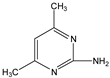
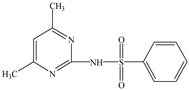
Bioremediation of Sulfamethazine Contaminated Environments by Bacillus cereus J2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Isolation and Identification of Strain
2.3. Experimental Procedures
2.3.1. SM2 Biodegradation Experiments
2.3.2. Degradation of Other Sulfonamides
2.4. Analysis Methods
2.5. Kinetic Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
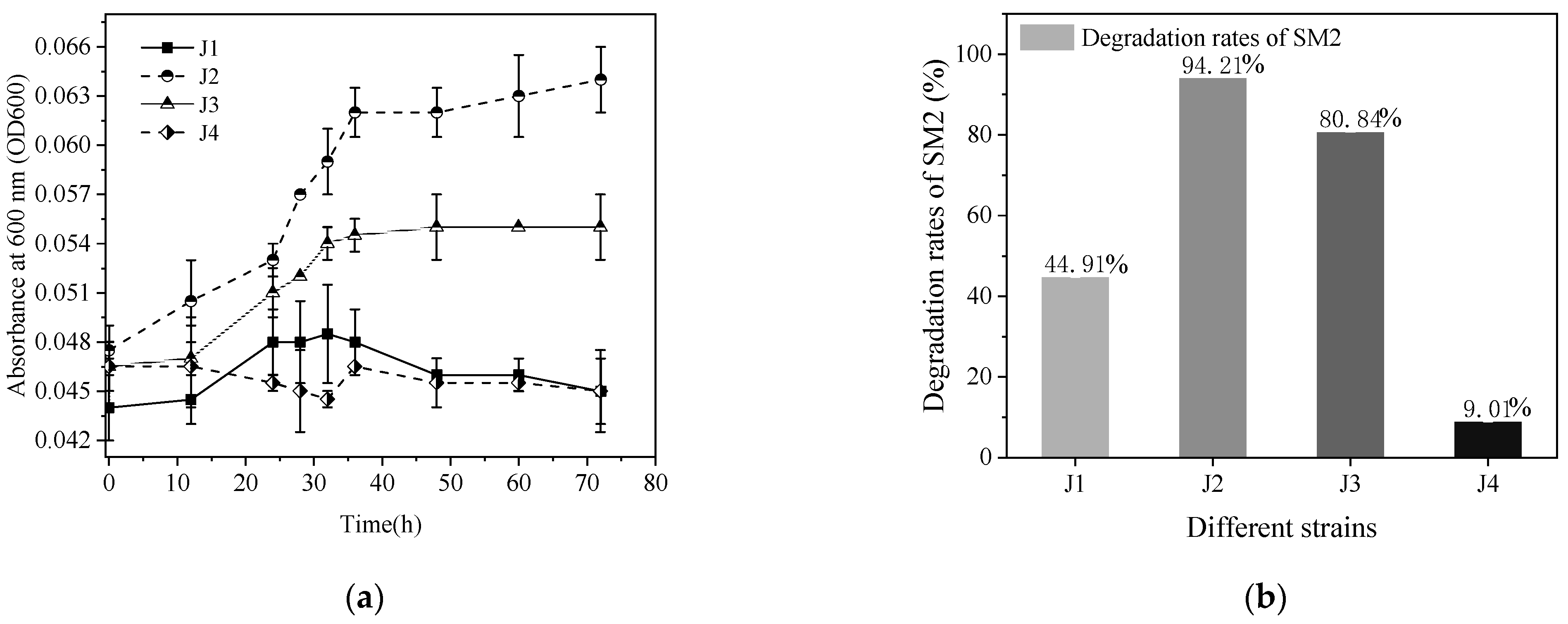
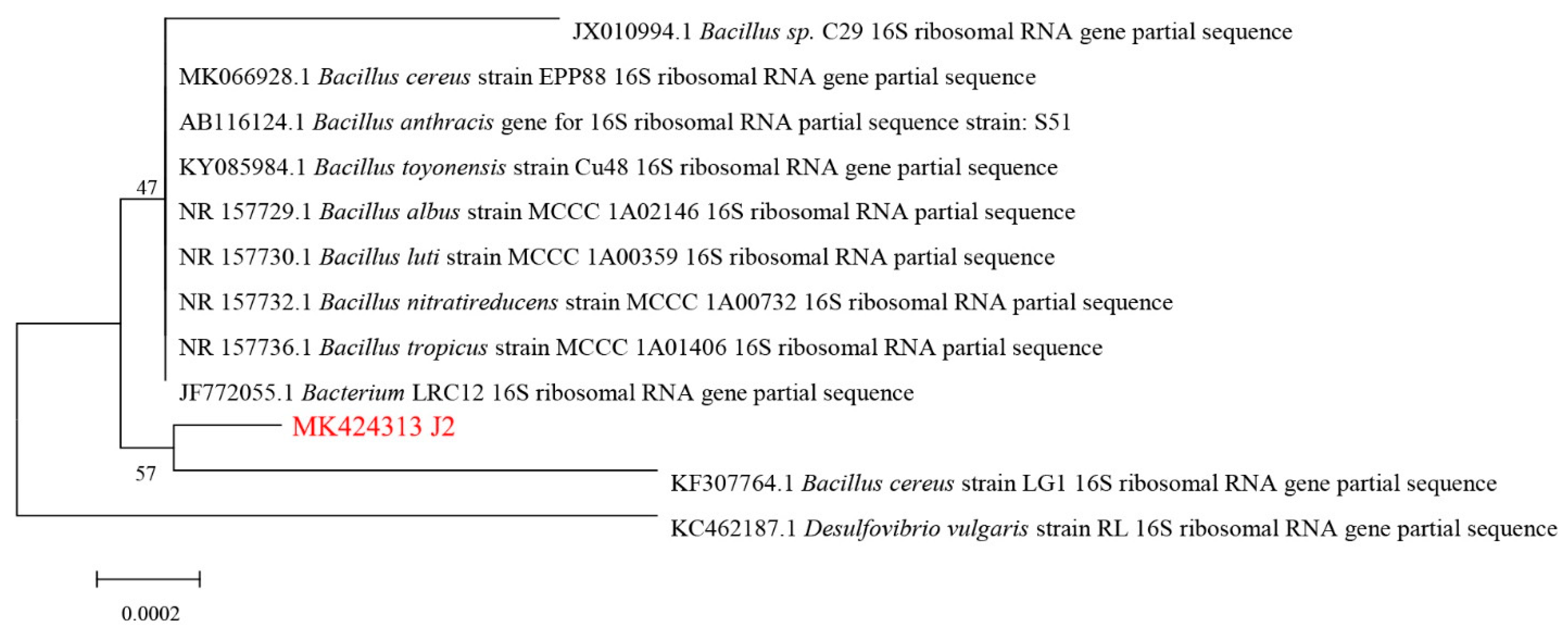
3.1. Isolation and Identification of the SM2-Degrading Strain
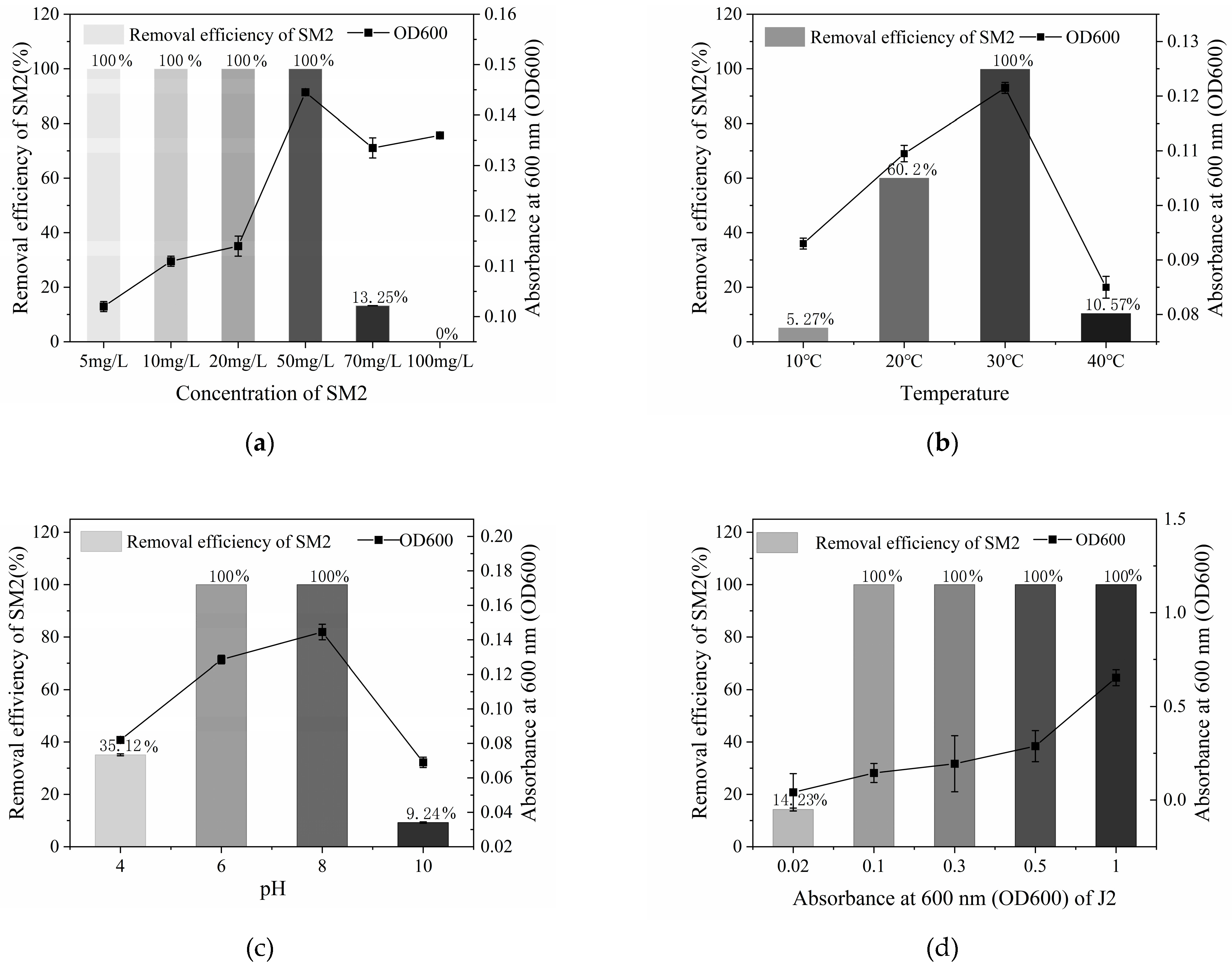
3.2. Optimal Conditions for SM2 Biodegradation by Strain J2
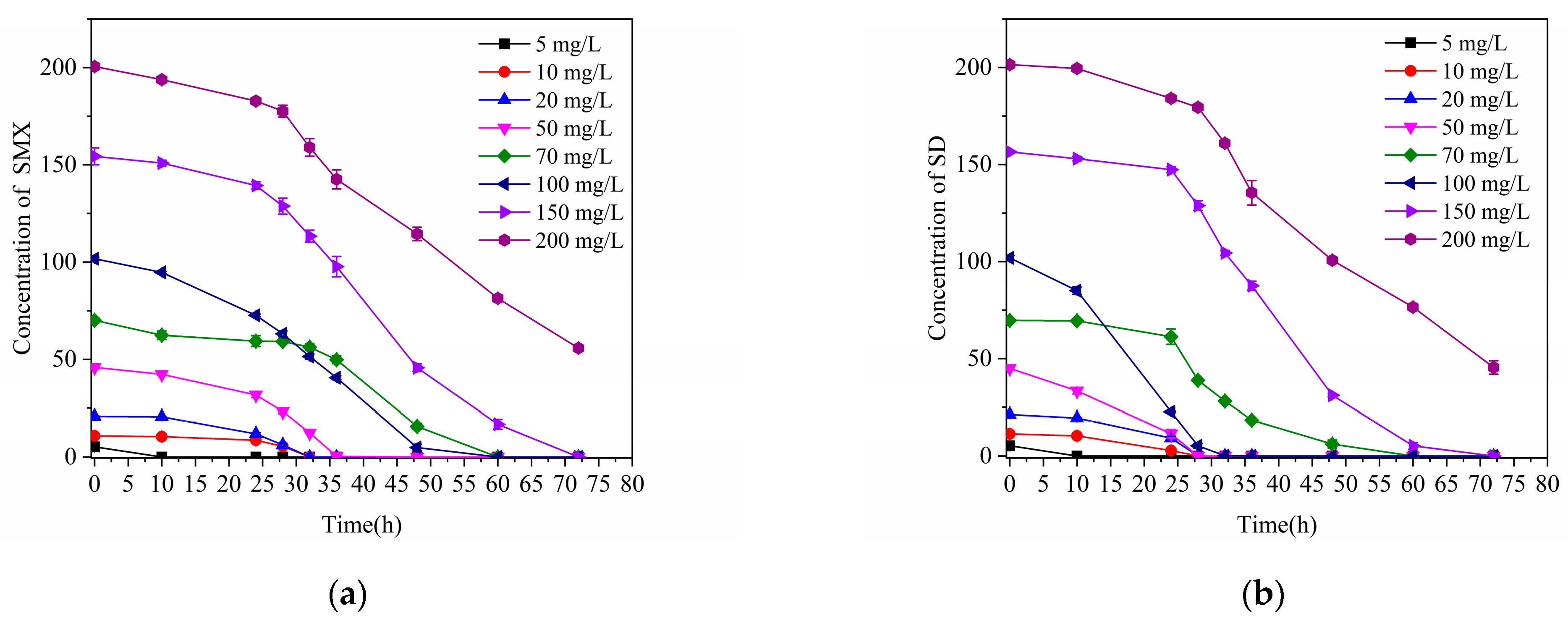
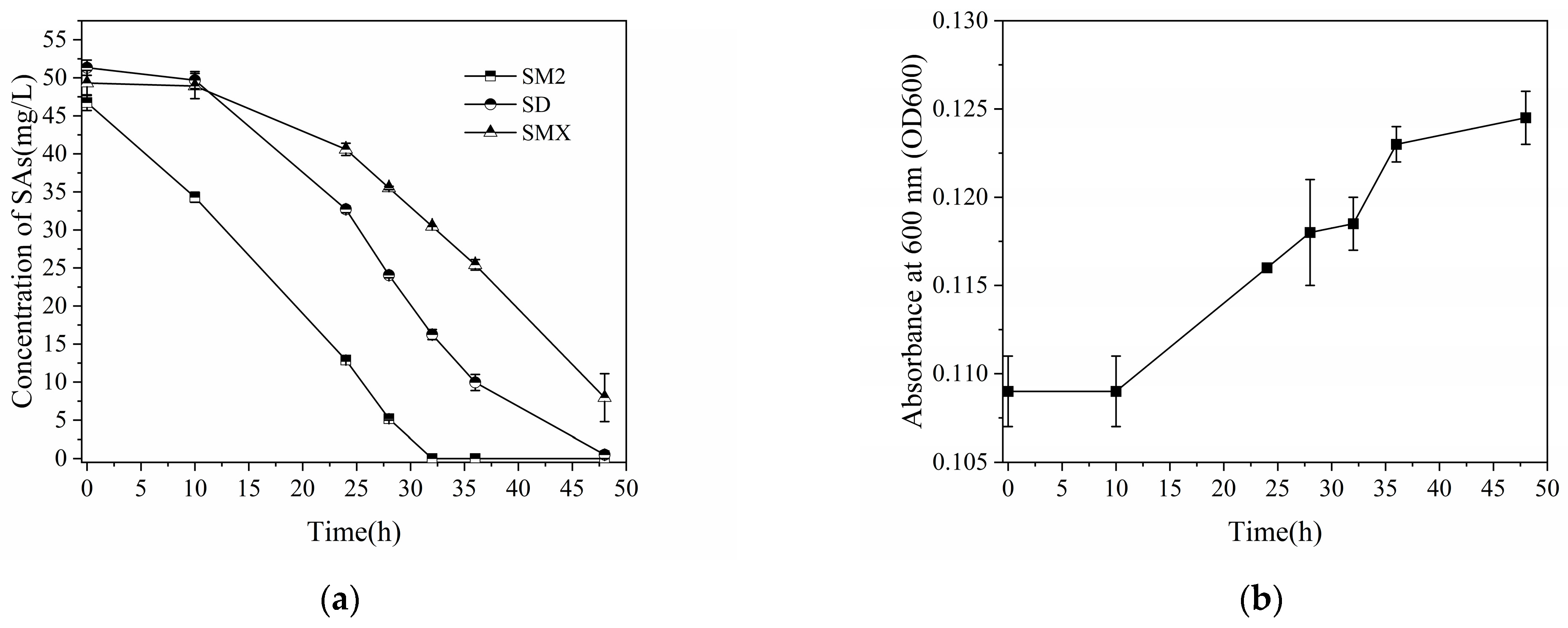
3.3. Degradation of Other Sulfonamides by Strain J2
3.4. SM2 Biodegradation and Cell Growth Kinetics Determination
| Microorganism | Carbon Source | Conc. Range (mg/L) | Conc.at μm (mg/L) | T (℃) | pH | Incubation Time (h) | Degradation Rate (%) | μm (h−1) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geobacillus sp. S-07 | glucose | 10 | 10 | 70 | 6.0 | - | 98.00 | - | [26] |
| Trametes versicolor | glucose | 9 | 9 | 25 | - | 48 | 100 | - | [53] |
| Achromobacter sp. S-3 | glucose | 5 | 5 | 30 | 8.0 | 24 | 33.00 | - | [54] |
| S. oneidensis MR-1 | SM2 | 2 | 2 | 30 | 7.0 | 120 | 23.00 ± 4.12 | - | [34] |
| Shewanella sp. MR-4 | SM2 | 2 | 2 | 30 | 7.0 | 120 | 33.00 ± 2.58 | - | [34] |
| Klebsiella Trevisan SX5 | glucose | 20 | 20 | 30 | 7.0 | 60 | 50.00 | 0.0115 | [55] |
| Acinetobacer | SM2 | 0.05~5.0 | 0.05 | 10 | 7.0 | 96 | 42.00 | −0.0089 | [56] |
| Fusarium solani | SM2 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 30 | 7.0 | 168 | 18.53 | - | [57] |
| Paenarthrobacter sp. A01 | SM2 | 10~500 | 100 | 25 | 7.8 | 96 | 96.7 | - | [58] |
| Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 14580 | SM2 | 40 | - | 30 | 6.9 | 100 | 0.2~7.8 | - | [59] |
| Achromobacter mucicolens JD417 | SM2 | 50 | 51 | 36 | 7 | - | 46 | 0.088 | [18] |
| Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens strain YL1. | SM2 | 100 | - | 30 | 7 | 72 | 98 | - | [60] |
| Bacillus thuringiensis H38 | SM2 | 5~20 | 10 | 25 | 7 | 36 | 97.3 | - | [61] |
| Bacillus cereus H38 | SM2 | 5 | - | 25 | 7.0 | 96 | 100 | - | [40] |
| Irpex lacteus WRF-IL | SM2 | 0~20 | 10 | 35 | 4.5 | 26 | 97.1 | - | [62] |
| Bacillus cereus J2 | SM2 | 5~100 | 51.35 | 30 | 8.0 | 36 | 100 | 0.066 | This study |
3.5. Products and Pathways of Sulfonamide Degradation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jeśman, C.; Młudzik, A.; Cybulska, M. History of antibiotics and sulphonamides discoveries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 30, 320–322. [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrienko, S.G.; Kochuk, E.V.; Apyari, V.V.; Tolmacheva, V.V.; Zolotov, Y.A. Recent Advances in Sample Preparation Techniques and Methods of Sulfonamides Detection—A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 850, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, W.; Adamek, E.; Ziemiańska, J.; Sobczak, A. Effects of the Presence of Sulfonamides in the Environment and Their Influence on Human Health. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottosen, C.F.; Bjerg, P.L.; Kümmel, S.; Richnow, H.H.; Middeldorp, P.; Draborg, H.; Lemaire, G.G.; Broholm, M.M. Natural Attenuation of Sulfonamides and Metabolites in Contaminated Groundwater—Review, Advantages and Challenges of Current Documentation Techniques. Water Res. 2024, 254, 121416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Cui, H.; Jia, X.; Huang, X. Occurrence and Ecotoxicity of Sulfonamides in the Aquatic Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Farooq, U.; Wang, B.; Qi, Z.; Miao, R. Transport of Sulfanilamide in Saturated Porous Media under Different Solution Chemistry Conditions: Role of Physicochemical Characteristics of Soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 11622–11632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R.; Park, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, J.-D.; Moon, G.-I. Simultaneous Determination of 31 Sulfonamide Residues in Various Livestock Matrices Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Thawng, C.N.; Lee, K.; Wellington, E.M.H.; Cha, C.-J. A Novel Sulfonamide Resistance Mechanism by Two-Component Flavin-Dependent Monooxygenase System in Sulfonamide-Degrading Actinobacteria. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.-T.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.-D.; Liao, X.-D.; Liang, J.-B.; Wu, Y.-B. Effect of Different Sulfadimidine Addition Methods on Its Degradation Behaviour in Swine Manure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7253–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W. Integrated Biomarker Responses in Zebrafish Exposed to Sulfonamides. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.E.; Moore, P.J.A.; Millar, B.C.; Goldsmith, C.E.; Loughrey, A.; Rooney, P.J.; Rao, J.R. The Presence of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria along the River Lagan. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Mao, D.; Rysz, M.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Trends in Antibiotic Resistance Genes Occurrence in the Haihe River, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7220–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, S.; Kang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, E.; Lin, Z.; Liu, W. Effects of Atmosphere and Stepwise Pyrolysis on the Pyrolysis Behavior, Product Characteristics, and N/S Migration Mechanism of Vancomycin Fermentation Residue. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Cuprys, A.K.; Maletskyi, Z.; Ratnaweera, H. Treatment Trends and Combined Methods in Removing Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products from Wastewater—A Review. Membranes 2023, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.-J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, Y.-K.; Liu, R.-D.; Pan, X.-R.; Li, W.-W.; Sheng, G.-P. Application of Membrane Bioreactor for Sulfamethazine-Contained Wastewater Treatment. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Wan, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y. Removal of Concentrated Sulfamethazine by Acclimatized Aerobic Sludge and Possible Metabolic Products. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lin, Z.; Li, F.; Tao, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y. Local O2 Concentrating Boosts the Electro-Fenton Process for Energy-Efficient Water Remediation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2317702121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Du, H.; Lin, X.; Liao, R.; Man, Y.; Fang, H.; Yang, Y.; Tao, R. Isolation, Identification and Whole-Genome Analysis of an Achromobacter Strain with a Novel Sulfamethazine Resistance Gene and Sulfamethazine Degradation Gene Cluster. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 399, 130598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Hu, X. Biochar-Bacteria Coupling System Enhanced the Bioremediation of Phenol Wastewater-Based on Life Cycle Assessment and Environmental Safety Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, T.; He, L.; Chai, B.; Zhou, S.; Wan, Q.; Lei, X.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, B. Micro-Pressure Promotes Endogenous Phosphorus Release in a Deep Reservoir by Favouring Microbial Phosphate Mineralisation and Solubilisation Coupled with Sulphate Reduction. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, G.-Q.; Dai, M.-X.; Kong, Q. Contaminant Removal and Microorganism Response of Activated Sludge in Sulfamethazine Wastewater Treatment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 143, 104705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Lai, Y.; Ke, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Han, X.; Ma, J. Recent Advances in Biofilm Technologies for Breeding Wastewater Treatment: Fundamentals, Performance and Impacts of Antibiotics. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 62, 105429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Liang, L.; Shi, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, L.; Xiao, J.; Huang, N.; Zhao, A.; Xia, Y.; Hou, J. Biofilms in Plastisphere from Freshwater Wetlands: Biofilm Formation, Bacterial Community Assembly, and Biogeochemical Cycles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 134930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xie, S. Overview of Sulfonamide Biodegradation and the Relevant Pathways and Microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, H.; Yargeau, V.; Cooper, D.G. Biodegradation of Pharmaceuticals by Rhodococcus rhodochrous and Aspergillus niger by Co-Metabolism. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Tang, X.; Li, C.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y. Biodegradation of Sulfamethazine by an Isolated Thermophile–Geobacillus sp. S-07. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkigt, J.; Gilevska, T.; Ricken, B.; Richnow, H.-H.; Vione, D.; Corvini, P.F.-X.; Nijenhuis, I.; Cichocka, D. Carbon Stable Isotope Fractionation of Sulfamethoxazole during Biodegradation by Microbacterium sp. Strain BR1 and upon Direct Photolysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6029–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappe, W.; Hofmann, D.; Disko, U.; Koeppchen, S.; Kummer, S.; Vereecken, H. A Novel Isolated Terrabacter-like Bacterium Can Mineralize 2-Aminopyrimidine, the Principal Metabolite of Microbial Sulfadiazine Degradation. Biodegradation 2015, 26, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Li, T.; Zheng, Q.; Lu, Y.; He, Y.; Tang, Y.; Qiu, R. Citrobacter sp. Y3 Harbouring Novel Gene HBCD-Hd-1 Mineralizes Hexabromocyclododecane via New Metabolic Pathways According to Multi-Omics Characterization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.-R.; Shang-Guan, P.-K.; Li, S.-H.; Zhang, C.-H.; Lou, J.-M.; Guo, L.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y. The Influence of Carbon Dioxide on Fermentation Products, Microbial Community, and Functional Gene in Food Waste Fermentation with Uncontrol pH. Environ. Research. 2025, 267, 120645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, T.; Yu, K.; Chai, B.; Tang, Q.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; He, L.; Lei, X.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y.; et al. Microplastics Increase the Microbial Functional Potential of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Water Pollution in a Freshwater Lake: A Metagenomic Study. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Huang, S.; Huang, J.; Zeng, H.; Xu, M.; Cai, A.; Zhou, S.; Ma, X.; Deng, J. Unveiling the Optical and Molecular Characteristics of Aging Microplastics Derived Dissolved Organic Matter Transformed by UV/Chlor(Am)Ine Oxidation and Its Potential for Disinfection Byproducts Formation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y. Isolation And Degradation Characteristic of A New Sulfamethazine-Degrading Bacterium. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technonogy, Harbin, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, F.; Liu, X.; Wu, K.; Zhou, C.; Si, Y. Biodegradation of Sulfonamides by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 and Shewanella sp. Strain MR-4. Biodegradation 2018, 29, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Biodegradation of Chlortetracycline by Bacillus cereus LZ01: Performance, Degradative Pathway and Possible Genes Involved. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, L.; Pan, K.; Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhong, G.; Lu, Q. Heavy Metal-Tolerant Bacteria Bacillus Cereus BCS1 Degrades Pyrethroid in a Soil–Plant System. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karale, M.A.; Kadam, T.A.; Bhosale, H.J.; More, R.A. A Plasmid Induces Biodegradation of Pyrene by Bacillus Cereus C7 and Identification of Its Degradation Metabolites. Indian J. Microbiol. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebashalomi, V.; Emmanuel Charles, P.; Rajaram, R. Microbial Degradation of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) and Polystyrene Using Bacillus cereus (OR268710) Isolated from Plastic-Polluted Tropical Coastal Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Li, X. Degradation of Organic Compounds by a Novel Bacillus cereus BX16 in Starch Waste. Process Biochem. 2024, 144, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Wen, S.; Kim, Y.M. Mechanism for Biodegradation of Sulfamethazine by Bacillus cereus H38. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 152237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, A.; Salam, J.A.; Das, N. Biodegradation of Cefdinir by a Novel Yeast Strain, Ustilago sp. SMN03 Isolated from Pharmaceutical Wastewater. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, W.; Jia, X. Biodegradation of Tetrabromobisphenol A by a Novel Comamonas sp. Strain, JXS-2-02, Isolated from Anaerobic Sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Chen, L.; Cai, T.; Yang, Q.; Ding, D. Isolation and characterization of norfloxacin-degrading bacterium strain NOR-36. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, W.; Bai, Y.; Tu, Y. Complexation of Sulfamethazine with Typical Dissolved Organic Matter. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 4103–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Dong, X.; Leong, Y.K.; Chang, J.-S. Ecological Risks of Sulfonamides and Quinolones Degradation Intermediates: Toxicity, Microbial Community, and Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 418, 131967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Lv, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Sulfamethoxazole Degradation by Aeromonas caviae and Co-Metabolism by the Mixed Bacteria. Chemosphere 2023, 317, 137882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, L.; Rysz, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Occurrence and Transport of Tetracycline, Sulfonamide, Quinolone, and Macrolide Antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhong, Z.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Chen, Y. Degradation of Sulfonamides Antibiotics in Lake Water and Sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 20, 2372–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutchelvan, V.; Kanakasabai, V.; Elangovan, R.; Nagarajan, S.; Muralikrishnan, V. Kinetics of High Strength Phenol Degradation Using Bacillus brevis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, I.; Modak, J.M.; Bandopadhyay, K.; Das, D.; Maiti, B.R. Mathematical Model for Evaluation of Mass Transfer Limitations in Phenol Biodegradation by Immobilized Pseudomonas putida. J. Biotechnol. 2001, 87, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Mao, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, C.; Zhang, T. Aerobic Degradation of Sulfadiazine by Arthrobacter spp.: Kinetics, Pathways, and Genomic Characterization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9566–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchu, S.R.; Panditi, V.R.; O’Shea, K.E.; Gardinali, P.R. Photodegradation of Antibiotics under Simulated Solar Radiation: Implications for Their Environmental Fate. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Galán, M.J.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C.E.; Vicent, T.; Caminal, G.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Biodegradation of Sulfamethazine by Trametes versicolor: Removal from Sewage Sludge and Identification of Intermediate Products by UPLC–QqTOF-MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 5505–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Tian, S.; Chen, D.; Zhang, W.; Wu, J.; Chen, L. Removal of Sulfamethazine Antibiotics by Aerobic Sludge and an Isolated Achromobacter sp. S-3. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F. The Degradation of Sulfamethazine by Microwave and Microorganism. Master’s Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, Y.; Si, C.; Chen, Z.; Qian, H.; Zhao, Z. Research on the Adsorption and Migration of Sulfa Antibiotics in Underground Environment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, P.; Xia, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Hou, Y. Screening and degradation properties of three kinds of agricultural antibiotics degrading fungi. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2018, 35, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Deng, Y.; Liu, J.; Fu, W.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Li, B. Genomic Characterization, Kinetics, and Pathways of Sulfamethazine Biodegradation by Paenarthrobacter sp. A01. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islas-Espinoza, M.; Reid, B.J.; Wexler, M.; Bond, P.L. Soil Bacterial Consortia and Previous Exposure Enhance the Biodegradation of Sulfonamides from Pig Manure. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Fu, Y.; Ma, F.; Guo, H. Biodiversity, Isolation and Genome Analysis of Sulfamethazine-Degrading Bacteria Using High-Throughput Analysis. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 43, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, R.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Kim, Y.M.; Wang, J. Immobilization of Bacillus thuringiensis and Applicability in Removal of Sulfamethazine from Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Yu, T.; Ma, F. Functional Fungal Pellets Self-Immobilized by Mycelium Fragments of Irpex Lacteus WRF-IL for Efficient Degradation of Sulfamethazine as the Sole Carbon Source. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 385, 129376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H. Study On Photochemical Behavior and Photocatalytic Degradation of Sulfamethazine in Aqueous Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B. Characteristic and Sulfamethoxazole From Aqueous Solution Degradation Mechanism of Pseudomonas psychrophila HA-4. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technonogy, Harbin, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]

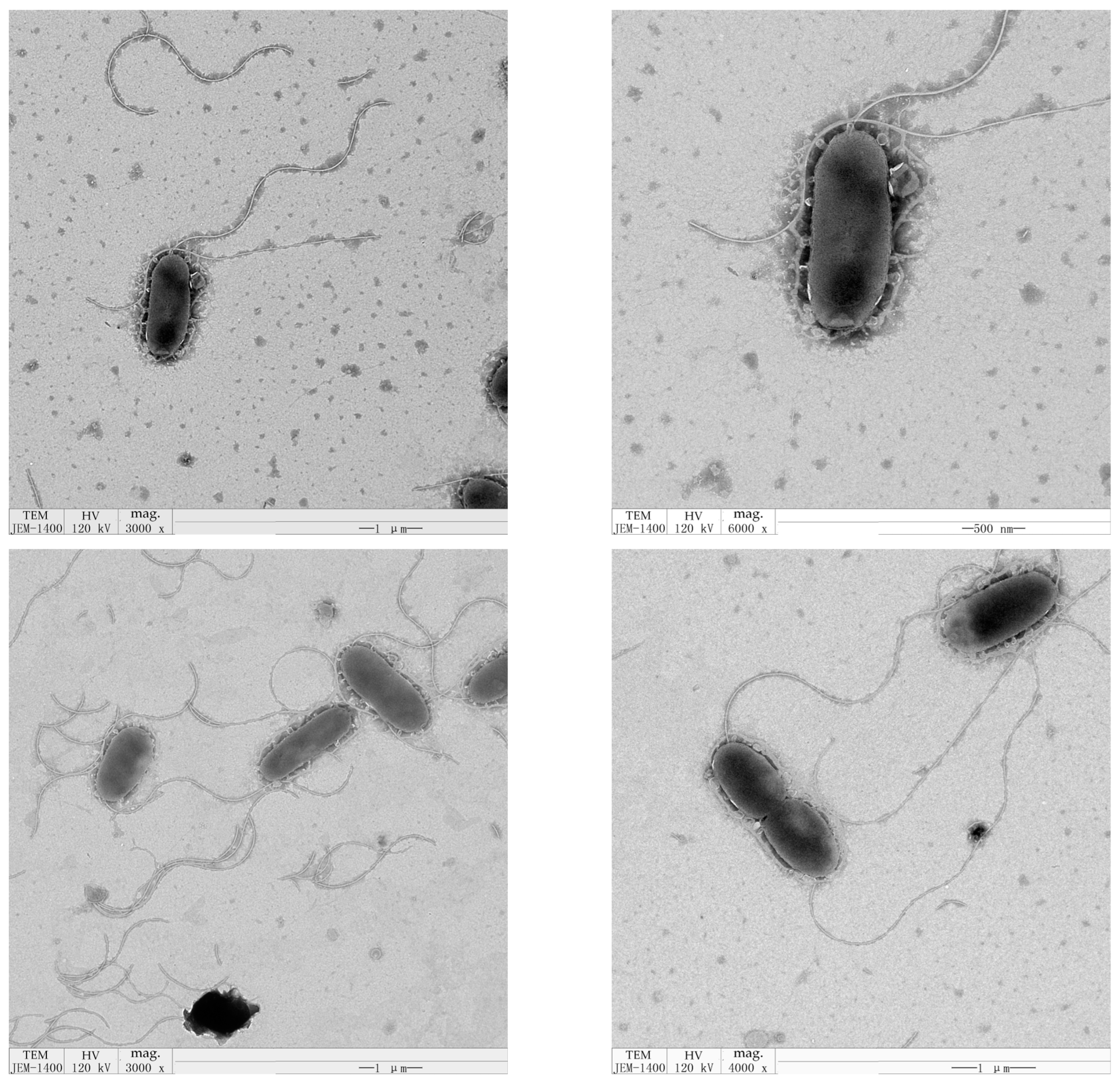


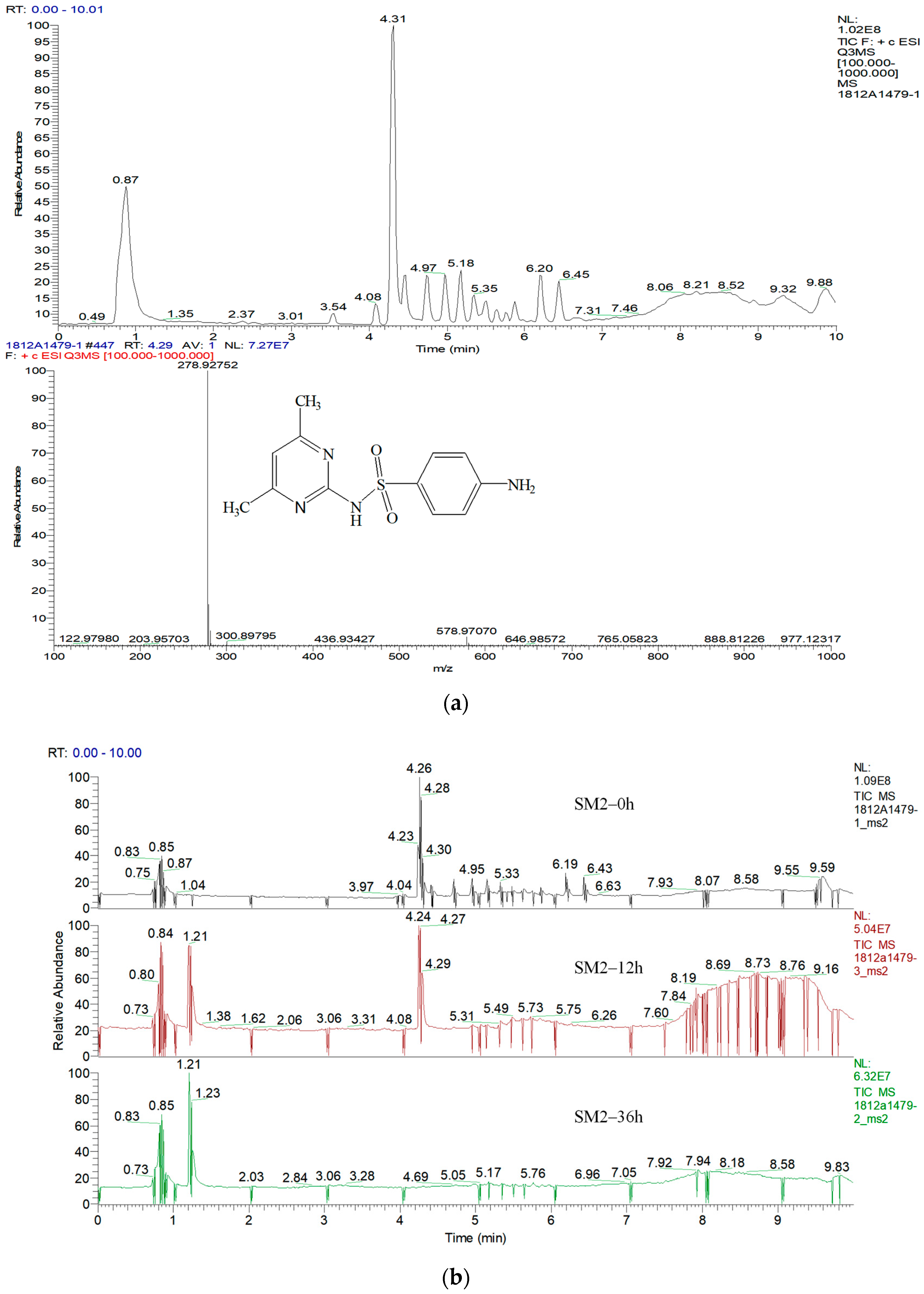
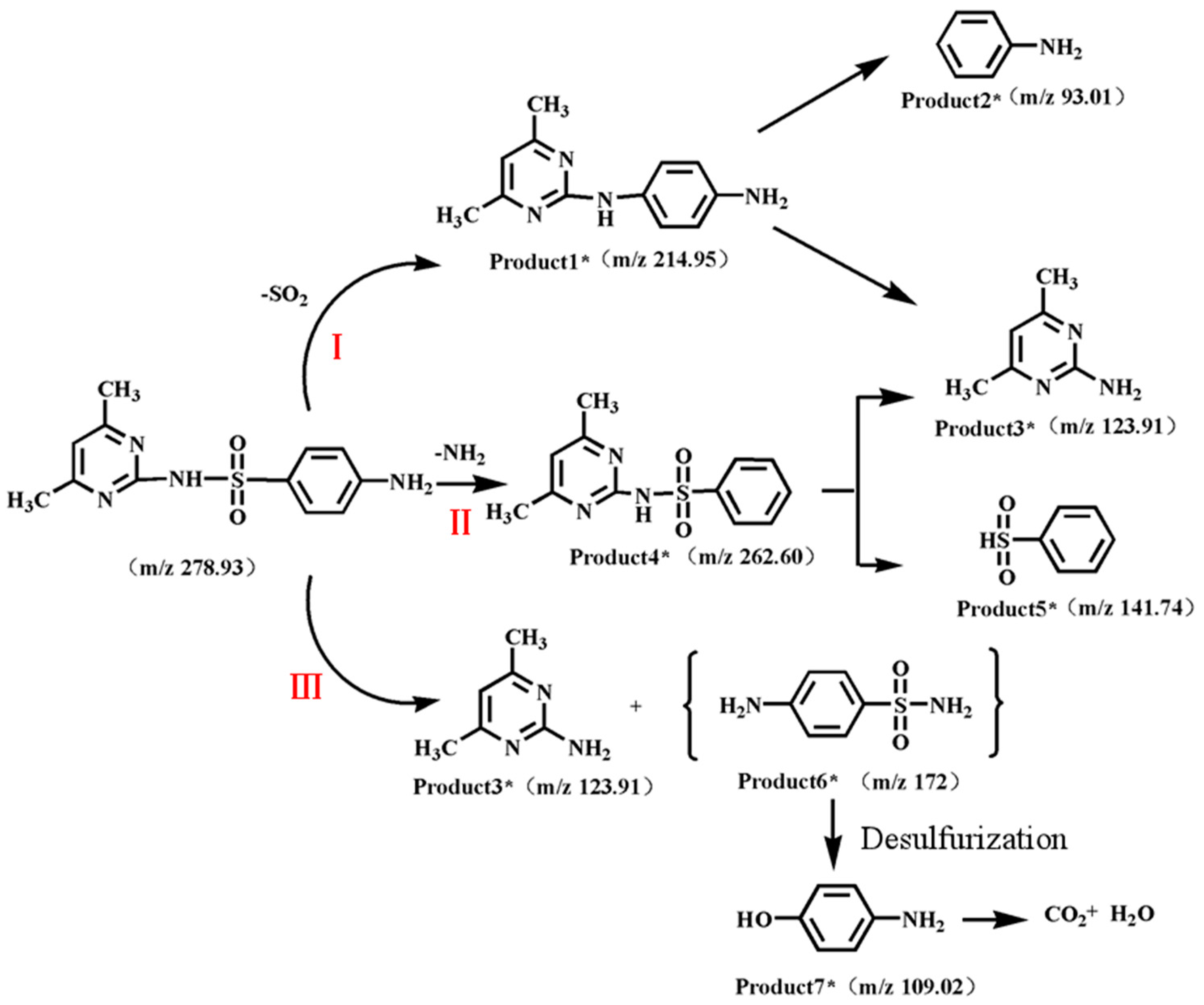
| Analytical Parameters | Results | Analytical Parameters | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| cell morphology | short rods | flagellum | flagellated |
| motility | motile | methyl red test | - |
| gram test | + | phenylalanine dehydrogenase test | - |
| catalase test | + | glucose acid salt test | - |
| Analytical Parameters | Results (48 h) | Analytical Parameters | Results (48 h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Erythritol | + | Salicin | + |
| D-Arabinose | - | Cellobiose | - |
| L-Arabinose | + | Maltose | + |
| Ribose | + | Melibiose | + |
| D-Xylose | + | Sucrose | + |
| L-Xylose | - | Trehalose | + |
| Chrysanthemel Alcohol | + | Inulin | - |
| Methyl β-D-Xyloside | - | Raffinose | - |
| Lactose | - | Melezitose | - |
| Glucose | + | Starch | - |
| D-Fructose | + | Glycogen | - |
| Mannose | + | Xylitol | - |
| Sorbose | - | Lactose | - |
| Rhamnose | - | Tagatose | - |
| Sorbitol | - | D-Fucose | + |
| Inositol | + | L-Fucose | - |
| Mannitol | - | D-Arabitol | - |
| Dulcitol | + | L-Arabitol | + |
| Methyl α-D-Mannose | - | Sodium Gluconate | - |
| Methyl α-D-Glucoside | - | Amygdalin | - |
| N-Acetylglucosamine | + | Arbutin | + |
| Concentration of SM2 (mg/L) | Logistic Equation | µ | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.002469 | 0.96482 | |
| 10 | 0.003289 | 0.9807 | |
| 20 | 0.004998 | 0.93607 | |
| 50 | 0.008438 | 0.97789 | |
| 70 | 0.007426 | 0.99927 | |
| 100 | 0.006514 | 0.99484 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, T.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Z. Bioremediation of Sulfamethazine Contaminated Environments by Bacillus cereus J2. Water 2025, 17, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040468
Zhang J, Tang Y, Li Z, Li T, Zhao X, Wu Z. Bioremediation of Sulfamethazine Contaminated Environments by Bacillus cereus J2. Water. 2025; 17(4):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040468
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiayu, Yuping Tang, Zhaokang Li, Tianyu Li, Xinfeng Zhao, and Zihao Wu. 2025. "Bioremediation of Sulfamethazine Contaminated Environments by Bacillus cereus J2" Water 17, no. 4: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040468
APA StyleZhang, J., Tang, Y., Li, Z., Li, T., Zhao, X., & Wu, Z. (2025). Bioremediation of Sulfamethazine Contaminated Environments by Bacillus cereus J2. Water, 17(4), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040468