Stable Isotope Monitoring in a Semi-Arid Olive Orchard Suggest Changes in Ecohydrological Dynamics from Contrasting Drip Irrigation Regimes
Abstract
1. Introduction
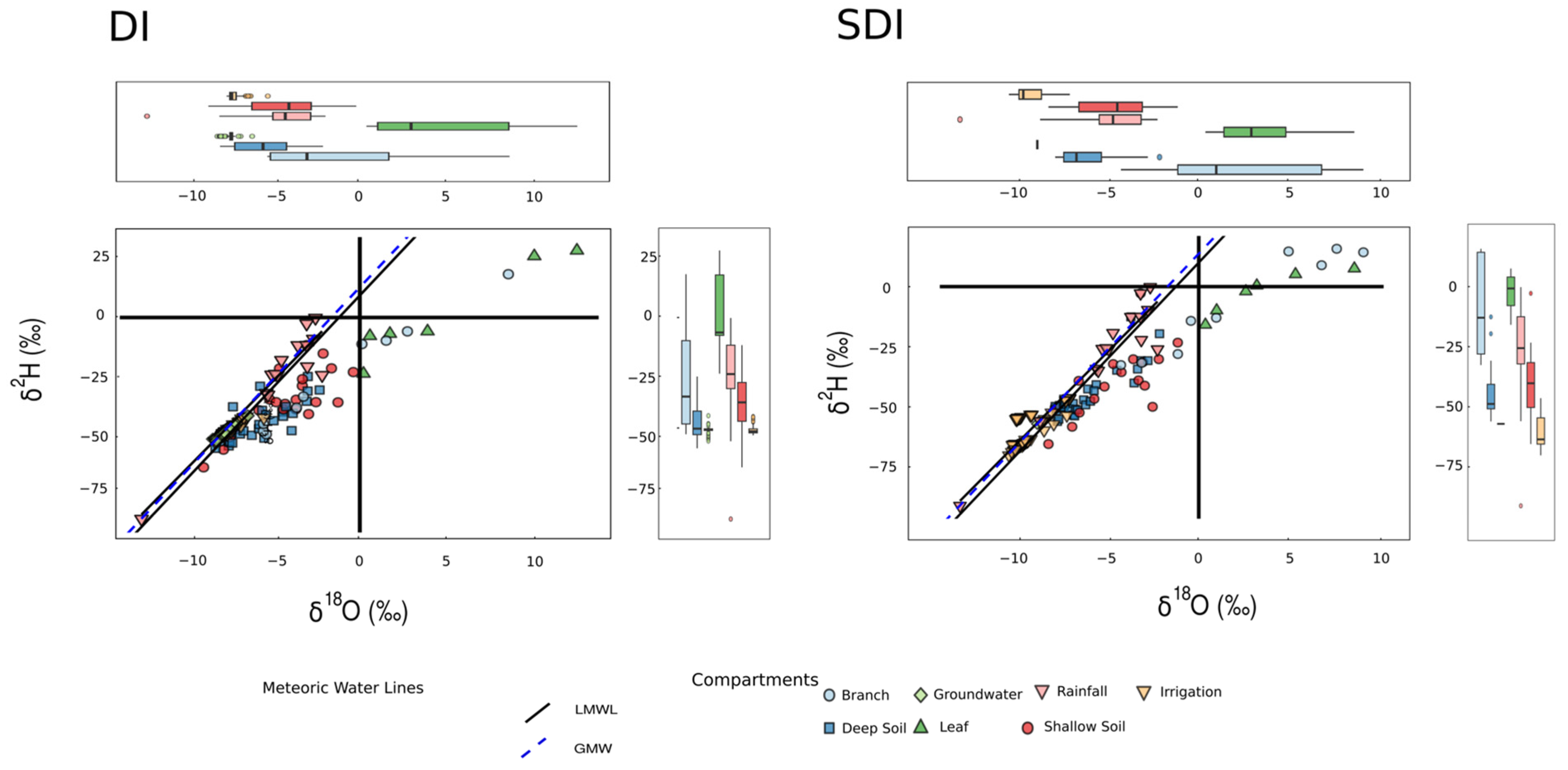
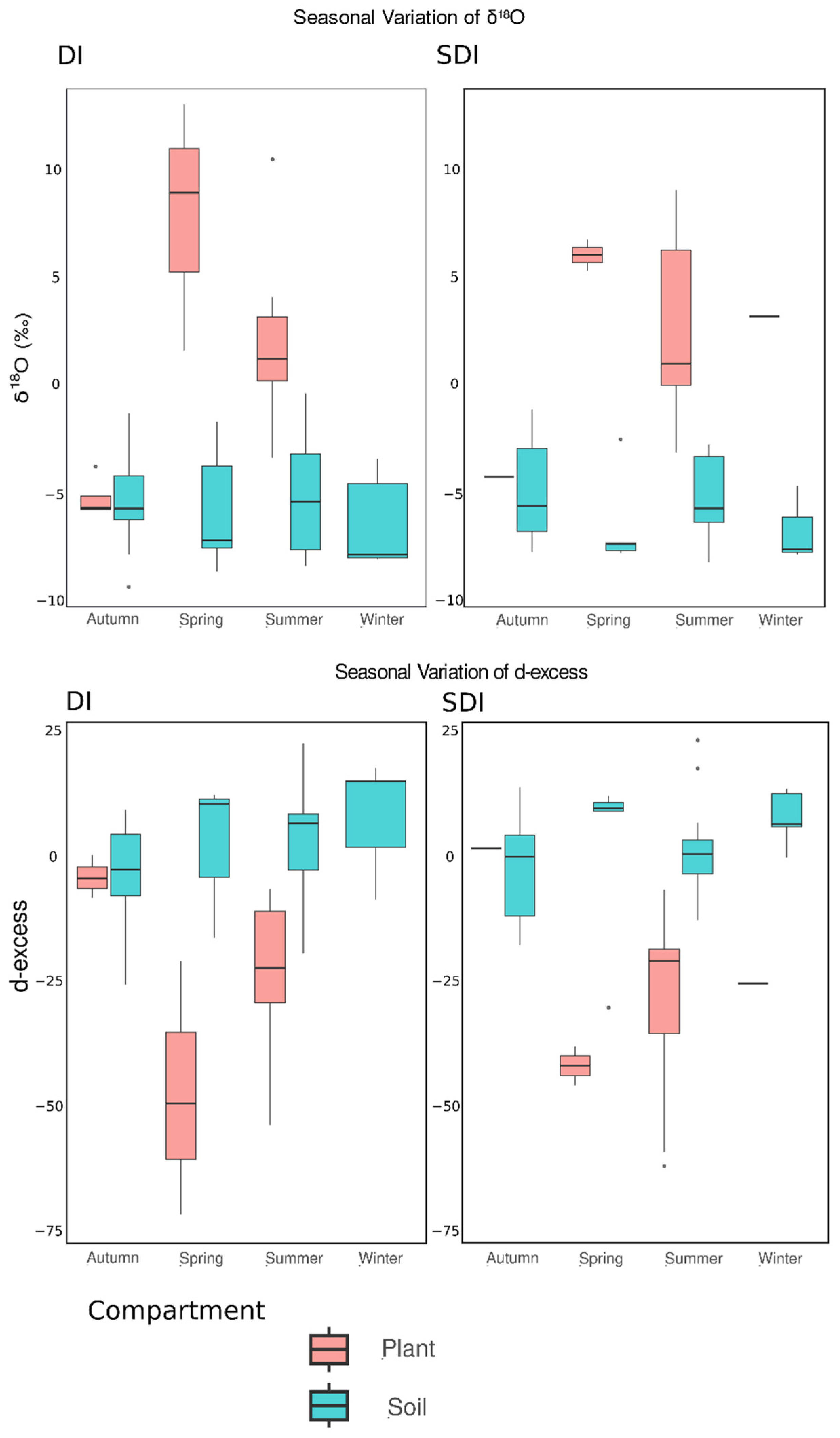
- Isotopic range of the soil profile is narrower in SDI than in DI, depending on the seasonal cycle in the isotopic composition of rainwater?
- Soil and plant water experience more evaporative, non-productive loss of water under DI than under SDI, as indicated by the isotopic enrichment in topsoil.
- Plants under SDI take consistently water from the subsurface irrigation layer throughout the season, while under DI it takes mainly water from the topsoil.
2. Materials and Methods
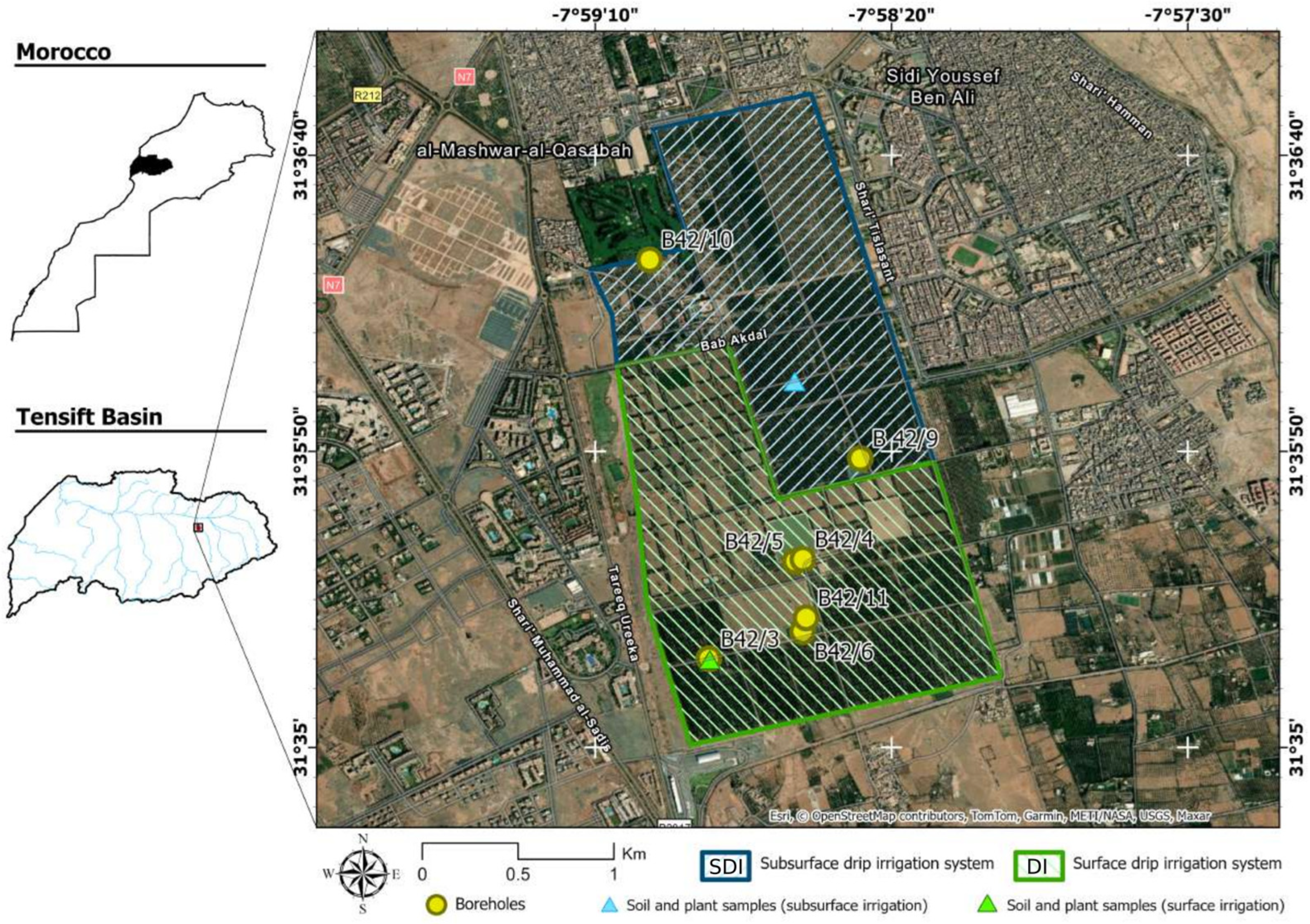
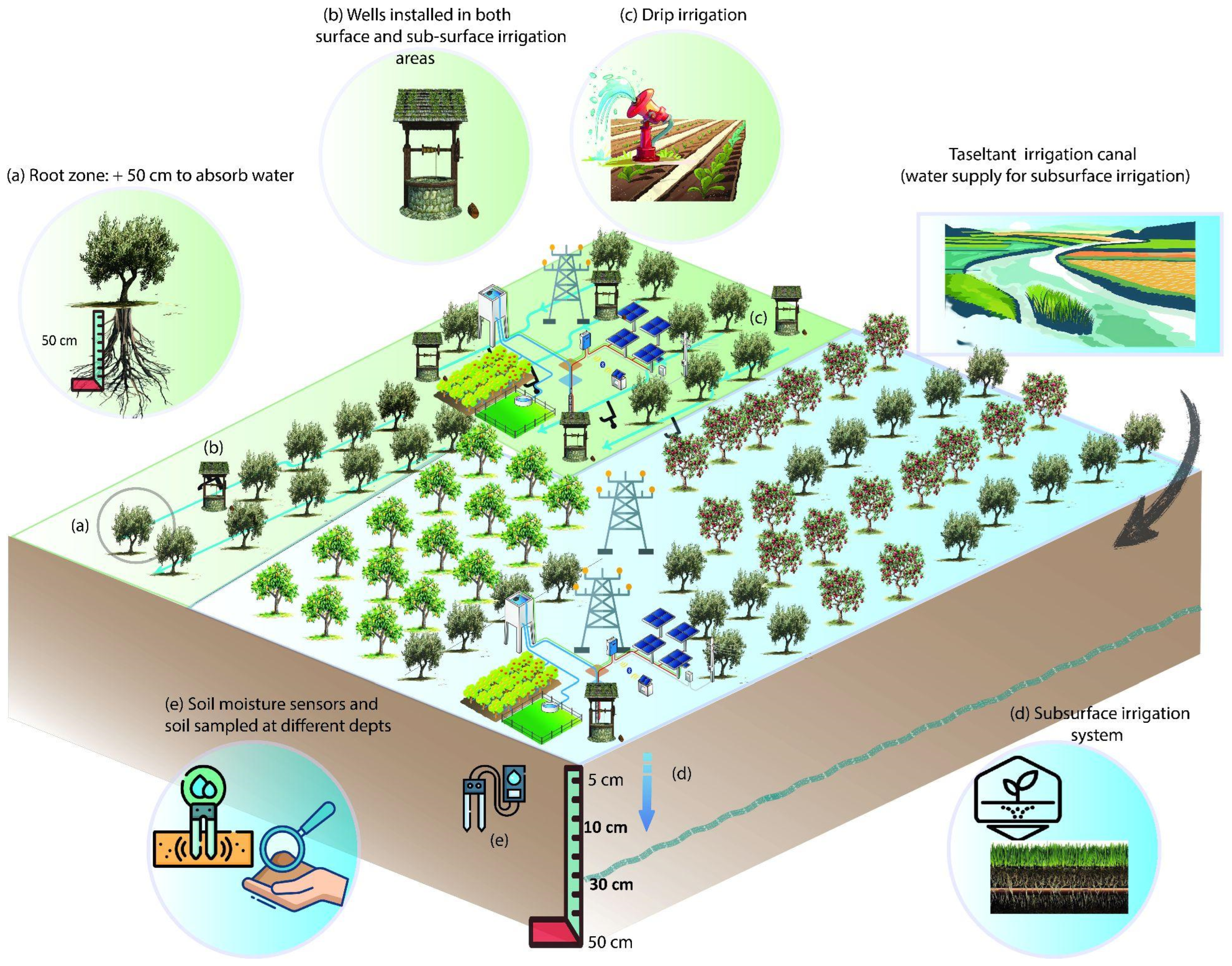
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Protocol
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
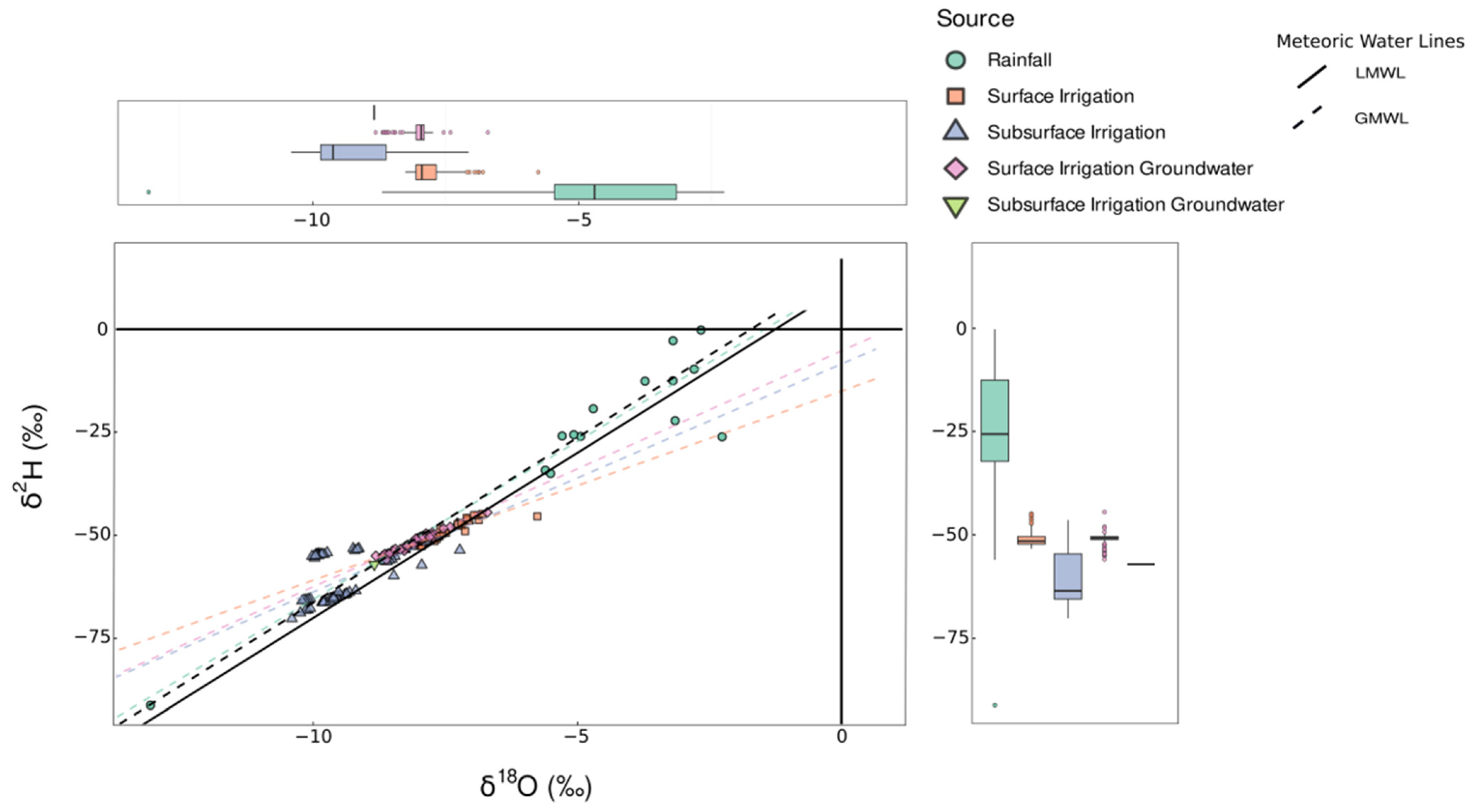
3.1. Description of δ18O and δ2H for Different Waters
3.1.1. Rainwater
3.1.2. Irrigation Water
3.1.3. Groundwater
3.1.4. Soil Water
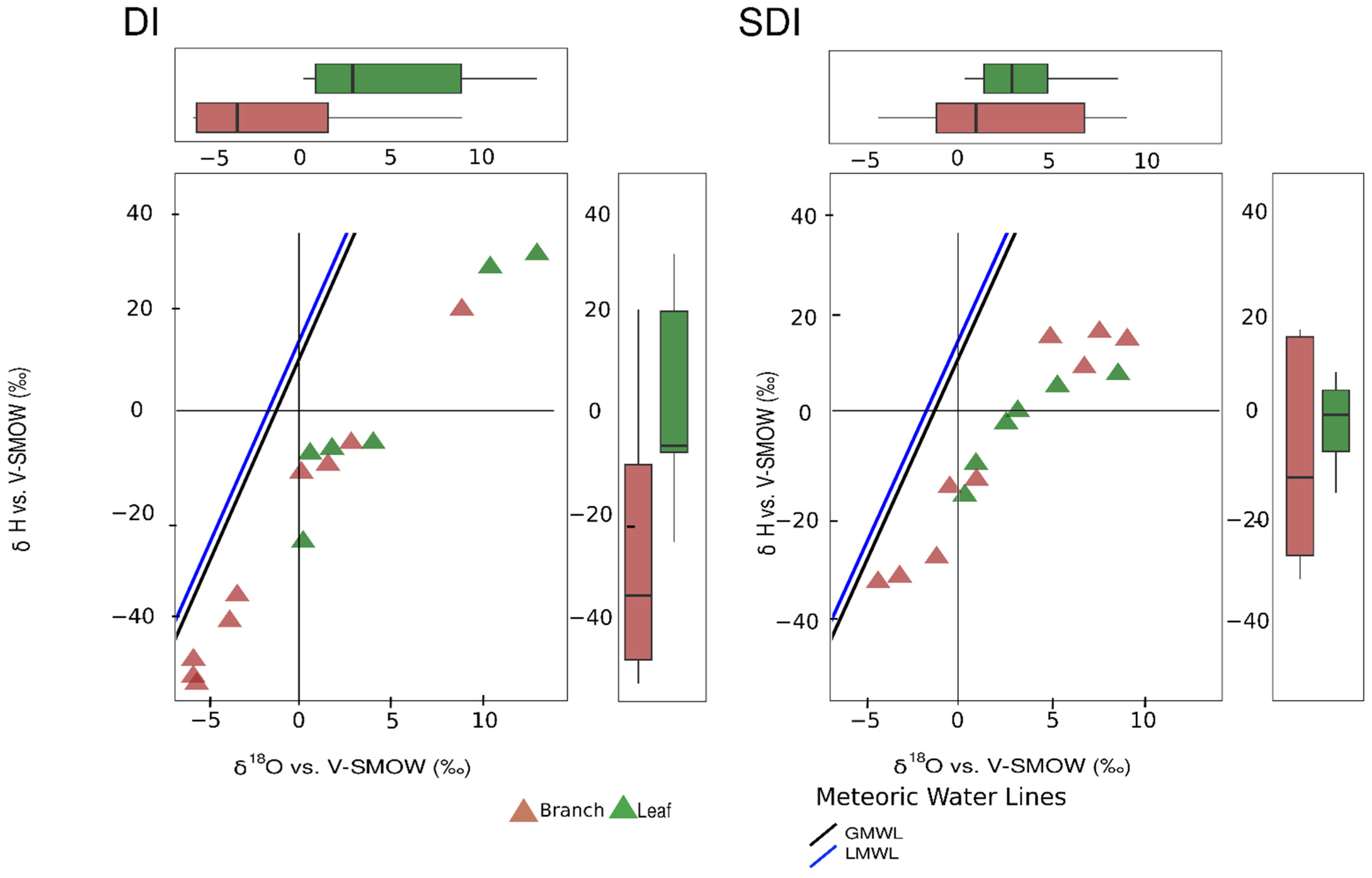
3.1.5. Plant Water
3.2. Relationships Between Soil Water and Plant Water: Implications for Root Water Uptake of Olive Trees
3.3. Seasonal Variation in Plant Xylem and Soil Water
3.4. Limitations and Perspective
4. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matthews, J.B.R.; Möller, V.; van Diemen, R.; Fuglestvedt, J.S.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Méndez, C.; Semenov, S.; Reisinger, A. Annex VII: Glossary. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 2215–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Sustainability of the blue water footprint of crops. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 143, 103679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenmark, M.; Wang-Erlandsson, L. A water-function-based framework for understanding and governing water resilience in the Anthropocene. One Earth 2021, 4, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Dhmane, L.; Saidi, M.E.; Moustadraf, J.; Rafik, A.; Hadri, A. Spatiotemporal characterization and hydrological impact of drought patterns in northwestern Morocco. Front. Water 2024, 6, 1463748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Siebert, S.; Kummu, M.; Deng, Q.; Ali, T.; Marston, L.; Xie, W.; Davis, K.F. Half of twenty-first century global irrigation expansion has been in water-stressed regions. Nat. Water 2024, 2, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, A.; Ragab, R.; Scarascia-Mugnozza, E. Coping with water scarcity: Water saving and increasing water productivity. Irrig. Drain. 2003, 52, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achli, S.; Ongoma, V.; Epule, T.E.; Dhiba, D.; Salih, W.; Ousayd, L.; Chehbouni, A. Exploring the key drivers of crop yields in Morocco—A systematic review. Front. Agron. 2025, 7, 1515938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabba, S.; Er-Raki, S.; Ezzahar, J.; Merlin, O.; Kharrou, M.H.; Chehbouni, A. Experimental assessment of irrigation efficiency over the dominant (flood and drip) irrigated crops in the Haouz plain, center of Morocco. Acta Hortic. 2025, 1422, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attou, T.; Kuppel, S.; Kharrou, M.H.; Ezzahar, J.; Bouchaou, L.; Ait Brahim, Y.; Demarez, V.; Chehbouni, A. A process-based modelling of groundwater recharge under contrasting irrigation methods in semi-arid crops. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 316, 109584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modanesi, S.; Massari, C.; Bechtold, M.; Lievens, H.; Tarpanelli, A.; Brocca, L.; Zappa, L.; De Lannoy, G.J.M. Challenges and benefits of quantifying irrigation through the assimilation of Sentinel-1 backscatter observations into Noah-MP. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 4685–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Brahim, Y.; Bouchaou, L.; Sifeddine, A.; Khodri, M.; Reichert, B.; Cruz, F.W. Elucidating the climate and topographic controls on stable isotope composition of meteoric waters in Morocco, using station-based and spatially-interpolated data. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Yong, L.; Sang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, K. Isotopic differences in soil–plant–atmosphere continuum composition and control factors of different vegetation zones on the northern slope of the Qilian Mountains. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, D.; Buttle, J.; Carey, S.K.; Kohn, M.J.; Laudon, H.; McNamara, J.P.; Smith, A.; Sprenger, M.; Soulsby, C. Stable isotopes of water reveal differences in plant—Soil water relationships across northern environments. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceperley, N.; Gimeno, T.E.; Jacobs, S.R.; Beyer, M.; Dubbert, M.; Fischer, B.; Geris, J.; Holko, L.; Kübert, A.; le Gall, S.; et al. Toward a common methodological framework for the sampling, extraction, and isotopic analysis of water in the Critical Zone to study vegetation water use. WIREs Water 2024, 11, e1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouade, G.; Ezzahar, J.; Amenzou, N.; Er-Raki, S.; Benkaddour, A.; Khabba, S.; Jarlan, L. Combining stable isotopes, Eddy Covariance system and meteorological measurements for partitioning evapotranspiration, of winter wheat, into soil evaporation and plant transpiration in a semi-arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowski, N.; Breuer, L.; Angeli, N.; Boeckx, P.; Brumbt, C.; Cook, C.S.; Dubbert, M.; Dyckmans, J.; Gallagher, B.; Gralher, B.; et al. Inter-laboratory comparison of cryogenic water extraction systems for stable isotope analysis of soil water. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 3619–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-F.; Yakir, D. Using stable isotopes of water in evapotranspiration studies. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliker, B.R.; Ehleringer, J.R. Differential 18O enrichment of leaf cellulose in C3 versus C4 grasses. Funct. Plant Biol. 2002, 29, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.G.; Cable, W.; Hultine, K.; Hoedjes, J.C.B.; Yepez, E.A.; Simonneaux, V.; Er-Raki, S.; Boulet, G.; de Bruin, H.A.R.; Chehbouni, A.; et al. Evapotranspiration components determined by stable isotope, sap flow and eddy covariance techniques. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 125, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Dawson, T.E. Water uptake by plants: Perspectives from stable isotope composition. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppel, S.; Tetzlaff, D.; Maneta, M.P.; Soulsby, C. EcH2O-iso 1.0: Water isotopes and age tracking in a process-based, distributed ecohydrological model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 3045–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, A.; Krishnamurthy, R.V. Factors controlling the stable hydrogen and carbon isotoperatios in regional ground water of the Eastern United Arab Emirates (UAE). Hydrol. Process. 2007, 22, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.M.; Krishnamurthy, R.V.; Kehew, A.E.; Crossey, L.J.; Karlstrom, K.K. Factors affecting the stable isotopes ratios in groundwater impacted by intense agricultural practices: A case study from the Nile Valley of Egypt. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, H.; Gordon, L.I.; Horibe, Y. Isotopic exchange effects in the evaporation of water: 1. Low-temperature experimental results. J. Geophys. Res. 1963, 68, 5079–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Page, M.; Toumi, J.; Khabba, S.; Hagolle, O.; Tavernier, A.; Kharrou, M.; Er-Raki, S.; Huc, M.; Kasbani, M.; Moutamanni, A.; et al. A Life-Size and Near Real-Time Test of Irrigation Scheduling with a Sentinel-2 Like Time Series (SPOT4-Take5) in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11182–11203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassah, H.; Younes, F.; Salah, E.; Said, K.; Mougenot, B. Mapping Soil Clay Content and Hydraulic Properties over an Agricultural Semiarid Plain Using Remote Sensing and Interpolation Techniques. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2024, 25, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wösten, J.H.M. Chapter 10 Pedotransfer functions to evaluate soil quality. Dev. Soil Sci. 1997, 25, 221–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; An, K.; Lei, X.; He, M. Real-Time Water Level Prediction in Open Channel Water Transfer Projects Based on Time Series Similarity. Water 2022, 14, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; Lartey, J.L.; Sanders, L.L. Isotopic (δ 18 O and δ 2 H) Integrity of Water Samples Collected and Stored by Automatic Samplers. Agric. Environ. Lett. 2018, 3, 180009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Katsuyama, M.; Kosugi, Y.; Okumura, M.; Matsuo, N. Effects of cryogenic vacuum distillation on the stable isotope ratios of soil water. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2019, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Risi, C.; Tian, L.; Yang, D.; Bowen, G.; Fan, S.; Su, Y.; Pang, H.; Li, L. Correcting for water vapor diffusion in air bag samples for isotope composition analysis: Cases studies with drone-collected samples. Preprints 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhari, K.; Fakir, Y.; Stigter, T.Y.; Hajhouji, Y.; Boulet, G. Origin of recharge and salinity and their role on management issues of a large alluvial aquifer system in the semi-arid Haouz plain, Morocco. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6195–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Qu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Soil moisture variability affected by sand mulch: An isotope-based assessment of irrigated farmland in Northwest China. Ecohydrology 2023, 16, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshun, J.; Dietrich, W.E.; Dawson, T.E.; Fung, I. Dynamic, structured heterogeneity of water isotopes inside hillslopes. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 164–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, M.J.; Sonnenthal, E.L.; Conrad, M.E.; DePaolo, D.J.; Gee, G.W. Multiphase Reactive Transport Modeling of Seasonal Infiltration Events and Stable Isotope Fractionation in Unsaturated Zone Pore Water and Vapor at the Hanford Site. Vadose Zone J. 2004, 3, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M.; Leistert, H.; Gimbel, K.; Weiler, M. Illuminating hydrological processes at the soil-vegetation-atmosphere interface with water stable isotopes. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 674–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowski, N.; Seeger, S.; Mennekes, D.; de Boer, H.; Weiler, M.; Rinderer, M. Monitoring tree species-specific water uptake strategies via continuous in-situ stable water isotope measurements. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly, Online, 4–8 May 2020. EGU2020-16786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbeta, A.; Gimeno, T.E.; Clavé, L.; Fréjaville, B.; Jones, S.P.; Delvigne, C.; Wingate, L.; Ogée, J. An explanation for the isotopic offset between soil and stem water in a temperate tree species. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.; Zuecco, G.; Marchina, C.; Engel, M.; Penna, D.; McDonnell, J.J.; Borga, M. No evidence of isotopic fractionation in olive trees (Olea europaea): A stable isotope tracing experiment. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2021, 66, 2415–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2012, 16, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasta, P.; Todini-Zicavo, D.; Zuecco, G.; Marchina, C.; Penna, D.; McDonnell, J.J.; Amin, A.; Allocca, C.; Marzaioli, F.; Stellato, L.; et al. Quantifying irrigation uptake in olive trees: A proof-of-concept approach combining isotope tracing and Hydrus-1D. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2023, 68, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighenti, S.; Tagliavini, M.; Comiti, F.; Aguzzoni, A.; Giuliani, N.; Abdelkader, A.B.; Penna, D.; Zanotelli, D. Drip irrigation frequency leads to plasticity in root water uptake by apple trees. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 298, 108870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, D.; Geris, J.; Hopp, L.; Scandellari, F. Water sources for root water uptake: Using stable isotopes of hydro--gen and oxygen as a research tool in agricultural and agroforestry systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 291, 106790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M.; Allen, S.T. Commentary: What ecohydrologic separation is and where we can go with it. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, M.; Kühnhammer, K.; Dubbert, M. In situ measurements of soil and plant water isotopes: A review of approaches, practical considerations and a vision for the future. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 4413–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhou, X. Improving sampling protocols for stable isotope analysis in agro-ecosystems. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 129031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeniger, P.; Gaj, M.; Wassenaar, L.I. Evaporation-induced oxygen-18 and deuterium enrichment in water sample storage: Field guidance for precipitation collectors. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 921–925. [Google Scholar]
- Oerter, E.J.; Siebert, G.; Bowling, D.R.; Bowen, G. Soil water vapour isotopes identify missing water source for streamside trees. Ecohydrology 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, T.; Crispin, M.; White, S. Advances in cryogenic vacuum distillation for stable isotope analysis. Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 1090–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Mahindawansha, A.; Orlowski, N.; Kraft, P.; Rothfuss, Y.; Racela, H.; Breuer, L. Quantification of plant water uptake by water stable isotopes in rice paddy systems. Plant Soil 2018, 429, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, M. Using stable isotopes to trace soil water movement in a semi-arid watershed. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothfuss, Y.; Javaux, M. Reviews and syntheses: Isotopic approaches to quantify root water uptake: A review and comparison of methods. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2199–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Attou, T.; Kharrou, M.H.; Kuppel, S.; Ait Brahim, Y.; Bouchaou, L.; Demarez, V.; Lehmann, M.M.; Raibi, F.; Elghali, T.; Elazhari, A.; et al. Stable Isotope Monitoring in a Semi-Arid Olive Orchard Suggest Changes in Ecohydrological Dynamics from Contrasting Drip Irrigation Regimes. Water 2025, 17, 3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213029
Attou T, Kharrou MH, Kuppel S, Ait Brahim Y, Bouchaou L, Demarez V, Lehmann MM, Raibi F, Elghali T, Elazhari A, et al. Stable Isotope Monitoring in a Semi-Arid Olive Orchard Suggest Changes in Ecohydrological Dynamics from Contrasting Drip Irrigation Regimes. Water. 2025; 17(21):3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213029
Chicago/Turabian StyleAttou, Taha, M. H. Kharrou, S. Kuppel, Y. Ait Brahim, L. Bouchaou, V. Demarez, M. M. Lehmann, F. Raibi, T. Elghali, A. Elazhari, and et al. 2025. "Stable Isotope Monitoring in a Semi-Arid Olive Orchard Suggest Changes in Ecohydrological Dynamics from Contrasting Drip Irrigation Regimes" Water 17, no. 21: 3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213029
APA StyleAttou, T., Kharrou, M. H., Kuppel, S., Ait Brahim, Y., Bouchaou, L., Demarez, V., Lehmann, M. M., Raibi, F., Elghali, T., Elazhari, A., Rhoujjati, N., Bouimouass, H., & Chehbouni, A. (2025). Stable Isotope Monitoring in a Semi-Arid Olive Orchard Suggest Changes in Ecohydrological Dynamics from Contrasting Drip Irrigation Regimes. Water, 17(21), 3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213029






