Definition of Groundwater Genesis of the Vidlič Mt. Complex Karst System as a Basis for Groundwater Utilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
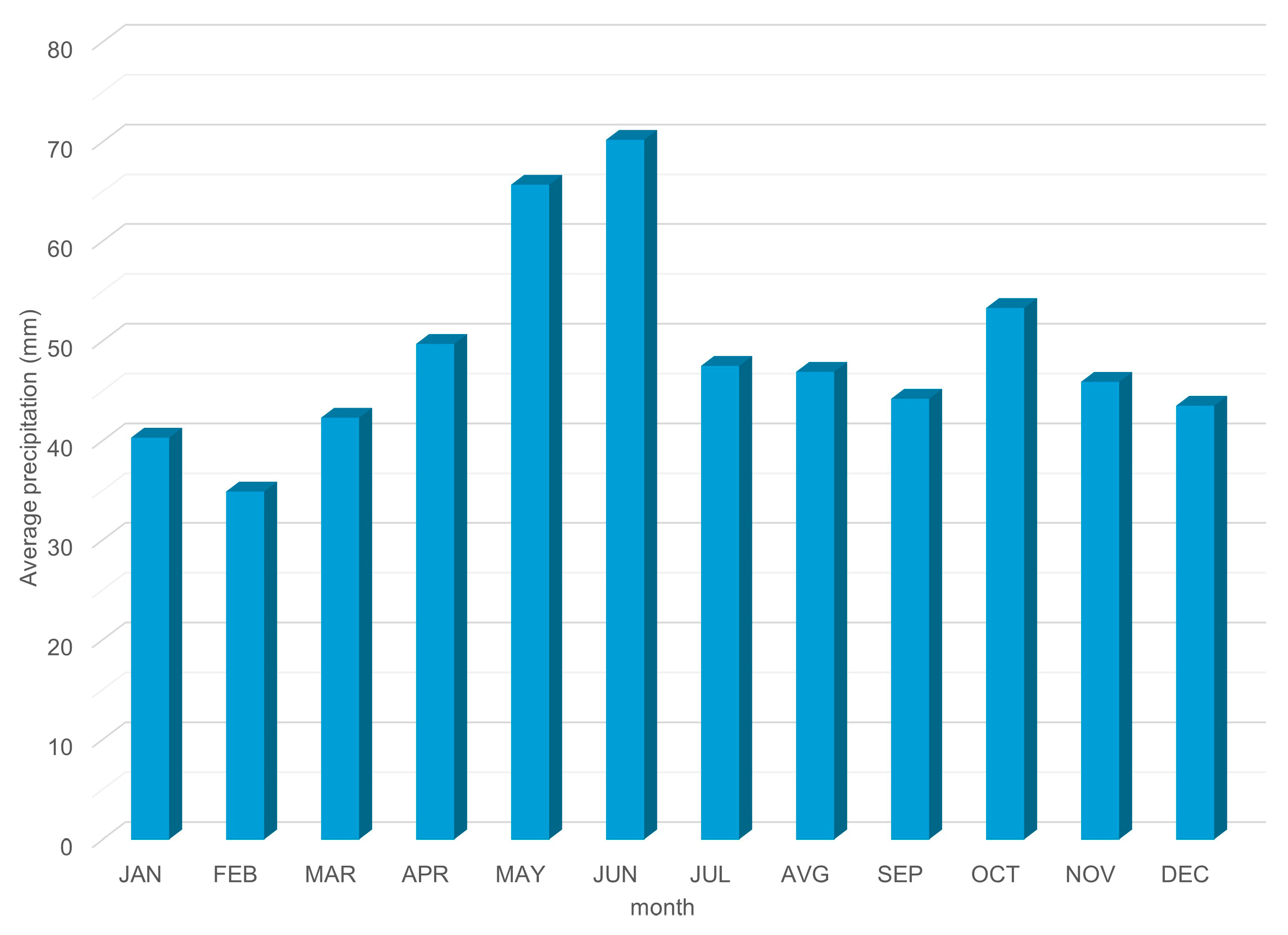
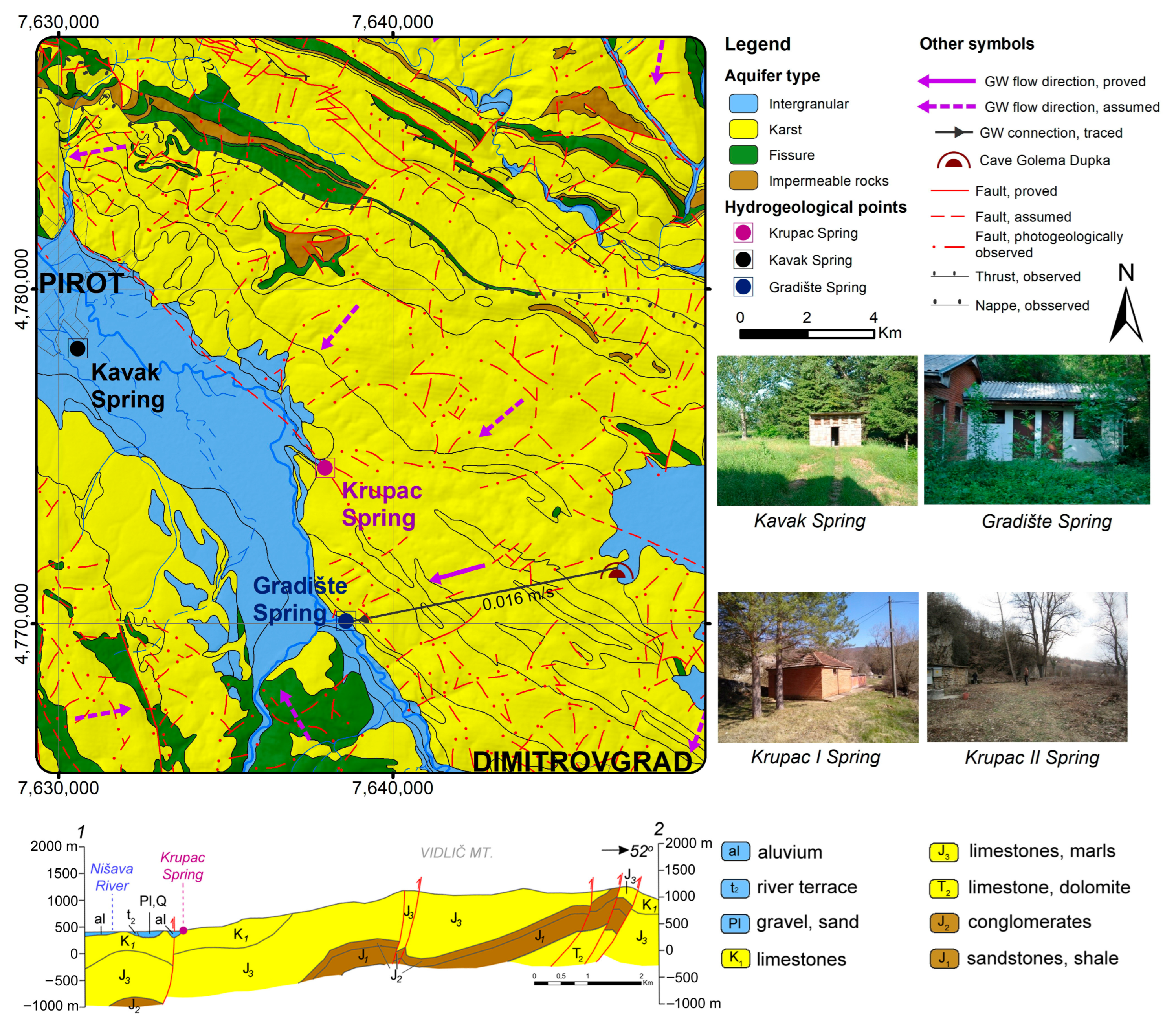
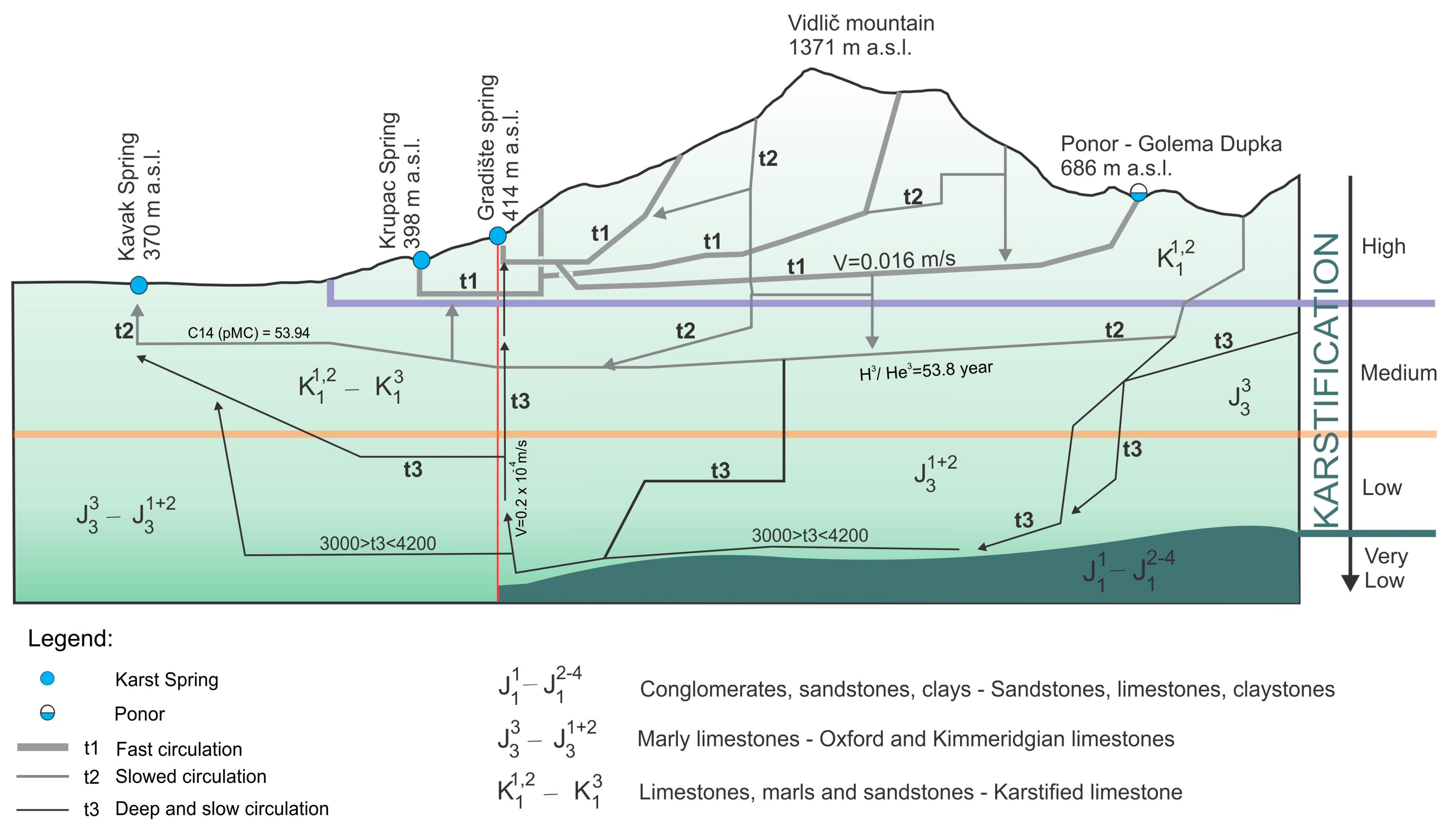
2. Climatic, Geological and Hydrogeological Setting of the Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
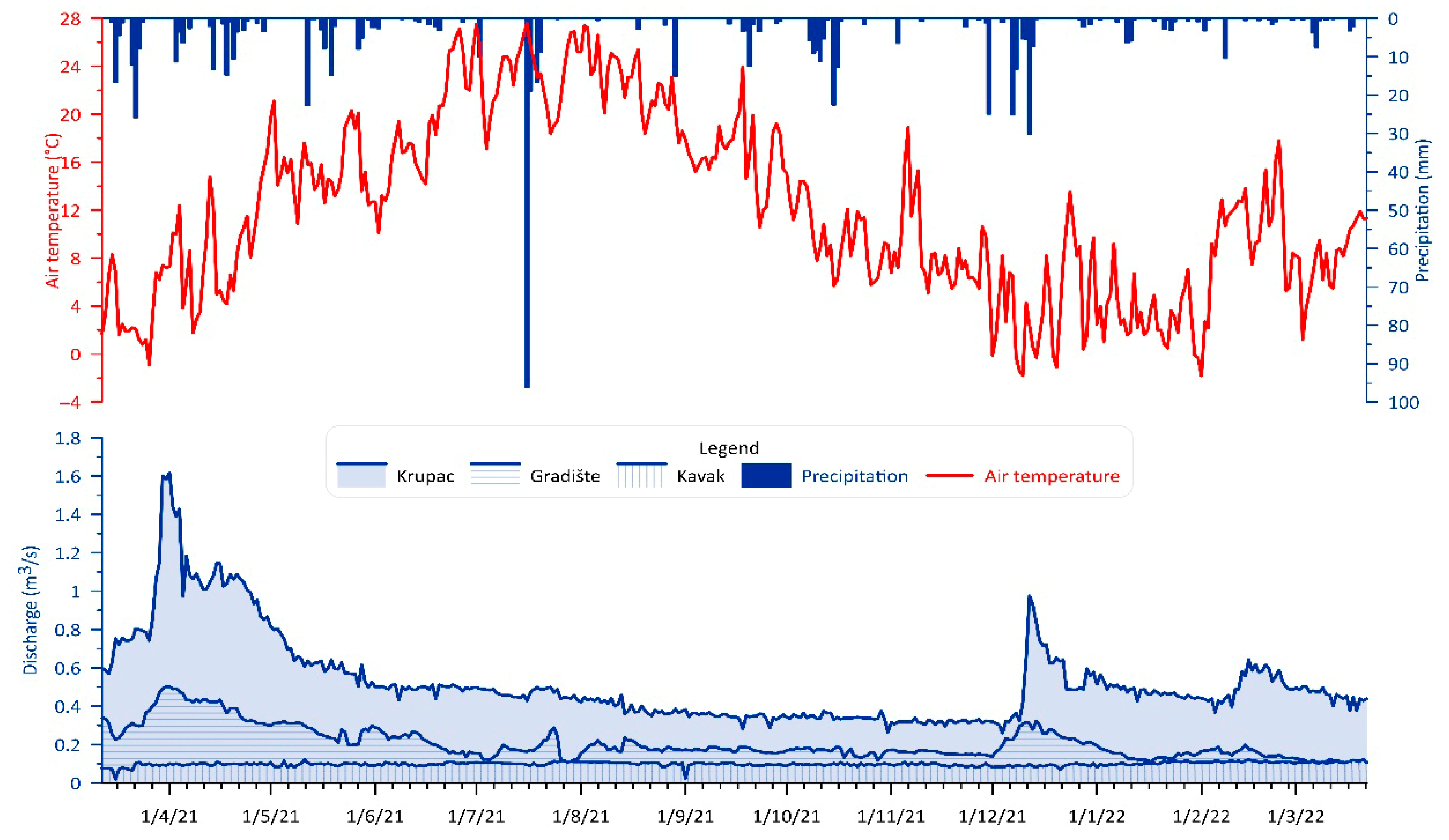
4.1. Results for Discharge Regime
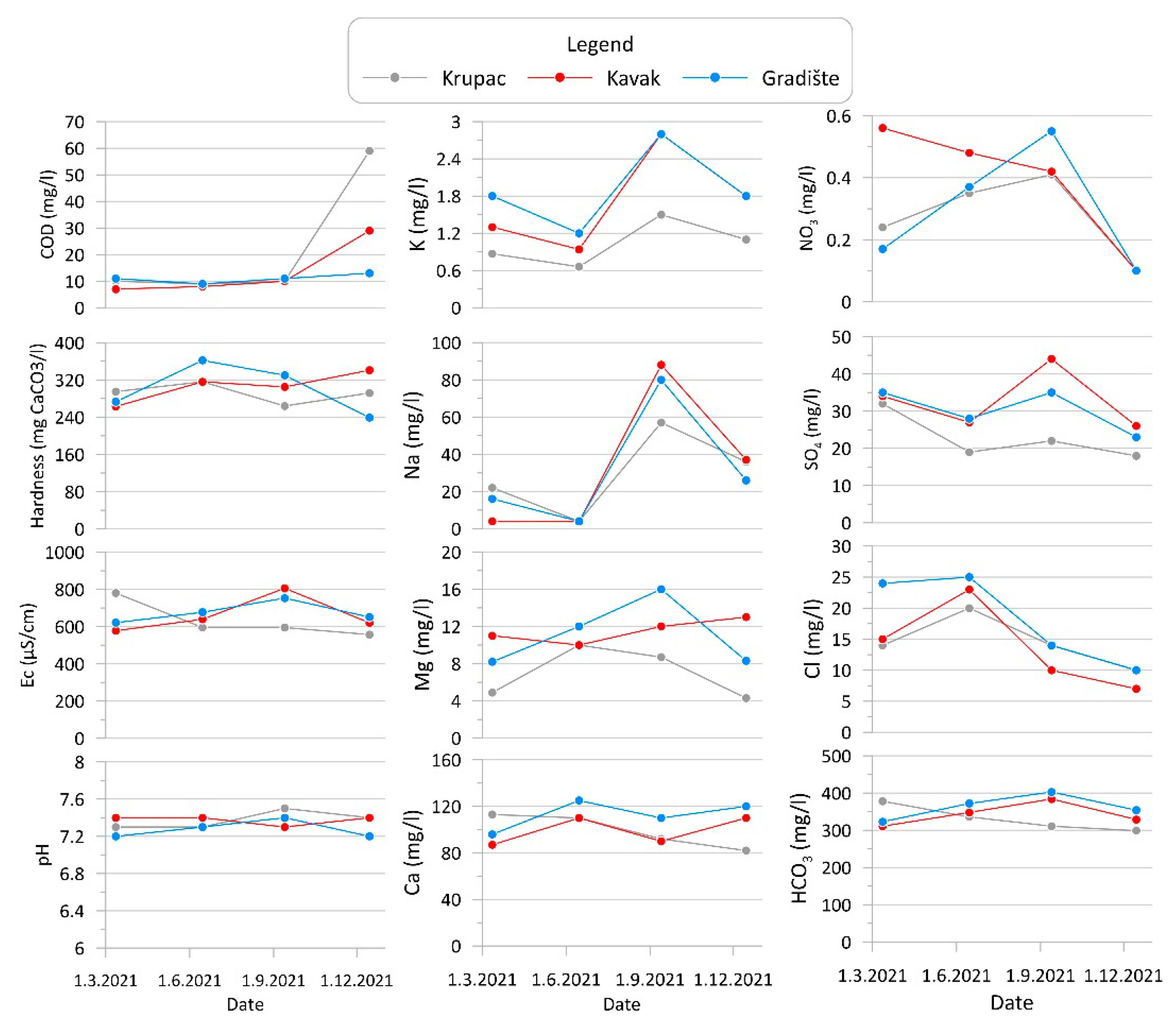
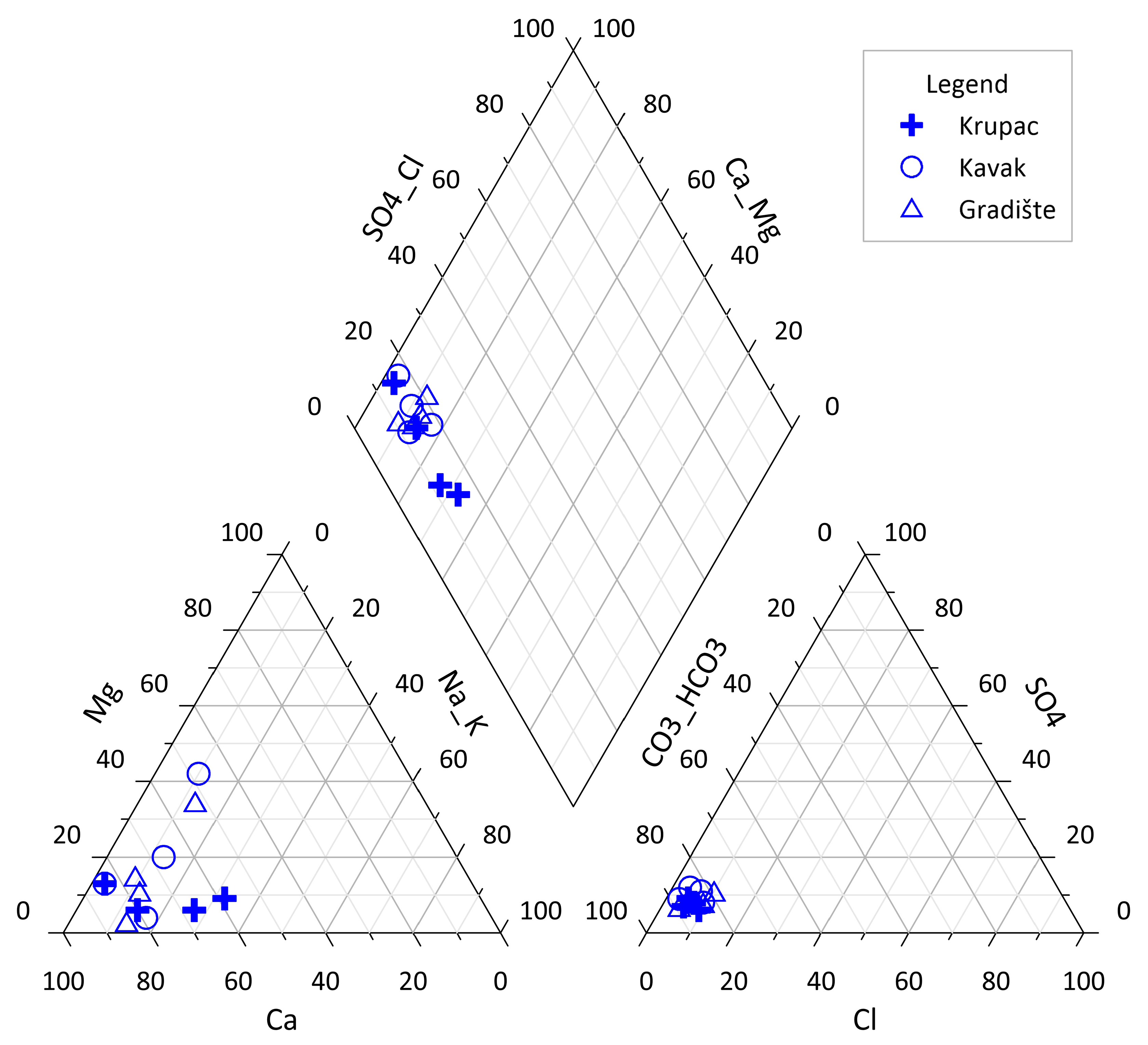
4.2. Results for Groundwater Quality Regime
4.3. Results of Tracer Test
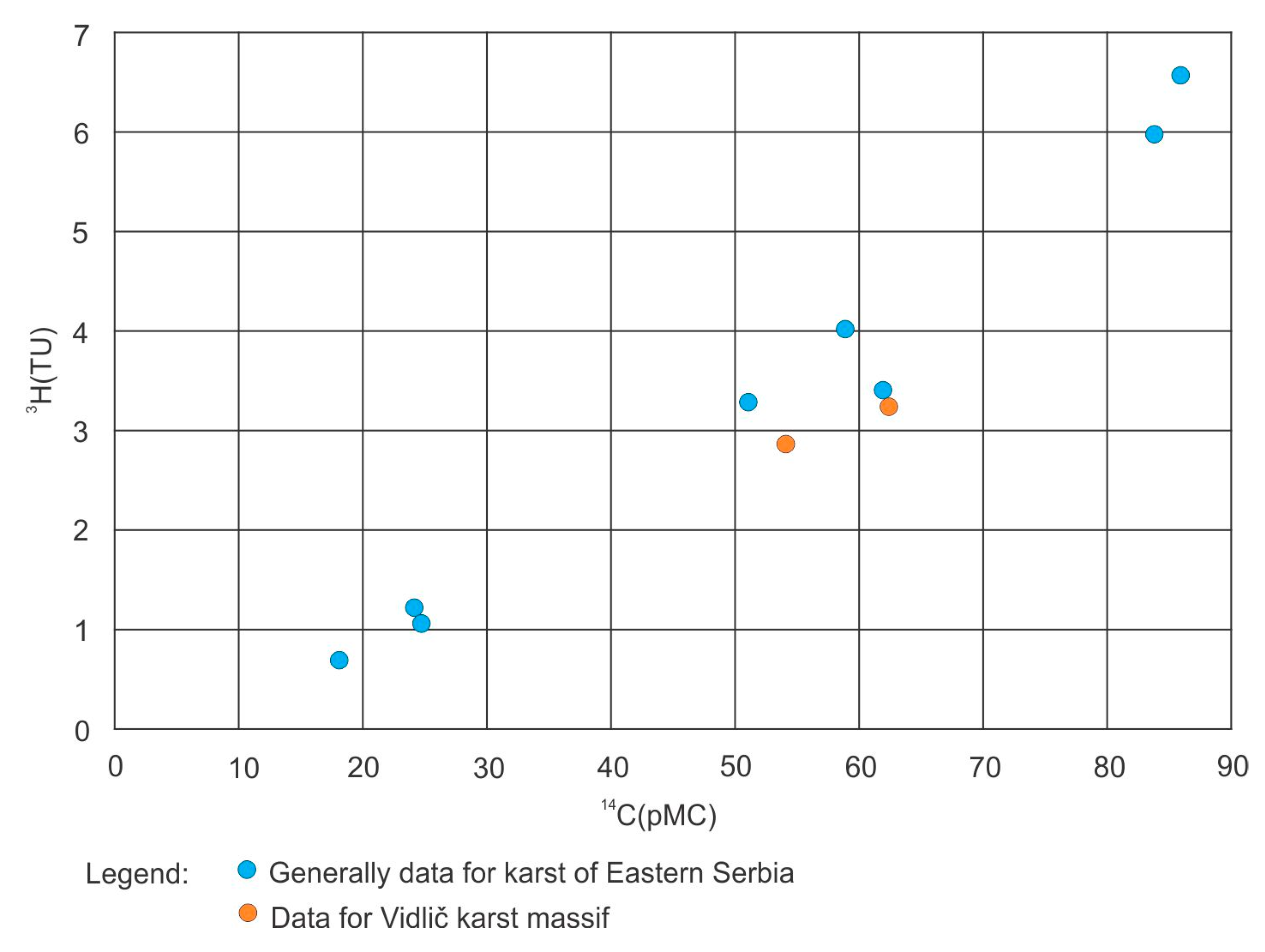
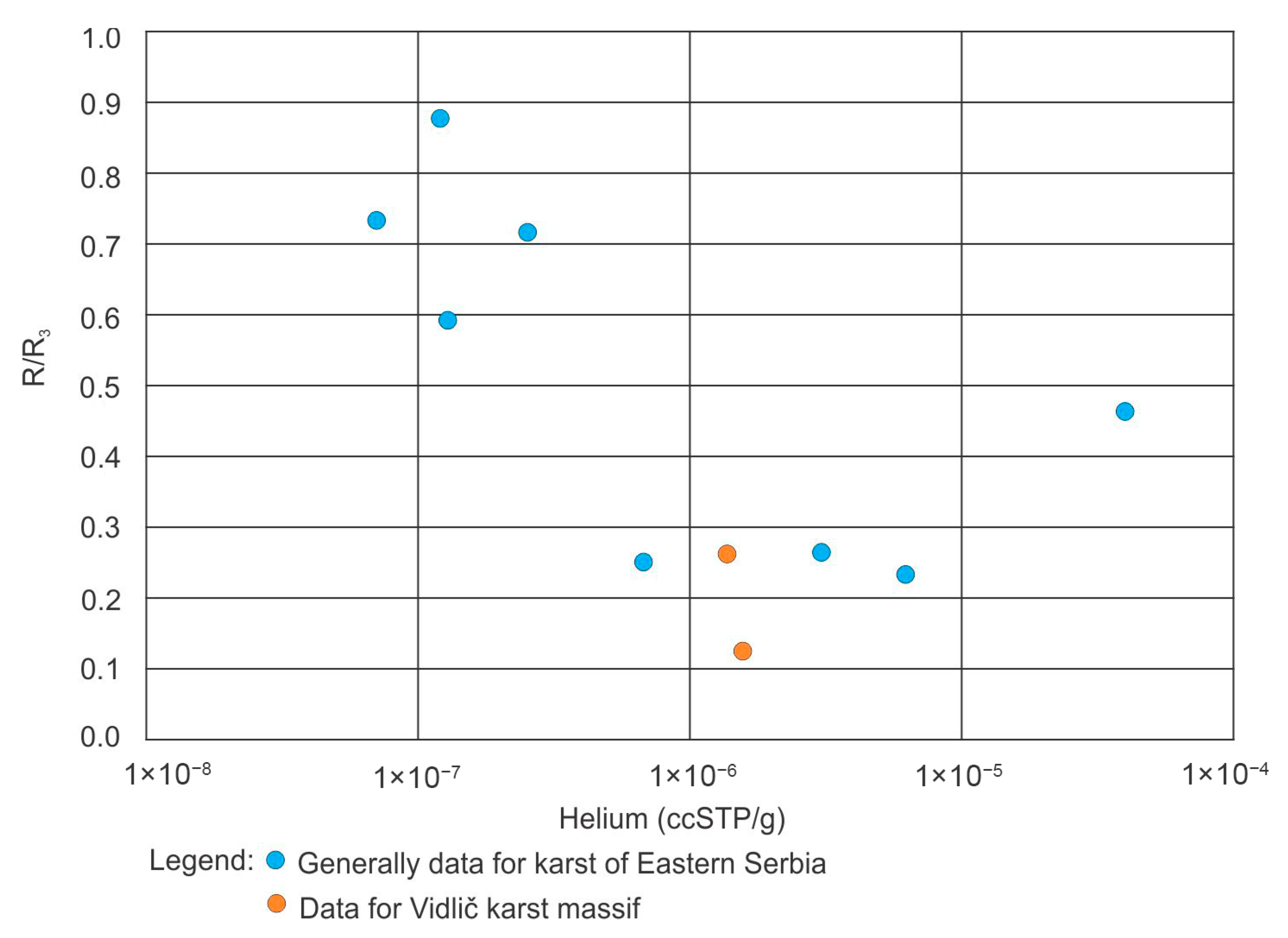
4.4. Results for Stable and Radioactive Isotopes
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ford, D.; Williams, P. Karst Geomorphology and Hydrology; Caphman & Hall: London, UK, 1989; ISBN 0 412 44590 5. [Google Scholar]
- Fatchurohman, H.; Adji, T.N.; Haryono, E.; Wijayanti, P. Baseflow index assessment and master recession curve analysis for karst water management in Kakap Spring, Gunung Sewu. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 148, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasić, L.; Milanović, S.; Stevanović, Z.; Palcsu, L. Definition of groundwater genesis and circulation conditions of the complex hydrogeological karst system Mlava-Belosavac-Belosavac-2 (eastern Serbia). Carbonates Evaporites 2020, 35, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacurto, S.; Grelle, G.; De Filippi, F.M.; Sappa, G. Karst Recharge Areas Identified by Combined Application of Isotopes and Hydrogeological Budget. Water 2021, 13, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Torres, M.; Paudel, P.; Hu, L.; Yang, G.; Chu, X. Assessing the Karst Groundwater Quality and Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of a Prominent Dolomite Aquifer in Guizhou, China. Water 2020, 12, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Rong, S.; Xiong, Y.; Teng, Y. Groundwater Vulnerability and Groundwater Contamination Risk in Karst Area of Southwest China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, D.; Williams, P. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology; Willey: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D. Karst of China; China Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D. Sensitivity of karst process to environmental change along the PEP II transect. Quat. Int. 1997, 37, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.X.; Cai, G.H. The Science of Karst Environment; Chongqing Publishing House: Chongqing, China, 1988. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vasić, L.; Palcsu, L.; Huang, F. Groundwater Gravitational Circulation of Karst Veliko Vrelo and Malo Vrelo Springs by Isotope and the Noble Gas Method: Case Study of the Beljanica Massif; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogančić, D.; Afrasiabian, A.; Kranjčić, N.; Đurin, B. Using Stable Isotope Analysis (δD and δ18O) and Tracing Tests to Characterize the Regional Hydrogeological Characteristics of Kazeroon County, Iran. Water 2020, 12, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.; Fahrmeier, N.; Goeppert, N.; Goldscheider, N. High-resolution multi-parameter monitoring of microbial water quality and particles at two alpine karst springs as a basis for an early-warning system. Hydrogeol. J. 2022, 30, 2285–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, C.; Mao, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, F.; Yu, X. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Drought and Waterlogging in Karst Mountains in Southwest China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zang, H.; Zheng, X.; Xu, Y. Climate Change and Its Influence on the Karst Groundwater Recharge in the Jinci Spring Region, Northern China. Water 2017, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa Bhering, A.; Antunes, I.M.H.R.; Nascimento Catão, G.; Gomes Marques, E.A.; de Paula, R.S.; Brito Andrade, I.; Rebelo Diório, G. Groundwater Model for Karst and Pelitic Aquifer Systems from a Semi-Arid Region Under Climate Change Scenarios: A Case Study in the Vieira River Watershed, Brazil. Water 2024, 16, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasić, L.; Milanović, S.; Dašić, T. Definition of Circulation Conditions and Groundwater Genesis of the Complex Krupaja Hydrogeological Karst System (Eastern Serbia). Sustainability 2023, 15, 11146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B. Karst hydrology: Recent developments and open questions. Eng. Geol. 2002, 65, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravbar, N.; Petrič, M.; Kogovšek, J. The characteristics of groundwater flow in karst aquifers during long lasting low flow conditions, example from SW Slovenia. In Advances in Research in Karst Media. Environmental Earth Sciences; Andreo, B., Carrasco, F., Durán, J., LaMoreaux, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovan, L.; Lojen, S.; Zuliani, T.; Kanduč, T.; Petrič, M.; Horvat, B.; Rusjan, S.; Štrok, M. Comparison of Uranium Isotopes and Classical Geochemical Tracers in Karst Aquifer of Ljubljanica River catchment (Slovenia). Water 2020, 12, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, M.; Rinyu, L.; Veres, M.; Seiler, M.; Wacker, L.; Synal, H.A. EnvironMICADAS: A mini 14 C AMS with enhanced gas ion source Interface in the Hertelendi Laboratory of Environmental Studies (HEKAL), Hungary. Radiocarbon 2013, 55, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palcsu, L.; Gessert, A.; Túri, M.; Kovács, A.; Futó, I.; Orsovszki, J.; Puskás-Preszner, A.; Temovski, M.; Koltai, G. Long-term time series of environmental tracers reveal recharge and discharge conditions in shallow karst aquifers in Hungary and Slovakia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 36, 100858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Peeters, F.; Beyerle, U.; Kipfer, R. Interpretation of dissolved atmospheric noble gases in natural waters. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 2779–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsányi, I.; Palcsu, L.; Kovács, L. Groundwater flow system as an archive of palaeotemperature: Noble gas, radiocarbon, stable isotope and geochemical study in the Pannonian Basin, Hungary, Applied Geochemistry. J. Int. Assos. Geochem. 2011, 26, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stute, M.; Schlosser, P. Principles and Applications of the Noble Gas Paleothermometer. Climate Change in Continental Isotopic Records; Geophysical Monograph Series; Swart, P.K., Lohmann, K.C., McKenzie, J., Savin, S., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 78, pp. 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kipfer, R.W.; Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Peeters, F.; Stute, M. Noble gases in lakes and groundwaters. In Noble Gases in Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, v. 47; Porcelly, D., Ballentine, D., Wieler, R., Eds.; AGU Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 615–700. [Google Scholar]
- Vasić, L. Genesis and Groundwater Circulation Conditions of Complex Karst Systems of the Kučaj-Beljanica Massif. Doctoral Dissertation, Faculty of Mining and Geology, University of Belgrade, Belgrade, Serbia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Benischke, R. Review: Advances in the methodology and application of tracing in karst aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldscheider, N.; Meiman, J.; Pronk, M.; Smart, C. Tracer tests in karst hydrogeology and speleology. Int. J. Speleol. 2008, 37, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanović, S.; Vetrović, B.; Ristić-Vakanjac, V.; Vasić, B.; Marinović, V.; Vojnović, P. Simulation of outlook of selected karst springs of the Pirot basin. Vodoprivreda 2022, 54, 315–316. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Z.; Lv, M.; Gang, S. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Evolution Processes of Karst Groundwater Affected by Multiple Influencing Factors in a Karst Spring Basin, Eastern China. Water 2023, 15, 3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubisiak-Banaszkiewicz, L.; Żukiewicz-Sobczak, W.; Starek-Wójcicka, A.; Mazur, J.; Sobczak, P. Methods of Assessing Water Quality in Terms of Public Health. Water 2025, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandić, M. Karstna vrela Pirotske kotline. Pirot. Zb. 2015, 40, 203–225. [Google Scholar]

| Spring | Date | δ13C (‰ VPDB) | Delta 2H | Delta 2H StDev | Delta 18O | Delta 18O StDev |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kavak | 1 July 2021 | −5.02 | −75.61 | 0.70 | −10.88 | 0.09 |
| Gradiste | 1 July 2021 | −6.05 | −71.23 | 0.29 | −10.35 | 0.09 |
| Spring | Date | 3H (TU) | ±1σ (TU) | 14C (pMC) | Error (abs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kavak | 1 July 2021 | 2.89 | 0.08 | 53.94 | 0.22 |
| Gradiste | 1 July 2021 | 3.26 | 0.09 | 62.18 | 0.20 |
| Spring | Date | He (ccSTP/g) | Ne (ccSTP/g) | Ar (ccSTP/g) | Kr (ccSTP/g) | Xe (ccSTP/g) | R/Ra | NGT (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kavak | 1 July 2021 | 1.37 × 10−06 | 3.64 × 10−07 | 4.68 × 10−04 | 9.90 × 10−08 | 1.38 × 10−08 | 0.265 | 8.14 |
| Gradiste | 1 July 2021 | 1.59 × 10−06 | 3.09 × 10−07 | 4.27 × 10−04 | 9.42 × 10−08 | 1.31 × 10−08 | 0.127 | 8.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasić, L.; Milanović, S.; Palcsu, L.; Petrović, B.; Marinović, V. Definition of Groundwater Genesis of the Vidlič Mt. Complex Karst System as a Basis for Groundwater Utilization. Water 2025, 17, 2807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192807
Vasić L, Milanović S, Palcsu L, Petrović B, Marinović V. Definition of Groundwater Genesis of the Vidlič Mt. Complex Karst System as a Basis for Groundwater Utilization. Water. 2025; 17(19):2807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192807
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasić, Ljiljana, Saša Milanović, Laszlo Palcsu, Branislav Petrović, and Veljko Marinović. 2025. "Definition of Groundwater Genesis of the Vidlič Mt. Complex Karst System as a Basis for Groundwater Utilization" Water 17, no. 19: 2807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192807
APA StyleVasić, L., Milanović, S., Palcsu, L., Petrović, B., & Marinović, V. (2025). Definition of Groundwater Genesis of the Vidlič Mt. Complex Karst System as a Basis for Groundwater Utilization. Water, 17(19), 2807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192807






