Impact of Rice–Fish Co-Culture on Sediment Phosphorus Forms and Resuspension in the Aquaculture Ponds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Measurement of Water and Sediment Samples
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Impact of Rice–Fish Co-Culture on the Phosphorus Budget Structure of Aquaculture Ponds
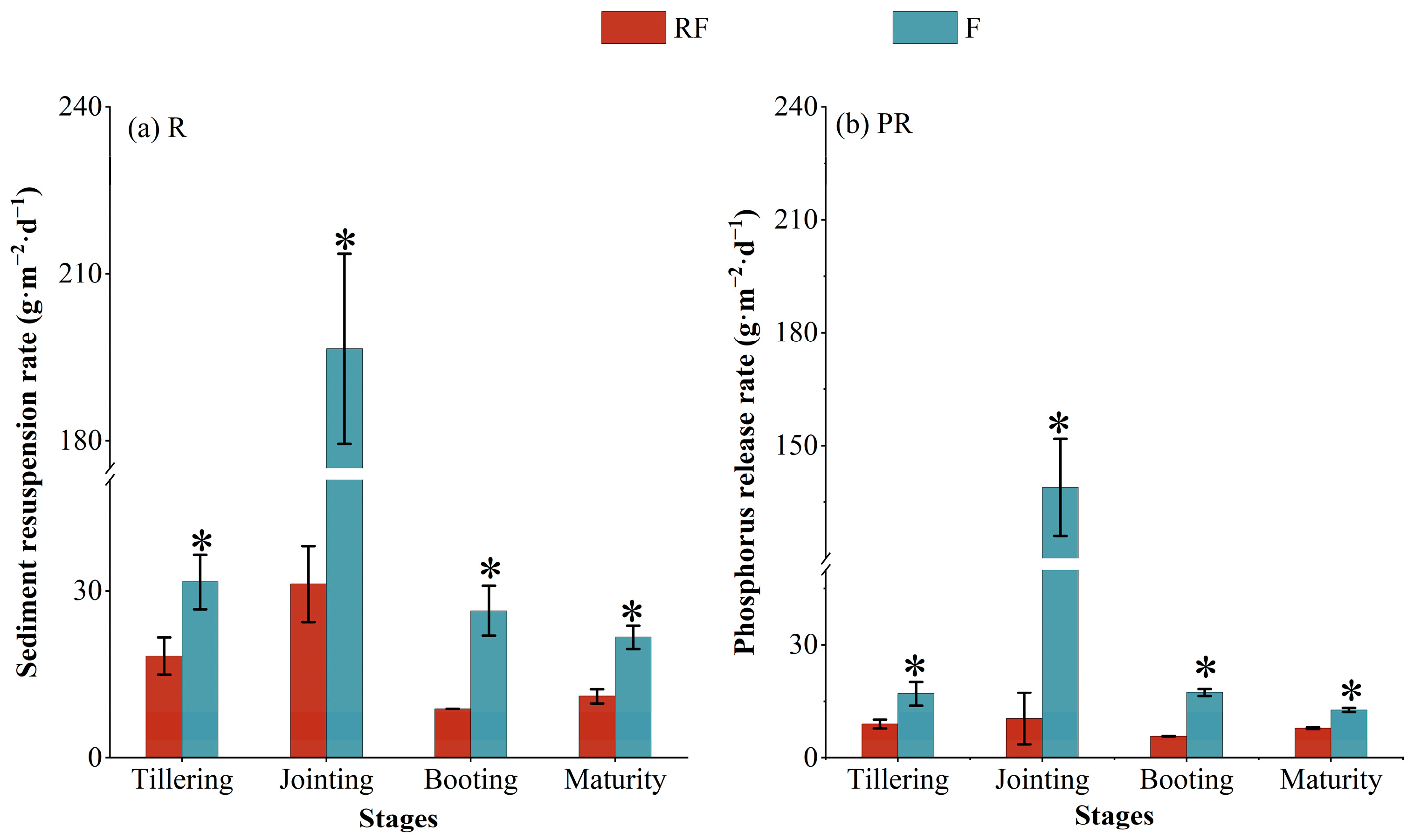
3.2. Depositional Dynamics and Resuspension Processes of Phosphorus in Aquaculture Pond Sediment
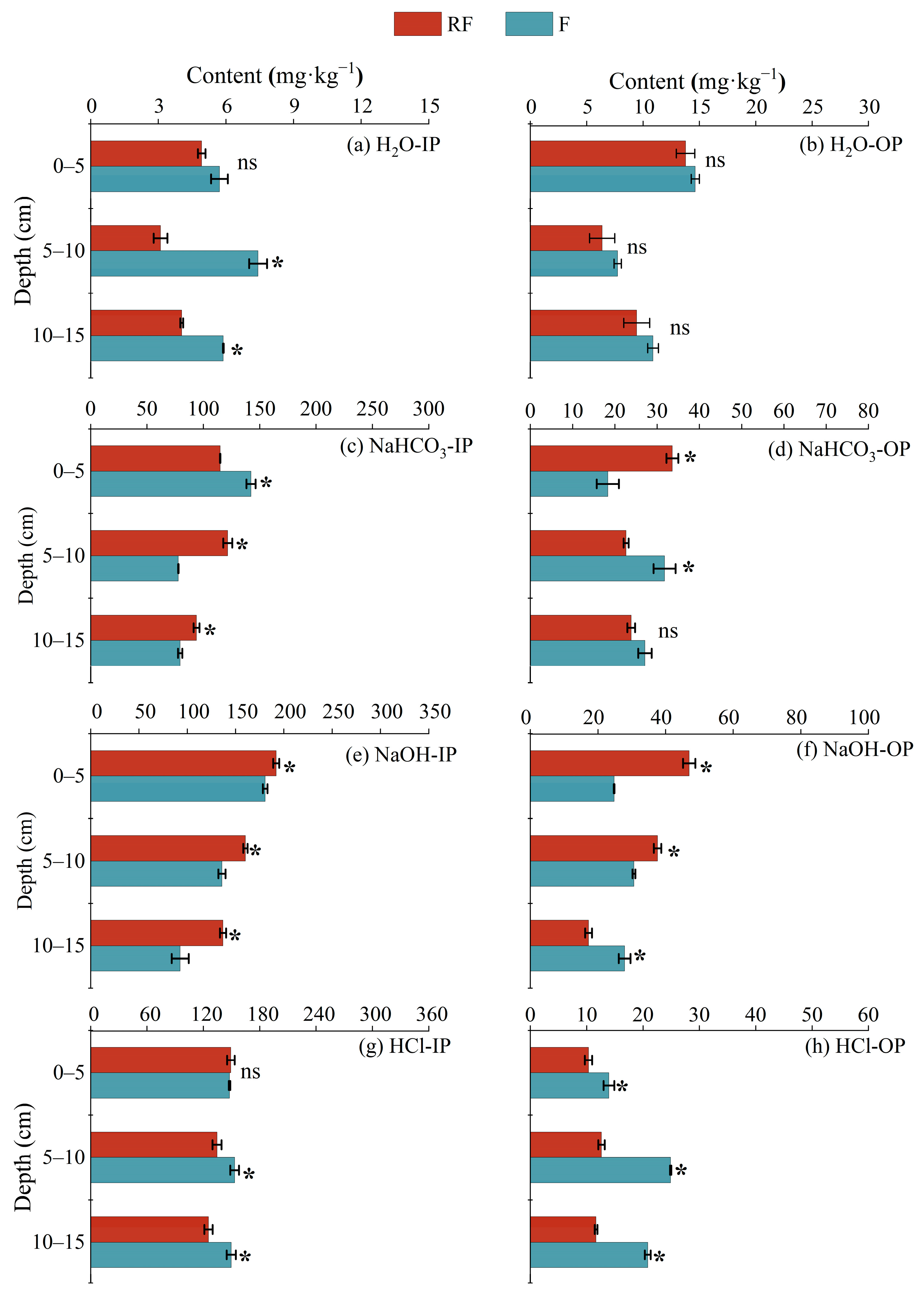
3.3. Phosphorus Species in Sediment Systems
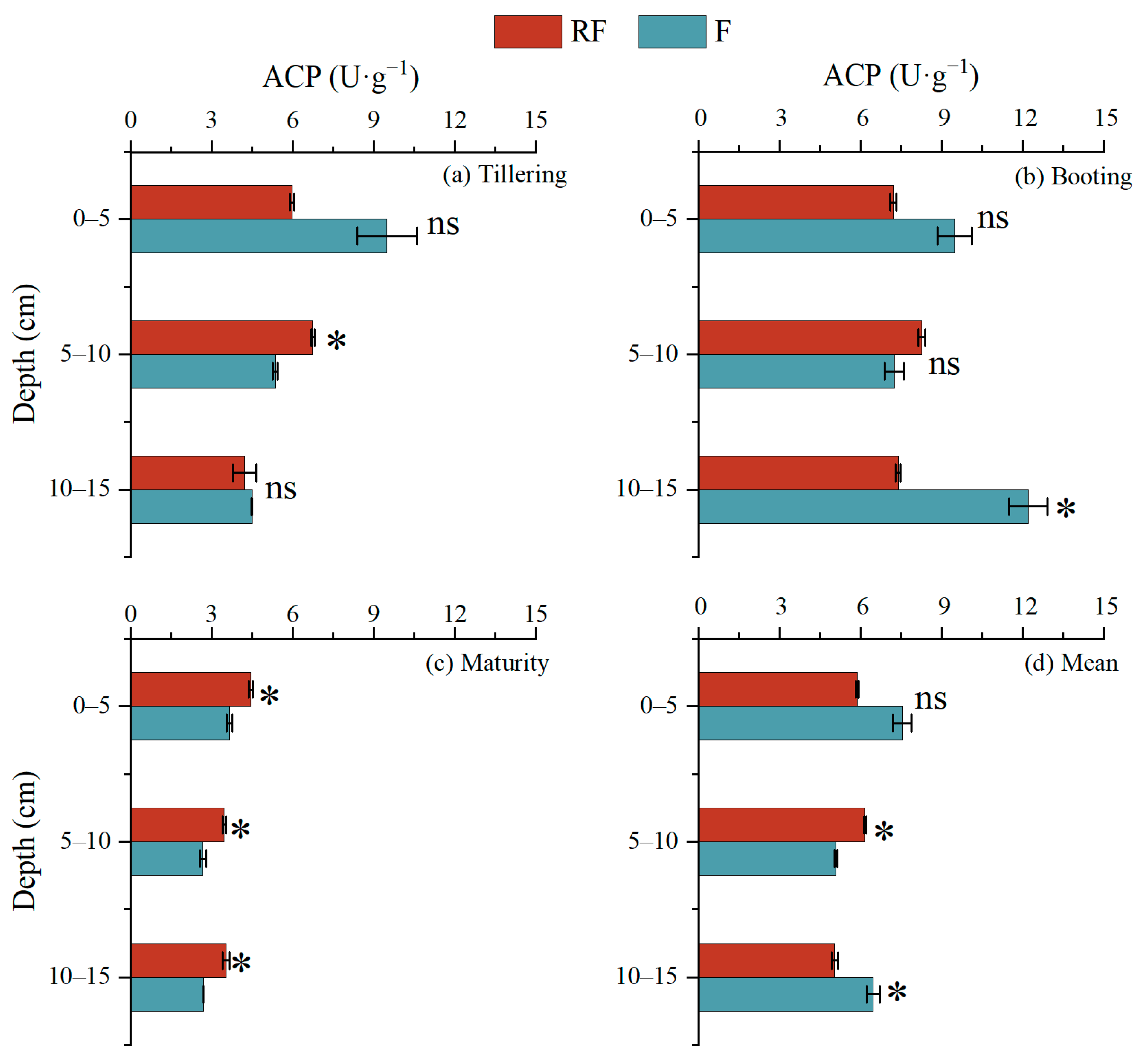
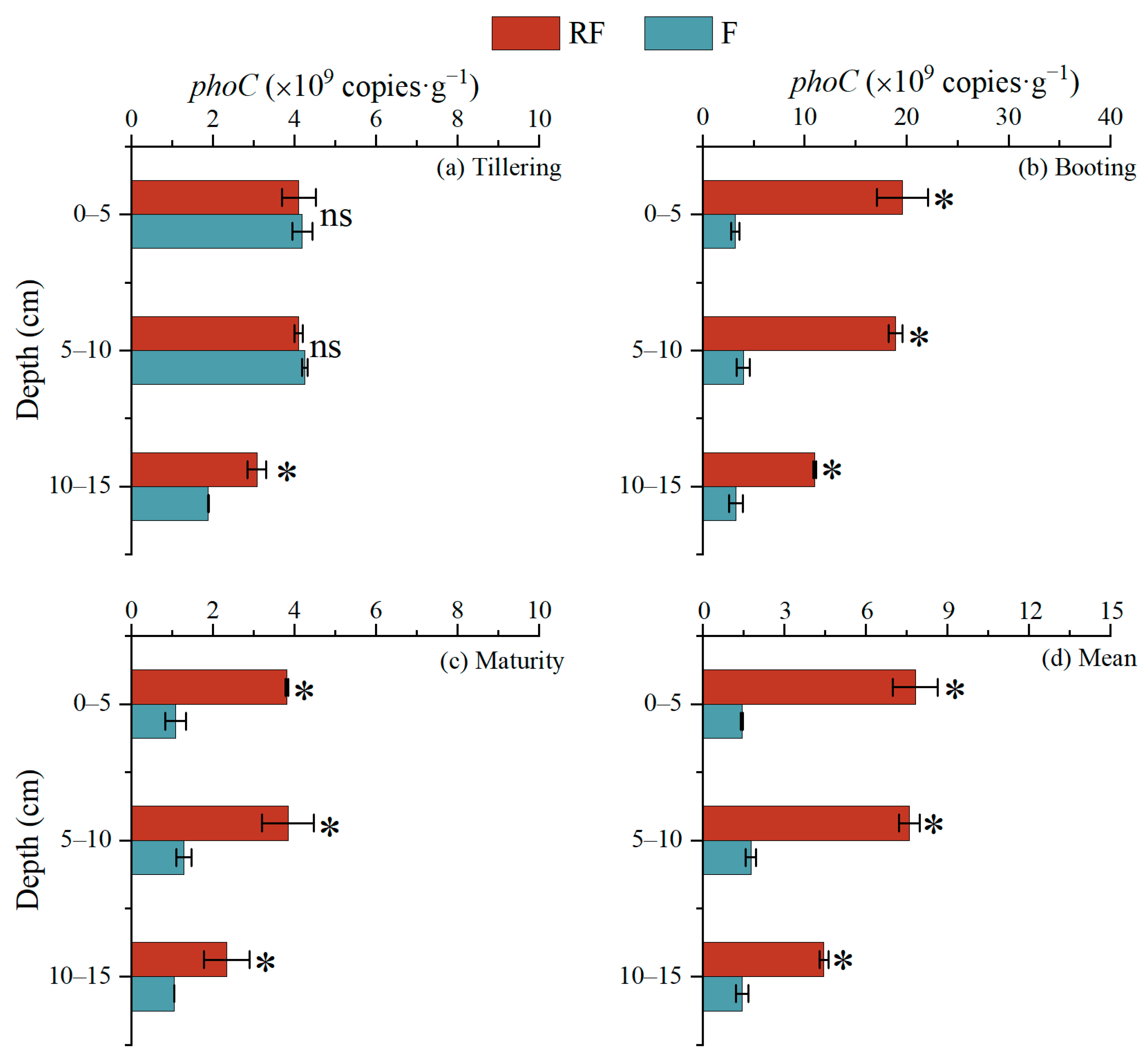
3.4. Activity and Functional Gene Abundance of Acid Phosphatase in Sediment Profiles
3.5. Main Sediment Properties Related to Phosphorus Species Changes
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Rice–Fish Co-Culture on the Phosphorus Residue in the Aquaculture Ponds
4.2. Effects of Rice–Fish Co-Culture on the Form Change in P in the Sediment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TP | Total Phosphorus |
| DIP | Dissolved Inorganic Phosphorus |
| RF | Rice–Yellow Catfish Co-culture |
| F | Yellow Catfish Monoculture |
| R | Sediment Resuspension Rate |
| PR | Phosphorus Release Rate |
| SOC | Soil Organic Carbon |
| ACP | Acid Phosphatase |
References
- Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022: Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; p. 266. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Li, F.; Wu, D.; Fang, F. Effects of rice cropping systems on the restoration of aquaculture pond eutrophication and its prospective application. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 4480–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Casillas-Hernández, R.; Magallón-Barajas, F.; Portillo-Clarck, G.; Páez-Osuna, F. Nutrient mass balances in semi-intensive shrimp ponds from Sonora, Mexico using two feeding strategies: Trays and mechanical dispersal. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.W.; Boyd, C.E.; Chappell, J.A. Approximate Water and Chemical Budgets for an Experimental, In-pond Raceway System. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2012, 43, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.C.; Adhikari, S.; Dey, L. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus budget in shrimp (Penaeus monodon) culture ponds in eastern India. Aquac. Int. 2013, 21, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangro, K.; Olli, K.; Tamminen, T.; Lignell, R. Species-specific responses of a cyanobacteria-dominated phytoplankton community to artificial nutrient limitation in the Baltic Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 336, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, H.; Yuan, X. Temporal-spatial distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in fishery waters of the dongting lake. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2013, 22, 928–936. [Google Scholar]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.; Doris Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2005, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Chauhan, B.S. Changes in inorganic and organic soil phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and by laboratory incubations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Shen, C.; Cheng, Y.; Ding, J.; Li, W. Phosphorus removal by aquatic vegetation in shallow eutrophic lakes: A laboratory study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 16166–16177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Hu, H.; He, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xu, W. Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus in farmland ditches using three aquatic plants. J. Zhejiang A&F Univ. 2019, 36, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Li, X.; Long, Z.; Pei, Y. Comprehensive analysis of the migration and transformation of nutrients between sediment and overlying water in complex habitat systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Li, F.; Barthel, M.; Six, J.; Feng, J.; Fang, F. Impact of rice-crab and rice-fish co-cultures on the methane emission and its transport in aquaculture ponds. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 378, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Feng, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, D.; Chen, F.; Xu, C.; Fang, F. Nutrients removal from fish pond by rice planting. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2015, 29, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Dam, T.; Hart, S.C.; Turner, B.L.; Chadwick, O.A.; Berhe, A.A.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, M. Quantifying uncertainties in sequential chemical extraction of soil phosphorus using XANES spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2257–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condron, L.K.; Goh, K.M.; Newman, R.H. Nature and distribution of soil phosphorus as revealed by a sequential extraction method followed by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance analysis. J. Soil Sci. 1985, 36, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Powlson, D.S.; Jenkinson, D.S. Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yu, L.; Luo, D.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ming, G. Responses of soil phoC and phoD gene microbial communities to the combined application of biochar with chemical fertilizers and organic fertilizers. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Feng, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Ji, L.; Chen, Z.; Jijakli, M.H.; Fang, F.; Zhang, W. Effect of rice-fish/shrimp co-culture on sediment resuspension and associated nutrients release in intensive aquaculture ponds. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horppila, J.; Nurminen, L. Effects of submerged macrophytes on sediment resuspension and internal phosphorus loading in Lake Hiidenvesi (southern Finland). Water Res. 2003, 37, 4468–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Hu, L.; Tang, J.; Wu, X.; Li, N.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Luo, S.; Chen, X. Ecological mechanisms underlying the sustainability of the agricultural heritage rice–fish coculture system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, L.; Ren, H.; Guo, L.; Tang, J.; Shu, M.; Chen, X. Rice-soft shell turtle coculture effects on yield and its environment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 224, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Meng, S.; Hu, G.; Qu, J.; Fan, L. Effect of Ipomoea aquatica cultivation on artificial floating rafts on water quality of intensive aquaculture ponds. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2010, 26, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Chen, J.; Ge, X.; Wu, W.; Fan, L.; Meng, S.; Hu, G. The Control of Nitrogen and Phosphorus to Tilapia Fish Pond by Floating-bed-grown Water Spinach (Ipomoea aquatica). Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2011, 27, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, G. Effects of Vallisneria natans density on phosphorus release by disturbance. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 21, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Gao, C.; Chen, F.; Yu, S. Response of organic carbon burial to trophic level changes in a shallow eutrophic lake in SE China. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 46, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.V.; Emerson, D.; Megonigal, J.P. Rhizosphere iron(III) deposition and reduction in a Juncus effusus L.-dominated wetland. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Xu, D.; Zou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Luo, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Impact of submerged vegetation, water flow field and season changes on sediment phosphorus distribution in a typical subtropical shallow urban lake: Water nutrients state determines its retention and release mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, G.J.D. Rice root properties for internal aeration and efficient nutrient acquisition in submerged soils. New Phytol. 2003, 159, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Feng, J.; Wu, D.; Fang, F. Impacts of rice-fish co-culture on the physical and chemical variables of the microprofiles at sediments-water interface in an intensive-culture pond. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2016, 30, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Vijaykumar, M.E.; Das, B.K.; Samanta, S.; Khan, M.F.; Kayal, T.; Jana, C.; Chowdhury, A.R. Geochemical distribution and forms of phosphorus in the surface sediment of Netravathi-Gurupur estuary, southwestern coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, H.P.; Weir, T.L.; Perry, L.G.; Gilroy, S.; Vivanco, J.M. The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Nguyen, C.; Finlay, R.D. Carbon flow in the rhizosphere: Carbon trading at the soil-root interface. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.E.; Simpson, R. Soil microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, S.F.; Liu, S.; Yang, B. Geochemical fractionation, potential bioavailability and ecological risk of phosphorus in surface sediments of the Cross River estuary system and adjacent shelf, South East Nigeria (West Africa). J. Mar. Syst. 2020, 201, 103244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Phosphorus speciation and availability in sediments off the eastern coast of Hainan Island, South China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 118, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chróst, R.J. Environmental control of the synthesis and activity of aquatic microbial ectoenzymes. In Microbial Enzymes in Aquatic Environments; Chróst, R.J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 29–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Vitousek, P.M. Responses of extracellular enzymes to simple and complex nutrient inputs. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, J.K.; Hofmockel, K.S. Soil microbiomes and climate change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 18, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, E.K. Assessment of gross and net mineralization rates of soil organic phosphorus—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 89, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; DeLaune, R.D. Biogeochemistry of Wetlands: Science and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 213–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Boot, C.M.; Denef, K.; Paul, E. The Microbial Efficiency-Matrix Stabilization (MEMS) framework integrates plant litter decomposition with soil organic matter stabilization: Do labile plant inputs form stable soil organic matter? Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleber, K.; Eusterhues, K.; Keiluweit, M.; Mikutta, C.; Mikutta, R.; Nico, P.S. Mineral–organic associations: Formation, properties, and relevance in soil environments. Adv. Agron. 2015, 130, 1–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Shen, J.; Liu, E.; Meng, X.; Wang, J. Characteristic of phosphorus release with the control of pH of sediments from Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu. Sci. Limno. Sin. 2009, 21, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, H.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Y. The effects of pH on different forms of phosphorus release in sediments under the condition of Eichhornia crassipe-growing. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2017, 40, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| P Input | P Harvest | Residue in Water (%) | Residue in Sediment (%) | P Utilization Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feed (g·m−2) | Fish (g·m−2) | Rice (g·m−2) | ||||
| F | 7.10 | 1.59 a | 4.37 a | 73.24 a | 22.39 b | |
| RF | 7.10 | 1.41 a | 2.22 | 0.99 b | 47.89 b | 51.13 a |
| Depth (cm) | Treatment | Fe (mg·kg−1) | Mn (mg·kg−1) | pH | SOM (g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–5 | F | 314.41 ± 2.57 b | 114.05 ± 3.16 a | 6.71 ± 0.01 a | 20.41 ± 0.23 b |
| RF | 336.53 ± 3.78 a | 98.70 ± 1.78 a | 6.57 ± 0.01 b | 23.48 ± 0.25 a | |
| 5–10 | F | 249.87 ± 7.39 b | 117.26 ± 1.75 a | 6.96 ± 0.05 a | 18.23 ± 0.39 b |
| RF | 361.74 ± 0.90 a | 123.68 ± 0.42 a | 6.57 ± 0.04 b | 20.38 ± 0.15 a | |
| 10–15 | F | 182.93 ± 3.50 b | 117.47 ± 1.36 a | 6.71 ± 0.06 a | 17.31 ± 0.27 a |
| RF | 308.02 ± 5.85 a | 113.68 ± 0.25 a | 6.48 ± 0.03 b | 18.11 ± 0.35 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Bao, T.; Yang, T.; Feng, J.; Xu, C.; Fang, F.; Li, F. Impact of Rice–Fish Co-Culture on Sediment Phosphorus Forms and Resuspension in the Aquaculture Ponds. Water 2025, 17, 3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213161
Wang M, Bao T, Yang T, Feng J, Xu C, Fang F, Li F. Impact of Rice–Fish Co-Culture on Sediment Phosphorus Forms and Resuspension in the Aquaculture Ponds. Water. 2025; 17(21):3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213161
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mengjie, Ting Bao, Tong Yang, Jinfei Feng, Chunchun Xu, Fuping Fang, and Fengbo Li. 2025. "Impact of Rice–Fish Co-Culture on Sediment Phosphorus Forms and Resuspension in the Aquaculture Ponds" Water 17, no. 21: 3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213161
APA StyleWang, M., Bao, T., Yang, T., Feng, J., Xu, C., Fang, F., & Li, F. (2025). Impact of Rice–Fish Co-Culture on Sediment Phosphorus Forms and Resuspension in the Aquaculture Ponds. Water, 17(21), 3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213161






