobic Conditions
2.4. Isolation and Identification of MC-Degrading Bacterial Strains
2.5. Comparison of MC-Degrading Ability of Isolated Bacterial Strains
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. MC Standards and Extracted Crude MCs
5.2. Sample Collection
5.3. MC Extraction and Determination
5.4. Selective Enrichment of Anaerobic MC-Degrading Bacterial Community
5.5. Analysis of MC-Degrading Activity of Enriched Bacterial Community
5.6. High-Throughput Sequencing and Data Analysis of Bacterial Community
5.7. Isolation and Identification of Anaerobic MC-Degrading Strains from Bacterial Communities S6 and I6
5.8. Analysis of MC-Degrading Activity of Anaerobic MC-Degrading Bacterial Strains
5.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, L.A.; Davis, D.A.; Whitis, G.N. Pond-to-pond variability in post-larval shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, survival and growth in inland low-salinity waters of west Alabama. Aquaculture 2009, 40, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xie, F.X.; Zhang, F.F.; Zhou, K.; Sun, H.B.; Zhao, Y.J.; Yang, Q. Analysis of bacterial community functional diversity in late-stage shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) ponds using Biolog EcoPlates and PICRUSt2. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhana, K.V.; Pandey, P.K.; Anand, T.; Bhuvaneswari, R.; Kumar, S. Effect of periphyton (aquamat) on water quality, nitrogen budget, microbial ecology, and growth parameters of Litopenaeus vannamei in a semi-intensive culture system. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, S.K.; Egerton, T.A.; Reece, K.S.; Sanderson, M.P.; Onofrio, M.D.; Yeargan, E. Co-occurrence of marine and freshwater phycotoxins in oysters, and analysis of possible predictors for management. Toxicon 2023, 19, 100166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, F.M.; Manganelli, M.; Vichi, S.; Stefanelli, M.; Funari, E. Cyanotoxins: Producing organisms, occurrence, toxicity, mechanism of action and human health toxicological risk evaluation. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1049–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F.; Ding, Z.; Shu, Y.; Jian, G.; Clara, T. Exposure routes and health effects of microcystins on animals and humans: A mini-review. Toxicon 2018, 151, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.B. Infant health impacts of freshwater algal blooms: Evidence from an invasive species natural experiment. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2019, 96, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Strand, D.A.; Rusch, J.C.; Ballot, A.; Haande, S.; Lvberg, K.L.E. Microcystin profiles in European noble crayfish Astacus astacus and water in Lake Steinsfjorden, Norway. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimba, P.V.; Camus, A.; Allen, E.H.; Burkholder, J.A.M. Co-occurrence of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, mortalities and microcystin toxin in a southeastern USA shrimp facility. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.Y.; Chen, Z.H.; Dong, X.N.; Shen, H.; Zhang, W. Biodegradation kinetics of microcystins-LR crude extract by Lysinibacillus boronitolerans strain CQ5. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosa, A.; Rachid, C.; Pacheco, A.B.; Magalhes, V. Biotic and abiotic factors affect microcystin-LR concentrations in water/sediment interface. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 236, 126452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowska, A.; Kaliński, T.; Chróst, R.J. Degradation of microcystins by water and bottom sediment bacterial communities from a eutrophic freshwater lake. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 82, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F. A mini review on microcystins and bacterial degradation. Toxins 2020, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Zhang, X.X.; Chen, X.G.; Wang, K.; Shen, Y.; Li, D. Isolation of a novel microcystin-degrading bacterium and the evolutionary origin of mlr gene cluster. Toxins 2019, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Huang, F.; Feng, H.; Wei, J.; Pu, Y. A complete route for biodegradation of potentially carcinogenic cyanotoxin microcystin-LR in a novel indigenous bacterium. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, S. Biodegradation of microcystin-RR by Bacillus flexus isolated from a Saudi freshwater lake. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 19, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Cheng, X.; Fang, L.; Huang, X. Flocculation and lysis of Microcystis aeruginosa by Paebubacillus sp. A9 and inhibition of microcystin release. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 31, 103512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.; Lopes, D.; Hector, R.; Nascimento, M.; Miguel, T.; Kuroda, E.; Nóbrega, G.; Harada, K.; Hirooka, E. Microcystin-detoxifying recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing the mlrA gene from Sphingosinicella microcystinivorans B9. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Han, Z.; Duan, J.; Shi, X.; Wang, T.; Sheng, G.; Wang, S.; Yuan, X. A novel pathway for the anaerobic biotransformation of microcystin- LR using enrichment cultures. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Feng, H.; Li, X.; Yi, X.; Yang, F. Anaerobic degradation of microcystin-LR by an indigenous bacterial Enterobacter sp. YF3. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2019, 82, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Tian, X.; Xu, P.; Sun, K.; Ren, N. Acute toxic effects of microcystin-LR on crayfish (Procambarus clarkii): Insights from antioxidant system, histopathology and intestinal flora. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 56608–56619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Dai, W.; Wang, X.; Dong, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D. Microcystins distribution, bioaccumulation, and Microcystis genotype succession in a fish culture pond. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babica, P.; Kohoutek, J.; Bláha, L.; Adamovský, O.; Maršálek, B. Evaluation of extraction approaches linked to ELISA and HPLC for analyses of microcystin-LR, -RR and -YR in freshwater sediments with different organic material contents. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maerki, M.; Muller, B.; Dinkel, C.; Wehrli, B. Mineralization pathways in lake sediments with different oxygen and organic carbon supply. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Song, X.; Yuan, M.; Sun, R.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L. Multiple pathways for the anaerobic biodegradation of microcystin-LR in the enriched microbial communities from Lake Taihu. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 297, 118787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawinata, M.; Sukenda, S.; Wahjuningrum, D.; Widanarni, W. Bacterial diversity and community composition in the gut and rearing water of pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei during an outbreak of white feces disease. Aquaculture 2022, 559, 738431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Luo, W.; Lu, Y.; Giesy, J. Bioaccumulation of microcystins (MCs) in four fish species from Lake Taihu, China: Assessment of risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Steinman, A.; Zhang, K.; Lin, Q.; Xue, Q.; Wang, X. Risk assessment and identification of factors influencing the historical concentrations of microcystin in Lake Taihu, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukhele, T.; Msagati, T. Evaluating the microcystin-LR-degrading potential of bacteria growing in extreme and polluted environments. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Codd, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; et al. Meta-analysis reveals cyanotoxins risk across African inland waters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 131160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoti, M.; Edokpayi, J.; Mutileni, N.; Durowoju, O.; Munyai, F. Cyanotoxins in groundwater; occurrence, potential sources, health impacts and knowledge gap for public health. Toxicon 2023, 226, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Deng, Z.; Wu, C.; Jin, M.; Hu, M. Characteristic of the temporal distribution of dissolved microcystins and its relationships with environmental factors in a typical fresh water shrimp aquaculture pond in south Taihu area. Freshw. Fish. 2018, 48, 43–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Affan, A.; Khomayis, H.; Al-Harbi, S.; Haque, M.; Khan, S. Effect of environmental factors on cyanobacterial abundance and cyanotoxins production in natural and drinking water, Bangladesh. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 18, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Liu, K.; Song, Z.; Sun, R.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. Effects of microcystin-LR on metabolic functions and structure succession of sediment bacterial community under anaerobic conditions. Toxins 2020, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Chen, Q.; Lauridsen, T. A systematic investigation into the environmental fate of microcystins and the potential risk: Study in Lake Taihu. Toxins 2016, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, L.; Xiao, B.; Wu, X.; Wang, J. An effective pathway for the removal of microcystin LR via anoxic biodegradation in lake sediments. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, T.; Jørgensen, N.; Jørgensen, C.; Johansen, A. Degradation of microcystin in sediments at oxic and anoxic, denitrifying conditions. Water Res. 2003, 38, 4748–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Ma, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Isolation and identification of an efficient algicidal bacteria strain and algicidal characteristics on Microcystis aeruginosa. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 4269–4275. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Xie, X.; Huang, F.; Xiang, L.; Yang, F. Simultaneous Microcystis algicidal and microcystin synthesis inhibition by a red pigment prodigiosin. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, S.; Liu, X.; Tan, J.; Pan, J.; Yang, H. A freshwater bacterial strain, Shewanella sp. Lzh-2, isolated from Lake Taihu and its two algicidal active substances, hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a] pyrazine-1,4-dione and 2, 3-indolinedione. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 4737–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.; Haas, B.; Clemente, J.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.; Caporaso, J. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2012, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 27, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| MC Isomer | Pond Water (μg/L) | Pond Sediment (μg/g) | Shrimp Hepatopancreas (μg/g) | Shrimp Muscle (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC-RR | ||||
| MC-LR | - | - | - | - |
| MC-YR | - | - | - | - |
| Observed_SPECIES | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | ACE | PD_Whole_Tree | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | a | a | a | a | a | a |
| S1 | b | c | c | b | b | b |
| S2 | c | b | b | c | c | b |
| S3 | d | d | b | d | d | c |
| S4 | d | d | bc | d | d | c |
| S5 | d | d | b | d | d | c |
| S6 | d | d | b | d | d | c |
| Observed_Species | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | ACE | PD_Whole_Tree | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I0 | a | a | a | a | a | a |
| I1 | a | bc | b | ab | ab | a |
| I2 | a | bc | b | b | b | ab |
| I3 | b | c | c | c | ||
| I4 | b | b | c | c | ||
| I5 | b | bc | a | c | c | b |
| I6 | b | b | a | bc | bc | b |
| Initial Concentration (mg/L) | Sample | Pond Sediment | Sample | Shrimp Intestine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Final Concentration (mg/L) | Degradation Rate (%) | Final Concentration (mg/L) | Degradation Rate (%) | |||
| S0 | e | e | I0 | e | e | |
| S1 | d | d | I1 | c | c | |
| S2 | d | d | I2 | c | c | |
| 0.38 | S3 | bc | bc | I3 | ab | ab |
| S4 | c | c | I4 | b | b | |
| S5 | ab | ab | I5 | a | a | |
| S6 | a | a | S6 | a | a | |
| Item | I6-1/S6-1 | I6-2/S6-2 | I6-3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gram stain | − | − | + |
| Glucose | − | + | + |
| Arabinose | − | − | − |
| Mannose | + | + | − |
| Mannitol | − | + | + |
| Maltose | − | + | + |
| Xylose | + | − | − |
| Sucrose | − | + | + |
| Lactose | + | − | − |
| Chlorhexidine | − | + | − |
| Nitrate reduction | − | − | − |
| Indole test | − | − | − |
| Voges–Proskauer test | − | − | − |
| Methyl red test | − | + | − |
| Bacterial Strain | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. marcescens | 26.31 | 66.15 | 87.72 |
| B. flexus | 35.90 | 64.65 | 100 |
| S. algae | 0.36 | 0.52 | 0.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Bi, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, D.; Dai, W. Anaerobic Enrichment and Succession of Microcystin-Degrading Bacterial Communities from Shrimp Pond Sediment and Shrimp Intestine. Water 2025, 17, 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060774
Zhao W, Bi X, Wang X, Liu C, Zhang D, Dai W. Anaerobic Enrichment and Succession of Microcystin-Degrading Bacterial Communities from Shrimp Pond Sediment and Shrimp Intestine. Water. 2025; 17(6):774. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060774
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wenjie, Xiangdong Bi, Xinyu Wang, Chuanyin Liu, Dajuan Zhang, and Wei Dai. 2025. "Anaerobic Enrichment and Succession of Microcystin-Degrading Bacterial Communities from Shrimp Pond Sediment and Shrimp Intestine" Water 17, no. 6: 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060774
APA StyleZhao, W., Bi, X., Wang, X., Liu, C., Zhang, D., & Dai, W. (2025). Anaerobic Enrichment and Succession of Microcystin-Degrading Bacterial Communities from Shrimp Pond Sediment and Shrimp Intestine. Water, 17(6), 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060774







