Source Apportionment and Potential Health Risks of Trace Metals in a Contaminated Urban River in New York/New Jersey Harbor System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
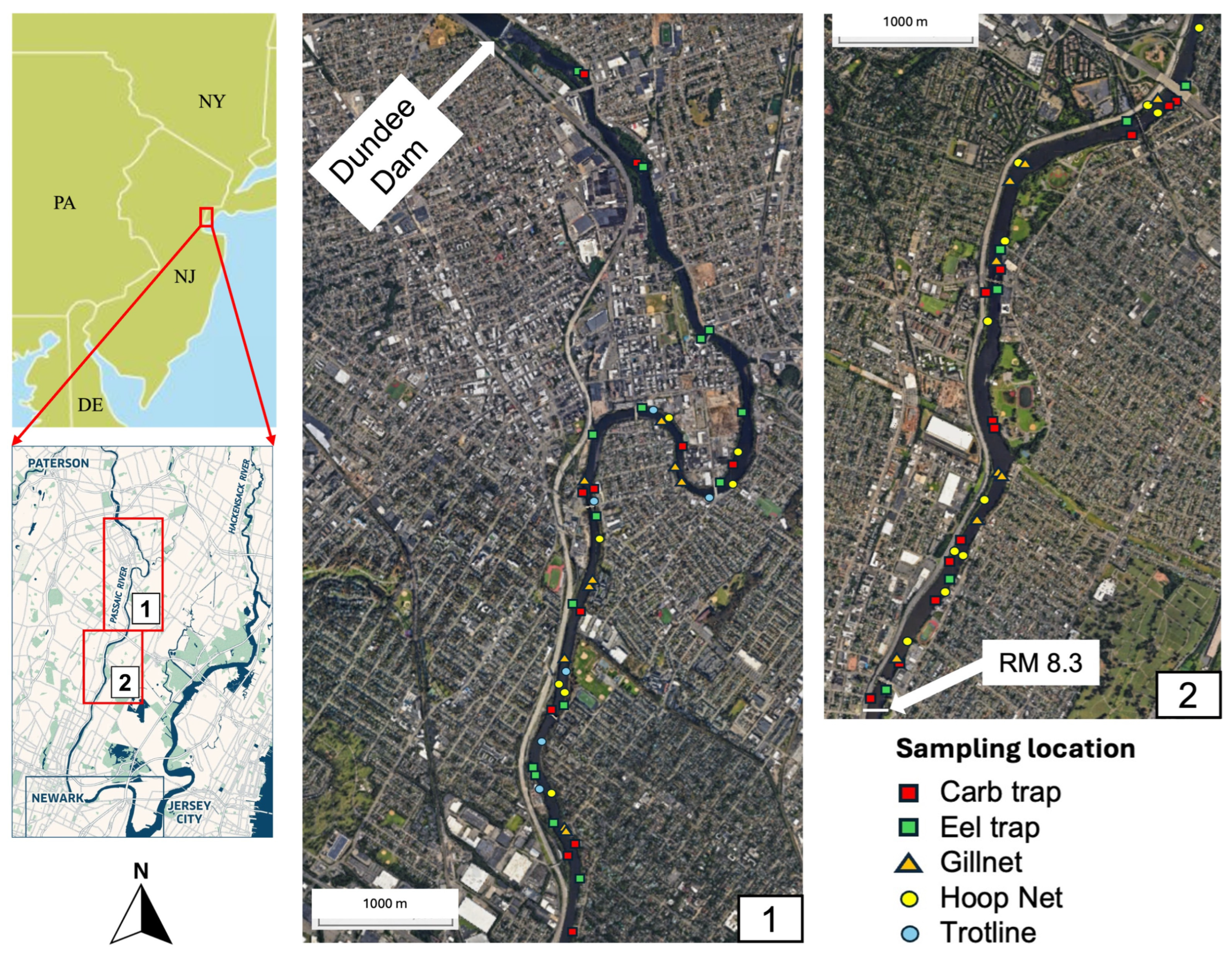
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection, Analytical Methods and Data Analysis
2.3. Water Bioaccumulation Factor (BCFW) and Sediment Bioaccumulation Factor (BCFS)
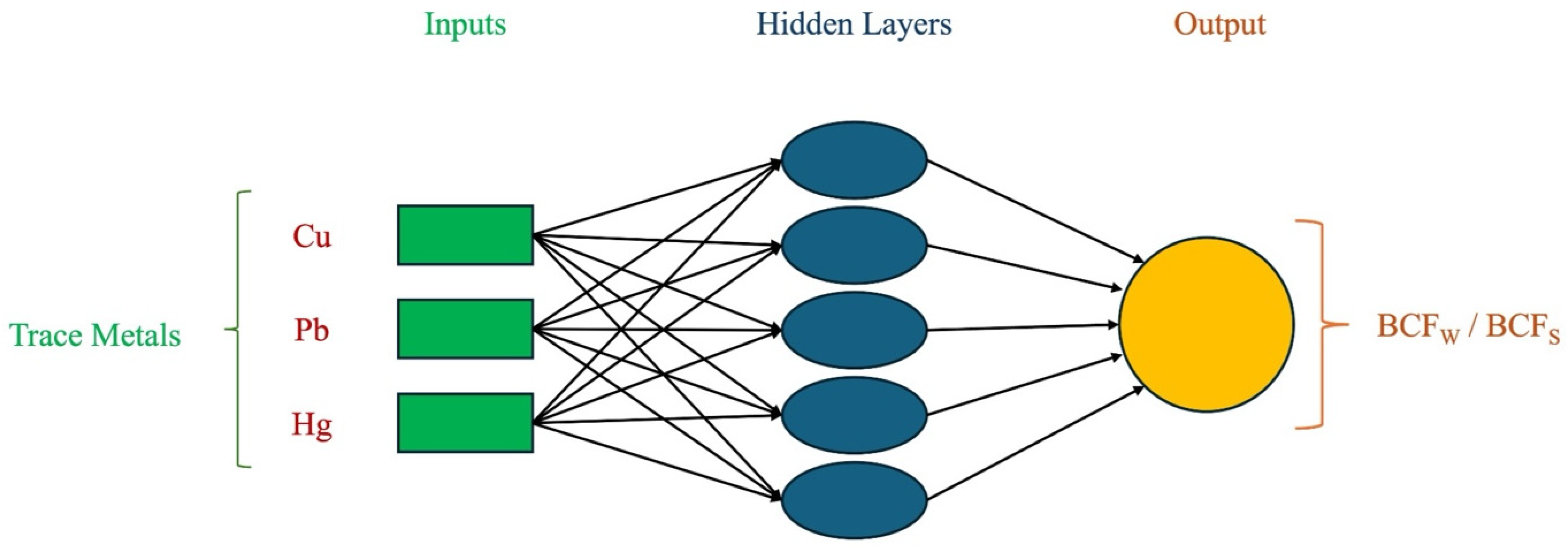
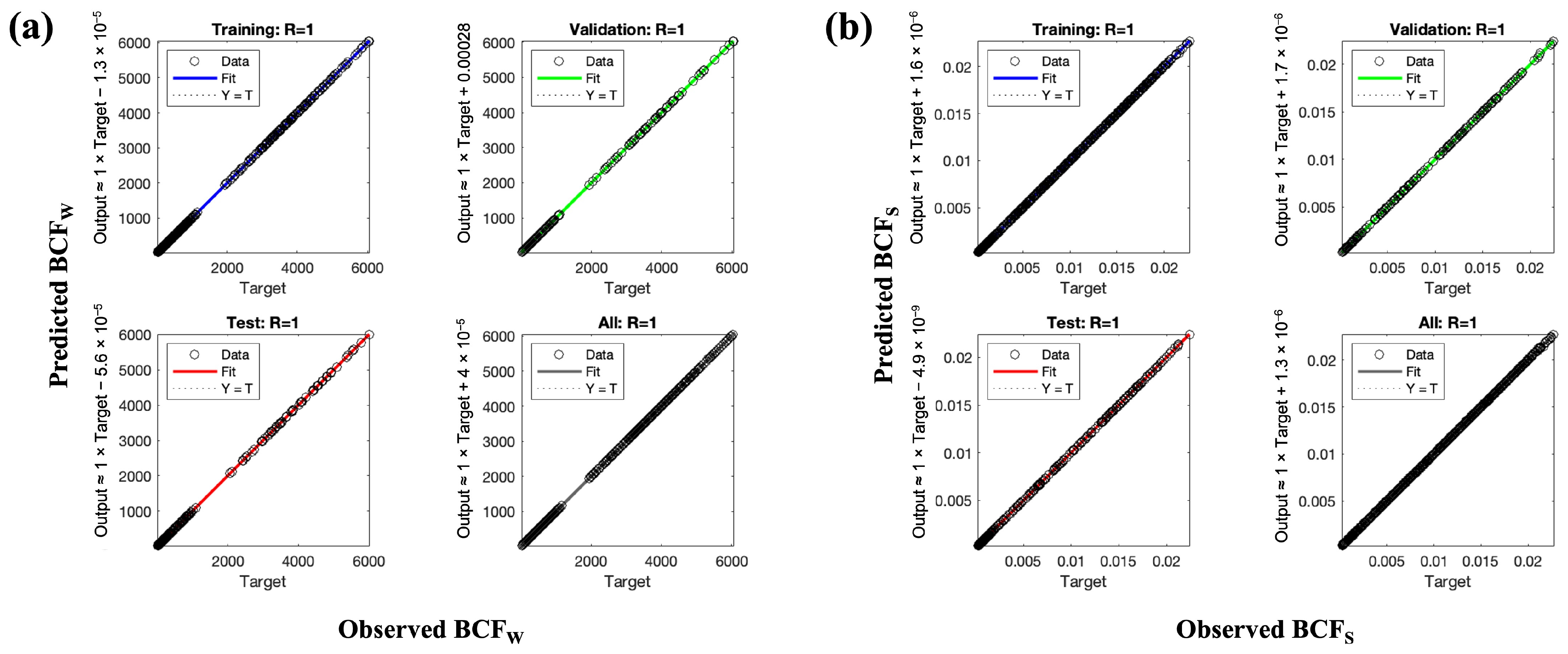
2.4. Artificial Neural Network Modeling
2.5. The Average Pollution Load Evaluation Technique
2.6. Human Health Risk Assessment Method
2.7. Monte Carlo Simulation
2.8. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF)
2.9. Analytical Workflow and Integration of Models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentrations of Trace Metals
3.2. Trace Metal Accumulation in Edible Aquatic Species
3.3. Artificial Neural Network Modeling for BCFW and BCFS
3.4. Pollution Evaluation Indices
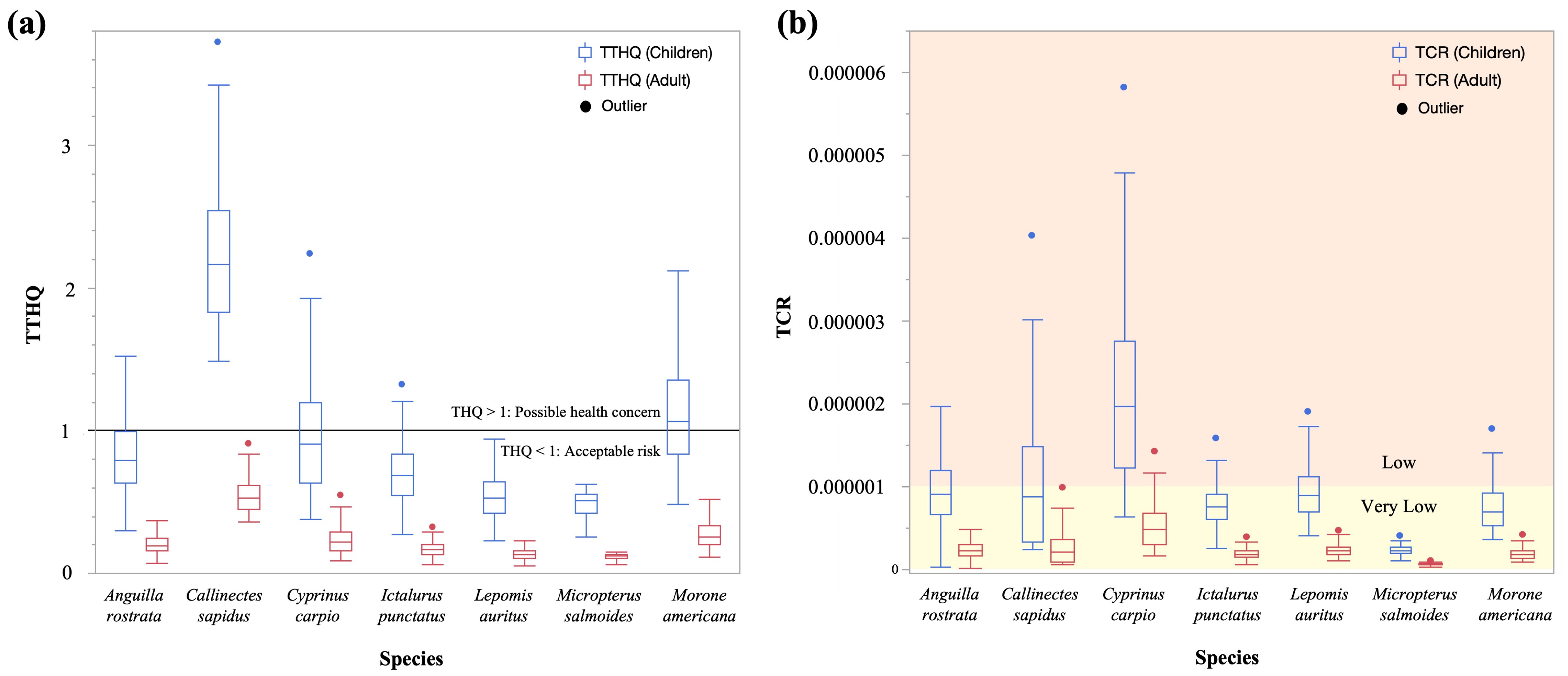
3.5. Human Health Risk Assessment
3.5.1. Estimated Daily Intake (EDI)
3.5.2. Non-Carcinogenic Risk
3.5.3. Carcinogenic Risk
3.5.4. Probabilistic Evaluation of Health Risks and Sensitivity Analysis
3.6. Multivariate Analysis
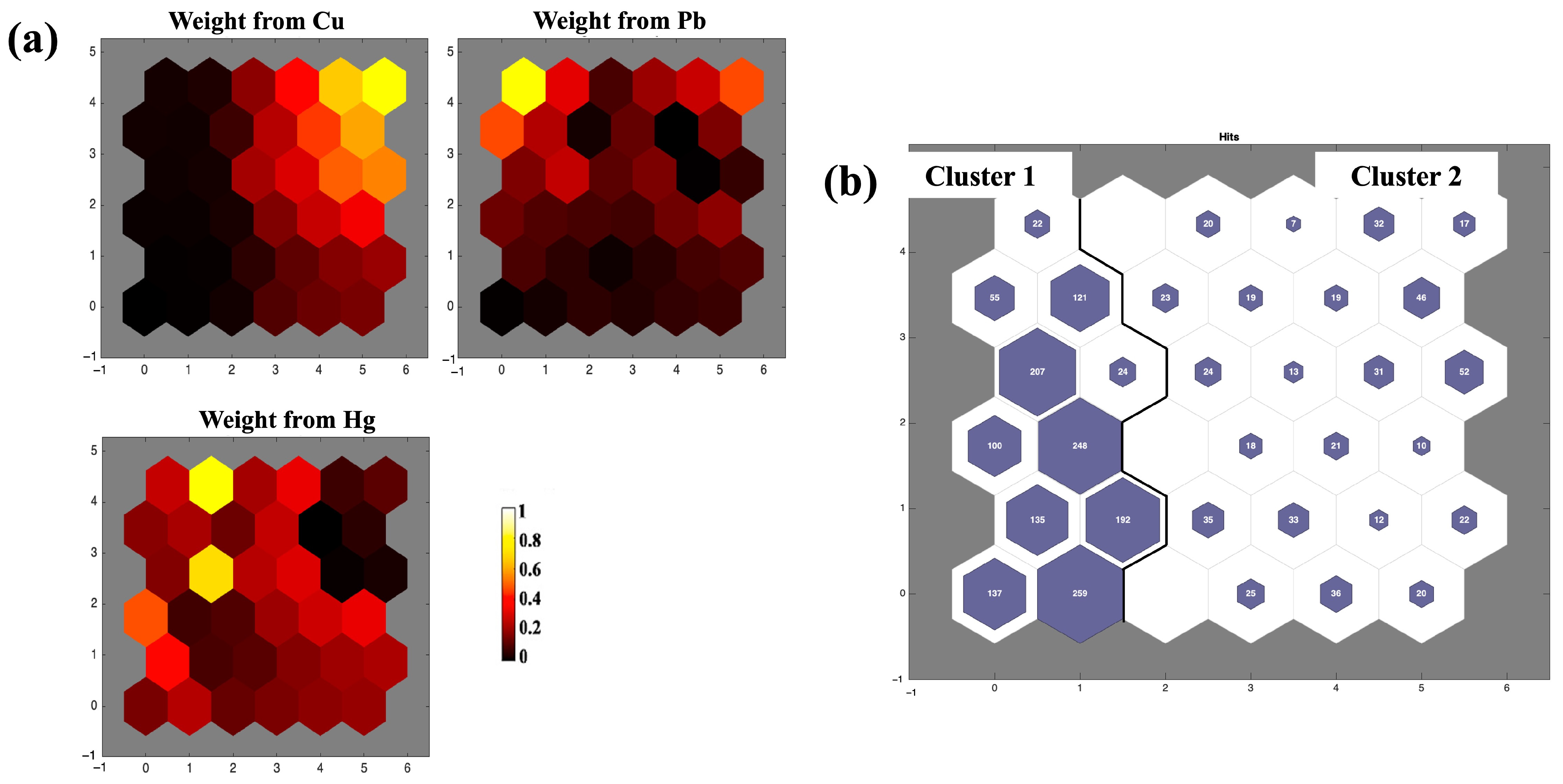
3.7. Self-Organizing Map
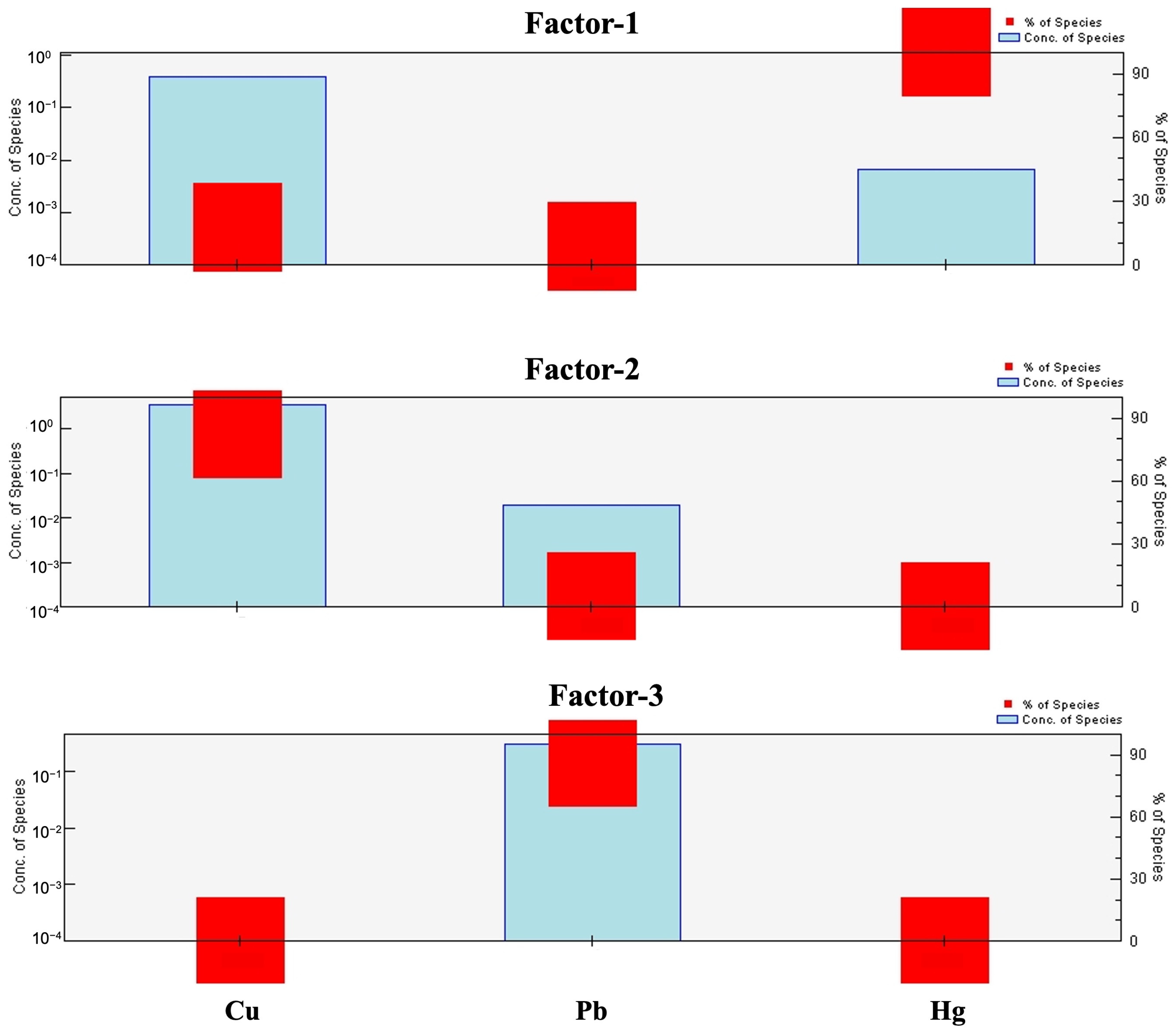
3.8. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) Model
3.9. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mansour, S.A.; Belal, M.H.; Abou-Arab, A.A.K.; Gad, M.F. Monitoring of Pesticides and Heavy Metals in Cucumber Fruits Produced from Different Farming Systems. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.; Irfan, N.M.; Khan, I.N.; Islam, S.; Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K. Presence of Heavy Metals in Fruits and Vegetables: Health Risk Implications in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S. Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediment and Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Fishes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Basin. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Islam, M.S.; Ghosh, G.C.; Ghosh, P.; Zaman, S.; Hossain, M.R.; Habib, A.; Nice, M.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, K.R.; et al. Receptor Model-Based Sources and Risks Appraisal of Potentially Toxic Elements in the Urban Soils of Bangladesh. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 10, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakir, H.M.; Quadir, Q.F.; Mollah, M.Z.I. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals Through the Consumption of Common Foodstuffs Collected from Two Divisional Cities of Bangladesh. Expo. Health 2021, 13, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.; Tarnawski, M. Assessment of Heavy Metals Mobility and Toxicity in Contaminated Sediments by Sequential Extraction and a Battery of Bioassays. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Lin, M.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Song, L.; Li, Z. Abundance and Spatial Variability of Invasive Fishes Related to Environmental Factors in a Eutrophic Yunnan Plateau Lake, Lake Dianchi, Southwestern China. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2015, 98, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revenga, J.E.; Campbell, L.M.; Arribére, M.A.; Ribeiro Guevara, S. Arsenic, Cobalt and Chromium Food Web Biodilution in a Patagonia Mountain Lake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 81, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataba, G.R.; Verhaert, V.; Blust, R.; Bervoets, L. Distribution of Trace Elements in the Aquatic Ecosystem of the Thigithe River and the Fish Labeo Victorianus in Tanzania and Possible Risks for Human Consumption. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.S.; Rahman, M.; Sultana, S.; Babu, S.M.O.F.; Sarker, M.S.I. Bioaccumulation and Heavy Metal Concentration in Tissues of Some Commercial Fishes from the Meghna River Estuary in Bangladesh and Human Health Implications. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Ghosh, G.C.; Ghosh, P.; Jahan, I.; Zaman, S.; Islam, M.S.; Hossain, M.R.; Habib, A.; Biswas, B.; Sultana, N.; et al. Arsenic, Iron, and Manganese in Groundwater and Its Associated Human Health Risk Assessment in the Rural Area of Jashore, Bangladesh. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 888–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobeille, A.K.; Morland, K.B.; Bopp, R.F.; Godbold, J.H.; Landrigan, P.J. Body Burdens of Mercury in Lower Hudson River Area Anglers. Environ. Res. 2006, 101, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M. Determination of Heavy Metals in Fish and Vegetables in Bangladesh and Health Implications. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2015, 21, 986–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Islam, M.S.; Ghosh, G.C.; Ghosh, P.; Zaman, S.; Habib, A.; Hossain, M.R.; Bosu, H.; Islam, M.R.; Imran, M.A.; et al. Human Health Risk and Hydro-Geochemical Appraisal of Groundwater in the Southwest Part of Bangladesh Using GIS, Water Quality Indices, and Multivariate Statistical Approaches. Toxin. Rev. 2023, 42, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Ghosh, G.C.; Hossain, M.R.; Islam, M.S.; Habib, A.; Zaman, S.; Bosu, H.; Nice, M.S.; Haldar, M.; Khan, A.S. Human Health Risk and Receptor Model-Oriented Sources of Heavy Metal Pollution in Commonly Consume Vegetable and Fish Species of High Ganges River Floodplain Agro-Ecological Area, Bangladesh. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.B.; Cuss, C.W.; Grant-Weaver, I.; Shotyk, W. Size-Resolved Pb Distribution in the Athabasca River Shows Snowmelt in the Bituminous Sands Region an Insignificant Source of Dissolved Pb. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, T.; Liu, Y.; Buchner, V.; Tchounwou, P.B. Neurotoxic Effects and Biomarkers of Lead Exposure: A Review. Rev. Environ. Health 2009, 24, 15–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Azevedo, B.; Barros Furieri, L.; Peçanha, F.M.; Wiggers, G.A.; Frizera Vassallo, P.; Ronacher Simões, M.; Fiorim, J.; Rossi de Batista, P.; Fioresi, M.; Rossoni, L.; et al. Toxic Effects of Mercury on the Cardiovascular and Central Nervous Systems. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 949048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, T.J.; Ludwig, D.F. Historical and Current Ecology of the Lower Passaic River. Urban Habitats 2004, 2, 147–173. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, K.R.; Tharp, M. How Did the Passaic River, a Superfund Site near Newark, New Jersey, Become an Agent Orange Dioxin TCDD Hotspot? J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 33A–37A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluthgun Hewage, S.; Batagoda, J.H.; Meegoda, J.N. Remediation of Contaminated Sediments Containing Both Organic and Inorganic Chemicals Using Ultrasound and Ozone Nanobubbles. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirgin, I.; Chambers, R.C.; Waldman, J.R.; Roy, N.K.; Witting, D.A.; Mattson, M.T. Effects of Hudson River Stressors on Atlantic Tomcod: Contaminants and a Warming Environment. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2023, 31, 342–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, K.R.; Cihacek, L. How United States Agricultural Herbicides Became Military and Environmental Chemical Weapons: Historical and Residual Effects. Open J. Soil Sci. 2022, 12, 13–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Karmaker, S.C.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Rakib, M.A.; Saha, B.B. Enrichment, Sources and Ecological Risk Mapping of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of Dhaka District Employing SOM, PMF and GIS Methods. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuerban, M.; Maihemuti, B.; Waili, Y.; Tuerhong, T. Ecological Risk Assessment and Source Identification of Heavy Metal Pollution in Vegetable Bases of Urumqi, China, Using the Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) Method. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Li, J.; Palansooriya, K.N.; Chen, Y.; Hou, D.; Meers, E.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Wang, X.; Ok, Y.S. Modeling Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils through Machine Learning. J. Hazard Mater. 2023, 441, 129904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windward, 2019 and 2021 Biota Data Summary Report. 2023. Available online: https://www.windwardenv.com/publications-and-presentations/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Windward. Quality Assurance Project Plan: Fish and Decapod Crustacean Tissue Collection for Chemical Analysis and Fish Community Survey. 2009. Available online: https://sharepoint.ourpassaic.org/Public%20Documents/2009-08-06%20FINAL%20Fish%20Tissue%20Collection%20QAPP%20CPG.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Windward. Current Conditions Addendum to the Quality Assurance Project Plan. Fish and Crab Tissue Collection for Chemical Analysis. Lower Passaic River Restoration Project Lower Passaic River Study Area RI/FS. 2021. Available online: https://www.windwardenv.com/publications-and-presentations/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- AECOM. Small Volume Chemical Water Column Monitoring—Data Summary Report Phase 1. 2022. Available online: https://sharepoint.ourpassaic.org/Datasets/20170130_Crosswalk_to_PassaicRiver-NewarkBay_Public_Datasets.xlsx (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Soetan, O.; Nie, J.; Feng, H. Preliminary Environmental Assessment of Metal-Contaminated Sediment Dredging in an Urban River, New Jersey, USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 184, 114212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, B. Bioaccumulation of Contaminants in Fish. In Fish Ecotoxicology; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 1998; pp. 353–387. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhanardakani, S. Tuna Fish and Common Kilka: Health Risk Assessment of Metal Pollution through Consumption of Canned Fish in Iran. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2017, 12, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhanardakani, S.; Tayebi, L.; Hosseini, S.V. Health Risk Assessment of Arsenic and Heavy Metals (Cd, Cu, Co, Pb, and Sn) through Consumption of Caviar of Acipenser Persicus from Southern Caspian Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2664–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Jan, K.; Fatma, S.; Dawood, M.A.O. Muscle Proximate Composition of Various Food Fish Species and Their Nutritional Significance: A Review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 106, 690–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnot, J.A.; Gobas, F.A. A Review of Bioconcentration Factor (BCF) and Bioaccumulation Factor (BAF) Assessments for Organic Chemicals in Aquatic Organisms. Environ. Rev. 2006, 14, 257–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.M.; Hoke, R.A.; Wolf, W.D.; Russell, M.H.; Buck, R.C. Are PFCAs Bioaccumulative? A Critical Review and Comparison with Regulatory Criteria and Persistent Lipophilic Compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, C.K.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H.; Dong, Y.H.; Leung, S.Y.; Wong, M.H. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Fish and Ardeid at Pearl River Estuary, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 106, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertato, L.; Chirico, N.; Papa, E. Predicting the Bioconcentration Factor in Fish from Molecular Structures. Toxics 2022, 10, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Mobaswara, M.Z.; Nice, M.S.; Islam, K.R.; Netema, B.N.; Rahman, M.S.; Habib, A.; Zaman, S.; Ghosh, G.C.; Tul-Coubra, K.; et al. Application of Machine Learning and Multivariate Approaches for Source Apportionment and Risks of Hazardous Elements in the Cropland Soils near Industrial Areas in Bangladesh. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzwayie, A.; El-shafie, A.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Afan, H.A.; Allawi, M.F. RBFNN-Based Model for Heavy Metal Prediction for Different Climatic and Pollution Conditions. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 1991–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, M.; Lu, J.; Lai, Z.; Tong, Y.; Wang, M. Trace Metals (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, Zn) and Stable Isotope Ratios (Δ13C and Δ15N) in Fish from Wulungu Lake, Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Ai, S.; Yi, J.; Wu, F.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Response of Aquatic Ecosystems Multi-Trophic Biological Communities under Multiple Pollutants Stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 177001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Ma, P.C.; Zhang, L.J.; Chen, M.B.; Huang, C.S.; Liu, X.L.; Hu, G.C.; Xu, Z.C. Accumulation Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Wild Fish Species from Diaojiang River, Guangxi. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 2600–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Screening Level Ecological Risk Assessment Protocol for Hazardous Waste Combustion Facilities. Appendix E: Toxicity Reference Values. 1999. Available online: https://lmpublicsearch.lm.doe.gov/sitedocs/sw-a-005922.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- USEPA Regional Screening Levels (RSLs)—Generic Tables. 2025. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls-generic-tables (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Eid, M.H.; Eissa, M.; Mohamed, E.A.; Ramadan, H.S.; Tamás, M.; Kovács, A.; Szűcs, P. New Approach into Human Health Risk Assessment Associated with Heavy Metals in Surface Water and Groundwater Using Monte Carlo Method. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lučić, M.; Momčilović, M.; Marković, J.; Jović, M.; Smičiklas, I.; Onjia, A. Monte Carlo Simulation of Health Risk from Cadmium, Lead, and Nickel in Cigarettes. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2023, 105, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Guiding Principles for Monte Carlo Analysis. 1997. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/guiding-principles-monte-carlo-analysis (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- USEPA. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide. 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-research/epa-positive-matrix-factorization-50-fundamentals-and-user-guide (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust, Its Composition and Evolution: An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary Rocks; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1985; ISBN 0632011483. [Google Scholar]
- JECFA. Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Sixty-First Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Technical Report Series 922; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; ISBN 92-4-120922-4. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/WHO. Report of the Eighth Session of the Codex Committee on Contaminants in Foods; Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme, Codex Alimentarius Commission; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Amiard, J.; Amiardtriquet, C.; Barka, S.; Pellerin, J.; Rainbow, P. Metallothioneins in Aquatic Invertebrates: Their Role in Metal Detoxification and Their Use as Biomarkers. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 76, 160–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, L.A.; Haack, E.A. Biogeochemical Controls on Metal Behaviour in Freshwater Environments. Earth Sci. Rev. 2001, 54, 261–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C. Partitioning of Trace Metals in Sediments: Relationships with Bioavailability. Hydrobiologia 1987, 149, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, C.C.; Henry, E.A.; Mitchell, R. Sulfate Stimulation of Mercury Methylation in Freshwater Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu-Kim, H.; Kucharzyk, K.H.; Zhang, T.; Deshusses, M.A. Mechanisms Regulating Mercury Bioavailability for Methylating Microorganisms in the Aquatic Environment: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2441–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Technical Support Document For Water Quality-Based Toxics Control. 1991. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2024-07/technical-support-document-for-water-quality-based-toxics-control.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Schwab, L.; Gallati, N.; Reiter, S.M.; Kimber, R.L.; Kumar, N.; McLagan, D.S.; Biester, H.; Kraemer, S.M.; Wiederhold, J.G. Mercury Isotope Fractionation during Dark Abiotic Reduction of Hg(II) by Dissolved, Surface-Bound, and Structural Fe(II). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 15243–15254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhang, Y. Climate-Driven Changes of Global Marine Mercury Cycles in 2100. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2202488120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosell, M. Copper. In Homeostasis and Toxicology of Essential Metals; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 53–133. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-W.; Choi, H.; Hwang, U.-K.; Kang, J.-C.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, J.-H. Toxic Effects of Lead Exposure on Bioaccumulation, Oxidative Stress, Neurotoxicity, and Immune Responses in Fish: A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu-Kim, H.; Eckley, C.S.; Achá, D.; Feng, X.; Gilmour, C.C.; Jonsson, S.; Mitchell, C.P.J. Challenges and Opportunities for Managing Aquatic Mercury Pollution in Altered Landscapes. Ambio 2018, 47, 141–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Bravo, A.G.; Skyllberg, U.; Björn, E.; Wang, D.; Yan, H.; Green, N.W. Influence of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) Characteristics on Dissolved Mercury (Hg) Species Composition in Sediment Porewater of Lakes from Southwest China. Water Res. 2018, 146, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Liu, L.; Zheng, N.; Yu, Y.; Xu, S.; Yao, H. Iron at the Helm: Steering Arsenic Speciation through Redox Processes in Soils. Environ. Res. 2025, 274, 121327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, R.A.; Jardine, T.D.; Chumchal, M.M.; Kidd, K.A.; Campbell, L.M. Biomagnification of Mercury in Aquatic Food Webs: A Worldwide Meta-Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13385–13394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-X.; Rainbow, P.S. Comparative Approaches to Understand Metal Bioaccumulation in Aquatic Animals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 148, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netema, B.N.; Chakraborty, T.K.; Nice, M.S.; Islam, K.R.; Debnath, P.C.; Chowdhury, P.; Rahman, M.S.; Halder, M.; Zaman, S.; Ghosh, G.C.; et al. Appraisal of Microplastic Pollution and Its Related Risks for Urban Indoor Environment in Bangladesh Using Machine Learning and Diverse Risk Evolution Indices. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 360, 124631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, N.M.; Batista, J.E.; Mariano, P.; Fonseca, V.; Duarte, B.; Silva, S. Artificial Intelligence Meets Marine Ecotoxicology: Applying Deep Learning to Bio-Optical Data from Marine Diatoms Exposed to Legacy and Emerging Contaminants. Biology 2021, 10, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, J.; Li, S.; Yang, Z. Trace Elements in Four Freshwater Fish from a Mine-Impacted River: Spatial Distribution, Species-Specific Accumulation, and Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8861–8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyeste, K.; Zulkipli, N.; Uzochukwu, I.E.; Somogyi, D.; Nagy, L.; Czeglédi, I.; Harangi, S.; Baranyai, E.; Simon, E.; Nagy, S.A.; et al. Assessment of Trace and Macroelement Accumulation in Cyprinid Juveniles as Bioindicators of Aquatic Pollution: Effects of Diets and Habitat Preferences. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Shahriar, A.; Hossain, N.; Shovon, I.K.; Hossain, A.; Jolly, Y.N.; Begum, B.A. Trace Metals Contamination in Riverine Captured Fish and Prawn of Bangladesh and Associated Health Risk. Expo. Health 2021, 13, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO. General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed. 1995. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/fr/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCXS%2B193-1995%252FCXS_193e.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume I Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A). 1989. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/risk-assessment-guidance-superfund-rags-part (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- USEPA. Exposure Factors Handbook: 2011 Edition. 2011. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/expobox/exposure-factors-handbook-2011-edition (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Faustman, E.M.; Silbernagel, S.M.; Fenske, R.A.; Burbacher, T.M.; Ponce, R.A. Mechanisms Underlying Children’s Susceptibility to Environmental Toxicants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCR. Pesticides in the Diets of Infants and Children; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; ISBN 978-0-309-04875-0. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, S.S.; Naz, S.; Fazio, F.; Cravana, C.; Ullah, M.; Rind, K.H.; Attaullah, S.; Filiciotto, F.; Khayyam, K. Assessment and Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Water, Fish (Wild and Farmed) and Associated Human Health Risk. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighara, P.; Mofid, V.; Mahmudiono, T.; Rahmani, A.; Tajdar-Oranj, B.; Peivasteh-Roudsari, L.; Farhangfar, A.; Moradi, M.; Fakhri, Y. Concentration of Heavy Metals in Canned Tuna Fish and Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment in Iran. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 104, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, M.; Shadboorestan, A.; Kalankesh, L.R.; Mohammadi-Bardbori, A.; Ghaffari, H.R.; Safa, O.; Farshidfar, G.; Omidi, M. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Toxicity in the Aquatic Environment of the Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut Bull. 2024, 202, 116360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NJDEP. Fish Smart, Eat Smart: A Guide to Healthier Fish Consumption. 2015. Available online: https://dep.nj.gov/dsr/fish-advisories-studies/ (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Bodrud-Doza, M.; Islam, S.M.D.-U.; Hasan, M.T.; Alam, F.; Haque, M.M.; Rakib, M.A.; Asad, M.A.; Rahman, M.A. Groundwater Pollution by Trace Metals and Human Health Risk Assessment in Central West Part of Bangladesh. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.M.; Niloy, N.M.; Khirul, M.A.; Alam, M.F.; Tareq, S.M. Appraisal of Probabilistic Human Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Vegetables from Industrial, Non-Industrial and Arsenic Contaminated Areas of Bangladesh. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, S.C. Biogeochemistry of Copper in the Fly River. In Developments in Earth and Environmental Sciences; Bolton, B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 9, pp. 321–373. ISBN 978-0-444-52964-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kruge, M.A.; Lara-Gonzalo, A.; Gallego, J.L.R. Environmental Forensics of Complexly Contaminated Sites: A Complimentary Fingerprinting Approach. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakizadeh, M. Spatial Distribution and Source Identification Together with Environmental Health Risk Assessment of PAHs along the Coastal Zones of the USA. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3333–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, Y.; Karadag, R.; Cheema, M.; Sayedahmed, M. Ion Selective Electrode Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen in Passaic River Waste Water in New Jersey Essex County Area. Am. J. Analyt. Chem. 2022, 13, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batagoda, J.H.; Hewage, S.D.A.; Meegoda, J.N. Remediation of Heavy-Metal-Contaminated Sediments in USA Using Ultrasound and Ozone Nanobubbles. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 14, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) for Coppers. 2009. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyNET.exe/P1004513.TXT?ZyActionD=ZyDocument&Client=EPA&Index=2006+Thru+2010&Docs=&Query=&Time=&EndTime=&SearchMethod=1&TocRestrict=n&Toc=&TocEntry=&QField=&QFieldYear=&QFieldMonth=&QFieldDay=&IntQFieldOp=0&ExtQFieldOp=0&XmlQuery=&File=D%3A%5Czyfiles%5CIndex%20Data%5C06thru10%5CTxt%5C00000008%5CP1004513.txt&User=ANONYMOUS&Password=anonymous&SortMethod=h%7C-&MaximumDocuments=1&FuzzyDegree=0&ImageQuality=r75g8/r75g8/x150y150g16/i425&Display=hpfr&DefSeekPage=x&SearchBack=ZyActionL&Back=ZyActionS&BackDesc=Results%20page&MaximumPages=1&ZyEntry=1&SeekPage=x&ZyPURL (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Walker, W.J.; McNutt, R.P.; Maslanka, C.K. The Potential Contribution of Urban Runoff to Surface Sediments of the Passaic River: Sources and Chemical Characteristics. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaglal, K. Contaminated Aquatic Sediments. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| English Name | Scientific Name | n | Cu | Pb | Hg | Weight (g) | Length (mm) | Feeding Habits b | Habitat c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| American eel | Anguilla rostrata | 266 | Mean ± S.D. | 0.76 ± 0.44 | 0.37 ± 0.17 | 0.27 ± 0.07 | Carnivorous | Bottom | ||
| Range | 0.48–2.61 | 0.13–0.78 | 0.14–0.42 | 86–522 | 330–810 | |||||
| Bass | Micropterus salmoides | 228 | Mean ± S.D. | 0.52 ± 0.17 | 0.09 ± 0.07 | 0.23 ± 0.05 | Carnivorous | Middle-Lower | ||
| Range | 0.29–1.05 | 0.02–0.37 | 0.11–0.35 | 84–396 | 151–405 | |||||
| Blue crab | Callinectes sapidus | 197 | Mean ± S.D. | 23.9 ± 3.56 | 0.36 ± 0.18 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | Omnivorous | Bottom | ||
| Range | 17.7–30.9 | 0.1–1.96 | 0.06–0.13 | 204–408 | 115–165 | |||||
| Carp | Cyprinus carpio | 184 | Mean ± S.D. | 1.23 ± 0.23 | 0.8 ± 0.5 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | Omnivorous | Bottom | ||
| Range | 0.9–1.84 | 0.25–2.3 | 0.07–0.2 | 1900–4000 | 500–764 | |||||
| Catfish | Ictalurus punctatus | 189 | Mean ± S.D. | 0.61 ± 0.26 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.29 ± 0.08 | Omnivorous | Bottom | ||
| Range | 0.35–1.5 | 0.1–0.65 | 0.09–0.4 | 400–1360 | 300–601 | |||||
| Sunfish | Lepomis auritus | 634 | Mean ± S.D. | 0.93 ± 0.36 | 0.36 ± 0.13 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | Carnivorous | Middle-Bottom | ||
| Range | 0.39–1.84 | 0.16–0.75 | 0.04–0.15 | 18–64 | 80–215 | |||||
| White perch | Morone americana | 338 | Mean ± S.D. | 7.62 ± 3.53 | 0.28 ± 0.12 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | Carnivorous | Middle-Lower | ||
| Range | 2.73–16.3 | 0.14–0.7 | 0.06–0.22 | 42–128 | 130–320 | |||||
| MAC a (mg/kg wet wt) | 30 | 1 | 0.6 | |||||||
| Species | Children | Adults | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Pb | Hg | Cu | Pb | Hg | ||
| Anguilla rostrata | Mean ± S.D. | 0.24 ± 0.11 | 0.11 ± 0.05 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 5.00 × 10−3 |
| Range | 0.14–0.66 | 3.00 × 10−3–0.23 | 0.04–0.12 | 0.04–0.16 | 7.00 × 10−4–0.06 | 0.01–0.03 | |
| Micropterus salmoides | Mean ± S.D. | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 1.00 × 10−3 | 0.01 ± 2.00 × 10−3 |
| Range | 0.08–0.31 | 0.01–0.05 | 0.03–0.07 | 0.02–0.08 | 3.00 × 10−3–0.01 | 0.01–0.02 | |
| Callinectes sapidus | Mean ± S.D. | 7.11 ± 0.95 | 0.12 ± 0.09 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 1.74 ± 0.23 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 1.00 × 10−3 |
| Range | 5.27–9.19 | 0.03–0.05 | 0.02–0.04 | 1.28–2.24 | 0.01–0.12 | 4.00 × 10−3–0.01 | |
| Cyprinus carpio | Mean ± S.D. | 0.37 ± 0.06 | 0.24 ± 0.13 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.01 ± 3.00 × 10−3 |
| Range | 0.27–0.55 | 0.07–0.68 | 0.02–0.06 | 0.07–0.13 | 0.02–0.17 | 5.00 × 10−3–0.02 | |
| Ictalurus punctatus | Mean ± S.D. | 0.19 ± 0.07 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Range | 0.1–0.43 | 0.03–0.19 | 0.03–0.12 | 0.03–0.11 | 7.00 × 10−3–0.05 | 0.01–0.03 | |
| Lepomis auritus | Mean ± S.D. | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 2.00 × 10−3 |
| Range | 0.12–0.42 | 0.05–0.22 | 0.01–0.04 | 0.03–0.1 | 0.01–0.05 | 3.00 × 10−3–0.01 | |
| Morone americana | Mean ± S.D. | 2.31 ± 0.97 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.56 ± 0.24 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 2.00 × 10−3 |
| Range | 0.81–4.85 | 0.04–0.2 | 0.03–0.07 | 0.2–1.18 | 0.01–0.05 | 0.01–0.02 | |
| Mean | 1.26 ± 0.12 | 0.11 ± 0.08 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.3 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 5.30 × 10−3 | |
| Maximum Tolerable Daily Intake (MDTI) | 4.50 * | 0.03 ** | 2.3 × 10−4 * | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.S.; Mirza, S.; Feng, H.; Chakraborty, T.K.; Qian, Y.; Yoo, S. Source Apportionment and Potential Health Risks of Trace Metals in a Contaminated Urban River in New York/New Jersey Harbor System. Water 2025, 17, 3254. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223254
Islam MS, Mirza S, Feng H, Chakraborty TK, Qian Y, Yoo S. Source Apportionment and Potential Health Risks of Trace Metals in a Contaminated Urban River in New York/New Jersey Harbor System. Water. 2025; 17(22):3254. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223254
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Md Shahnul, Sana Mirza, Huan Feng, Tapos Kumar Chakraborty, Yu Qian, and Shinjae Yoo. 2025. "Source Apportionment and Potential Health Risks of Trace Metals in a Contaminated Urban River in New York/New Jersey Harbor System" Water 17, no. 22: 3254. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223254
APA StyleIslam, M. S., Mirza, S., Feng, H., Chakraborty, T. K., Qian, Y., & Yoo, S. (2025). Source Apportionment and Potential Health Risks of Trace Metals in a Contaminated Urban River in New York/New Jersey Harbor System. Water, 17(22), 3254. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223254







