Spatiotemporal Variations and Driving Factors of Water Hardness in Drinking-Water Sources in Taihu Lake (2011–2023)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
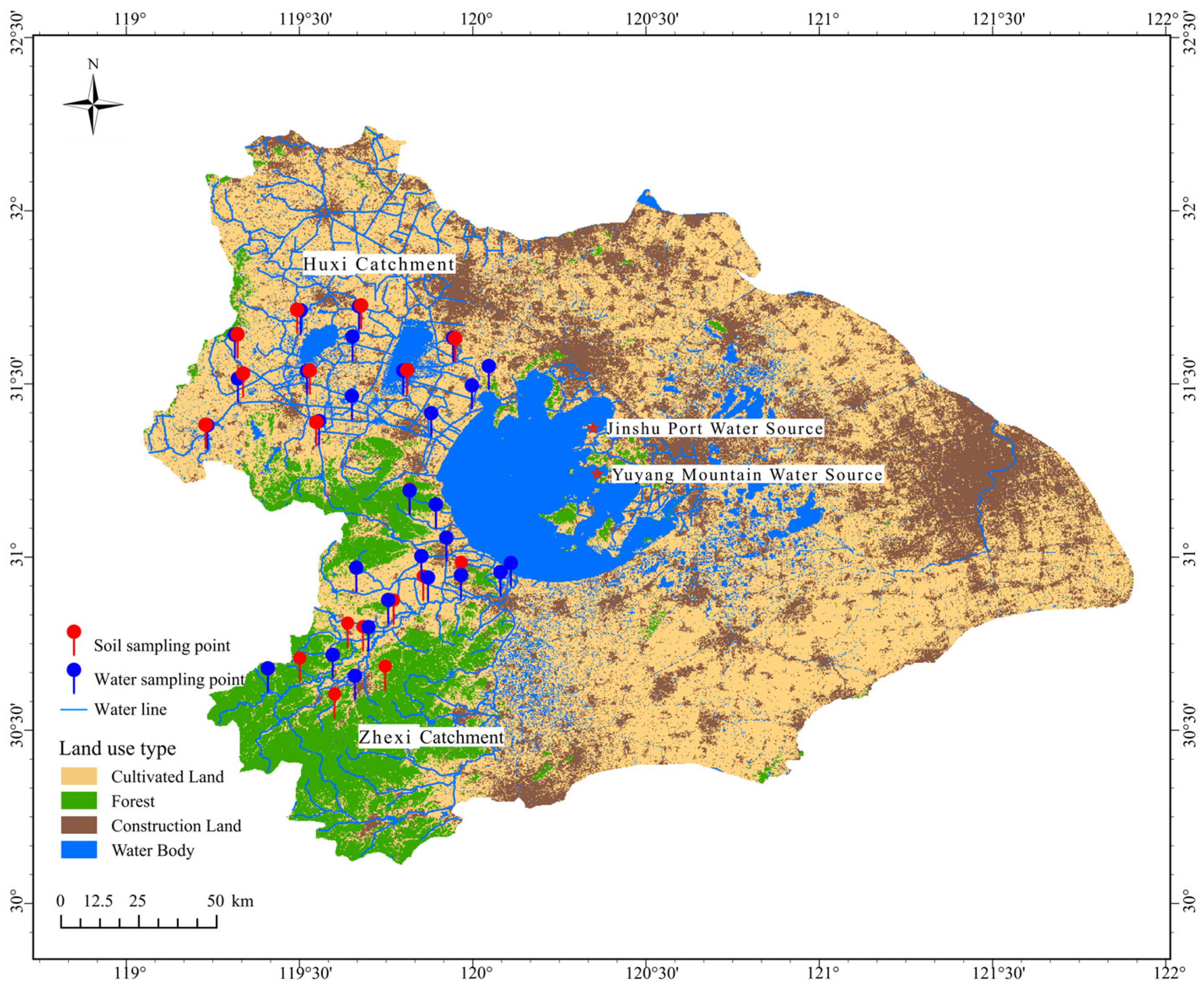
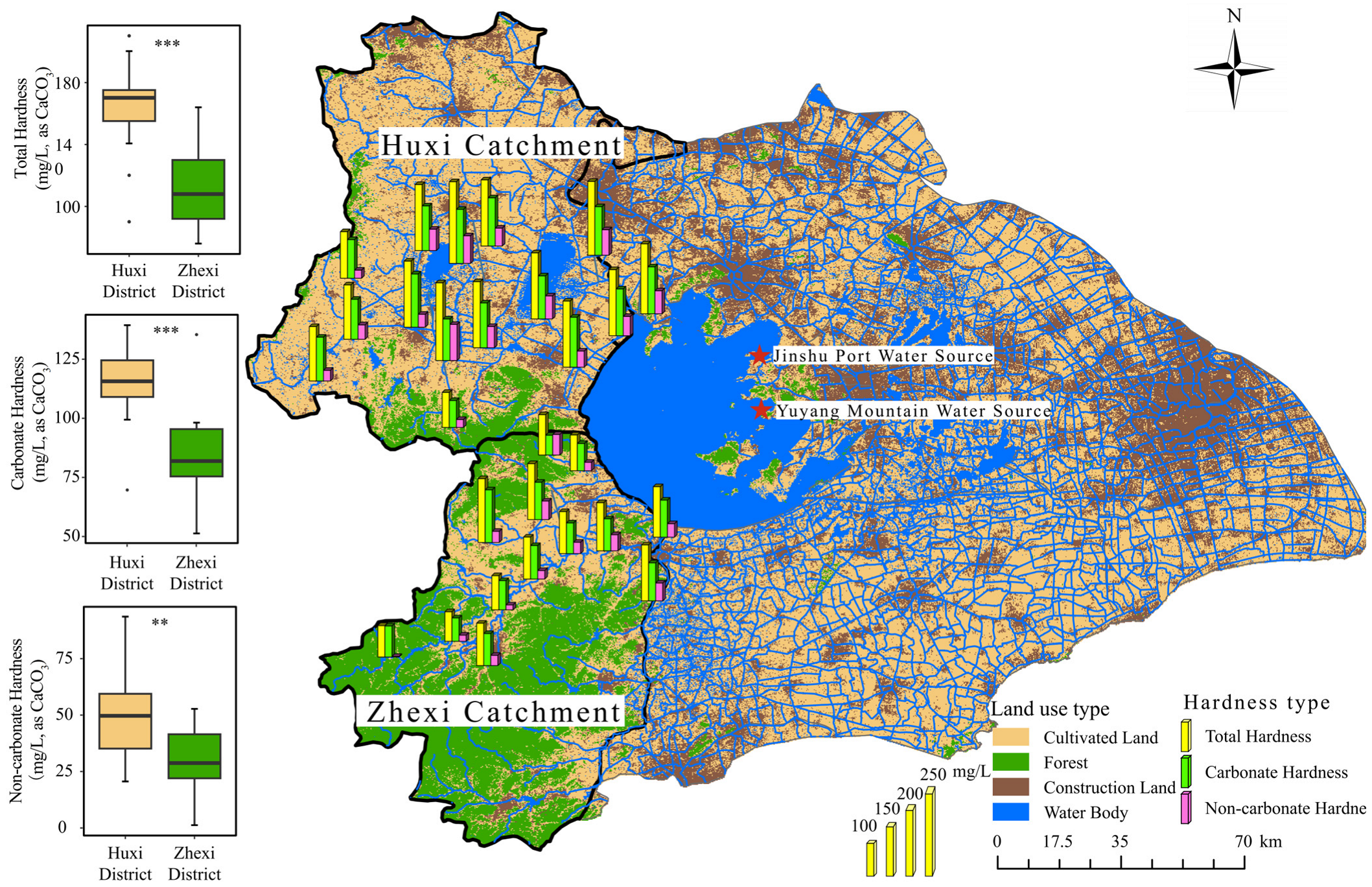
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Historical Data Collection and Sample Collection
2.3. Analytical Testing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
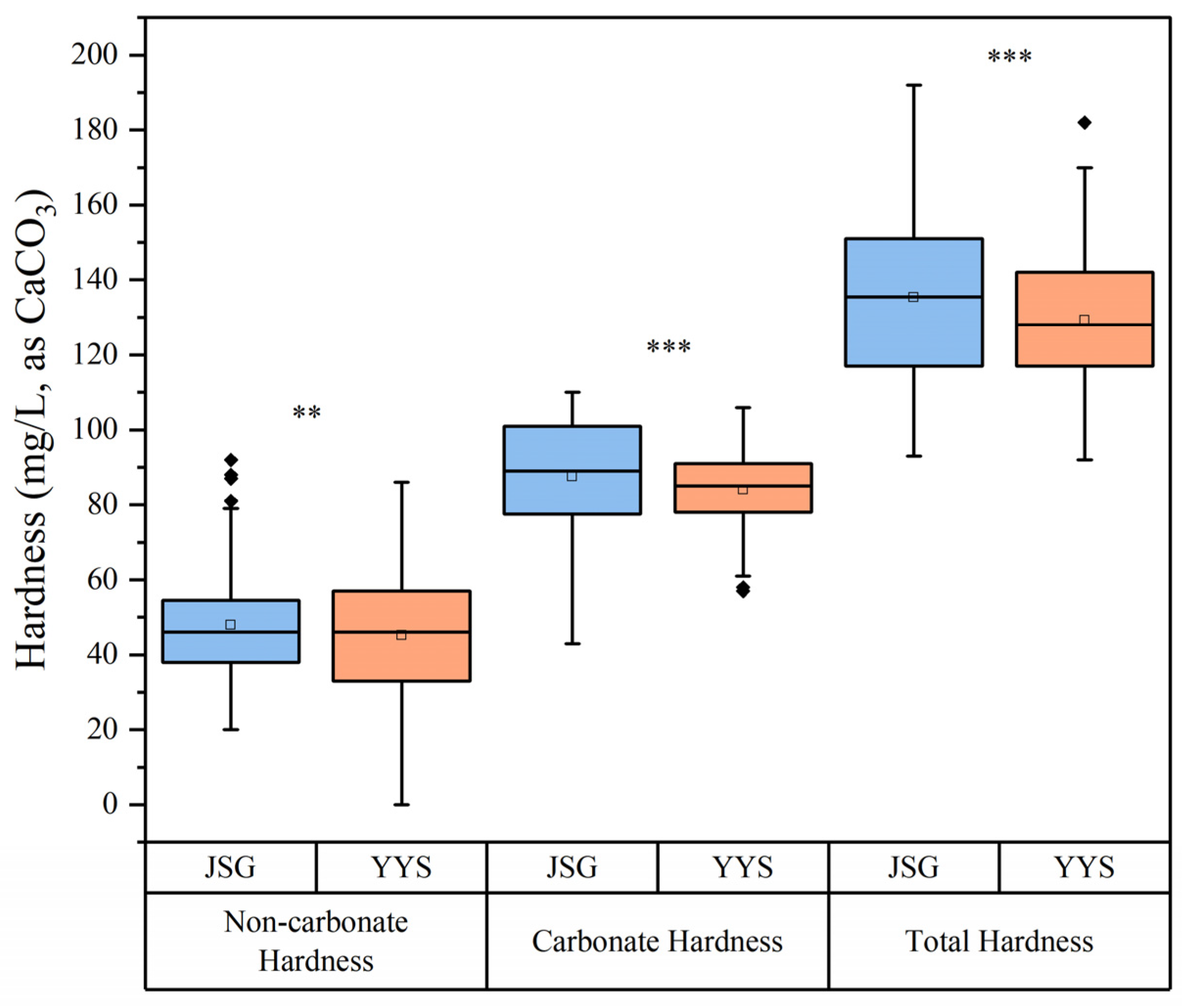
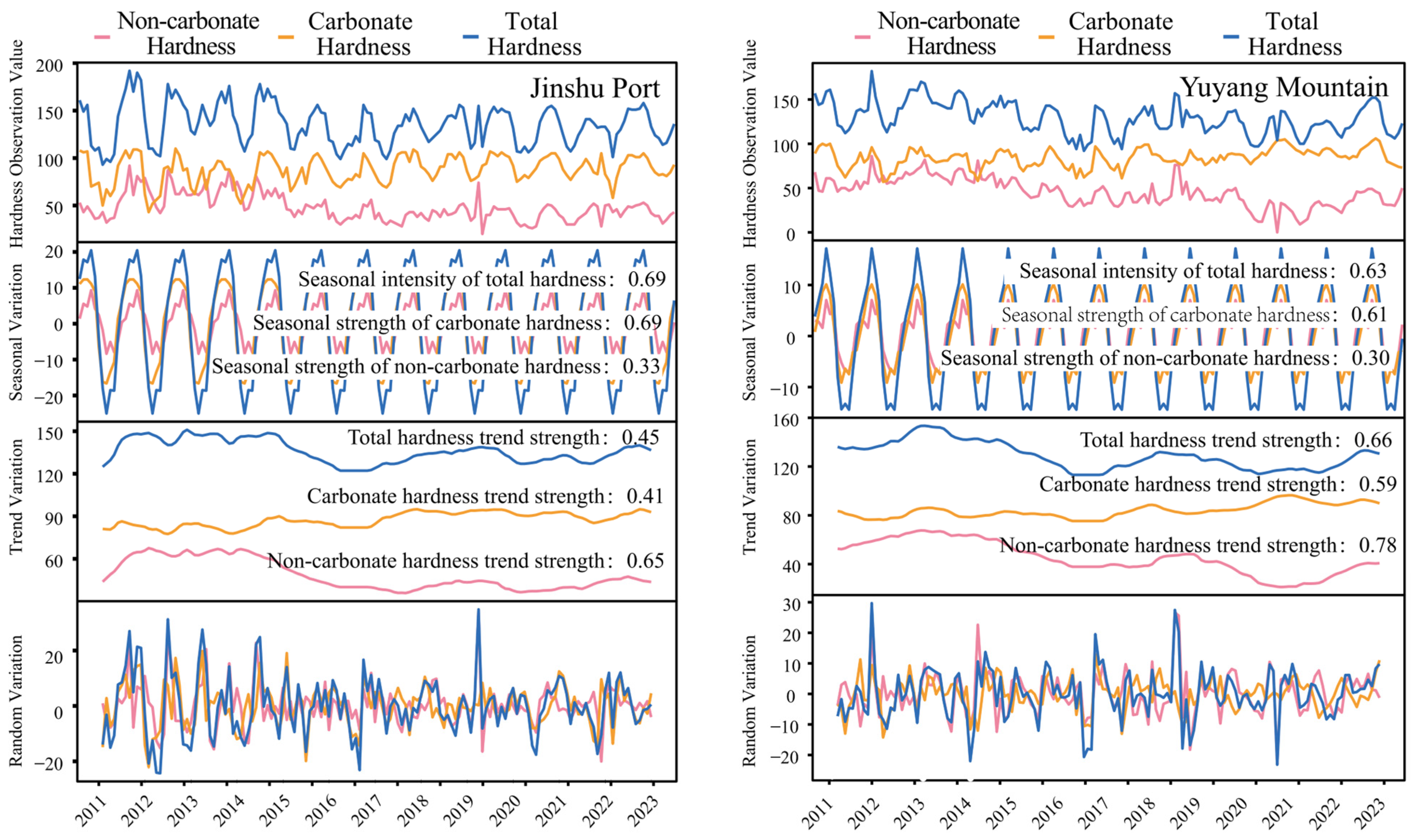
3.1. Variation Characteristics of the Water Hardness in the JP and YM Water Sources
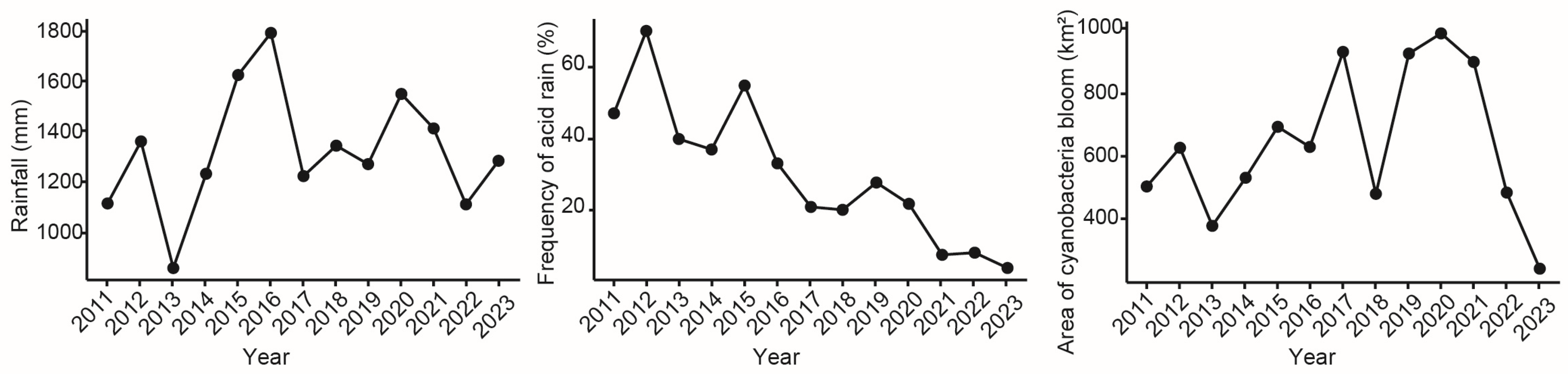
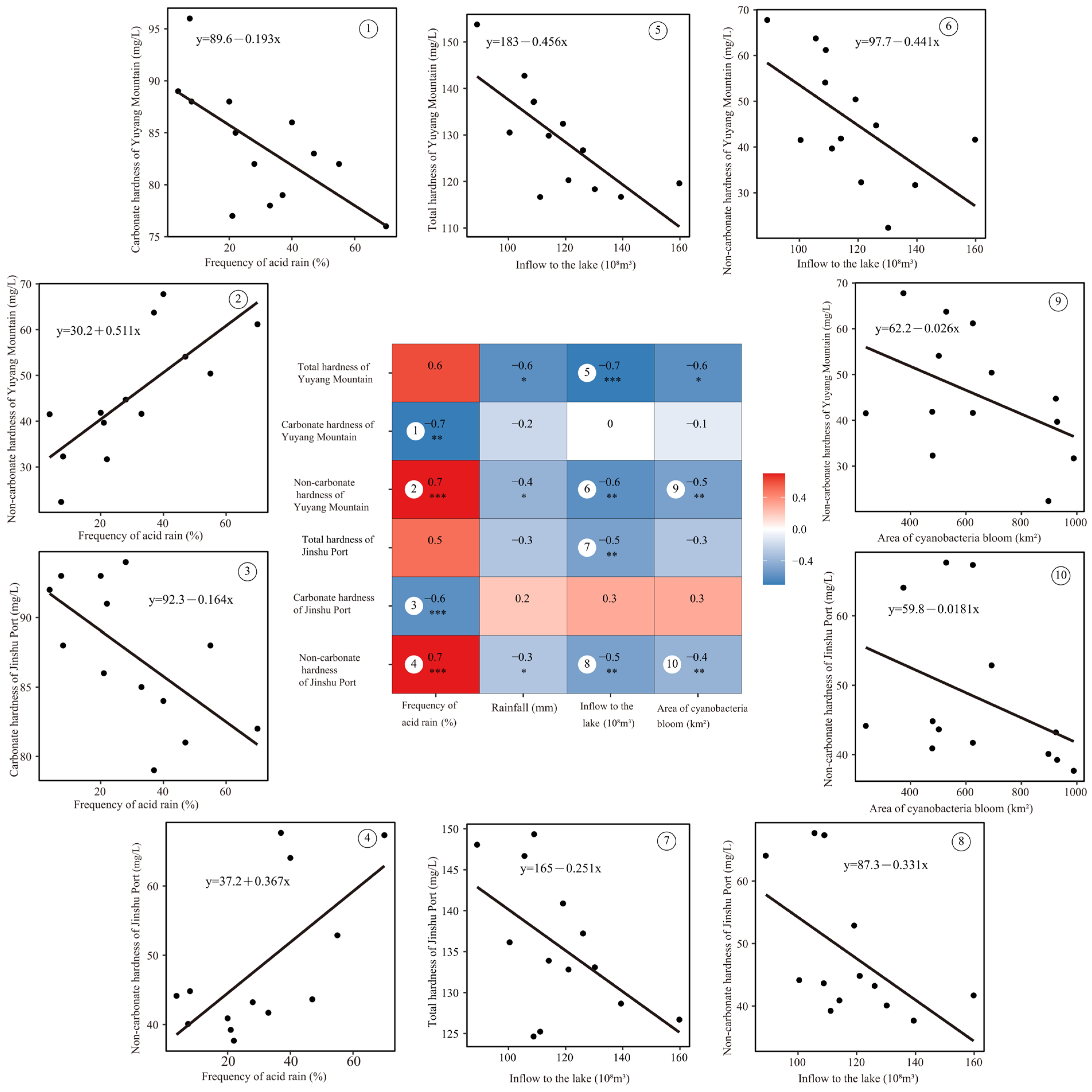
3.2. Correlation Analysis Between Water Hardness and Environmental Factors
3.3. Hardness Distribution Characteristics of Major Inflow Rivers to Taihu Lake
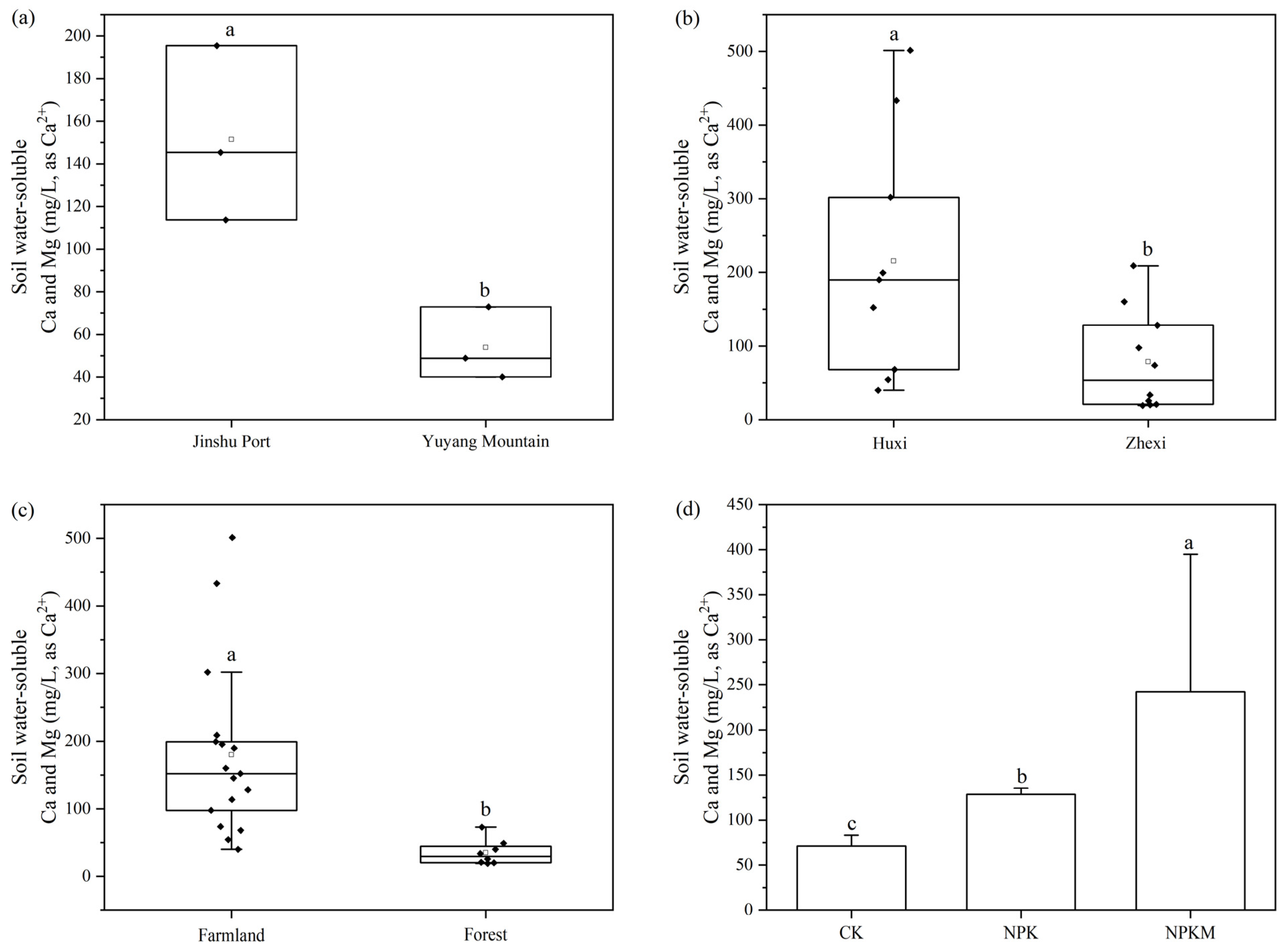
3.4. Soil Water-Soluble Calcium and Magnesium Under Different Land Use Types
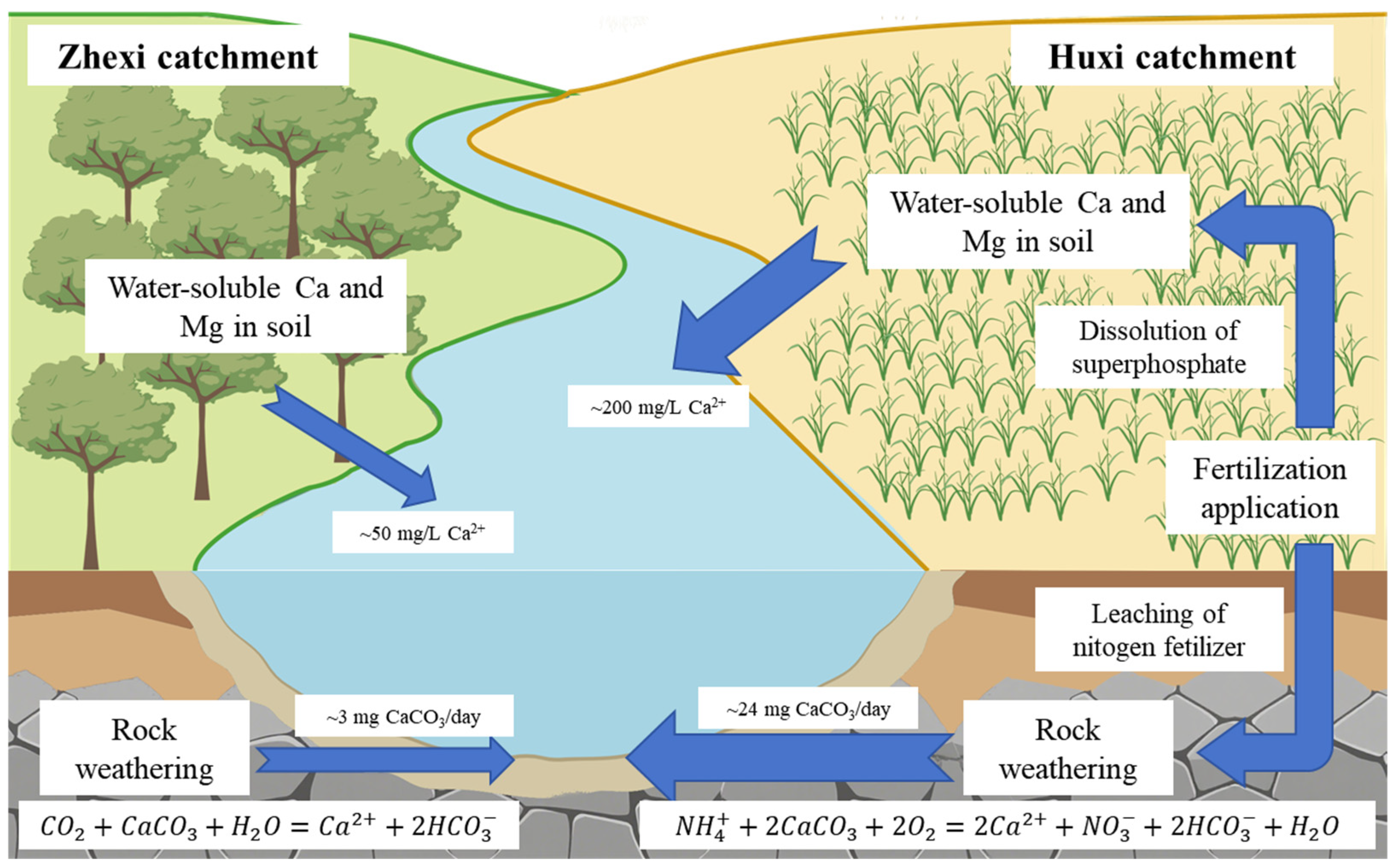
3.5. Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer Application on Carbonate Rock Dissolution
4. Discussion
4.1. The Variation Characteristics of Water Hardness
4.2. The Influencing Factors of Water Hardness
4.3. The Effects of Land Use Types on Water Hardness
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EPS | Extracellular polymeric substances |
| JP | Jinshu Port |
| YM | Yuyang Mountain |
References
- Morr, S.; Cuartas, E.; Alwattar, B.; Lane, J.M. How Much Calcium is in your Drinking Water? A Survey of Calcium Concentrations in Bottled and Tap Water and Their Significance for Medical Treatment and Drug Administration. HSS J. ®: Musculoskelet. J. Hosp. Spec. Surg. 2006, 2, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Lu, T.; Xiong, S.; Ferrer, A.S.N.; Wang, Y. Calcium and magnesium in China’s public drinking water and their daily estimated average requirements. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 3447–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, P. Potential Health Impacts of Hard Water. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubis, M. Relation of water hardness to the occurrence of acute myocardial infarct. Acta Univ. Palacki. Olomuc. Fac. Medicae 1985, 111, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Mu, W.; Deng, X.; Shen, C.; Han, L.; Ran, J. Water quality and neurodegenerative disease risk in the middle-aged and elderly population. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 289, 117647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhong, Y.; Meng, X.; Yi, C.; Wang, F.; Li, J. Associations between domestic hard water exposure and incident psoriasis in adults: Insights from the UK Biobank cohort study. J. Autoimmun. 2025, 151, 103373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, R.S.; Khangarot, B.S. Effects of Water Hardness and Metal Concentration on a Freshwater Tubifex tubifex Muller. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 142, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lv, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Jiang, H. Electrolyte Cations Binding with Extracellular Polymeric Substances Enhanced Microcystis Aggregation: Implication for Microcystis Bloom Formation in Eutrophic Freshwater Lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9034–9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Xia, X. Geochemistry of water quality of the Yangtze River basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2006, 13, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L. Analysis of Total Hardness of Drinking Water in Changzhou City. Jiangsu J. Prev. Med. 1995, 1, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, K.; Zhang, J. Analysis of evolution tendency of surface water quality in the Yangtze River Basin. Yangtze River 2008, 39, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Effect of Watershed Acidification on Calcium and Magnesium (Hardness) in Taihu Lake. Master’s Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis analysis of main ions in Zhangjiachong small watershed. Hydraul. Sci. Technol. 2019, 2, 21–25+28. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Xia, Y.; Ti, C.; Shan, J.; Wu, Y.; Yan, X. Thirty years of experience in water pollution control in Taihu Lake: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, D.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Feng, S.; Yu, T. Impact of sewage discharge on the water chemistry of Lake Taihu. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2015, 35, 3121–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Dai, X.; Fan, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G. Cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Taihu: Temporal trends and potential drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 942, 173684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Smith, K.; Hyndman, R. Characteristic-Based Clustering for Time Series Data. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2006, 13, 335–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Wan, J.; Cheng, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X. Study on Hydrochemical Characteristics and Interactions between Groundwater and Surface Water in the Dongting Lake Plain. Water 2024, 16, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhou, W. Spatiotemporal variations of hydrochemistry parameters in the Poyang lake catchment. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2014, 23, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Chetelat, B.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Wang, Q.L.; Li, S.L.; Li, J.; Wang, B.L. Geochemistry of the dissolved load of the Changjiang Basin rivers: Anthropogenic impacts and chemical weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4254–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Dreybrodt, W.; Liu, H. Atmospheric CO2 sink: Silicate weathering or carbonate weathering. Quat. Sci. 2011, 31, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Tao, Z.; Gao, Q.; Peng, H.; Zhou, M. Chemical Weathering and Riverine Carbonate System Driven by Human Activities in a Subtropical Karst Basin, South China. Water 2018, 10, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytsyura, L.; Szczepanik-Scislo, N.; Desyatnyuk, O.; Shakhovska, N.; Scislo, L.; Sachenko, A.; Lototska, O.; Shevchuk, I.; Sofinska, O. Research on Surface Water State for Rivers in Western Ukraine Using Time Series Forecasting Methods. Water 2025, 17, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Mujalli, G.; Hartmann, J.; Börker, J. Temperature and CO2 dependency of global carbonate weathering fluxes—Implications for future carbonate weathering research. Chem. Geol. 2019, 527, 118874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Liu, Z.; Kaufmann, G. Sensitivity of the global carbonate weathering carbon-sink flux to climate and land-use changes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Fan, Y.; Long, Y.; Pang, Z. Quantitative calculation for the contribution of acid rain to carbonate weathering. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, S.; Jiang, P.; Sun, P.a. Water Chemical Characteristics and Influence of Exogenous Acids in the Yangtze River Basin. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 4687–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, D.; Tao, Y.; Yixiang, D.; Fuhong, S.; Jian, Z.; Chengda, H. Acid deposition induced base cation loss and different responses of soils and sediments in Taihu Lake watershed, China. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamérand, C.; Shirokova, L.S.; Bénézeth, P.; Rols, J.-L.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Carbon sequestration potential of Mg carbonate and silicate biomineralization in the presence of cyanobacterium Synechococcus. Chem. Geol. 2022, 599, 120854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Dan, D.; Chengda, H.; Qiujin, X.; Fengchang, W. Response of sediment calcium and magnesium species to the regional acid deposition in eutrophic Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 22489–22499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhonghua, C.; Yan, Z.; Xiaoke, Z.; Gaoying, X.; Tao, Y. Shift of major driver for chemical weathering from the natural control to human dominance since 1980s in the Taihu watershed, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 20558–20569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yu, M.; He, X.; Luo, Y. Pollution Characteristics Analysis in Shallow Groundwater of Typical Farmland Area, Southern China. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 4680–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.T.; Raymond, P.A. The contribution of agricultural and urban activities to inorganic carbon fluxes within temperate watersheds. Chem. Geol. 2009, 266, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, M.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Hu, T. Spatiotemporal Variations and Driving Factors of Water Hardness in Drinking-Water Sources in Taihu Lake (2011–2023). Water 2025, 17, 3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17233415
Xu H, Wang Y, Li X, Zhou X, Xia X, Zhang Y, Guo M, Li X, Li D, Hu T. Spatiotemporal Variations and Driving Factors of Water Hardness in Drinking-Water Sources in Taihu Lake (2011–2023). Water. 2025; 17(23):3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17233415
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hang, Yiqi Wang, Xinhua Li, Xun Zhou, Xingyu Xia, Yanhui Zhang, Micheng Guo, Xiaonuo Li, Danping Li, and Tianlong Hu. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Variations and Driving Factors of Water Hardness in Drinking-Water Sources in Taihu Lake (2011–2023)" Water 17, no. 23: 3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17233415
APA StyleXu, H., Wang, Y., Li, X., Zhou, X., Xia, X., Zhang, Y., Guo, M., Li, X., Li, D., & Hu, T. (2025). Spatiotemporal Variations and Driving Factors of Water Hardness in Drinking-Water Sources in Taihu Lake (2011–2023). Water, 17(23), 3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17233415





