Phytoremediation of Zinc-Contaminated Industrial Effluents with Phragmites australis and Typha latifolia in Constructed Wetlands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experiment with Industrial Effluent
2.3. Batch Experiment
2.4. Sample Analysis
2.5. Data Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Zn Removal from Galvanic Industrial Effluent
3.2. Zn Removal from Synthetic Effluents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Werkneh, A.A. Decentralized constructed wetlands for domestic wastewater treatment in developing countries: Field-scale case studies, overall performance and removal mechanisms. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakare, M.; Sarma, H.; Datar, S.; Roy, A.; Pawar, P.; Gupta, K.; Pandit, S.; Prasad, R. Understanding the holistic approach to plant-microbe remediation technologies for removing heavy metals and radionuclides from soil. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2021, 3, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayangbenro, A.S.; Babalola, O.O. A New Strategy for Heavy Metal Polluted Environments: A Review of Microbial Biosorbents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Aslam, A.; Qadeer, A.; Javied, S.; Nisar, N.; Hassan, N.; Hussain, A.; Ali, B.; Iqbal, R.; Chaudhary, T.; et al. Domestic wastewater treatment by Pistia stratiotes in constructed wetland. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandros, S. (Ed.) Constructed Wetlands for Industrial Wastewater Treatment; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, V.T.T.; Bui, K.Q.; Le, D.V.; Chau, D.H.; Hoang, B.N.; Pham, H.T.; Nguyen, A.T. Domestic Wastewater Treatment Using Constructed Wetland with Para Grass Combined with Sludge Adsorption, Case Study in Vietnam: An Efficient and Alternative Way. Processes 2022, 10, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, Y.; Vargas, E.; García-Cortés, D.; Hernández, W.; Checo, H.; Jáuregui-Haza, U. Efficiency and effectiveness of systems for the treatment of domestic wastewater based on subsurface flow constructed wetlands in Jarabacoa, Dominican Republic. Water Sci. Eng. 2024, 17, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Arya, S.; Kumar, S. 2021 Industrial wastewater treatment: Current trends, bottlenecks, and best practices. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, A.; Saleh, T.A. Removal of toxic metals from wastewater in constructed wetlands as a green technology; catalyst role of substrates and chelators. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, L.; Zamora-Castro, S.A.; Vidal-Álvarez, M.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L. Role of Wetland Plants and Use of Ornamental Flowering Plants in Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, A.; Timilsina, A.; Gautam, A.; Adhikari, K.; Bhattarai, A.; Aryal, N. Phytoremediation: Mechanisms, plant selection and enhancement by natural and synthetic agents. Environ. Adv. 2022, 8, 100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angon, P.B.; Islam, M.S.; KC, S.; Das, A.; Anjum, N.; Poudel, A.; Suchi, S.A. Sources, effects and present perspectives of heavy metals contamination: Soil, plants and human food chain. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Kaur, H.; Kaur, H.; Srivastava, S. The beneficial roles of trace and ultratrace elements in plants. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 100, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowczyk, A.; Szymańska-Pulikowska, A. Micro- and Macroelements Content of Plants Used for Landfill Leachate Treatment Based on Phragmites australis and Ceratophyllum demersum. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.W.; Pang, Y.L.; Lim, S.; Chong, W.C. A state-of-the-art of phytoremediation approach for sustainable management of heavy metals recovery. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 30, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Emergent plants used in free water surface constructed wetlands: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larakeb, M.; Youcef, L.; Achour, S. Removal of Zinc from Water by Adsorpion on Bentonite and Kaolin. Athens. J. Sci. 2017, 4, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkiew, S.; Amnuaychaichana, S.; Srithadindang, K.; Paisuwan, W.; Ajavakom, A.; Polprasert, C.; Lek Noophan, P.; Supakata, N.; Koottatep, T.; Surendra, K.C.; et al. Enhancing Digestate-Based Bioponics through Ceramsite Addition with and without Biochar: Effects on Water Quality, Nutrient Recovery, Heavy Metal Removal, and Microbial Community Composition. ACS ES T Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.E.; Rehuman, N.A.; Harilal, S.; Vincent, A.; Rajamma, R.G.; Behl, T.; Uddin, M.S.; Ashraf, G.M.; Mathew, B. Molecular mechanism of zinc neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 43542–43552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Khan, M.; Sheikh, T.M.M.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Chohan, T.A.; Shamim, S.; Liu, Y. Zinc Essentiality, Toxicity, and Its Bacterial Bioremediation: A Comprehensive Insight. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 900740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plum, L.M.; Rink, L.; Hajo, H. The Essential Toxin: Impact of Zinc on Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cerqueira, A.M.M.; De Souza Cardoso, F. Nutritional Diseases. In Tropical Dermatology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomikoski, S.; Kupila, R.; Romar, H.; Bergna, D.; Kangas, T.; Runtti, H.; Lassi, U. Zinc Adsorption by Activated Carbon Prepared from Lignocellulosic Waste Biomass. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlan, R.G.; Hossain, S.M.G.; Al-Mashaqbeh, O.A. Zinc sorption by permanganate treated pine chips. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinc Statistics and Information|U.S. Geological Survey. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/national-minerals-information-center/zinc-statistics-and-information (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Machemer, S.D.; Wildeman, T.R. Adsorption compared with sulfide precipitation as metal removal processes from acid mine drainage in a constructed wetland. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1992, 9, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Chakraborty, S. Zinc removal from highly acidic and sulfate-rich wastewater in horizontal sub-surface constructed wetland. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3403–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghoum, I.; Edahbi, M.; Melián, J.A.H.; Rodriguez, J.M.D.; Durães, N.; Pascual, B.A.; Salmoun, F. Passive Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage Effluents Using Constructed Wetlands: Case of an Abandoned Iron Mine, Morocco. Water 2025, 17, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, L.; Shutes, R.B.E.; Revitt, D.M.; Forshaw, M.; Purchase, D. The treatment of metals in urban runoff by constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 214, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Shen, Z.; Hu, K. Preparation of Ceramsite Based on Waterworks Sludge and Its Application as Matrix in Constructed Wetlands. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Nan, Y.; Jing, X.; Cang, D. Phosphorus recovery from simulated urine using non-sintered ceramsite: Adsorption performance and mechanism. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 201, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, H.; He, C. Porous red mud ceramsite for aquatic phosphorus removal: Application in constructed wetlands. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 360, 124688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.A.; Yiwen, M.; Saleh, M.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Giap, S.G.E.; Chinni, S.V.; Gobinath, R. Bioaccumulation and Translocation of Heavy Metals in Paddy (Oryza sativa L.) and Soil in Different Land Use Practices. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. National Recommended Water Quality Criteria: 2002; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Knox, A.S.; Paller, M.H.; Seaman, J.C.; Mayer, J.; Nicholson, C. Removal, distribution and retention of metals in a constructed wetland over 20 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 149062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, I.E. Behaviour of Heavy Metals in Constructed Treatment Wetlands. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, September 2006; p. 256. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J.; Krása, P. Distribution of Mn, Al, Cu and Zn in a constructed wetland receiving municipal sewage. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejna, M.; Moscatelli, A.; Stroppa, N.; Onelli, E.; Pilu, S.; Baldi, A.; Rossi, L. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals from wastewater through a Typha latifolia and Thelypteris palustris phytoremediation system. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Salem, Z.; Laffray, X.; Al-Ashoor, A.; Ayadi, H.; Aleya, L. Metals and metalloid bioconcentrations in the tissues of Typha latifolia grown in the four interconnected ponds of a domestic landfill site. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 54, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, C. Zinc distribution and zinc-binding forms in Phragmites australis under zinc pollution. J. Plant. Physiol. 2008, 165, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balafrej, H.; Bogusz, D.; Triqui, Z.-E.A.; Triqui, Z.-E.A.; Guedira, A.; Bendaou, N.; Smouni, A.; Fahr, M. Zinc Hyperaccumulation in Plants: A Review. Plants 2020, 9, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanno, G.; Vymazal, J.; Cirelli, G.L. Translocation, accumulation and bioindication of trace elements in wetland plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
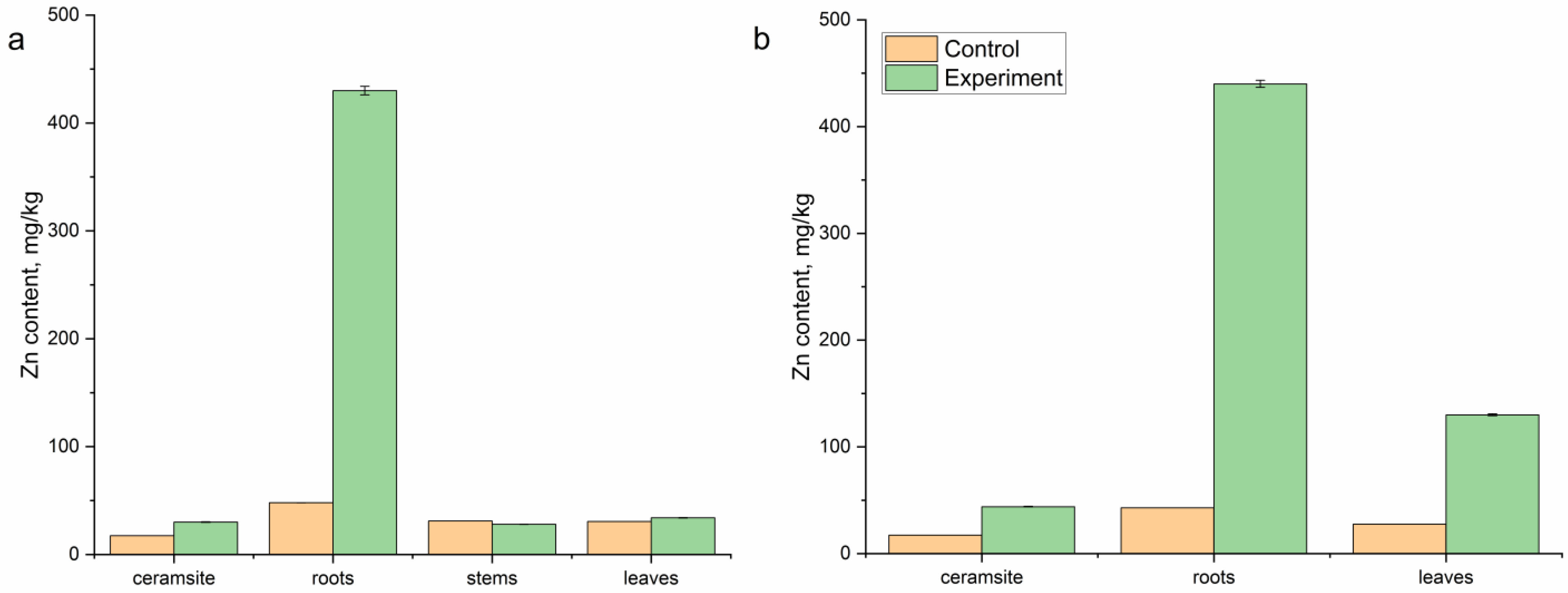
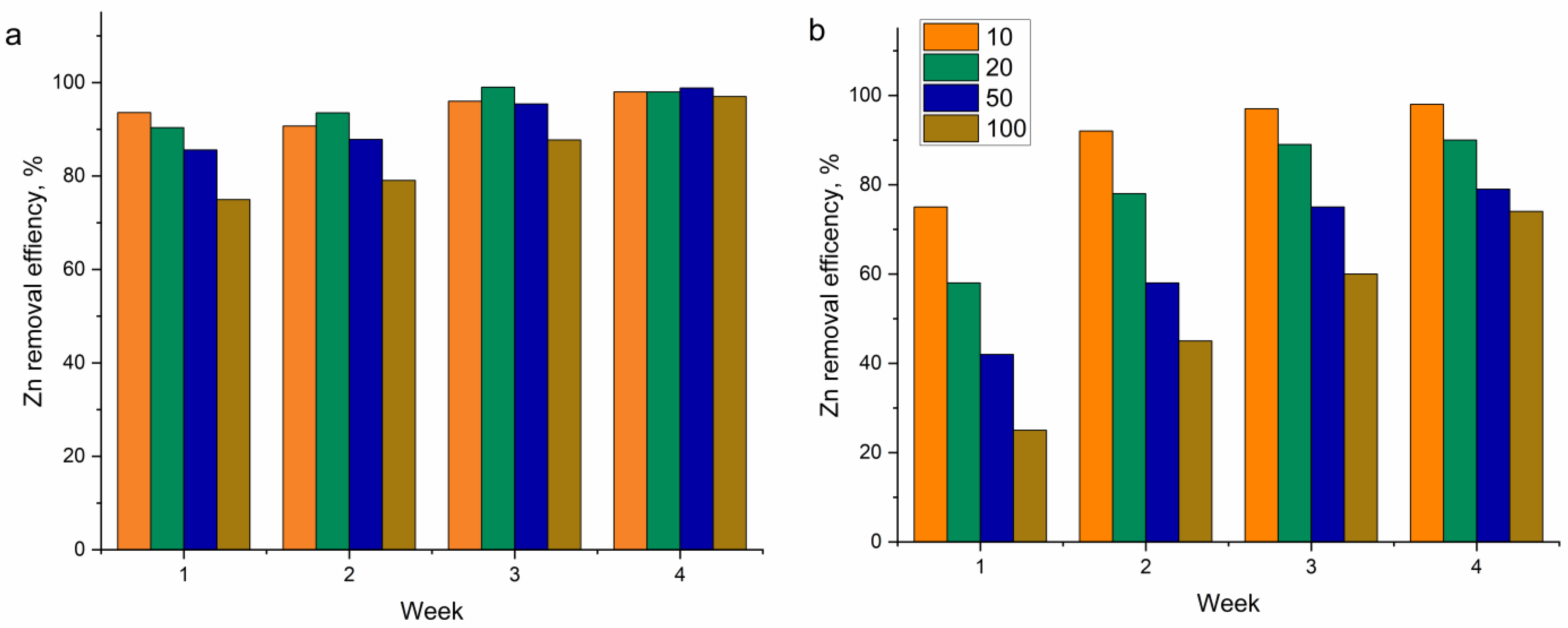
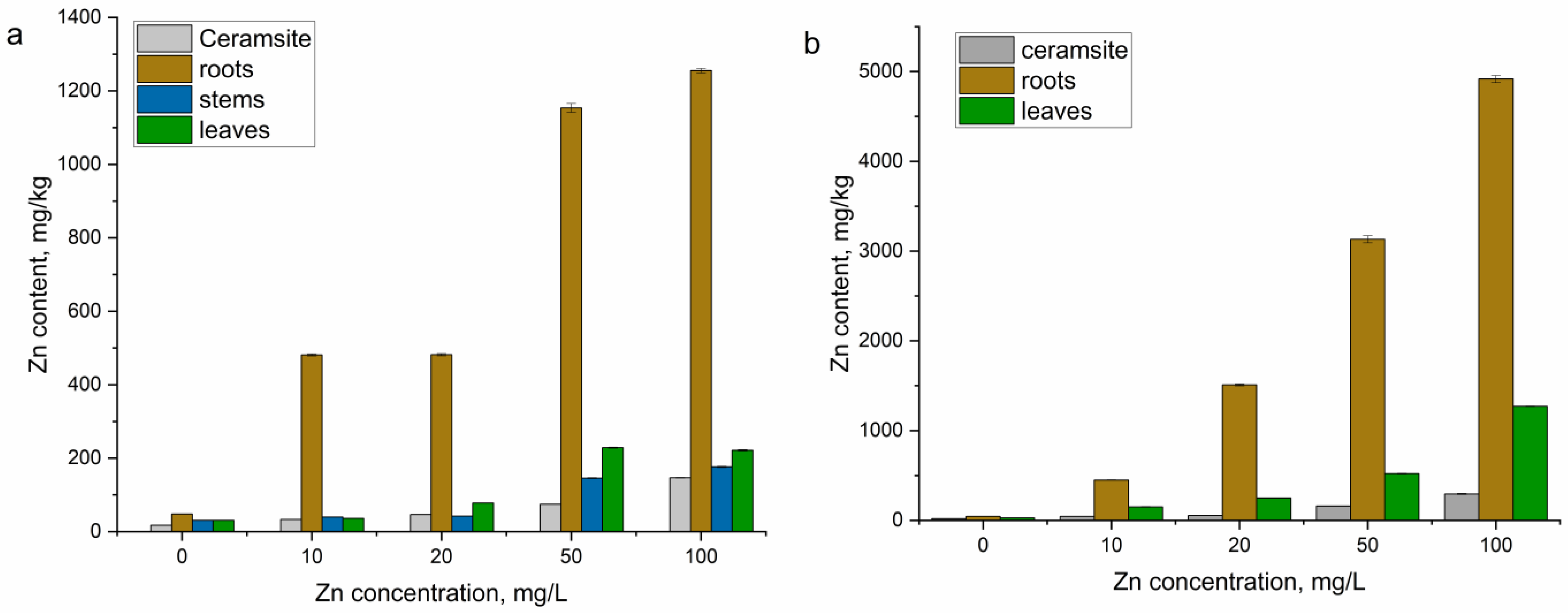
| Plant | 1st Week | 2nd Week | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Zn Concentration mg/L | Zn Concentration, mg/L | RE, % | Zn Concentration, mg/L | RE, % | |
| Phragmites australis | 9.54 | 0.18 | 98.0 | 0.09 | 99.0 |
| Typha latifolia | 9.54 | 0.26 | 97.0 | 0.12 | 98.7 |
| Zn Concentration, mg/L | Phragmites australis | Typha latifolia | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TL/S | TSt/R | TL/R | TL/R | |
| 10 | 0.91 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.34 |
| 20 | 1.85 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| 50 | 1.57 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 0.17 |
| 100 | 1.25 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zinicovscaia, I.; Svozilíková Krakovská, A.; Yushin, N.; Peshkova, A.; Grozdov, D. Phytoremediation of Zinc-Contaminated Industrial Effluents with Phragmites australis and Typha latifolia in Constructed Wetlands. Water 2025, 17, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162358
Zinicovscaia I, Svozilíková Krakovská A, Yushin N, Peshkova A, Grozdov D. Phytoremediation of Zinc-Contaminated Industrial Effluents with Phragmites australis and Typha latifolia in Constructed Wetlands. Water. 2025; 17(16):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162358
Chicago/Turabian StyleZinicovscaia, Inga, Aneta Svozilíková Krakovská, Nikita Yushin, Alexandra Peshkova, and Dmitrii Grozdov. 2025. "Phytoremediation of Zinc-Contaminated Industrial Effluents with Phragmites australis and Typha latifolia in Constructed Wetlands" Water 17, no. 16: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162358
APA StyleZinicovscaia, I., Svozilíková Krakovská, A., Yushin, N., Peshkova, A., & Grozdov, D. (2025). Phytoremediation of Zinc-Contaminated Industrial Effluents with Phragmites australis and Typha latifolia in Constructed Wetlands. Water, 17(16), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162358








