Groundwater Pollution Source Identification Based on a Coupled PCA–PMF–Mantel Framework: A Case Study of the Qujiang River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
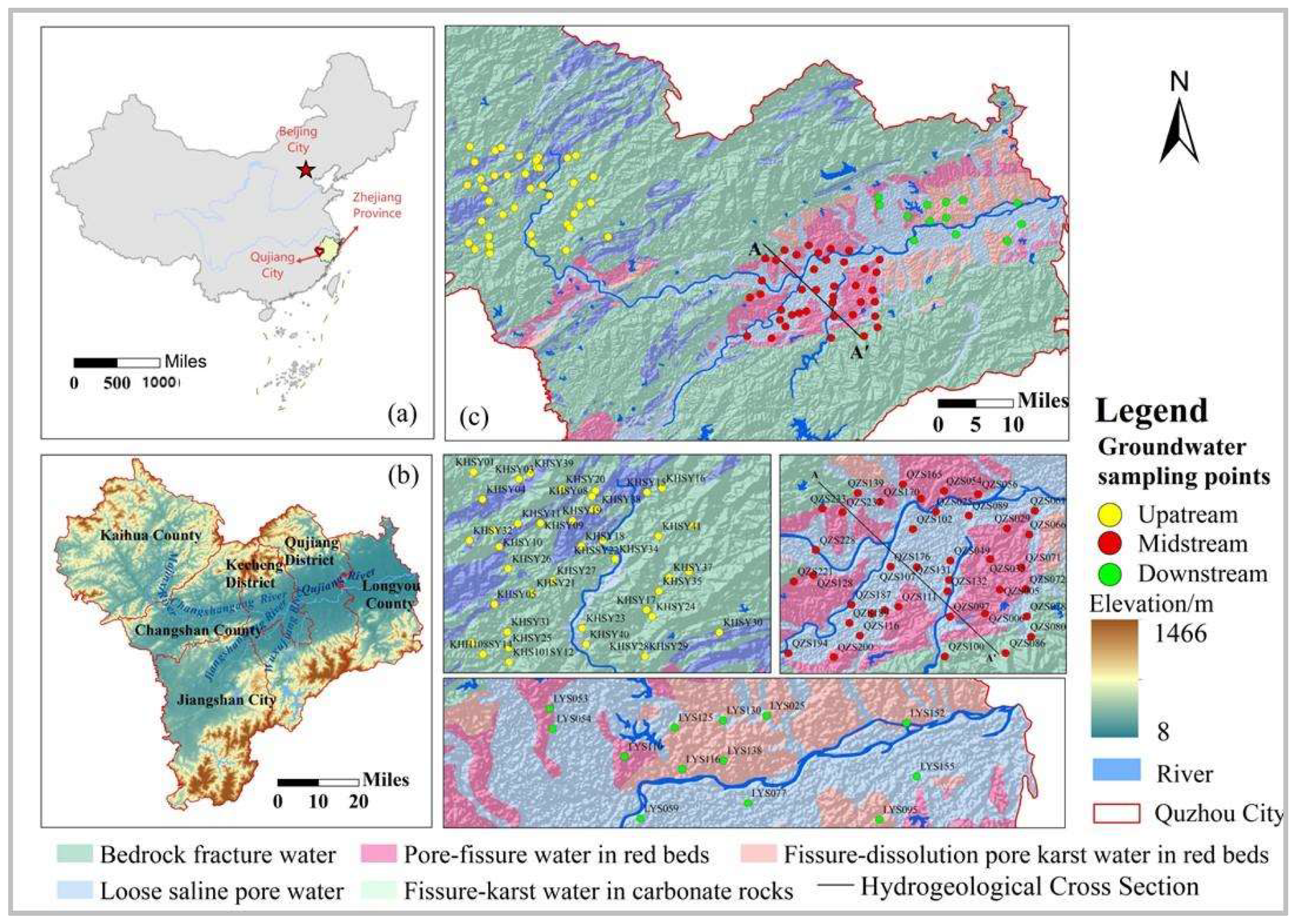
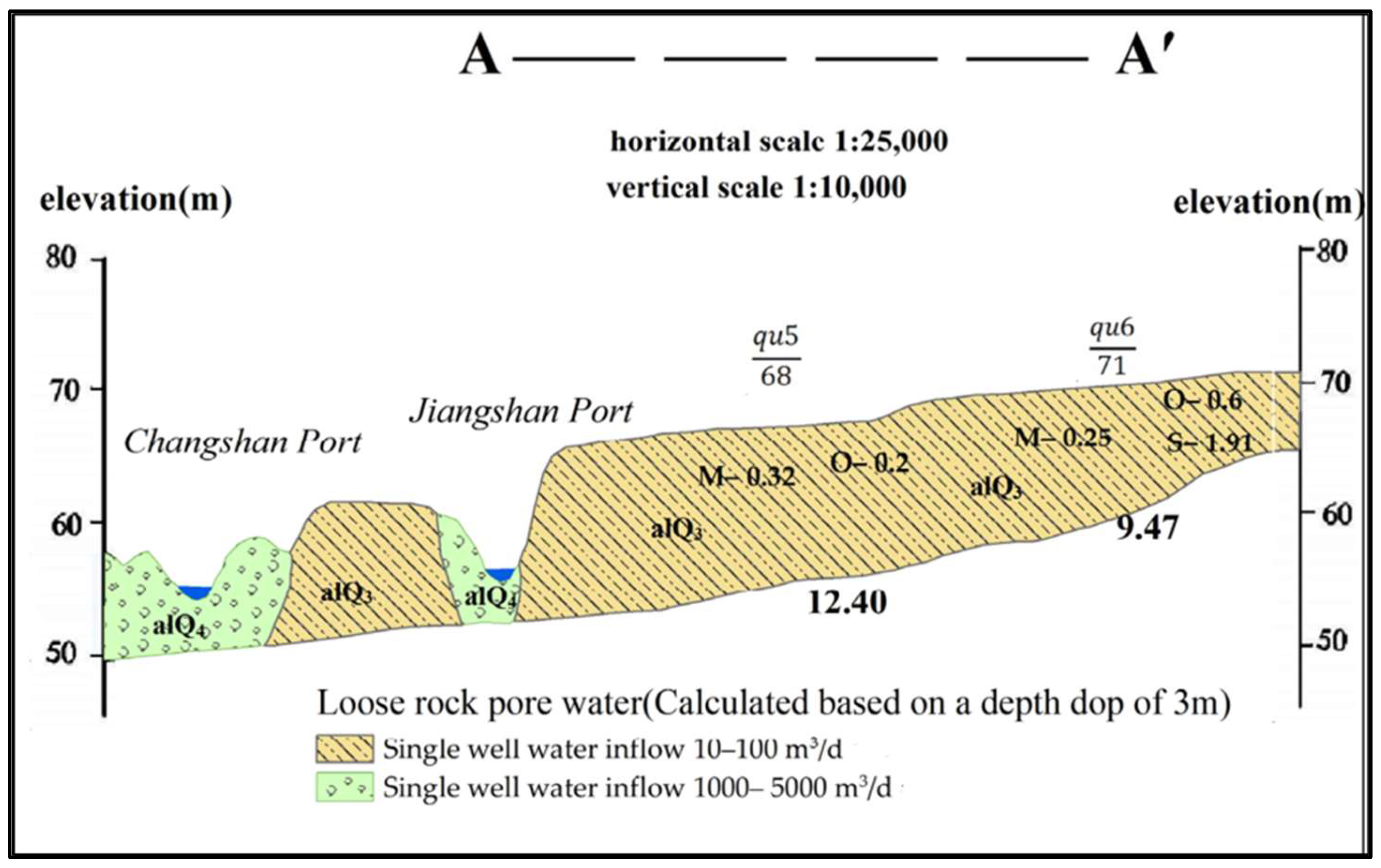
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analytical Procedures
2.2.1. Sample Collection
2.2.2. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
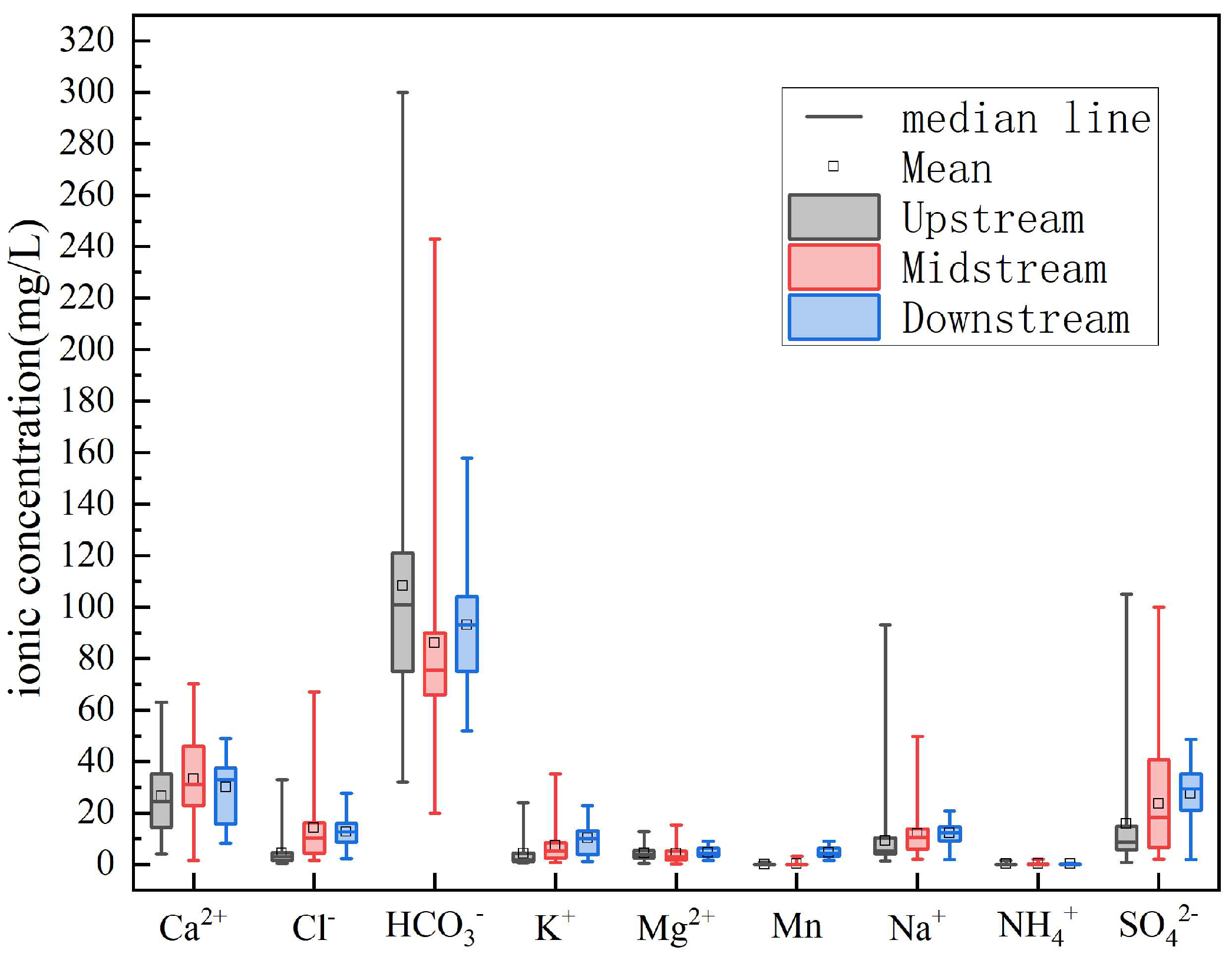
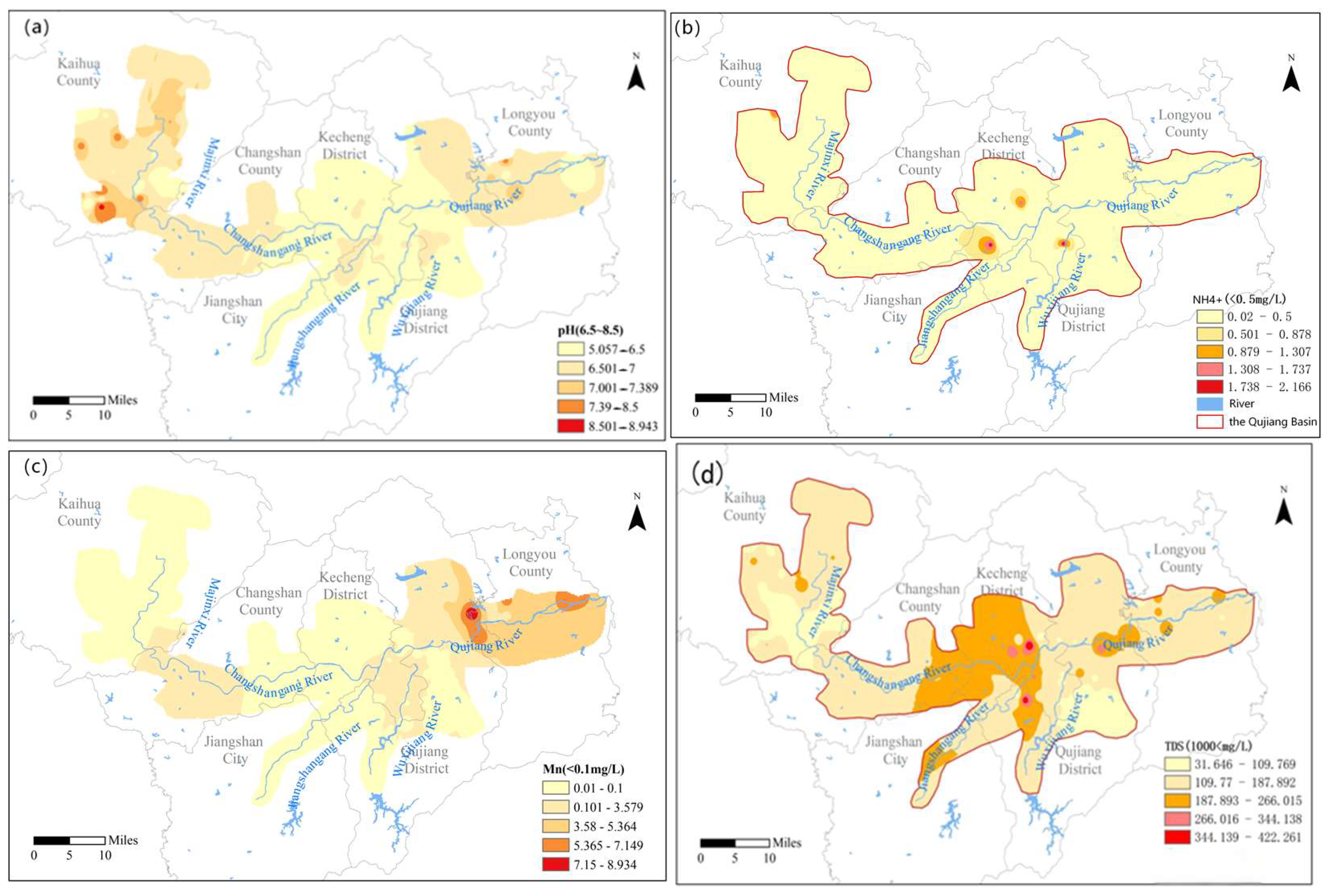
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Spatial Distribution
3.2. Dominant Hydrogeochemical Processes
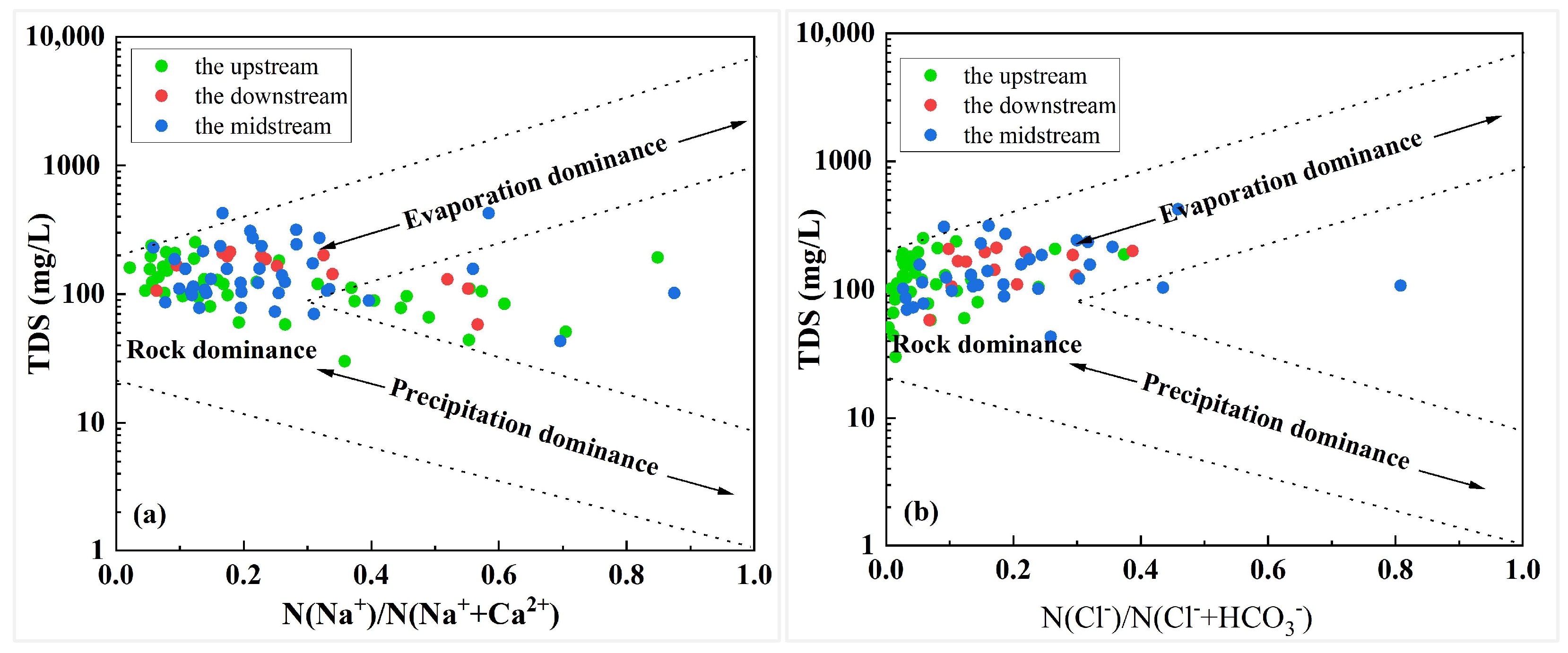
3.2.1. Gibbs Diagram
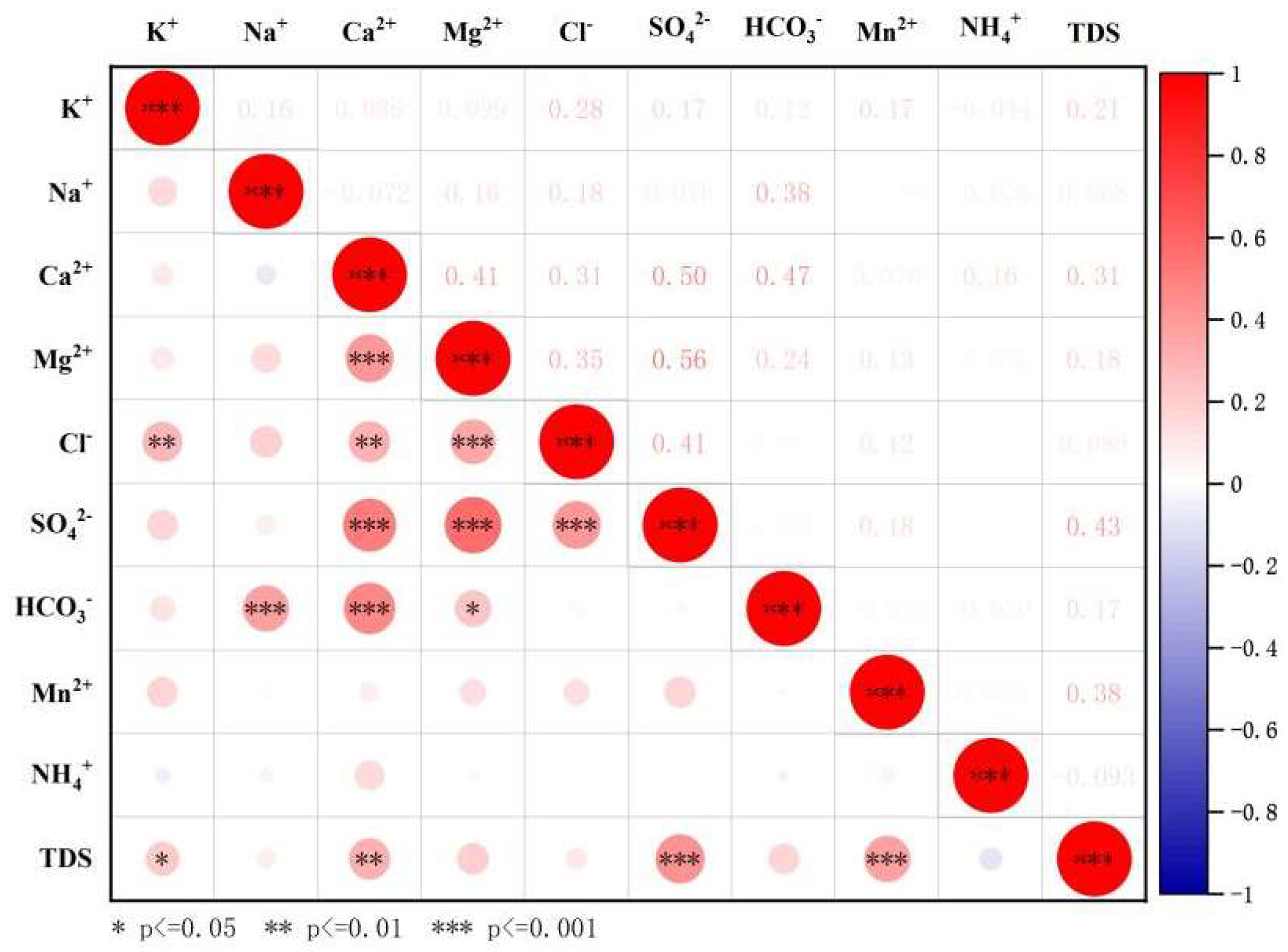
3.2.2. Correlation Analysis
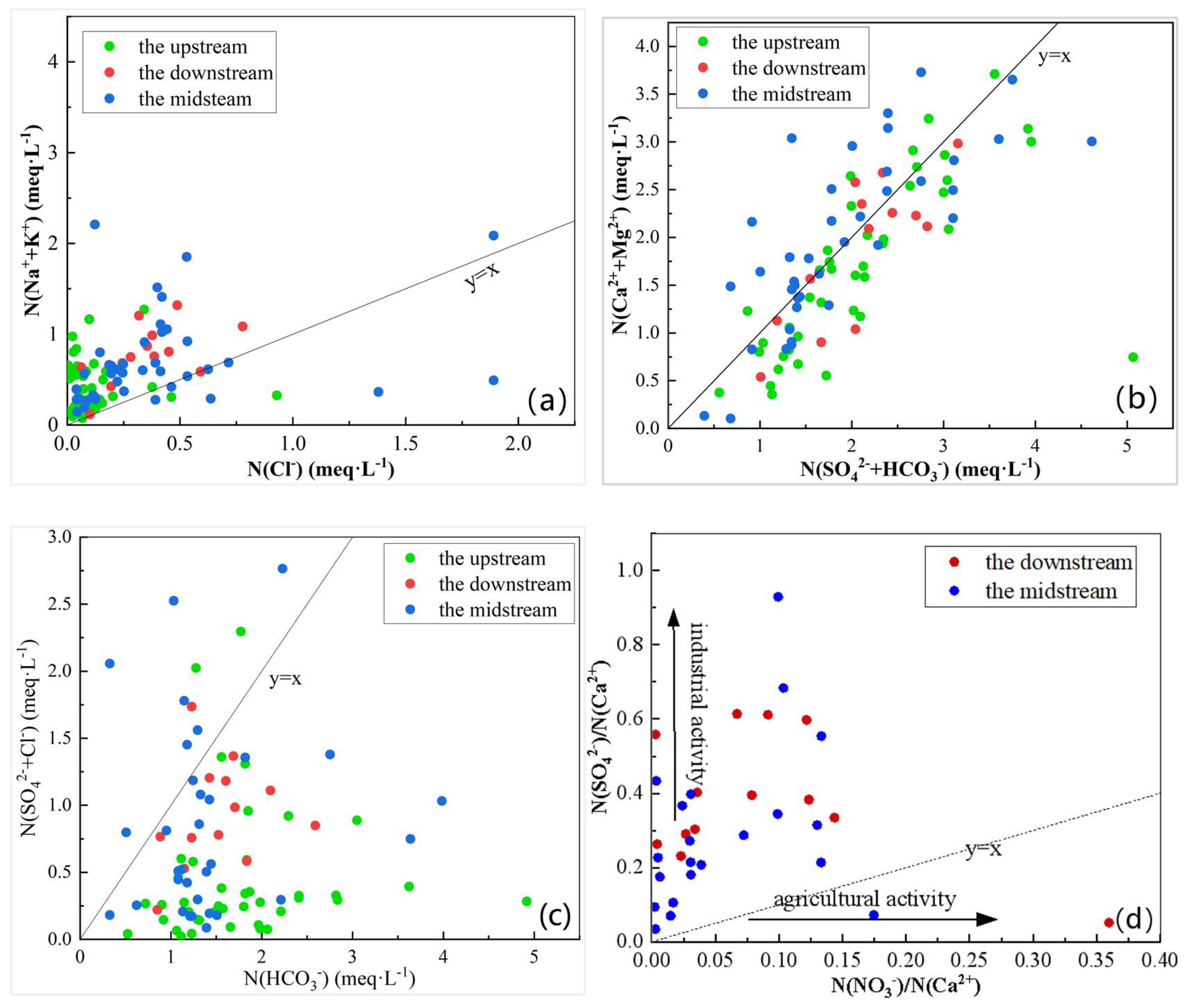
3.2.3. Ion Ratio Analysis
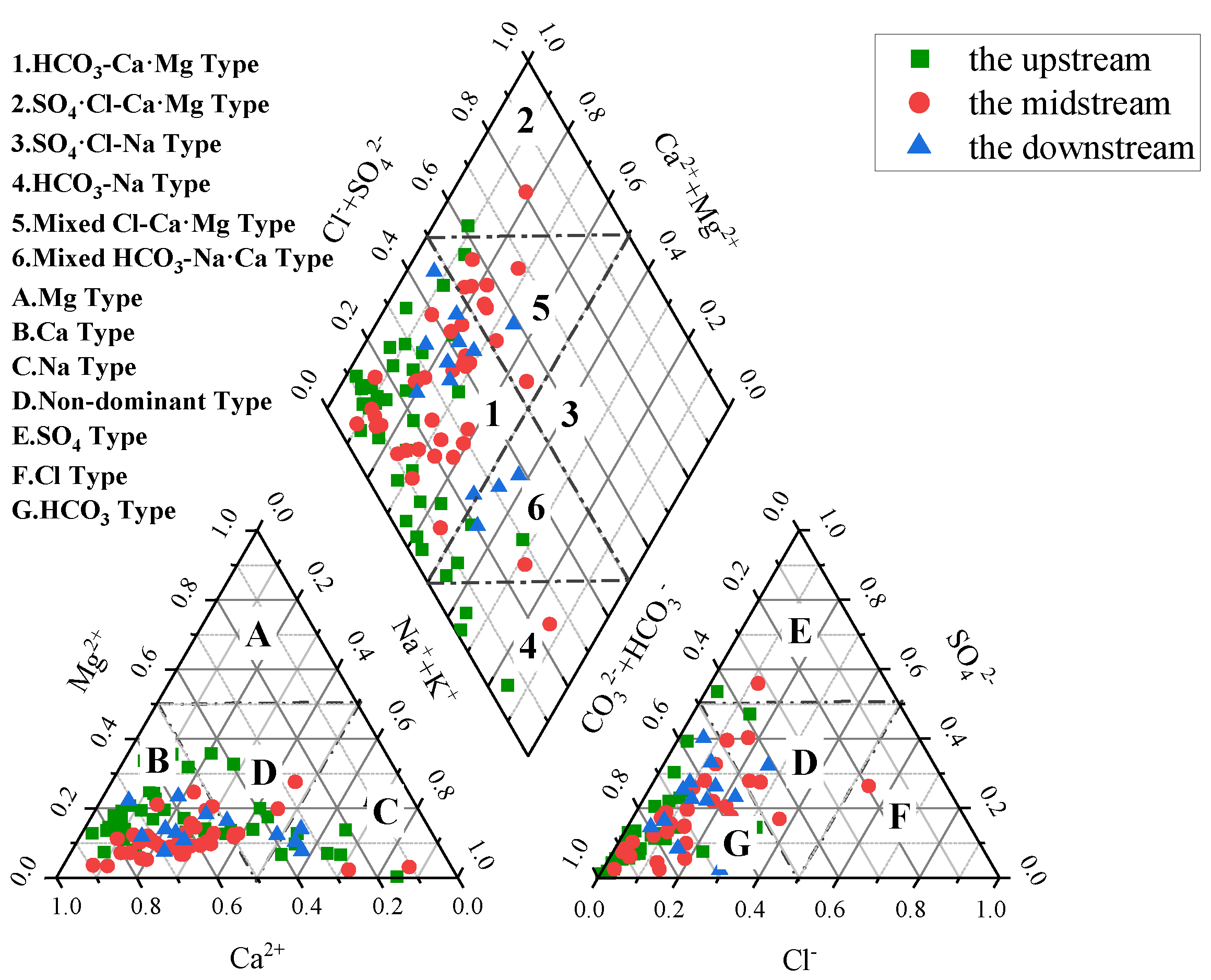
3.3. Hydrochemical Types
3.4. Pollution Source Identification and Quantitative Analysis
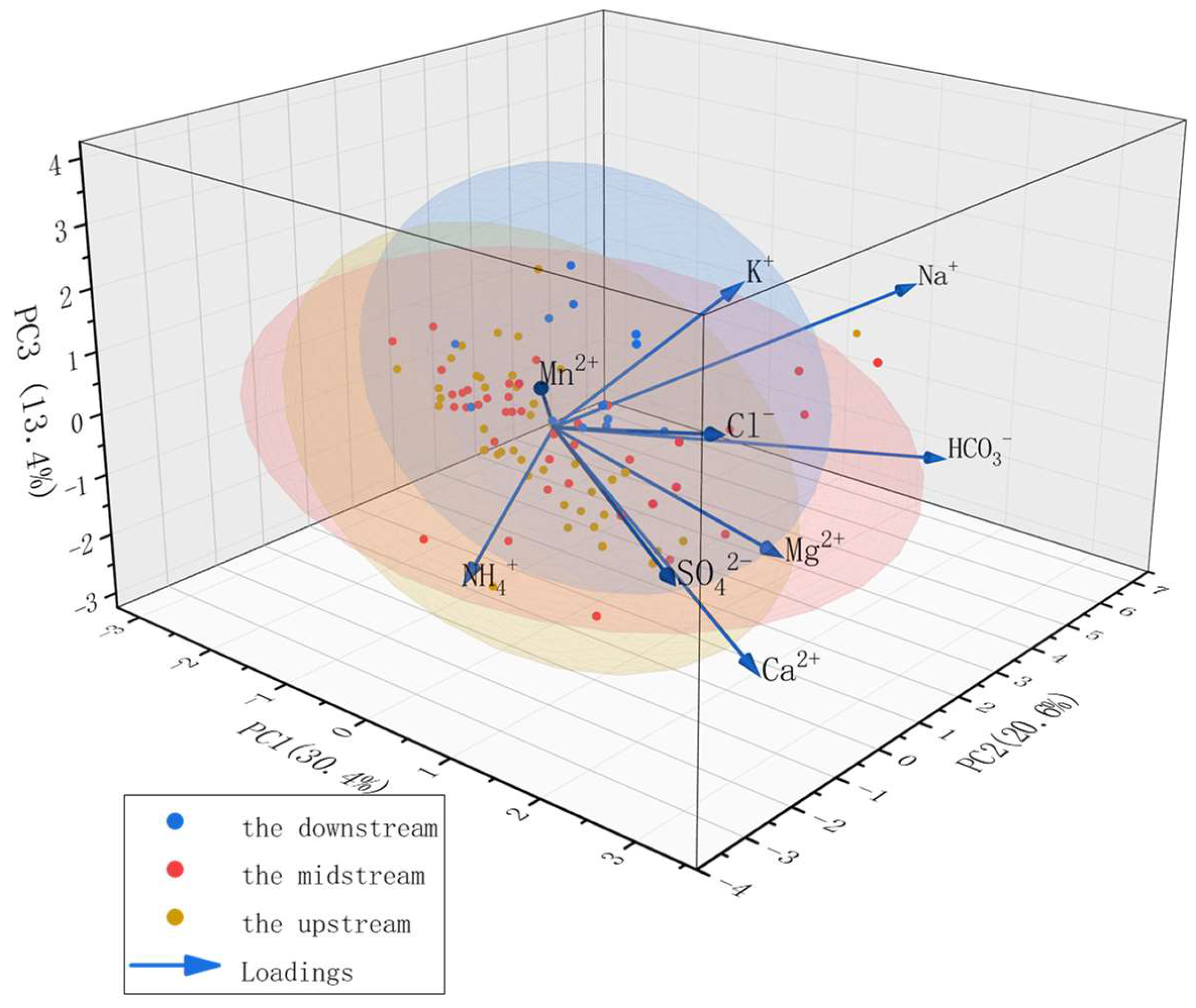
3.4.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
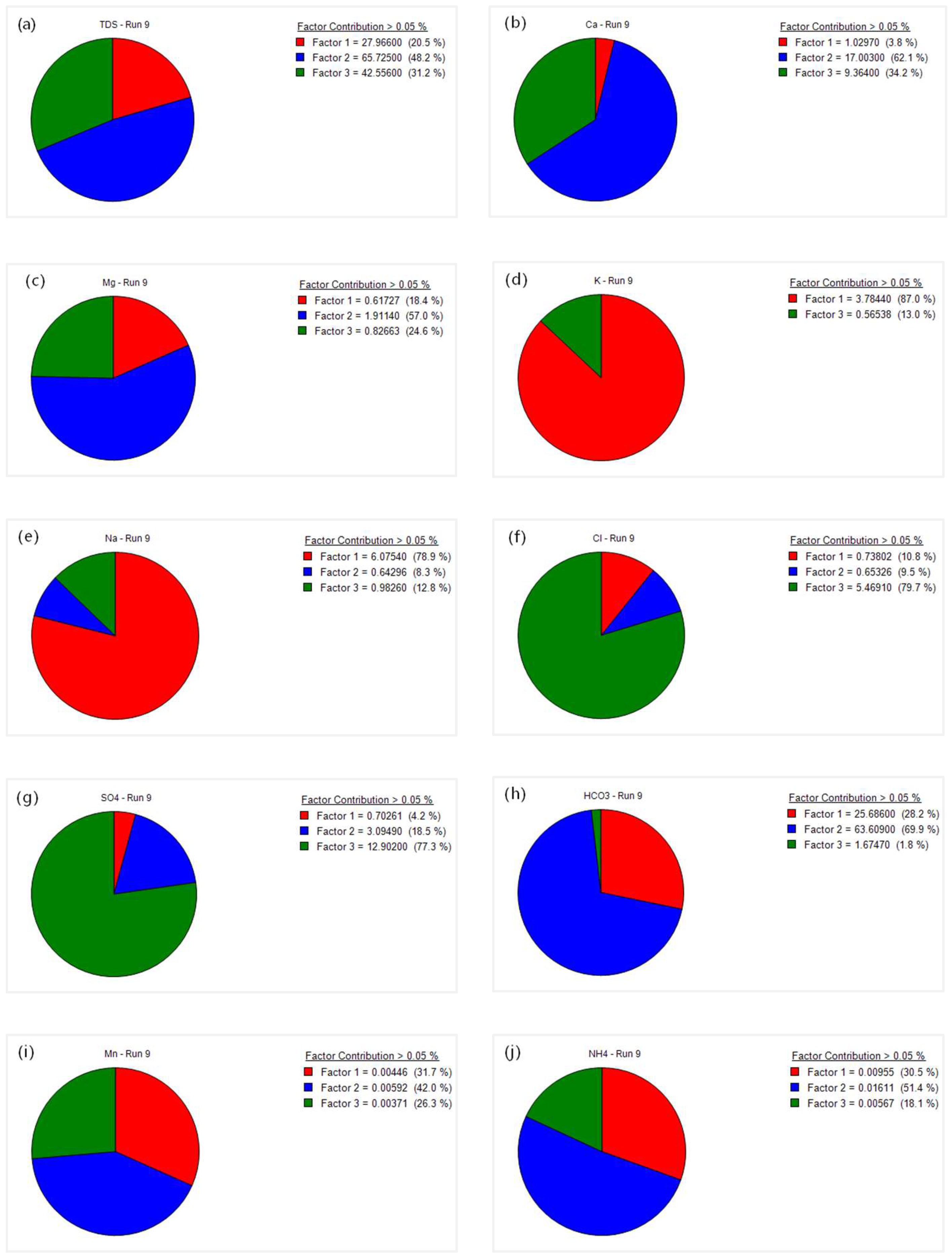
3.4.2. PMF Source Apportionment
3.4.3. Mantel Test Validation
3.5. Comparison with Other Regional Studies
4. Conclusions and Suggestions
- Groundwater hydrochemistry in the Qujiang River Basin is dominated by Ca2+ and HCO3−, with HCO3–Ca·Mg as the principal water type. Carbonate dissolution is the primary control, while spatial variations reflect combined influences of natural water–rock interactions and anthropogenic activities. Specifically, upstream groundwater is mainly Ca–HCO3 type, midstream samples show higher proportions of Ca–SO4–HCO3 type due to sulfate dissolution and irrigation return flow, and downstream groundwater locally exhibits Ca–SO4 type under acidic or reducing conditions.
- PCA and PMF consistently identified three major sources: natural rock weathering (26.3%), agricultural and domestic anthropogenic activities (38.5%), and industrial anthropogenic activities (35.2%). Agricultural and domestic contributions were most significant in the midstream agricultural belt, industrial contributions were concentrated in downstream industrial clusters, while natural sources dominated the upstream with strong geological background control.
- Mantel test results confirmed significant spatial correlations between pollution sources and environmental drivers: agricultural and domestic sources were positively correlated with farmland proportion and rural settlement density; natural sources were associated with carbonate rock outcrops and topographic elevation; industrial sources were strongly linked to industrial land use and urban density. These findings validate the robustness and spatial rationality of the proposed framework.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, D.; Bian, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Gu, Z. Identification of groundwater pollution sources and health risk assessment in the Songnen Plain based on PCA-APCS-MLR and trapezoidal fuzzy number-Monte Carlo stochastic simulation model. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zou, H.; Ren, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. Study on Pollution Characteristics, Sources, and Health Risks of Potentially Toxic Elements in Groundwater of Dongting Lake Basin, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhou, H.; Lu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhan, L.; Shi, Z. Groundwater nitrate responses to extreme rainfall in alluvial-diluvial plain aquifers: Evidence from hydrogeochemistry and isotopes. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2025, 273, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapworth, J.D.; Boving, T.B.; Kreamer, D.K.; Kebede, S.; Smedley, P.L. Groundwater quality: Global threats, opportunities and Realising the potential of groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 811, 152471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lou, K.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Tan, M. Comprehending hydrochemical fingerprint, spatial patterns, and driving forces of groundwater in a topical coastal plain of Northern China based on hydrochemical and isotopic evaluations. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 461, 142640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, J.; Xi, B.; Yang, Y.; Lu, H.; Shi, J. Groundwater Pollution Prevention and Control in China: Current Status and Countermeasures. Strateg. Study CAE 2022, 24, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Jiang, J.; Li, C. Relationship between Surface Water and Groundwater Transformation in Qu River Basin. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2021, 21, 6165–6174. [Google Scholar]
- Jakóbczyk-Karpierz, S.; Ślósarczyk, K. Isotopic signature of anthropogenic sources of groundwater contamination with sulfate and its application to groundwater in a heavily urbanized and industrialized area (Upper Silesia, Poland). J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Galvão, P.; Miotlinski, K.; Schuch, C. Numerical modeling applications for the evaluation of the past and future scenarios of groundwater use in an urbanized complex karst aquifer in the city of Sete Lagoas, State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Su, H.; Han, F.; Li, Z. Source identification of trace elements in groundwater combining APCS-MLR with geographical detector. J. Hydrol. 2023, 623, 129771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; He, P. Change and Pollution Evaluation of Groundwater from Wet and Dry Periods of Ion-adsorbed Rare Earth Mine in Northern Guangdong Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 42, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, F.; Ding, Q.; Lei, M. Identifying Hydrochemical Characteristics, Control Factors, and Pollution Source of Groundwater in the Oasis Area of Toksun County, Xinjiang. China Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 2179–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antelmi, M.; Mazzon, P.; Höhener, P.; Marchesi, M.; Alberti, L. Evaluation of MNA in A Chlorinated Solvents-Contaminated Aquifer Using Reactive Transport Modeling Coupled with Isotopic Fractionation Analysis. Water 2021, 13, 2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Duan, L.; Mao, H.; Wang, C.; Liang, X.; Luo, A.; Huang, L.; Yu, R.; Miao, P.; Zhao, Y. Hydrochemical and isotopic fingerprints of groundwater origin and evolution in the Urangulan River basin, China's Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taloor, A.K.; Bala, A.; Mehta, P. Human health risk assessment and pollution index of groundwater in Jammu plains of India: A geospatial approach. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.D.; Bai, Y.Y.; Yuan, D.L. Chemical Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Environmental Driving Factors of Groundwater in Hetao Irrigation Area. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2024, 45, 5777–5789. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, M.A.A.; Szabó, N.P.; Szűcs, P. Multivariate statistical and hydrochemical approaches for evaluation of groundwater quality in north Bahri city-Sudan. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, X.; Duan, H.; Ruan, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Combination of UNMIX, PMF model and Pb-Zn-Cu isotopic compositions for quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in suburban agricultural soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Si, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, M.; Liu, R.; Zhou, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, G. Identification of Pollution Sources and Health Risk Assessment of Shallow Groundwater in the North Anhui Plain Based on the PMF Model and Monte Carlo Simulation. China Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Luo, Y.; Mi, Z.; Liu, C. Source identification of groundwater pollution based on PMF model and stable isotope. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 47, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Qi, P.; Sun, Y.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, G. Assessment of groundwater quality variation characteristics and influencing factors in an intensified agricultural area: An integrated hydrochemical and machine learning approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, C.; Zhen, P.; Guo, X.; Wang, S. Groundwater quality variability with inter-basin water transfer and overexploitation control in an agriculture-dominant subregion of North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 317, 109660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, J.; Xue, L.; Shen, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Hu, L. Characterizing Aquifer Properties and Groundwater Storage at North China Plain Using Geodetic and Hydrological Measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2025, 61, e2024WR037425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, X. Assessment of the Quality of Groundwater in Huang-hua-i hai Plain. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2005, 32, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Li, P.; Liu, B. Health Risk Assessment of Pollution in Groundwater—A Case Study in Changjiang Delta. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2008, 15, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Jiang, S.; Dai, L. Quality Assessment of Shallow Groundwater in the Jiangsu Region of the Yangtze River Delta. Ground Water 2013, 35, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, T. Assessment of Groundwater Vulnerability in Red-bed Area Based on AHP and DRASTIC Model—Take the Middle and Lower Reaches of Qujiang River as an Example. J. Inst. Disaster Prev. 2021, 23, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Onjia, A.; Huang, X.; González, J.M.T.; Egbueri, J.C. Editorial: Chemometric approach to distribution, source apportionment, ecological and health risk of trace pollutants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, L.; Qu, Z. Interaction between Groundwater and Surface Water in the Qujiang River Basin in China: Evidence from Chemical Isotope Measurements. Water 2023, 15, 3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tian, D. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Dominant Controlling Factors of the Qujiang River Under Dual Natural–Anthropogenic Influences. Water 2025, 17, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T 164-2004; Technical Specifications for Environmental Monitoring of Groundwater. Environmental Science Press of China: Beijing, China, 2004; p. 41.
- GB 5749-2022; Chinese Standards for Drinking Water Quality. The Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U.J.E. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Wang, G.; Liao, F.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Qiao, Z.; Li, B.; Bai, Y. Spatial variability of source contributions to nitrate in regional groundwater based on the positive matrix factorization and Bayesian model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.; Yuan, S.; Wen, S.; HUang, B.; Feng, X.; XIe, Z. Effects of landscape pattern on water quality at multi-spatial scales in the Liuxi River. ACTA Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Y.; Qian, H.; Liu, R.; Ma, H. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Quality Assessment of Groundwater in an Irrigated Region, Northwest China. Water 2019, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H. Anomaly Analysis of Chemical Components of Shallow Groundwater in Red Bed Area of Quzhou. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Disaster Prevention, Langfang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakerkhatibi, M.; Mosaferi, M.; Pourakbar, M.; Ahmadnejad, M.; Safavi, N.; Banitorab, F. Comprehensive investigation of groundwater quality in the north-west of Iran: Physicochemical and heavy metal analysis. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marandi, A.; Shand, P. Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs Diagram. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 97, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lv, W.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, L. Hydrochemical characteristics and genetic mechanism of high TDS groundwater in Xinjulong Coal Mine. COAL Geol. Explor. 2021, 49, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Luan, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, C. Spatial patterns and driving mechanisms of groundwater chemistry in Pearl River Delta Region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 48, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ouyang, H.; Zhou, J. Controlling Factors of Groundwater Salinization and Pollution in the Oasis Zone of the Cherchen River Basin of Xinjiang. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; Liu, Z. Hydrochemical characteristics and health risk assessment of groundwater in Dingbian county of the Chinese Loess Plateau, northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, Y.; Fang, L.; Wang, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristic and Control Factors of Groundwater in the Northwest Salt Lake Basin. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 6767–6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Song, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Ma, Y.; Bu, H. Identifying the origin and geochemical evolution of groundwater using hydrochemistry and stable isotopes in the Subei Lake basin, Ordos energy base, Northwestern China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Sun, B.; Qi, H.; Wu, X.; Xu, Q. Analysis on Spatial Variability of Hydrochemical Characteristics and Control Factors of Jinan Baotu Spring Area. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 4565–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qian, H.; Ren, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, F. Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater based on integrated-weight water quality index in a concentrated urban area. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Yang, W.; Nadine Ferrer, A.S.; Xiong, S.; Li, X.; Niu, G.; Lu, T. Hydrochemical characteristics and health risk assessment of groundwater in karst areas of southwest China: A case study of Bama, Guangxi. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, W.; Wang, J.; Kang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Hydrochemical analysis and groundwater suitability for drinking and irrigation in an arid agricultural area of the Northwest China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2023, 259, 104256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wen, R.; Qian, H.; Hong, M. Chemical Characteristics and Transformation Relationship of Groundwater and Surface Water in Fenghe River Basin at the Northern Foot of Qinling Mountains, China. J. Earch Sci. Environ. 2024, 46, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, K.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, R.; Li, R. Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals in Moqi Area on the Northwest Edge of Songnen Plain Based on the PCA-PMF Model. China Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 3220–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Xiong, Q.; Meng, J.; Mu, D.; Xiao, S. Hydrochemical characteristics of a karst basin and its response to world heritage protection. npj Herit. Sci. 2025, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffioen, J. Potassium adsorption ratios as an indicator for the fate of agricultural potassium in groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2001, 254, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesković, J.; Deršek-Timotić, I.; Lučić, M.; Miletić, A.; Đolić, M.; Ražić, S.; Onjia, A. Entropy-weighted water quality index, hydrogeochemistry, and Monte Carlo simulation of source-specific health risks of groundwater in the Morava River plain (Serbia). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, B.; Shu, L. Mechanisms of evolution and pollution source identification in groundwater quality of the Fen River Basin driven by precipitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Hu, Q.; Shen, W.; Guo, J.; Yang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Lu, X.; Wang, L. Identification of nitrate sources of groundwater and rivers in complex urban environments based on isotopic and hydro-chemical evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranesevic, M.; Zemunac, R.; Grabic, J.; Salvai, A. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Suitability Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Li, P.; Wu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, F.; Zheng, L. Source apportionment of groundwater nitrate pollution in irrigation districts along the Jing River, Guanzhong Basin: Insights from hydrochemistry, isotopes, and the MixSIAR model. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Detection Limit | Detection Method | Parameters | Detection Limit | Detection Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | 0.10 | flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry | Cl- | 0.10 | silver nitrate volumetric method |
| Na+ | 0.01 | flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry | SO42- | 0.20 | barium sulfate turbidimetric method |
| Ca2+ | 0.004 | disodium edetate titration | NO3- | 0.02 | ultraviolet spectrophotometry |
| Mg2+ | 0.01 | disodium edetate titration | F- | 0.01 | ion-selective electrode method |
| HCO3- | 5.00 | acid titration | NH4+ | 0.04 | UV-Vis spectrophotometry |
| TH | 10.00 | disodium edetate titration | Mn | 0.005 | flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry |
| TDS | 4.00 | dry residue method | As | 0.01 | HG-AFS |
| Ba | 0.005 | ICP-MS1 | Cd | 0.001 | ICP-MS1 |
| Pb | 0.005 | ICP-MS1 | Cr | 0.01 | ICP-MS1 |
| Parameters | pH | TDS | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | K+ | Na+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | Mn | NH4+ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream | Min (mg·L−1) | 5.27 | 30 | 4.08 | 0.30 | 0.5 | 1.28 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 32 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Max (mg·L−1) | 8.98 | 252 | 63.00 | 12.80 | 24.1 | 93.00 | 33.0 | 105.0 | 300 | 0.92 | 1.59 | |
| Mean (mg·L−1) | 6.85 | 125 | 26.46 | 4.43 | 4.2 | 9.20 | 4.4 | 15.7 | 108 | 0.32 | 0.13 | |
| SD (mg·L−1) | 0.65 | 53 | 15.06 | 3.00 | 5.1 | 14.29 | 5.8 | 20.9 | 50 | 0.52 | 0.34 | |
| CV (%) | 9.4% | 42.8% | 56.9% | 67.7% | 121.8% | 155.3% | 132% | 132.9% | 46.2% | 162.4% | 270.8% | |
| Midstream | Min (mg·L−1) | 5.05 | 43 | 1.58 | 0.13 | 0.7 | 2.16 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 20 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Max (mg·L−1) | 6.95 | 426 | 70.10 | 15.30 | 35.2 | 49.80 | 67.1 | 100.0 | 243 | 3.14 | 2.17 | |
| Mean (mg·L−1) | 6.27 | 162 | 33.29 | 4.12 | 7.2 | 11.88 | 14.2 | 23.6 | 86 | 0.14 | 0.22 | |
| SD (mg·L−1) | 0.53 | 92 | 15.50 | 3.58 | 7.5 | 9.52 | 15.2 | 21.2 | 47 | 0.54 | 0.49 | |
| CV (%) | 8.5% | 57% | 46.6% | 87% | 103.5% | 80.1% | 107% | 89.6% | 54.3% | 372.3% | 223.3% | |
| Downstream | Min (mg·L−1) | 6.17 | 58 | 8.25 | 1.50 | 1.0 | 1.860 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 52 | 1.50 | 0.02 |
| Max (mg·L−1) | 7.54 | 212 | 49.00 | 8.95 | 22.8 | 20.800 | 27.6 | 48.6 | 158 | 8.95 | 0.30 | |
| Mean (mg·L−1) | 6.79 | 1560 | 29.99 | 4.57 | 10.2 | 12.062 | 12.6 | 27.5 | 93 | 4.57 | 0.08 | |
| SD (mg·L−1) | 0.40 | 47 | 13.23 | 2.09 | 7.1 | 5.346 | 6.9 | 14.1 | 30 | 2.09 | 0.10 | |
| CV (%) | 5.9% | 29.7% | 44.1% | 45.7% | 69.7% | 44.3% | 54.8% | 51.3% | 31.8% | 45.7% | 112.4% | |
| Parameters | Rotated Factor Loadings | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| K+ | 0.233 | 0.135 | 0.524 |
| Na+ | 0.187 | 0.636 | 0.209 |
| Ca2+ | 0.450 | −0.101 | −0.451 |
| Mg2+ | 0.465 | −0.076 | −0.079 |
| Cl− | 0.398 | −0.116 | 0.289 |
| SO42− | 0.472 | −0.308 | 0.025 |
| HCO3− | 0.282 | 0.594 | −0.355 |
| Mn2+ | 0.169 | −0.215 | 0.383 |
| NH4+ | 0.039 | −0.234 | −0.339 |
| eigenvalue | 2.57 | 1.31 | 1.21 |
| explained variance /% | 30.37 | 20.59 | 13.36 |
| cumulative explained variance /% | 30.37 | 50.69 | 64.32 |
| Study Area | Method | Major Sources Identified | Contribution (%) | Key Tracers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qujiang River Basin (this study) | PCA–PMF–Mantel | Natural weathering | 26.3 | Ca2+, HCO3−, Mg2+ |
| Agricultural & domestic | 38.5 | NO3−, NH4+, Cl− | ||
| Industrial discharge | 35.2 | SO42−, Mn | ||
| Fenhe River Basin [57] (FRB) | PMF–GIS | Rock weathering & evaporation | ~40–50 | F−, As, Cr, Ca2+ |
| Agricultural inputs | ~30 | NO3−, Cl− | ||
| Anthropogenic discharge | ~20–30 | Na+, SO42− | ||
| Guanzhong Basin [60] | Dual isotopes (δ15N–NO3−, δ18O–NO3−) + Bayesian model | Agricultural fertilizers | 45–60% | NO3−, δ15N |
| Manure & sewage | 25–35% | NH4+, Cl−, δ15N > +15‰ | ||
| Atmospheric deposition | 10–15% | NO3−, low δ15N | ||
| Hetao Plain [59] | Hydrochemical + statistical analysis | Irrigation return flow | ~40–50 | TDS, Cl−, NO3− |
| Evaporative concentration | ~30–40 | Cl−, Na+, TDS | ||
| Natural dissolution | ~10–20 | Ca2+, HCO3− | ||
| Yangtze River Basin [58] | SIAR + δ15N/δ18O–NO3− | Manure and sewage | 43–60% | NH4+, Cl−, δ15N > +10‰ |
| Chemical fertilizers | 23–44% | NO3−, low δ15N | ||
| Soil organic N | 21–39% | δ15N~+5‰ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Huan, H.; Tian, D.; Guo, J. Groundwater Pollution Source Identification Based on a Coupled PCA–PMF–Mantel Framework: A Case Study of the Qujiang River Basin. Water 2025, 17, 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192881
Li X, Zhang Y, Xu L, Jiang J, Zhang C, Wang G, Huan H, Tian D, Guo J. Groundwater Pollution Source Identification Based on a Coupled PCA–PMF–Mantel Framework: A Case Study of the Qujiang River Basin. Water. 2025; 17(19):2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192881
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiao, Ying Zhang, Liangliang Xu, Jiyi Jiang, Chaoyu Zhang, Guanghao Wang, Huan Huan, Dengke Tian, and Jiawei Guo. 2025. "Groundwater Pollution Source Identification Based on a Coupled PCA–PMF–Mantel Framework: A Case Study of the Qujiang River Basin" Water 17, no. 19: 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192881
APA StyleLi, X., Zhang, Y., Xu, L., Jiang, J., Zhang, C., Wang, G., Huan, H., Tian, D., & Guo, J. (2025). Groundwater Pollution Source Identification Based on a Coupled PCA–PMF–Mantel Framework: A Case Study of the Qujiang River Basin. Water, 17(19), 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192881





