Synergistic Ozone-Ultrasonication Pretreatment for Enhanced Algal Bioresource Recovery: Optimization and Detoxification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Experiments
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Fluorescence EEMs Spectra
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.3. Other Analysis Methods
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Study of Solubilization of Algal Polymers with Different Pretreatment
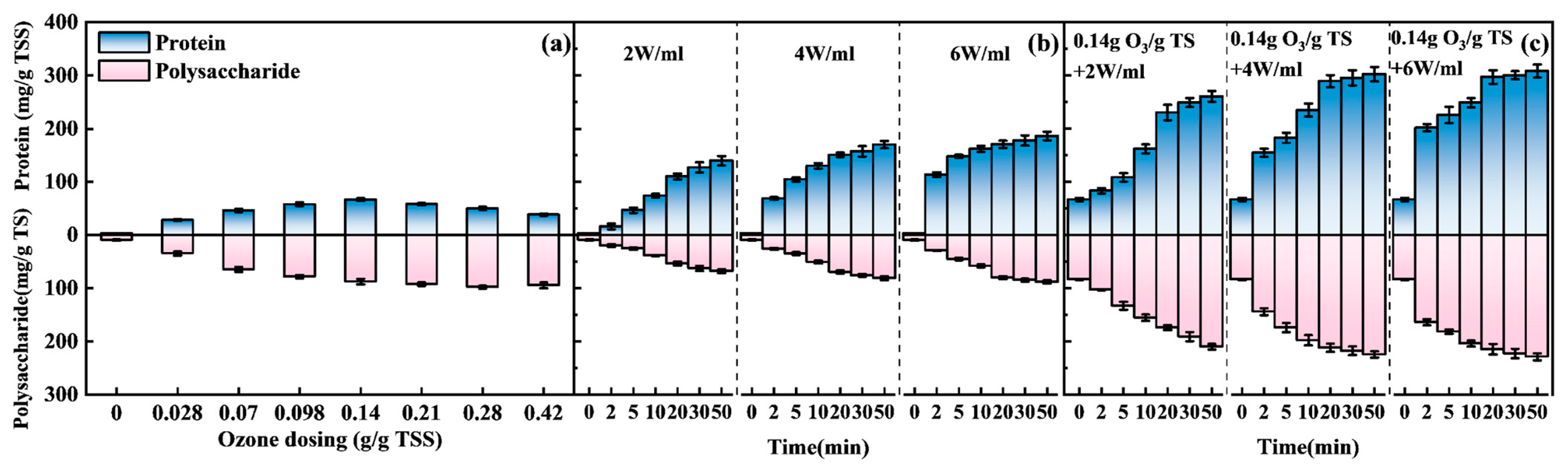
3.1.1. Release Properties of Proteins and Polysaccharides
3.1.2. SCOD Release Characteristics
3.1.3. Dynamic Analysis of Algal Cell Disruption Using a O3-US Pretreatment
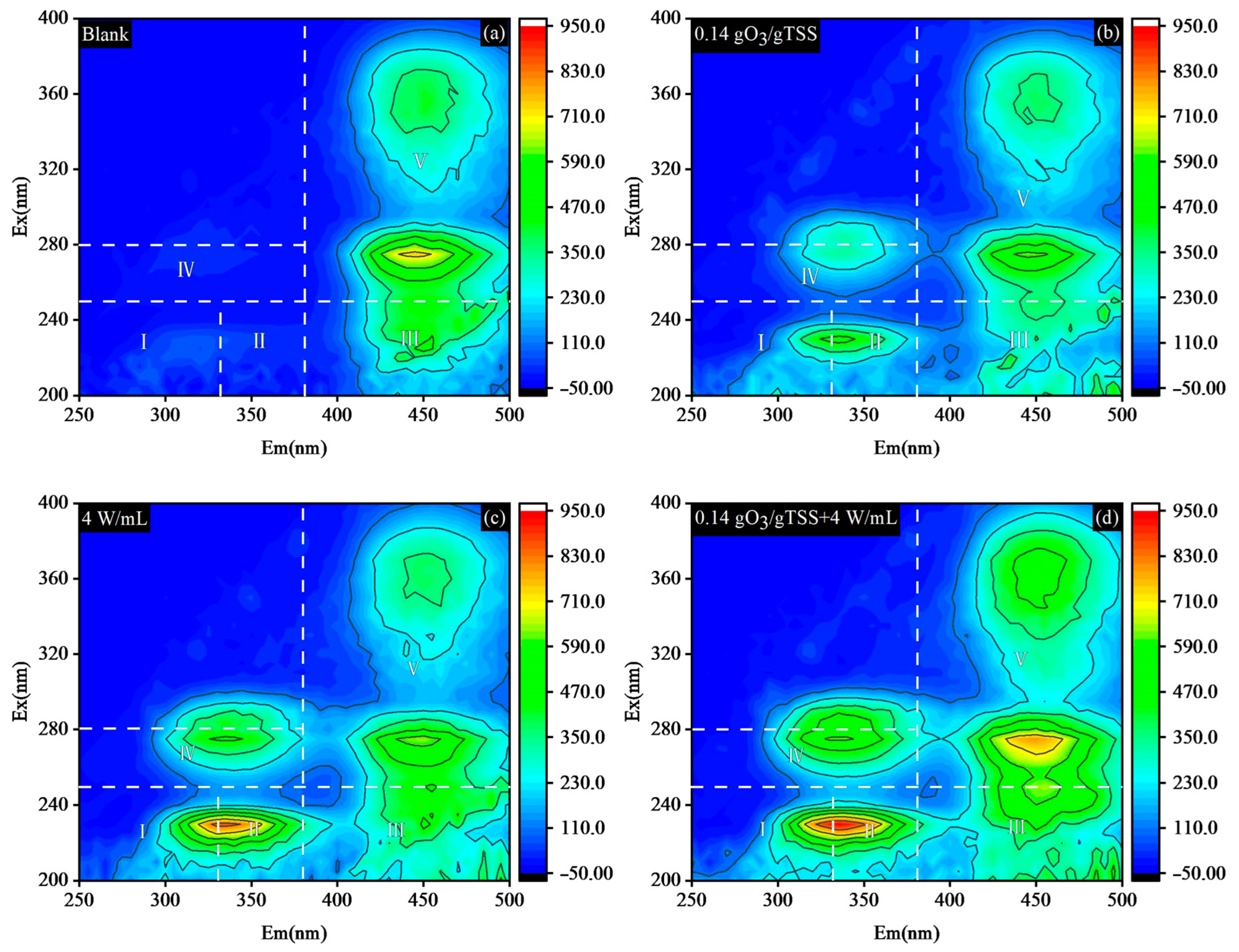
3.1.4. EEMs Spectrometry Analysis
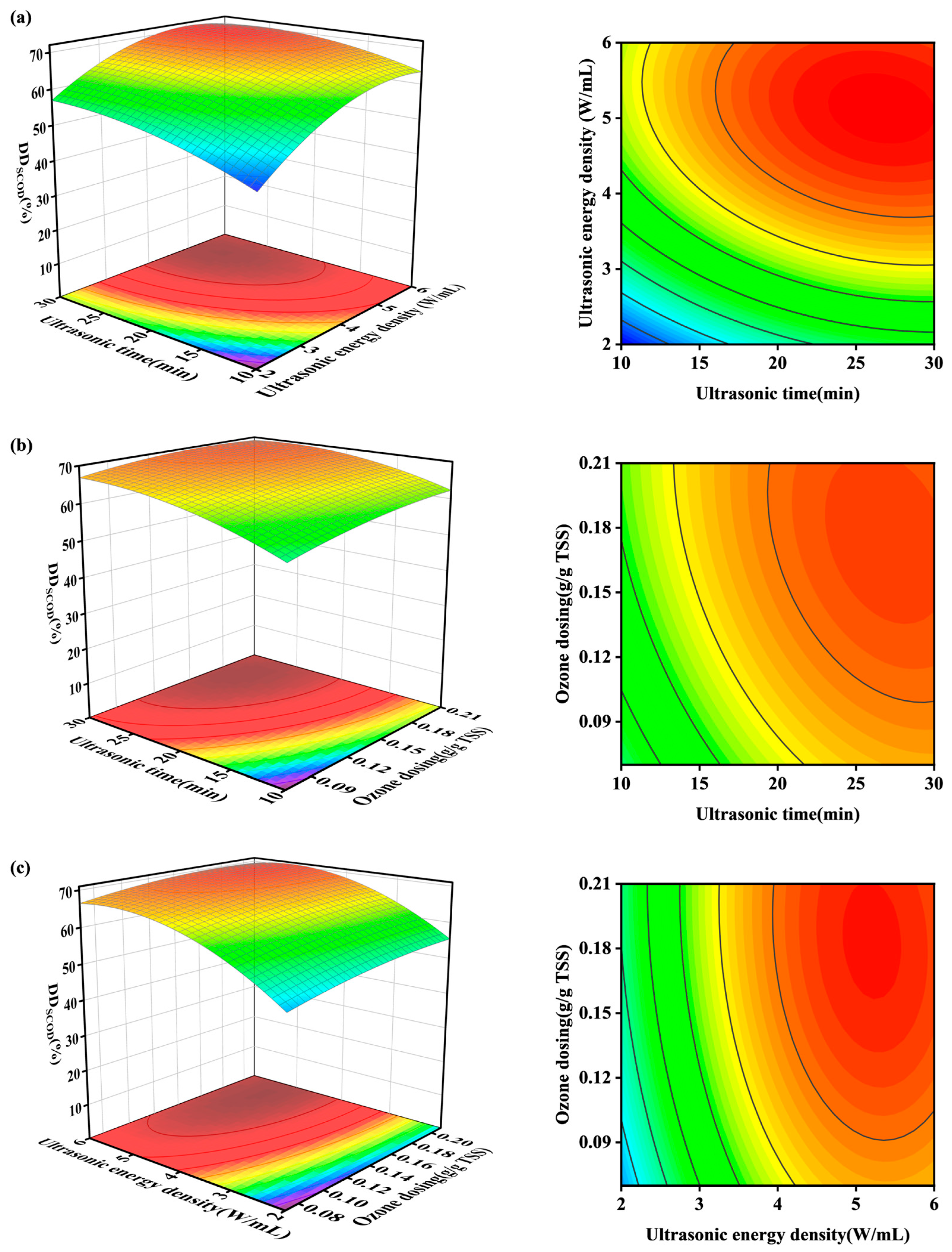
3.2. Optimization of Parameters for Combined O3-US Treatment
3.3. Disruption of Algal Cell Structure by Different Pretreatments
3.3.1. Algae Morphology Before and After Pretreatment
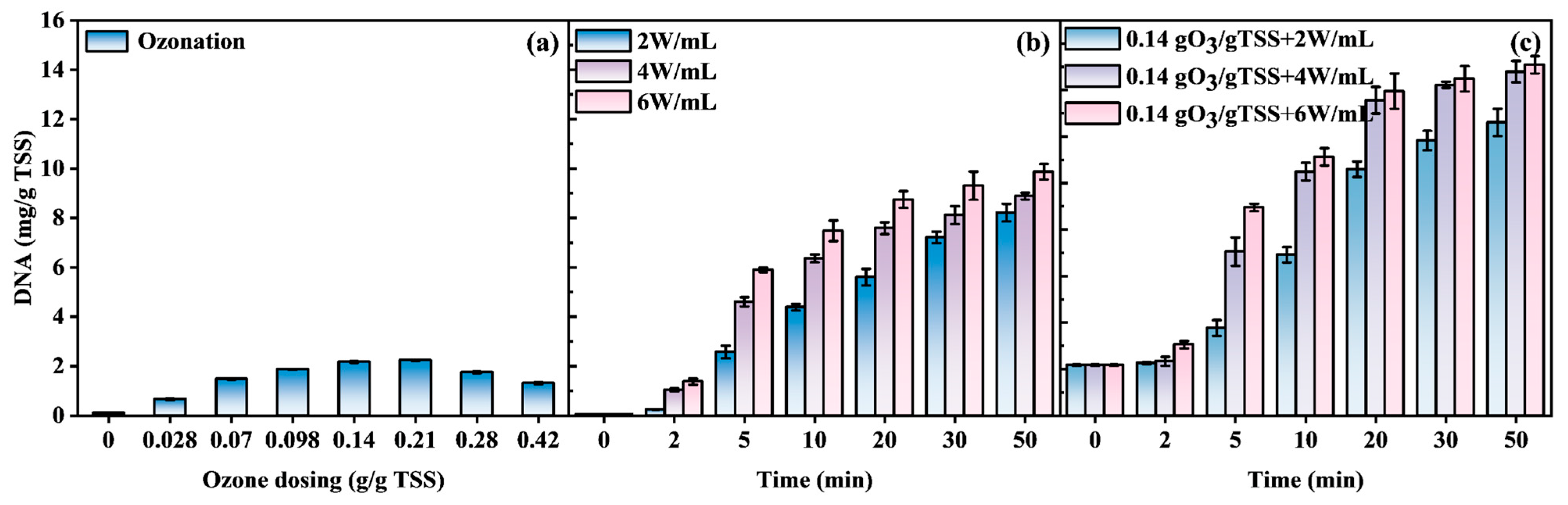
3.3.2. DNA Release Characteristics
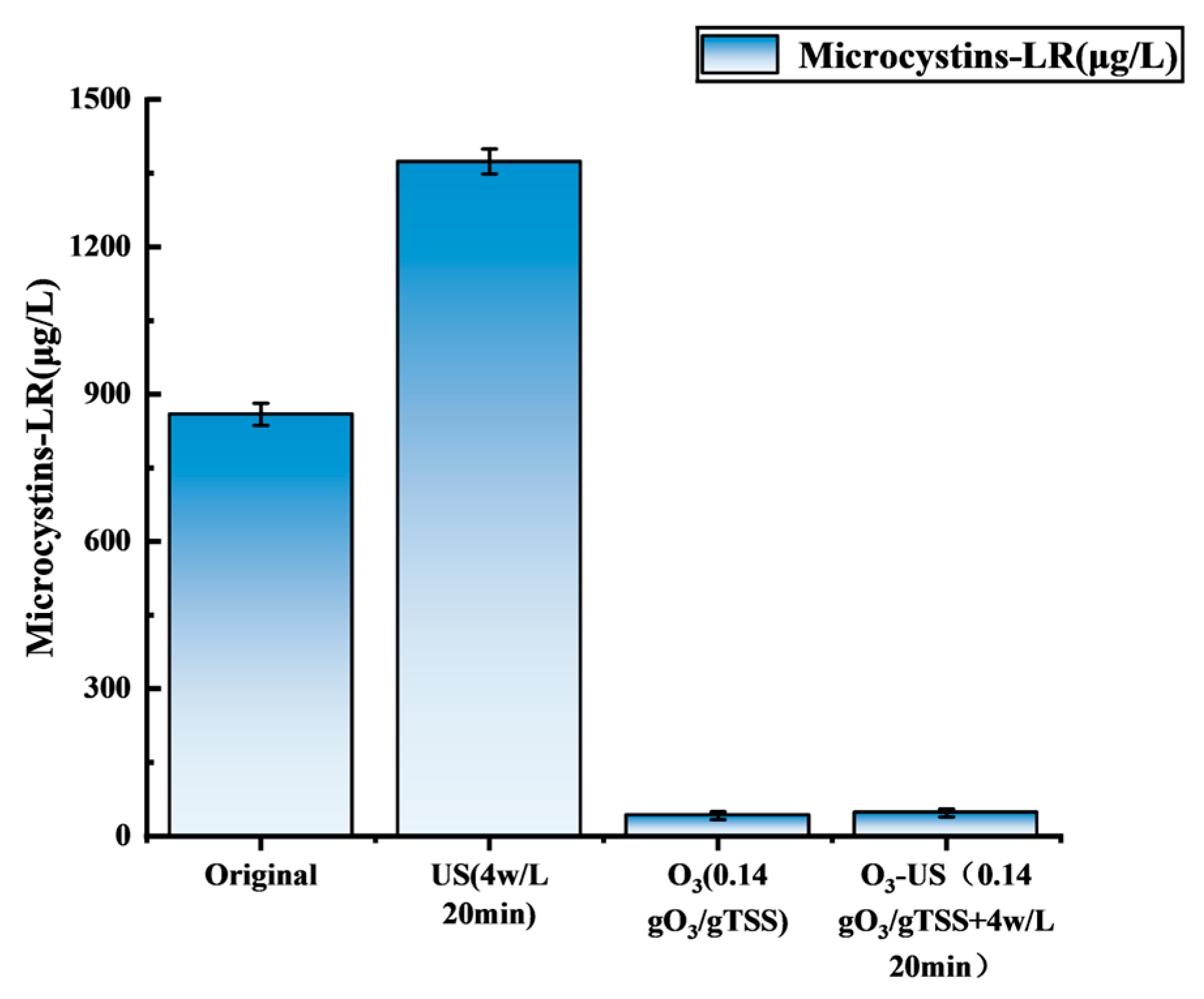
3.4. Other Risk Factors: Behavior of MC-LR in Different Pretreatment Processes
4. Conclusions
- Synergistic disruption mechanism: The integration of ozone oxidation targeting EPS and cell wall polymers with ultrasonication treatment—inducing cavitation-driven mechanical disruption—significantly enhances the release of intracellular resources. Optimized conditions (0.14 gO3/gTSS, 4 W/mL, 20 min) achieved a protein content of 289.2 mg/g TSS, representing 4.3-fold and 1.9-fold increases compared to standalone O3 and US treatment, respectively. Additionally, polysaccharide content reached 87.5 mg/g TSS, corresponding to 2.4-fold and 3.1-fold enhancements over singular treatments, achieving 65.2% cell disruption efficiency. Fluorescence EEM spectroscopy further confirmed that biodegradable organic compounds predominate post-treatment, ensuring compatibility with subsequent downstream processes.
- Detoxification and energy efficiency: The synchronized degradation of MC-LR achieved a removal efficiency of 94.5%, representing a 96.6% reduction in risk compared to US alone, thereby addressing biosafety concerns. Additionally, this integrated approach reduced ultrasonic intensity by 33.3% and lowered treatment duration by 60% relative to systems employing US-only treatments.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lima, G.M.; Teixeira, P.C.; Teixeira, C.M.; Filócomo, D.; Lage, C.L. Influence of spectral light quality on the pigment concentrations and biomass productivity of Arthrospira platensis. Algal Res. 2018, 31, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, S.; Sharma, M.; Banerjee, S.; Nayak, B.K.; Das, D.; Khilari, S.; Prasad, R. Pretreatment of cyanobacterial biomass for the production of biofuel in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 370, 128505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsolek, M.D.; Kendall, E.; Thompson, P.L.; Shuman, T.R. Thermal pretreatment of algae for anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 151, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, M.; King, P.M.; Wu, X.; Joyce, E.M.; Mason, T.J.; Yamamoto, K. Effect of sonication frequency on the disruption of algae. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xu, J.; Xue, H.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Gu, S.; Miao, H.; Ruan, W. Improving hydrogen recovery from anaerobic co-digestion of algae and food waste by high-pressure homogenisation pre-treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3497–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagurunathan, P.; Kumar, G.; Mudhoo, A.; Rene, E.R.; Saratale, G.D.; Kobayashi, T.; Xu, K.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, D.-H. Fermentative hydrogen production using lignocellulose biomass: An overview of pre-treatment methods, inhibitor effects and detoxification experiences. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagurunathan, P.; Kumar, G.; Kobayashi, T.; Xu, K.; Kim, S.-H. Effects of various dilute acid pretreatments on the biochemical hydrogen production potential of marine macroalgal biomass. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27600–27606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulfahri; Mushlihah, S.; Langford, A.; Tassakka, A.C.M.A. Ozonolysis as an effective pretreatment strategy for bioethanol production from marine algae. Bioenergy Res. 2020, 13, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Quan, Y.; Liu, S.; Hao, J. Effectiveness of ultrasound (US) and slightly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW) treatments for removing Listeria monocytogenes biofilms. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 112, 107190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, W.N.; Show, P.L.; Le, C.F.; Tao, Y.; Chang, J.-S.; Ling, T.C. Improving cell disruption efficiency to facilitate protein release from microalgae using chemical and mechanical integrated method. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 135, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Anwer, H.; Park, J.W. Oxidative power loss control in ozonation: Nanobubble and ultrasonic cavitation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xia, H.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Pei, Q.; Dai, L.; Zhang, L. Efficient recovery of valuable metals from low-grade zinc residue by ultrasonic strengthening. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2025, 211, 110240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, F.; Uggetti, E.; Carrère, H.; Ferrer, I. Pretreatment of microalgae to improve biogas production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 172, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Tan, X.; Li, N. Ultrasonic selectivity on depressing photosynthesis of cyanobacteria and green algae probed by chlorophyll-a fluorescence transient. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, G.T.; Meng, T.K.; Kassim, M.A. Green ultrasonication-assisted extraction of microalgae Chlorella sp. for polysaturated fatty acid (PUFA) rich lipid extract using alternative solvent mixture. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 46, 1499–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, B.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, W.; Zhuang, J.; Li, H.; Huang, T. Enhanced VFAs production from microalgal hydrolytic acidification with ultrasonic-alkali pretreatment. Algal Res. 2023, 71, 103056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Huang, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, C. Towards zero excess sludge discharge with built-in ozonation for wastewater biological treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardeña, R.; Moreno, G.; Bakonyi, P.; Buitrón, G. Enhancement of methane production from various microalgae cultures via novel ozonation pretreatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranowo, R.; Lee, D.; Liu, J.; Chang, J.S. Effect of O3 and O3/H2O2 on algae harvesting using chitosan. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Chen, Z.-l.; Wang, Z.; Kang, J.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, L.; Shen, J.-M. Oxidation of microcystin-LR in water by ozone combined with UV radiation: The removal and degradation pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 276, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncay, S.; Akcakaya, M.; Icgen, B. Ozonation of sewage sludge prior to anaerobic digestion led to Methanosaeta dominated biomethanation. Fuel 2022, 313, 122690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dytczak, M.A.; Londry, K.L.; Siegrist, H.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A. Ozonation reduces sludge production and improves denitrification. Water Res. 2007, 41, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundle, P.; Nirmalkar, N.; Momotko, M.; Boczkaj, G. Ozone nanobubble technology as a novel AOPs for pollutants degradation under high salinity conditions. Water Res. 2024, 263, 122148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, G.; Shangguan, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, X. Feasibility and mechanism of removing Microcystis aeruginosa and degrading microcystin-LR by dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Abramova, A.; Nikonov, R.; Cravotto, G. Sonozonation (sonication/ozonation) for the degradation of organic contaminants–A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 68, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Xi, J.; Yeung, M. Degradation of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) extracted from activated sludge by low-concentration ozonation. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parandoush, S.; Mokhtarani, N. Reducing excess sludge volume in sequencing batch reactor by integrating ultrasonic waves and ozonation. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAfifi, F.; Jasim, S.; Mohseni, M. Microcystin-LR Removal by Ozone (O3) and Vacuum-UV (VUV): The Effect of Chloride Ions. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2024, 46, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keris-Sen, U.D.; Sen, U.; Gurol, M.D. Combined effect of ozone and ultrasound on disruption of microalgal cells. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Balderas, R.; Velasquez-Orta, S.; Ledesma, M.O. Biorefinery process intensification by ultrasound and ozone for phosphorus and biocompounds recovery from microalgae. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2020, 153, 107951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, R.; Cao, L.; Shi, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Q. Algal sludge from Taihu Lake can be utilized to create novel PGPR-containing bio-organic fertilizers. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 132, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, J.; Lu, M.; Shangguan, Y.; Liu, X. Mechanism of dielectric barrier discharge plasma coupled with calcium peroxide to improve the quantity and quality of short chain fatty acids in anaerobic fermentation of cyanobacteria. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Sinha, R.P.; Incharoensakdi, A. The cyanotoxin-microcystins: Current overview. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2014, 13, 215–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shechter, H. Spectrophotometric method for determination of ozone in aqueous solutions. Water Res. 1973, 7, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, N. New advances in fluorescence excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy for the characterization of dissolved organic matter in drinking water treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.; Bridgewater, L.; American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirpour, N.; Ravanshad, O.; Mousavi, S.M. Ultrasonic-assisted acid and ionic liquid hydrolysis of microalgae for bioethanol production. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 13, 16001–16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, K.W.; Myers, A. An Improved Diphenylamine Method for the Estimation of Deoxyribonucleic Acid. Nature 1965, 206, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.-M.; Wu, Y.-S.; Gan, N.-Q.; Song, L.-R. An ELISA-like time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay for microcystin detection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 348, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, Z.T.; Meng, L.; Saingam, P.; Xi, J. Ozonation and depolymerization of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) extracted from a biofilter treating gaseous toluene. Polymers 2018, 10, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.-H.; He, P.-J.; Shao, L.-M.; Zhu, Y.-S. Extracellular proteins, polysaccharides and enzymes impact on sludge aerobic digestion after ultrasonic pretreatment. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Balderas, R.M.; Velásquez-Orta, S.B.; Valdez-Vazquez, I.; Orta Ledesma, M.T. Intensified recovery of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates from wastewater-grown microalgae Desmodesmus sp. by using ultrasound or ozone. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 62, 104852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keris-Sen, U.D.; Gurol, M.D. Using ozone for microalgal cell disruption to improve enzymatic saccharification of cellular carbohydrates. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 105, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, M.; Pishbin, E. Ozone-based advanced oxidation processes in water treatment: Recent advances, challenges, and perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 3531–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicker, R.J.; Kumar, G.; Khan, E.; Bhatnagar, A. Emergent green technologies for cost-effective valorization of microalgal biomass to renewable fuel products under a biorefinery scheme. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H. Physical cell disruption technologies for intracellular compound extraction from microorganisms. Processes 2024, 12, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezhneva, N.; Dezhkunov, N.V.; Ulasevich, S.A.; Skorb, E.V. Characterization of transient cavitation activity during sonochemical modification of magnesium particles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 70, 105315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xiong, X.; Shui, Y.; Huang, Z.; Tian, K. A systematic study of enhanced ozone mass transfer for ultrasonic-assisted PTFE hollow fiber membrane aeration process. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, R.; Rupasinghe, T.W.; Tull, D.L.; Webley, P.A. Mechanical cell disruption for lipid extraction from microalgal biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 140, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence Excitation−Emission Matrix Regional Integration to Quantify Spectra for Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Pei, H.; Hou, Q.; Nie, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X. The effects of algal extracellular substances on algal growth, metabolism and long-term medium recycle, and inhibition alleviation through ultrasonication. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Tian, Z.; Song, Y.; Jiang, W.; Tian, Y.; Li, S. Influence of solids retention time on membrane fouling: Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances and soluble microbial products. Biofouling 2015, 31, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.-S.; Xi, B.-D.; Wei, Z.-M.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.; An, D.; Cao, J.-L.; Liu, H.-L. Fluorescence excitation–emission matrix spectroscopy with regional integration analysis for characterizing composition and transformation of dissolved organic matter in landfill leachates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, D.; Kong, H. Optimisation of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of wheat straw for ethanol production. Fuel 2013, 112, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Song, K.; Gu, Y.; Gao, X. Improving methane production from algal sludge based anaerobic digestion by co-pretreatment with ultrasound and zero-valent iron. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geada, P.; Loureiro, L.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Vicente, A.A.; Fernandes, B.D. Evaluation of disruption/permeabilization methodologies for Microcystis aeruginosa as alternatives to obtain high yields of microcystin release. Algal Res. 2019, 42, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Shi, J.L.; von Gunten, U.; McCurry, D.L. Ozonation of organic compounds in water and wastewater: A critical review. Water Res. 2022, 213, 118053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Average |
|---|---|
| pH | 6.2 |
| TS (Total Solid) (%) | 1.7 |
| TSS (Total Suspended Solids) (g/L) | 17.4 |
| VSS/TSS | 0.9 |
| TCOD (Total Chemical Oxygen Demand) (mg/gTSS) | 1567.7 |
| SCOD (Soluble Chemical Oxygen Demand) (mg/gTSS) | 45.2 |
| Soluble Protein (mg/gTSS) | 3.1 |
| Soluble Polysaccharides (mg/gTSS) | 9.2 |
| Variables | Coded | Max & Min Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Ultrasonic time (min) | A | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| Sound intensity (W/mL) | B | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| Ozone dose (g/gTSS) | C | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.21 |
| Parameters | Kp /(min−1) | Rm /(mg/g TSS) | R2 Statistical | Kc /(min−1) | Fc /(mg/g TSS) | R2 Statistical |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.14 g O3/g TSS + 2 W/mL | 0.06193 | 211.1 | 0.993 | 0.11532 | 605.4 | 0.996 |
| 0.14 g O3/g TSS + 4 W/mL | 0.1383 | 234.2 | 0.992 | 0.25452 | 741.4 | 0.995 |
| 0.14 g O3/g TSS + 6 W/mL | 0.15835 | 239.2 | 0.992 | 0.35847 | 775.0 | 0.996 |
| Process Group | A: Ultrasonic Time /(min) | B: Ultrasonic Density /(W/mL) | C: Ozone Dose /(g/g TSS) | DDSCOD /(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 2 | 0.21 | 56.0 |
| 2 | 20 | 6 | 0.21 | 69.9 |
| 3 | 30 | 6 | 0.14 | 69.7 |
| 4 | 10 | 2 | 0.14 | 45.1 |
| 5 | 20 | 4 | 0.14 | 65.2 |
| 6 | 20 | 4 | 0.14 | 64.9 |
| 7 | 30 | 4 | 0.21 | 69.2 |
| 8 | 20 | 4 | 0.14 | 65.1 |
| 9 | 20 | 6 | 0.07 | 65.6 |
| 10 | 10 | 6 | 0.14 | 66.2 |
| 11 | 20 | 4 | 0.14 | 65.2 |
| 12 | 30 | 2 | 0.14 | 57.3 |
| 13 | 30 | 4 | 0.07 | 67.2 |
| 14 | 20 | 2 | 0.07 | 49.1 |
| 15 | 20 | 4 | 0.14 | 65.3 |
| 16 | 10 | 4 | 0.07 | 55.6 |
| 17 | 10 | 4 | 0.21 | 66.0 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 844.90 | 9 | 93.88 | 197.35 | <0.0001 |
| A | 109.82 | 1 | 109.82 | 230.86 | <0.0001 |
| B | 514.56 | 1 | 514.56 | 1081.72 | <0.0001 |
| C | 75.52 | 1 | 75.52 | 158.76 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 18.02 | 1 | 18.02 | 37.88 | 0.0005 |
| AC | 13.73 | 1 | 13.73 | 28.86 | 0.0010 |
| BC | 1.63 | 1 | 1.63 | 3.42 | 0.1070 |
| A2 | 3.42 | 1 | 3.42 | 7.20 | 0.0314 |
| B2 | 104.08 | 1 | 104.08 | 218.79 | <0.0001 |
| C2 | 0.4634 | 1 | 0.4634 | 0.9742 | 0.3565 |
| Residual | 3.33 | 7 | 0.4757 | ||
| Lack of fit | 2.33 | 3 | 0.7768 | 3.11 | 0.1510 |
| Pure Error | 0.9995 | 4 | 0.2499 | ||
| Cor Total | 848.23 | 16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, B.; Zhuang, J.; Yang, J. Synergistic Ozone-Ultrasonication Pretreatment for Enhanced Algal Bioresource Recovery: Optimization and Detoxification. Water 2025, 17, 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111614
Huang T, Zhu Y, Liu J, Zhou X, Wu B, Zhuang J, Yang J. Synergistic Ozone-Ultrasonication Pretreatment for Enhanced Algal Bioresource Recovery: Optimization and Detoxification. Water. 2025; 17(11):1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111614
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Tianyin, Yefeng Zhu, Junjun Liu, Xinyi Zhou, Bingdang Wu, Jinlong Zhuang, and Jingjing Yang. 2025. "Synergistic Ozone-Ultrasonication Pretreatment for Enhanced Algal Bioresource Recovery: Optimization and Detoxification" Water 17, no. 11: 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111614
APA StyleHuang, T., Zhu, Y., Liu, J., Zhou, X., Wu, B., Zhuang, J., & Yang, J. (2025). Synergistic Ozone-Ultrasonication Pretreatment for Enhanced Algal Bioresource Recovery: Optimization and Detoxification. Water, 17(11), 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111614










