Efficiency of a DAF System in Removing Organic Matter and Lipid Compounds from Municipal Effluent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Municipal Wastewater
2.2. Physicochemical Characterisation of the Effluent
2.3. System Configuration and Operation
2.4. System Start-Up Period
2.5. Removal Efficiency Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Municipal Effluent
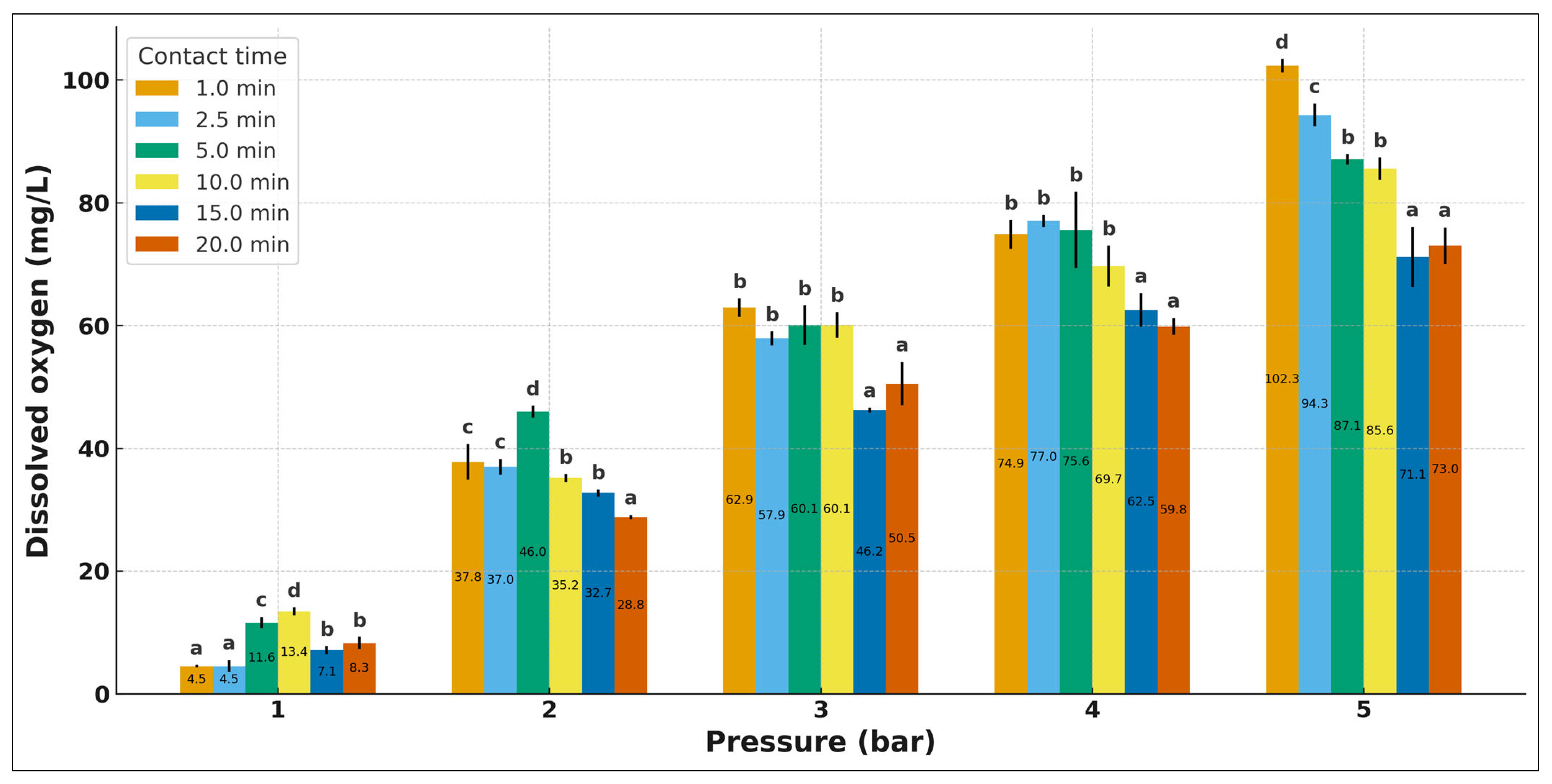
3.2. Water–Air Saturation and Oxygen Transfer Efficiency
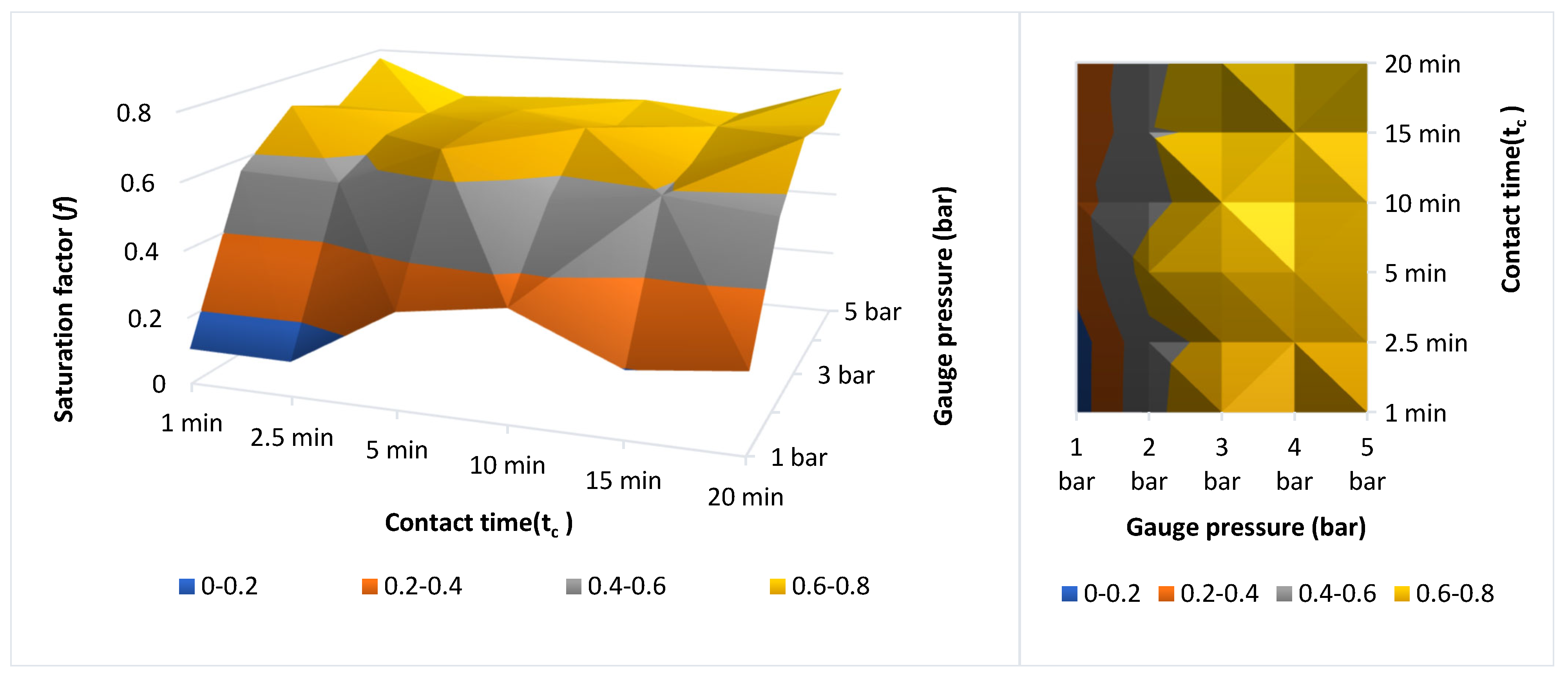
3.3. Determination of the Saturation Factor (f) and Operating Conditions
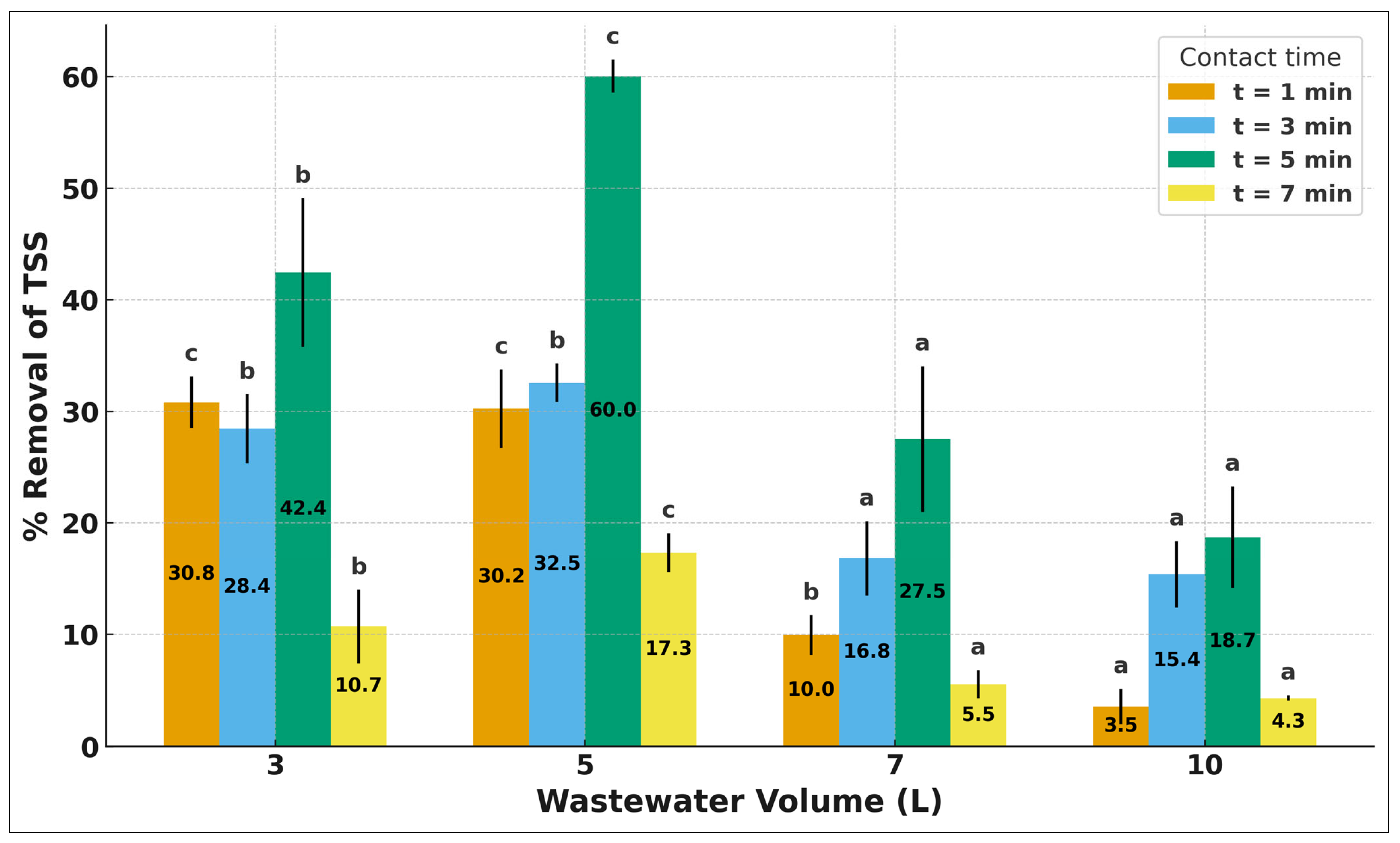
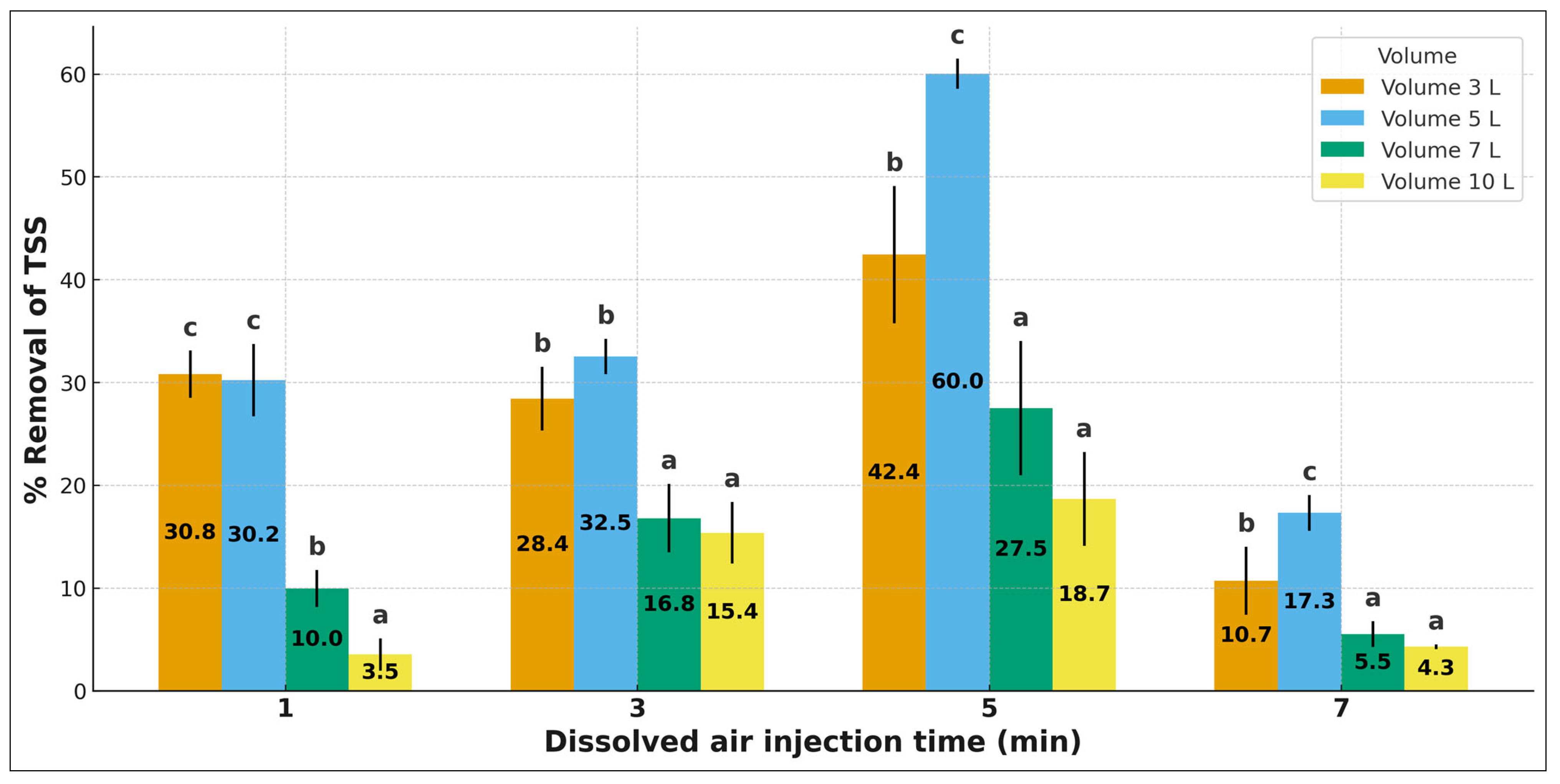
3.4. Removal of Total and Suspended Solids
3.5. Efficiency of the DAF System in Removing Organic Matter and Lipid Compounds from Municipal Effluent
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Tayawi, A.N.; Sisay, E.J.; Beszédes, S.; Kertész, S. Wastewater Treatment in the Dairy Industry from Classical Treatment to Promising Technologies: An Overview. Processes 2023, 11, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Blas, F.M.; Ramos-Saravia, J.C.; Cossío-Rodríguez, P.L. Eliminación de nitrógeno y fósforo de las aguas residuales municipales mediante el cultivo de microalgas Chlorella sp. en consorcio. Water 2025, 17, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obotey Ezugbe, E.; Rathilal, S. Membrane Technologies in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Adeniyi, A.G.; Adeniran, J.A.; Ogunniyi, S. A Systematic Literature Analysis of Water Pollution Sources in Nigeria. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Yousaf, M.; Nasir, A.; Bhatti, I.A.; Mahmood, A.; Fang, X.; Jian, X.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Mahmood, N. Porous Eleocharis@MnPE Layered Hybrid for Synergistic Adsorption and Catalytic Biodegradation of Toxic Azo Dyes from Industrial Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2161–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chariguamán, L.A.; Gómez, L.K.; Guerrero, L.E.; Moya, R.B. Treatment of Wastewater Generated in a Dairy Processing Plant in the Ecuadorian Amazon. Reincisol 2024, 3, 2311–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R.S.; Mishra, J.; Ighalo, J.O. Rising Demand for Rain Water Harvesting System in the World: A Case Study of Joda Town, India. World Sci. News 2020, 146, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Dharwal, M.; Parashar, D.; Shuaibu, M.S.; Abdullahi, S.G.; Abubakar, S.; Bala, B.B. Water Pollution: Effects on Health and Environment of Dala LGA, Nigeria. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 3036–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharnejad, H.; Khorshidi Nazloo, E.; Madani Larijani, M.; Hajinajaf, N.; Rashidi, H. Comprehensive Review of Water Management and Wastewater Treatment in Food Processing Industries. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4779–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, S.; Wasko, C.; Sharma, A. Do Longer Dry Spells Associated with Warmer Years Compound the Stress on Global Water Resources? Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Cruz, B.; Amin, M.O.; Al-Hetlani, E. Polyoxometalate-Based Materials for Removal of Contaminants from Wastewater: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 10960–10977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Russo, F.; Macedonio, F.; Criscuoli, A.; Curcio, E.; Figoli, A. PVDF Membrane Preparation for Membrane Distillation and Crystallization: Use of Non-Toxic Solvents. Membranes 2025, 15, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Messaoudi, N.; El Mouden, A.; Fernine, Y.; El Khomri, M.; Bouich, A.; Faska, N.; Ciğeroğlu, Z.; Pinheiro, J.H.A.; Jada, A.; Lacherai, A. Green Synthesis of Ag2O Nanoparticles Using Punica granatum Leaf Extract for Sulfamethoxazole Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 81352–81369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen-Chiang, C.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y. Responsibility under International Law to Prevent Marine Pollution from Radioactive Waste. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 227, 106294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimonda, A.; Kowalska, I. Water Recovery from Laundry Wastewater by Integrated Purification Systems. Membranes 2025, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afolalu, S.A.; Ikumapayi, O.M.; Ogedengbe, T.S.; Kazeem, R.A.; Ogundipe, A.T. Waste Pollution, Wastewater and Effluent Treatment Methods: An Overview. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 3282–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadeja, N.B.; Banerji, T.; Kapley, A.; Kumar, R. Water Pollution in India—Current Scenario. Water Secur. 2022, 16, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Yadav, P.; Pal, A.K.; Mishra, V. Water Pollutants: Origin and Status. In Sensors in Water Pollutants Monitoring; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Responsible for Water Quality Degradation: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, D.M.; Abbott, B.W.; Khamis, K.; Kelleher, C.; Lynch, I.; Krause, S.; Ward, A.S. Illuminating the ‘Invisible Water Crisis’. Hydrol. Process. 2022, 36, e14525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and Disadvantages of Techniques Used for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quist-Jensen, C.A.; Macedonio, F.; Drioli, E. Membrane Technology for Water Production in Agriculture: Desalination and Wastewater Reuse. Desalination 2015, 364, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Herazo, L.; Álvarez-Hernández, L.; Marín-Muñiz, J.; Zitácuaro-Contreras, I. Wastewater Treatment through Home Bioengineered Wetlands. J. Energy Eng. Optim. Sustain. 2024, 8, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.R.; Mohamed, R.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Aziz, H.A. Advanced Technologies for Poultry Slaughterhouse Wastewater Treatment: A Systematic Review. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 880–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Cobo, L.E.; Alcázar-Espinoza, J.A.; Vera-Guerrero, D.I.; Verdugo-Arcos, J.A. Proposal for a Pilot-Scale Domestic Wastewater Treatment Plant. J. Econ. Soc. Sci. Res. 2024, 4, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, P.R.; Sacchi, G.D.; Daniel, L.A.; Reali, M.A.P. Treatment of Secondary Effluent Using Dissolved Air Flotation on a Pilot Scale. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 70, 107033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmideder, S.; Thurin, L.; Kaur, G.; Briesen, H. Inline Imaging Reveals Evolution of Microbubble Size Distribution in DAF. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikfar, M.H.; Parsaeian, H.; Amani Tehrani, A.; Kouhestani, A.; Masoumi Isfahani, H.; Bazargan, A. Two-Stage DAF Saturator for Improved Microbubble Production. Environ. Technol. 2021, 44, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Guzmán, S.M.; Hernández-Aguilar, E.; Rosas-Mendoza, E.S.; Alvarado-Lassman, A.; Méndez-Contreras, J.M. Effect of Saturation Pressure in Batch DAF Operation for Municipal Effluents. Trends Renew. Energy Sustain. 2024, 3, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Meza, A.; Vigueras-Cortes, J.M.; Allen, C.D. Municipal Wastewater Treatment in a Hybrid Biofiltration System. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quím. 2024, 23, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez González, E.C.; Sánchez Contreras, M.V.; Caldera Marín, Y. Dissolved Air Flotation with PAC for Poultry Wastewater. Boliv. J. Eng. 2020, 1, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Alegría, J.A.; Muñoz-España, E.; Flórez-Marulanda, J.F. Dissolved Air Flotation: A Review. TecnoLógicas 2021, 24, e2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinaga, F.A.; Lubis, M.T.; Husin, A. Reduction of TSS, COD, Oil and Fat in Palm Oil Mill Waste Using DAF. J. Serambi Eng. 2022, 7, 4179–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wen, S.; Wan, Z.; Xin, H.; Li, K. Treatment of Oil-Containing Wastewater Using Air Flotation Coupled with Fine Filtration. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autoridad Nacional del Agua (ANA). National Protocol for Monitoring Surface Water Quality; ANA: Lima, Peru, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
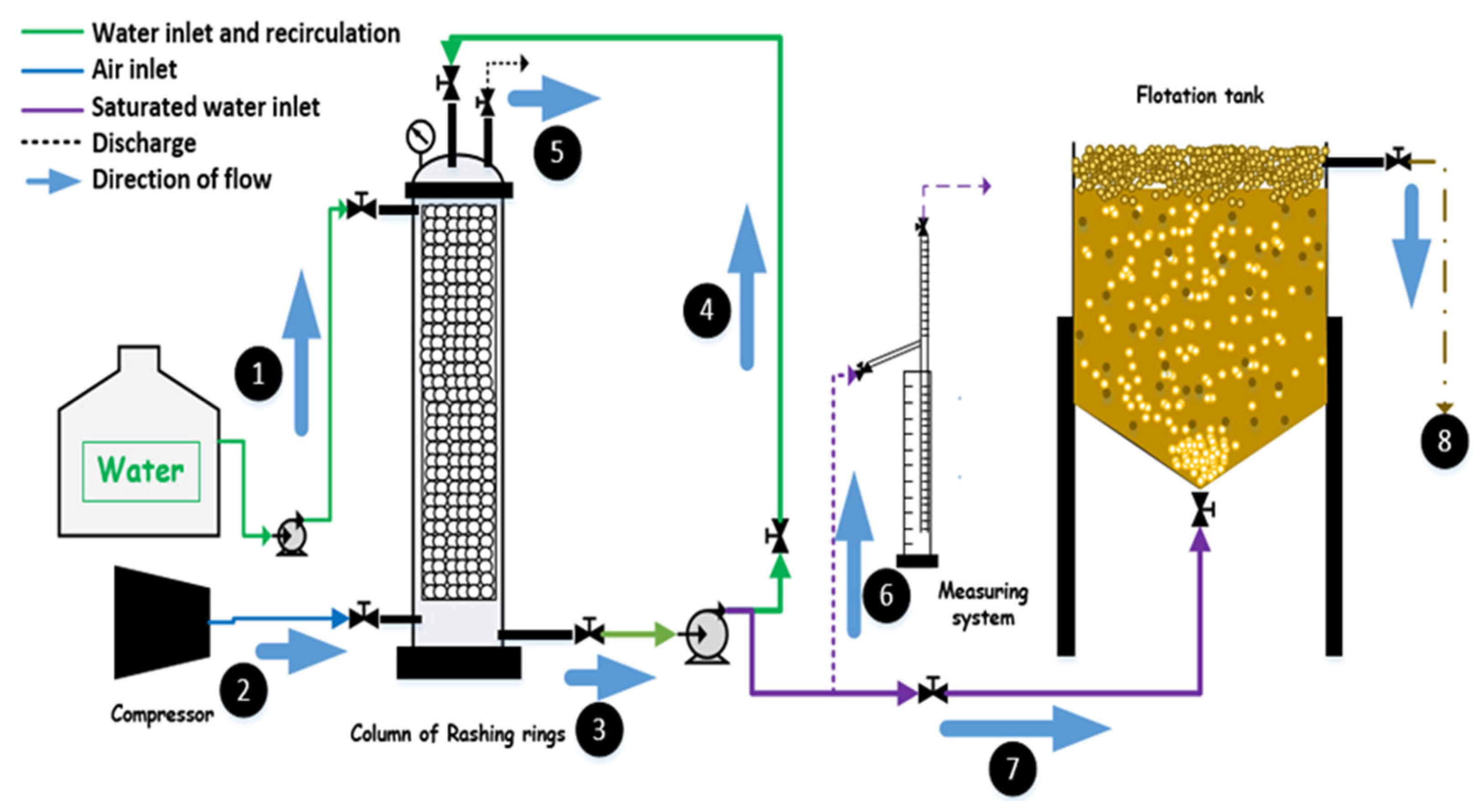
| Technology | Typical Removal (BOD/COD/O&G) | Advantages | Limitations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAF | 85–99% (BOD/COD), >90% O&G | High efficiency for lipids and suspended solids; microbubble selectivity; low sludge production | Limited removal of dissolved solids; requires pressurization | [29] |
| Coagulation–Flocculation | 60–85% | Simple, low cost | High chemical consumption; sludge generation | [31] |
| Sedimentation | ≤60% TSS | Common and easy operation | Inefficient for oily wastewater | [21] |
| Biofilters/Hybrid systems | 80–95% | Excellent biodegradation; stable | Sensitive to shock loads | [30] |
| Reverse Osmosis (RO) | >97% | High-quality effluent | Very high energy; fouling; costly | [3,24] |
| Parameter | Unit | Sample | MAV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Solids (TS) | mg/L | 800 | 500 |
| Oils and Fats (OF) | mg/L | 450 | 100 |
| Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5) | mg/L | 360 | 500 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | mg/L | 710 | 1000 |
| pH | 7.6 | 6.5–8.5 | |
| Dissolved Solids (DS) | mg/L | 210 | |
| Suspended Solids (SS) | mg/L | 590 |
| Contact Time (tC) | P (Bar) | Dissolved Oxygen Concentration (mg/L) | Saturation Factor (f) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 4.5 a ± 0.2 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 37.8 c ± 2.9 | 0.7 | |
| 3 | 62.9 b ± 1.5 | 0.7 | |
| 4 | 74.9 b ± 2.4 | 0.7 | |
| 5 | 102.3 d ± 1.1 | 0.8 | |
| 2.5 | 1 | 4.5 a ± 0.9 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 37.0 c ± 1.6 | 0.6 | |
| 3 | 57.9 b ± 1.2 | 0.6 | |
| 4 | 77.0 b ± 1.0 | 0.7 | |
| 5 | 94.3 c ± 1.9 | 0.7 | |
| 5 | 1 | 11.6 c ± 0.9 | 0.3 |
| 2 | 46.0 d ± 1.0 | 0.7 | |
| 3 | 60.1 b ± 3.2 | 0.7 | |
| 4 | 75.6 b ± 6.2 | 0.7 | |
| 5 | 87.1 b ± 0.9 | 0.7 | |
| 10 | 1 | 13.4 d ± 0.7 | 0.3 |
| 2 | 35.2 b ± 0.7 | 0.6 | |
| 3 | 60.1 b ± 2.1 | 0.7 | |
| 4 | 69.7 b ± 3.4 | 0.7 | |
| 5 | 85.6 b ± 1.8 | 0.7 | |
| 15 | 1 | 7.1 b ± 0.6 | 0.2 |
| 2 | 32.7 b ± 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 3 | 46.2 a ± 0.4 | 0.6 | |
| 4 | 62.5 a ± 2.7 | 0.7 | |
| 5 | 71.1 a ± 4.9 | 0.7 | |
| 20 | 1 | 8.3 b ± 1.0 | 0.2 |
| 2 | 28.8 a ± 0.3 | 0.6 | |
| 3 | 50.5 a ± 3.5 | 0.7 | |
| 4 | 59.8 a ± 1.4 | 0.7 | |
| 5 | 73.0 a ± 3.0 | 0.8 |
| Analysis | Unit | M1 Before the DAF | M2 After the DAF | % Removal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Solids (TS) | mg/L | 800 | 270 | 66.3 |
| Oils and Fats (OF) | mg/L | 450 | 70 | 84.4 |
| Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) | mg/L | 360 | 40 | 88.9 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | mg/L | 710 | 80 | 88.7 |
| Dissolved Solids (DS) | mg/L | 210 | 210 | 0.0 |
| Suspended Solids (SS) | mg/L | 590 | 60 | 89.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paredes-Quiroz, L.R.; Ccasani-Dávalos, H.; Bejarano-Luján, D.L.; Ccopa-Flores, R.M.; Lozano, F. Efficiency of a DAF System in Removing Organic Matter and Lipid Compounds from Municipal Effluent. Water 2025, 17, 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243474
Paredes-Quiroz LR, Ccasani-Dávalos H, Bejarano-Luján DL, Ccopa-Flores RM, Lozano F. Efficiency of a DAF System in Removing Organic Matter and Lipid Compounds from Municipal Effluent. Water. 2025; 17(24):3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243474
Chicago/Turabian StyleParedes-Quiroz, Luis R., Hermógenes Ccasani-Dávalos, Dagnith L. Bejarano-Luján, Ruth M. Ccopa-Flores, and Franklin Lozano. 2025. "Efficiency of a DAF System in Removing Organic Matter and Lipid Compounds from Municipal Effluent" Water 17, no. 24: 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243474
APA StyleParedes-Quiroz, L. R., Ccasani-Dávalos, H., Bejarano-Luján, D. L., Ccopa-Flores, R. M., & Lozano, F. (2025). Efficiency of a DAF System in Removing Organic Matter and Lipid Compounds from Municipal Effluent. Water, 17(24), 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243474







