Abstract
Freshwater quality criteria (FWQC) are essential scientific thresholds established to protect human health and aquatic ecosystems, serving as the foundation for water quality standards, environmental risk management, and pollution control. The latest research advancements were summarized, including the screening of priority pollutants for FWQC and the theory and methodology for environmental criteria in China in the last decade. The potential work has been meticulously analyzed and discussed concerning FWQC to be conducted in the short-term future. The possible prioritized list of pollutants for FWQC should be concerned with including nine categories of heavy metal ions, three categories of non-metal ions, and five categories of organic compounds in the short-term future research. The guidelines for deriving FWQC for the protection of human health for organoleptic effects and for sediment need to be modified and emphasized to ensure the safety of drinking water sources, address issues related to black and odorous surface water, and protect the biodiversity of benthic organisms. Toxicity data, water quality parameters, exposure data, and the geographical distribution of freshwater species should be systematically collected to support the development of FWQC in China. The potential applications of FWQC were also explored in the evaluation and formulation of WQS, ecological risk assessments, and the management of environmental emergencies and damage assessments to support environmental protection and management in China.
1. Introduction
Freshwater quality criteria (FWQC) were defined as the maximum permissible concentrations or levels of contaminants and harmful factors in freshwater environments that do not adversely impact human health and aquatic ecosystems [1,2]. The FWQC provided the scientific foundation for the establishment of water quality standards (WQS), the response to environmental pollution incidents, and the management of risks associated with toxic or emerging contaminants in aquatic systems [3,4]. Over the past 40 years, a comprehensive environmental standard system has been developed in China, including WQS, discharge standards, and monitoring standards for freshwater systems [5,6]. The last and current publication of the Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water in 2002 (named as GB3838-2002), this standard has been formulated and revised three times, in 1983, 1988, and 1999, respectively, to advance freshwater environmental protection in China (Table S1) [1,7]. However, due to economic and social development constraints resulting from the lack of FWQC, the item limits of GB3838-2002 were based on the referencing or adoption of FWQC and environmental standards from developed countries and international organizations in China. It has been noted that directly referencing or adopting foreign environmental criteria, standards, and other documents may result in either over-protection or under-protection of human health or aquatic ecosystems because of significant differences among countries in geographical and climatic conditions, economic development levels, etc. Therefore, the development of a scientific and specific FWQC system based on the national environmental system is considered essential to reduce the uncertainties caused by referencing foreign environmental criteria and standards in China.
The importance of FWQC has been recognized and emphasized at the national level for the past 20 years (Table S1). Since the national goal of scientifically determining criteria was set in 2005, a series of laws and regulations have been issued, with environmental criteria being designated as key research areas in the ecological and environmental sectors (Table S1) [4,8]. As mentioned in the Environmental Protection Law, the development of environmental criteria research was formally established to provide strong legal support for advancing environmental criteria development in China (Table S1). National policies have also emphasized the development of water environment criteria for organic compounds (nitrobenzene, volatile phenol, etc.) and heavy metals (Tl, Cr, etc.) due to their widespread occurrence and long-term environmental impact (Figure 1) [9,10]. The establishment of such a legal foundation has not only legitimized research efforts but has also ensured that the outcomes are integrated into policy decisions and environmental management practices. To protect water ecological safety and public health, the number of environmental criteria published and implemented by China was limited.
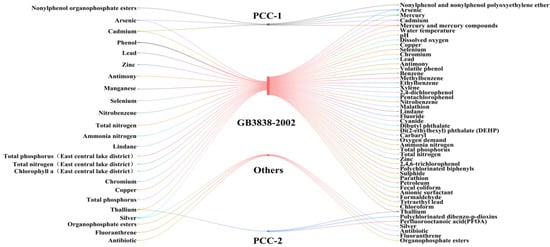
Figure 1.
The possible priority pollutants for FWQC in China for short-term (left), originating file names of priority pollutants (middle), and long-term (right), respectively. PCC-1 and PCC-2 were the first and second batches of the list of priority controlled chemicals in China (Table S1).
Since the mid-20th century, FWQC have been established by developed countries such as the USA and Canada, along with international organizations such as the OECD and the WHO, based on specific management needs for public health and environmental protection [11,12,13,14]. Based on internationally recognized classification methods, these criteria are categorized into FWQC for the protection of human health, for the protection of aquatic organisms, for nutrients, and for sediment, respectively [15,16]. However, significant differences have been observed in terms of water quality characteristics, biota, and patterns of human behavior among countries [2]. For example, the species numbers (ratios) of fish, zoobenthos, zooplankton, phytoplankton, and hydrophytes were recorded as 107 (24.2%), 66 (14.93%), 103 (23.3%), 81 (18.3%), and 85 (19.2%) species, respectively, in Lake Taihu in China, compared to 134 (7.1%), 165 (8.7%), 132 (7.0%), and 1456 (77.2%) species, respectively, in the Great Lakes in the USA [17]. In detail, 107 fish species from 25 families were recorded in Lake Taihu in China, with Cyprinidae being the dominant family, while 134 fish species from 24 families were reported in the Great Lakes in the USA, with Salmonidae being the predominant family [15,18]. The average daily drinking water consumption for Chinese residents (31 mL/kg) was approximately 2.4 times greater than that of American residents (13 mL/kg). Additionally, the average daily bathing time of American residents (17 min) was about 2.4 times longer than that of Chinese residents (7 min) (Table S1). These differences have likely resulted in clear discrepancies in the FWQC published for different countries and even for different districts (Figure 2c,d) [12,19]. These clear differences in criteria highlighted the necessity for developing and establishing FWQC that are appropriate for the specific environmental conditions and requirements of each country.
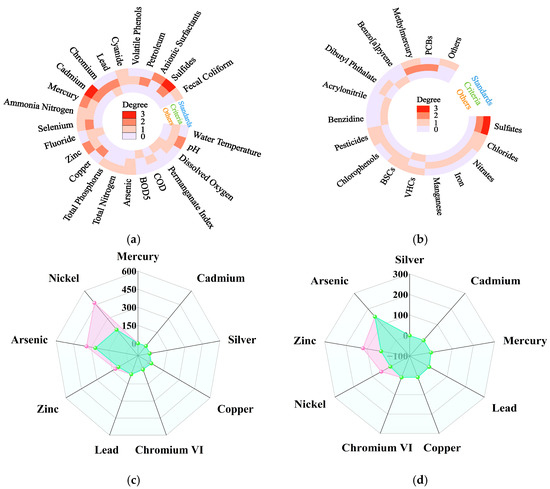
Figure 2.
References for limits of 24 basic items (a) and other items (b) in the GB3838-2002 in China. The SWQC (c) and LWQC (d) for aquatic organism protection in China ( ) and the USA (
) and the USA ( ). The first circle, second circle, and third circle represented environmental quality standards, water quality criteria, and other documents from various countries, respectively, in (a,b), (Table S2). The number of cited limits is indicated by the degree of reference within each category in (a,b). Volatile Halogenated Hydrocarbons (VHCs) include ten pollutants: chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, bromoform, dichloromethane, 1,2-dichloroethane, vinyl chloride, 1,1-dichloroethane, trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, and hexachlorobutadiene. Benzene Series Compounds (BSCs) include ten pollutants: benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylene, chlorobenzene, 1,2-dichlorobenzene, 1,4-dichlorobenzene, hexachlorobenzene, nitrobenzene, and 2,4-dinitrotoluene. Chlorophenols include three pollutants: 2,4-dichlorophenol, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, and pentachlorophenol. Pesticides include nine pollutants: DDT, lindane, parathion, methyl parathion, malathion, dimethoate, dichlorvos, trichlorfon, and atrazine. Other pollutants include epichlorohydrin, 1,2-dichloroethylene, chloroprene, and 39 other pollutants.
). The first circle, second circle, and third circle represented environmental quality standards, water quality criteria, and other documents from various countries, respectively, in (a,b), (Table S2). The number of cited limits is indicated by the degree of reference within each category in (a,b). Volatile Halogenated Hydrocarbons (VHCs) include ten pollutants: chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, bromoform, dichloromethane, 1,2-dichloroethane, vinyl chloride, 1,1-dichloroethane, trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, and hexachlorobutadiene. Benzene Series Compounds (BSCs) include ten pollutants: benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylene, chlorobenzene, 1,2-dichlorobenzene, 1,4-dichlorobenzene, hexachlorobenzene, nitrobenzene, and 2,4-dinitrotoluene. Chlorophenols include three pollutants: 2,4-dichlorophenol, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, and pentachlorophenol. Pesticides include nine pollutants: DDT, lindane, parathion, methyl parathion, malathion, dimethoate, dichlorvos, trichlorfon, and atrazine. Other pollutants include epichlorohydrin, 1,2-dichloroethylene, chloroprene, and 39 other pollutants.
 ) and the USA (
) and the USA ( ). The first circle, second circle, and third circle represented environmental quality standards, water quality criteria, and other documents from various countries, respectively, in (a,b), (Table S2). The number of cited limits is indicated by the degree of reference within each category in (a,b). Volatile Halogenated Hydrocarbons (VHCs) include ten pollutants: chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, bromoform, dichloromethane, 1,2-dichloroethane, vinyl chloride, 1,1-dichloroethane, trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, and hexachlorobutadiene. Benzene Series Compounds (BSCs) include ten pollutants: benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylene, chlorobenzene, 1,2-dichlorobenzene, 1,4-dichlorobenzene, hexachlorobenzene, nitrobenzene, and 2,4-dinitrotoluene. Chlorophenols include three pollutants: 2,4-dichlorophenol, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, and pentachlorophenol. Pesticides include nine pollutants: DDT, lindane, parathion, methyl parathion, malathion, dimethoate, dichlorvos, trichlorfon, and atrazine. Other pollutants include epichlorohydrin, 1,2-dichloroethylene, chloroprene, and 39 other pollutants.
). The first circle, second circle, and third circle represented environmental quality standards, water quality criteria, and other documents from various countries, respectively, in (a,b), (Table S2). The number of cited limits is indicated by the degree of reference within each category in (a,b). Volatile Halogenated Hydrocarbons (VHCs) include ten pollutants: chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, bromoform, dichloromethane, 1,2-dichloroethane, vinyl chloride, 1,1-dichloroethane, trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, and hexachlorobutadiene. Benzene Series Compounds (BSCs) include ten pollutants: benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylene, chlorobenzene, 1,2-dichlorobenzene, 1,4-dichlorobenzene, hexachlorobenzene, nitrobenzene, and 2,4-dinitrotoluene. Chlorophenols include three pollutants: 2,4-dichlorophenol, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, and pentachlorophenol. Pesticides include nine pollutants: DDT, lindane, parathion, methyl parathion, malathion, dimethoate, dichlorvos, trichlorfon, and atrazine. Other pollutants include epichlorohydrin, 1,2-dichloroethylene, chloroprene, and 39 other pollutants.
Extensive research on FWQC has been conducted, including the establishment of the protection of aquatic organisms (Cu, Cd, etc.) and the protection of human health (nitrobenzene, etc.) using the corresponding derivation methods in China (Figure 1) [20]. The target contaminants investigated by scientists were selected based on individual interests, areas of expertise, and the needs of various research projects, rather than being aligned with the priorities of national environmental management [2]. The contaminants listed as nationally prioritized control pollutants, toxic and hazardous substances, and typical emerging pollutants still lacked associated FWQC research by the national environmental management authorities of China. Therefore, it is necessary to develop techniques for selecting environmental contaminants and to establish a list of environmental contaminants that should be prioritized for FWQC in future scientific research in China. In the process of establishing FWQC, the application of different methodologies and data selection methods can lead to differences in criteria, particularly for FWQC for the protection of aquatic organisms [7]. FWQC for the protection of aquatic organisms for sulfamethoxazole: the acute criterion derived using the TPR (Toxicity Percentile Ranking) method was approximately 4.5 times lower than that derived using the species sensitivity distribution method (SSD) based on the same organism of acute toxicity data [21,22,23]. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a standardized theoretical methodology and data collection approach to ensure the scientific validity and accuracy of FWQC.
This paper summarizes the achievements in developing theoretical methodologies for FWQC, deriving FWQC values, and prioritizing contaminants in China over the last decade. The novelty of this paper was reflected in the following aspects: (1) systematically summarizing the current status and challenges of FWQC in China, (2) clarifying the future research objectives for FWQC and the rationale behind their establishment, and (3) exploring the potential applications of FWQC in China. This research benefited from understanding the development trends of FWQC in China and contributed to expanding the application of environmental criteria in environmental management.
2. Development of FWQC in China
2.1. Priority Pollutants for FWQC in China
Currently, the management of surface water quality is primarily based on GB 3838-2002 with 109 items [24], the List of Priority Controlled Chemicals (the first batch with 28 items and the second batch with 12 items), and the List of Toxic and Hazardous Water Pollutants (the first batch with 10 items) published by the national environmental management authorities of China (Table S2). The limit values for most items were formulated by referencing or adopting one or more categories of FWQC, standards, and other documents published by other countries, especially the USA, Europe, etc., because of the lack of support for FWQC in China, as mentioned above (Figure 2a,b, and Table S2 in the SI). In detail, the standard limit in GB3838-2002 for Cd (0.01 mg/L for Grade V) was set based on criteria and WQS of the USA (WQS for drinking water sources of 0.01 mg/L), Japan (drinking WQS of 0.01 mg/L, WQS for drinking water sources of 0.01 mg/L), the UK (drinking WQS of 0.01 mg/L), and others. Additionally, ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) of Grade II (0.5 mg/L) of GB3838-2002 was based on the WQS for drinking water sources of both the USA and Switzerland (0.5 mg/L) (Table S2) [8]. It is necessary to select a batch of priority pollutants for future research to protect the ecosystem and human health based on management needs in China.
From 2020, the national environmental management authorities of China have released four FWQC for the protection of aquatic life for Cd, NH3-N, and phenol, as well as FWQC for nutrients of the central and eastern lake districts in China, summarized in Table S1. More than 50 substances of a total of 143 substances were screened as priority pollutants for FWQC for long-term use in the future. The selection process was primarily based on factors such as toxicity, detection frequency, and physicochemical properties, as well as the ecological and human health risks associated with each pollutant. A comprehensive scoring method and fuzzy mathematics approach were applied to select and prioritize the pollutants (Figure 1) [9,25]. Differences existed between China and the USA in the number and types of priority pollutants due to differences in industrial structures. Several organic chemicals, including 1,2-Dichloropropane, 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine, and Acrolein, are designated as priority pollutants of FWQC in the USA. In contrast, emerging pollutants such as pesticides and antibiotics are prioritized due to concerns over the environmental impact of China’s rapidly growing modern chemical industry. For the current availability of toxicity data of pollutants to freshwater organisms and management needs, the short-term objectives should prioritize the development of criteria for nine metal ions—Pb, Cr, Zn, Sb, Tl, Ag, Mn, Fe, and Cu; three non-metal ions—As, Se, and fluoride; and five categories of organic compounds—nitrobenzene, perfluorinated compounds, nonylphenol, antibiotics, and pesticides (Figure 1). Lakes and reservoirs showed varying degrees of eutrophication, representing a significant environmental challenge for freshwater systems in China [26,27]. The FWQC for nutrients will be extended to four additional lake districts in the northeastern, Mongolian–Xinjiang, Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, and Yunnan–Guizhou regions, respectively, in China. Additionally, organoleptic effects were defined as the impact of substances on the sensory properties of water, such as taste, smell, and appearance. For example, when the concentration of pollutants like phenol exceeded safe levels in water, unpleasant odors or harmful sensory characteristics were caused. FWQC for organoleptic effects will be developed for phenol to protect the sensory attributes of water bodies. The criteria to protect people from organisms, such as viruses and bacteria, and their associated toxins in water bodies should have been given sufficient attention.
2.2. Methodological Guidelines for FWQC Development
Since the mid-20th century, theoretical and methodological research on FWQC has been systematically conducted by developed countries such as the USA, Canada, and Australia (Table 1) [11,12,28]. Research on FWQC for the protection of both aquatic organisms and human health began in the late 20th century, focusing on both theoretical and methodological aspects as well as its application in China. Although the investigation of environmental criteria started approximately 50 years later in China, significant progress has been made in the areas of freshwater biota protection, lake eutrophication control, test species selection, and toxicity testing techniques [6,29]. The derivation of FWQC for the protection of human health, for the protection of aquatic organisms, for nutrients, and for sediment in China has been primarily achieved through the adoption, modification, and development of methods applied in developed countries [20]. Three technical guidelines for the derivation of FWQC were released for the protection of aquatic organisms, for nutrients in lakes, and for the protection of human health, which represented an initial step in constructing a national technical system for environmental criteria in China [19,30,31]. The technical guideline stipulated that the FWQC for the protection of aquatic life should be derived using SSD for both LWQC and SWQC with acute and chronic toxicity of pollutants to freshwater organisms, respectively [5,19]. Under the technical guideline for developing FWQC for the protection of human health, both carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic effects of pollutants were derived based on toxicological data from mammalian and/or human cohort studies, exposure assessment data for the Chinese population (including water consumption, etc.), and dose–response data involving both drinking water and consumption of aquatic products to ensure the safety of drinking water sources [31]. The technical guideline for developing FWQC for nutrients of lakes indicated that the total N and P should be calculated based on concentration monitoring data of at least three years within the past decade, involving statistical analysis methods and pressure-response models [27,30].
A substantial amount of research has been conducted on FWQC for sediment, leading to the development of various derivation methods based on toxicity data and sediment types, including the biological effect database, the equilibrium partitioning approach, and the background approach [10,32]. The widely applied biological effect database method derives criteria directly using the SSD and TPR model based on toxicity data of pollutants to benthic organisms in the freshwater-sediment systems. In the process of deriving FWQC for the protection of aquatic life for specific pollutants, the SSD was shown to use all available toxicity data for pollutants to aquatic organisms for formula fitting, while TPR relied on toxicity data based on specific percentiles to derive water quality criteria. The SSD was designated as the method for deriving FWQC in China, while the TPR method was designated for deriving FWQC in the USA. The equilibrium partitioning approach was conducted by leveraging FWQC for the protection of aquatic organisms and the equilibrium partitioning by indirectly considering the bioavailability of pollutants affected by acid volatile sulfide, total organic carbon, and particle size of sediment [3,33]. Within the framework of FWQC systems, guidelines for deriving FWQC for sediment, organoleptic effects, and criteria to protect people from viruses and bacteria should be proposed to protect the biodiversity of benthic organisms in freshwater ecosystems and to control black and odorous surface waters, respectively. The highly accumulative substances were characterized by their strong bioaccumulation potential, persistence, toxicity, widespread distribution, and gradual accumulation along the food chains of freshwater organisms, posing long-term risks to aquatic ecosystems and human health [34,35]. The tissue residue criteria for aquatic life can reduce the uncertainty and variability of bioaccumulation and bioconcentration in aquatic systems, providing distinct advantages in the assessment of toxicity effects and evaluation of FWQC for highly accumulative substances [17]. In contrast to traditional pollutants, endocrine disruptors exhibited non-monotonic dose–response curves, such as U-shaped, inverted U-shaped, or more complex patterns due to the overlap of two (or more) opposing monotonic effects, as well as receptor downregulation and receptor desensitization. No suitable derivation methods for the FWQC of endocrine disruptors currently exist, due to their distinct toxic mechanisms, effects, and pathways affecting aquatic organisms in surface waters [7]. Therefore, the methods for deriving FWQC for aquatic organisms should be developed for both endocrine disruptors and highly accumulative chemical substances in China. Additionally, to ensure the safety of drinking water sources, the method for deriving FWQC for the protection of human health, published by the national environmental management authorities of China in 2017, should be revised and modified because of the lack of basic data. The biotic ligand model (BLM) was a mechanistic model used to predict the toxicity of heavy metals to aquatic organisms, based on the interactions between metal ions and biotic ligands on the surface of aquatic organisms. The multiple linear regression model (MLRM) was a statistical tool used to analyze the relationship between a dependent variable and multiple independent variables. The BLM and MLRM were used to correct the toxicity of pollutants to aquatic organisms under different water quality conditions. The BLM was found to be more suitable for correcting the toxicity effects of metal pollutants, while the MLRM was unable to correct for non-linear toxicity effects. The BLM and MLRM have been developed for application in both FWQC and regional risk assessments for Cu, Pb, Ni, and Zn in Europe and the USA, which should also be investigated and considered in the process of deriving FWQC for the protection of aquatic organisms in China [36].
The clear differences in criteria values, including SWQC and LWQC, were observed among different countries, including the USA, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and China. For Cd, at a water hardness of 100 mg/L as CaCO3, the SWQC in China (4.2 µg/L) was 75% and 68% greater than the SWQC established in the USA (1.8 µg/L) and in Canada (2.5 µg/L), respectively (Table 1, Figure 2c). The LWQC in China (0.23 µg/L) was 68% less than that in the USA (0.72 µg/L), while it was 28% greater than the value in Canada (0.18 µg/L) at the same water hardness of 100 mg/L as CaCO3 (Table 1, Figure 2d). For NH3-N, under conditions of pH 7.0 and a temperature of 20 °C, the SWQC in China (12 µg/L) was 29% less than that in the USA (17 µg/L). The LWQC in China (1.5 µg/L) was 21% and 69% less than that in the USA (1.9 µg/L) and in Canada (4.82 µg/L), respectively, for NH3-N at pH 7.0 and 20 °C. For phenol, the SWQC in China (2470 µg/L) was 76% less than that in the USA (10,200 µg/L). The LWQC of phenol in China (290 µg/L) was 89% and 10.34% less than that in the USA (2560 µg/L) and in Australia and New Zealand (320 µg/L), respectively, while it was 72.5 times greater than the value in Canada (4 µg/L).
The differences in SWQC and LWQC values among different countries could be mainly attributed to the different calculation models for FWQC for the protection of aquatic organisms and the sensitive organisms in different regions and nations. In detail, the TPR method and the SSD were employed in the USA and other countries (e.g., China, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand) during the derivation of FWQC for the protection of freshwater organisms. The most sensitive species identified were Morone saxatilis, Oncorhynchus mykiss, and Salvelinus confuentus in China, while the most sensitive species were Salvelinus confluentus, Cottus bairdii, and Salmo trutta for Cd in the USA for deriving the FWQC of Cd for the protection of freshwater organisms. For long-term exposure, the most sensitive species included Daphnia magna, Oncorhynchus mykiss, and Ceriodaphnia dubia in China, while the most sensitive species were Hyalella azteca, Ceriodaphnia dubia, and Cottus bairdii in the USA for the deriving FWQC of Cd for the protection of freshwater organisms [21,22].
2.3. Collection and Compilation of Fundamental Data for FWQC
The FWQC were categorized within the field of natural scientific research and were derived from the analysis of foundational data and mathematical modeling. The toxicological data quantitatively described the effects of pollutants on aquatic organisms and human health as core data of criteria derivation, including EC50, LC50, NOEC, and LOEC [16]. Water quality parameters such as temperature, pH, and hardness can affect the toxicity of pollutants to aquatic life, resulting in FWQC for the protection of aquatic organisms (Figure 3 and Figure S1 in the SI). The linear correlation was observed between the acute toxicity data of Cd for 57 native aquatic species and the chronic toxicity data for 23 species, along with their corresponding water hardness parameters, with R2 values of 0.1181 (n = 277) and 0.1193 (n = 67), respectively, after logarithmic-logarithmic transformation in China (Figure S1) [21]. Although the R2 value was low, the p-value was found to be less than 0.05, indicating a significant correlation between the two variables. The low R2 value might be influenced by the experimental errors of toxicity data from different literature, laboratories, and various experimental conditions. Similar low R2 values were also observed when calculating the FWQC for Zn and Pb to protect aquatic organisms [37,38]. The key exposure parameters of the Chinese population, including drinking water intake, fish consumption rates, etc., served as foundational data in determining the FWQC for the protection of human health limits [31,33]. With the developing FWQC in China, toxicological data were preliminarily collected, including acute and chronic toxicity data of pollutants affecting aquatic organisms. Water quality monitoring data were gathered from major rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, covering parameters such as pH, hardness, and nutrients. For example, 9044, 8029, and 8187 data were involved in the derivation of FWQC for Cd, NH3-N, and phenol to protect aquatic life, respectively [21,39,40]. A total of 96,210 water quality monitoring data of total P, total N, and chlorophyll a were included from 207 lakes between 1991 and 2019 in the derivation of FWQC for nutrients of lakes [41]. A significant amount of data on aquatic organisms and human health was generated during surface water environmental science research in China and was often dispersed across various sources, such as academic literature, government reports, and project completion documents. Currently, due to the lack of systematic collection and organization of toxicity data for local aquatic species and human health exposure data, the derivation, formulation, and revision of FWQC in China largely depend on toxicological databases from developed countries and international organizations [25].
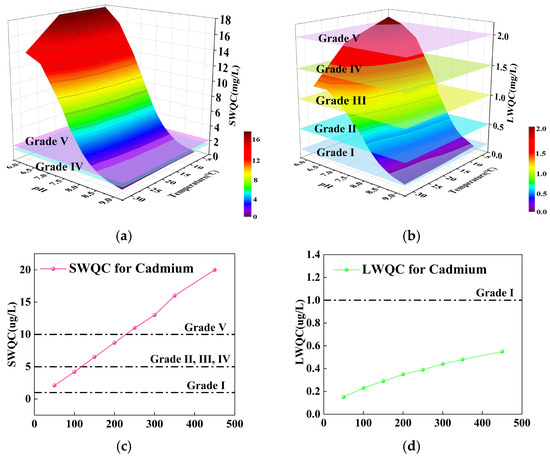
Figure 3.
Comparison of the limits of GB3838-2002 and FWQC for the protection of aquatic organisms. (a) The SWQC for NH3-N, (b) the LWQC for NH3-N, (c) the SWQC for Cd, and (d) the LWQC for Cd in China.

Table 1.
Water quality parameters, number of species, and derivation methods of FWQC in different countries.
Table 1.
Water quality parameters, number of species, and derivation methods of FWQC in different countries.
| Pollutants | Country | Year | FWQC for the Protection of Aquatic Organisms (μg/L) | Number of Species | Derivation Methods | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWQC a | LWQC b | SWQC a | LWQC b | |||||
| Cd | China | 2020 | 4.2 * | 0.23 * | 57 | 23 | SSD | [21,22] |
| USA | 2016 | 1.8 * | 0.72 * | 101 | 27 | TPR | ||
| Canada | 2014 | 2.5 * | 0.18 * | 62 | 36 | SSD | ||
| NH3-N | China | 2020 | 12 ** | 1.5 ** | 53 | 16 | SSD | [39] |
| USA | 2013 | 17 ** | 1.9 ** | 100 | 21 | TPR | ||
| Canada | 2010 | -- | 4.82 ** | -- | 7 | SSD | ||
| Australia and New Zealand | 2000 | -- | 2.18 ** | -- | -- | SSD | ||
| Phenol | China | 2020 | 2470 | 290 | 60 | 18 | SSD | [40] |
| USA | 1980 | 10,200 | 2560 | 17 | 1 | AFM | ||
| Canada | 1999 | -- | 4 | -- | 9 | AFM | ||
| Australia and New Zealand | 2000 | -- | 320 | -- | -- | SSD | ||
Note: a SWQC is short-term water quality criteria; b LWQC is short-term water quality criteria; *: hardness of water with 100 mg/L as CaCO3; **: pH = 7.0, T = 20 °C; SSD, TPR, and AFM are species sensitivity distribution, Toxicity Percentage Ranking, and Assessment Factor Methods, respectively.
Using network information technology and data collection modules, scientific data should be collected, including toxicity data on pollutants of conventional pollutants, nutrients, and emerging contaminants, as well as data on water consumption and fish intake of residents in China [33,36]. Due to the differences in geographical and geological background, even in the same water body, this may have reduced the applicability of FWQC across different regions in China. Therefore, data on the geographical distribution of freshwater species and the concentration of pollutants should also be collected as valuable supplements for the development and establishment of aquatic life criteria in China [42]. In the surface water of China, water quality parameters such as temperature, pH, hardness, and organic carbon content should also be collected to adjust the FWQC limits (Figure 3) [43]. In addition, based on standardized toxicity testing methods, toxicity tests on pollutants should be conducted to obtain acute and chronic toxicity data for economically significant freshwater species and endemic species in China [18,44]. The Quantitative structure–activity relationships (QSARs) were a computational modeling technique used to predict the toxicity of chemical compounds based on their molecular structure. The Interspecies correlation estimation (ICE) model was used to predict the toxicity of a chemical to species that lacked direct toxicity data by utilizing the toxicity data of surrogate species. The QSAR was used to predict toxicity based on molecular structure, showing high accuracy in predicting the toxicity of organic chemicals to aquatic organisms, while ICE estimated the toxicity of untested species by using data from surrogate species. The two models should also be developed to fill in data gaps of toxicity for emerging pollutants and rare/protected species that cannot be applied as test species in toxicological experiments as supplementary data.
3. Application of FWQC
The scientific validity of existing WQS can be applied to identify the impacted aquatic species and to evaluate the proportion of the human population potentially affected (Figure 3c,d). For example, assuming a water hardness of 100 mg/L, and based on the LWQC for Cd, Daphnia magna was an impacted species under Grade I of GB3838-2002, the current environmental standard for surface water in China. Under Grade V of GB3838-2002, 12 aquatic species were affected by Cd in surface water, including Cyprinus carpio, etc., accounting for 52% of the species applied in deriving the chronic FWQC for Cd (Figure 3c) [21,25]. Therefore, the limit of WQS items should be promptly evaluated through the identification and evaluation of impacted aquatic species and the human population once the FWQC values are derived, assessed, confirmed, and authorized by the national environmental management authorities in China. Ecological risk assessment of metal ions, organic compounds, and pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) was estimated by risk quotients, prioritization indexes, and joint probability curves based on FWQC for the protection of aquatic organisms in surface waters in China [3,9]. Previous research showed that 4 of 50 PPCPs (e.g., caffeine, nonylphenol, tonalide, and galaxolide) posed an ecological risk to 100% of surface waters, and 15 chemicals (e.g., nonylphenol, sulfamethoxazole, 17β-ethynyl estradiol, etc.) were identified as high or moderate risks according to prioritization indexes in China [35]. The risk quotients ranging from 0 to 4.55 were calculated based on the FWQC for glyphosate, indicating that it exhibited medium to high hazard risk in some samples of surface water in Jiangsu, Guizhou, and Henan provinces, as well as Chongqing City in China [34]. The environmental risk of oxytetracycline to freshwater aquatic organisms was generally low except in the Ziya River and tributaries of the Haihe River, based on a total of 803 oxytetracycline concentration data collected over the past 15 years, with concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 97,433.8 ng/L in China [45]. Therefore, the application of FWQC in risk assessment should be further explored and investigated to provide a basis for protecting aquatic organisms and human health.
At the national level, two main protection laws, the Yangtze River Protection Law and the Yellow River Protection Law, proposed the development of water environment quality standards for key basins, supplementing or imposing stricter limits on national WQS to ensure the biodiversity and integrity of aquatic ecosystems in surface freshwater (Table S1). For example, heavy metals such as Sb and Tl, due to their high toxicity and non-biodegradability in aquatic systems, were identified as major factors affecting the security of the water ecological environment in the Yangtze River Basin in China [46,47]. Preliminary research was conducted by scientists on the toxicity and toxic mechanisms of Sb and Tl to aquatic organisms, including Danio rerio, Oreochromis mossambicus, and Cyprinus carpio [18,46]. Acute and chronic FWQC for Sb were regressed using 33 acute toxicity data and 15 chronic toxicity data to aquatic organisms distributed in China [6]. However, inconsistencies in data screening methods and model calculations applied in these studies and the national technical guidelines resulted in the ineligible consideration as national FWQC and the inapplicable references for setting national WQS in China. Therefore, FWQC of priority pollutants in key basins must be developed, and these FWQC must be refined into enforceable WQS by considering the local biota, the water quality characteristics of the basins, and the concentrations and distributions of water pollution. The dose–response relationships of contaminants and FWQC were successfully applied in setting temporary restoration target values and determining liability in environmental emergencies and damage assessments in China [7]. For instance, in the 2015 tailings pond leakage incident involving Longxing Antimony Industry in Gansu Province, Sb pollution affected the waters of the Jialing River, Xihan River, and Taishi River. During the environmental incident, the Sb concentration reached 93 μg/L, which was 18.6 times higher than the standard value of 5 μg/L for Sb in GB3838-2002 [25]. This elevated concentration of antimony may have impacted some aquatic organisms in freshwater, such as Chlorella vulgaris, with LOEC 64 μg/L and NOEC 32 μg/L [48]. During the early emergency response, the FWQC of Sb for the protection of aquatic organisms was successfully applied as the core target for emergency restoration, which reduced remediation costs and enhanced the scientific validity of the response to the Sb pollution incident [7,49]. For another example, the mortality case of fish larvae in the Yangtze River Basin was recognized by the Ministry of Justice as a classic case for environmental damage compensation in China. Based on FWQC for the protection of aquatic organisms for NH3-N, it was confirmed that pollutant discharge from a pig farm significantly elevated NH3-N levels in the surrounding river, establishing a significant causal relationship between river pollution and fish larvae deaths in aquaculture farms [39]. Environmental pollution incidents remain frequent in China, with a total of 3178 cases reported between 2013 and 2022, averaging over 300 cases annually (Table S3). Therefore, the application of FWQC in environmental emergencies and damage assessments should be further explored to provide a basis for the precise handling of pollution incidents.
4. Conclusions
FWQC reflected national needs at the legal and regulatory level, directly supporting the formulation of WQS, environmental risk management, and emergency response efforts. Three technical guidelines for deriving FWQC, critical values for four pollutants, and the compilation of relevant data entries were formulated and published in China. Within the last decade, a possible prioritized list of pollutants for FWQC has been identified and should be considered, including nine categories of heavy metal ions, three categories of non-metal ions, and five categories of organic compounds for the protection of aquatic organisms in short-term future research. Phenol has been proposed as a target for FWQC for organoleptic effects, while FWQC for nutrients should be prioritized for the four lake districts in China. The guidelines for deriving FWQC for the protection of human health and for organoleptic effects, as well as for sediment, need to be emphasized to ensure the safety of drinking water sources, address issues related to black and odorous surface water, and protect the biodiversity of benthic organisms. Furthermore, the importance of developing derivation methods for FWQC related to endocrine disruptors and highly accumulative chemical substances should be highlighted in the future in China. New models, including BLM, MLRM, QSAR, and ICE, should be introduced for deriving FWQC and extrapolating acute and chronic toxicity data for aquatic organisms. Toxicity data, water quality parameters, exposure data, and the geographical distribution of freshwater species should be systematically collected to support the development of FWQC in China. The potential applications of FWQC in China, such as the evaluation and formulation of WQS, ecological risk assessments, and the management of environmental emergencies and damage assessments, should also be explored to support environmental protection and management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17223201/s1, Figure S1: The linear relationship between the hardness (HA, HC) and (a) acute toxicity value (ATV) of 277 and (b) the chronic toxicity value (CTV) of 67 for Cd in China; Table S1: National environmental laws, regulations, or policy documents in different countries; Table S2: The reference documents for the 109-item limit of GB3838-2002; Table S3: The reference documents for the 109-item limit of GB3838-2002; The number of environmental emergencies in China from 2013 to 2022.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.Z. and Z.Z.; Methodology, Z.Z.; Software, Y.F. and W.Z.; Validation, R.H.; Formal analysis, A.L.; Investigation, B.Z. and Z.Z.; Resources, Z.J.; Writing—Original draft preparation, B.Z.; Writing—Review and editing, B.Z. and Y.B.; Visualization, Y.F. and W.Z.; Supervision, Z.J., X.W., C.F. and Y.B.; Project administration, C.F.; Funding acquisition, Y.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2023YFC3208401).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Bo Zhang was employed by the company Environmental Technology & Engineering Co., Ltd., Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| FWQC | Freshwater quality criteria |
| WQS | Water quality standards |
| LWQC | Long-term water quality criteria |
| SWQC | Short-term water quality criteria |
| TPR | Toxicity Percentile Ranking |
| SSD | Species sensitivity distribution method |
| VHCs | Volatile Halogenated Hydrocarbons |
| BSCs | Benzene Series Compounds |
| BLM | Biotic ligand model |
| MLRM | Multiple linear regression model |
| QSARs | Quantitative structure–activity relationships |
| ICE | Interspecies correlation estimation model |
| PPCPs | Pharmaceuticals and personal care products |
| ATV | Acute toxicity value |
| CTV | Chronic toxicity value |
References
- Wu, F. Medium and Long-Term Roadmap for the Development of the Environmental Quality Standard System in China, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Meng, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Cao, Y.; Liao, H. China embarking on development of its own national water quality criteria system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7992–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W.; Ru, S.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Y.; Song, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, J. Pollution level and ecological risk assessment of triazine herbicides in Laizhou bay and derivation of seawater quality criteria. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Ji, D.; Lin, M.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huo, S.; Zhu, J.; Xi, B. Developing surface water quality standards in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 117, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F. Water Quality Criteria Theory, Methodology and Case Studies; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Yan, Z.; Feng, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, X. Derivation of aquatic life water quality criteria for antimonyin freshwater and its implication for water quality standard in China. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Mu, Y.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Su, H.; Wu, F.; Chang, H. China is establishing its water quality standards for enhancing protection of aquatic life in freshwater ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 124, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; C, Y.; Liu, X. Water Quality Criteria and Water Quality Standard; Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Riva, F.; Zuccato, E.; Davoli, E.; Fattore, E.; Castiglioni, S. Risk assessment of a mixture of emerging contaminants in surface water in a highly urbanized area in Italy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 361, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tu, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hou, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yan, Z. Research on freshwater water quality criteria, sediment quality criteria and ecological risk assessment of triclosan in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCME. Canadian Tissue Residue Guidelines for the Protection of Wildlife Consumers of Aquatic Biota; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2000.
- EPA. National Recommended Water Ouality Criteria; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality: Incorporation 1st and 2nd Addenda, 3rd ed.; Technical Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Guidance Document for Aquatic Effects Assessment, OECD Series on Testing and Assessment; Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development: Paris, France, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, T.; Du, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, L. Derivation of water quality criteria for nitrobenzene in shaying river basin and ecological risk assessment. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 15, 256–267. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Mu, Y.; Chang, H.; Zhao, X.; Giesy, J.P.; Wu, K.B. Predicting water quality criteria for protecting aquatic life from physicochemical properties of metals or metalloids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Feng, C.; Chang, H.; Mu, Y.; Wu, F. Study on tissue residue guidelines of DDTs for protection of aquatic mammalian species in china. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2015, 10, 110–118. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Tsai, J.-F.; Chen, P.-J.; Huang, Y.-T.; Liu, B.-H. Thallium exposure interfered with heart development in embryonic zebrafish (Danio rerio) from phenotype to genotype. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 162901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ831-2022; Technical Guideline for Deriving Water Quality Criteria for Freshwater Organisms. Minisitry of Ecology and Environment of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Wen, J.; Cui, X.; Gibson, M.; Li, Z. Water quality criteria derivation and ecological risk assessment for Triphenyltin in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEEC. Water Quality Criteria for Freshwater Aquatic Organisms-Cadmium; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- EPA. Aquatic Life Ambient Water Quality Criteria Cadmium; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- GB3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water. State Environmental Protection Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Li, S.; Li, Y. Research progress on screening priority pollutants in aquatic environments. Environ. Chem. 2024, 43, 1966–1979. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Gu, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L. Ecological and environmental changes and protection measures of lakes in China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2023, 38, 358–364. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, S.; Ma, C.; Xi, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Liu, H. Development of methods for establishing nutrient criteria in lakes and reservoirs: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANZECC; ARMCANZ. Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Fresh and Marine Water Quality; Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council and Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand: Auckland, New Zealand, 2000.
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs exhibiting higher chronic ecological risks? Exploring water quality criteria for ibuprofen in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 392, 1126724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Bi, C.; Lu, Y.; He, G.; Giesy, J.P. Determination of water environment standards based on water quality criteria in China: Limitations and feasibilities. Environ. Sci. 2017, 57, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HJ837-2017; Technical Guideline for Deriving Water Quality Criteria for the Protection of Human Health. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, J.; Qv, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L. Deriving freshwater sediment quality guidelines of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using method of species sensitivity distribution and application for risk assessment. Water Res. 2022, 225, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Liang, W.; Wang, J.; Niu, L.; Zhao, X.; Wu, F. Deriving convincing human health ambient water quality criteria for benzo[a]pyrene and providing basis for the water quality management: The impacts of national bioaccumulation factors and probabilistic modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, R.; Guo, G.; Li, H.; Bai, Y.; Lin, Y.; Cai, T. Derivation of water quality criteria for glyphosate and its formulations to protect aquatic life in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 51860–51870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Jin, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, F.; Johnson, A.C.; Xiao, H.; Hollert, H.; Giesy, J.P. Ecological risk assessment of fifty pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Chinese surface waters: A proposed multiple-level system. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Xie, M.; Tan, Q. Making the Biotic Ligand Model kinetic, easier to develop, and more flexible for deriving water quality criteria. Water Res. 2021, 188, 1116548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEEC. Water Quality Criteria for Freshwater Aquatic Organisms-Ammonia Nitrogen; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Guo, Y.; Yang, M.; He, J.; Qin, N.; Wu, F. Effect of hardness on water quality criteria and ecological risk assessment of zinc. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 2497–2508. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Niu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, A.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X. Effect of water hardness on water quality criteria of lead and correction method. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2021, 16, 191–206. [Google Scholar]
- MEEC. Water Quality Criteria for Freshwater Aquatic Organisms-Phenol; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- MEEC. Nutrient Criteria for Lakes—Central and Eastern Lake Districts (Total Phosphorus, Total Nitrogen, Chlorophyll-A); Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Si, J.; Hong, Y.; Xia, P.; Bai, Y.; Feng, C. Water quality criteria/standards and ecological risk assessment of oxytetracycline for freshwater organisms in China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2023, 36, 403–413. [Google Scholar]
- HJ838-2017; Technical Guideline for Deriving Nutrient Criteria for Lakes. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Chen, L.H.; Yang, J.L. Acute toxicity of antimony chloride and its effects on oxygen consumption of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 78, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chang, S.; Tu, X.; Wang, E.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Fu, Q. Heavy metals in centralized drinking water sources of the Yangtze river: A comprehensive study from a basin-wide perspective. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.X.; Hu, W.X.; He, J.X.; Ni, P.; Xu, K.Q. Regional variations in ore composition and fluid features of massive sulphide deposits in south China: Implications for genetic modelling. Episodes 2000, 23, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Niu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X. Water quality criteria and ecological risk assessment of lead (Pb) in China considering the total hardness of surface water: A national-scale study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Qiao, L.; Ji, L.; Ren, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, R.; Ren, Z. Toxic responses of zebrafish (Danio rerio) to thallium and deltamethrin characterized in the electrocardiogram. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, L.D.D.; Roman, W. Tolerance of Chlorella vulgaris for metallic and non-metallic ions. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 1965, 31, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wu, F.C.; Yu, F.; Bai, Y.C.; Fu, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.R.; Guo, W.J. Fate and removal of antimony in response to stringent control activities after a mine tailing spill. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).