Study on Natural Background Levels and Mechanisms of Groundwater Contamination in an Overexploited Aquifer Region: A Case Study of Xingtai City, North China Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Geological and Hydrogeological Setting
2.3. Sampling and Analytical Procedures
2.4. Methodology
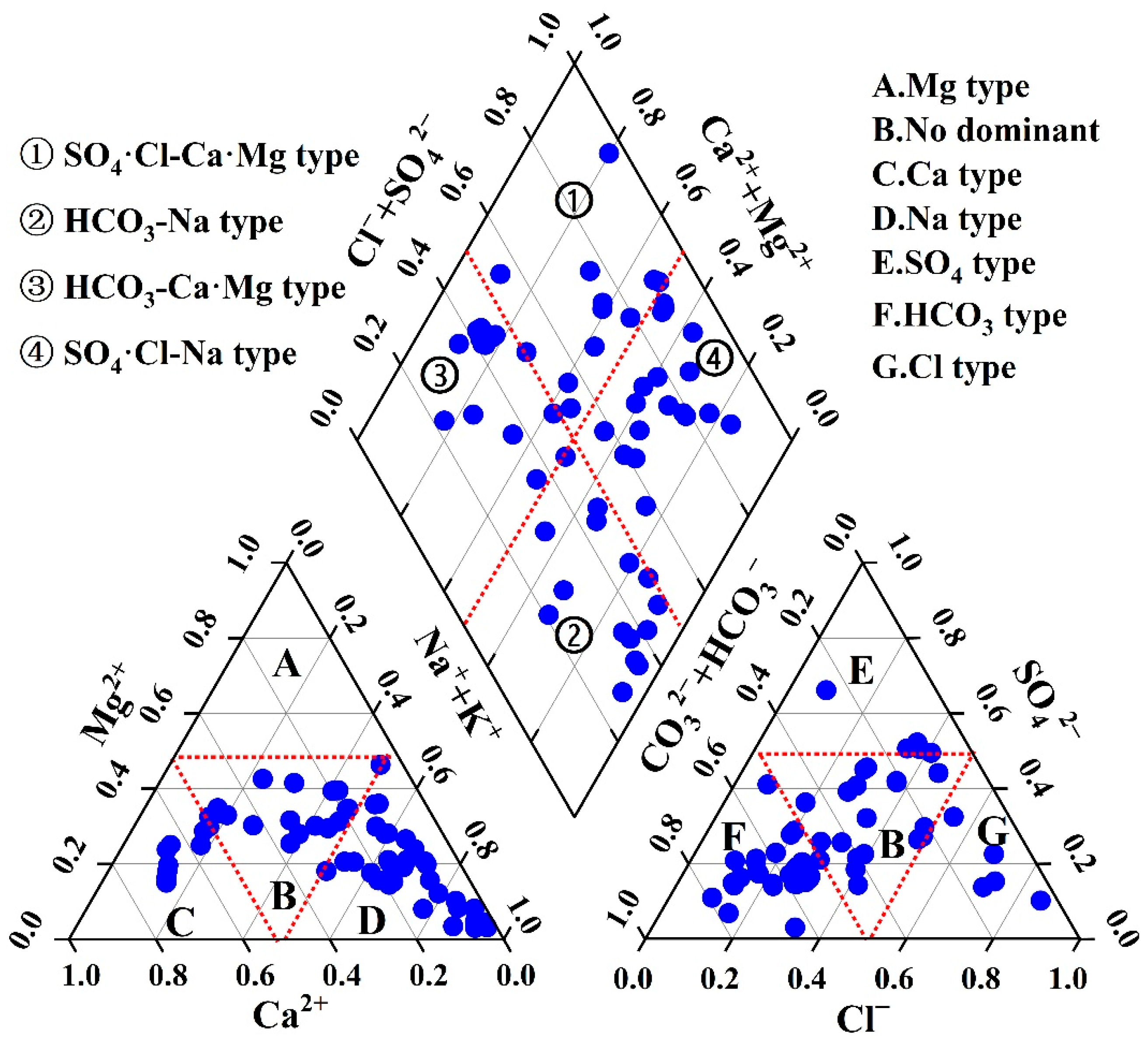
2.4.1. Determination of Hydrochemical Facies
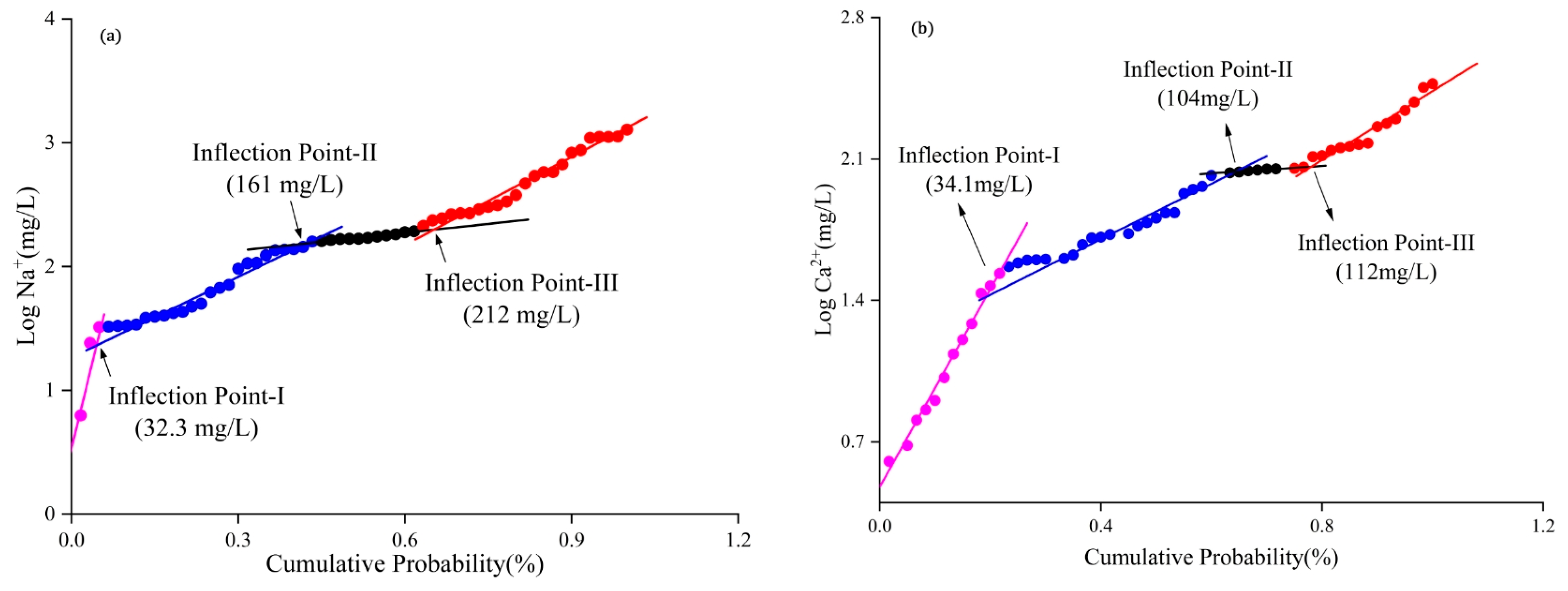
2.4.2. Calculation of NBLs
2.4.3. Calculation of TVs
2.4.4. Determination of Pollution Load
2.4.5. Identification of Controlling Factors Using Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Groundwater
3.2. Hydrochemical Facies
3.3. Controlling Factors and Sources of Major Ions
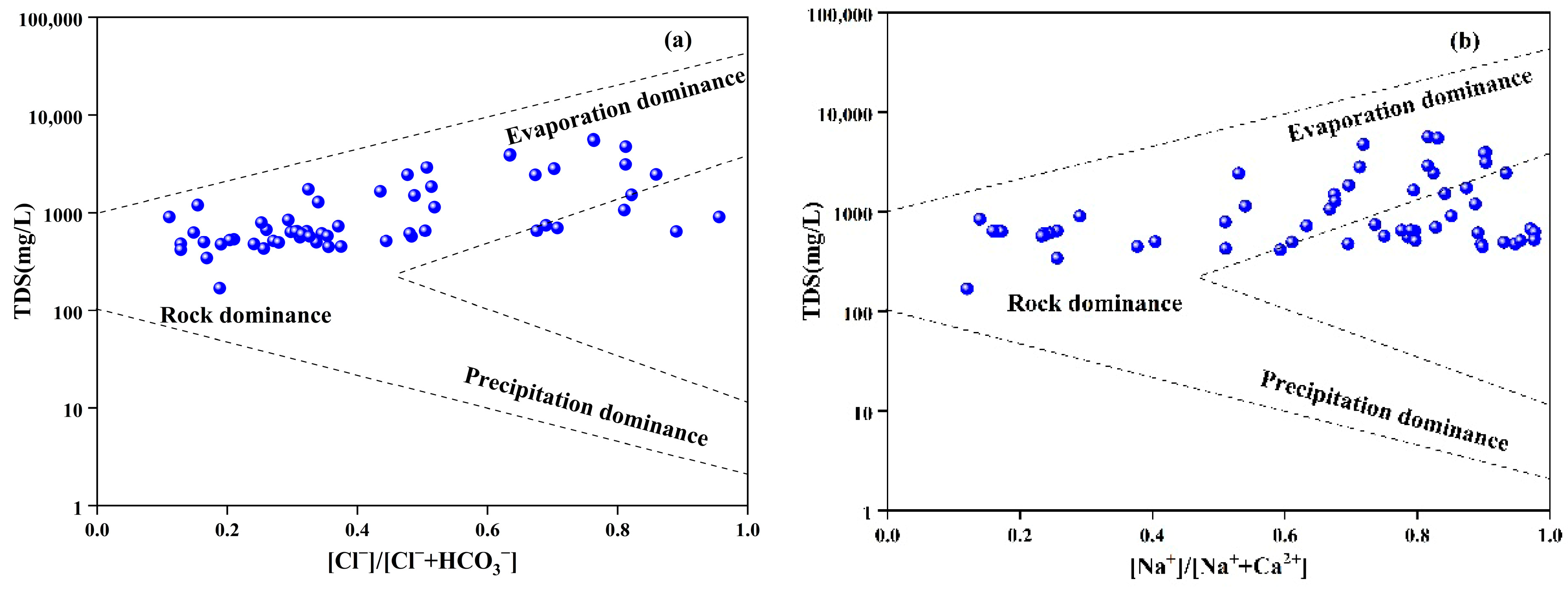
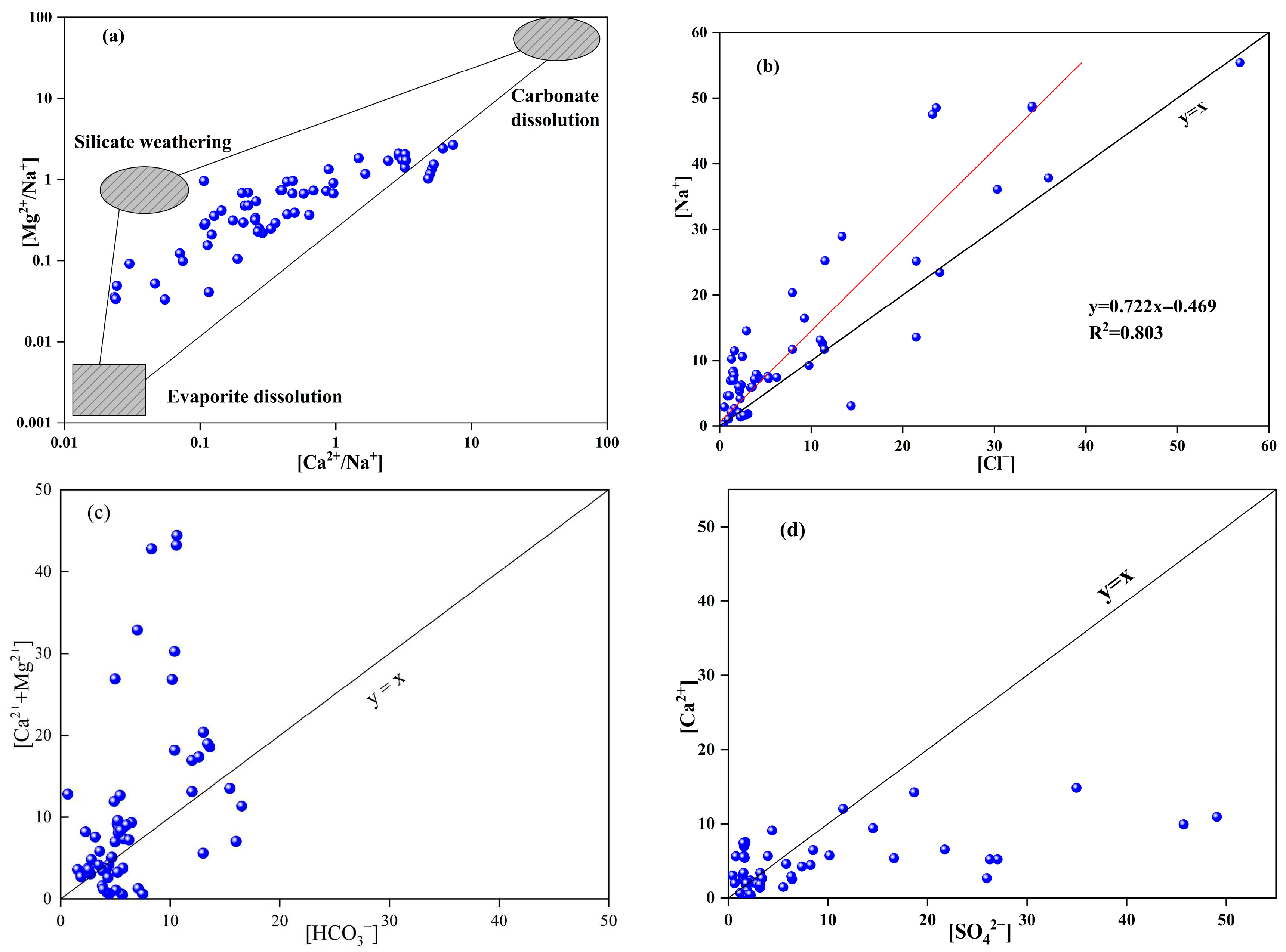
3.3.1. Controlling Factors
3.3.2. Ion Sources
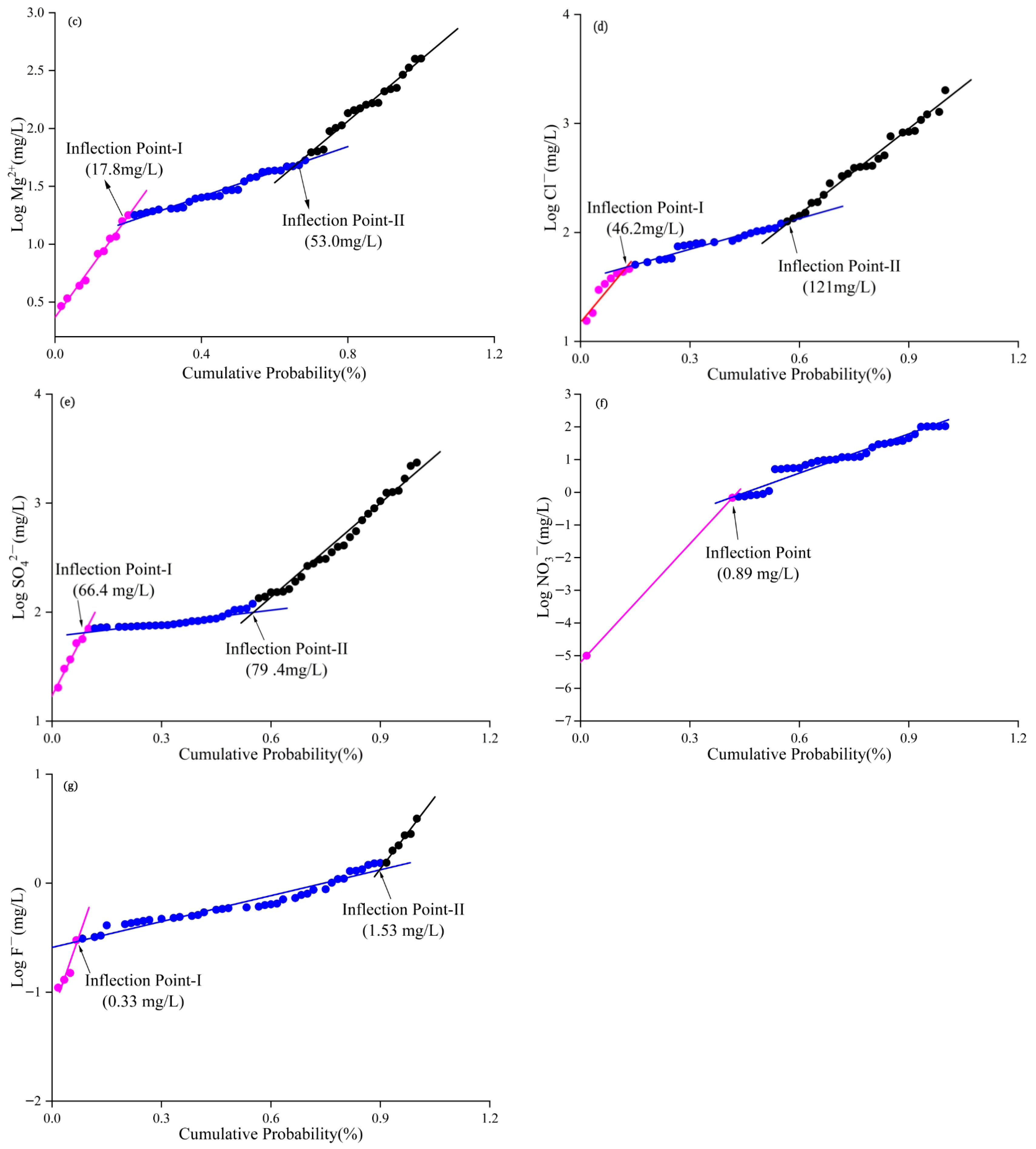
3.4. NBLs and TVs of Groundwater Chemical Components in Overexploited Areas
3.4.1. Analysis of NBLs and TVs
3.4.2. Comparative Analysis of Groundwater Chemical NBLs in Different Regions
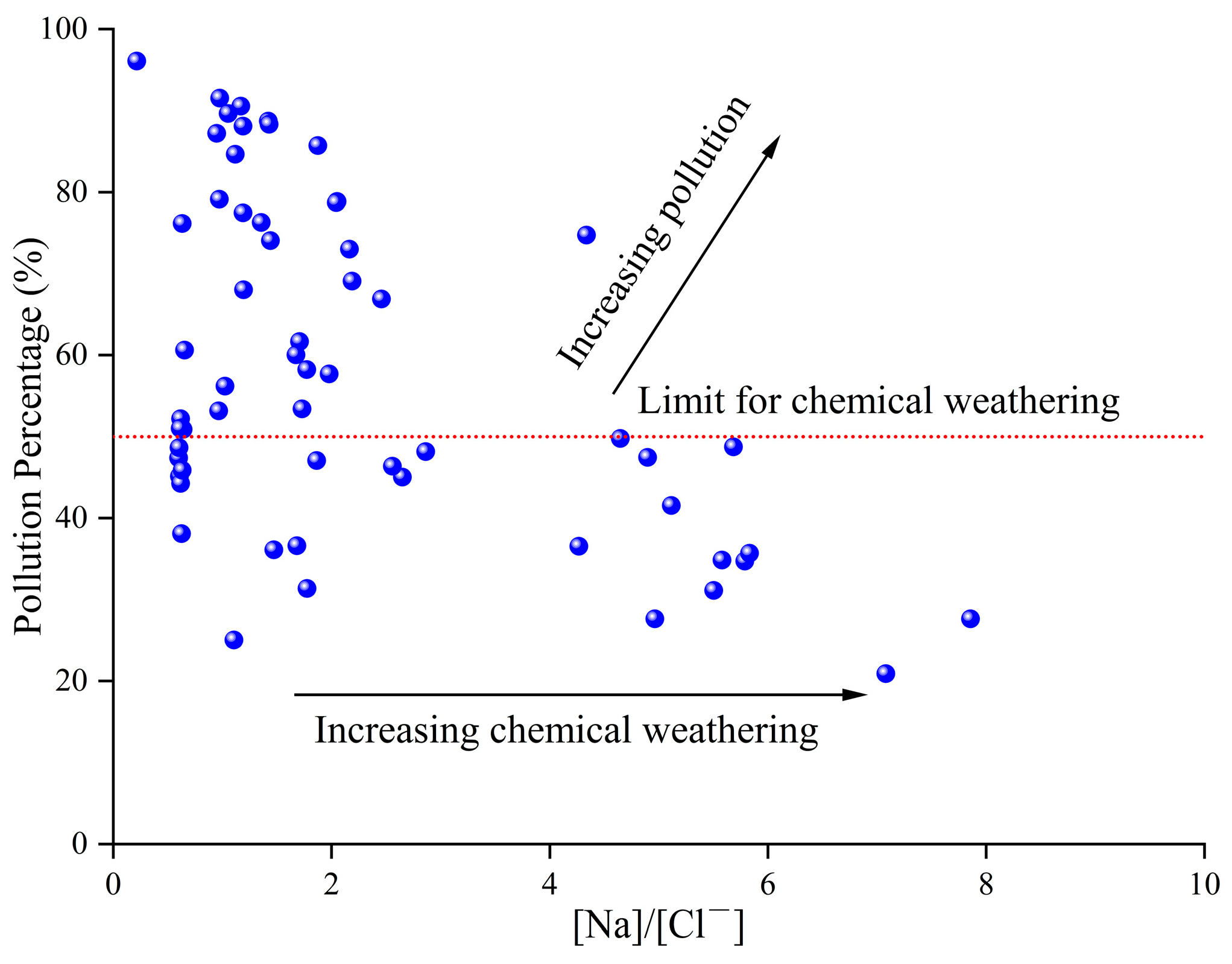
3.5. Contamination Characteristics and Controlling Factors in the Over-Exploited Zone
3.5.1. Contamination Characteristics
3.5.2. Controlling Factors of Groundwater Contamination
4. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, A.; Tiwari, K.K.; Mondal, N.C. Assessment of hydrochemical backgrounds and threshold values of groundwater in a part of desert area, Rajasthan, India. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, C.M.; Crosta, G.B.; Frattini, P. Hydrogeochemical characterization and natural background levels in urbanized areas: Milan Metropolitan area (Northern Italy). J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 455–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Liu, J.; Scanlon, B.R.; Jiao, J.J.; Jasechko, S.; Lancia, M.; Zheng, C. The changing nature of groundwater in the global water cycle. Science 2024, 383, eadf0630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, G.B.; Salama, R.B. Modeling point sources of groundwater contamination: A review and case study. In Contamination of Groundwaters; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Urresti-Estala, B.; Carrasco-Cantos, F.; Vadillo-Pérez, I.; Jiménez-Gavilán, P. Determination of background levels on water quality of groundwater bodies: A methodological proposal applied to a Mediterranean river basin (Guadalhorce River, Málaga, southern Spain). J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 117, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Gao, X.; Guo, W.; Chen, W. Hydrochemical background levels and threshold values of phreatic groundwater in the greater Xi’an region, China: Spatiotemporal distribution, influencing factors and implication to water quality management. Expo. Health 2022, 15, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijioma, U.D. Delineating the impact of urbanization on the hydrochemistry and quality of groundwater wells in Aba, Nigeria. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 240, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, Q. Groundwater chemical characteristics and controlling factors in a region of Northern China with intensive human activity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, F. Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a rapidly urbanized coastal area, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xie, D.; Zhang, C. Assessing the impact of natural and anthropogenic activities on groundwater quality in coastal alluvial aquifers of the lower Liaohe River Plain, NE China. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H. Rapid urbanization has changed the driving factors of groundwater chemical evolution in the large groundwater depression funnel area of Northern China. Water 2023, 15, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhinan, Z.; Lirong, W.; Congmei, W.; Xiaoqing, H. Risk Distribution Characteristics of Rainstorm and Flood Disaster Based on Flood Area Model in the Xiaoma River Basin of Xingtai. J. Arid Meteorol. 2021, 39, 486. [Google Scholar]
- Amadi, A.N.; Olasehinde, P.I.; Nwadioha, I.J.; Okunlola, I.A.; Shaibu, I.; Nwakife, C.N. Comparative assessment of groundwater suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in Agbara and Ota area of Southwestern Nigeria. Int. J. Sci. Glob. Sustain. 2016, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Liu, W.; Pan, Z.; Ling, K. Comparative study of hydrochemical classification based on different hierarchical cluster analysis methods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runnells, D.D.; Dupon, D.P.; Jones, R.L.; Cline, D.J. Determination of background chemistry of water at mining and milling sites, Salt Lake Valley, Utah, USA. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Water-Rock Interaction, Taupo, New Zealand, 30 March–3 April 1998; A A Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Garrett, R.G. Background and threshold: Critical comparison of methods of determination. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 346, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, A.; Matta, G.; Uniyal, D.P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Pant, G. Assessment of potentially toxic elements in groundwater through interpolation, pollution indices, and chemometric techniques in dehradun in uttarakhand state. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 36241–36263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, F.; Weijden, C.H. Contributions of water-rock interactions to the composition of groundwater in areas with a sizeable anthropogenic input: A case study of the waters of the Fundo area, Central Portugal. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 3553–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumya, B.S.; Sekhar, M.; Riotte, J.; Banerjee, A.; Braun, J.J. Characterization of groundwater chemistry under the influence of lithologic and anthropogenic factors along a climatic gradient in upper Cauvery basin, South India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2311–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeater, K.M.; Duke, S.E.; Riedell, W.E. Multivariate analysis: Greater insights into complex systems. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onjia, A.; Huang, X.; Trujillo González, J.M.; Egbueri, J.C. Chemometric approach to distribution, source apportionment, ecological and health risk of trace pollutants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1107465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Nganje, T.N.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Edet, A.; Stirling, D.; Adamu, C.I. Hydrochemistry of surface water and groundwater in the shale bedrock, cross river basin and niger delta region, nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 961–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Chen, J.; Jiang, T.; Li, K.; Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Z. Identification of the dominant hydrogeochemical processes and characterization of potential contaminants in groundwater in Qingyuan, China, by multivariate statistical analysis. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 33243–33255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Y.; Qian, H.; Liu, R.; Ma, H. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and quality assessment of groundwater in an irrigated region, Northwest China. Water 2019, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herojeet, R.; Dewangan, R.K.; Naik, P.K.; Verma, J.R. Probabilistic modelling is superior to deterministic approaches in the human health risk assessment: An example from a tribal stretch in Central India. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Song, X.; Yang, L.; Han, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Bu, H. The role of anthropogenic and natural factors in shaping the geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Subei Lake basin, Ordos energy base, Northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupre, B.; Louvat, P.; Allegre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.T.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.H.; Yang, J.M.; Jia, B.J. Water sources and factors controlling on hydro-chemical compositions in the Yiluo River basin. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 1184–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, M.A.; Abiye, T.A.; Ibrahim, K.O.; Abubakar, H.O. Hydrogeochemical and salinity appraisal of surficial lens of freshwater aquifer along Lagos coastal belt, South West, Nigeria. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhy, N.T.; Ramli, M.F.; Aris, A.Z.; Sulaiman, W.N.A.; Juahir, H.; Fakharian, K. Identification of the hydrogeochemical processes in groundwater using classic integrated geochemical methods and geostatistical techniques, in Amol-Babol Plain, Iran. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 419058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Wu, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhou, G. Exploration of hydrogeochemical characterization and assessment of organic pollution characteristics of shallow groundwater near a chemical plant that discharged sewage illegally. Sustainability 2022, 14, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Research on the features and driving factors of shallow groundwater quality in arid areas, Northwest China. Water 2025, 17, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Hao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Meng, J.; Wang, F. Hydrogeochemical disparities and constraints of water produced from various coal seams in the Baode Block, Ordos Basin, China. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 4905–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmunds, W.M.; Doherty, P.; Griffiths, K.; Shand, P.; Peach, D. Baseline Report Series: The Chalk of Dorset; The Environment Agency: London, UK, 2002.
- Serianz, L.; Cerar, S.; Šraj, M. Hydrogeochemical characterization and determination of natural background levels (NBL) in groundwater within the main lithological units in Slovenia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, B.L.; Lawrence, A.R.; Chilton, P.J.; Adams, B.; Calow, R.C.; Klinck, B.A. Groundwater and Its Susceptibility to Degradation: A Global Assessment of the Problem and Options for Management; The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): Nairobi, Kenya, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.J.; Jiang, R.G.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, J.C.; Yu, X. Spatiotemporal characteristics of groundwater depth in Xingtai City on the North China Plain: Changing patterns, causes and prediction. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 6605–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, D.; Lv, S.; Zhang, J.; Yan, M.; Han, G.; Li, H. Hydrochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater in the southern plain of Hebei Province, China. Water 2023, 15, 3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shimabukuro, M.; Kishida, R.; Yokoi, T.; Kawashita, M. Effects of pH on the microarchitecture of carbonate apatite granules fabricated through a dissolution–precipitation reaction. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1396275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhu, L. Groundwater quality assessment and pollution source apportionment in an intensely exploited region of northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16639–16650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, W.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z. Cascade reservoir regulations on nitrogen source and transformation in the Tibetan Plateau river: Constraints from high frequency data of Lancang river. J. Hydrol. 2025, 650, 132563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, O.; Assal, A.; Devlin, J.F. Performance of a field-scale biological permeable reactive barrier for in-situ remediation of nitrate-contaminated groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Range (mg/L) | Average (mg/L) | CV (%) | Standard * | Over Standard Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.78–8.47 | 7.84 | 5.46 | 6.5–8.5 | 0 |
| K+ | 0.420–15.4 | 2.21 | 137 | - | 3.3 |
| Na+ | 6.26–1275 | 285 | 112 | 200 | 38.3 |
| Ca2+ | 4.01–297 | 86.7 | 78.8 | - | 46.7 |
| Mg2+ | 2.92–402 | 74.7 | 127 | - | 33.3 |
| 40.2–1008 | 405 | 58.2 | - | - | |
| Cl− | 15.4–2017 | 301 | 132 | 250 | 33.3 |
| 20.3–2355 | 344 | 149 | 250 | 31.7 | |
| 0–106 | 16.0 | 183 | 88.6 | 8.3 | |
| F− | 0.11–3.91 | 0.84 | 83.1 | 1 | 23.3 |
| TH | 24.0–2202 | 533 | 97.1 | 450 | 40.0 |
| TDS | 169–5659 | 1271 | 99.6 | 1000 | 33.3 |
| Parameters | Standard (mg/L) | NBLs | TVs | Exceeding the TVs Points | Percentage Occupied (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | 200 | 32.3 | 116 | 40 | 66.7 |
| Ca2+ | 75 | 34.1 | 54.6 | 33 | 55.0 |
| Mg2+ | 50 | 17.8 | 33.9 | 30 | 50.0 |
| Cl− | 450 | 46.2 | 248 | 20 | 33.3 |
| 450 | 66.4 | 258 | 19 | 31.7 | |
| 88.6 | 0.89 | 44.7 | 7 | 11.7 | |
| F− | 1 | 0.33 | 0.67 | 23 | 38.3 |
| Region | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | F− | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study area | 32.3 | 34.1 | 17.8 | 46.2 | 66.4 | 0.89 | 0.33 |
| Xi’an alluvial plain [6] | 101–121 | 76.1–80.0 | 43–184 | 40.0–73.6 | 340–696 | - | - |
| Milan area, Italy [2] | 25.2 | - | - | 29.3 | 44 | 12 | - |
| Rajasthan, India [1] | 158 | - | - | 242 | 28 | 26 | 0.35 |
| Slovenia [36] | 12 | 110 | 25.9 | 30.8 | 26 | 6.3 | - |
| Parameters | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.941 | 0.205 | 0.108 | |
| Mg2+ | 0.912 | 0.308 | 0.091 |
| TDS | 0.860 | 0.396 | −0.006 |
| Cl− | 0.850 | 0.073 | 0.496 |
| K+ | 0.836 | −0.306 | −0.026 |
| Ca2+ | 0.828 | 0.395 | −0.165 |
| TH | 0.817 | 0.369 | 0.261 |
| Na+ | 0.669 | 0.291 | 0.579 |
| 0.241 | 0.855 | −0.133 | |
| pH | −0.223 | −0.712 | −0.467 |
| −0.165 | −0.084 | 0.897 | |
| Eigenvalue | 6.65 | 1.61 | 1.14 |
| Contribution rate (%) | 51.8 | 18.9 | 14.6 |
| Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 51.8 | 70.7 | 85.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Guo, B.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, C.; Yuan, Z. Study on Natural Background Levels and Mechanisms of Groundwater Contamination in an Overexploited Aquifer Region: A Case Study of Xingtai City, North China Plain. Water 2025, 17, 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192836
Wang Q, Wang M, Li Y, Guo B, Li H, Liu Y, Zhao L, Ma C, Yuan Z. Study on Natural Background Levels and Mechanisms of Groundwater Contamination in an Overexploited Aquifer Region: A Case Study of Xingtai City, North China Plain. Water. 2025; 17(19):2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192836
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qi, Meili Wang, Yan Li, Binghao Guo, Hongchao Li, Yang Liu, Liya Zhao, Chunyang Ma, and Ziting Yuan. 2025. "Study on Natural Background Levels and Mechanisms of Groundwater Contamination in an Overexploited Aquifer Region: A Case Study of Xingtai City, North China Plain" Water 17, no. 19: 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192836
APA StyleWang, Q., Wang, M., Li, Y., Guo, B., Li, H., Liu, Y., Zhao, L., Ma, C., & Yuan, Z. (2025). Study on Natural Background Levels and Mechanisms of Groundwater Contamination in an Overexploited Aquifer Region: A Case Study of Xingtai City, North China Plain. Water, 17(19), 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192836





