The Shrinkage of Lakes on the Semi-Arid Inner Mongolian Plateau Is Still Serious
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
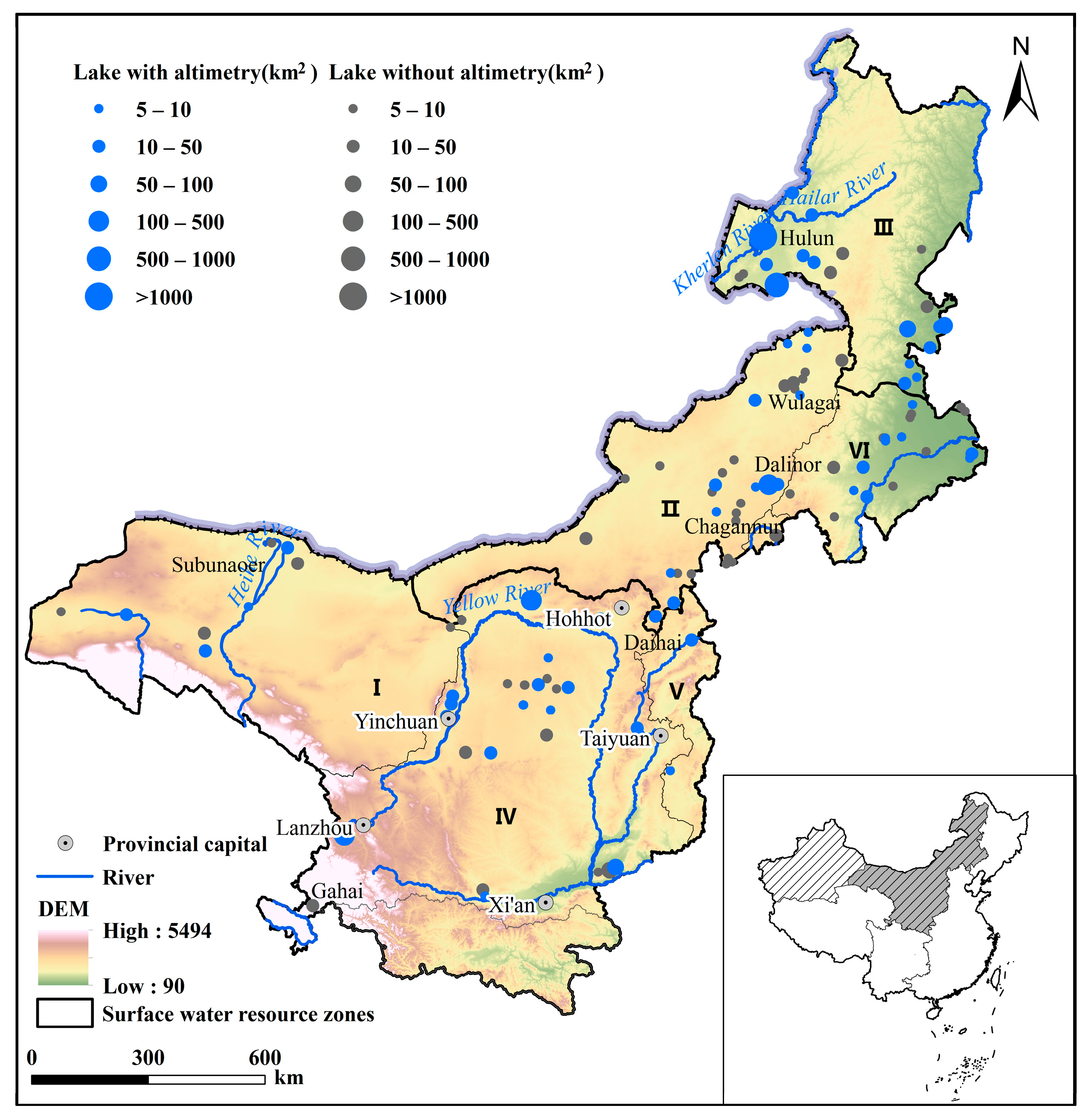
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials
2.3. Methods
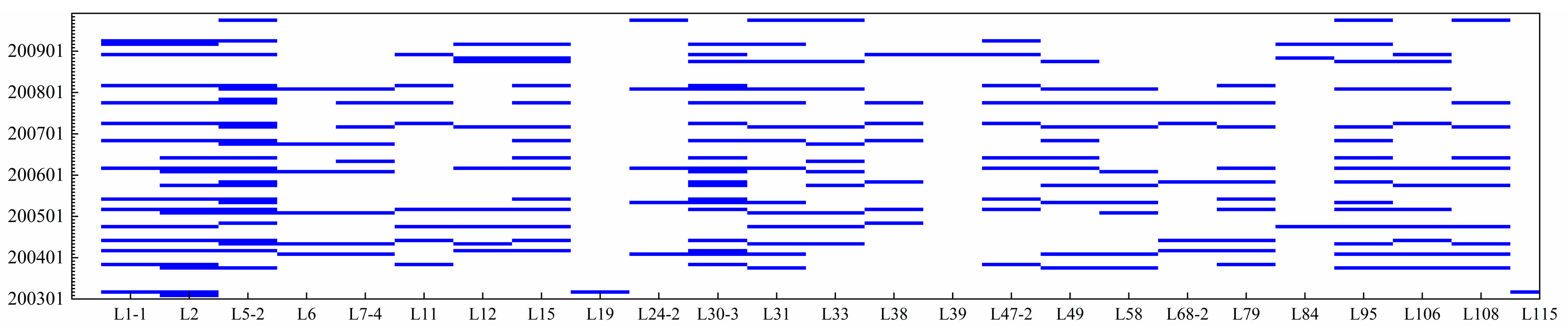
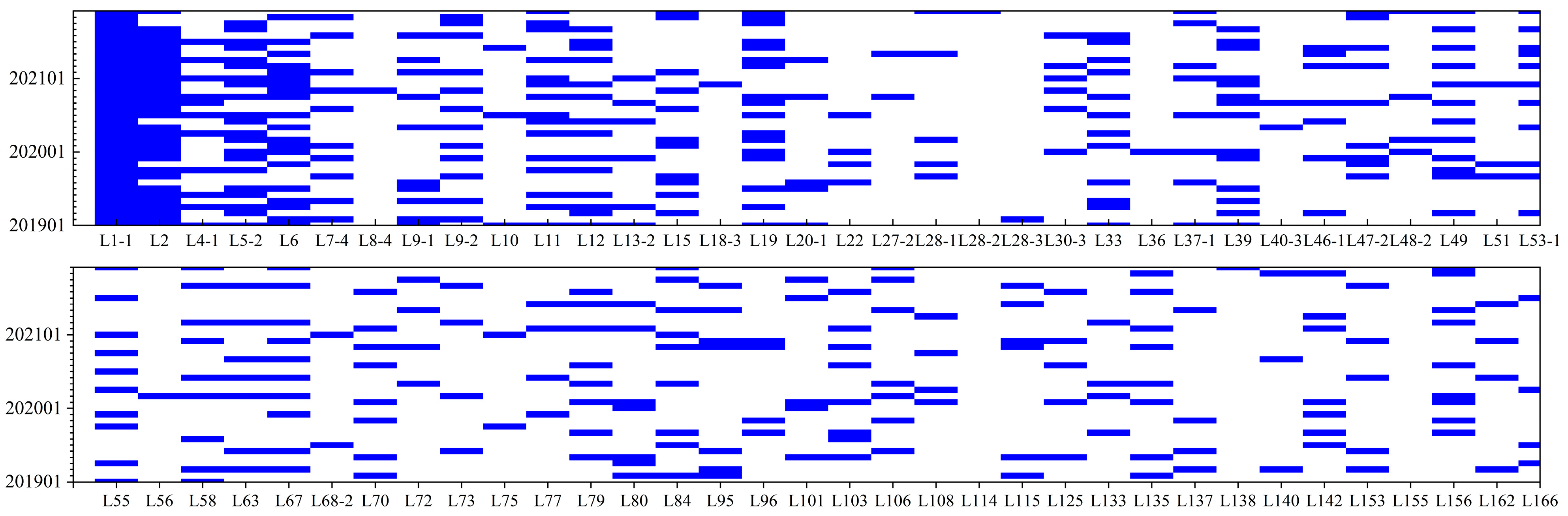
2.3.1. Data Acquisition and Preparation
2.3.2. Reconstruction of Long-Term Lake Level Series
2.3.3. Estimation of Water Level in Unobserved Lakes
2.3.4. Calculating Lake Water Storage Changes
3. Results
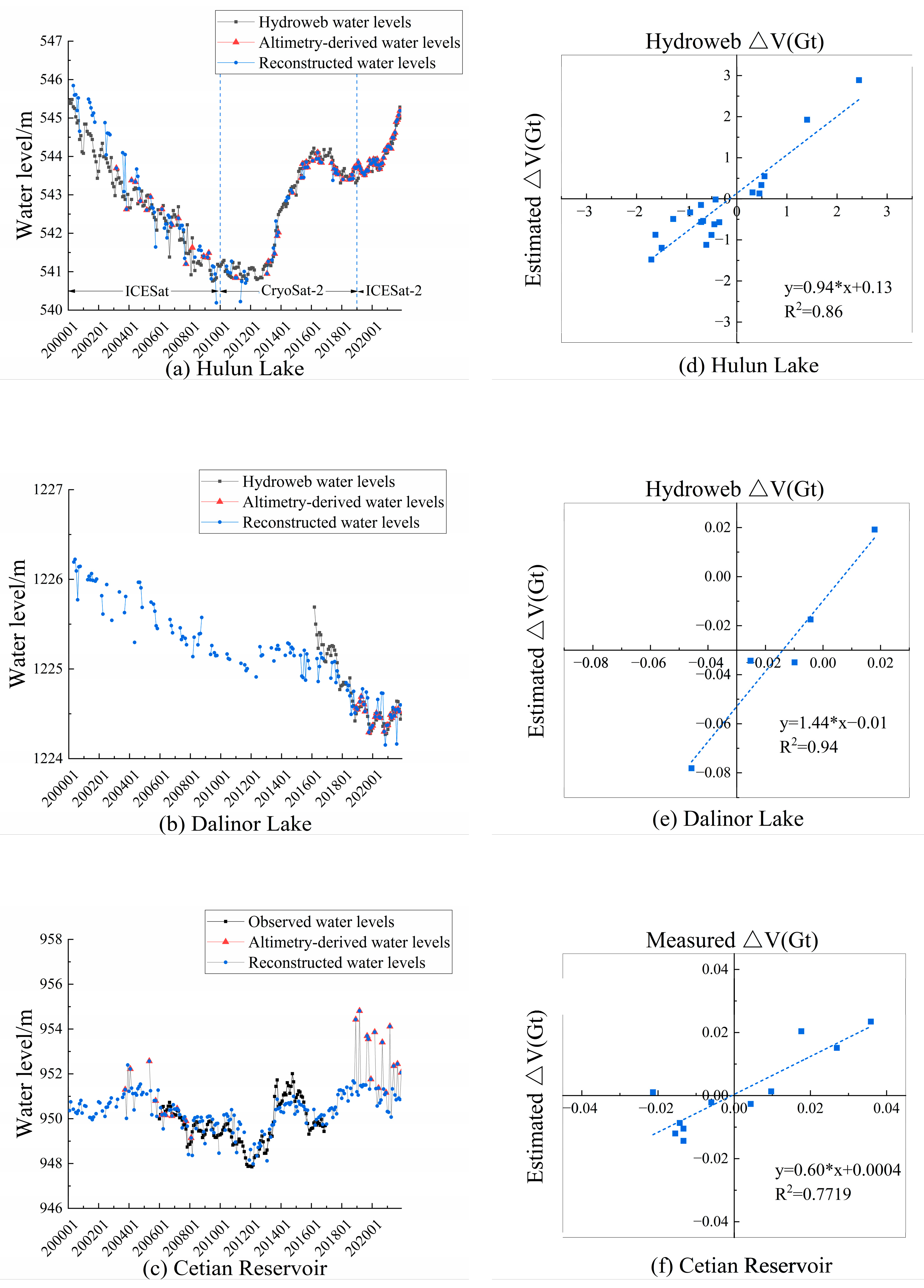
3.1. Accuracy Validation of Lake Level and LWS Estimation on the IMP
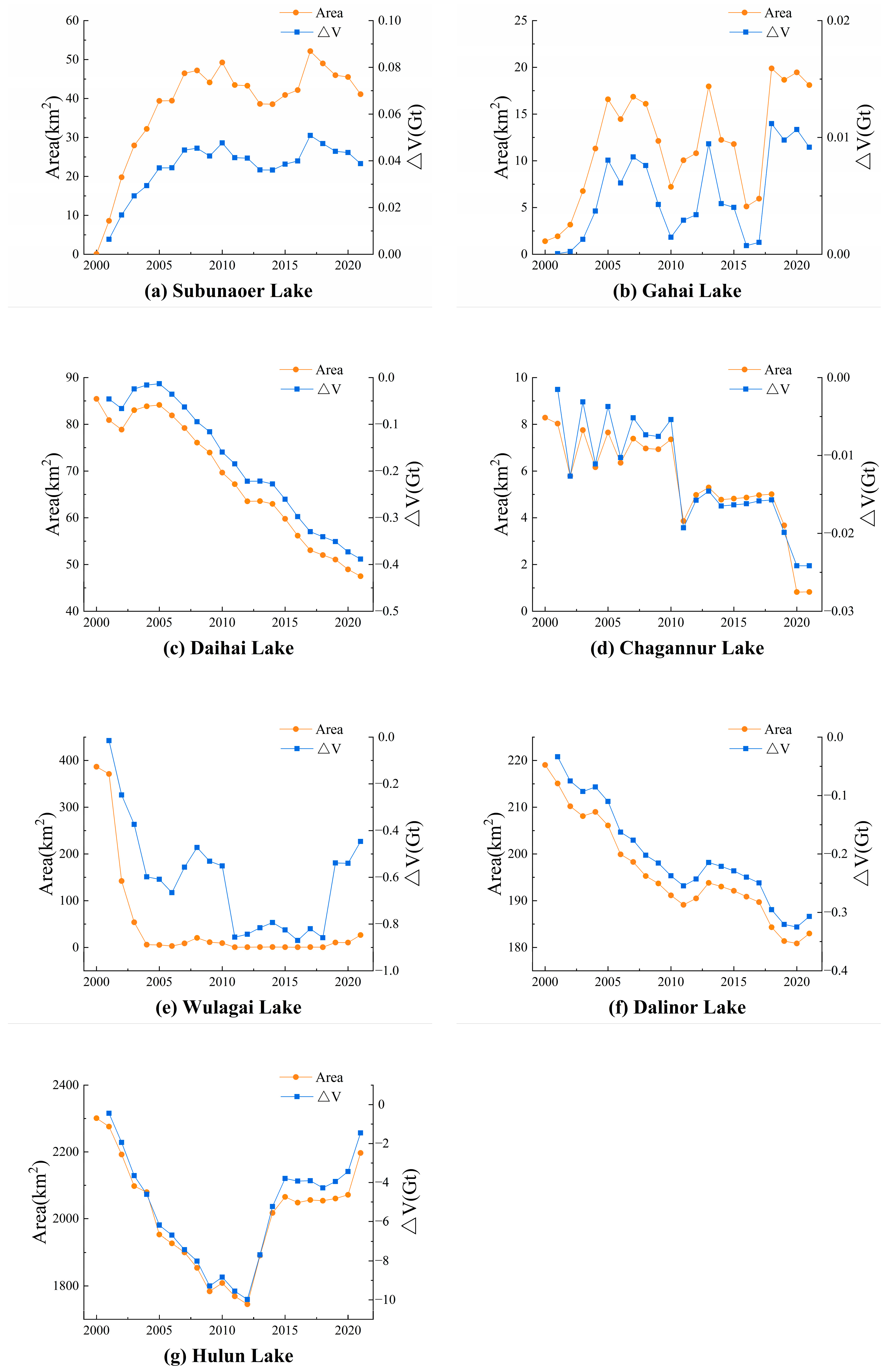
3.2. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Lake Level and Storage
4. Discussion
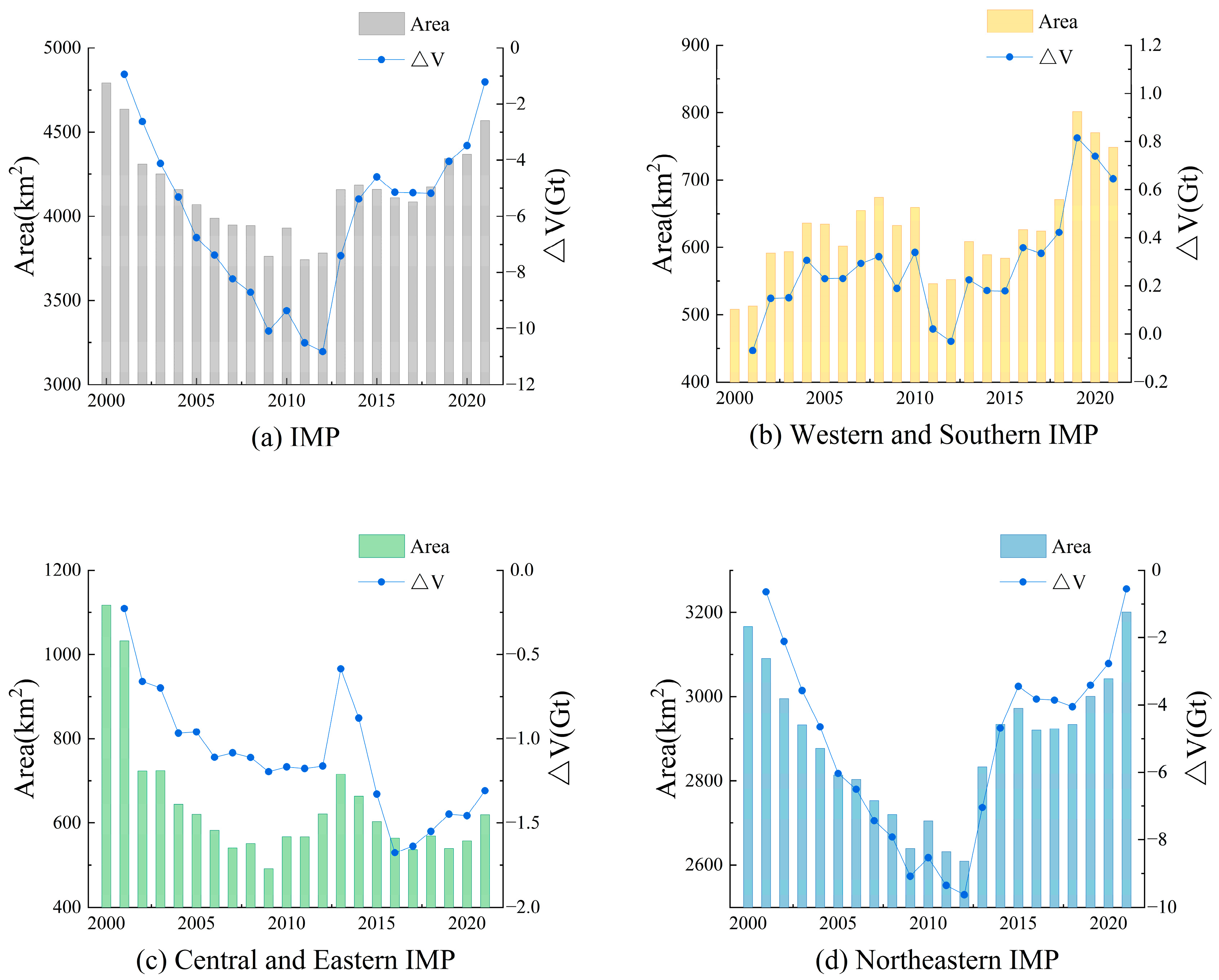
4.1. Regional Variation in Lake Water Storage Changes on the IMP
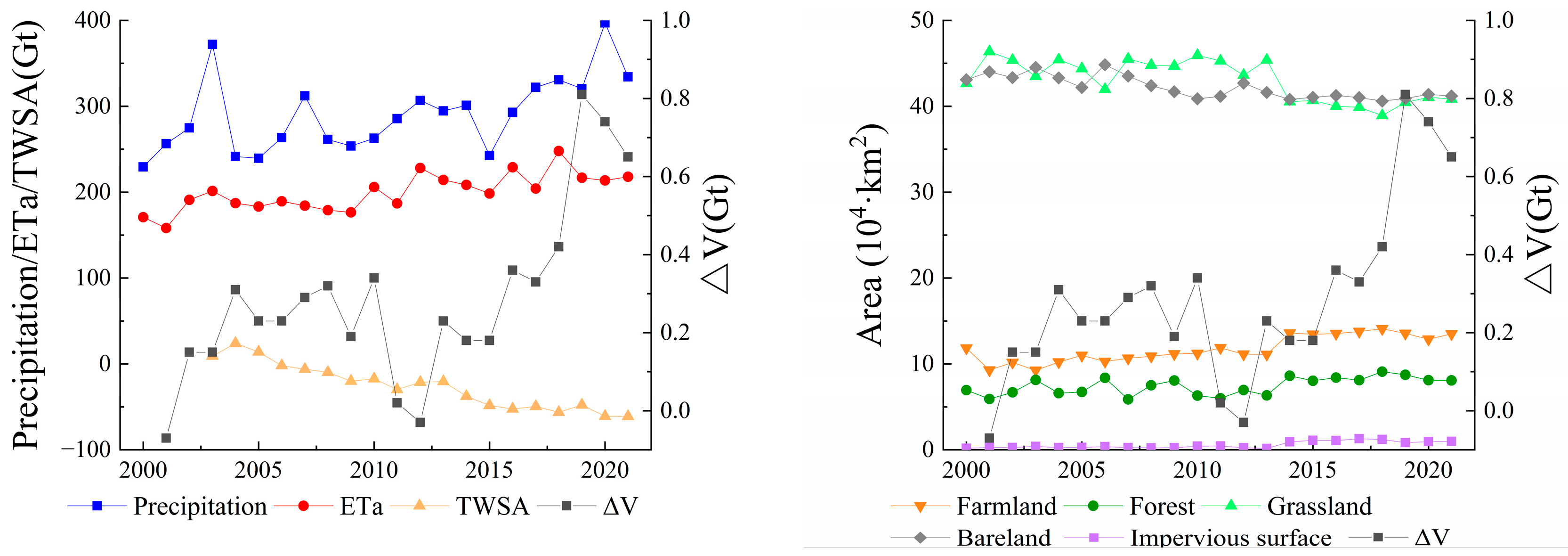
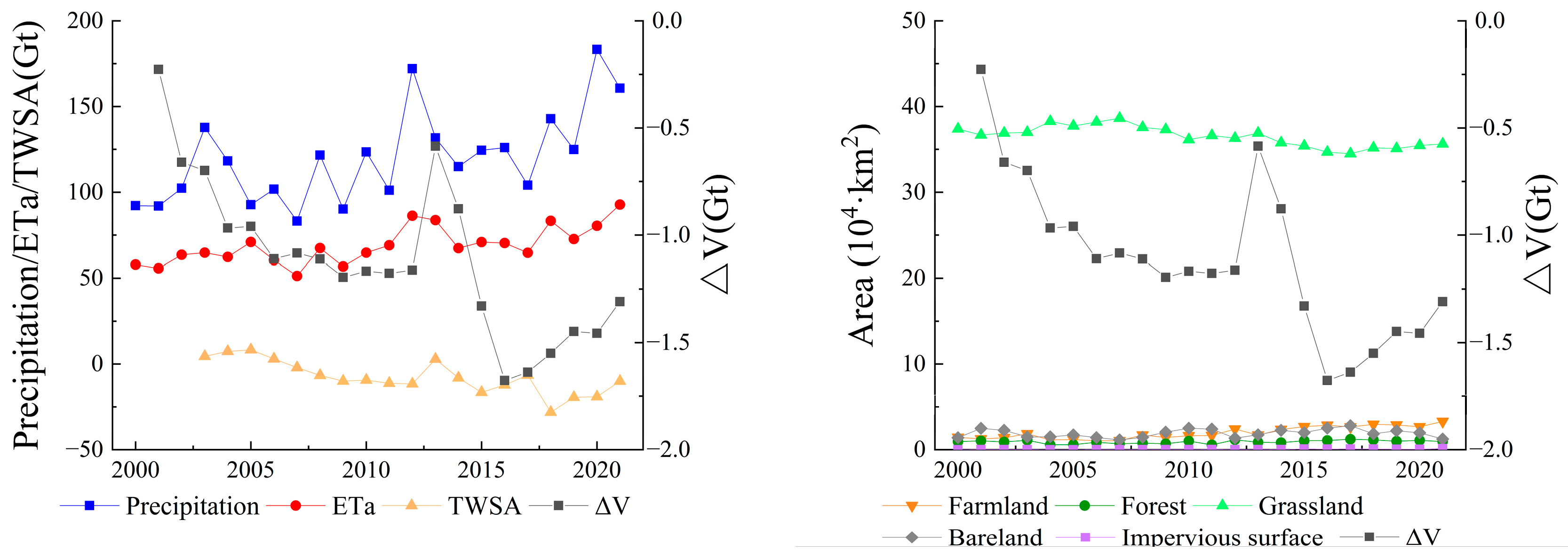
4.2. Key Drivers of Lake Water Storage Changes on the IMP
4.2.1. Western and Southern IMP: Areal Expansion and Storage Increase Driven by Enhanced Precipitation and Reduced Aridity
4.2.2. Central–Eastern IMP: Storage Decline and Surface Shrinkage from Intensive Water Diversion and Groundwater Exploitation
4.2.3. Northeastern IMP: Decline–Recovery–Net Loss Trend from Precipitation Deficit and Ecological Replenishment
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Reconstructed water levels for lakes lacking altimetry data showed strong consistency with validation data (Hulun Lake RMSE = 0.46 m; Dalinor Lake RMSE = 0.22 m; Cetian Reservoir RMSE = 0.56 m) using water level/area fitting relationships. Lake water storage (LWS) changes exhibited high reliability (Hulun Lake RMSE = 0.63 Gt; Dalinor Lake RMSE = 0.02 Gt; Cetian Reservoir RMSE = 0.009 Gt).
- (2)
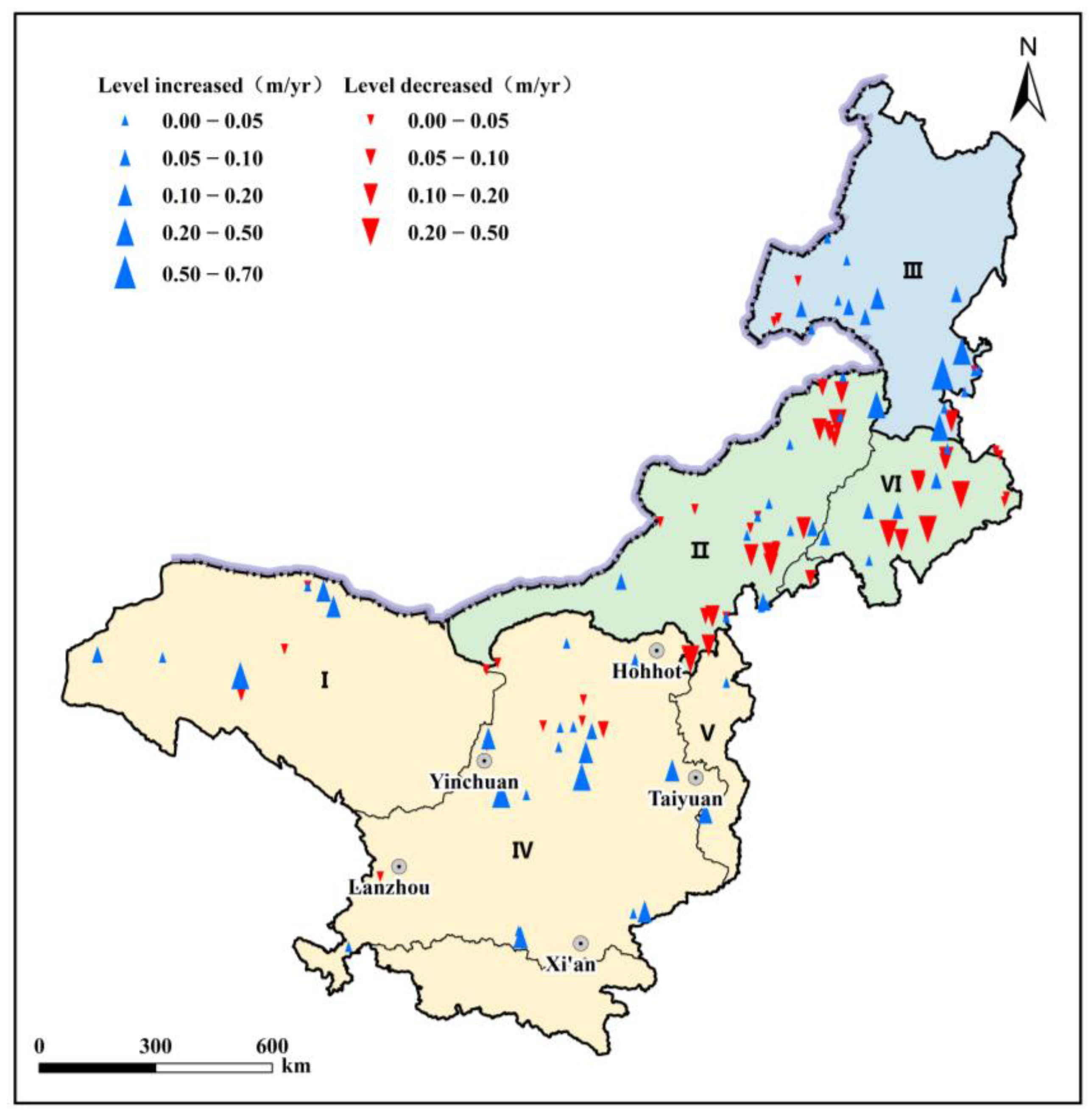
- Among the studied lakes (≥5 km2), 49 exhibited water level increases, 40 showed decreases, and 20 experienced minimal changes. Decreasing trends dominated central–eastern regions, while increasing levels prevailed elsewhere.
- (3)
- Using 2000 as the baseline year, the total LWS has decreased by 1.21 Gt until 2021. The western lakes gained storage, the central–eastern lake storage has declined significantly, and northeastern lake storage followed a decline-to-recovery trajectory. These spatial patterns demonstrate partial agreement with prior studies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Li, X.; Long, D.; Huang, Q.; Han, P.; Zhao, F.; Wada, Y. High-temporal-resolution water level and storage change data sets for lakes on the Tibetan Plateau during 2000–2017 using multiple altimetric missions and Landsat-derived lake shoreline positions. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1603–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global lake responses to climate change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lv, A.; Jia, S.; Qi, S. Longterm multisource satellite data fusion reveals dynamic expansion of lake water area and storage in a hyperarid basin of China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Chen, W.; Zheng, G.; Shum, C.K.; Yang, K.; Piao, S.; Sheng, Y.; Yi, S.; Li, J.; et al. Regional differences of lake evolution across China during 1960s–2015 and its natural and anthropogenic causes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 386–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Zhang, F.; Chan, N.W.; Johnson, V.C.; Shi, J. A review on the research progress of lake water volume estimation methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 115057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Fu, C.; Wang, X.; Dong, L.; Yao, S.; Xue, B.; Wu, H.; Wu, H. Decoding the dramatic hundred-year water level variations of a typical great lake in semi-arid region of northeastern Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Song, C.; Ke, L.; Zhan, P.; Fan, C.; Liu, K.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J. Satellite Laser Altimetry Reveals a Net Water Mass Gain in Global Lakes with Spatial Heterogeneity in the Early 21st Century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, S.W.; Ryan, J.C.; Smith, L.C. Human alteration of global surface water storage variability. Nature 2021, 591, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Song, C.; Reager, J.T.; Yao, F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M.; Brun, F.; Schmied, H.M.; Marston, R.A.; et al. Recent global decline in endorheic basin water storages. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Fang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S.; Shen, H.; Hu, H.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Q. Rapid loss of lakes on the Mongolian Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2281–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Pei, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y. Expansion of irrigation led to inland lake shrinking in semi-arid agro-pastoral region, China: A case study of Chahannur Lake. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretaux, J.-F.; Letolle, R.; Bergé-Nguyen, M. History of Aral Sea level variability and current scientific debates. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 110, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Jin, T.; Li, C.; Ofterdinger, U.; Zhang, S.; Ding, A.; Li, J. Is China’s fifth-largest inland lake to dry-up? Incorporated hydrological and satellite-based methods for forecasting Hulun lake water levels. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 94, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Li, H.; Wan, W.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Z.; Hong, Y.; Wang, H. Assessment of Water Storage Change in China’s Lakes and Reservoirs over the Last Three Decades. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. Estimating water volume variations in lakes and reservoirs from four operational satellite altimetry databases and satellite imagery data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crétaux, J.F.; Abarca-del-Río, R.; Bergé-Nguyen, M.; Arsen, A.; Drolon, V.; Clos, G.; Maisongrande, P. Lake Volume Monitoring from Space. Surv. Geophys. 2016, 37, 269–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabajal, C.C.; Boy, J.-P. Lake and reservoir volume variations in South America from radar altimetry, ICESat laser altimetry, and GRACE time-variable gravity. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 652–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crétaux, J.F.; Arsen, A.; Calmant, S.; Kouraev, A.; Vuglinski, V.; Bergé-Nguyen, M.; Gennero, M.C.; Nino, F.; Abarca Del Rio, R.; Cazenave, A.; et al. SOLS: A lake database to monitor in the Near Real Time water level and storage variations from remote sensing data. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liao, J. Monitoring lake level changes in China using multi-altimeter data (2016–2019). J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Lu, Z.; Lee, H.; Shum, C.K.; Swarzenski, C.M.; Doyle, T.W.; Baek, S.-H. Integrated analysis of PALSAR/Radarsat-1 InSAR and ENVISAT altimeter data for mapping of absolute water level changes in Louisiana wetlands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2356–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, C.E.; Gomez-Enri, J.; Alonso, J.J.; Villares, P. Water level fluctuations derived from ENVISAT Radar Altimeter (RA-2) and in-situ measurements in a subtropical waterbody: Lake Izabal (Guatemala). Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3604–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, C.M.; O’Brien, K.; Kinsey, S.; Ricko, M.; Li, Y. Enhancement of a global lake and reservoir database to aid climate studies and resource monitoring utilizing satellite radar altimetry. J. Great Lakes Res. 2022, 48, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Kang, S.; Yi, D.; Ackley, S.F. Monitoring lake level changes on the Tibetan Plateau using ICESat altimetry data (2003–2009). Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.C.; Smith, L.C.; Cooley, S.W.; Pitcher, L.H.; Pavelsky, T.M. Global Characterization of Inland Water Reservoirs Using ICESat-2 Altimetry and Climate Reanalysis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Z.; Huang, C.; Li, G.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.H. Satellite observed recent rising water levels of global lakes and reservoirs. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 074013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Song, C.; Zhan, P.; Liu, K.; Chen, T.; Li, W.; Ke, L. Refined estimation of lake water level and storage changes on the Tibetan Plateau from ICESat/ICESat-2. Catena 2021, 200, 105177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Y. Monitoring long-term water storage of lakes and reservoirs in arid ungauged basin based on underwater topography derived from multi-source satellite data. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 966, 178662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Nielsen, K.; Andersen, O.B.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. A Bigger Picture of how the Tibetan Lakes Have Changed over the Past Decade Revealed by CryoSat-2 Altimetry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Zhu, L. Difference and cause analysis of water storage changes for glacier-fed and non-glacier-fed lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, G.; Woolway, R.I.; Yang, K.; Wada, Y.; Wang, J.; Crétaux, J.-F. Widespread societal and ecological impacts from projected Tibetan Plateau lake expansion. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bolch, T.; Chen, W.; Cretaux, J.F. Comprehensive estimation of lake volume changes on the Tibetan Plateau during 1976–2019 and basin-wide glacier contribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Shum, C.K.; Bolch, T.; Yi, S.; Allen, S.; Jiang, L.; et al. Response of Tibetan Plateau lakes to climate change: Trends, patterns, and mechanisms. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ju, J.; Qiao, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, R.; Ma, Q.; Guo, L.; Pang, S. Physical and biogeochemical responses of Tibetan Plateau lakes to climate change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Huang, B.; Ke, L. Modeling and analysis of lake water storage changes on the Tibetan Plateau using multi-mission satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 135, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, G.; Duan, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Li, A.; Kong, F.; Xue, B.; Wu, J.; et al. China’s lakes at present: Number, area and spatial distribution. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gun, Z.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, X. Variations in lake water storage over Inner Mongolia during recent three decades based on multi-mission satellites. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, B. Human-Induced water loss from closed inland Lakes: Hydrological simulations in China’s Daihai lake. J. Hydrol. 2022, 607, 127552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Liu, X.; Shi, H.; Wei, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Feng, W. Lake-area shrinkage driven by the combined effects of climate change and human activities. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 175, 113606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Zhang, Y.; Nourani, V.; Tian, X.; Miao, P. Both climate and anthropogenic impacts on recent lake area change in the Erdos Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; A, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, B. Landsat Satellite Image-Derived Area Evolution and the Driving Factors Affecting Hulun Lake from 1986 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, S.; Sun, B.; Yu, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Q. Evaluating the effects of ecological water replenishment on lake water exchange in semi-arid regions insights from an 11-year modeling study. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 391, 126491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Chen, P.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, L.; Ning, K. Identification of ecological restoration standard for lakes on the Inner Mongolia Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 162, 111993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, N.; Gan, F.; Yan, B.; Bai, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Li, R. Dynamic Monitoring and Change Analysis of Lake Area on the Inner-Mongolian Plateau over the Past 22 Years. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gan, F.; Yan, B.; Bai, J.; Xing, N.; Zhuo, Y. Evaluation of Terrestrial Water Storage Changes and Major Driving Factors Analysis in Inner Mongolia, China. Sensors 2022, 22, 9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihret, T.T.; Zemale, F.A.; Worqlul, A.W.; Ayalew, A.D.; Fohrer, N. Unlocking watershed mysteries: Innovative regionalization of hydrological model parameters in data-scarce regions. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, M.; Haberlandt, U.; Dietrich, J. A one-step similarity approach for the regionalization of hydrological model parameters based on Self-Organizing Maps. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Regionalising rainfall-runoff modelling for predicting daily runoff: Comparing gridded spatial proximity and gridded integrated similarity approaches against their lumped counterparts. J. Hydrol. 2017, 550, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Lei, Y. Suitable water surface area of the tail lake under the constraint of water diversion scheme in arid areas based on emergy theory. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 49, 101491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Fu, B.; Gao, G.; Shen, Q. Ecological effects and potential risks of the water diversion project in the Heihe River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, S.; Ni, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H. Dynamic and driving evolution of lake basin pressure in cold and arid regions based on a new method: A case study of three lakes in Inner Mongolia, China. J Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Liu, R.; Zou, Z.; Zhao, G.; Ge, Q. Continuous monitoring of lake dynamics on the Mongolian Plateau using all available Landsat imagery and Google Earth Engine. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Ryan, M.; Li, C.; Sun, B. Understanding the Role of Groundwater in a Remote Transboundary Lake (Hulun Lake, China). Water 2017, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item | Dataset | Attribute | Application Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Landsat 5/7/8 [43] | Spatial resolution: 30 m Temporal scale: 16 days Time span: 2000–2021 | Extract water area and LUCC | http://glovis.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 1 June 2025) |
| 2 | Sentinel-2 [43] | Spatial resolution: 10–30 m Temporal scale: 5 days Time span: 2019–2021 | Extract water area and LUCC | https://scihub.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 1 May 2023) |
| 3 | ICEsat | Footprints: 70 m Temporal scale: 183 days Time span: 2002.03–2009.10 | Extract water level | https://nsidc.org/data/GLAH14/versions/34 (accessed on 1 June 2025) |
| 4 | ICEsat-2 | Footprints: 17 m Temporal scale: 91 days Time span: 2018.10–2021.12 | Extract water level | https://nsidc.org/data/ATL13/versions/6 (accessed on 1 June 2025) |
| 5 | Cryosat-2 | Footprints: 800 m Temporal scale:369 days Time span: 2010.07–2021.08 | Extract water level | https://science-pds.cryosat.esa.int (accessed on 1 June 2025) |
| 6 | China LakeDataset [4] | Spatial resolution: 1:250,000 Temporal scale: 5 years Time span: 2000–2020 | Provide boundary information of lakes | https://doi.org/10.11888/Hydro.tpdc.270302 |
| 7 | Hydroweb [18] | Provides dense time series of water level data in large lakes and reservoirs | Verify the accuracy of water level and water storage changes | https://hydroweb.next.theia-land.fr/ (accessed on 20 June 2025) |
| 8 | In-situ observations of lake level and water storage | Spatial resolution: single reservoir Temporal scale: daily Time span: 2006–2017 | Verify the accuracy of water level and water storage changes | Hai River Water Conservancy Commission |
| 9 | Precipitation | Spatial resolution: 10 km Temporal scale: monthly Time span: 2000–2021 | Cause analysis | Fusion of Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) data and in situ precipitation data |
| 10 | Evapotranspiration (Eta) | Spatial resolution: 1 km Temporal scale: monthly Time span: 2000–2021 | Cause analysis | Model simulation (Complementary relationship principle) |
| 11 | GRACE/ GRACE-FO [44] | Spatial resolution: 100 km Temporal scale: monthly Time span: 2003–2021 | Cause analysis (Extract TWSA) | https://nasagrace.unl.edu/ (accessed on 1 June 2025) |
| The Variability of Water Level | IMP | I | II | III | IV | V | VI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water level rise (lakes) | 49 | 6 | 7 | 12 | 17 | 2 | 5 |
| Water level down (lakes) | 40 | 2 | 18 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 10 |
| No obvious change (lakes) | 20 | 0 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 2 |
| The Variability of LWS (Gt) | IMP | I | II | III | IV | V | VI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural lakes | −2.12 | 0.10 | −1.25 | −1.32 | 0.41 | −0.01 | −0.04 |
| Reservoirs | 0.90 | −0.02 | 0.09 | 0.77 | 0.13 | 0.03 | −0.11 |
| Sum | −1.21 | 0.08 | −1.16 | −0.55 | 0.54 | 0.02 | −0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, J.; Zhuo, Y.; Xing, N.; Gan, F.; Guo, Y.; Yan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R. The Shrinkage of Lakes on the Semi-Arid Inner Mongolian Plateau Is Still Serious. Water 2025, 17, 3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213056
Bai J, Zhuo Y, Xing N, Gan F, Guo Y, Yan B, Zhang Y, Li R. The Shrinkage of Lakes on the Semi-Arid Inner Mongolian Plateau Is Still Serious. Water. 2025; 17(21):3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213056
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Juan, Yue Zhuo, Naichen Xing, Fuping Gan, Yi Guo, Baikun Yan, Yichi Zhang, and Ruoyi Li. 2025. "The Shrinkage of Lakes on the Semi-Arid Inner Mongolian Plateau Is Still Serious" Water 17, no. 21: 3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213056
APA StyleBai, J., Zhuo, Y., Xing, N., Gan, F., Guo, Y., Yan, B., Zhang, Y., & Li, R. (2025). The Shrinkage of Lakes on the Semi-Arid Inner Mongolian Plateau Is Still Serious. Water, 17(21), 3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213056






