A Newly Developed Approach for Analyzing the Degradation of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in Different Salinity Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Analytical Chemicals
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
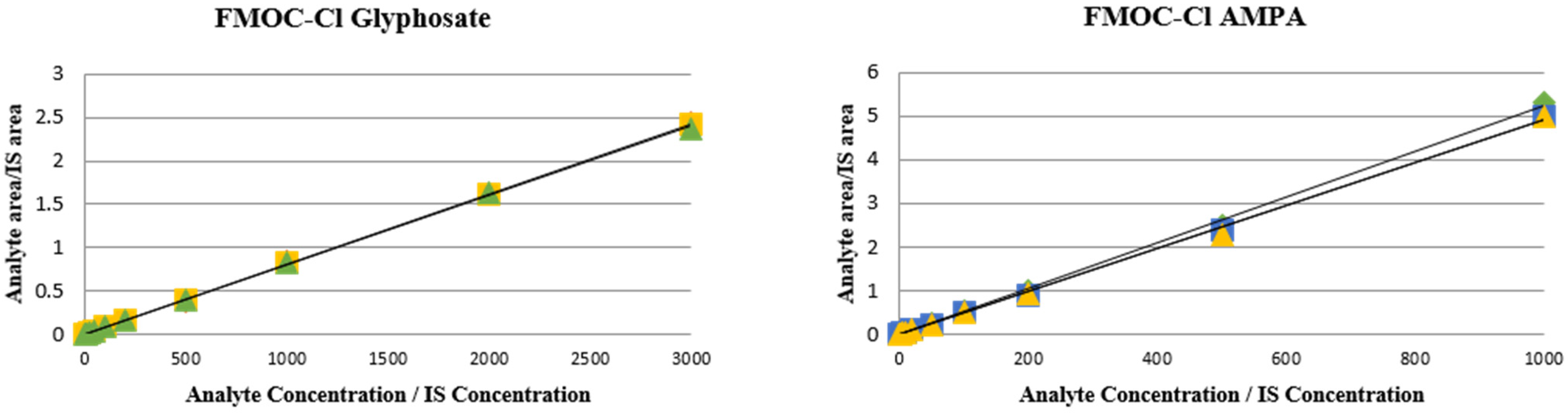
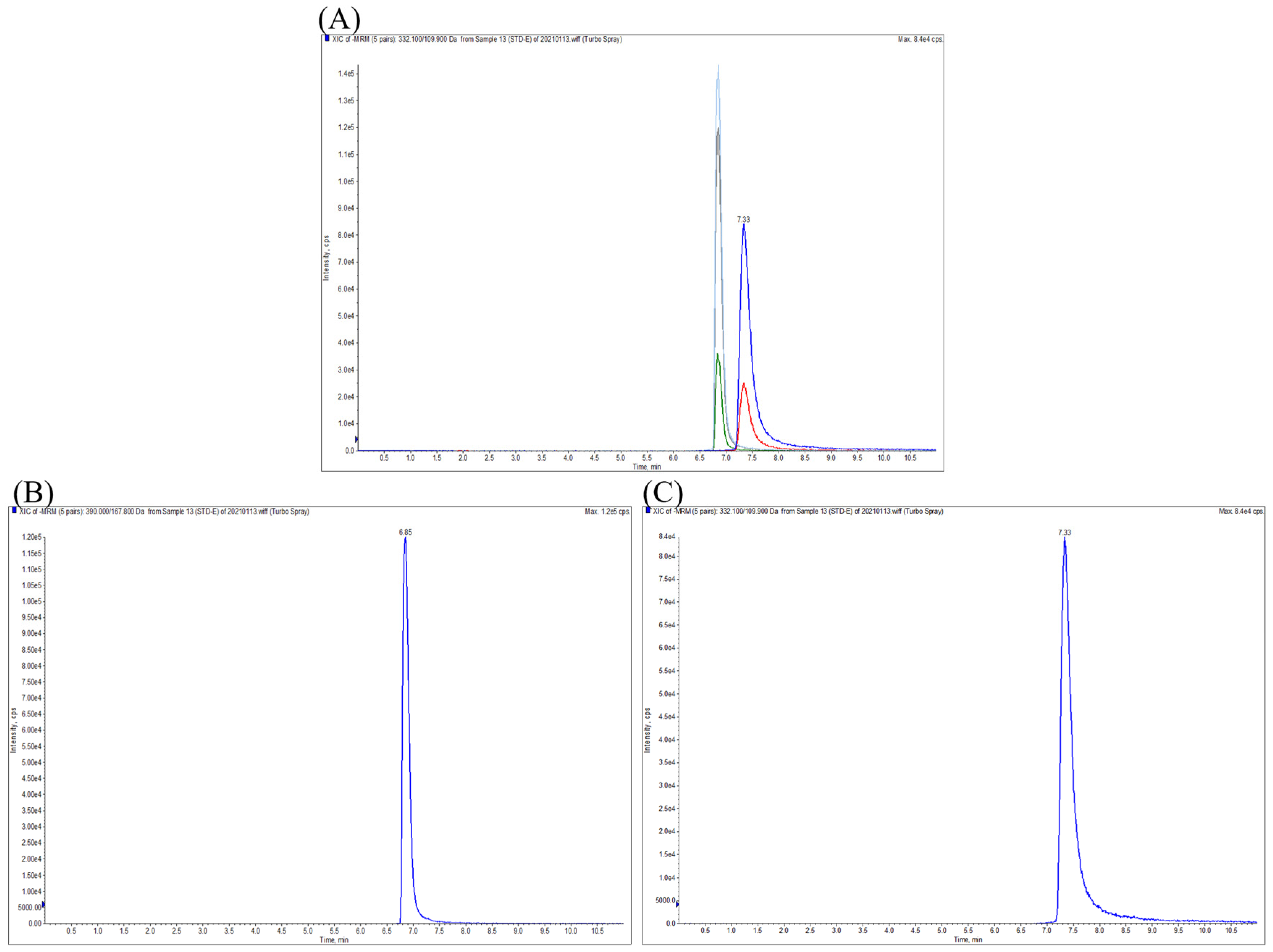
3.1. Method Validation
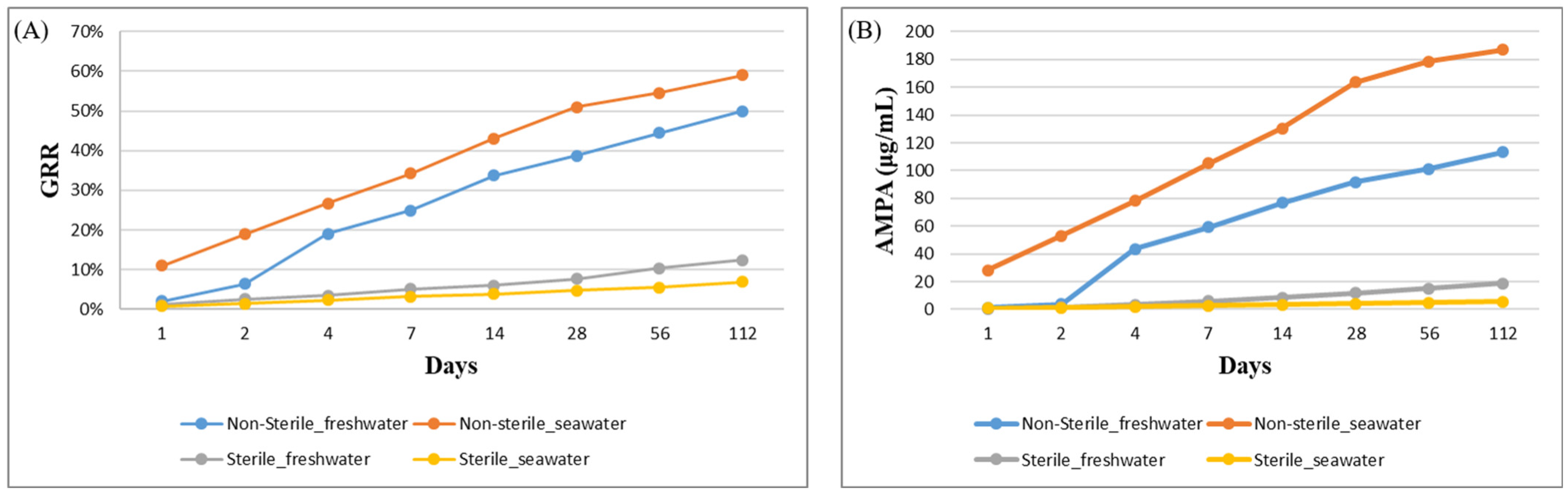
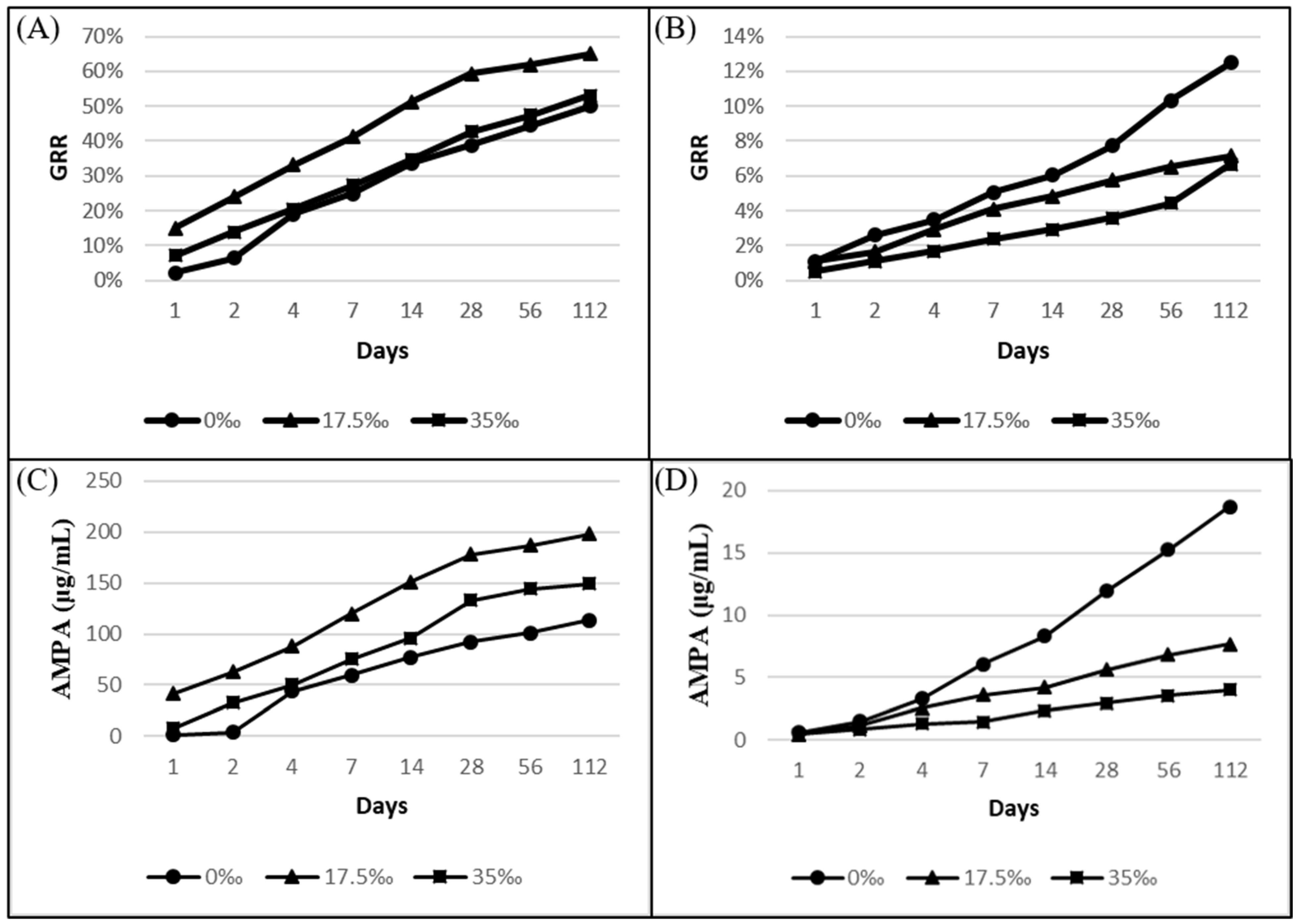
3.2. Effect of Sterilization and Salinity on Glyphosate Degradation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evalen, P.S.; Barnhardt, E.N.; Ryu, J.; Stahlschmidt, Z.R. Toxicity of glyphosate to animals: A meta-analytical approach. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 347, 123669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torretta, V.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Viotti, P.; Rada, E.C. Critical Review of the Effects of Glyphosate Exposure to the Environment and Humans through the Food Supply Chain. Sustainability 2018, 10, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, I.; Duke, S.O. Overview of glyphosate-resistant weeds worldwide. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annett, R.; Habibi, H.R.; Hontela, A. Impact of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on the freshwater environment. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 458–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Lu, Q.R.; Guo, J.C.; Ares, I.; Martínez, M.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Wang, X.; Anadón, A.; Martínez, M.A. Oxidative Stress and Metabolism: A Mechanistic Insight for Glyphosate Toxicology. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 62, 617–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrejón-Godínez, M.L.; Tovar-Sánchez, E.; Valencia-Cuevas, L.; Rosas-Ramírez, M.E.; Rodríguez, A.; Mussali-Galante, P. Glyphosate Pollution Treatment and Microbial Degradation Alternatives, a Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaah, V.B.K.; Ahmadi, S.; Quimbayo, M.J.; Morales-Torres, S.; Ojala, S. Recent technologies for glyphosate removal from aqueous environment: A critical review. Environ. Res. 2024, 240, 117477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.S.; Chen, W.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Li, J.Y.; Zhong, J.F.; Zhang, W.P.; Zou, Y.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S.H. Insights into the microbial degradation and resistance mechanisms of glyphosate. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Triozzi, M.; Losacco, D.; Ragonese, A.; Massarelli, C. Assessing glyphosate and AMPA pesticides in the Ofanto River waters and sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 202, 116376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lares, B.A.; Vignatti, A.M.; Echaniz, S.A.; Gutiérrez, M.F. Effects of glyphosate on cladocera: A synthetic review. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 249, 106232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.R.; Moraes, J.S.; Martins, C.D.G. Effects of the herbicide glyphosate on fish from embryos to adults: A review addressing behavior patterns and mechanisms behind them. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 251, 106281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, V.L.; Paolucci, E.M.; Sabatini, S.E.; Abad, T.N.; Muñoz, C.; Liquin, F.; Hollert, H.; Sylvester, F. Assessing the impact of imidacloprid, glyphosate, and their mixtures on multiple biomarkers in Corbicula largillierti. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 942, 173685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.H.; Xiao, W.J.; Xu, Y.P.; Sun, X.J.; Li, M.Y.; Lin, H.M.; Tong, Y.D.; Xie, H.; Wang, X.J. Spatial-temporal characteristics of mercury and methylmercury in marine sediment under the combined influences of river input and coastal currents. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Pan, Y.N.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Cui, J.Y.; Yin, R.L.; Li, H.S.; Qin, J.H.; Li, A.J.; Qiu, R.L. Biomonitoring of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid: Current insights and future perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 463, 132814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, W.C.; Marek, L.J.; Hall, K.E. Analysis of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in water, plant materials and soil. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Tang, T.; Shi, T.Y.; Wang, F.; Li, J.Q.; Cao, Y.S. Residue determination of glyphosate in environmental water samples with high-performance liquid chromatography and UV detection after derivatization with 4-chloro-3,5-dinitrobenzotrifluoride. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 635, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeff, W.; Neumann, C.; Schulz-Bull, D.E. Glyphosate and AMPA in the estuaries of the Baltic Sea method optimization and field study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreeken, R.J.; Speksnijder, P.; Bobeldijk-Pastorova, I.; Noij, T.H.M. Selective analysis of the herbicides glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in water by on-line solid-phase extraction high-performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 794, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.A.; Schulz-Bull, D.E.; Kanwischer, M. The challenge of detecting the herbicide glyphosate and its metabolite AMPA in seawater—Method development and application in the Baltic Sea. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Malleret, L.; Soric, A.; Boutin, O. Kinetic study of glyphosate degradation in wet air oxidation conditions. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Júnior, H.A.; Lebre, D.T.; Wang, A.Y.; Pires, M.A.F.; Bustillos, O.V. Residue Analysis of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid (AMPA) in Soybean Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. In Soybean—Biochemistry, Chemistry and Physiology; Ng, T.B., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; pp. 495–506. [Google Scholar]
- Mol, H.G.J.; van Dam, R.C.J. Rapid detection of pesticides not amenable to multi-residue methods by flow injection–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6817–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.G.; Kleintop, B.; Raglione, T. Suppression of peak tailing of phosphate prodrugs in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 98, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA; Medina-Pastor, P.; Triacchini, G. The 2018 European Union report on pesticide residues in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06057. [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio, P.; Flores, F.; Mueller, J.F.; Carter, S.; Negri, A.P. Glyphosate persistence in seawater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lares, B.A.; Vignatti, A.M.; Echaniz, S.A.; Cabrera, G.C.; Jofré, F.C.; Gutierrez, M.F. Sensitivity of Daphnia spinulata Birabén, 1917 to glyphosate at different salinity levels. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 35308–35319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, L.; Welch, A.M. Assessment of Interactive Effects of Elevated Salinity and Three Pesticides on Life History and Behavior of Southern Toad (Anaxyrus terrestris) tadpoles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Shen, S.; Wang, M.M.; Li, J.H. Mild salinization stimulated glyphosate degradation and microbial activities in a riparian soil from Chongming Island, China. J. Environ. Biol. 2013, 34, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, Y.; Pourbabaei, A.A.; Javadi, A.; Abdolmohammadi, M.H.; Saffari, M.; Morovvati, A. Biodegradation of glyphosate herbicide by Salinicoccus spp. isolated from Qom Hoze-soltan lake, Iran. Environ. Health Eng. Manag. 2015, 2, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Janßen, R.; Skeff, W.; Werner, J.; Wirth, M.A.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Schulz-Bull, D.; Labrenz, M. A Glyphosate Pulse to Brackish Long-Term Microcosms Has a Greater Impact on the Microbial Diversity and Abundance of Planktonic Than of Biofilm Assemblages. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabaloy, M.C.; Allegrini, M.; Guijarro, K.H.; Kraemer, F.B.; Morrás, H.; Erijman, L. Microbiomes and glyphosate biodegradation in edaphic and aquatic environments: Recent issues and trends. World J. Microb. Biot. 2022, 38, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analyte | Q1 Mass (Amu) Precursor Ion | Q3 Mass (Amu) Product Ion | DP (V) | EP (V) | CE (V) | CXP (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMOC-Cl- Glyphoste | 390.0 | 149.9 (Qual.) | −70 | −10 | −35 | −10 |
| 167.8 (Quan.) | −70 | −10 | −20 | −13 | ||
| FMOC-Cl-AMPA | 332.1 | 135.8 (Qual.) | −29 | −10 | −22 | −8 |
| 109.9 (Quan.) | −29 | −10 | −14 | −8 | ||
| FMOC-Cl- Glyphoste 13C215N | 393.2 | 170.8 | −30 | −10 | −16 | −14 |
| Concentration (ng/mL) | S/N | CV (%) | Remark | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMOC-Cl-Glyphosate | 0.5 | 13.7 | LOD | |
| 1 | 26.1 | LOQ | ||
| 2 | 73.1 | 10.2 | LLOQ | |
| 10 | 2.3 | |||
| 50 | 1.6 | |||
| 200 | 1.8 | |||
| 1000 | 0.9 | |||
| 3000 | 1.3 | |||
| FMOC-Cl-AMPA | 0.05 | 15.2 | LOD | |
| 0.1 | 21.9 | LOQ | ||
| 0.5 | 45.8 | 4.4 | LLOQ | |
| 2 | 1.7 | |||
| 10 | 2.1 | |||
| 50 | 4.6 | |||
| 200 | 5.3 | |||
| 1000 | 3.7 |
| n = 3 | Conc. (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | Accuracy (%) | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.0 | |||||
| QC-L | 1 | 99.6 | 100.41 | 1.94 | |
| 102.6 | |||||
| 108.5 | |||||
| AMPA | QC-M | 100 | 102.5 | 105.92 | 2.91 |
| 106.8 | |||||
| 101.3 | |||||
| QC-H | 500 | 102.3 | 102.10 | 0.72 | |
| 102.8 | |||||
| 97.8 | |||||
| QC-L | 5 | 99.7 | 98.83 | 0.97 | |
| 99.0 | |||||
| 101.2 | |||||
| Glyphosate | QC-M | 500 | 103.0 | 102.98 | 1.75 |
| 104.8 | |||||
| 103.9 | |||||
| QC-H | 2000 | 103.4 | 105.54 | 3.15 | |
| 109.4 | |||||
| n = 3 | Conc. (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | Accuracy (%) | CV (%) |
| QC-L day1 | 99.6 | ||||
| QC-L day2 | 1 | 99.9 | 100.51 | 1.34 | |
| QC-L day3 | 102.1 | ||||
| QC-M day1 | 108.6 | ||||
| AMPA | QC-M day2 | 100 | 102.4 | 106.07 | 3.07 |
| QC-M day3 | 107.2 | ||||
| QC-H day1 | 101.6 | ||||
| QC-H day2 | 500 | 102.8 | 102.13 | 0.59 | |
| QC-H day3 | 102.0 | ||||
| QC-L day1 | 99.3 | ||||
| QC-L day2 | 5 | 98.8 | 99.39 | 0.63 | |
| QC-L day3 | 100.0 | ||||
| QC-M day1 | 101.0 | ||||
| Glyphosate | QC-M day2 | 500 | 103.8 | 103.04 | 1.69 |
| QC-M day3 | 104.2 | ||||
| QC-H day1 | 104.7 | ||||
| QC-H day2 | 2000 | 104.3 | 106.03 | 2.51 | |
| QC-H day3 | 109.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, L.-C.; Liao, Z.-H.; Nan, F.-H. A Newly Developed Approach for Analyzing the Degradation of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in Different Salinity Levels. Water 2025, 17, 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050645
Chang L-C, Liao Z-H, Nan F-H. A Newly Developed Approach for Analyzing the Degradation of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in Different Salinity Levels. Water. 2025; 17(5):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050645
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Lai-Chuan, Zhen-Hao Liao, and Fan-Hua Nan. 2025. "A Newly Developed Approach for Analyzing the Degradation of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in Different Salinity Levels" Water 17, no. 5: 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050645
APA StyleChang, L.-C., Liao, Z.-H., & Nan, F.-H. (2025). A Newly Developed Approach for Analyzing the Degradation of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in Different Salinity Levels. Water, 17(5), 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050645







