Extraction and Characterization of Microplastics in Soil: A Case Study from the Hetao Irrigation District
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
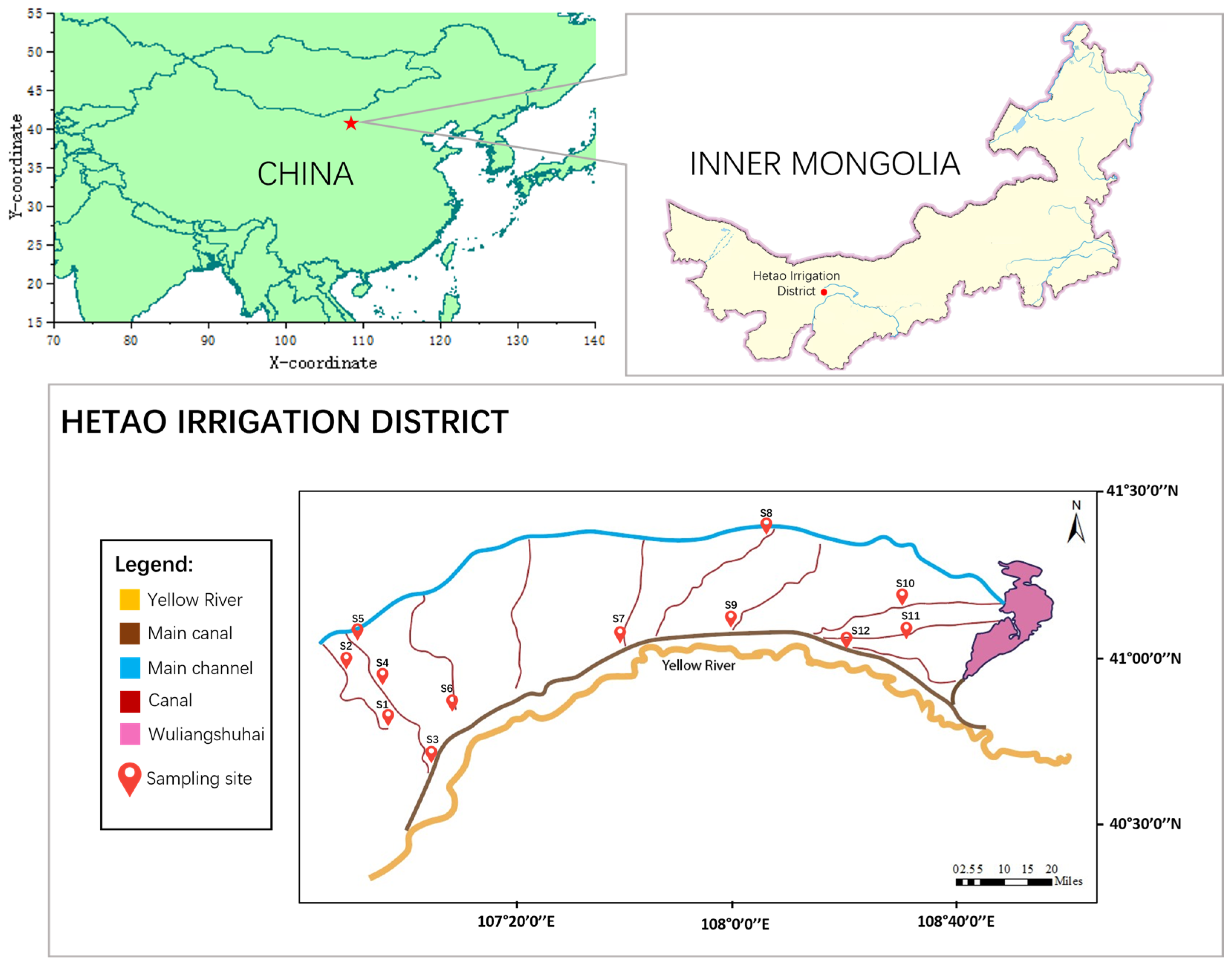
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Materials and Reagents
- i.
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (1.2 g cm−3) for density separation was obtained from Xiangyun Huida Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) (Purity: ≥99.0%). A saturated solution was prepared by dissolving NaCl in ultrapure water.
- ii.
- Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (30% w/w) was purchased from Xiangyun Huida Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) and used for organic matter digestion without further dilution.
- iii.
- Anhydrous ethanol (HPLC grade, ≥99.9%) was obtained from Xiangyun Huida Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) for the final rinsing and concentration steps.
- iv.
- Metal filter membranes (10 µm pore size, 47 mm diameter) were custom-made by Jiuding High-Tech Filtration Equipment Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China).
- v.
- Custom vacuum filtration device was fabricated by Boyuan Hongda Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China).
- vi.
- Standard reflective slides for Laser Direct Infrared (LDIR) analysis were purchased from Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA).
- vii.
- Polyethylene (PE MP) with 100 µm was purchased from Si Ye Zi Chemical Co., Ltd. (Dongguan, China) for quality control.
2.3. MPs Extraction Methods
2.4. Quantity Control
2.5. Rationale for LDIR Analysis
2.6. MP Quantification and Abundance Calculation
3. Results
3.1. Concentration of MPs
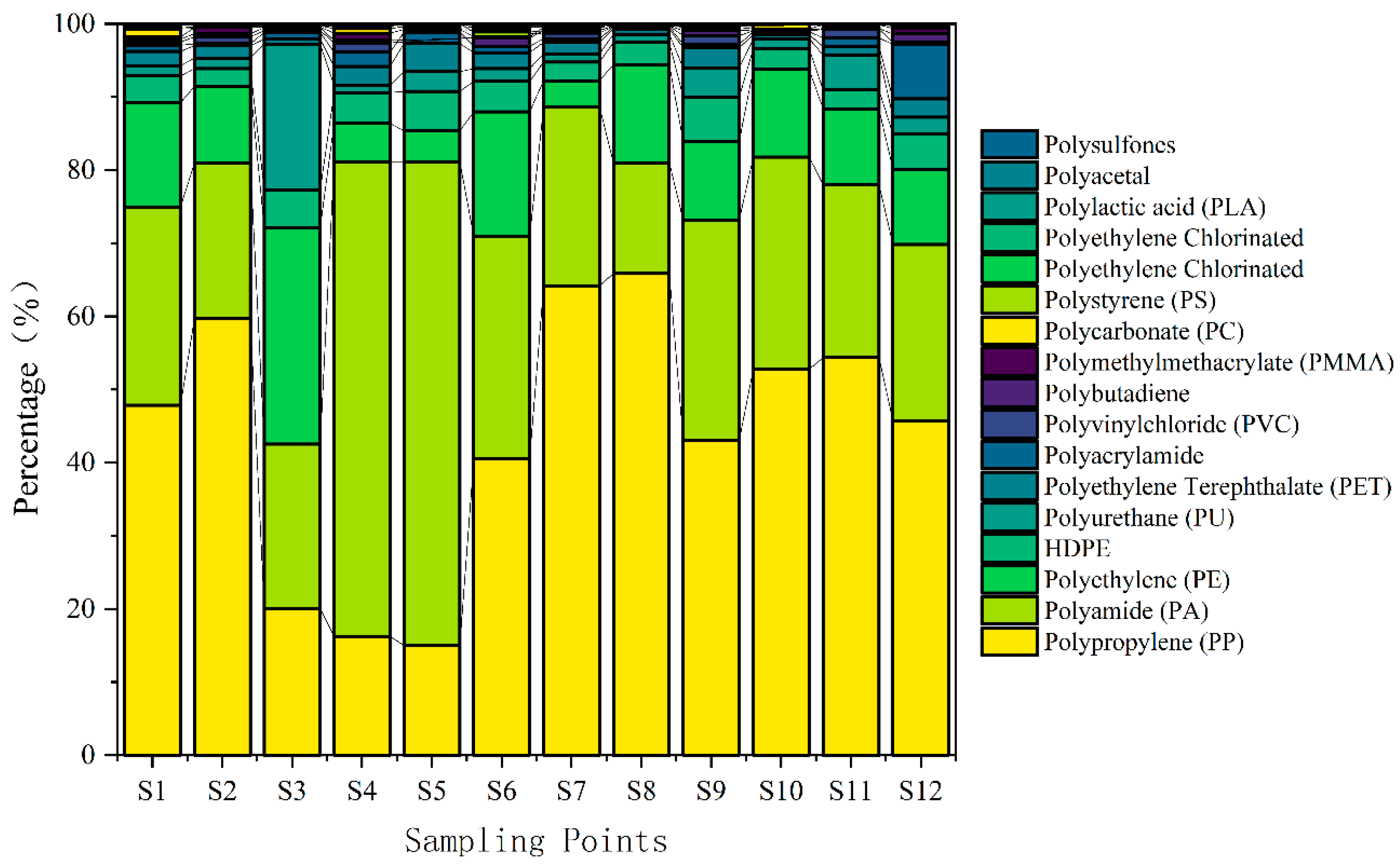
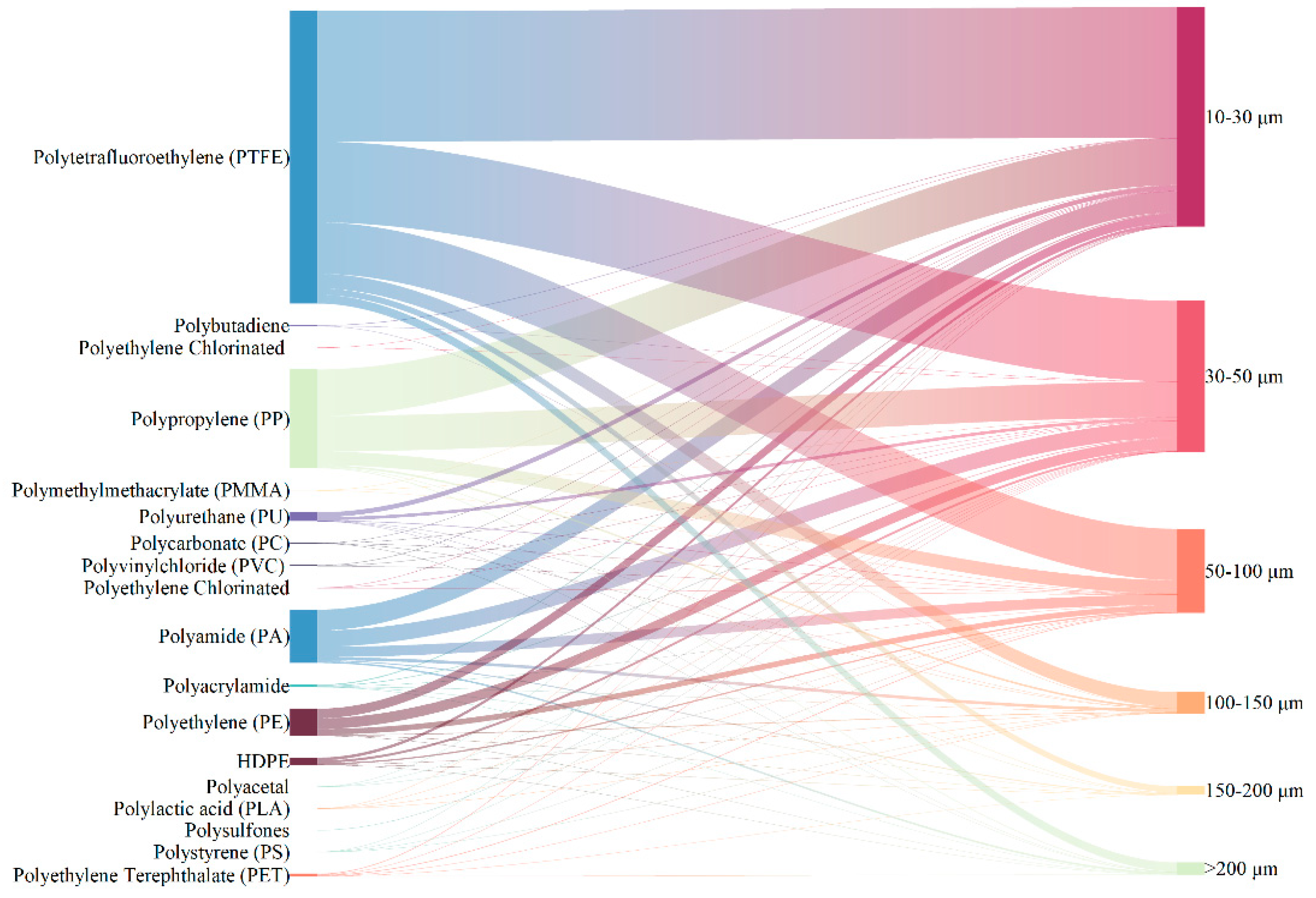
3.2. Types of MPs
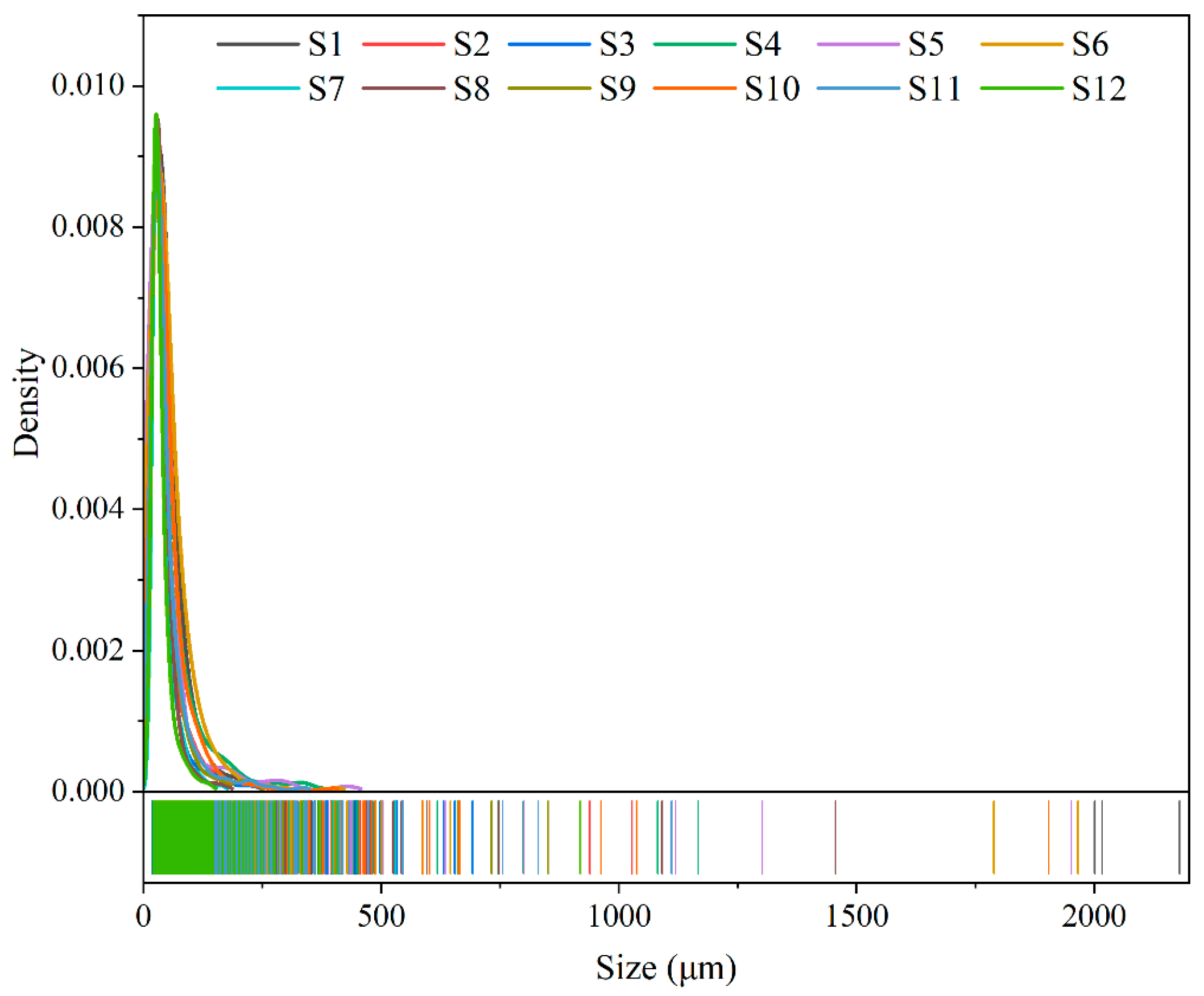
3.3. Particles Size of MPs
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, F. Ecological risks of biodegradable plastics. Science 2025, 388, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Almroth, B.C.; Brander, S.M.; Dey, T.; Green, D.S.; Gundogdu, S.; Krieger, A.; Wagner, M.; Walker, T.R. A global plastic treaty must cap production. Science 2022, 376, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, V.H.; Nguyen, M.K.; Hoang, T.D.; Ha, M.C.; Huyen, N.T.T.; Bui, V.K.H.; Pham, M.T.; Nguyen, C.M.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D. Sources, environmental fate, and impacts of microplastic contamination in agricultural soils: A comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 950, 175276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalrinfela, P.; Vanlalsangi, R.; Lalrinzuali, K.; Babu, P.J. Microplastics: Their effects on the environment, human health, and plant ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. Manag. 2024, 1, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. World Leaders Set Sights on Plastic Pollution; UNEP: Athens, Greece, 2022; Available online: https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/story/world-leaders-set-sights-plastic-pollution (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Talukdar, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Dey, A. Microplastic pollution in the Himalayas: Occurrence, distribution, accumulation and environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, M.; Selvam, S.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Q.; Pitchaimani, V.S.; Huang, P.; Ke, H.; Zheng, H.; Liu, F.; et al. Microplastics in the surface waters of the South China sea and the western Pacific Ocean: Different size classes reflecting various sources and transport. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.M.; Feng, W.; Li, X.; Ngien, S.K.; Yu, X.; Song, F.; Yang, F.; Liao, H. Microplastic distribution and its implications for human health through marine environments. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 382, 125427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Deng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Miao, Q.; Yang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Giesy, J. Biotechnology Remediation and Environmental Behavior of Microplastics in Soils: A Review. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 261, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Singh, K.; Singh, B. Microplastics in soil: Impacts and microbial diversity and degradation. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhao, S.; Qiu, T.; Cui, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Huang, M.; Zhan, A.; Fang, L. Interaction of microplastics with heavy metals in soil: Mechanisms, influencing factors and biological effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Fang, W.; Liang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. A critical review on interaction of microplastics with organic contaminants in soil and their ecological risks on soil organisms. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroshaka Gregory Marcelus Cooray, P.L.; Chalmers, G.; Chittleborough, D. A review of properties of organic matter fractions in soils of mangrove wetlands: Implications for carbon storage. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 201, 109660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhao, X.; Gu, X.; Ji, R. Separation and identification of microplastics from soil and sewage sludge. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramage, S.J.F.F.; Pagaling, E.; Haghi, R.K.; Dawson, L.A.; Yates, K.; Prabhu, R.; Hillier, S.; Devalla, S. Rapid extraction of high- and low-density microplastics from soil using high-gradient magnetic separation. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 831, 154912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, S.; Wei, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Lv, Y. Novel Pyrolysis-Assisted Cataluminescence System for Fingerprint Discrimination of Various Microplastics. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 6804–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.M.; Elsayed, A.A.; Sabry, Y.M.; Khalil, D.; Bourouina, T. Detection of Sub-20 μm Microplastic Particles by Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Comparison with Raman Spectroscopy. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 10335–10341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Chevali, V.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, G.; Burey, P.; Wang, S.; Song, P. Microplastics in soils: A comparative review on extraction, identification and quantification methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirkey, A.; Upadhyay, L.S.B. Microplastics: An overview on separation, identification and characterization of microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, M.; Ducoli, S.; Depero, L.E.; Prica, M.; Tubić, A.; Ademovic, Z.; Morrison, L.; Federici, S. A Complete Guide to Extraction Methods of Microplastics from Complex Environmental Matrices. Molecules 2023, 28, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Z.; Zuo, J.; Cai, L.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, M. Comparison of Oil Extraction and Density Extraction Method to Extract Microplastics for Typical Agricultural Soils in China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, V.S.N.S.; Singh, D.N. Effect of ultrasonication conditions on polyethylene microplastics sourced from landfills: A precursor study to establish guidelines for their extraction from environmental matrices. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grause, G.; Kuniyasu, Y.; Chien, M.-F.; Inoue, C. Separation of microplastic from soil by centrifugation and its application to agricultural soil. Chemosphere 2021, 288, 132654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, E.; Stubbins, A. An optimized acidic digestion for the isolation of microplastics from biota-rich samples and cellulose acetate matrices. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X. Evaluation of organic matter removal by H2O2 from microplastic surface by nano-physicochemical methods. Green Anal. Chem. 2022, 3, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, F.; Kochleus, C.; Bänsch-Baltruschat, B.; Brennholt, N.; Reifferscheid, G. Sampling techniques and preparation methods for microplastic analyses in the aquatic environment—A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.; Fernández-González, V.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; Caetano, M.; Raimundo, J. Improved methodology for microplastic extraction from gastrointestinal tracts of fat fish species. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhou, P.; Yang, Y.; Hall, T.; Nie, G.; Yao, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Degradation of Microplastics by a Thermal Fenton Reaction. ACS EST Eng. 2022, 2, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, D.; Pei, J.; Fei, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y. Identification and quantification of microplastics using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy: Current status and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 18, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parobková, V.; Holub, D.; Kizovský, M.; Kalčíková, G.; Rozman, U.; Urík, M.; Novotný, K.; Samek, O.; Zikmund, T.; Pořízka, P.; et al. Raman microspectroscopy and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for the analysis of polyethylene microplastics in human soft tissues. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dümichen, E.; Eisentraut, P.; Celina, M.; Braun, U. Automated Thermal Extraction—Desorption Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry: A Multifunctional Tool for Comprehensive Characterization of Polymers and their Degradation Products. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1592, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Qiu, C.; Qu, Q.; Hu, X.; Mu, L.; Gao, Z.; Tang, X. Sources and identification of microplastics in soils. Soil Environ. Health 2023, 1, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Song, N.; Li, X.; Jirigalantu; Mi, X.; Sun, C.; Sun, Y.; Feng, S.; Wang, G.; Qiu, J. Detection of microplastics via a confocal-microscope spatial-heterodyne Raman spectrometer with echelle gratings. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 313, 124099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andoh, C.N.; Attiogbe, F.; Bonsu Ackerson, N.O.; Antwi, M.; Adu-Boahen, K. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy: An analytical technique for microplastic identification and quantification. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2024, 136, 105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac Chandran, P.J.; Veerasingam, S. Laser Direct Infrared Spectroscopy: A cutting-edge approach to microplastic detection in environmental samples. Talanta 2025, 284, 127284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ccanccapa-Cartagena, A.; Gopakumar, A.N.; Salehi, M. A straightforward Py-GC/MS methodology for quantification of microplastics in tap water. MethodsX 2025, 14, 103173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragoobur, D.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Somaroo, G.D. Microplastics in agricultural soils, wastewater effluents and sewage sludge in Mauritius. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, M.N.; Komakech, H.C.; Lugomela, G. Analysis of Macro- and Microplastics in Riverine, Riverbanks, and Irrigated Farms in Arusha, Tanzania. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 82, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, F.; Meza, P.; Eguiluz, R.; Casado, F.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Geissen, V. Evidence of microplastic accumulation in agricultural soils from sewage sludge disposal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ding, F.; Flury, M.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, S.; Jones, D.L.; Wang, J. Macro- and microplastic accumulation in soil after 32 years of plastic film mulching. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossman, J.; Hurley, R.R.; Futter, M.; Nizzetto, L. Transfer and transport of microplastics from biosolids to agricultural soils and the wider environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa’adu, I.; Farsang, A. Plastic contamination in agricultural soils: A review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Deng, L.; Rao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, T.; Qian, X. Spatiotemporal dynamics of microplastics in an urban river network area. Water Res. 2022, 212, 118116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Bian, P.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, W. Effects of irrigation on the fate of microplastics in typical agricultural soil and freshwater environments in the upper irrigation area of the Yellow River. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Liu, H.; Cui, J.; Wu, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Gao, H.; Yan, C.; He, W. The characteristics and influencing factors of farmland soil microplastic in Hetao Irrigation District, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Leng, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Microplastic pollution in vegetable farmlands of suburb Wuhan, central China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Lin, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, Z. Characteristics of Microplastic Pollution in Agricultural Soils in Xiangtan, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jia, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, J. Agricultural plastic mulching as a source of microplastics in the terrestrial environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, T.; Yang, K.; Chang, L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, B.; Li, Y. Microplastics sequestered in the soil affect the turnover and stability of soil aggregates: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Shang, L.; Zhong, R. Microplastic pollution in soils, plants, and animals: A review of distributions, effects and potential mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 157857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Kim, S.W.; Zhu, Y.-G. The soil plastisphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, X.-H.; Yu, M. Microbial colonization and degradation of marine microplastics in the plastisphere: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1127308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Shi, R.; Fu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, W. Impact of microplastics on plant physiology: A meta-analysis of dose, particle size, and crop type interactions in agricultural ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 177245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, A.; Ashour, F.H.; Hakim, A.A.A.; Bassyouni, M. Recent advances in biodegradable polymers for sustainable applications. npj Mater. Degrad. 2022, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, M.; Vogt, R.D.; Lu, X. A commonly available and easily assembled device for extraction of bio/non-degradable microplastics from soil by flotation in NaBr solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, S.S.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Prata, J.C.; Duarte, A.C.; Girão, A.V.; Lopes, P.; Cristovão, T.; da Costa, J.P. A straightforward method for microplastic extraction from organic-rich freshwater samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Physicochemical Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 8.65 |
| Salinity (mg/kg) | 510 ± 15 |
| Organic matter (g/mg) | 12.98 ± 0.34 |
| Exchangeable calcium (mg/kg) | 5400 ± 75 |
| Exchangeable magnesium (mg/kg) | 1350 ± 90 |
| Available nitrogen (mg/kg) | 118.34 ± 35.21 |
| Available phosphorus (mg/kg) | 42.99 ± 15.19 |
| Available potassium (mg/kg) | 92.33 ± 28.36 |
| Method | Size Range | Key Advantages | Major Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| FTIR [36] | 10–20 μm to 5 mm | Excellent polymer identification, Quantitative capabilities, relatively standardized | Limited spatial resolution, Time-consuming mapping |
| Raman [35] | 1 μm to 5 mm | Superior spatial resolution, no water interference, Detailed molecular information | Fluorescence interference, longer analysis times |
| Py-GC-MS [38] | Not size-specific | Excellent sensitivity, Unambiguous identification, Provides mass concentration | Destructive, No particle information, Complex sample preparation |
| LDIR | 10 μm to 5 mm | Rapid analysis, Automated counting, good sensitivity | Limited spectral range, Polymer library dependence |
| Study Location | Dominant Polymer(s) | Postulated Main Sources | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hetao Irrigation District, China | Polypropylene (PP) Polyamide (PA) | Agricultural nets, agricultural irrigation, aquaculture activities | This study |
| Vegetable farmlands of suburb Wuhan, China | Polyamide (PA) Polypropylene (PP) | Plastic mulch films, sewage and wastewater | [48] |
| Cotton fields in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China | Polyethylene (PE) | Plastic mulch films | [50] |
| Jiangshe Modern Agricultural Demonstration Park, China | Polypropylene (PP) Polyethylene (PE) Polyamide (PA) | Agricultural film, domestic wastewater | [49] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, C.M.; Feng, W.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Ngien, S.K. Extraction and Characterization of Microplastics in Soil: A Case Study from the Hetao Irrigation District. Water 2025, 17, 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182700
Ho CM, Feng W, Deng Y, Li X, Ngien SK. Extraction and Characterization of Microplastics in Soil: A Case Study from the Hetao Irrigation District. Water. 2025; 17(18):2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182700
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Chia Min, Weiying Feng, Yuxin Deng, Xiaofeng Li, and Su Kong Ngien. 2025. "Extraction and Characterization of Microplastics in Soil: A Case Study from the Hetao Irrigation District" Water 17, no. 18: 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182700
APA StyleHo, C. M., Feng, W., Deng, Y., Li, X., & Ngien, S. K. (2025). Extraction and Characterization of Microplastics in Soil: A Case Study from the Hetao Irrigation District. Water, 17(18), 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182700







