The Role of Smart Infrastructure in Residential Water Demand Management: A Global Survey
Abstract
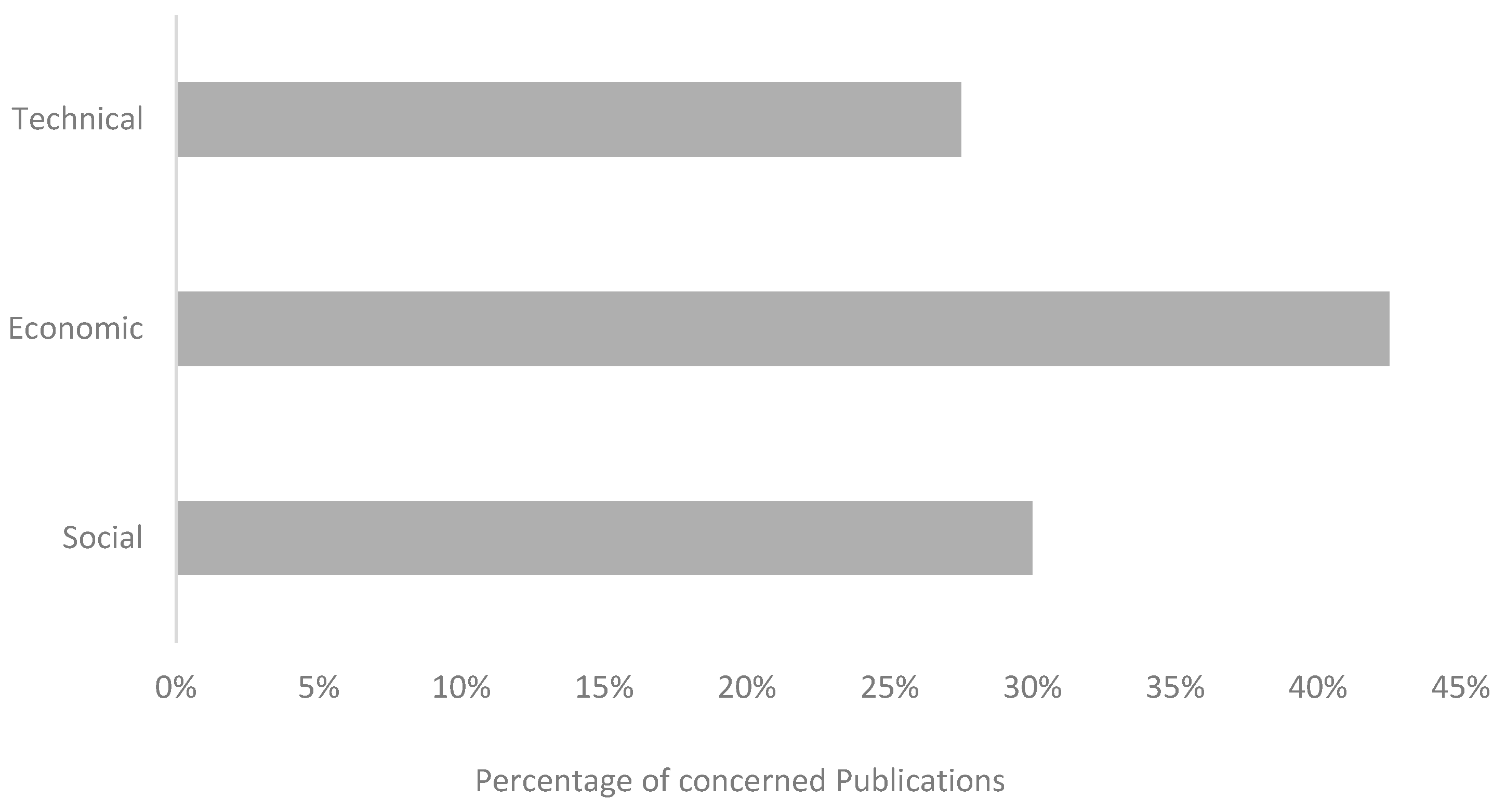
1. Introduction
- High-resolution data collection over smart metering to capture granular, time-stamped water use configurations.
- Behavioral and socio-demographic investigation to find high-consumption parts (e.g., small, older households) and patterns of incompetent usage.
- Disaggregated end-use modelling, allowing exact credit of demand to specific activities such as showers, laundry, and irrigation.
- Efficiency-based interference, including the elevation of water-saving applications and detection of non-compliant irrigation performs.
- Temporal demand profiling, using daytime water use patterns to update infrastructure design, peak-demand management, and strategy timing.
- Equity-aware design, accounting for varied local, demographic, and household characteristics that affect water stress levels.
2. Methodology
2.1. Research Questions
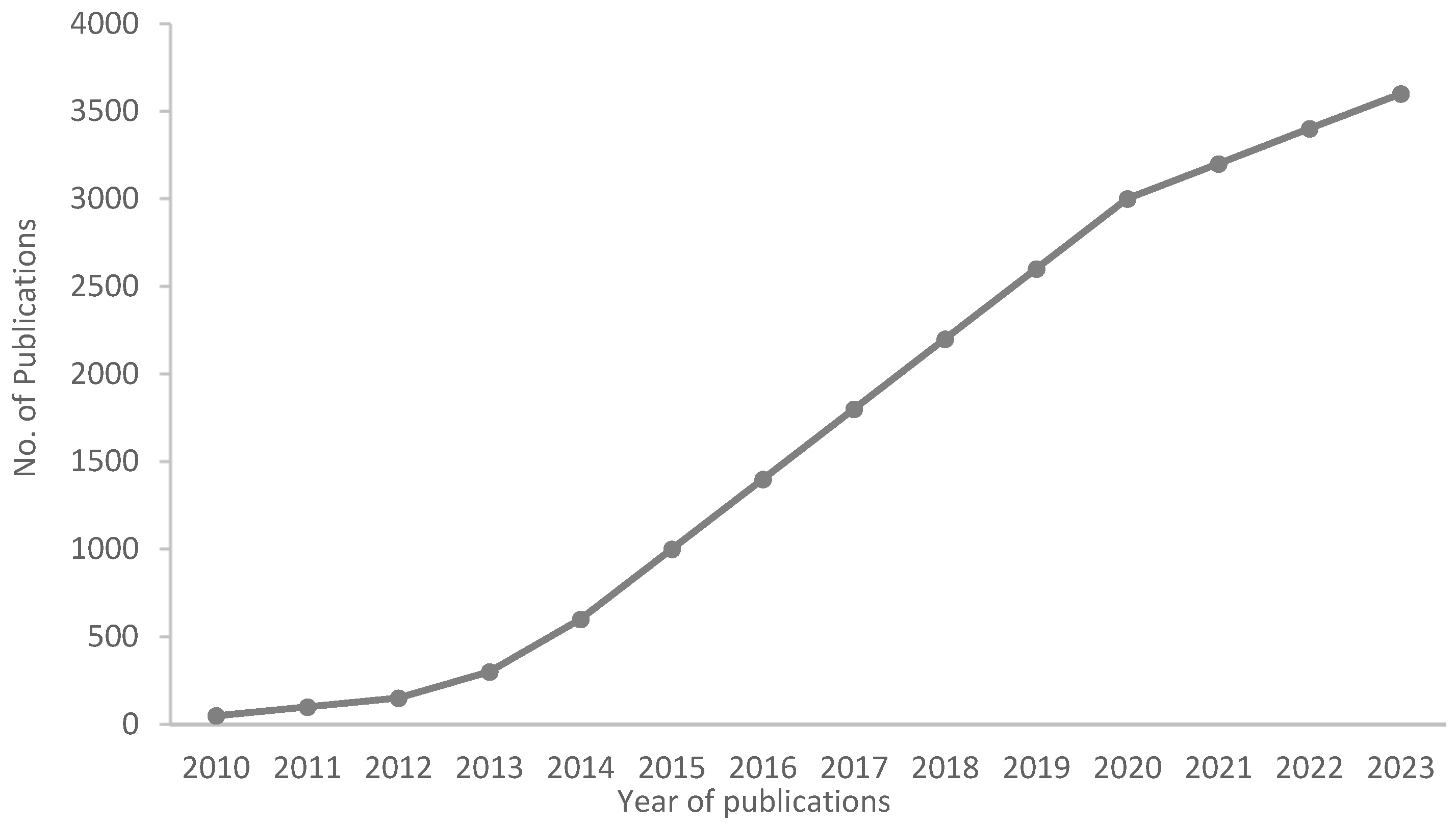
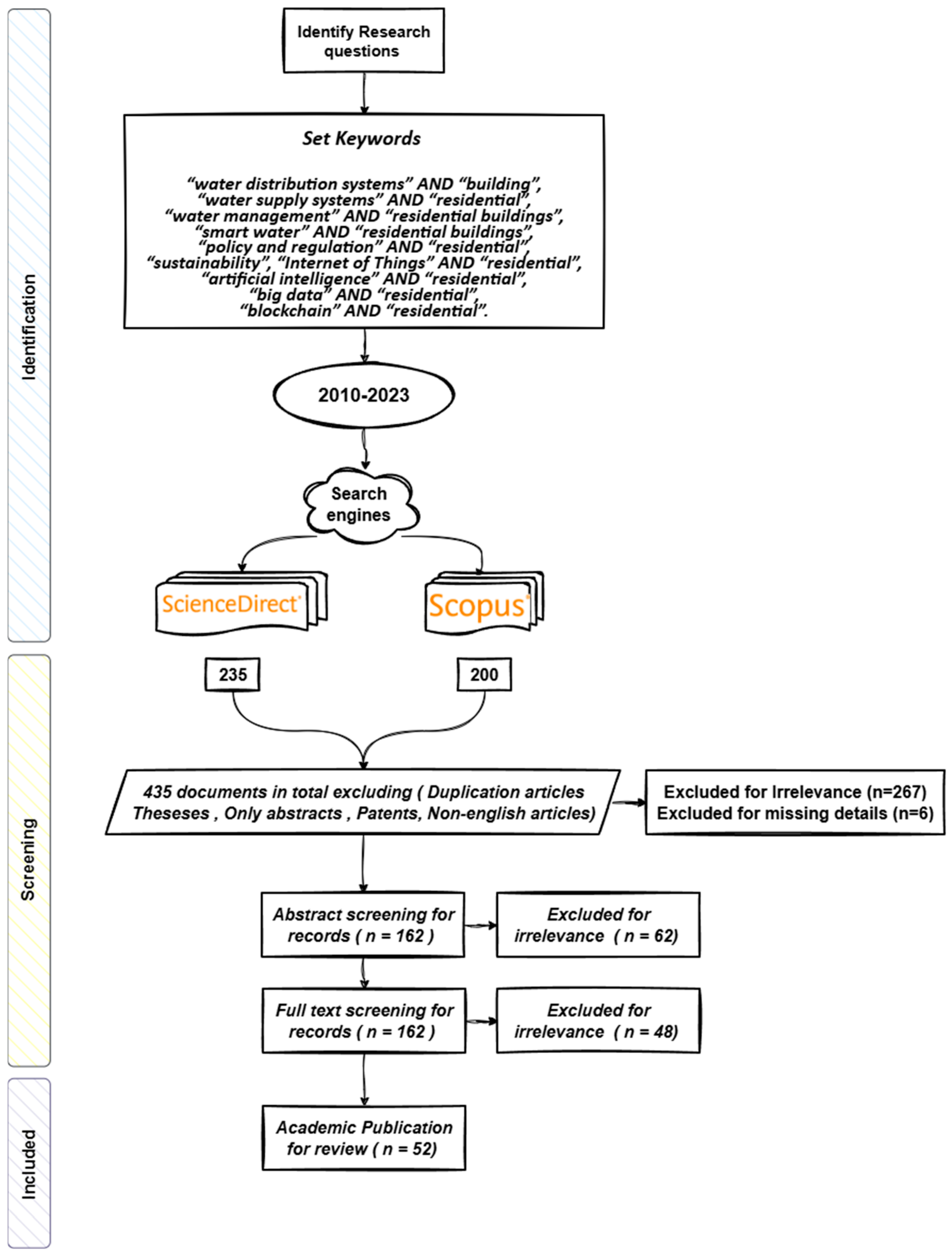
2.2. Literature Search Strategy
3. Global Motivations for WDM
3.1. Overview
3.2. Role of Policies and Regulations in WDM Adaptation
4. Assessment of Current Techniques in Smart WDM
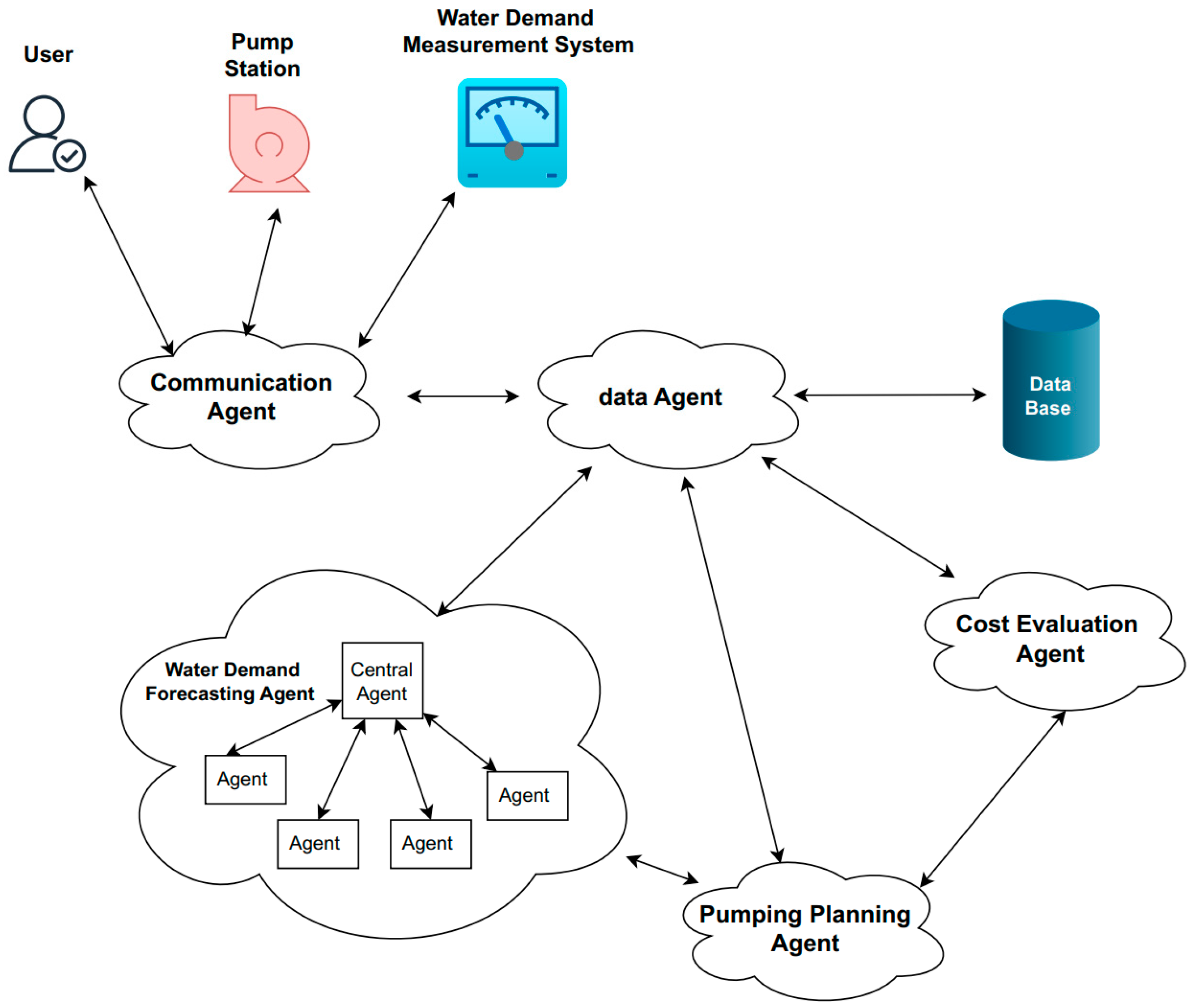
5. Smart Agents for WDM
5.1. Smart City Concept
5.1.1. Smart Water Management (SWM)
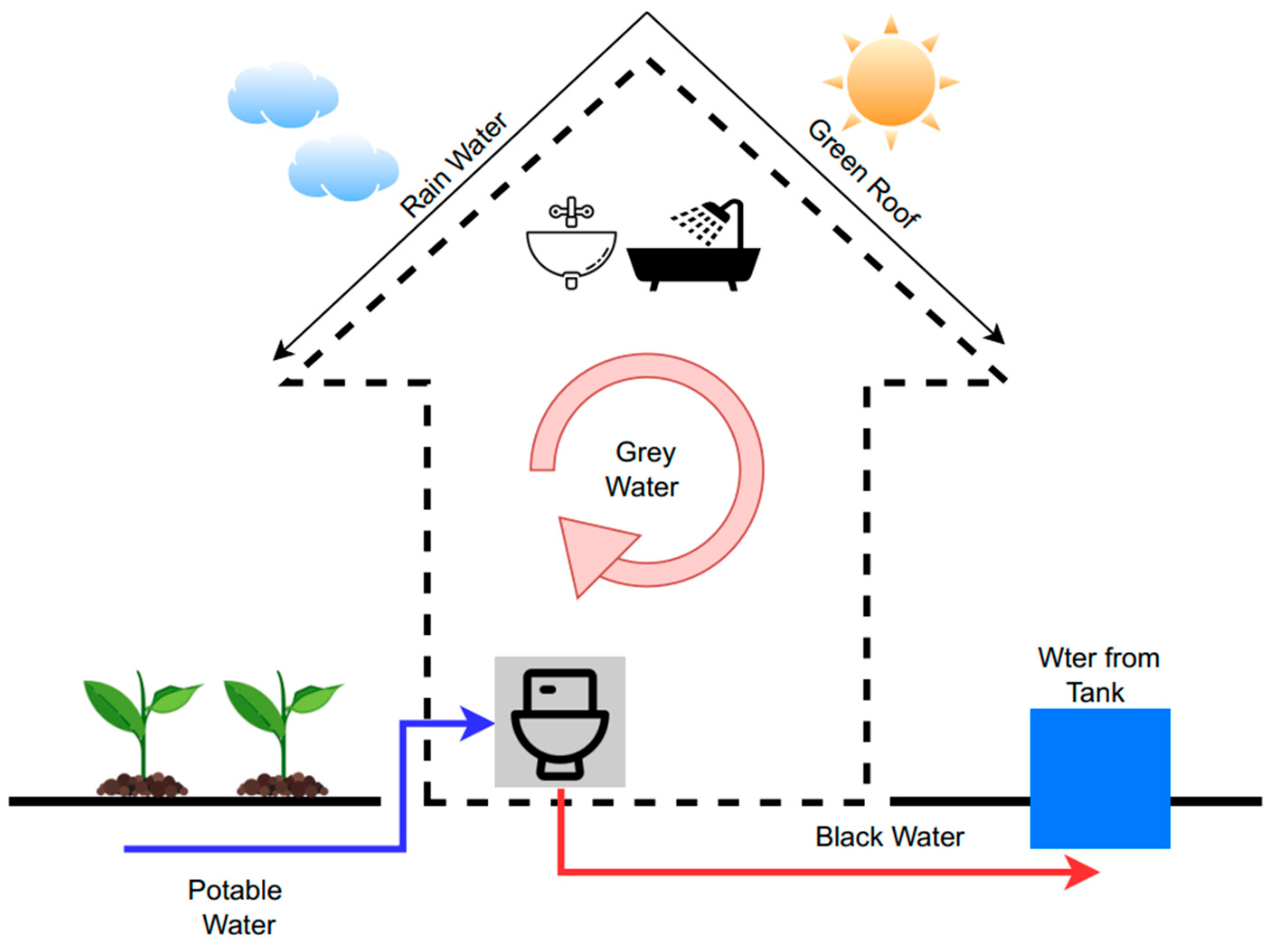
5.1.2. Smart Water Management at Residential Buildings
5.1.3. Information and Communication Technologies (ICT)
5.1.4. IoT
- Connectivity: Connecting sensors to the cloud and other “things” has never been easier because of the proliferation of network protocols for the internet.
- Cloud computing systems: The proliferation of cloud platforms gives companies and individuals easy access to scalable infrastructure without the overhead of managing it themselves.
- Analytics and ML: Businesses now have easier and quicker access to valuable insights due to developments in ML and analytics, as well as the diverse and large volumes of data stored on the cloud. The data generated by IoT also fuels these ancillary technologies, whose rise continues to push the frontiers of IoT.
- AI capable of human-like conversation: IoT devices (such as digital personal assistants like Alexa, Cortana, and Siri) now have access to natural language processing (NLP) thanks to developments in neural networks.
5.1.5. Smart Metering
- Detection/transduction system to convert the analytical signal into a measurable electrical quantity.
- Suitable measurement and signal processing interface to shape the electrical signal.
- Data processing together with a calibration system to ensure the measurement is accurate.
- Autonomous power source to guarantee the nonstop operation of the entire process.
5.1.6. Demand Response (DR)
6. Common Barriers of Applying WDM
- (a)
- Lacking in Education and Awareness: The necessity of water conservation and effective distribution practices may not be well known in many areas due to a lack of awareness and education. Because of this, water may be used inefficiently, and distribution systems may not be properly maintained.
- (b)
- Resistance to Change: Stakeholders may be hesitant to adopt new water distribution practices due to their comfort with the status quo. This may be a barrier to implementing new methods of administration and cutting-edge technology.
- (c)
- Inadequate Community Engagement: The effectiveness of water distribution management plans may be hampered by a lack of active engagement and involvement from local communities, which is often the result of Inadequate Community Engagement. Sustainable water management relies heavily on public participation, education, and involvement in policymaking.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baumann, D.D.; Boland, J.J.; Hanemann, W.M. Urban Water Demand Management and Planning; McGraw-Hill Professional: Columbus, OH, USA, 1997; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, D.B. An operational definition of water demand management. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2006, 22, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, F.M.D. Water Demand Management; IWA: Singapore, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, L.E.; Puz, G. A Review of Selected Hydrology Topics to Support Bank Operations: Report. HEF Technical Report 1. 2010. Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/282691468331807322/pdf/598080v10WP0Hy10BOX358294B01PUBLIC1.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Gleick, P.H. Global Freshwater Resources: Soft-Path Solutions for the 21st Century. Science 2003, 302, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzetti, S. The Economics of Water Demands; Springer Nature: Durham, NC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, L. Water demand management in England and Wales: Constructions of the domestic water user. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2006, 49, 869–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.J.; Mcdonald, G.W.; Murray, C.F. The costs and benefits of water demand management: Evidence from New Zealand. Water Environ. J. 2015, 29, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampragou, E.; Lekkas, D.F.; Assimacopoulos, D. Water demand management: Implementation principles and indicative case studies. Water Environ. J. 2011, 25, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Vairavamoorthy, K. Urban water demand management: Prospects and challenges for the developing countries. Water Environ. J. 2009, 23, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmstead, S.M.; Stavins, R.N. Comparing price and nonprice approaches to urban water conservation. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanke, A.; Rozelle, S.; Lohmar, B.; Wang, J.; Huang, J. Water saving technology and saving water in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savenije, H.H.G.; van der Zaag, P. Water as an economic good and demand management: Paradigms with pitfalls. Water Int. 2002, 27, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, D.M. Water demand management in Canada: A review and assessment. Can. Water Resour. J. 1989, 14, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, A.R.; Moug, P.; Lerner, D.N. The Network Governance of Urban River Corridors. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.F.; Chiu, C.Y. Institutional Nesting and Robustness of Self-Governance: The Adaptation of Irrigation Systems in Taiwan. Int. J. Commons 2016, 10, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijani, M.; Hayati, D.; Azadi, H.; Tanaskovik, V.; Witlox, F. Causes and Consequences of the Conflict Among Agricultural Water Beneficiaries in Iran. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsegaye, S.; Missimer, T.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Hock, J. A Clustered, Decentralized Approach to Urban Water Management. Water 2020, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katusiime, J.; Schütt, B. Integrated Water Resources Management Approaches to Improve Water Resources Governance. Water 2020, 12, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, F.; Wei, Y.; Hussey, K.; Pittock, J.; Ison, R. Improving the Role of River Basin Organisations in Sustainable River Basin Governance by Linking Social Institutional Capacity and Basin Biophysical Capacity. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 33, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, K.S.; Stenstrom, M.K. A Feasibility Analysis Methodology for Decentralized Wastewater Systems—Energy-Efficiency and Cost. Water Environ. Res. 2016, 88, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, X.C. Cost–benefit Evaluation of a Decentralized Water System for Wastewater Reuse and Environmental Protection. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, J.C.; Granville, L.Z. Consistency Maintenance of Policy States in Decentralized Autonomic Network Management. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Network Operations and Management Symposium-NOMS 2010, Osaka, Japan, 19–23 April 2010; pp. 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, J.G.; Waite, T.D.; Luthy, R.G.; Drewes, J.E.; Sedlak, D.L. A Changing Framework for Urban Water Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10721–10726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Byrne, A.; Nguyen, L.; Jaramillo, E.; Fox, G.J. Decentralized Care for Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, C.; Li, H. Decision and Coordination of Low-Carbon Supply Chain Considering Technological Spillover and Environmental Awareness. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabi, A.; Stokes-Draut, J.; Horvath, A. Energy and Air Emission Implications of a Decentralized Wastewater System. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 024007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boavida, S.; Pinto, M.P.; Salvador, T.; Hind, M.; Neto, S. Centralized Versus Decentralized Wastewater Systems—Potential of Water Reuse Within a Transboundary Context. New Water Policy Pract. 2016, 2, 54–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieker, S.; Cornel, P.; Wagner, M. Semicentralised Supply and Treatment Systems: Integrated Infrastructure Solutions for Fast Growing Urban Areas. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2905–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laminu, M.-D.; Ahadzie, D.K.; Okrah, M. Domestic End-Users’ Participation in Managing Urban Water Supply in Emerging Cities: Evidence From Wa, Ghana. Ghana J. Dev. Stud. 2021, 18, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faysse, N. Troubles on the Way: An Analysis of the Challenges Faced by Multi-Stakeholder Platforms. Nat. Resour. Forum 2006, 30, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Meknassi Yousoufi, E.; Hammani, A.; Kuper, M.; Bouarfa, S.; Vallée, D. Water Accounting in the Berrechid Plain (Morocco): A Process Approach. Irrig. Drain. 2023, 73, 180–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandvoort, M.; van der Brugge, R.; van der Vlist, M.J.; van den Brink, A. Dealing With Uncertainty in Collaborative Planning: Developing Adaptive Strategies for the IJsselmeer. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2018, 62, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.H.; Chan, N.W.; Roy, R. Understanding Public Perception of and Participation in Non-Revenue Water Management in Malaysia to Support Urban Water Policy. Water 2017, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.; Mallory, S.J.L. The Importance of Operating Rules and Assessments of Beneficial Use in Water Resource Allocation Policy and Management. Water Policy 2009, 11, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwambu, B.W.; Kimani, E.; Maina, L. Enhancing the Participation of Men and Women in the Management of Water Resources at the Bridge Water Supply Project in Kakamega County, Kenya. J. Adv. Humanit. 2015, 4, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlimann, A.; Wilson, E. Sustainable Urban Water Management Under a Changing Climate: The Role of Spatial Planning. Water 2018, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, P.; Qureshi, R.; Porter, S.; Chao, Y.-Y.; Pacquiao, D.; Chase, S.; O’bRien-Richardson, P. Utilizing a Mobile Health Intervention to Manage Hypertension in an Underserved Community. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2019, 42, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ako, A.A.; Eyong, G.E.T.; Nkeng, G.E. Water Resources Management and Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) in Cameroon. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 24, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnell, N.W. Climate change and global water resources. Glob. Environ. Change 1999, 9, S31–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Sources and Solutions: Wastewater. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/nutrientpollution/sources-and-solutions-wastewater (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Falkenmark, M.; Lundqvist, J.; Widstrand, C. Macro-scale water scarcity requires micro-scale approaches: Aspects of vulnerability in semi-arid development. Nat. Resour. Forum 1989, 13, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Green, P.; Salisbury, J.; Lammers, R.B. Global water resources: Vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 2000, 289, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Gosling, S.N.; Kummu, M.; Flörke, M.; Pfister, S.; Hanasaki, N.; Wada, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; et al. Water scarcity assessments in the past, present, and future. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guppy, L.; Mehta, P.; Qadir, M. Sustainable development goal 6: Two gaps in the race for indicators. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 14, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Water. Coping with Water Scarcity: A Strategic Issue and Priority for System-Wide Action. 2006. Available online: https://www.preventionweb.net/files/1770_VL102303.pdf?startDownload=true (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Rijsberman, F.R. Water scarcity: Fact or fiction? Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockaway, T.D.; Coomes, P.A.; Joshua, R.; Barry, K. Residential water use trends in North America. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2011, 103, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, E.; Cinperi, N.C. Water efficiency and wastewater reduction in an integrated woolen textile mill. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mini, C.; Hogue, T.S.; Pincetl, S. The effectiveness of water conservation measures on summer residential water use in Los Angeles, California. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 94, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumaran, S.; Baskaran, K.; Sexton, N. Quantification of potable water savings by residential water conservation and reuse—A case study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, D.M.; Lohman, H.A.C.; Cook, S.M.; Peters, G.M.; Guest, J.S. Life cycle assessment (LCA) of urban water infrastructure: Emerging approaches to balance objectives and inform comprehensive decision-making. Environ. Sci. 2017, 3, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Kim, J.; Sovacool, B.K.; Griffiths, S.; Bazilian, M.; Yang, M. Decarbonizing the chemical industry: A systematic review of sociotechnical systems, technological innovations, and policy options. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2023, 96, 102955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattachan, A.; Skaff, N.K.; Irish, A.M.; Vimal, S.; Remais, J.V.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Outdoor Residential Water Use Restrictions during Recent Drought Suppressed Disease Vector Abundance in Southern California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Ward, P.J.; De Moel, H.; Varis, O. Is physical water scarcity a new phenomenon? Global assessment of water shortage over the last two millennia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 034006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolf, C.; Xie, Y.; Vannoorbeeck, F.; Chen, B. Delta management in evolution: A comparative review of the Yangtze River Delta and Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt Delta. Asia-Pac. J. Reg. Sci. 2021, 5, 597–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickert, G.E.H. Water and the future of humanity: Revisiting water security. Can. Water Resour. J./Rev. Can. Des Ressour. Hydr. 2015, 40, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water, a Shared Responsibility: The United Nations World Water Development Report 2. Choice Rev. Online 2007, 44, 5. [CrossRef]
- Ondrasek, G. Water scarcity and water stress in agriculture. In Physiological Mechanisms and Adaptation Strategies in Plants Under Changing Environment; Springer Nature: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, W.K.; Plantinga, A.J.; Chang, H.; Dello, K.; Grant, G.; Hulse, D.; McDonnell, J.J.; Lancaster, S.; Moradkhani, H.; Morzillo, A.T.; et al. Toward a formal definition of water scarcity in natural-human systems. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4506–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utari, T.J. Pengaruh Penerapan Peraturan Pemerintah Satu Tarif Untuk Transportasi Online Terhadap Pendapatan Driver Transportasi Online Dalam Perspektif Ekonomi Islam (Studi Pada Driver Ojek Online di Kota Bandar Lampung). 2021. Available online: https://repository.radenintan.ac.id/17852/1/SKRIPSI%201-5.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Mehta, L. Whose scarcity? Whose property? The case of water in western India. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, C.; Flancher, D. Focus on Total Water Solutions. J. AWWA 2015, 107, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, N.; Vlăduț, V.; Voicu, G. Water scarcity and wastewater reuse in crop irrigation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Urban Water Scarcity Guidance Note; United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF): New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vranayová, Z.; Káposztásová, D. Water Demand Management and Its Impact on Water Resources at the Building Level. In Water Resources in Slovakia: Part II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 70, pp. 225–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kaposztasova, D.; Rysulova, M.; Purcz, P. Integrated Building Water Management Options. WSEAS Trans. Environ. Dev. 2015, 11, 282–288. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, N.A.; Moradi, E.; Hoseini, S.M.; Shahraki, A.S. Simulation of the dynamics of water resources in the Hirmand watershed under economic and environmental scenarios. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 15091–15117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.-L.; Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S. Artificial Neural Network Modeling of the Rainfall-Runoff Process. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2517–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Shahsavari, Z. Water allocation for agriculture in southwestern Iran using a programming model. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pearce, D.W.; Warford, J.J. World without end: Economics, environment and sustainable development. Econ. J. 1993, 104, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, A. Modelling Household Water Demand in Europe Insights from a Cross-Country Econometric Analysis of EU-28 Countries; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kenney, D.S.; Goemans, C.; Klein, R.; Lowrey, J.; Reidy, K. Residential water demand management: Lessons from Aurora, Colorado. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2008, 44, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalhuisen, J.M.; Florax, R.J.G.M.; de Groot, H.L.F.; Nijkamp, P. Price and income elasticities of residential water demand: A meta-analysis. Land Econ. 2003, 79, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, E.T.; Olmstead, S.M. The value of scarce water: Measuring the inefficiency of municipal regulations. J. Urban Econ. 2012, 71, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimlou, K.; Hassani, N.; Mehrabadi, A.R.; Nazari, M.R. Calculating Price Elasticity of Water Demand Using Gene Expression Programming Based on Economic, Social and Meteorological Variables. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 4171–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos, D.; Artabe, A. Regional Differences in the Price Elasticity of Residential Water Demand in Spain. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 847–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Peeters, P.; Hall, C.M.; Ceron, J.-P.; Dubois, G.; Lehmann, L.V.; Scott, D. Tourism and water use: Supply, demand, and security. An international review. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araral, E.; Wang, Y. Water demand management: Review of literature and comparison in South-East Asia. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2013, 29, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Limón, J.A.; Martínez, Y. Multi-criteria modelling of irrigation water market at basin level: A Spanish case study. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 173, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Development Report, 2006: Beyond Scarcity: Power, Poverty and the Global Water Crisis. Choice Reviews Online vol. 44, no. 12, 2007. Available online: https://choicereviews.org/login (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Kumura, T.; Suzuki, N.; Takahashi, M.; Tominaga, S.; Morioka, S.; Ivan, S. Smart water management technology with intelligent sensing and ICT for the integrated water systems. NEC Tech. J. 2015, 9, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Nasser, A.A.; Rashad, M.Z.; Hussein, S.E. A Two-Layer Water Demand Prediction System in Urban Areas Based on Micro-Services and LSTM Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 147647–147661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, A.J.; Allen, M.; Preis, A.; Iqbal, M. Sensor networks for monitoring and control of water distribution systems. In Structural Health Monitoring for Infrastructure Sustainability, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Structural Health Monitoring of Intelligent Infrastructure, SHMII 2013, Hong Kong, 9–11 December 2013; Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University: Hong Kong, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.; Singh, D.; Purwar, A.; Patel, M. Automated learning based water management and healthcare system using cloud computing and iot. In Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, A.; Jurasz, J.; Skowron, R. Forecasting surface water level fluctuations of lake Serwy (Northeastern Poland) by artificial neural networks and multiple linear regression. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2017, 25, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Kaa, G.; Fens, T.; Rezaei, J.; Kaynak, D.; Hatun, Z.; Tsilimeni-Archangelidi, A. Realizing smart meter connectivity: Analyzing the competing technologies Power line communication, mobile telephony, and radio frequency using the best worst method. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rote, S.; Mourya, A.; Oak, T.; Yadav, A. Automatic Water Distribution System using PLC. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2017, V6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Mu, G.; Liao, R. Big Data Analytics in China’s Electric Power Industry: Modern Information, Communication Technologies, and Millions of Smart Meters. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2018, 16, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildirici, M.E. Economic growth and electricity consumption: MS-VAR and MS-G ranger causality analysis. OPEC Energy Rev. 2013, 37, 447–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esther, B.P.; Kumar, K.S. A survey on residential Demand Side Management architecture, approaches, optimization models and methods. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillo, J.; Dahlquist, E.; Wallin, F.; Vassileva, I. Is real-time electricity pricing suitable for residential users without demand-side management? Energy 2016, 109, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grønhøj, A.; Thøgersen, J. Feedback on household electricity consumption: Learning and social influence processes. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2011, 35, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Liu, X. Electricity tariff reform and rebound effect of residential electricity consumption in China. Energy 2013, 59, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, M.; Jarrah, M.; Bousselham, A.; Jararweh, Y.; Al-Ayyoub, M. The internet of energy: Smart sensor networks and big data management for smart grid. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 56, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Kumar, A.; Rathod, N.; Jain, P.; Mallikarjun, S.; Subramanian, R.; Amrutur, B.; Kumar, M.S.M.; Sundaresan, R. Towards an IoT based water management system for a campus. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 1st International Smart Cities Conference, ISC2 2015, Guadalajara, Mexico, 25–28 October 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, T.; Alcarria, R.; Martín, D.; Navarro, M.; Calero, R.; Iglesias, S.; López, M. An iot based reference architecture for smart water management processes. J. Wirel. Mob. Netw. Ubiquitous Comput. Dependable Appl. 2015, 6, 4–23. [Google Scholar]
- Perumal, T.; Sulaiman, M.N.; Leong, C.Y. Internet of Things (IoT) enabled water monitoring system. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 4th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics, GCCE 2015, Osaka, Japan, 27–30 October 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malche, T.; Maheshwary, P. Internet of Things (IoT) based water level monitoring system for smart village. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Chen, S. Application of Environmental Internet of Things on water quality management of urban scenic river. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2013, 20, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukta, M.; Islam, S.; Das Barman, S.; Reza, A.W.; Khan, M.S.H. IoT based smart water quality monitoring system. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems, ICCCS 2019, Singapore, 23–25 February 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujar, P.M.; Kenchannavar, H.H.; Kulkarni, R.M.; Kulkarni, U.P. Real-time water quality monitoring through Internet of Things and ANOVA-based analysis: A case study on river Krishna. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danh, L.V.Q.; Dung, D.V.M.; Danh, T.H.; Ngon, N.C. Design and deployment of an IoT-Based water quality monitoring system for aquaculture in mekong delta. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Robot. Res. 2020, 9, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarwar, M.A.; Ali, S.; Chong, I. Microservices model to enhance the availability of data for buildings energy efficiency management services. Energies 2019, 12, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylovskiy, A.; Jahn, M.; Patti, E. Designing a Smart City Internet of Things Platform with Microservice Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud, FiCloud 2015 and 2015 International Conference on Open and Big Data, OBD 2015, Rome, Italy, 24–26 August 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedliacik, I.; Dadob, J. Unintended Consequences of Interventions in Electricity Production and Consumption. New Trends Issues Proc. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2017, 3, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Aquino, R.; Ibarreche, J.; Pérez, I.; Castellanos, E.; Álvarez, E.; Rentería, R.; Anguiano, L.; Edwards, A.; Lepper, P.; et al. Rivercore: IoT device for river water level monitoring over cellular communications. Sensors 2019, 19, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamienski, C.; Soininen, J.-P.; Taumberger, M.; Dantas, R.; Toscano, A.; Cinotti, T.S.; Maia, R.F.; Neto, A.T. Smart water management platform: IoT-based precision irrigation for agriculture. Sensors 2019, 19, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasperowicz, R. Electricity consumption and economic growth: Evidence from Poland. J. Int. Stud. 2014, 7, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalehkhondabi, I.; Ardjmand, E.; Young, W.A.; Weckman, G.R. Water demand forecasting: Review of soft computing methods. Env. Monit Assess 2017, 189, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, J.; Lai, C.M. Reliability impacts of the dynamic thermal rating and battery energy storage systems on wind-integrated power networks. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2019, 20, 100268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentan, B.M.; Luvizotto, E.; Herrera, M.; Izquierdo, J.; Pérez-García, R. Hybrid regression model for near real-time urban water demand forecasting. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2017, 309, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, C.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y. Dynamic Forecast of Daily Urban Water Consumption Using a Variable-Structure Support Vector Regression Model. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2015, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.; Yamagata, Y.; Chen, Y.; Poskitt, C.M.; Sun, J. Anomaly detection for a water treatment system using unsupervised machine learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, ICDMW, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–21 November 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayanan, S.K.; McCrae, J. A comparative study of SVM and LSTM deep learning algorithms for stock market prediction. In CEUR Workshop Proceedings; RWTH Aachen University: Aachen, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, A.U.; Li, X.; Feng, J. Artificial Intelligence Approaches for Urban Water Demand Forecasting: A Review. In Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, LNICST; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, E.I.; Poczȩta, K.; Laspidou, C. Hybrid model for water demand prediction based on fuzzy cognitive maps and artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, FUZZ-IEEE 2016, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, S.; Yousefi, P.; Naser, G. Support Vector Machines in Urban Water Demand Forecasting Using Phase Space Reconstruction. Procedia Eng. 2017, 186, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeddi, S.; Sharifian, S. A water cycle optimized wavelet neural network algorithm for demand prediction in cloud computing. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, L.K.; Sankaranarayanan, S. IoT-based water demand forecasting and distribution design for smart city. J. Water Clim. Change 2020, 11, 1411–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Laghari, A.A.; Karim, S.; Shakir, M.; Brohi, A.A. Comparison of Fog Computing & Cloud Computing. Int. J. Math. Sci. Comput. 2019, 5, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, R.; Kaur, M.; Lenka, H. Design and Development of Automatic Water Flowmeter. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2013, 3, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovykh, A.; Oosterlee, C.W.; Bohté, S.M. Generalization in fully-connected neural networks for time series forecasting. J. Comput. Sci. 2019, 36, 101020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardell-Oliver, R. Discovering water use activities for smart metering. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 8th International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing: Sensing the Future, ISSNIP 2013, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2–5 April 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharath, V.C.; Suhas, S.; Jain, B.N.S.; Kumar, S.B.V.; Kumar, C.P. Smart aqua meter. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Advances in Electronics, Computers and Communications, ICAECC 2014, Bangalore, India, 10–11 October 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, J. A kind of design schema of wireless smart water meter reading system based on Zigbee technology. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on E-Product E-Service and E-Entertainment, ICEEE2010, Wuhan, China, 7–9 November 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, S.; Sahana, M.N.; Ankith, S.; Natarajan, K.; Shobha, K.R.; Paventhan, A. An IoT based 6LoWPAN enabled experiment for water management. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Advanced Networks and Telecommunication Systems, ANTS, Kolkata, India, 15–18 December 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sui, X.; Shi, J.; Liu, F. Design of wireless remote meter reading based on bluetooth and GPRS. Sci. Technol. 2007, 9, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.B.; Jiang, P.; Wu, K.H. Design of water environment data monitoring node based on ZigBee technology. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Software Engineering, CiSE 2009, Wuhan, China, 11–13 December 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, M.; Douglas, E.P.; Amelink, C.T. Quantitative, qualitative, and mixed research methods in engineering education. J. Eng. Educ. 2009, 98, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, B.; De La Fuente, D.; Pino, R.; Priore, P. Multiagent system for intelligent Water Demand Management. In Proceedings of the Conference and Exhibition—2013 International Conference on New Concepts in Smart Cities: Fostering Public and Private Alliances, SmartMILE 2013, Gijon, Spain, 11–13 December 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athapaththu, A.M.H.N.; Illeperumarachchi, D.U.S.; Herath, H.M.K.U.; Jayasinghe, H.K.; Rankothge, W.H.; Gamage, N. Supply and demand planning for water: A sustainable water management system. In Proceedings of the ICAC 2020—2nd International Conference on Advancements in Computing, Malabe, Sri Lanka, 10–11 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Durham, B. Water recycling and reuse in EUREAU countries: Trends and challenges. Desalination 2008, 218, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, B.; Graymore, M.; O’Toole, K. Household water use behavior: An integrated model. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortajada, C.; Joshi, Y.K. Water Demand Management in Singapore: Involving the Public. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2729–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayato, Y. WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Eisei Kagaku 1989, 35, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cominola, A.; Giuliani, M.; Piga, D.; Castelletti, A.; Rizzoli, A.E. Benefits and challenges of using smart meters for advancing residential water demand modeling and management: A review. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 72, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhouse, P.; Muller, M. Water Governance—An Historical Perspective on Current Debates. World Dev. 2017, 92, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Water and Cities: Ensuring Sustainable Futures; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2015; Volume 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbel, J.; Borrego-Marin, M.M.; Exposito, A.; Giannoccaro, G.; Montilla-Lopez, N.M.; Roseta-Palma, C. Analysis of irrigation water tariffs and taxes in Europe. Water Policy 2019, 21, 806–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Resolution 64/292. The Human Right to Water and Sanitation—Adopted by the General Assembly on 28 July 2010; United Nations: New York City, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, F.; Mehdizadeh, S.; Mohammadi, B.; Pham, Q.B.; Doan, T.N.C.; Vo, N.D. Application of an artificial intelligence technique enhanced with intelligent water drops for monthly reference evapotranspiration estimation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Fan, T.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Shankar, A.; Manickam, A. Big Data analytics and IoT in Operation safety management in Under Water Management. Comput. Commun 2020, 154, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Goswami, S. IoT and Cloud Computing based Smart Water Metering System. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Power Electronics and IoT Applications in Renewable Energy and its Control, PARC 2020, Mathura, India, 28–29 February 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Dhiman, G.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, A.; Tselykh, A. An IoT and Blockchain-based approach for the smart water management system in agriculture. Expert Syst. 2023, 40, e12892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberascher, M.; Kinzel, C.; Kastlunger, U.; Kleidorfer, M.; Zingerle, C.; Rauch, W.; Sitzenfrei, R. Integrated urban water management with micro storages developed as an IoT-based solution—The smart rain barrel. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 139, 105028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, L.M.; Boxall, J.; Speight, V.; Holden, B.; Tam, B. Data driven analysis of customer flow meter data. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sahin, O.; Bertone, E.; Beal, C.D. A systems approach for assessing water conservation potential through demand-based water tariffs. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, T.R.; Stewart, R.A.; Beal, C.D.; Sharma, A.K. Smart meter enabled informatics for economically efficient diversified water supply infrastructure planning. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, G.; Stewart, R.A. Smart meter enabled disaggregation of urban peak water demand: Precursor to effective urban water planning. Urban Water J. 2013, 10, 174–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.A.; Willis, R.M.; Panuwatwanich, K.; Sahin, O. Showering behavioural response to alarming visual display monitors: Longitudinal mixed method study. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2013, 32, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, A.L.; Pullinger, M.; Medd, W.; Anderson, B. Patterns of practice: A reflection on the development of quantitative/mixed methodologies capturing everyday life related to water consumption in the UK. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2014, 17, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, O.; Turkiya, S. A survey of household domestic water consumption patterns in rural semi-arid village, India. GeoJournal 2013, 78, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaki, Y.; Otaki, M.; Sugihara, H.; Mathurasa, L.; Pengchai, P.; Aramaki, T. Comparison of residential indoor water consumption patterns in Chiang Mai and Khon Kaen, Thailand. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2011, 103, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Majowicz, S.; Edge, V.; Thomas, M.; MacDougall, L.; Fyfe, M.; Atashband, S.; Kovacs, S. Drinking water consumption patterns in British Columbia: An investigation of associations with demographic factors and acute gastrointestinal illness. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 388, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, R.M.; Stewart, R.A.; Panuwatwanich, K.; Williams, P.R.; Hollingsworth, A.L. Quantifying the influence of environmental and water conservation attitudes on household end use water consumption. J. Environ Manag. 2011, 92, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J. General regression neural network forecasting model based on PSO algorithm in water demand. In Proceedings of the 2010 3rd International Symposium on Knowledge Acquisition and Modeling, KAM 2010, Wuhan, China, 20–21 October 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimakawa, M.; Murakami, S. Fuzzy prediction model for water demand prediction using an interpolative fuzzy reasoning method. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2003, 34, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, A.; Schmitt, T. Urban and tourist land use patterns and water consumption: Evidence from Mallorca, Balearic Islands. Land Use Policy 2011, 28, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimanzira, D.; Jacobi, M. A feasible and adaptive water-usage prediction and allocation based on a machine learning method. In Proceedings of the—UKSim 10th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation, EUROSIM/UKSim2008, Cambridge, UK, 1–3 April 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Torgo, L.; Izquierdo, J.; Pérez-García, R. Predictive models for forecasting hourly urban water demand. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gato, S.; Jayasuriya, N.; Roberts, P. Temperature and rainfall thresholds for base use urban water demand modelling. J. Hydrol. 2007, 337, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, D.L.; Solomatine, D.P. Machine learning approaches for estimation of prediction interval for the model output. Neural Networks 2006, 19, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, A.; Shan, N.; Chan, C.; Cercone, N.; Ziarko, W. Discovering rules for water demand prediction: An enhanced rough-set approach. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 1996, 9, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, N.; Khan, I.; Ullah, M.N.; Mahmood, A.; Farooq, M.U. A survey of home energy management systems in future smart grid communications. In Proceedings of the—2013 8th International Conference on Broadband, Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications, BWCCA 2013, Compiegne, France, 28–30 October 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipperer, A.; Aloise-Young, P.A.; Suryanarayanan, S.; Roche, R.; Earle, L.; Christensen, D.; Bauleo, P.; Zimmerle, D. Electric energy management in the smart home: Perspectives on enabling technologies and consumer behavior. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 2397–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.N.; Javaid, N.; Khan, I.; Mahmood, A.; Farooq, M.U. Residential energy consumption controlling techniques to enable autonomous demand side management in future smart grid communications. In Proceedings of the—2013 8th International Conference on Broadband, Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications, BWCCA 2013, Compiegne, France, 28–30 October 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annuk, A.; Jogi, E.; Hovi, M.; Marss, M.; Uiga, J.; Hoimoja, H.; Peets, T.; Kalder, J.; Jasinskas, A.; Allik, A. Increasing self electricity consumption by using double water heating tanks for residential net zero-energy buildings. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 6th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 November 2017; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8191249/ (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Marchiori, A.; Hakkarinen, D.; Han, Q.; Earle, L. Circuit-level load monitoring for household energy management. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2011, 10, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S.; Chan, A.D.C.; Goubran, R.A. Usage monitoring of electrical devices in a smart home. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Li, H.; Ji, Y. Home energy management system for the residential load control based on the price prediction. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Online Conference on Green Communications, GreenCom’11, Piscataway, NJ, USA, 26–29 September 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.; El-Zonkoly, A.M.; Aziz, N.; M’Sirdi, N.K. Smart Home Energy Management System for Peak Average Ratio Reduction. Ann. Univ. Craiova Electr. Eng. Ser. 2014, 38, 180–188. [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulou, S.E.; Kourti, E.; Agathokleous, A. Waterloss detection in streaming water flow timeseries using change-point anomaly methods. Eur. Water 2017, 58, 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Baanu, B.B.; Babu, K.S.J. Smart water grid: A review and a suggestion for water quality monitoring. Water Supply 2022, 22, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrappa, V.Y.; Ray, B.; Ashwath, N.; Shrestha, P. Application of Internet of Things (IoT) to Develop a Smart Watering System for Cairns Parklands—A Case Study. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Region 10 Symposium, TENSYMP 2020, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 5–7 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmanbar, M.; Parham, K.; Arild, O.; Rong, C. A widespread review of smart grids towards smart cities. Energies 2019, 12, 4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, S.A.; Shine Let, G.; Pratap, C.B. Development of Water Management System for Smart Irrigation. In International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things (ICICI); Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 633–639. [Google Scholar]
- Regan, F.; Lawler, A.; McCarthy, A. SmartCoast Project-Smart Water Quality Monitoring System; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Darshan, R.S.; Pavan, H.; Pratheesh, R.; Raj, M.S.; Suresh, K.V.; Prathap, C. An IoT Enabled Water Management System with Water Usage Prediction using ANN. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd Global Conference for Advancement in Technology, GCAT 2021, Bangalore, India, 1–3 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W Intelligence. Using AI to Diagnose Water Consumption Patterns. Available online: https://wint.ai/blog/using-ai-to-diagnose-water-consumption-patterns/ (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Kamyab-Talesh, F.; Mousavi, S.F.; Khaledian, M.; Yousefi-Falakdehi, O.; Norouzi-Masir, M. Prediction of Water Quality Index by Support Vector Machine: A Case Study in the Sefidrud Basin, Northern Iran. Water Resour. 2019, 46, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, H.; Liao, D.; Mahadeo, K. A Review of Artificial Intelligence Applications to Achieve Water-related Sustainable Development Goals. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ITU International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Good, AI4G 2020, Geneva, Switzerland, 21–25 September 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebere, E.V.; Francisca, O.O. Microcontroller based automatic water level control system. Innov. Res. Comput. Commun. 2013, 1, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, S.; Fang, Z. Comparison of China’s primary energy consumption forecasting by using ARIMA (the autoregressive integrated moving average) model and GM(1,1) model. Energy 2016, 100, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbola, S.; Coors, V. COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS of LSTM, RF and SVM ARCHITECTURES for PREDICTING WIND NATURE for SMART CITY PLANNING. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, IV-4/W9, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmiani, D.; Kazi, R.; Nambisan, A.; Shah, A.; Kamble, V. Comparison of Predictive Algorithms: Backpropagation, SVM, LSTM and Kalman Filter for Stock Market. In Proceedings of the—2019 Amity International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AICAI 2019, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 4–6 February 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.N.; Shufian, A.; Al Masum, M.A.; Al Noman, A. Efficient smart water management system using IoT technology. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Automation, Control and Mechatronics for Industry 4.0, ACMI 2021, Rajshahi, Bangladesh, 8–9 July 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Ormsbee, L.E. Short-term water demand forecast modeling techniques—Conventional methods versus AI. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2002, 94, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, J.M.; López-Paredes, A.; Del Olmo, R. An agent-based model for domestic water management in Valladolid metropolitan area. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Preis, A.; Iqbal, M.; Whittle, A.J. Case study: A smart water grid in Singapore. Water Pract. Technol. 2012, 7, wpt2012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithole, B.; Rimer, S.; Ouahada, K.; Mikeka, C.; Pinifolo, J. Smart water leakage detection and metering device. In Proceedings of the 2016 IST-Africa Conference, IST-Africa 2016, Durban, South Africa, 11–13 May 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.; Seto, E.; Northcross, A.; Quinn, N.W.; Convertino, M.; Jones, R.L.; Maier, H.R.; Schlink, U.; Steinle, S.; Vieno, M.; et al. Integrating modelling and smart sensors for environmental and human health. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 74, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoras, G.; Bizon, N.; Enescu, F.M.; Guede, J.M.L.; Salado, G.F.; Brennan, R.; O’DRiscoll, C.; Dinka, M.O.; Alalm, M.G. ICT based Smart Management Solution to Realize Water and Energy Savings through Energy Efficiency Measures in Water Distribution Systems. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Electronics, Computers and Artificial Intelligence, ECAI 2018, Iasi, Romania, 28–30 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, M.; Camhy, D.; Steffelbauer, D.; Neumayer, M.; Fuchs-Hanusch, D. Showcasing a smart water network based on an experimental water distribution system. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmbrecht, J.; Pastor, J.; Moya, C. Smart Solution to Improve Water-energy Nexus for Water Supply Systems. Procedia Eng. 2017, 186, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, W.S.R. Drinking Water Critical Infrastructure and Its Protection; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Savić, D.; Vamvakeridou-Lyroudia, L.; Kapelan, Z. Smart meters, smart water, smart societies: The iWIDGET project. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, R.; Abraham, E.; Parpas, P.; Stoianov, I. Extending the Envelope of Demand Response Provision though Variable Speed Pumps. Procedia Eng. 2017, 186, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vašak, M.; Banjac, G.; Baotić, M.; Matuško, J. Dynamic day-ahead water pricing based on smart metering and demand prediction. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, E.; Biddau, P.; Delogu, A.; Gandolfi, M.; Deidda, R.; Viola, F. Automatic detection of water consumption temporal patterns in a residential area in Northen Italy. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 38, 6213–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.; Stewart, R.A.; Beal, C.D. ANN-based residential water end-use demand forecasting model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulhim, A.I.; Aina, Y.A. Water, and Undefined 2022, Understanding Household Water-Use Behavior and Consumption Patterns During COVID-19 Lockdown in Saudi Arabia. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/14/3/314 (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Khambati, A.; Pinto, K.; Joshi, D.; Karamchandani, S.H. Innovative Smart Water Management System Using Artificial Intelligence. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. 2021, 12, 4726–4734. [Google Scholar]
- Stanelyte, D.; Radziukyniene, N.; Radziukynas, V. Overview of Demand-Response Services: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, N.; Kang, C.; Li, M.; Huo, M. From demand response to integrated demand response: Review and prospect of research and application. Prot. Control. Mod. Power Syst. 2019, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | Centralized WDM | Decentralized WDM | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Top-down, single authority | Bottom-up, individual users | [20] |
| Efficiency | High system-wide optimization | Moderate individual optimization | [21] |
| Cost | High due to infrastructure and management overhead | Lower upfront and operational costs | [22] |
| User Engagement | Low (limited user input) | High users actively participate | [21] |
| Equity/Fairness | May lack fairness due to one-size-fits-all mandates | High fairness through local customization | [23] |
| Resilience | Vulnerable to system-wide failures | More resilient due to Localized autonomy | [24,25] |
| Scalability | Scales well with central planning | May face challenges at large scale | [21,26] |
| Environmental Impact | May struggle with local sustainability and nutrient recovery | More adaptable to ecological design | [24,27] |
| Effectiveness | High effectiveness in control and consistency | High effectiveness in adaptability and resilience | [28,29] |
| Concept | Definition | Key Thresholds | Main Drivers | Smart-MISS Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Scarcity | Insufficient availability of renewable freshwater resources to meet wants | <1700 m3/cap/yr (scarcity), <500 (absolute) | Climate, geography, and overuse of sources | Monitors obtainability, informs infrastructure resilience |
| Water Stress | Extreme pressure on available water resources due to extractions | >25% withdrawal (moderate), >100% (critical) | Population growth, lifestyle, and inefficient use | Targets mandate decrease, promote conservation behaviors |
| Definition | Definition Type | Source |
|---|---|---|
| When individuals lack access to sufficient, safe, and affordable water for personal or livelihood needs, the area is considered water scarce. | Access-Based | [47,55,56,57] |
| Scarcity occurs when aggregate user demands (including environmental) cannot be met due to limitations in supply or institutional arrangements. | Institutional/UN Definition | [58,59] |
| Defined by the marginal value of water, it is the opportunity cost of not having an additional unit of water. | Economic (Marginal Value) | [60] |
| There is insufficient water to meet all demands. | Physical Scarcity | [56] |
| Water is physically available, but access is limited by a lack of investment or institutional capacity. | Economic Scarcity | [47] |
| It is the yearly accumulated difference between daily water demand and availability. A persistent gap leading to resource depletion defines water scarcity. | Quantitative (Water Gap) | [61] |
| Water scarcity is shaped and often manufactured by political and institutional processes that marginalize certain populations. | Governance-Based | [62] |
| Influence Factors | Contents | Details |
|---|---|---|
| The external environment | Geographical environment Climate environment | Longitude, latitude, altitude temperature, humidity |
| Water supply and drainage system | Water supply and drainage facilities Water-saving measures Water supply and drainage management | Domestic water, irrigation water Reuse of recycled water and rainwater Management level, intelligent control system |
| Building design | Building design, shape, landscape | Various buildings like residential, commercial, and public buildings Shape, area, number of layers |
| Human dimensions | Life habit Other factors | Cultural qualities, energy-saving awareness, income |
| Study | [96] | [97] | [98] | [99] | [100] | [101] | [102] | [103] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | |||||||||
| Water Level | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | |
| pH | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Dissolved Oxygen | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | ✓ | ✕ | ✕ | |
| Turbidity | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✕ | ✕ | |
| Conductivity | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✕ | |
| Redox Potential | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | |
| TDS | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | ✕ | |
| Chlorophyll | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | ✓ | ✕ | ✓ | ✕ | ✕ | |
| Temperature | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | ✕ | ✓ | ✕ | ✓ | |
| Salinity | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | |
| Flow rate (Litre/S) | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | |
| Algorithm/Model | Application Context | Performance Indicators | Strengths | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VS-SVR | Dynamic daily urban water consumption forecasting | MAE = 5320.7 m3/day; MAPE = 2.65%; RMSE = 7048.6 m3/day; R2 ≈ 0.93 | Dynamic model adapts to changing conditions; 33% RMSE reduction over static LSSVR | [113,114] |
| Deep Neural Network (LSTM-based) | Unsupervised anomaly detection in SWaT plant | Precision = 0.91; Recall = 0.80; F1 = 0.86 | Fewer false alarms; captures nonlinear temporal patterns | [114] |
| SVM (Base Model) | Time-series regression | RMSE = 682.63; MSE = 467,214.38; MAE = 597.96; R2 = 0.30; MAPE = 2.47% | Stable linear regression baseline | [115] |
| LSTM (Base Model) | Time-series regression | RMSE = 399.39; MSE = 159,519.52; MAE = 356.04; R2 = 0.76; MAPE = 1.41% | Learns long-term dependencies; high accuracy | [115] |
| LSTM (Advanced + Moving Averages) | Combined time-series dataset | RMSE = 347.46; MSE = 120,731.41; MAE = 262.42; R2 = 0.83; MAPE = 1.03% | Best overall accuracy; robust for multivariate data | |
| Backpropagation ANN | Short-term forecasting and classification | Accuracy = 68.6%; SD = 0.55; Time = 12.6 s | Fast convergence; simple architecture |
| Tariff Mechanism | Definition | Purpose/Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Charge | A constant fee is charged regardless of consumption | Ensures basic revenue for utility |
| Volumetric Pricing | Users pay per unit of water consumed | Promotes conservation, links cost to use |
| Increasing Block Tariff (IBT) | Price per unit increases with higher usage (e.g., blocks of m3) | Encourages conservation, supports equity |
| Decreasing Block Tariff | Price per unit decreases with higher usage | Favors large users, promotes economies of scale |
| Two-Part Tariff | Combines a fixed charge and a variable (volumetric) component | Balances cost recovery and consumption-based billing |
| Seasonal Tariffs | Higher rates in peak season (e.g., summer), lower in off-peak | Reflects supply stress and scarcity during certain times |
| Quota-Exceeding Tariff | Users are allocated a quota, with higher rates above that | Discourages overuse beyond “essential” need |
| Flat Fee | Single fixed amount per month, regardless of use | Simplicity, but lacks conservation signal |
| Free Allowance/Lifeline Tariff | The initial volume of water (e.g., 10–20 m3) provided at low or zero price | Basic human rights, affordability |
| Marginal Cost Pricing | Price reflects long-run marginal cost of water provision | Economic efficiency, cost-reflective pricing |
| Market-Based Pricing | Water rights or permits are bought and sold | Reflects true market value, allocates efficiently |
| Subsidized Block Pricing | Lower prices for lower-income households in initial block | Promotes affordability and equity |
| Index-Linked Tariffs | Tariffs adjusted regularly based on inflation or cost index | Keeps tariffs sustainable over time |
| Wastewater Tariffs (Add-on) | Separate charge for wastewater treatment | Ensures environmental cost recovery |
| Pollutant-Based Charges | Fees based on volume and concentration of pollutants discharged | “Polluter Pays Principle”, incentivizes cleaner processes |
| Country | Pricing Basis | Main Sectors | Cost Recovery Focus | Environmental Pricing | Social Equity Consideration | Key Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | State-based, national framework | Urban, irrigation | High | Medium | Medium | Variability, drought regulation |
| Brazil | River basin (ANA) | All | Medium | Low | Medium | Regional disparities |
| Canada | Local/province | All | Low to Medium | Low | Medium | Low price incentives |
| Chile | Market-based | Urban, agriculture | High | Medium | Low | Groundwater management |
| China | Central and local hybrid | All | Medium | Low | Medium | Institutional overlap |
| Colombia | Centralized (post-1994) | All | High | Low | High | Implementation of tariff reforms |
| France | National system | Urban, agriculture | Medium | Medium | High | Pricing complexity |
| India | State jurisdiction | Irrigation, urban | Low | Low | Medium | Low pricing efficiency |
| Italy | Decentralized | Urban, industry | Medium | Low | Medium | Investment support via taxes |
| Mexico | Regional zones | All | Medium | Medium | Medium | Sector equity |
| Netherlands | National taxes + pricing | Domestic, industry | Medium | Medium | Medium | Fiscal efficiency |
| New Zealand | Local control | Urban, irrigation | Low to Medium | Low | Medium | Irrigation water scarcity |
| South Africa | National + local tier | All | Medium | Medium | High | Implementation & affordability |
| Spain | National + EU directive | All | Medium | High | Medium | Climate adaptation, CAP linkages |
| Saudi Arabia | Nationally regulated | Urban, agriculture | Low | Low | High | Heavy subsidies, low tariffs |
| GCC Countries | National frameworks | Urban, agriculture | Low | Low | Medium | Low-cost recovery, high consumption |
| Egypt | Centralized | Urban, agriculture | Medium | Low | High | Low tariffs, high subsidies |
| Yemen | Local corporations | Urban, agriculture | Low | Low | Low | Weak enforcement, over-extraction |
| Key Points | Definitions | References |
|---|---|---|
| IoT-based system | There are alternatives to manual metering systems, and these include smart water systems. These are examples of wireless sensor networks, in which water meters in thousands of homes gather data at regular intervals and relay that information in real time to a central database. Water temperature, phosphate, dissolved oxygen, conductivity, pH, turbidity, and water-level sensors may all be integrated into the “SmartCoast” Multi-Sensor System for water quality monitoring. ThingSpeak is a cloud-based IoT analytics solution that enables the collection, visualization, and analysis of real-time data streams. The ThingSpeak platform provides access to MATLAB analysis, which computes statistics like the lowest, maximum, and average amounts of water consumed daily, weekly, and monthly. | [125,178,179] |
| AI-IoT–enabled WDS | Building managers can keep tabs on water use and demand, as well as examine the efficiency of their water systems, with the help of AI-enabled IoT water management systems. The water quality index fluctuation can be explained by the Support Vector Machine (SVM) models 87% of the time. SVM’s findings may potentially be used to better manage rivers to ensure a high-quality water supply. In Ohio, USA, AI is used in conjunction with IoT data on water levels, flow, and storage capacity across stormwater and combined sewer collection networks to create a wet weather management system. This aids in the monitoring of utility networks and the optimization of storage capacity to avoid floods and overflows during rainy weather events. | [180,181,182] |
| Water Smart meters | The smart water meter’s prototype includes a microprocessor, a Wi-Fi module, a water flow sensor, and a GPS module. One of the most well-known and widely applied stochastic time series models, the autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), captures a variety of common temporal features in time series data. When it comes to fine-tuning Holt’s Winter method’s coefficients, deep learning techniques like the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) and its variant, the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), are able to learn predictions from sequences of data. | [115,183,184,185,186] |
| Efficiency in IoT technology | From the outset, power is fed into the system from the generator. When the ultrasonic sensor has been properly calibrated, the system may begin functioning. A model of a physical system that is stored digitally. Clustering and Kohonen networks are used in an integrated water and energy forecasting model to provide accurate predictions of future water and energy needs. | [187] |
| Application of AI in WDM | The goal of ML in the field of AI is to enable the development of systems that can generalize behavior based on examples presented in an unstructured style. Inside it, in 2002, NNs were employed to predict the highest possible weekly demand based on weather conditions (water temperature, frequency, and volume of rainfall), as well as on demand levels from the previous years. The bulk of the published methodologies in the literature regarding AI applied to WDM are based on demand forecasting. | [188,189] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzahrani, A.; Alogla, A.; Aljlil, S.; Alshehri, K. The Role of Smart Infrastructure in Residential Water Demand Management: A Global Survey. Water 2025, 17, 3119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213119
Alzahrani A, Alogla A, Aljlil S, Alshehri K. The Role of Smart Infrastructure in Residential Water Demand Management: A Global Survey. Water. 2025; 17(21):3119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213119
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzahrani, Ateyah, Ageel Alogla, Saad Aljlil, and Khaled Alshehri. 2025. "The Role of Smart Infrastructure in Residential Water Demand Management: A Global Survey" Water 17, no. 21: 3119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213119
APA StyleAlzahrani, A., Alogla, A., Aljlil, S., & Alshehri, K. (2025). The Role of Smart Infrastructure in Residential Water Demand Management: A Global Survey. Water, 17(21), 3119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213119










