Optimization of Synergistic Water Resources, Water Environment, and Water Ecology Remediation and Restoration Project: Application in the Jinshan Lake Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology: Intelligent Platform of Remediation and Restoration Project Optimization
2.1. Platform Architecture
2.2. Multi-Source Data Fusion
2.3. Model Coupling
2.4. Dynamic Decision Optimization
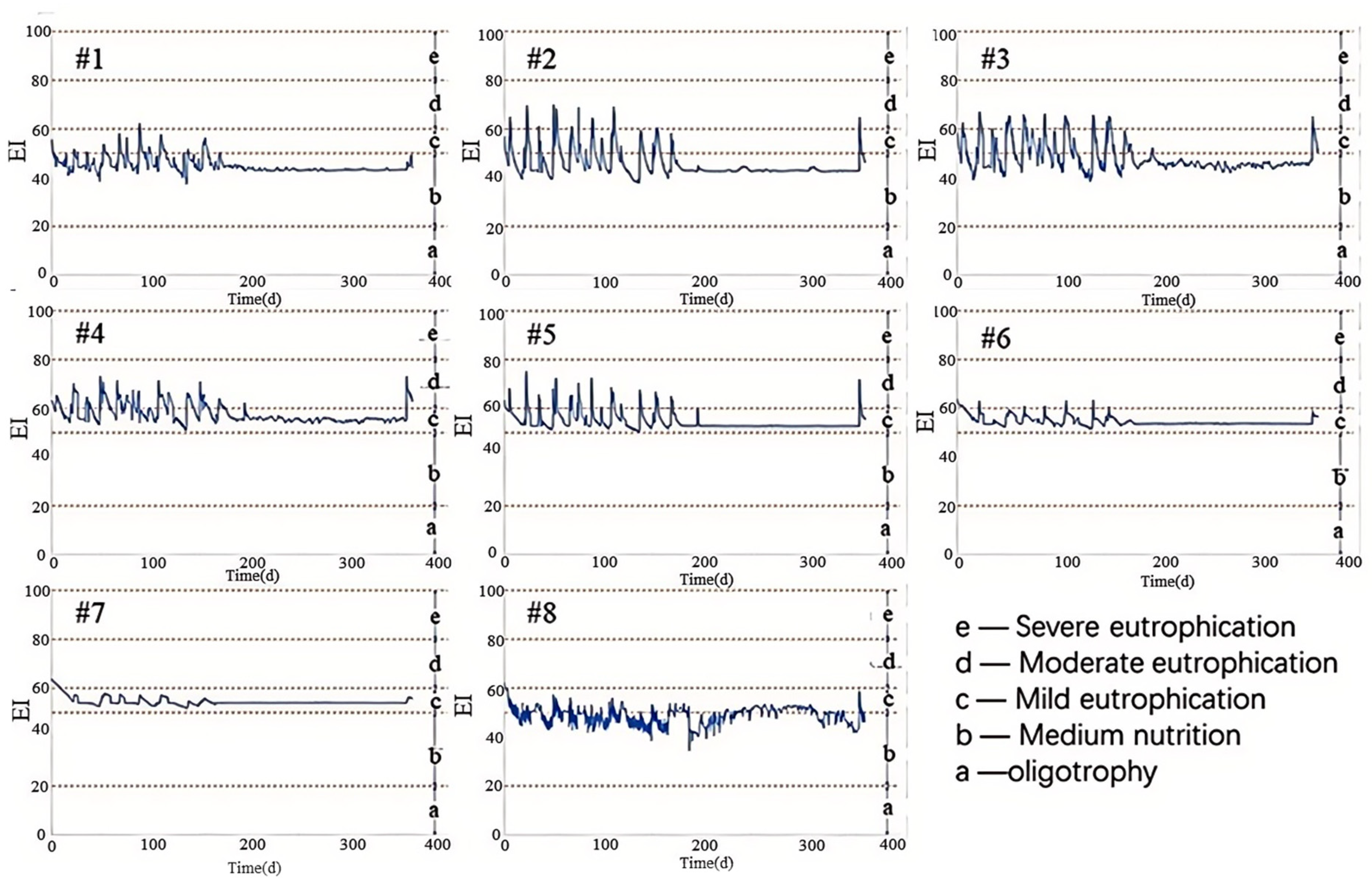
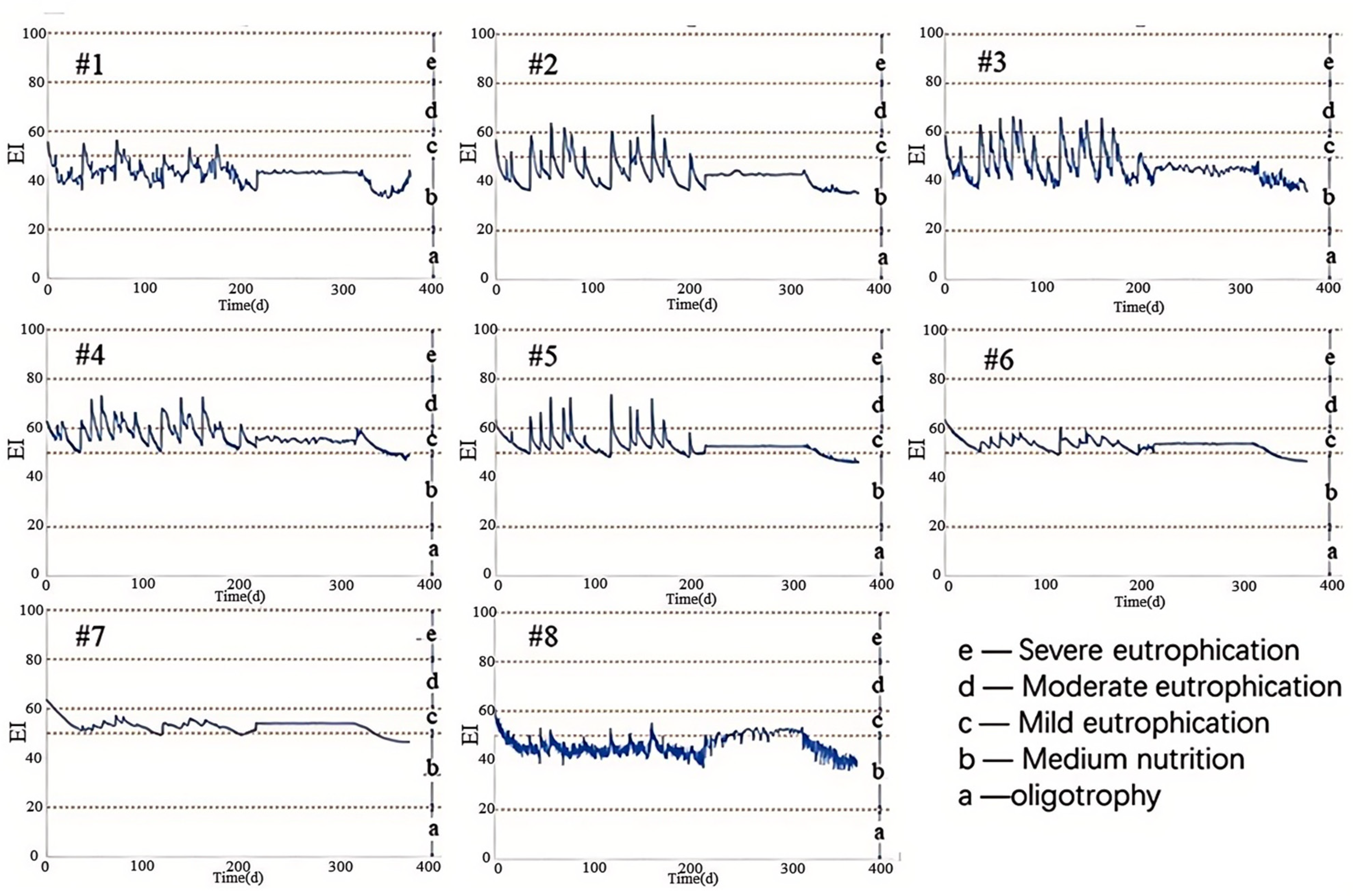
3. Results and Discussion
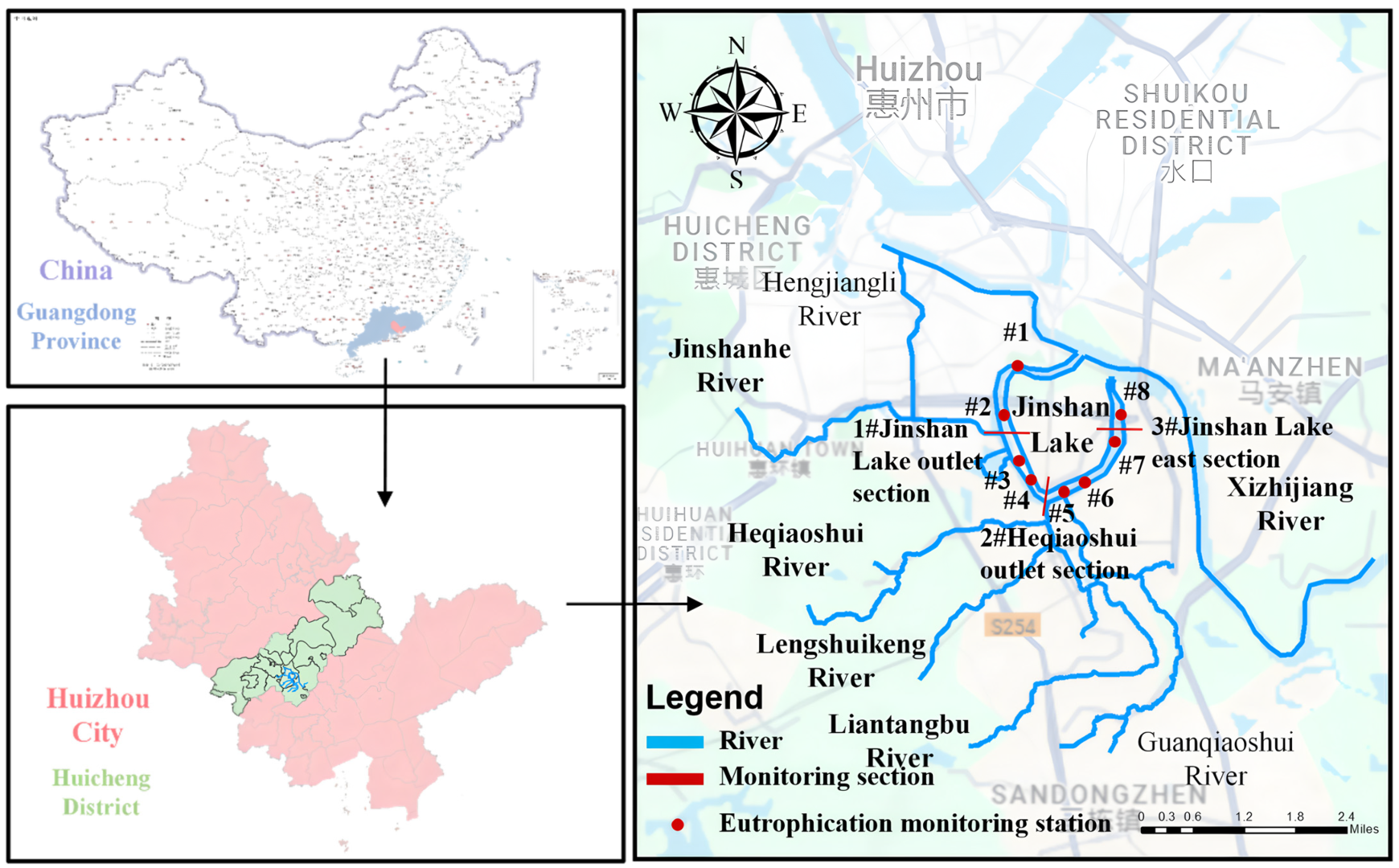
3.1. Study Area
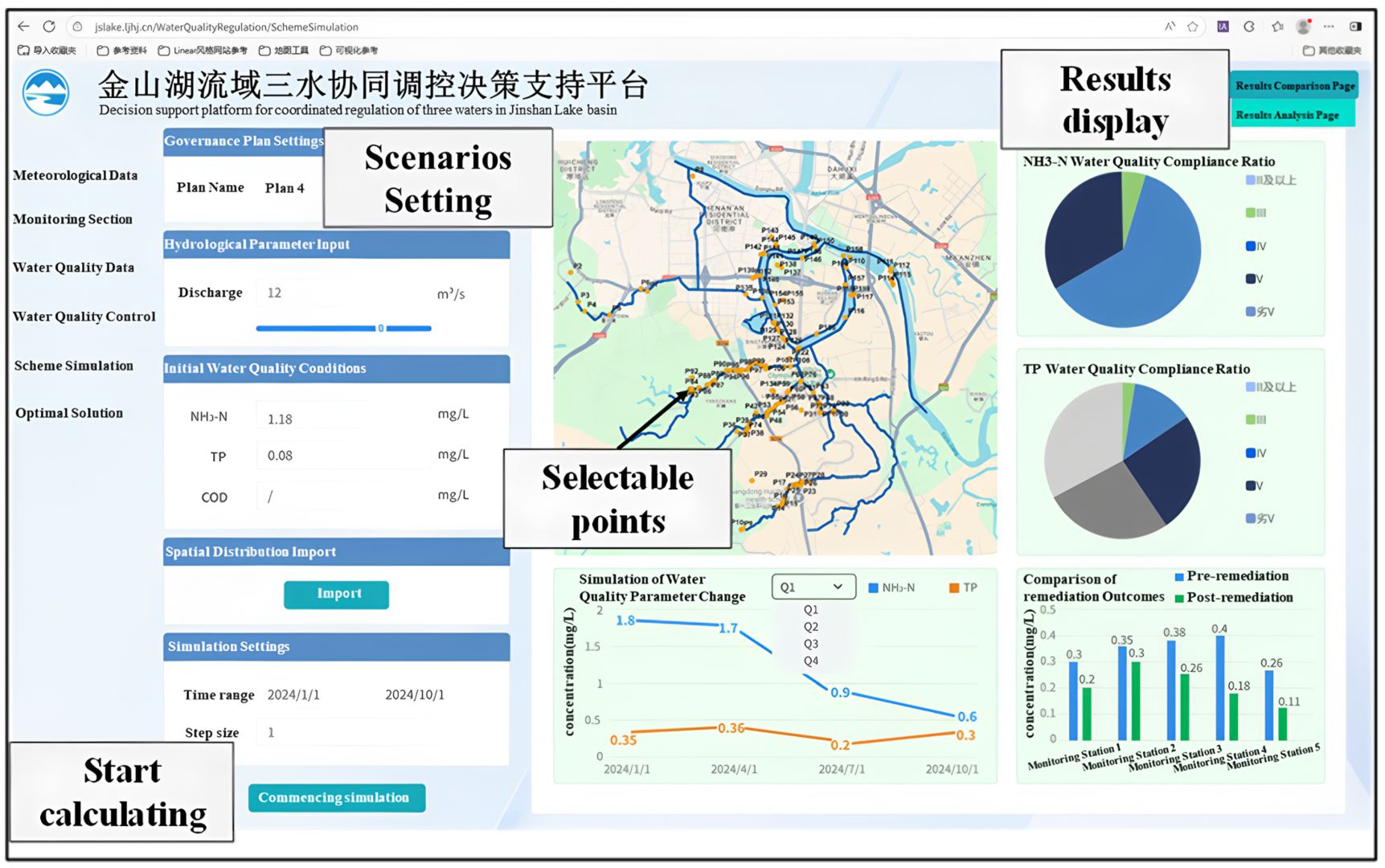
3.2. Jinshan Lake Basin Platform
3.3. Multi-Project Simulation and Optimization
3.3.1. Tributary
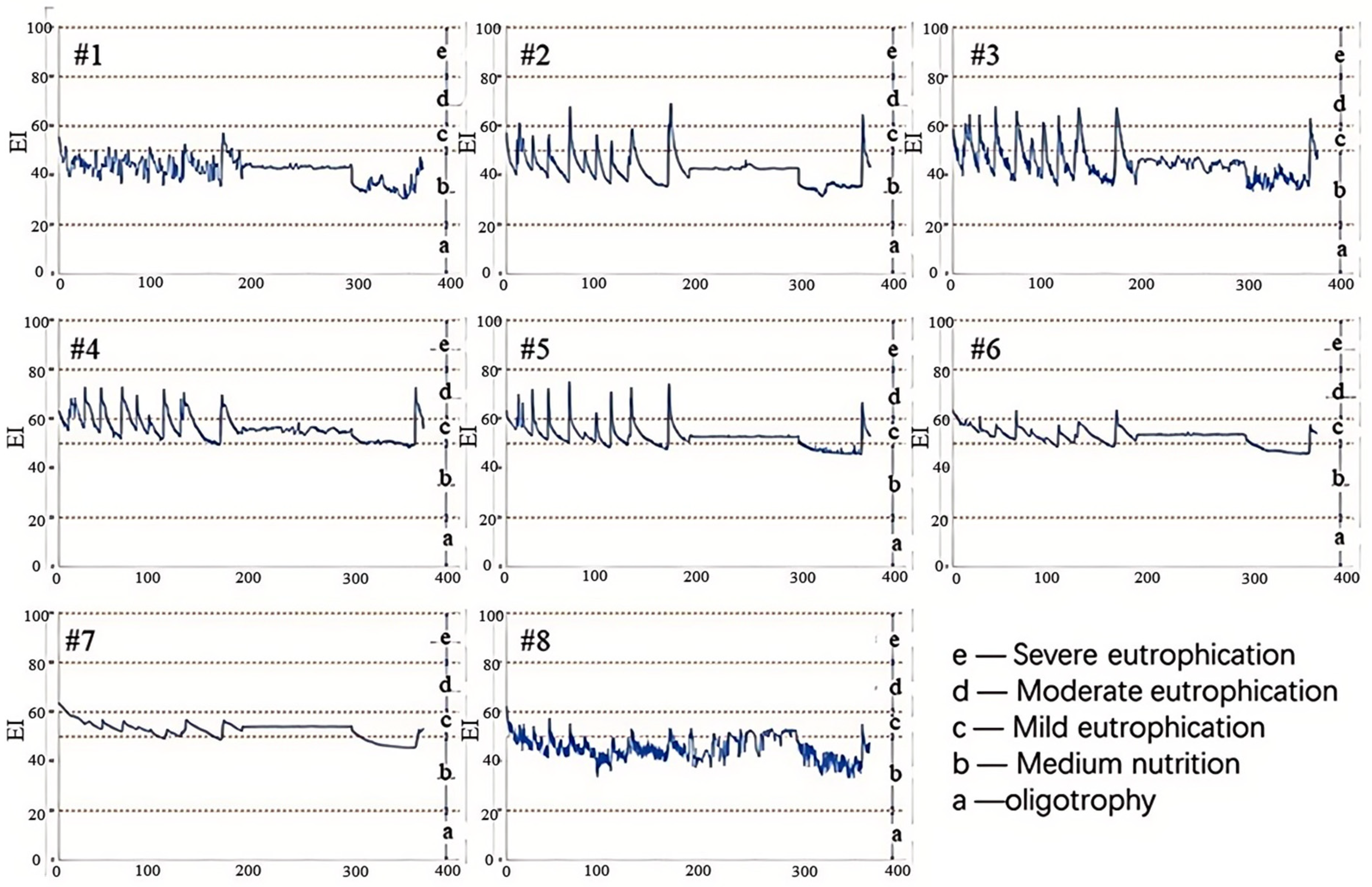
3.3.2. Lake
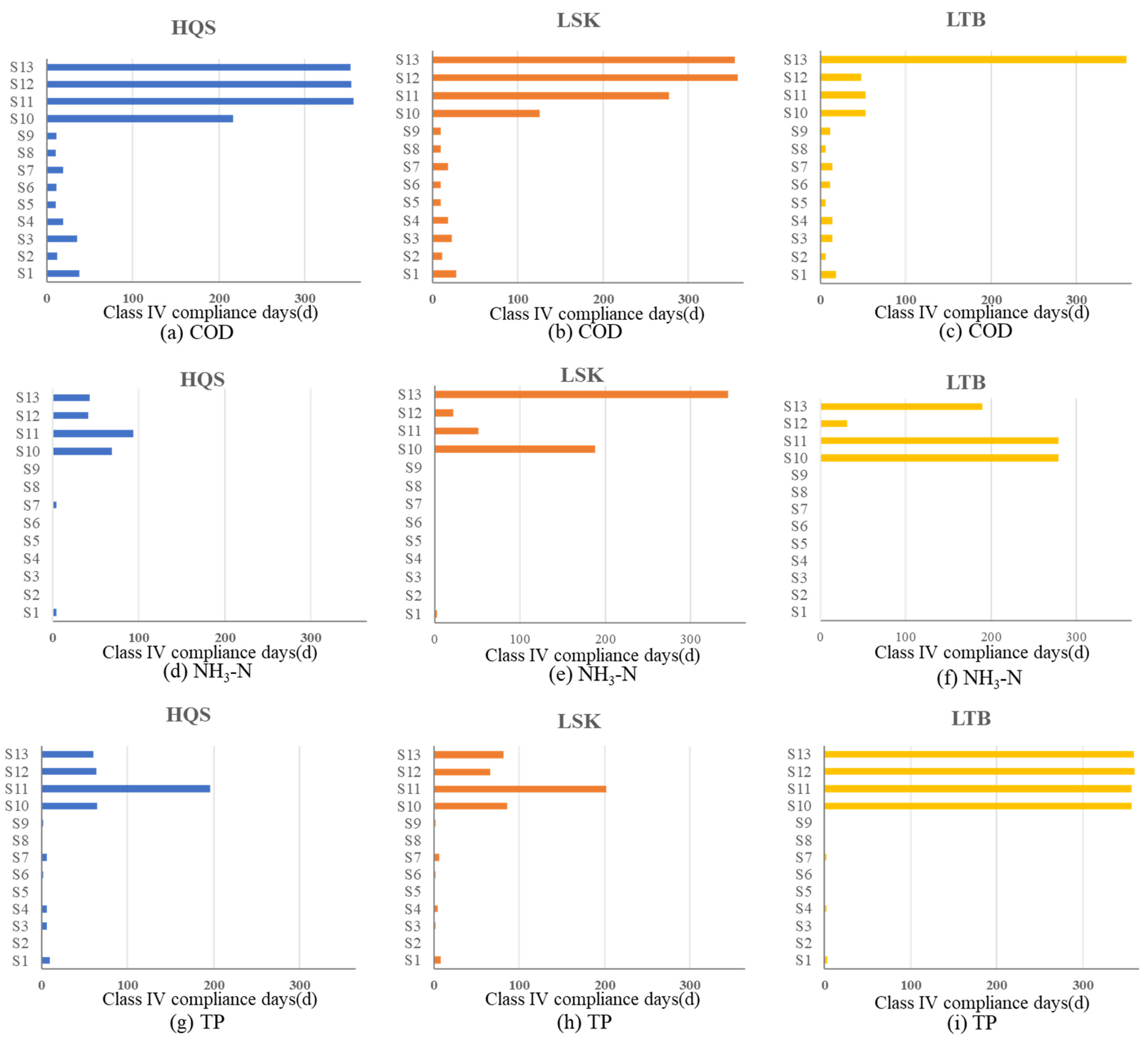
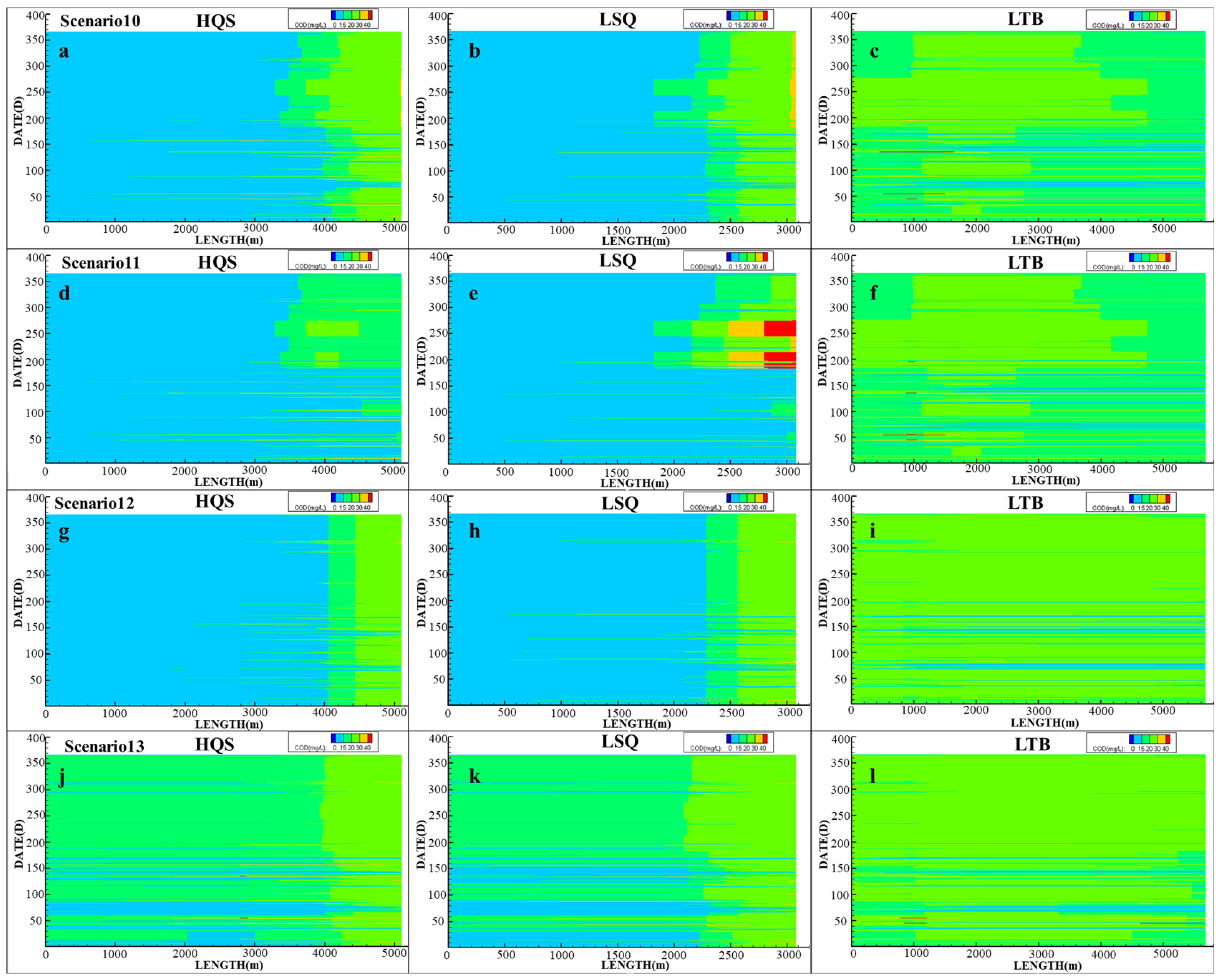
3.3.3. Decision for Optimal 3WRR Projects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.S.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Peng, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Xia, H.; Zhang, L. Water quality variations of Jinshan Lake Basin in Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao Great Bay Area. Water Resour. Prot. 2021, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.S.; Wang, H.; Zhou, F. Application prospects of key technologies for synergistic management of water resource-water environment-water ecology in Yangtze River Basin incontext of building ecological civilization. Yangtze River 2023, 54, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.X.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, D.H.; Xu, M.Y.; Shen, Q.S.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S.M. A critical review of the appearance of black-odorous waterbodies in China and treatment methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.W.; Dong, X.S.; Hou, B.D.; Fan, G.H.; Zhang, X.Y. Visual platform for water quality prediction and pre-warning of drinking water source area in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 309, 127398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Song, Y.C.; Zhang, P.Y.; Zou, Y. Distribution dynamics of waterbirds in Dongting Lake and surrounding lakes. Anim. Biol. 2025, 75, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, H.; Huntingford, C.; Ciais, P.; Piao, S.L. Strong direct and indirect influences of climate change on water yield confirmed by the Budyko framework. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaymaker, O. Research developments in the hydrological sciences in Canada (1995–1998): Surface water—Quantity, quality and ecology. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 14, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.H.; Wan, R.R.; Ahmad, S.; Eyvaz, M. Editorial: Sustainable development on water resources management, policy and governance in a changing world. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1297585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekri, S.; Jabeur, N.; Gharrad, H. Smart water management using intelligent digital twins. Comput. Inf. 2022, 41, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, W.S.; Liu, X.; Peng, H.; Zhou, F.; Wang, H.; Ke, Q.; Xiao, B.Y. Development and application of a multi-centre cloud platform architecture for water environment management. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 344, 118670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.F.; Hou, D.B.; Zhang, G.X.; Huang, P.J. Cloud simulation platform for water environment assessment. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 316–317, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Duan, J.J.; Zhai, J.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Y.L.; Gao, F.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhao, Y.F. Research on a cloud model intelligent computing platform for water resource management. J. Hydroinf 2024, 26, 2902–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwevedi, R.; Krishna, V.; Kumar, A. Environment and big data: Role in smart cities of India. Resources 2018, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, J.; Patel, J.; Chopra, J.; Chhaya, K.; Taravia, J.; Shah, M. Advent of Big Data technology in environment and water management sector. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Control Ser. 2021, 28, 64084–64102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Li, N. Big data platform of provincial key basin’s ecological environment information. IOP Conf. Series. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 295, 12073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, S.; Shin, C.M.; Sumihar, J.; Kim, K.; Cho, J.; Weerts, A.H. Ensemble data assimilation methods for improving river water quality forecasting accuracy. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Yue, J.; Li, Q.; Lin, J.; Liu, Q. Water-quality assessment and pollution-risk early-warning system based on web crawler technology and LSTM. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, K.R.; Kumar, S.V.; Geiger, J.V.; Wang, S.; Kemp, E.; Mocko, D.M.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Getirana, A.; Navari, M.; Li, B.; et al. The Land surface Data Toolkit (LDT v7.2)—A data fusion environment for land data assimilation systems. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2018, 11, 3605–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangdamrongsub, N.; Han, S.; Tian, S.; Müller, S.H.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; Ran, J.; Feng, W. Evaluation of Groundwater Storage Variations Estimated from GRACE Data Assimilation and State-of-the-Art Land Surface Models in Australia and the North China Plain. Rem. Sens. 2018, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Babovic, V.; Gin, K.Y. A comprehensive integrated catchment-scale monitoring and modelling approach for facilitating management of water quality. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 120, 104489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Wang, X.K. Intelligent Information System Design on Water Quality Monitoring, Water Bloom Prediction and Emergency Treatment Decision-Making. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 128–129, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.S.; You, H. A digital twin dam and watershed management platform. Water 2023, 15, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mure-Ravaud, M.; Binet, G.; Bracq, M.; Perarnaud, J.J.; Fradin, A.; Litrico, X. A web based tool for operational real-time flood forecasting using data assimilation to update hydraulic states. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 84, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostou, E.; Gianni, A.; Zacharias, I. Ecological Modeling and Eutrophication—A Review. Nat. Resour. Model. 2017, 30, e12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, W.; Li, W.; Mu, L.; Jin, Z. Coupled Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Simulation of Algal Bloom in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 119, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garuba, O.A.; Rasch, P.J. A partial coupling method to isolate the roles of the atmosphere and ocean in coupled climate simulations. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2019MS002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquesne, F.; Vallaeys, V.; Vidaurre, P.J.; Hanert, E. A Coupled Ecohydrodynamic Model to Predict Algal Blooms in Lake Titicaca. Ecol. Model. 2021, 440, e109418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larabi, S.; Schnorbus, M.A.; Zwiers, F. A coupled streamflow and water temperature (VIC-RBM-CE-QUAL-W2) model for the Nechako Reservoir. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J. Study on financial cost evaluation of urban water environment management and pollution prevention and control. AQUA-Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2024, 73, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandmeyer, J.E.; Karimi, H.A. Coupling Methodologies for Environmental Models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2000, 15, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallouin, T.; Bruen, M.; Christie, M.; Bullock, C.; Kelly-Quinn, M. Challenges in Using Hydrology and Water Quality Models for Assessing Freshwater Ecosystem Services: A Review. Geosciences 2018, 8, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janga, R.M.; Nagesh, K.D. Evolutionary algorithms, swarm intelligence methods, and their applications in water resources engineering: A state-of-the-art review. H2Open J. 2020, 3, 135–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwal, N.; Huang, X.; Kuriqi, A.; Chen, Y.; Pandey, K.P.; Bhattarai, K.P. Optimisation of cascade reservoir operation considering environmental flows for different environmental management classes. Renew. Energy 2020, 158, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahi, M.M.; Ahmadi, M.; Dabir, B. Model-based water-flooding optimization using multi-objective approach for efficient reservoir management. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 196, 107988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Q.; Guo, S.X.; Xiong, W. Model Design of Self-service Intelligent Resource Management System Based on Cloud Platform. Adv. Mat. Res. 2014, 846, 1491–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.Q.; Mao, J.Q.; Wang, Y.; Dai, H.C.; Zhang, P.P.; Guo, J.L. Optimal operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir subject to the ecological water level of Dongting Lake. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Liu, S.Q.; Luo, Q.Q.; Zhang, M.; Song, C.S. Analysis of spatial and temporal differences and influencing factors of urban land use efficiency based on DEA: Taking Guizhou Province as an example. Value Eng. 2025, 44, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Peng, H. Estimation and prediction of water conservation in the upper reaches of the Hanjiang River Basin based on InVESTPLUS model. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, W.S.; Wang, Y.; Peng, H.; Jiang, A.N.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. An Improved Coupled Water Quantity-Quality-ecology Model Incorporating Diurnal Cycle As a Key Factor Affecting Algal Blooms and Application in Large Rivers. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Hu, W.P.; Xu, J.D.; Ma, R.H. Development of a visualization platform oriented to Lake water quality targets management—A case study of Lake Taihu. Ecol. Inf. 2017, 41, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Shen, S.J.; Wen, D.; Peng, H. Research on the Restoration of Urban Lake Water Environment under the Impact of River Network. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2020, 12, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, W.S.; Zhou, F.; Peng, H.; Lin, Y.N.; Chen, G.; Li, A. Decision support platform for coordinated regulation of three waters in Jinshan Lake Basin. Water Sav. Irrig. 2024, 11, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.S.; Wang, H. Cloud platform and application of watershed water environment and aquatic ecology intelligent management. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2021, 52, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.S.; Li, L.; Peng, H.; Zhang, X.; Xia, H.; Zhang, Z.Q. Dynamic water environment capacity of urban river network for water environment improvement. Water Resour. Prot. 2022, 38, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.D. Analysis on Hydrogeological Characteristics of Jinshan New Town Planning Area in Huizhou City. China Resour. Compr. Util. 2022, 40, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.D.; Liu, J.; Jeppesen, E.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Shi, K.; Deng, J. Why Lake Taihu continues to be plagued with cyanobacterial blooms through 10 years (2007–2017) efforts? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.F.; Shi, L.; Li, Z.M.; Wu, C.Q.; Huang, Y.B.; Lu, X.Z. Eutrophication Trend Analysis and Forewarning Model Construction of Water Source Reservoirs: Gaozhou Reservoir, China. Ecohydrology 2021, 15, e2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prater, C.; Frost, P.C.; Howell, E.T.; Watson, S.B. Variation in particulate C: N: P stoichiometry across the Lake Erie watershed from tributaries to its outflow. Limnol. Ocean. 2017, 62, S194–S206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Data Type | Data Sources |
|---|---|
| DEM | Chinese Academy of Sciences Geospatial Data Cloud |
| Landuse | Resource and Environmental Science and Data Centre |
| Soil | Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| Meteorology | China Meteorological Science Data Sharing Center |
| River network system | Google Earth High-Definition Satellite Map |
| Hydrology and water quality | Huizhou Water Quality Testing Services Ltd. |
| Water quality and aquatic ecology | Remote sensing monitoring |
| Socioeconomic data | Statistical yearbook of counties and cities in the study area |
| 3WRR projects | Field investigation and assessment of local water environmental and ecological conditions |
| Scenarios | Hydrological Years | Point Source Pollution Reduction | Non-Point Source Pollution Reduction | Sediment Dredging | Recycled Water Reuse | Ecological Water Replenishment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | 1 | P10 | 95% | × | × | × | - |
| 2 | P50 | ||||||
| 3 | P90 | ||||||
| 4 | P10 | × | 95% | × | × | × | |
| 5 | P50 | ||||||
| 6 | P90 | ||||||
| 7 | P10 | × | × | √ | × | × | |
| 8 | P50 | ||||||
| 9 | P90 | ||||||
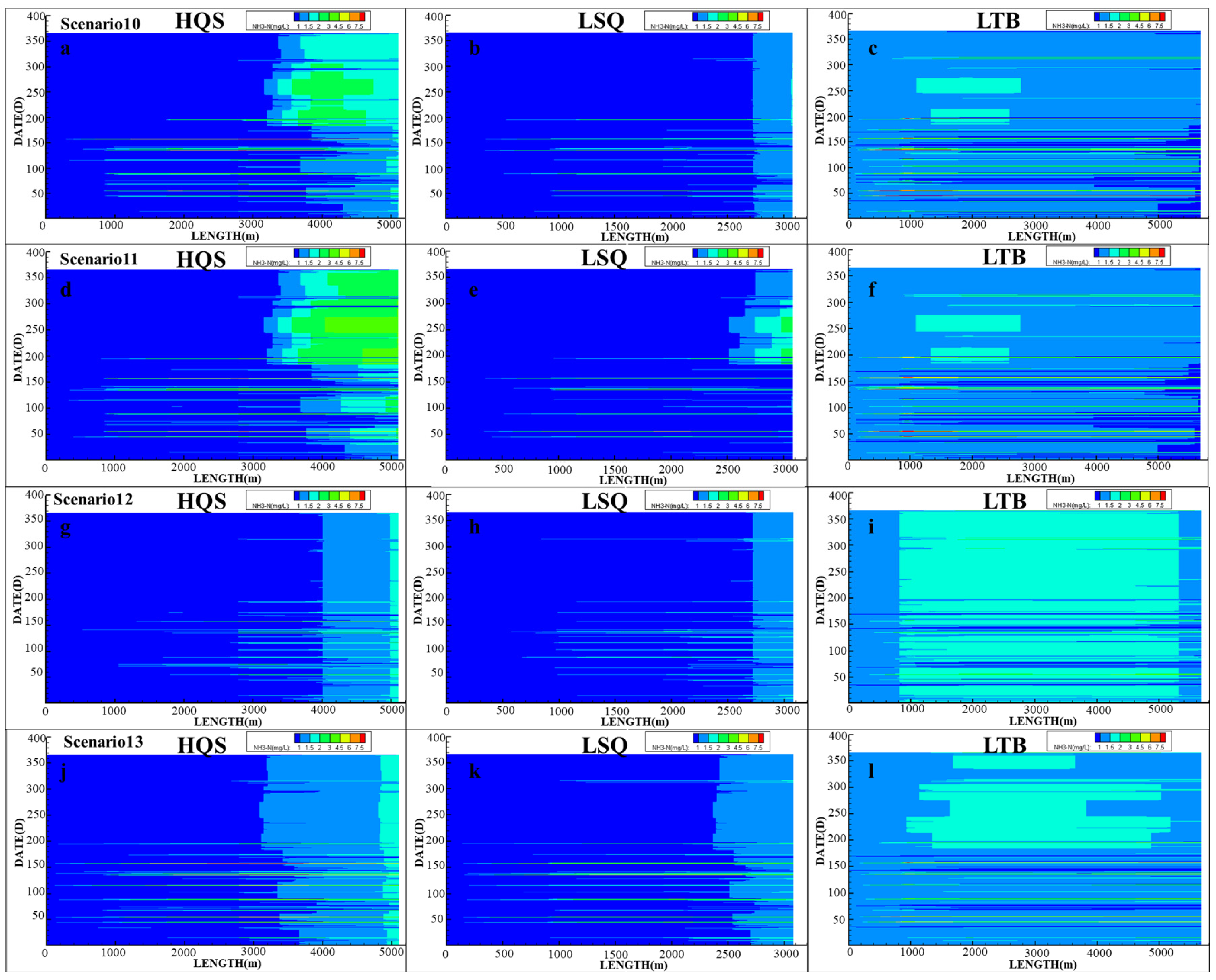
| Group B | 10 | P50 | 95% | 60% | √ | × | × |
| 11 | P50 | 95% | 60% | √ | √ | × | |
| 12 | P50 | 90% | 40% | √ | √ | Local Water Source (0.5 m3/s) | |
| 13 | P50 | 90% | 40% | √ | √ | Xizhijiang River water diversion (26.1 m3/s × 4 days) | |
| Group A Scenarios | P10 | P50 | P90 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQS | LSK | LTB | HQS | LSK | LTB | HQS | LSK | LTB | |
| Proportion of Class IV Compliance Days Per Year (%) | |||||||||
| Point source reduction alone 95% | 1.10 | 0.82 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 |
| Non-point source reduction alone 95% | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sediment dredging alone | 1.10 | 0.27 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.00 | 0.27 |
| Group B Scenarios | Proportion of Class IV Compliance Days Per Year (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQS | LSK | LTB | ||
| Scenarios 10 | No Replenishment | 12.57 | 19.95 | 9.29 |
| Scenarios 11 | Recycled water reuse | 24.32 | 13.93 | 9.29 |
| Scenarios 12 | Recycled water reuse + Local Water Source (0.5 m3/s) | 8.47 | 6.01 | 4.64 |
| Scenarios 13 | Recycled water reuse + Xizhijiang Replenishment (26.1 m3/s × 4 days) | 10.11 | 16.94 | 51.91 |
| Scenarios | Hydrological Years | Period | Sluice Gate Control | Ecological Water Exchange | Point Source Pollution Reduction | Non-Point Source Pollution Reduction | Sediment Dredging | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
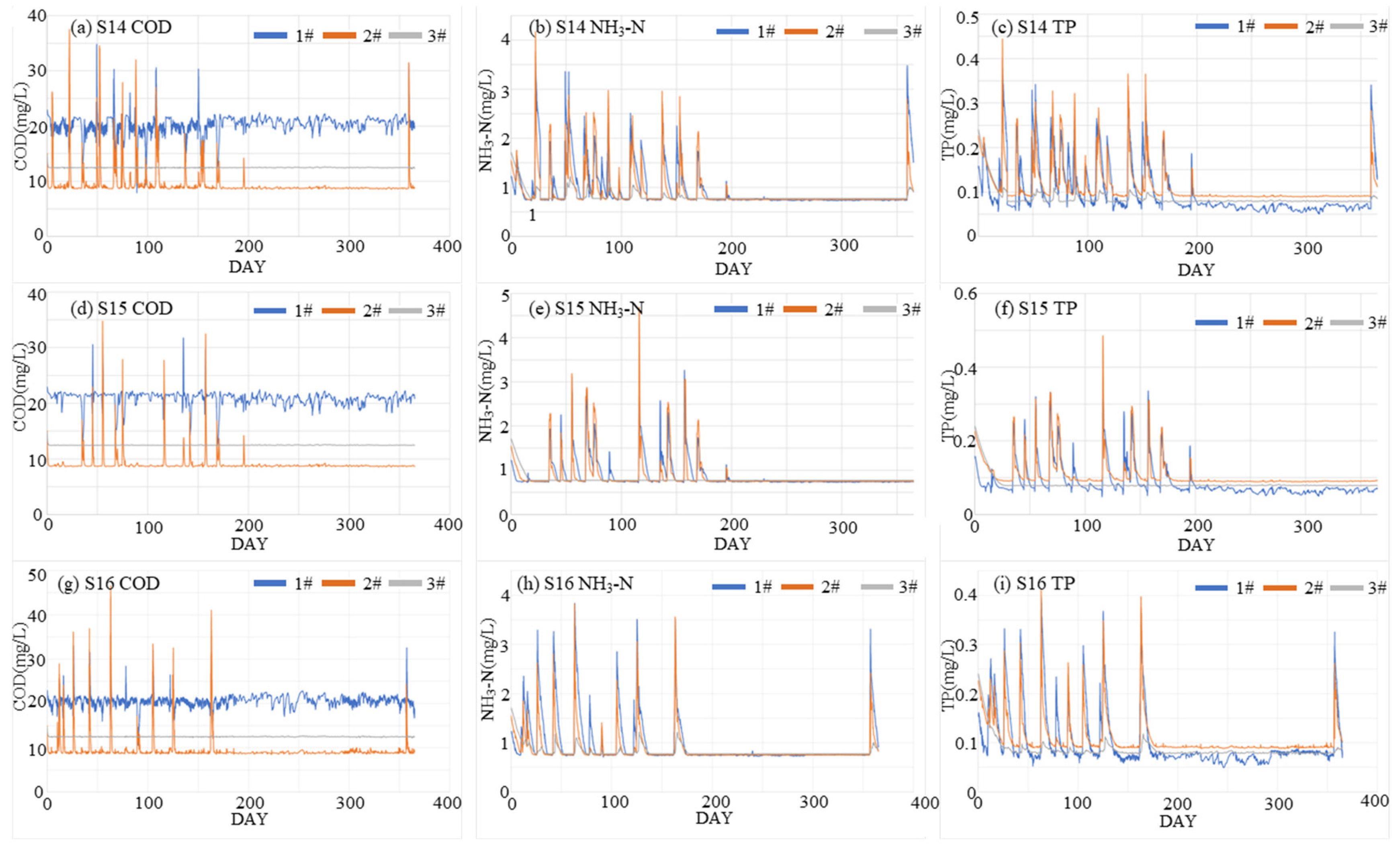
| Group C | 14 | P10 | annual | × | × | 95 | × | √ |
| 15 | P50 | |||||||
| 16 | P90 | |||||||
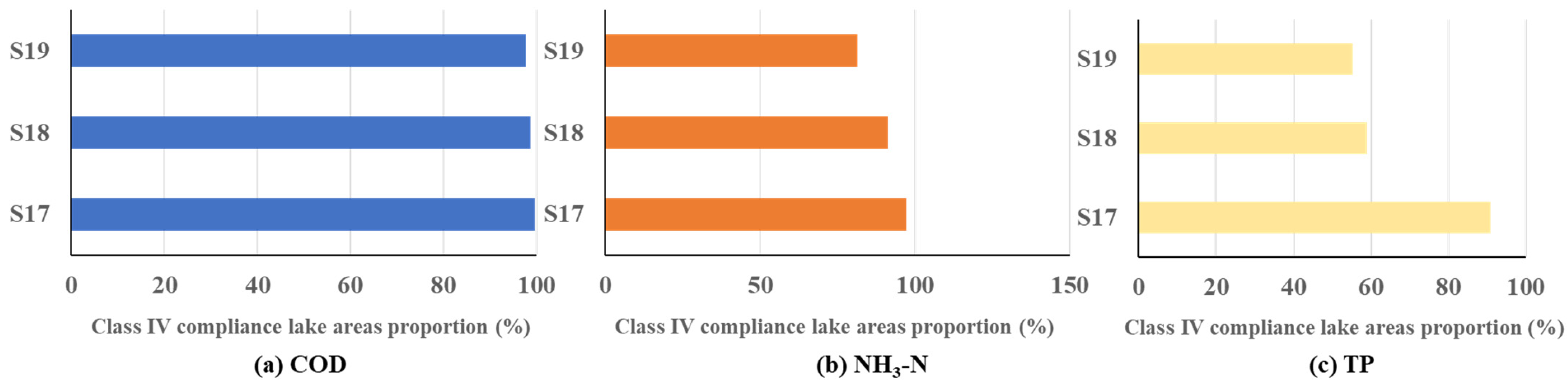
| Group D | 17 | P50 | dry season | √ | water exchange flows at 26.1 m3/s | 95 | 60 | √ |
| 18 | water exchange flows at 0.5 m3/s | |||||||
| 19 | water exchange flows at 1 m3/s | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W. Optimization of Synergistic Water Resources, Water Environment, and Water Ecology Remediation and Restoration Project: Application in the Jinshan Lake Basin. Water 2025, 17, 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202986
Jiang W, Liu X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Chen X, Sun Y, Chen J, Zhang W. Optimization of Synergistic Water Resources, Water Environment, and Water Ecology Remediation and Restoration Project: Application in the Jinshan Lake Basin. Water. 2025; 17(20):2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202986
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Wenyang, Xin Liu, Yue Wang, Yue Zhang, Xinxin Chen, Yuxing Sun, Jun Chen, and Wanshun Zhang. 2025. "Optimization of Synergistic Water Resources, Water Environment, and Water Ecology Remediation and Restoration Project: Application in the Jinshan Lake Basin" Water 17, no. 20: 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202986
APA StyleJiang, W., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Sun, Y., Chen, J., & Zhang, W. (2025). Optimization of Synergistic Water Resources, Water Environment, and Water Ecology Remediation and Restoration Project: Application in the Jinshan Lake Basin. Water, 17(20), 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202986






