A Practical Model Framework for Describing the Flow of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in a Cascade Reservoir Watershed
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
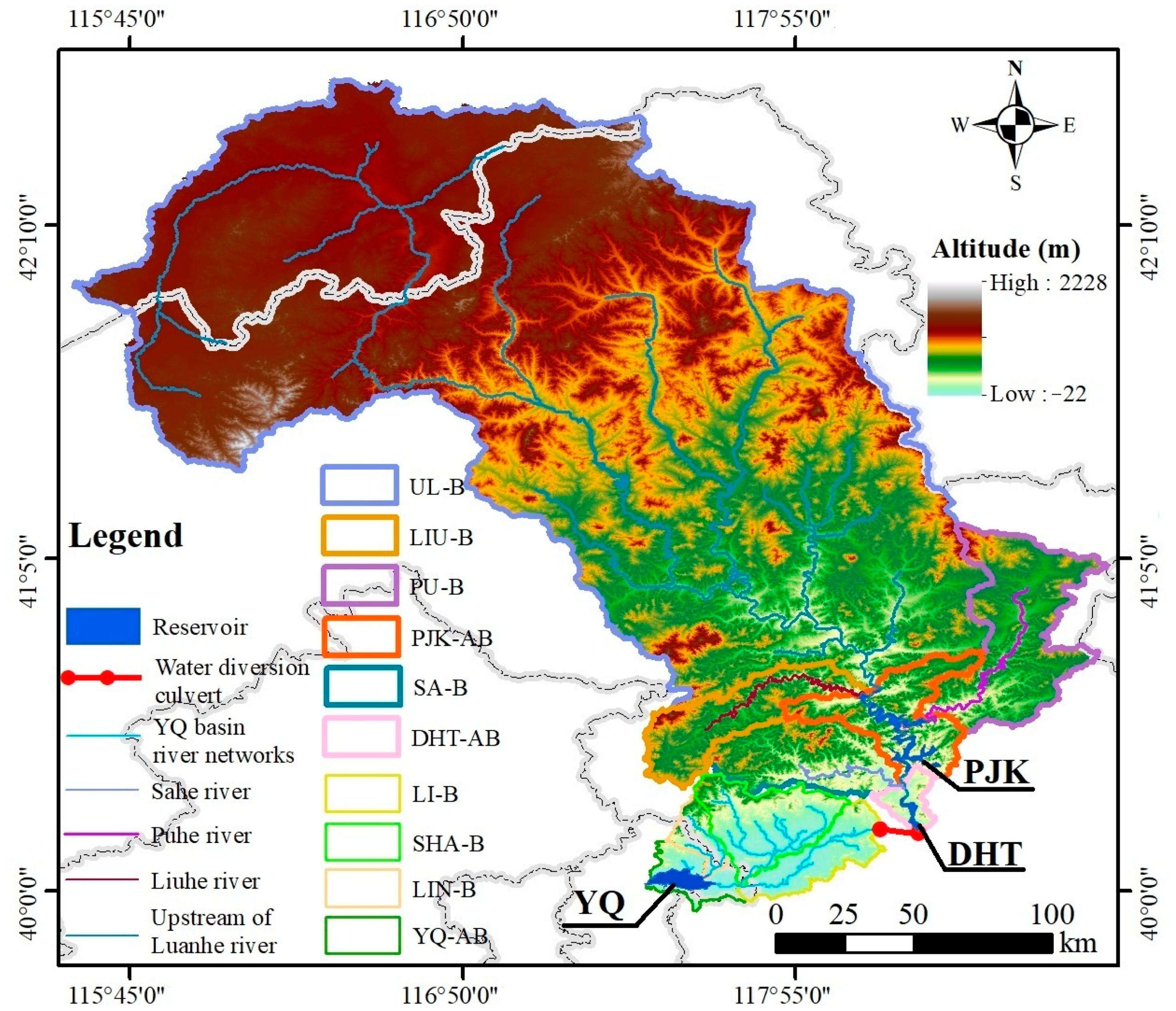
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Meteorological Data
2.2.2. Land Use Land Cover (LULC) and Population
2.2.3. Water Quality and Pollution Source Data
2.2.4. Hydrological Data
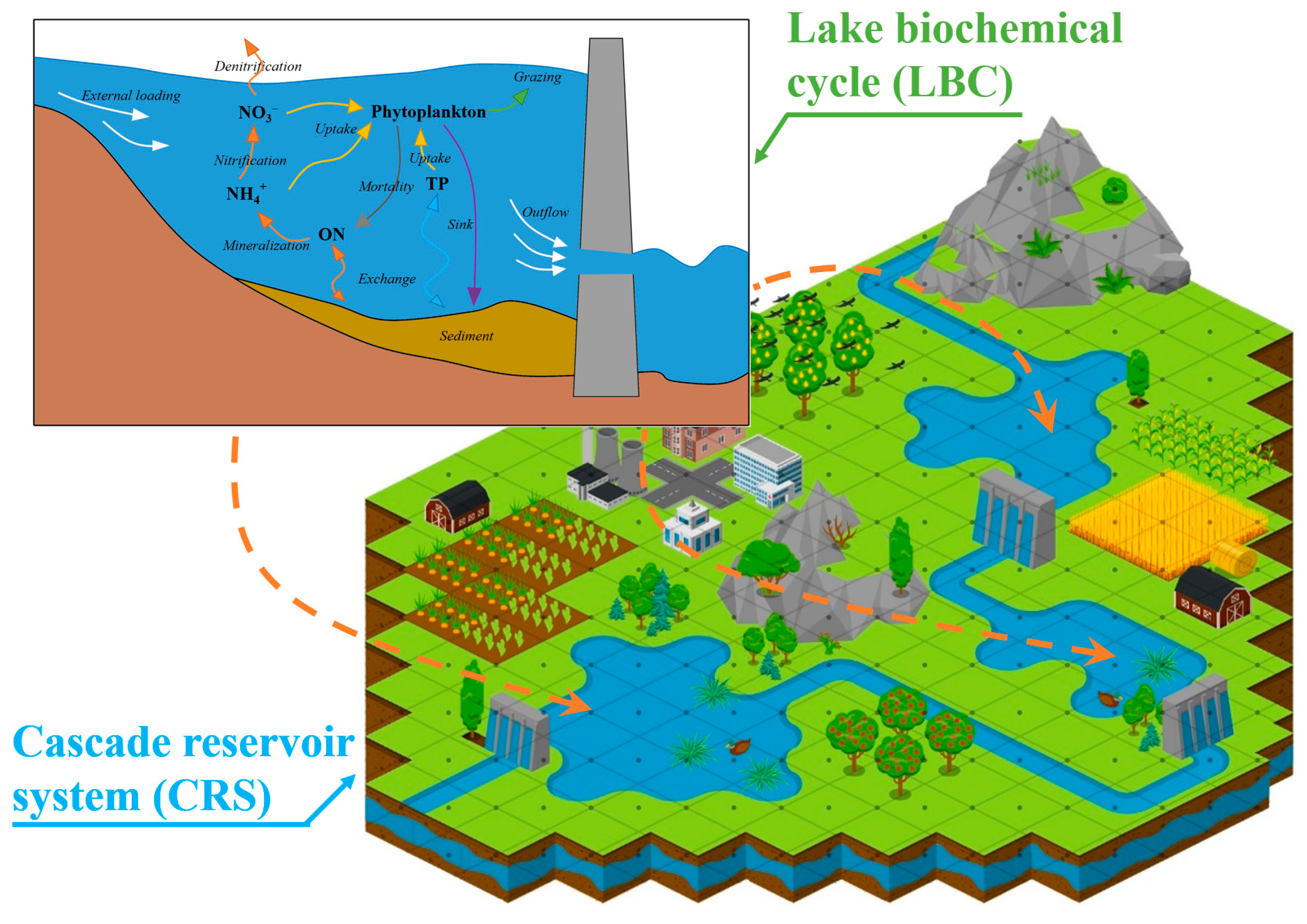
2.3. Watershed Water Quality Model
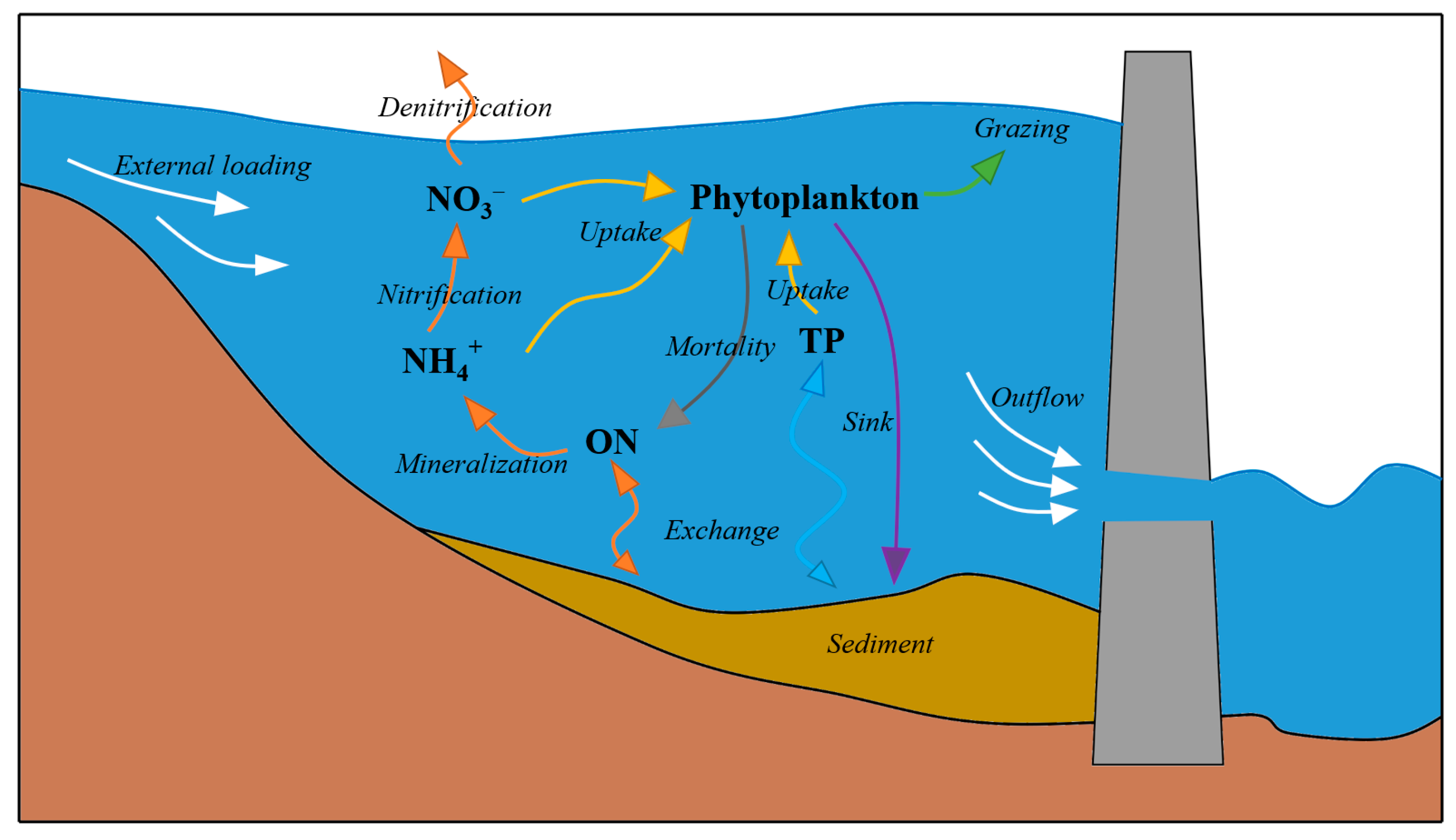
2.4. Lake and Reservoir Water Quality Model
3. Results
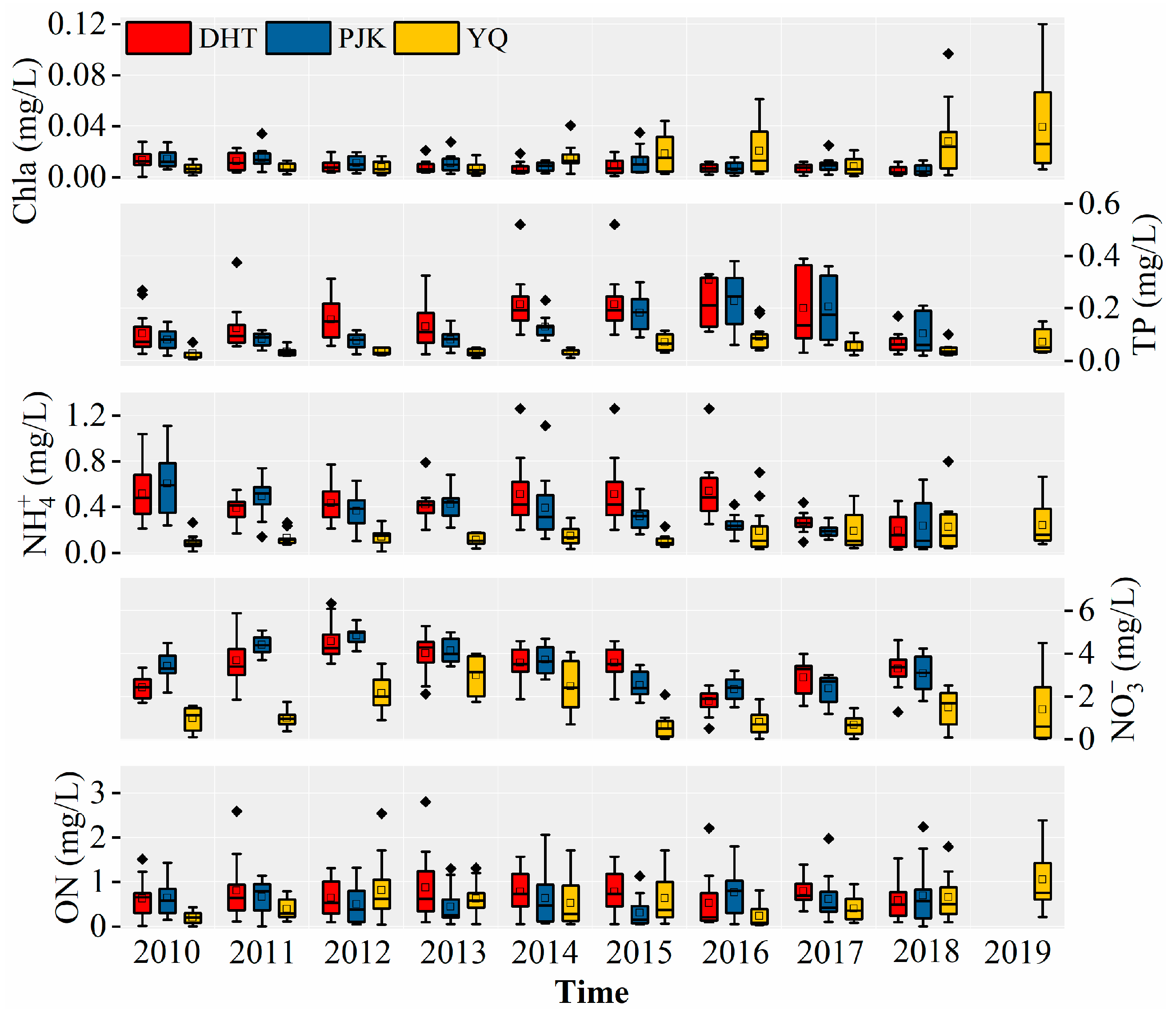
3.1. The Trend of Water Quality
3.2. Simulation of Three Reservoirs by IHBLM
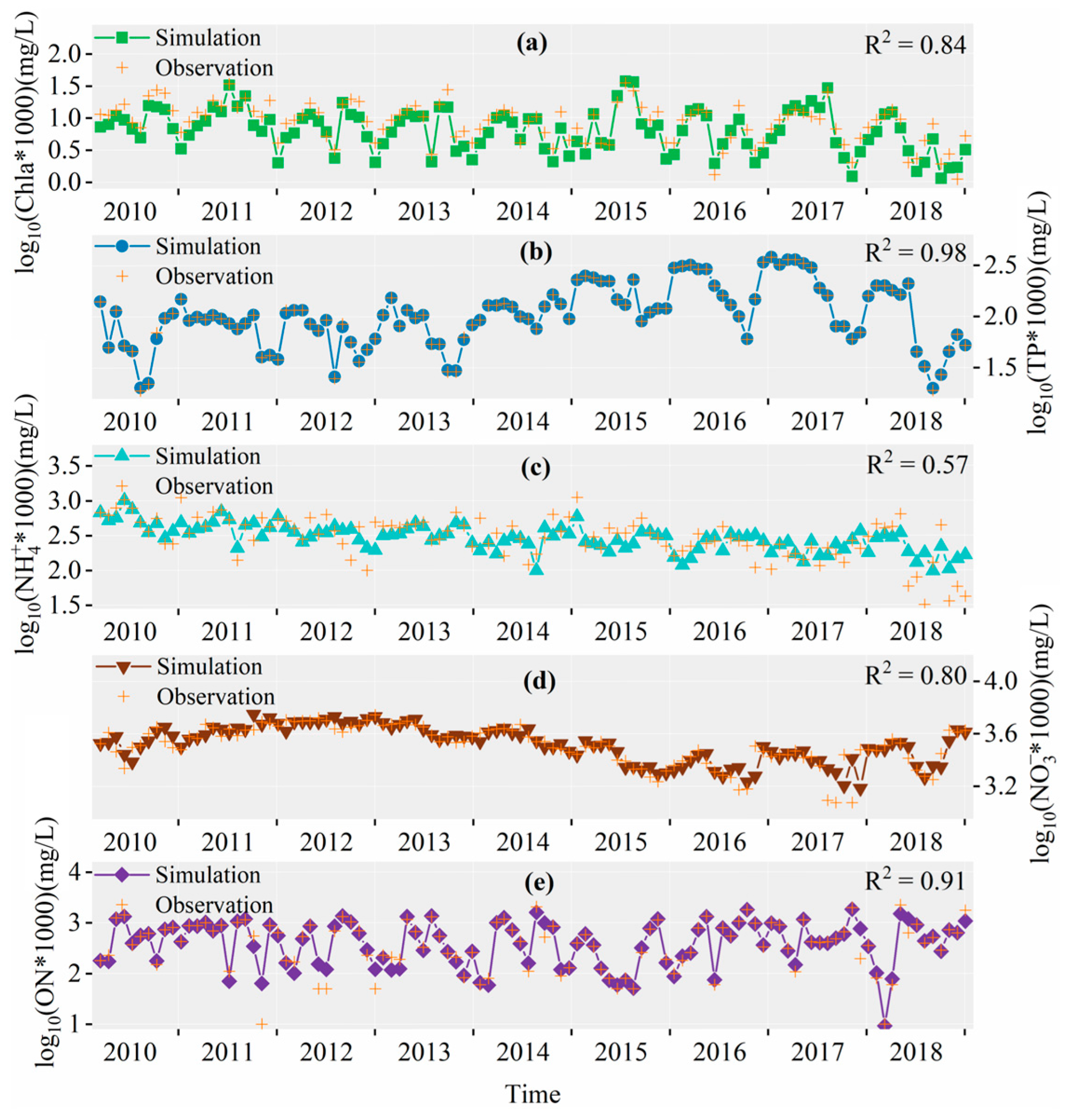
3.2.1. Simulation Results of PJK
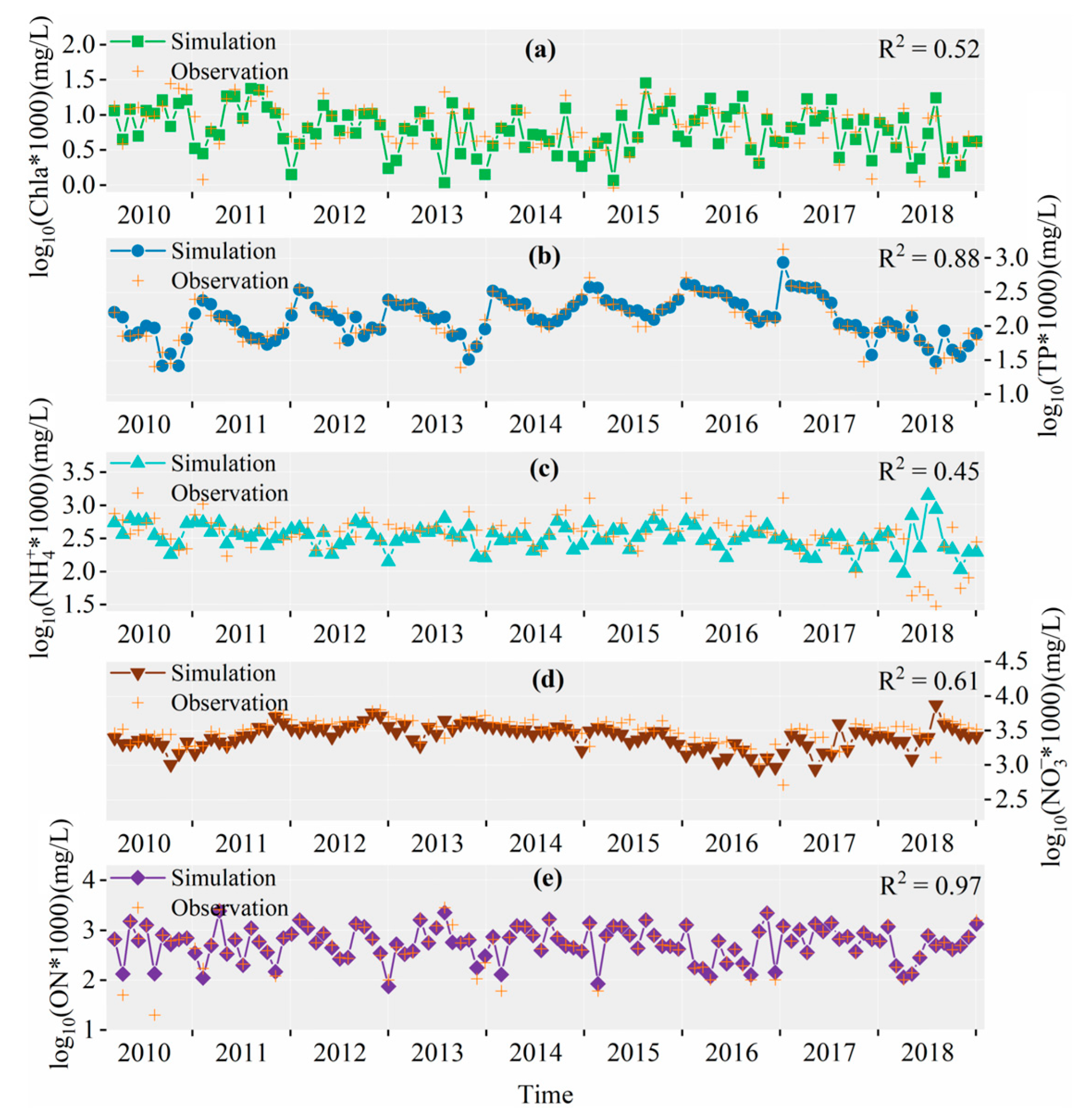
3.2.2. Simulation Results of DHT
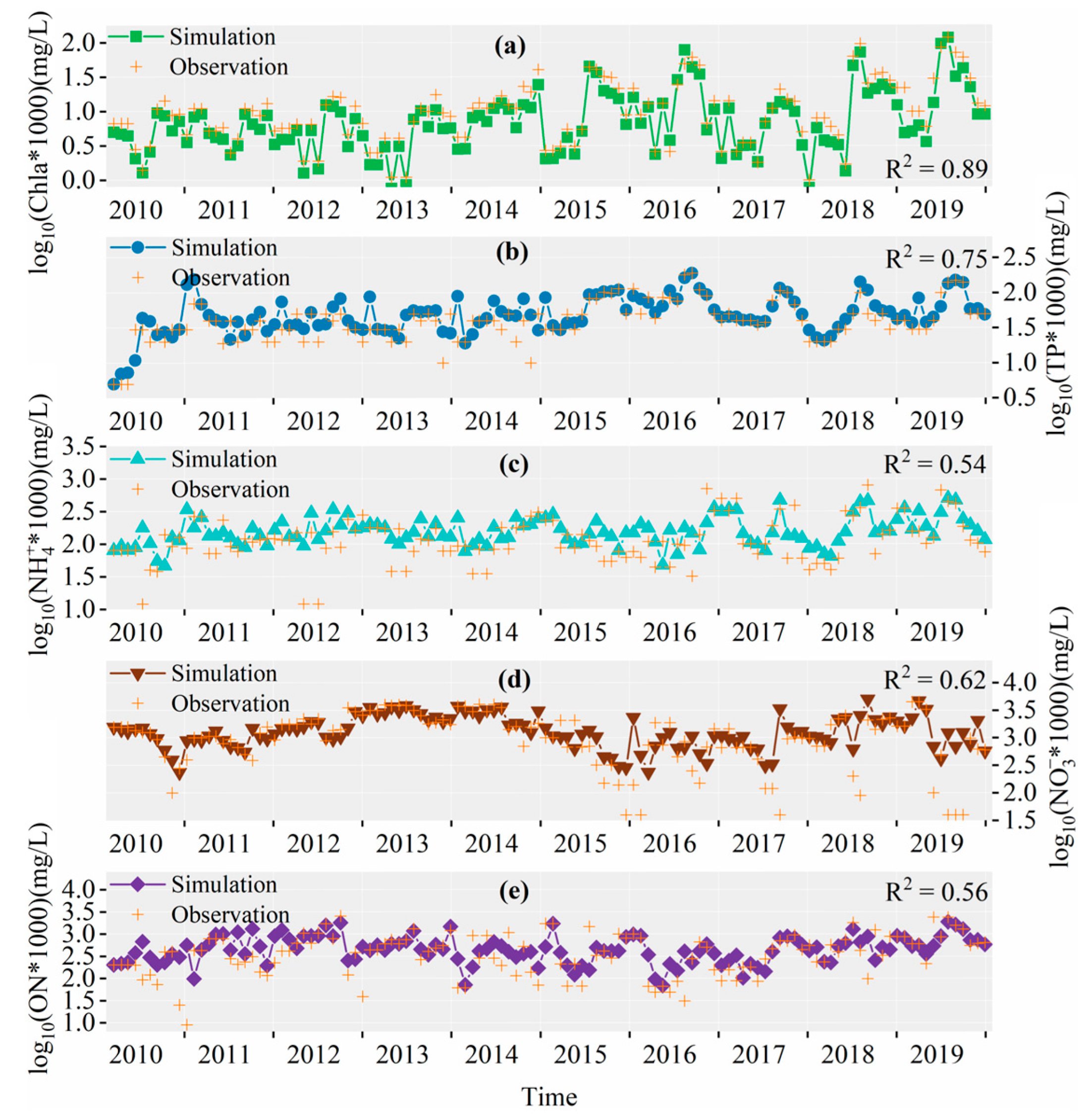
3.2.3. Simulation Results of YQ
3.2.4. Simulation Error Analysis
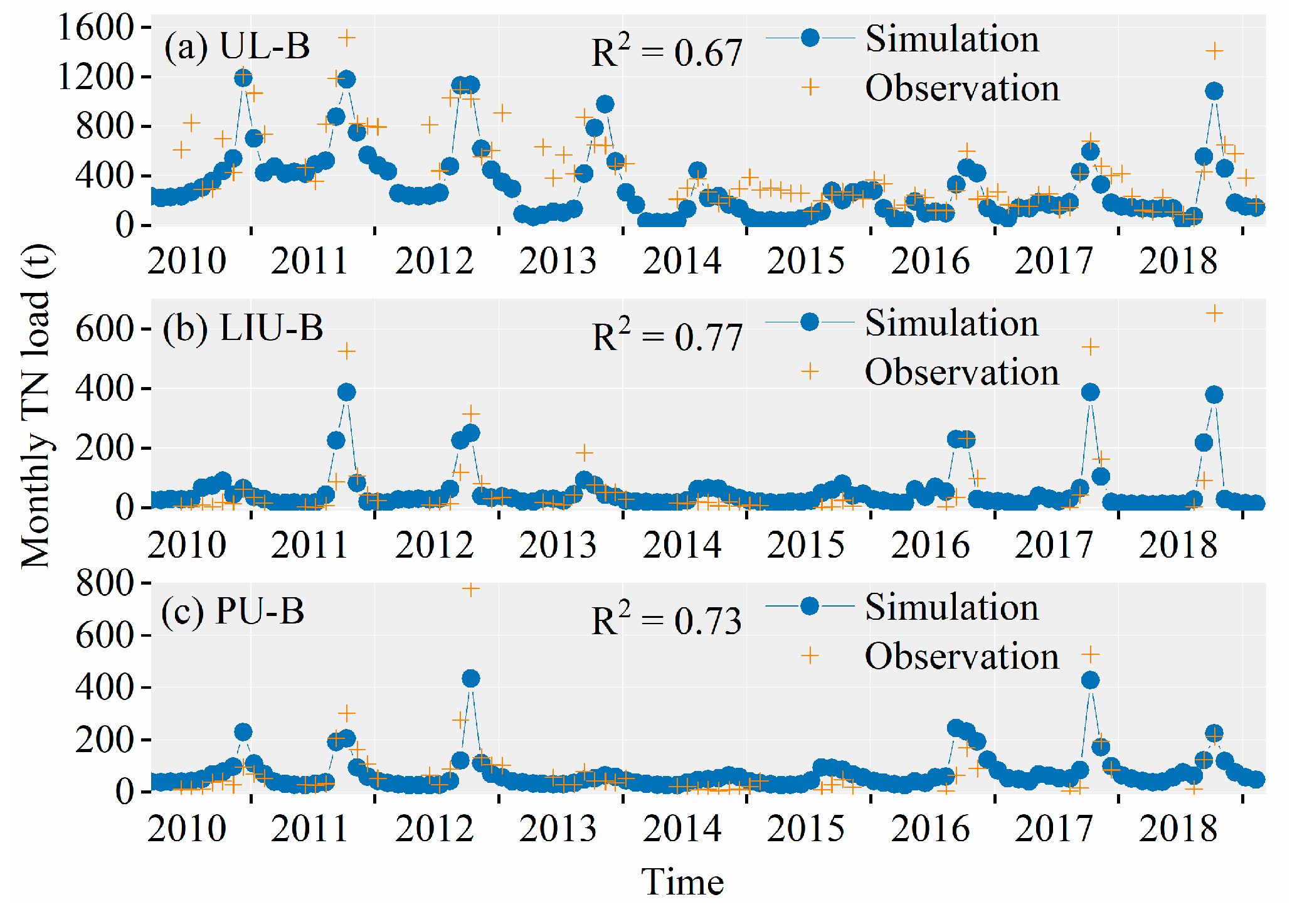
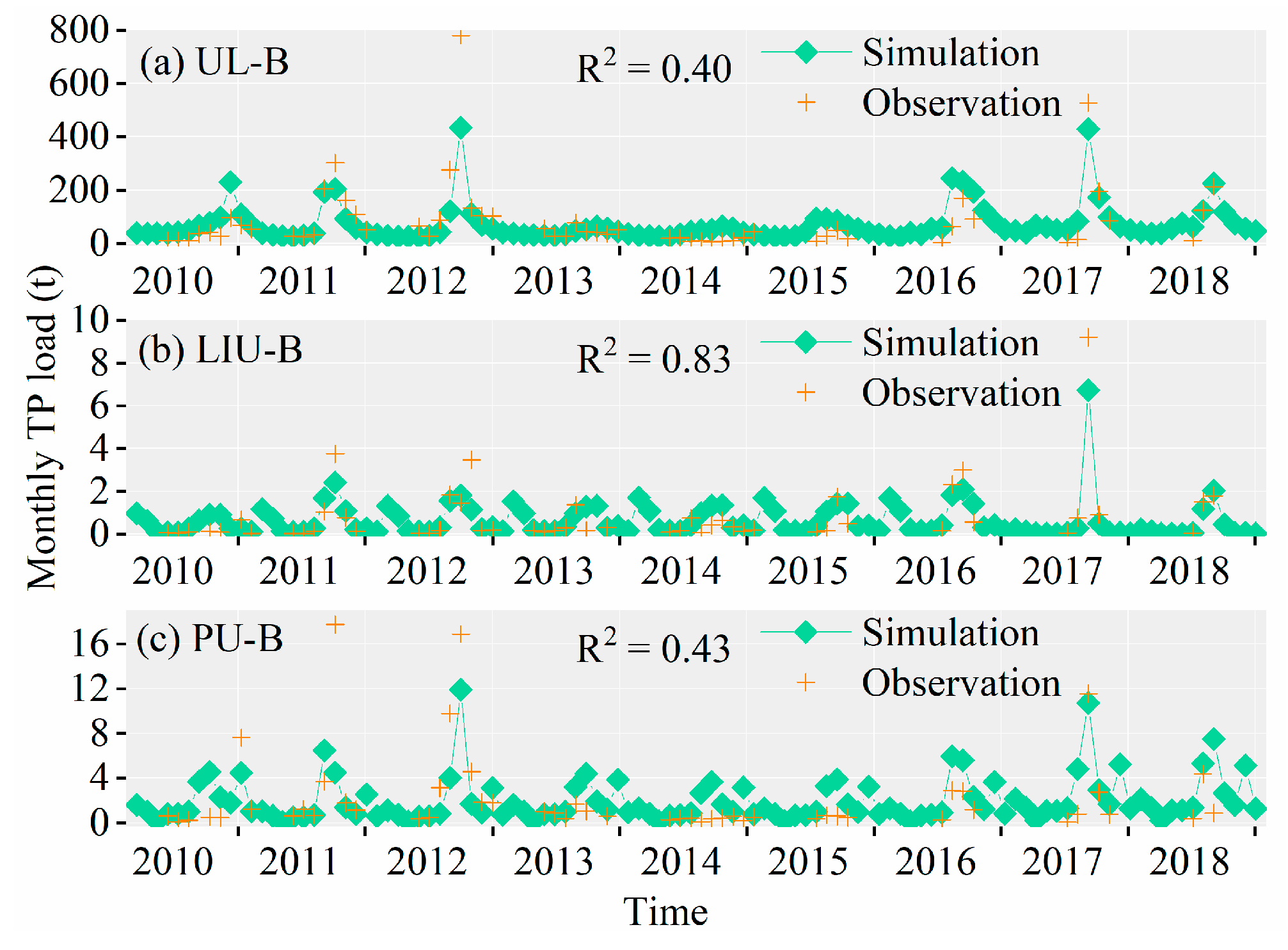
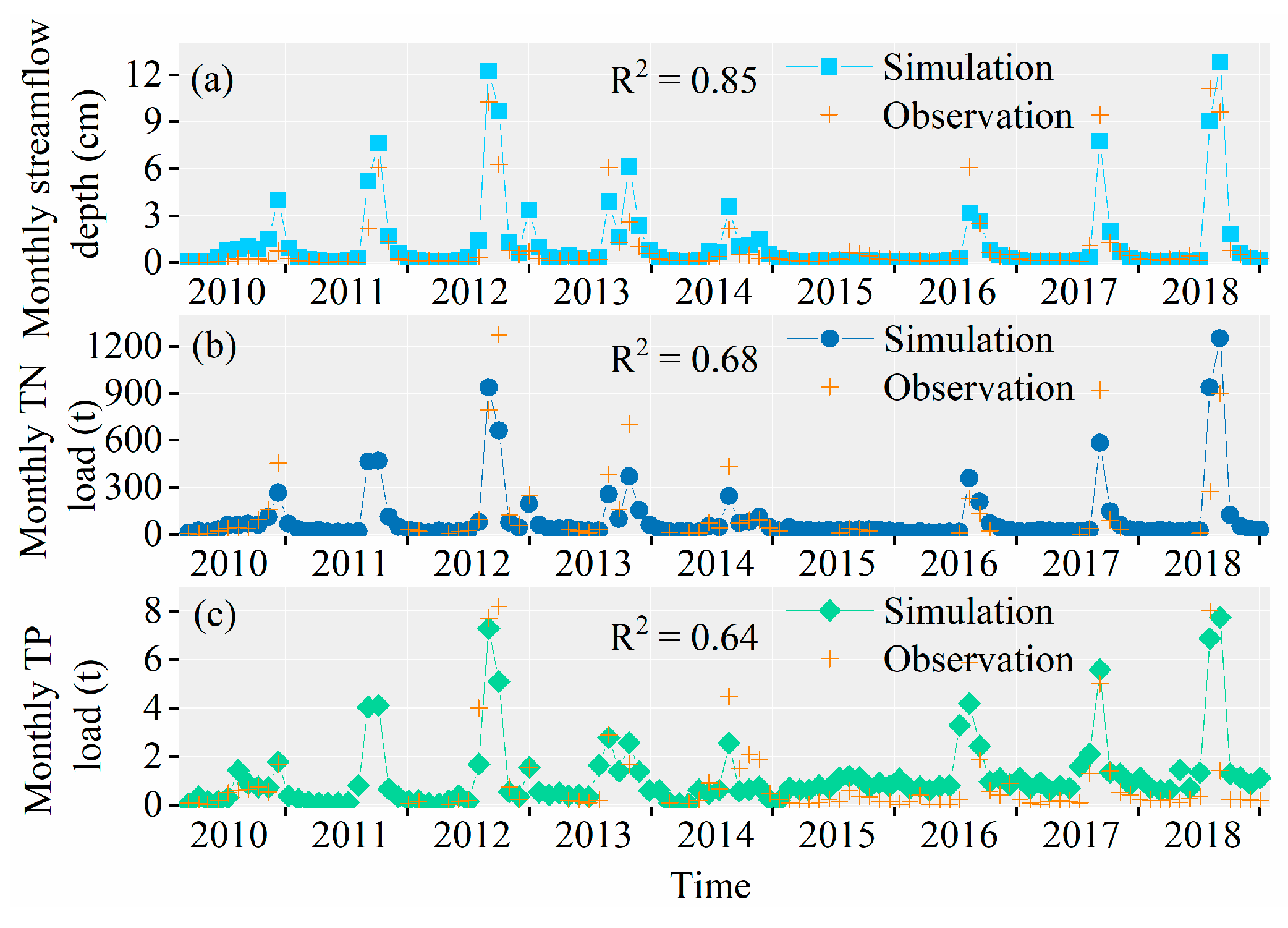
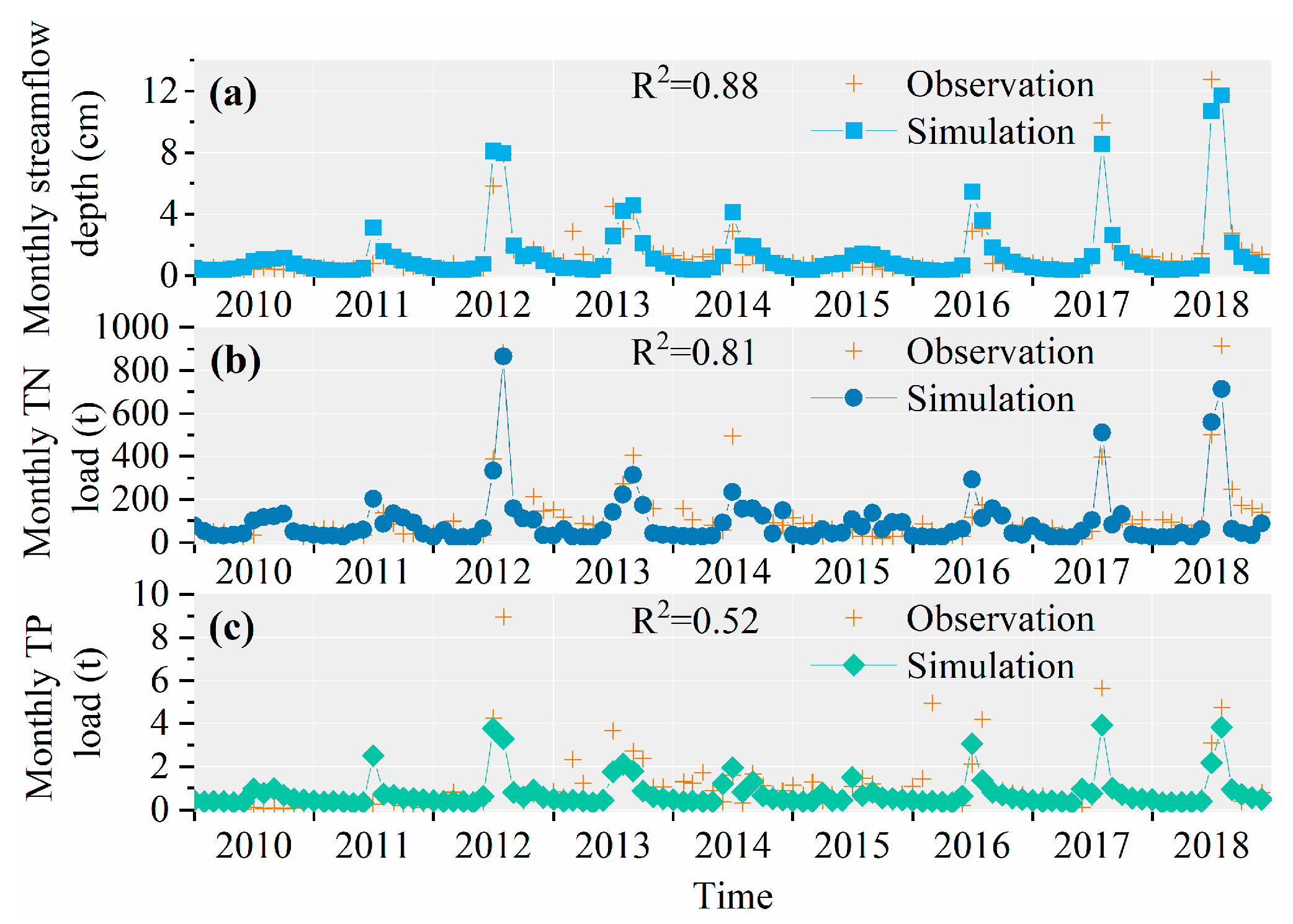
3.3. Simulation of TN and TP Load for WDBLT by ReNuMa
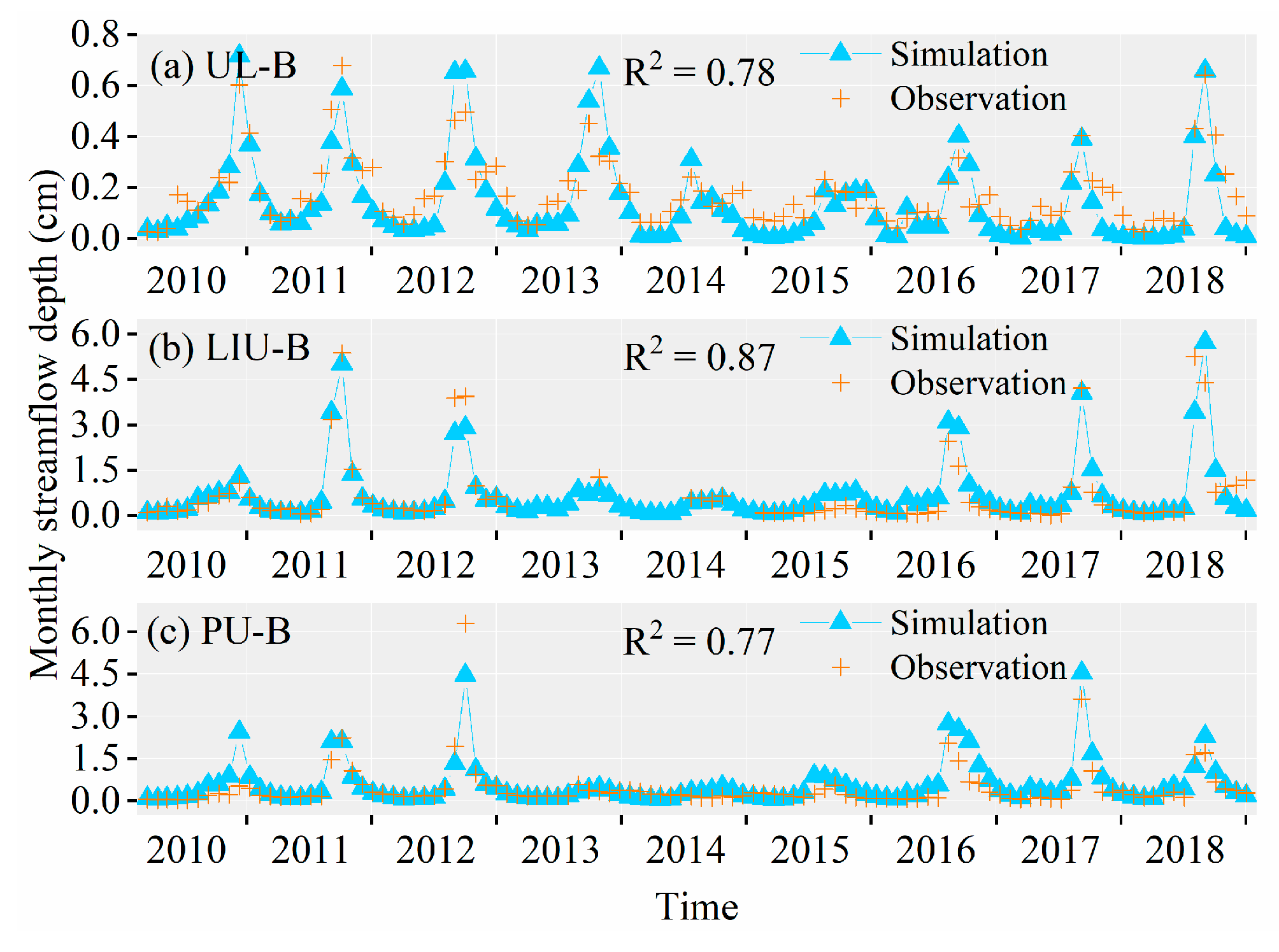
3.3.1. Simulation Results of PJK Watershed
3.3.2. Simulation Results of DHT Watershed
3.3.3. Simulation Results of YQ Watershed
4. Discussion
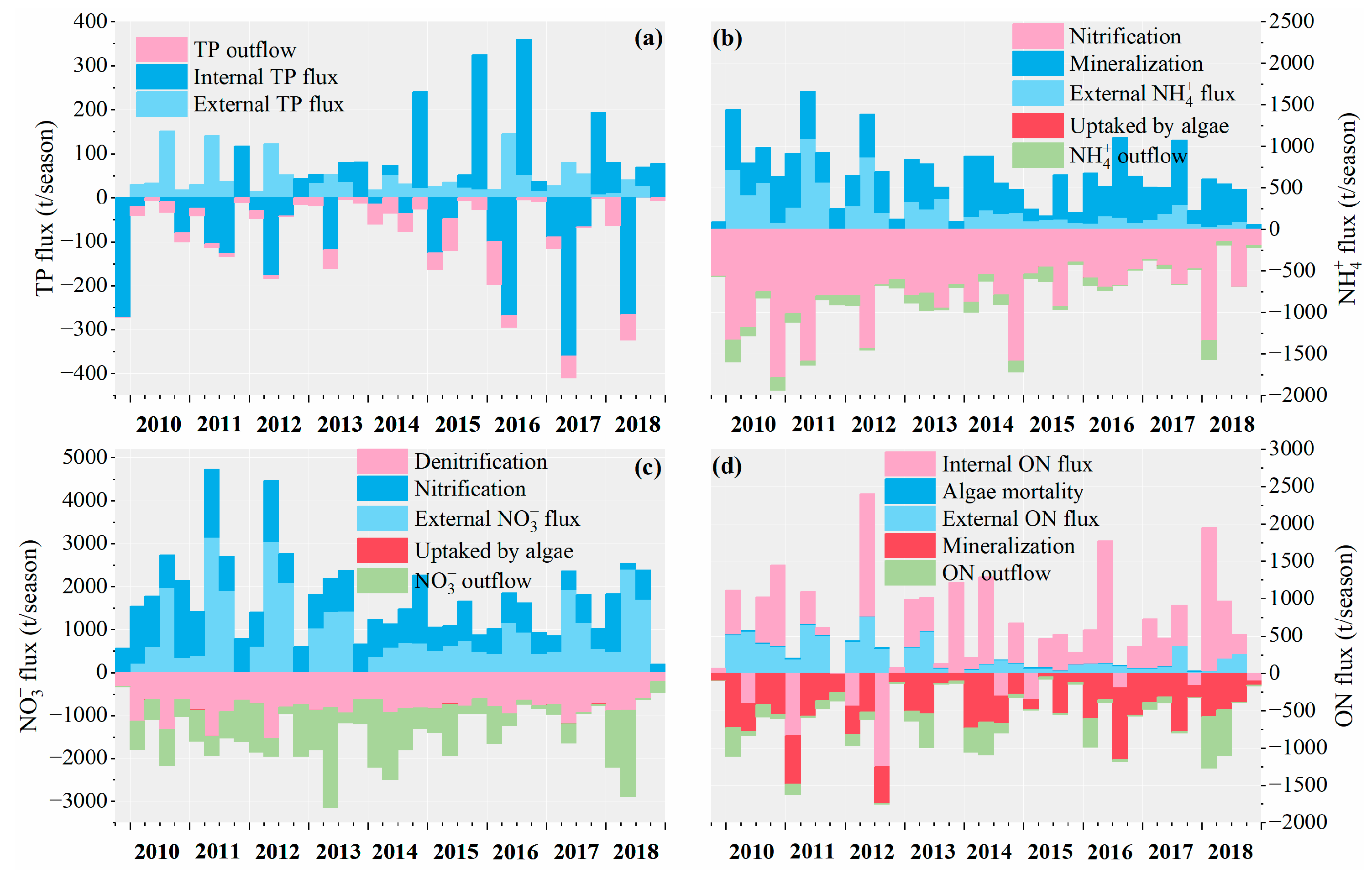
4.1. The Flux Analysis of Reservoir Biochemical Processes
4.1.1. Seasonal Flux of PJK
- (1)
- Total Phosphorus Flux
- (2)
- Ammonia Nitrogen Flux
- (3)
- Nitrate Nitrogen Flux
- (4)
- Organic Nitrogen Flux
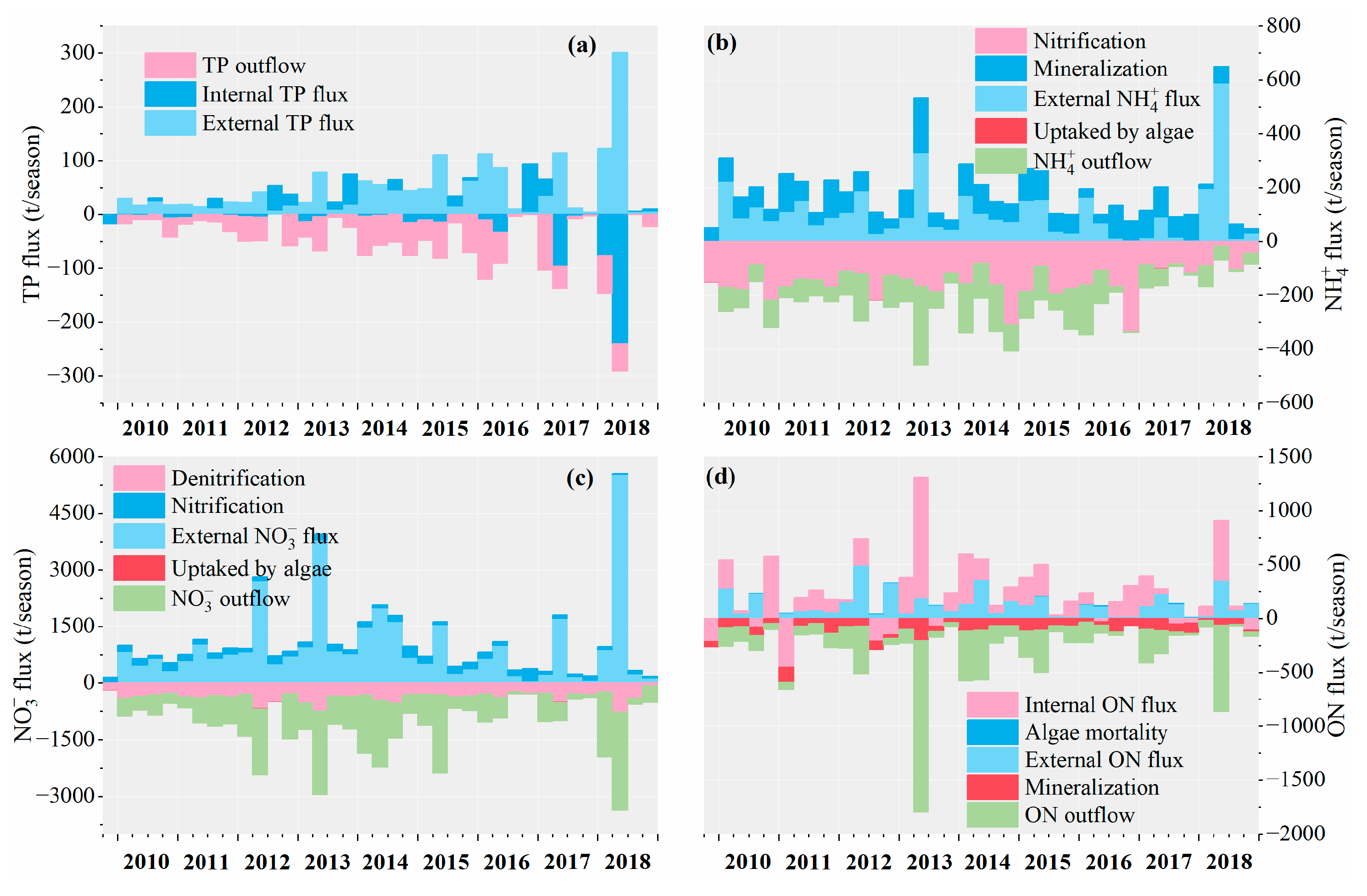
4.1.2. Seasonal Flux of DHT
- (1)
- Total Phosphorus Flux
- (2)
- Ammonia Nitrogen Flux
- (3)
- Nitrate Nitrogen Flux
- (4)
- Organic Nitrogen Flux
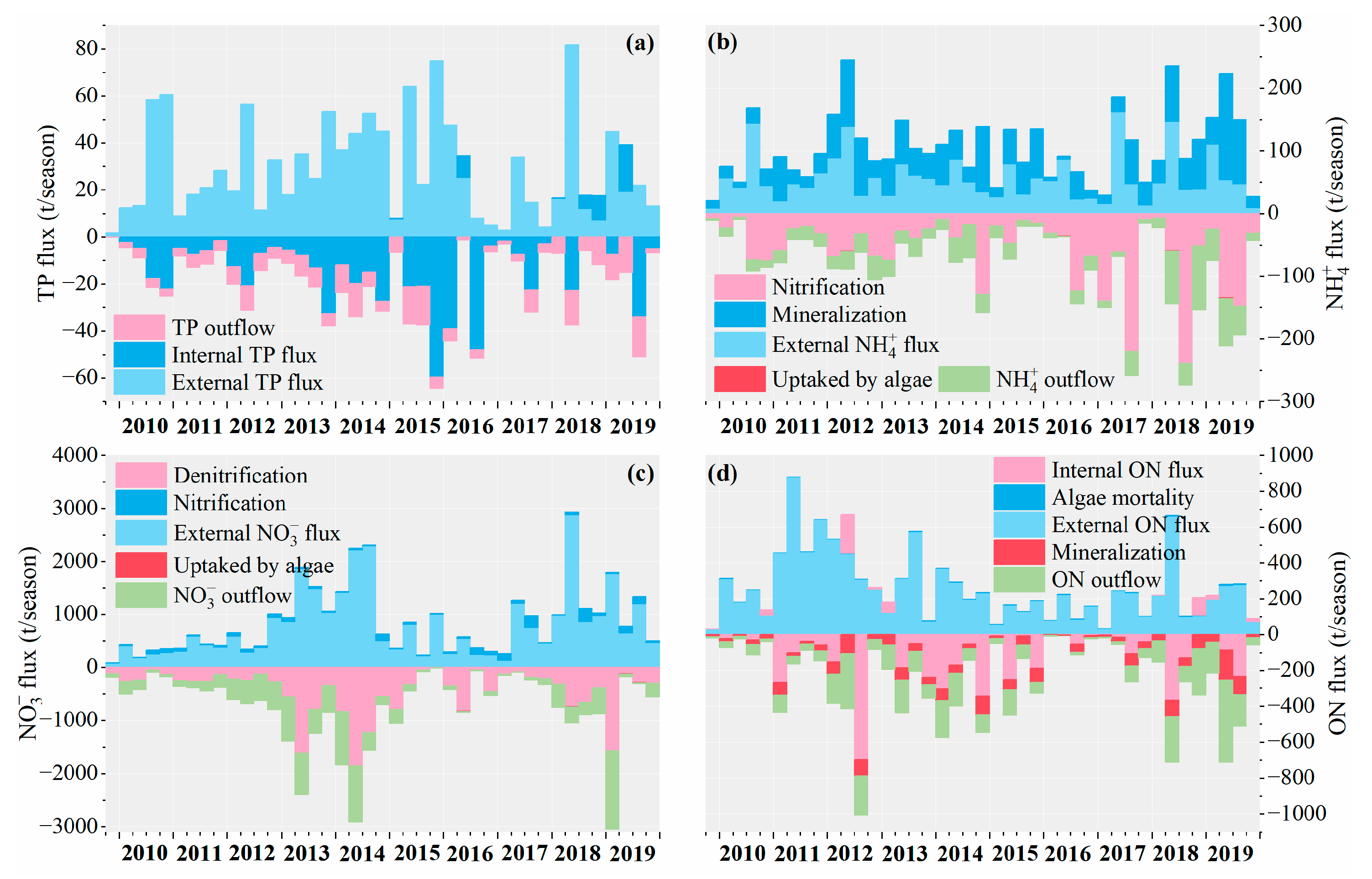
4.1.3. Seasonal Flux of YQ
- (1)
- Total Phosphorus Flux
- (2)
- Ammonia Nitrogen Flux
- (3)
- Nitrate Nitrogen Flux
- (4)
- Organic Nitrogen Flux
4.1.4. Monthly Flux and Annual Flux of Three Reservoirs
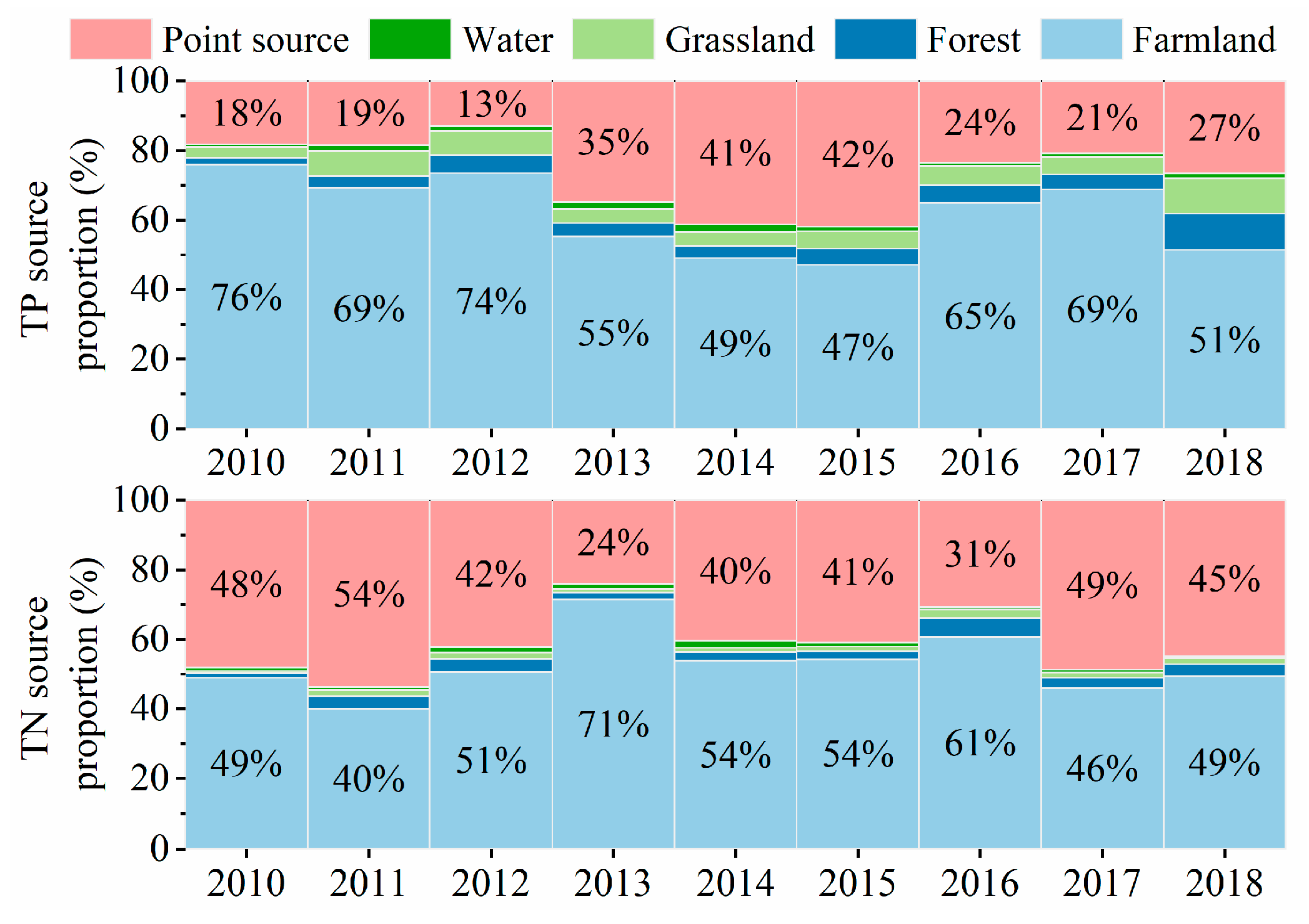
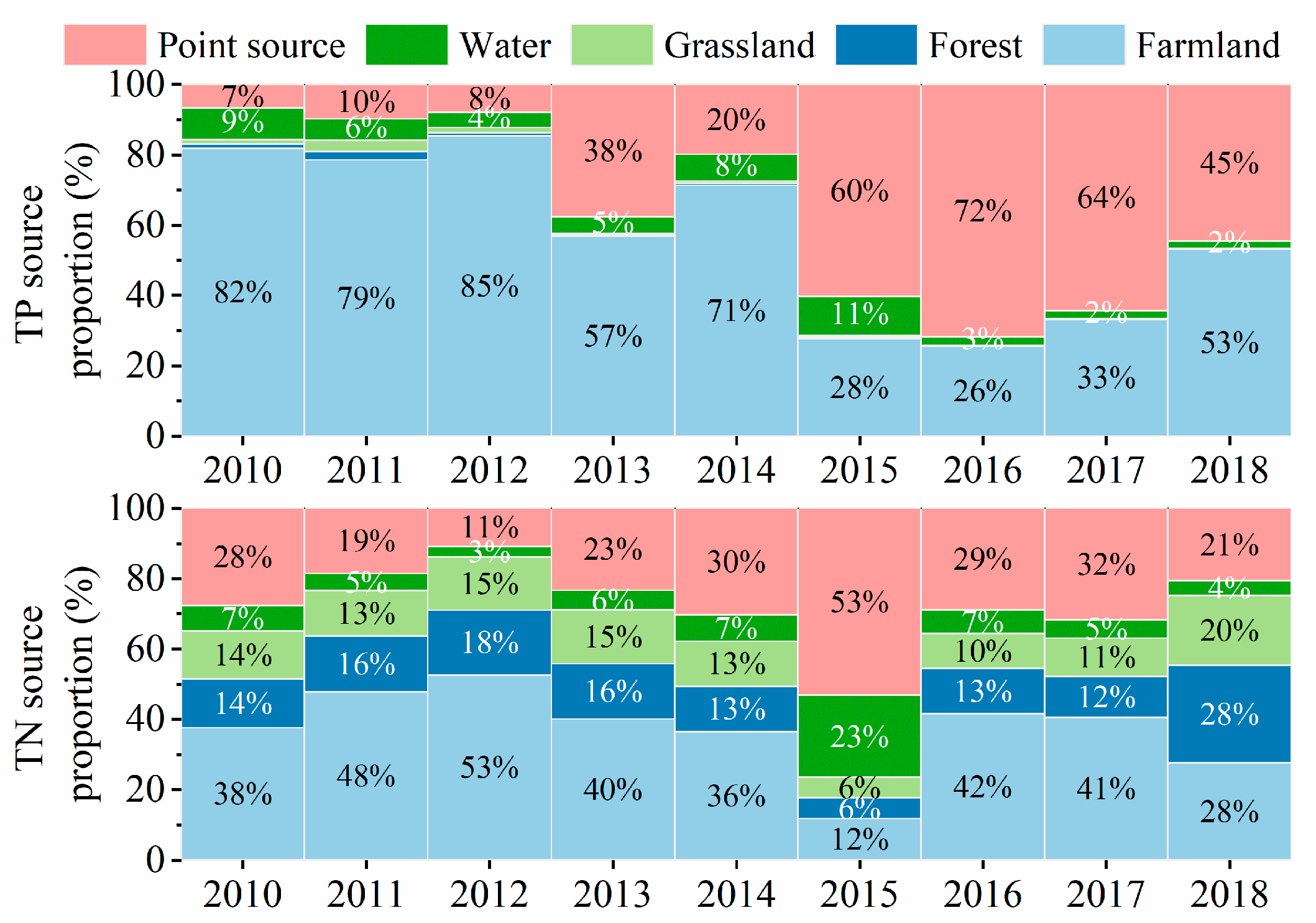
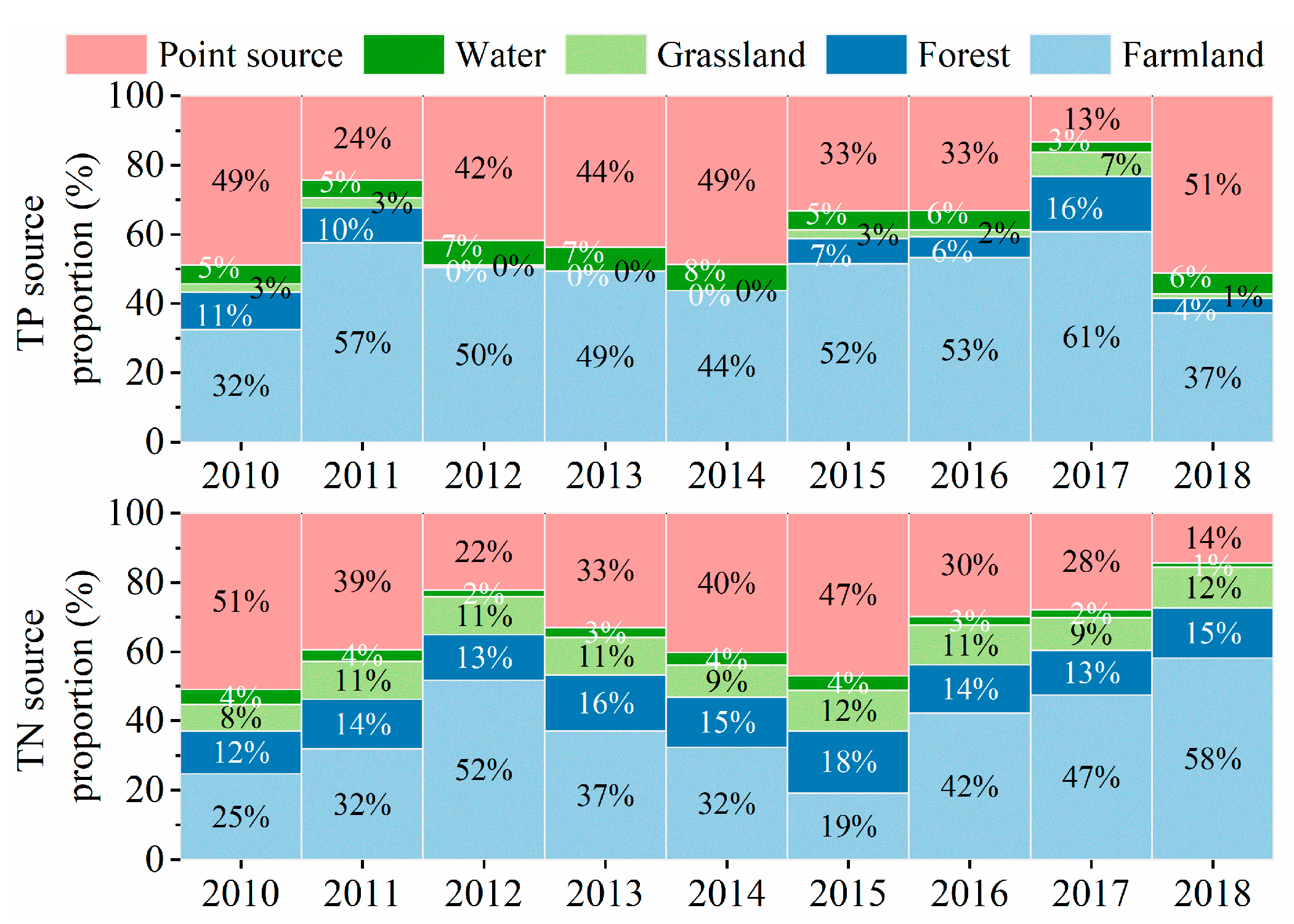
4.2. Source Analysis of TN and TP for WDBLT
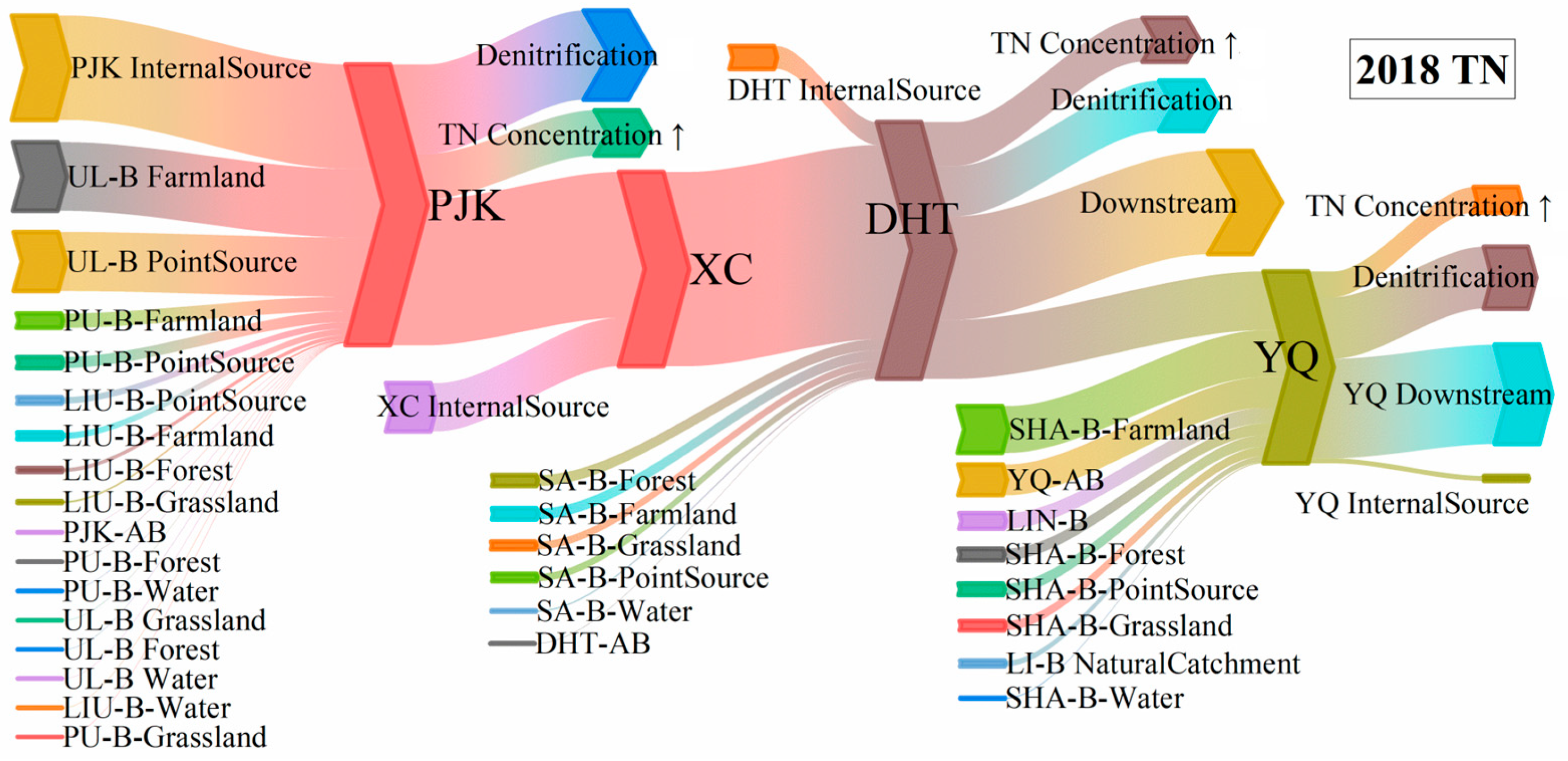
4.3. Substance Flow of TN and TP for WDBLT
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.F.; Lu, X.X.; Walling, D.E.; Zhang, T.; Steiner, J.F.; Wasson, R.J.; Harrison, S.; Nepal, S.; Nie, Y.; Immerzeel, W.W.; et al. High Mountain Asia hydropower systems threatened by climate-driven landscape instability. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.N.; Fang, G.H.; Wen, X.; Tan, Q.F.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Z.H. Coordinated operation of conventional hydropower plants as hybrid pumped storage hydropower with wind and photovoltaic plants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 277, 116654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Milliman, J.D.; Xu, K.H.; Deng, B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Luo, X.X. Downstream sedimentary and geomorphic impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.L.; Zuo, Q.T.; Wu, Q.S.; Li, Q.W.; Ma, J.X. Achieving the tradeoffs between pollutant discharge and economic benefit of the Henan section of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project through water resources-environment system management under uncertainty. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, D.; Swaney, D.P.; Wang, Y.Q. Application of the ReNuMa model in the Sha He river watershed: Tools for watershed environmental management. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 124, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.G.; Liu, Q.Y.; Tillotson, M.R.; Guan, D.B.; Hubacek, K. Physical and virtual water transfers for regional water stress alleviation in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Gao, B.; Xu, D.Y.; Peng, W.Q.; Liu, X.B.; Qu, X.D.; Zhang, M. Hydrodynamic impact on trace metals in sediments in the cascade reservoirs, North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.C.; Tang, W.Z.; Webber, M. Can interbasin water transfer affect water consumption and pollution? Lessons from China’s South-North water transfer project. Environ. Policy Gov. 2020, 30, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maavara, T.; Akbarzadeh, Z.; Van Cappellen, P. Global Dam-Driven Changes to Riverine N:P:Si Ratios Delivered to the Coastal Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maavara, T.; Chen, Q.W.; Van Meter, K.; Brown, L.E.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ni, J.R.; Zarfl, C. River dam impacts on biogeochemical cycling. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maavara, T.; Parsons, C.T.; Ridenour, C.; Stojanovic, S.; Dürr, H.H.; Powley, H.R.; Van Cappellen, P. Global phosphorus retention by river damming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15603–15608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Deng, Y.; Xing, X.; Yuan, Q.; Du, C.; Gan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Y.; et al. Impacts of cascade hydropower development on river ecosystem homeostasis: A review. J. Hydrol. 2024, 638, 131484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yan, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Tang, J.; et al. Impact of cascade reservoirs on nutrients transported downstream and regulation method based on hydraulic retention time. Water Res. 2024, 252, 121187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, W.; Srinivasan, R.; Pérez-Miñana, E.; Willcock, S.P.; Quintero, M. Using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) to model ecosystem services: A systematic review. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.P.; Liu, Y.M.; Wang, J.H.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Chen, D.J. A modification of the Regional Nutrient Management model (ReNuMa) to identify long-term changes in riverine nitrogen sources. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R.B.; Elliott, A.H.; Shankar, U.; McBride, G.B. Estimating the sources and transport of nutrients in the Waikato River Basin, New Zealand. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 4-1–4-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R.B.; Smith, R.A.; Schwarz, G.E. Effect of stream channel size on the delivery of nitrogen to the Gulf of Mexico. Nature 2000, 403, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Kaluskar, S.; Mugalingam, S.; Blukacz-Richards, A.; Long, T.Y.; Morley, A.; Arhonditsis, G.B. A Bayesian approach for estimating phosphorus export and delivery rates with the SPAtially Referenced Regression On Watershed attributes (SPARROW) model. Ecol. Inform. 2017, 37, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debele, B.; Srinivasan, R.; Parlange, J.Y. Coupling upland watershed and downstream waterbody hydrodynamic and water quality models (SWAT and CE-QUAL-W2) for better water resources management in complex river basins. Environ. Model. Assess. 2008, 13, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhi, X.; Meng, X.; Shen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; et al. The cumulative effects of cascade reservoirs control nitrogen and phosphorus flux: Base on biogeochemical processes. Water Res. 2024, 252, 121177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, J.; Moridi, A. Interactive Reservoir-Watershed Modeling Framework for Integrated Water Quality Management. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 2105–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, S.M. Modeling the Physical and Biogeochemical Processes in Lake Superior Using LAKE2K. Master’s Thesis, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, K.; Thattaramppilly, R.M.; Manisha, M.; Jayakumar, S.; Marigoudar, S.R.; Pranesh, A.T.; Rao, L. Determination of degradation/reaction rate for surface water quality of recycled water using Lake2K model for large-scale water recycling. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 120207–120224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Zhang, X.D.; Chu, X.F.; Zheng, H.C. Automatic Calibration for CE-QUAL-W2 Model Using Improved Global-Best Harmony Search Algorithm. Water 2021, 13, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.D.; Xu, X.W.; Qi, M.; Sun, J.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.Z.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, Y. Lake warming intensifies the seasonal pattern of internal nutrient cycling in the eutrophic lake and potential impacts on algal blooms. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Huang, M.T.; Wang, R.H. Numerical Simulation of Donghu Lake Hydrodynamics and Water Quality Based on Remote Sensing and MIKE 21. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.W.; Li, M. The Simulation of Shallow Reservoir Eutrophication Based on MIKE21: A Case Study of Douhe Reservoir in North China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1975–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.T.; Wible, T.C.; Arabi, M.; Records, R.M.; Ditty, J. Assessing regional-scale spatio-temporal patterns of groundwater-surface water interactions using a coupled SWAT-MODFLOW model. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 4420–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajib, A.; Liu, Z.; Merwade, V.; Tavakoly, A.A.; Follum, M.L. Towards a large-scale locally relevant flood inundation modeling framework using SWAT and LISFLOOD-FP. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B.; Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, P.K.; Talchabhadel, R. Evaluation and application of a SWAT model to assess the climate change impact on the hydrology of the Himalayan River Basin. Catena 2019, 181, 104082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.; Arnold, J.G.; Gassman, P.W.; Giorgi, F.; Gu, R.R. Climate change sensitivity assessment on Upper Mississippi River Basin streamflows using SWAT. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 42, 997–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xu, Y.P.; Chen, Y.; Xu, C.Y.; Gao, Y.Q.; Du, J.K. Hydrological response to urbanization at different spatio-temporal scales simulated by coupling of CLUE-S and the SWAT model in the Yangtze River Delta region. J. Hydrol. 2013, 485, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Z.Y.; Wu, S.F.; Guo, H.C. Internal cycling, not external loading, decides the nutrient limitation in eutrophic lake: A dynamic model with temporal Bayesian hierarchical inference. Water Res. 2017, 116, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.Z.; Xu, X.W.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.Q.; Sun, P.Z.; Wen, Y.T.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.J.; et al. Seasonal Pattern of Nutrient Limitation in a Eutrophic Lake and Quantitative Analysis of the Impacts from Internal Nutrient Cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13675–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.L.; Yin, J.C.; Cui, N.X.; Ding, H.; Wang, S.M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Qi, Z.D. The Long-Term and Retention Impacts of the Intervention Policy for Cage Aquaculture on the Reservoir Water Qualities in Northern China. Water 2020, 12, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, S.Y.; Liu, X.B.; Zhou, H.D.; Li, B.D.; Du, Y.L.; Wang, L. Characteristics of water quality response to hypolimnetic anoxia in Daheiting Reservoir. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dong, M.Y.; Xu, D.X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X. Using a water quality index to assess the water quality of the upper and middle streams of the Luanhe River, northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, G.L.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, Q.X.; Qi, Z.D.; Sun, Y.T.; Wang, Y.Q. Exploration of the critical factors influencing the water quality in two contrasting climatic regions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12601–12612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.D.; Kang, G.L.; Chu, C.L.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.Q. Comparison of SWAT and GWLF Model Simulation Performance in Humid South and Semi-Arid North of China. Water 2017, 9, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.D.; Kang, G.L.; Shen, M.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chu, C.L. The Improvement in GWLF Model Simulation Performance in Watershed Hydrology by Changing the Transport Framework. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, A.P.; Baker, P.A.; Fritz, S.C.; Poulter, B. Climate-mediated nitrogen and carbon dynamics in a tropical watershed. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2011, 116, G02013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chave, J. The problem of pattern and scale in ecology: What have we learned in 20years? Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, A. Timescales, dynamics, and ecological understanding. Ecology 2010, 91, 3471–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Ren, Q.R.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, H.T.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, Z.L. Rain Pattern Deeply Reshaped Total Phosphorus Load Pattern in Watershed: A Case Study from Northern China. Water 2023, 15, 2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.L.; Wang, H.W.; Wu, T.; Yang, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhong, J.C. Vertical profiles of phosphorus fractions in the sediment in a chain of reservoirs in North China: Implications for pollution source, bioavailability, and eutrophication. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Li, Z.L.; Ren, Q.R.; Chen, H.T.; Song, M.L.; Wang, Y.Q. Single-variable method for predicting trends in chlorophyll a concentration based on the similarity of time series. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 109027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbie, S.E.; Finlay, J.C.; Janke, B.D.; Nidzgorski, D.A.; Millet, D.B.; Baker, L.A. Contrasting nitrogen and phosphorus budgets in urban watersheds and implications for managing urban water pollution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4177–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Reservoir | River | Sub-Basin |
|---|---|---|
| PJK | Upstream of Luanhe River | Upstream of Luanhe River basin (UL-B) |
| Liuhe River | Liuhe River basin (LIU-B) | |
| Puhe River | Puhe River basin (PU-B) | |
| Rivers around PJK | PJK around basin (PJK-AB) | |
| DHT | Sahe River | Sahe River basin (SA-B) |
| Rivers around DHT | DHT around basin (DHT-AB) | |
| YQ | Shahe River | Shahe River basin (SHA-B) |
| Lihe River | Lihe River basin (LI-B) | |
| Linhe River | Linhe River basin (LIN-B) | |
| Rivers around YQ | YQ around basin (YQ-AB) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, H.; Han, L.; Li, Z.; Han, T.; Jiang, W.; Kang, G.; Wang, Q. A Practical Model Framework for Describing the Flow of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in a Cascade Reservoir Watershed. Water 2025, 17, 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162479
Ding H, Han L, Li Z, Han T, Jiang W, Kang G, Wang Q. A Practical Model Framework for Describing the Flow of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in a Cascade Reservoir Watershed. Water. 2025; 17(16):2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162479
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Han, Long Han, Zeli Li, Tong Han, Wei Jiang, Gelin Kang, and Qiulian Wang. 2025. "A Practical Model Framework for Describing the Flow of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in a Cascade Reservoir Watershed" Water 17, no. 16: 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162479
APA StyleDing, H., Han, L., Li, Z., Han, T., Jiang, W., Kang, G., & Wang, Q. (2025). A Practical Model Framework for Describing the Flow of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in a Cascade Reservoir Watershed. Water, 17(16), 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162479





