Hydrogeochemical Characterization, Processes, and Water Quality Assessment of Groundwater in an Agricultural Reclamation Area of the Sanjiang Plain, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Entropy-Weighted Water Quality Index (EWQI)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Hydrogeochemical Characteristics
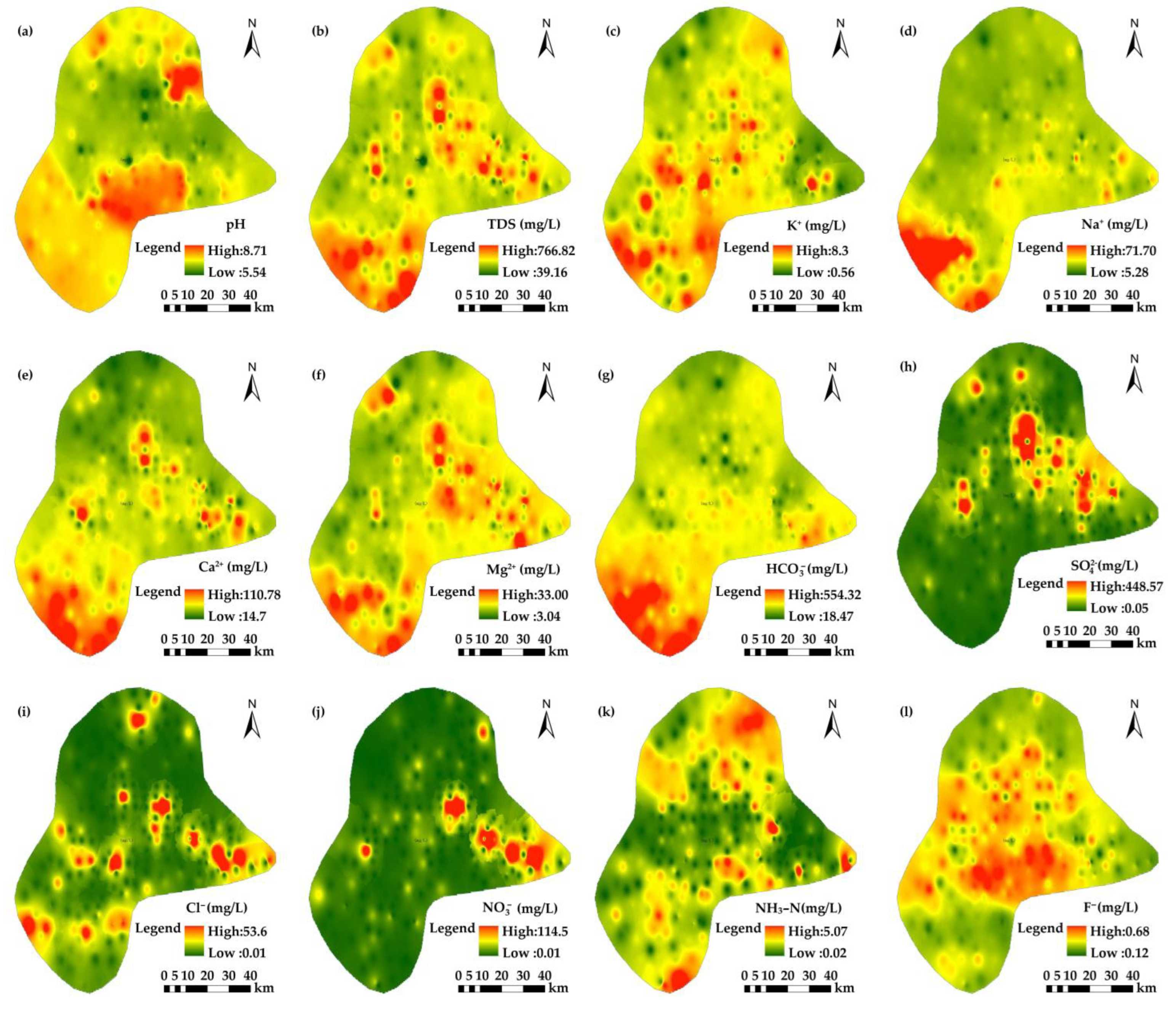
3.1.1. Chemical Composition Characteristics of Groundwater
3.1.2. Hydrochemical Type
3.1.3. Relationship Between Chemical Indexes
3.2. Control Factors of Groundwater Hydrochemistry
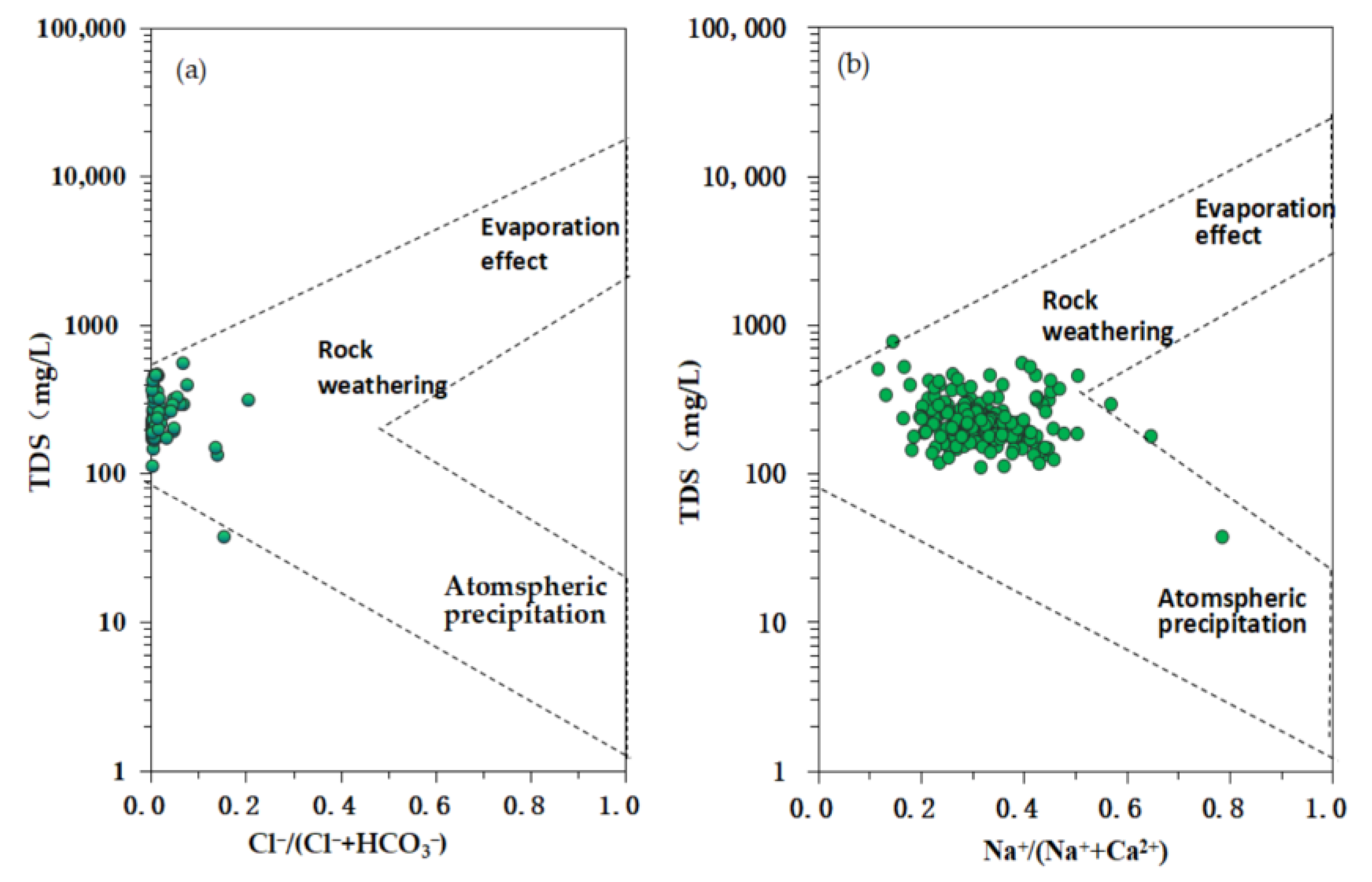
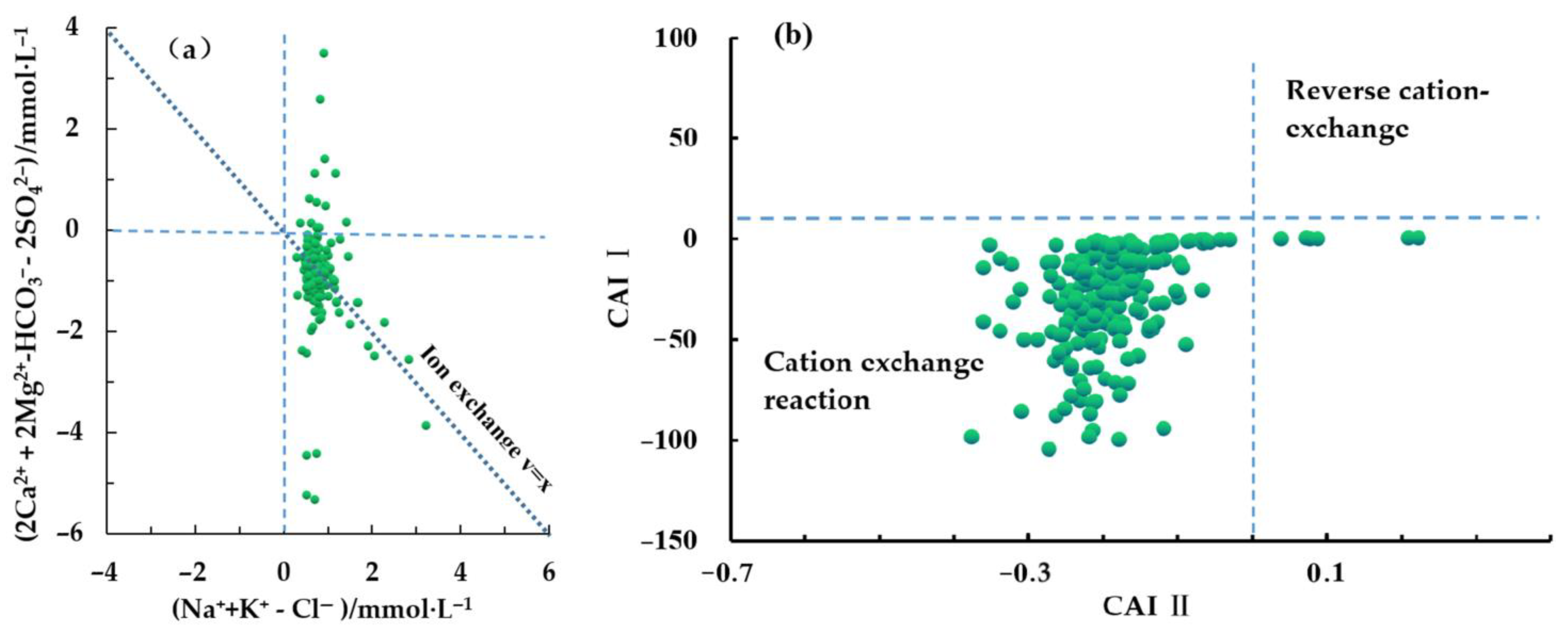
3.2.1. Natural Factors
3.2.2. Human Activity Input
3.3. Groundwater Quality
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dass, B.; Rao, M.S.; Sen, S. Hydrogeochemical characterization and water quality assessment of mountain springs: Insights for strategizing water management in the lesser Indian Himalayas. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Du, Y.; Xu, J.; Tian, H.; Deng, Y.; Gan, Y.; Wang, Y. Control of groundwater-lake interaction zone structure on spatial variability of lacustrine groundwater discharge in oxbow lake. Water Resour. Res. 2025, 61, e2024WR039334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W.M.; Healy, R.W.; LaBaugh, J.W.; Reilly, T.E. Hydrology—Flow and storage in groundwater systems. Science 2002, 296, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Fakhreddine, S.; Rateb, A.; de Graaf, I.; Famiglietti, J.; Gleeson, T.; Grafton, R.Q.; Jobbagy, E.; Kebede, S.; Kolusu, S.R.; et al. Global water resources and the role of groundwater in a resilient water future. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, F.; Lamontagne, J.; Link, R.; Hejazi, M.; Reed, P.; Edmonds, J. Evaluating the economic impact of water scarcity in a changing world. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Paul, S.K. Groundwater quality assessment and health issues in coastal zone of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 10, 100278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Wang, J. Insights into groundwater salinization from hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence in an arid inland basin. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 3108–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panday, D.P.; Kumari, A.; Kumar, M. Alkalinity-salinity-sustainability: Decadal groundwater trends and its impact on agricultural water quality in the Indian Peninsula. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 978, 179459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, B.; Shu, L. Mechanisms of evolution and pollution source identification in groundwater quality of the Fen River Basin driven by precipitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Shaw, S.; Hoffmann, R. Assessing groundwater quality and its association with child undernutrition in India. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 943, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, S. Characterization of the hydrochemistry of water resources of the Weibei Plain, Northern China, as well as an assessment of the risk of high groundwater nitrate levels to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Rahman, A.; Asefa, E.M.; Parveen, M.; Uddin, M.R. Assessing spatial distribution of heavy metal contamination in groundwater and associated human health risk in the Chittagong industrial area, Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 18, 100728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Zhou, J. Hydrochemical evolution characteristics, controlling factors, and high nitrate hazards of shallow groundwater in a typical agricultural area of Nansi lake basin, north China. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugulothu, S.; Rao, N.S.; Das, R.; Duvva, L.K.; Dhakate, R. Judging the sources of inferior groundwater quality and health risk problems through intake of groundwater nitrate and fluoride from a rural part of Telangana, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 32, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Pei, Q. Groundwater chemistry, quality and potential health risk appraisal of nitrate enriched groundwater in the Nanchong area, southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Li, X.; Cui, J.; Yang, Z. A Preliminary Study on The Organic and Inorganic Pollution of Groundwater of Jiansanjiang Farm of Sanjiang Plain. Geol. Resour. 2014, 23, 38–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.-Q.; Nakagawa, K.; Berndtsson, R.; Hiraoka, T.; Suzuki, Y. Groundwater nitrogen response to regional land-use management in South Japan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tang, C.; Song, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Identifying the hydrochemical characteristics of rivers and groundwater by multivariate statistical analysis in the Sanjiang Plain, China. Appl. Water Sci. 2016, 6, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Yang, T.; Li, J.; Chen, Y. Distribution Characteristics and Genesis of Iron and Manganese Ions in Groundwater of Eastern Sanjiang Plain, China. Water 2023, 15, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, P.; He, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Xia, S. Hydrochemical Characteristics, Water Quality, and Evolution of Groundwater in Northeast China. Water 2023, 15, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dai, C.; Jing, J.; Liu, G.; Ru, Q.; Li, J.; LIU, P. Study on the relationship between surface water and groundwater transformation in the middle and lower reaches of songhua river basin. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J. Spatiotemporal groundwater recharge estimation for the largest rice production region in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua. 2014, 63, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J.; Sun, G. Identifying the regional-scale groundwater-surface water interaction on the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 16951–16961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, T.; Li, T.; Li, H. Temporal-spatial evolution patterns of the annual precipitation considering the climate change conditions in the Sanjiang Plain. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2016, 7, jwc2015012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, Y.; Du, X. Hydrochemical Evolution and Quality Assessment of Groundwater in the Sanjiang Plain, China. Water 2022, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, Y.; Shao-Min, D.U.; Wei-Qing, Y.; Wei, Z.; Shu-You, S.; Yang, G. Status Overdraft of Groundwater on Sanjiang Plain (2). J. Heilongjiang Hydraul. Eng. Coll. 2008, 35, 18–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Z.; Shu, L.; Wang, D.; Lu, C.; Liu, B. Assessment and projection of the groundwater drought vulnerability under different climate scenarios and land use changes in the Sanjiang Plain, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 49, 101498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Tang, C.; Yang, L.; WANG, Z.; LIU, T. A study of the interrelation between surface water and groundwater using isotopes and chlorofluorocarbons in Sanjiang plain, Northeast China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 3901–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ164-2020; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Technical Specifications for Environmental Monitoring of Groundwater. China Environment Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese)
- GB5750-2006; Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. China National Standardization Administration. Sanitary Standard Test Method for Drinking Water. Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese)
- Adimalla, N. Application of the Entropy Weighted Water Quality Index (EWQI) and the Pollution Index of Groundwater (PIG) to Assess Groundwater Quality for Drinking Purposes: A Case Study in a Rural Area of Telangana State, India. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.T.; Gao, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Sun, Z.B.; Sun, T.Z.; Fan, H.B.; Wu, B.; Li, M.B.; Qian, L.L. Hydrochemical evaluation of groundwater quality and human health risk assessment of nitrate in the largest peninsula of China based on high-density sampling: A case study of Weifang. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 129164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskooni, E.K.; Naseri-Rad, M.; Berndtsson, R.; Nakagawa, K. Use of Heavy Metal Content and Modified Water Quality Index to Assess Groundwater Quality in a Semiarid Area. Water 2020, 12, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; ISBN 978-92-4-154815-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lahjouj, A.; Hmaidi, A.E.; Achtak, H.; Nakhcha, C.; Bouhafa, K. Hydrogeochemical characterization and human health risks associated with groundwater nitrate concentrations in the Saiss basin, Morocco. HydroResearch 2025, 8, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiklomanov, I.A. Ground-Water Classification Based on Chemical Composition and Total Dissolved Solids. In Hydrology and Water Resources: A Global Perspective; Gordon & Breach Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Malov, A.I. The Conditions for the Formation of Strontium in the Water of Ancient Silicate Deposits Near the Arctic Coast of Russia. Water 2024, 16, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilongjiang Geological Survey Institute. Geological Map of Heilongjiang Province. Scale 1:500,000.; Heilongjiang Geological Survey Institute: Harbin, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Li, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, F.; Liu, G. Hydrochemistry of waters in snowpacks, lakes and streams of Mt. Dagu, eastern of Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 610–611, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Niu, F.; Gao, Z. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and processes of thermokarst lake and groundwater during the melting of the active layer in a permafrost region of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, H.; Shahryari, A. Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking, irrigation, and industrial purposes using water quality indices and GIS technique in Gorgan aquifer. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Qian, H.; Zhou, Y.H.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.K.; Ren, W.H.; Qu, W.G. Cumulative health risk assessment of multiple chemicals in groundwater based on deterministic and Monte Carlo models in a large semiarid basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 352, 131567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupre, B.; Louvat, P.; Allegre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.B.; Wu, J.L.; Zhan, S.E.; Jin, M.; Saparov, A.S.; Abuduwaili, J. Spatial variations and controls on the hydrochemistry of surface waters across the Ili-Balkhash Basin, arid Central Asia. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H.; Nandan, M.J. Groundwater chemistry integrating the pollution index of groundwater and evaluation of potential human health risk: A case study from hard rock terrain of South India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Miao, J.; Hu, B.X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Z. Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality assessment in intruded coastal brine aquifers (Laizhou Bay, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21073–21090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argamasilla, M.; Barbera, J.A.; Andreo, B. Factors controlling groundwater salinization and hydrogeochemical processes in coastal aquifers from southern Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ye, M.; Tang, Z.; Jiao, T.; Liu, H. Using cluster analysis for understanding spatial and temporal patterns and controlling factors of groundwater geochemistry in a regional aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3: A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. In Techniques and Methods; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Cao, X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, H.; Duan, G.; Qu, J. Isotopic and chemical evidence for nitrate sources and transformation processes in a plateau lake basin in Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Ma, T.; Du, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; LUO, K. Contrastive mechanisms of groundwater ammonium enrichment in different hydrogeologic settings. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolaosho, T.L.; Mustapha, A.A.; Hundeyin, S.T. Hydrogeochemical evolution and heavy metal characterization of groundwater from southwestern, Nigeria: An integrated assessment using spatial, indexical, irrigation, chemometric, and health risk models. Heliyon 2024, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Teng, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, C. Hydrochemical analysis and quality assessment of groundwater in southeast North China plain using hydrochemical, entropy-weight water quality index, and GIS technique. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

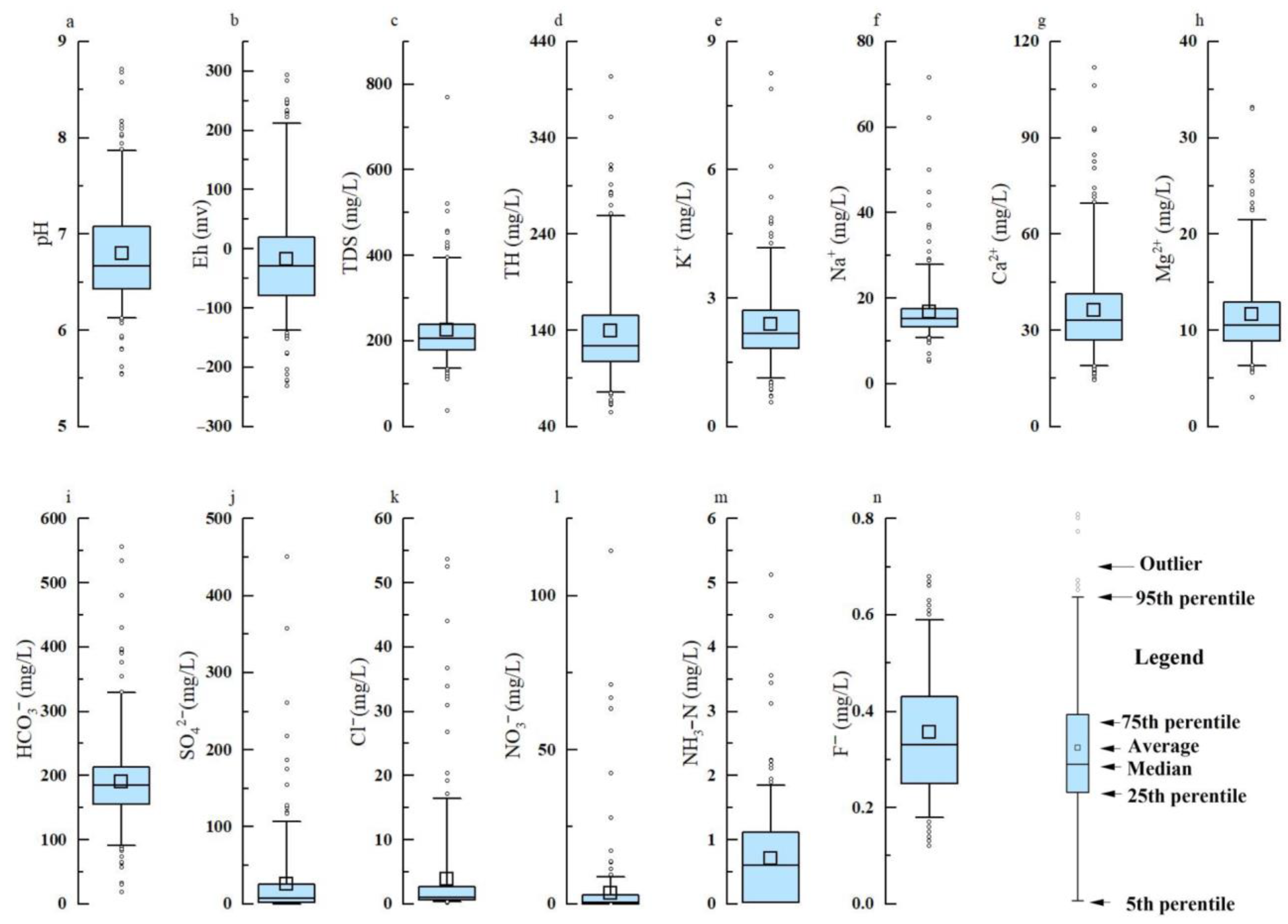






| Eh | pH | TDS | TH | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | HCO3− | SO42− | Cl− | NO3− | NH3-N | F− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | −17.8 | 6.80 | 224.1 | 139.0 | 2.4 | 16.7 | 36.3 | 11.6 | 190.5 | 25.6 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 0.7 | 0.4 |
| Median | −29.1 | 6.67 | 206.5 | 123.8 | 2.2 | 15.2 | 33.0 | 10.5 | 184.3 | 7.4 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| SD | 96.3 | 0.54 | 82.1 | 54.6 | 1.0 | 7.3 | 15.6 | 4.6 | 72.3 | 52.1 | 7.9 | 11.3 | 0.8 | 0.1 |
| Min | −231.9 | 5.54 | 37.3 | 55.2 | 0.6 | 5.3 | 14.6 | 3.0 | 17.7 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.1 |
| Max | 292.8 | 8.71 | 770.0 | 403.2 | 8.3 | 71.7 | 112.0 | 33.1 | 555.9 | 450.9 | 53.7 | 114.6 | 5.1 | 0.7 |
| CV | −5.42 | 0.08 | 0.37 | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 2.04 | 2.07 | 3.40 | 1.10 | 0.37 |
| WHO (2011) [34] | 6.5–8.5 | 1000 | 450 | - | 200 | 200 | 150 | - | 250 | 250 | 45 | 0.5 | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Wang, M. Hydrogeochemical Characterization, Processes, and Water Quality Assessment of Groundwater in an Agricultural Reclamation Area of the Sanjiang Plain, China. Water 2025, 17, 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223257
Wang M, Wang M. Hydrogeochemical Characterization, Processes, and Water Quality Assessment of Groundwater in an Agricultural Reclamation Area of the Sanjiang Plain, China. Water. 2025; 17(22):3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223257
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Min, and Mingguo Wang. 2025. "Hydrogeochemical Characterization, Processes, and Water Quality Assessment of Groundwater in an Agricultural Reclamation Area of the Sanjiang Plain, China" Water 17, no. 22: 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223257
APA StyleWang, M., & Wang, M. (2025). Hydrogeochemical Characterization, Processes, and Water Quality Assessment of Groundwater in an Agricultural Reclamation Area of the Sanjiang Plain, China. Water, 17(22), 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223257





