Distribution Characteristics, Mobility, and Influencing Factors of Heavy Metals at the Sediment–Water Interface in South Dongting Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
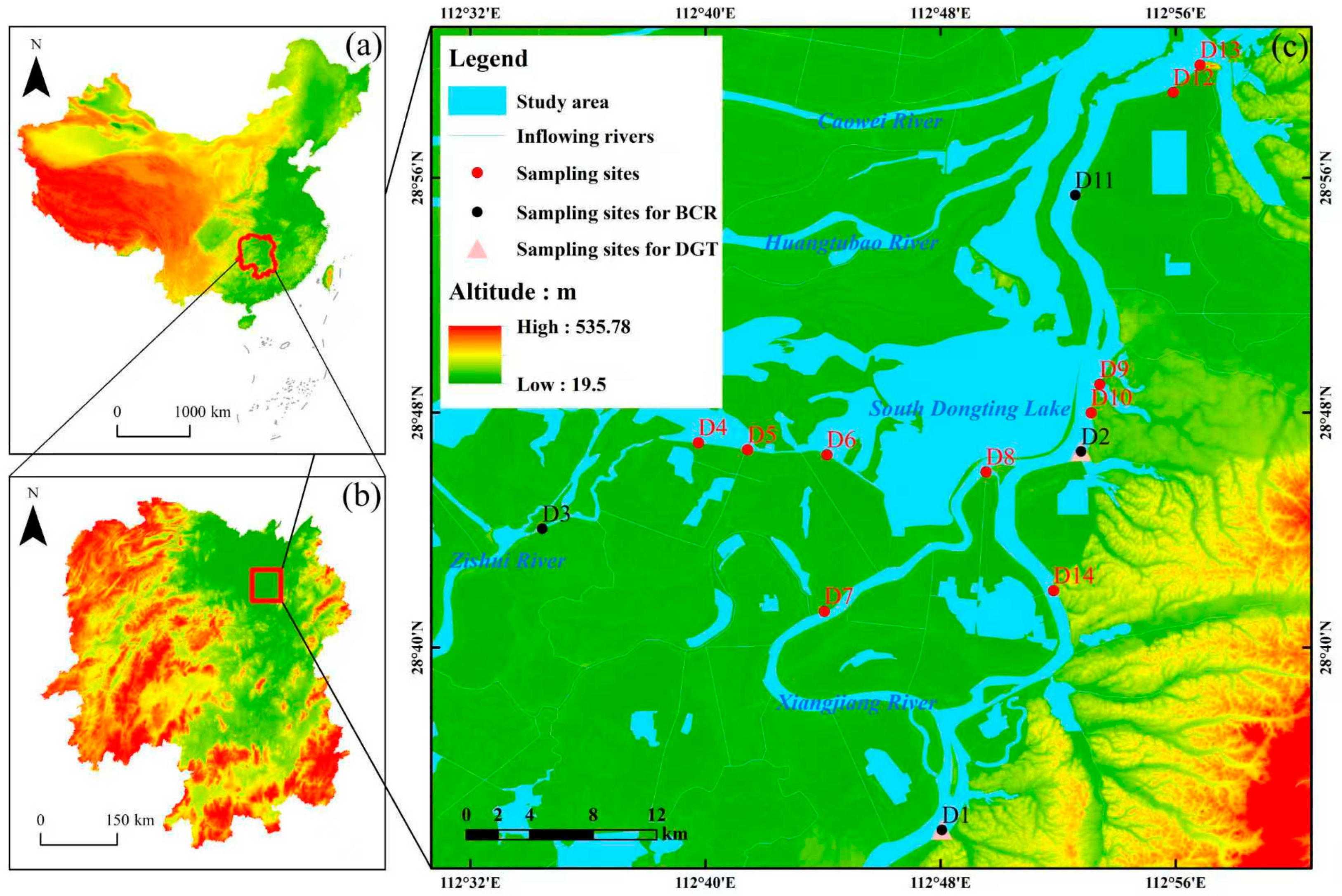
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.2.1. Sample Collection
2.2.2. Sample Analysis
2.3. Evaluation Methods
3. Results
3.1. Sedimentary Environmental Characteristics of South Dongting Lake
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Sediments of South Dongting Lake
3.3. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Nutrients in South Dongting Lake Sediments
3.4. Geochemical Fractionation of Heavy Metals in Sediments
4. Discussion
4.1. Contamination Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments
4.1.1. Assessment Results Based on Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
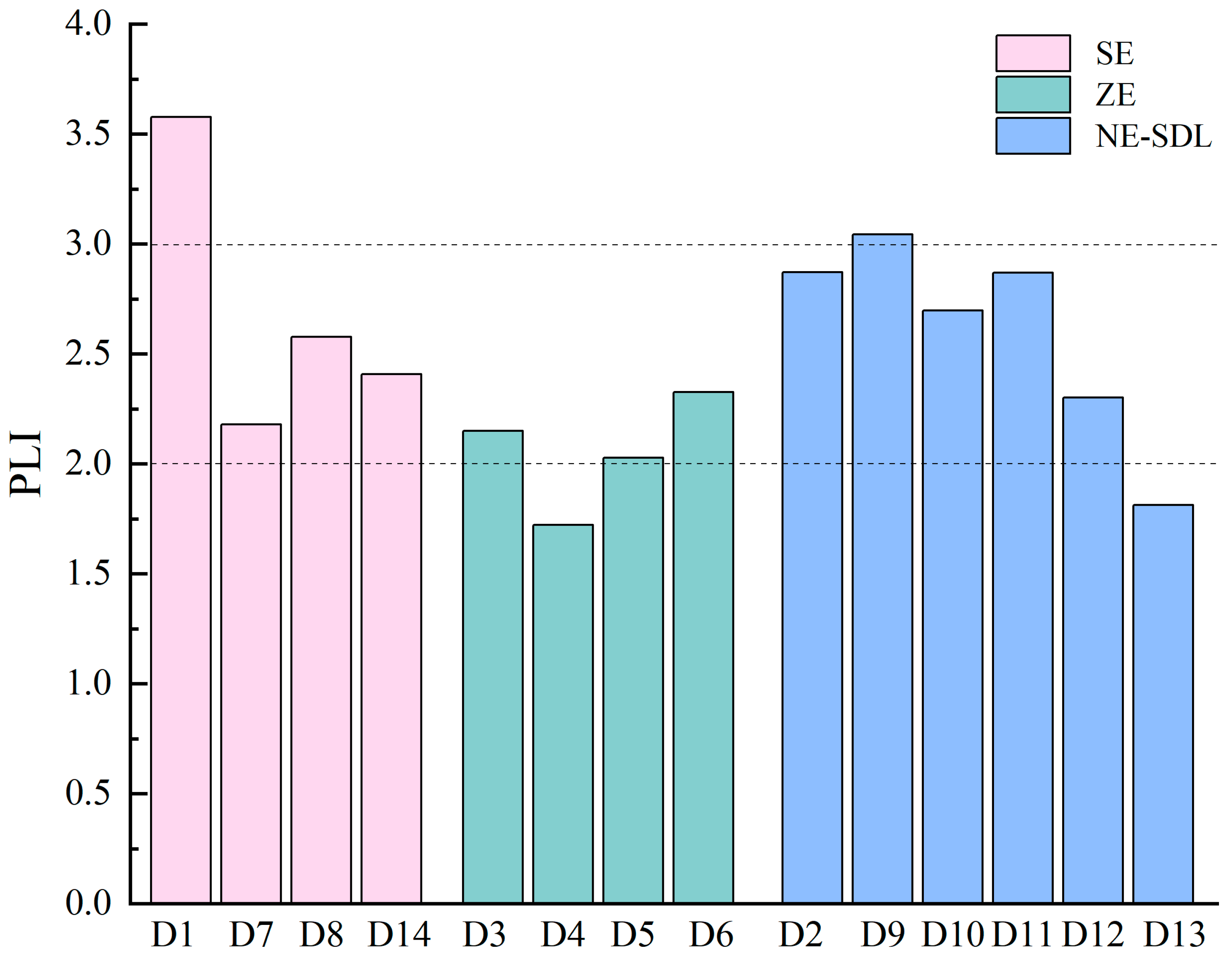
4.1.2. Pollution Load Index Evaluation Results
4.2. Ecological Risk Assessment of Sediment Heavy Metals
4.2.1. Risk Assessment Coding Evaluation Results
4.2.2. Potential Ecological Risk Index
4.3. Analysis of Factors Influencing the Activity of Heavy Metals in Sediments
4.4. Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Sediments
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the surface sediments of South Dongting Lake, HMs such as Cr, Cu, Pb, Bi, Ni, As, Se, Cd, Sb, Mn, Zn, and Fe exhibit considerable variability (Cv > 0.20), while metals including V, Tl, and Co show relatively stable concentrations (Cv < 0.20) and more uniform spatial distribution. The concentrations of all 15 HMs exceed background values for the upper continental crust of eastern China, the Yangtze River, and Dongting Lake. Spatially, HM concentrations display significant heterogeneity, with the highest levels observed in XE, followed by the northeast region. Pb, Bi, As, Cd, Mn, and Zn are markedly enriched in both regions, while the ZE shows the lowest levels, with Sb being the only metal showing notable enrichment.
- (2)
- Integrated BCR and DGT analyses revealed that V, Cr, Cu, Ni, and As predominantly exist in the residual fraction (F4). Pb and Co are mainly present in the oxidizable fraction (F3), exhibiting relatively high mobility, with their concentrations increasing from pore water to overlying water. Mn and Zn are primarily associated with exchangeable and reducible fractions (F1 and F2), showing strong mobility, with concentrations decreasing from pore water to overlying water. These patterns indicate that the release of metals into pore water varies with depth and oxygen availability. Cd is mainly found in the F1 fraction, and its unstable concentration profile is influenced by both its chemical speciation and the sedimentary environment.
- (3)
- The geo-accumulation index (Igeo) indicated that Pb, Bi, Ni, As, Se, Cd, and Sb—particularly Bi and Cd—pose a relatively serious threat to the environment. Pollution load index (PLI) assessments showed that all three zones are heavily polluted, in the order of XE (PLIzone = 2.64) > northeast region (PLIzone = 2.56) > ZE (PLIzone = 2.04). Risk Assessment code (RAC) analysis revealed higher risk levels for Cd, Mn, and Zn. According to the Potential Ecological Risk Index (RI), Cd was identified as the primary contributor to ecological risk in all three regions. The comprehensive RI values indicated predominantly high ecological risk, consistent with the PLI ranking: XE (RI = 597) > northeast region (RI = 366) > ZE (RI = 154.91), with Cd being the dominant contributor to RI.
- (4)
- The composite contamination of HMs in South Dongting Lake sediments is influenced by multiple environmental factors. The contamination levels of Cd, Zn, and Tl are mainly affected by sediment grain size, pH, and nutrient content. V, Cr, Bi, Mn, As, and Se are more susceptible to the combined effects of electrical conductivity and nutrient concentrations. The distribution of Co, Sb, Cu, and Ni is closely linked to sediment texture. Pb contamination is driven by a combination of grain size, pH, electrical conductivity, and nutrient levels.
- (5)
- Based on the PMF model, the primary sources of HMs in the sediments were identified as metal smelting–natural mixed sources (25.4%), agricultural sources (29.1%), natural sources (25.1%), and mining and smelting sources (20.4%).
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Teng, Y. Source apportionment and source-oriented risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of an urban river-lake system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Ma, J.; Wang, G.; Xu, X.; Huang, H.; Zhu, Y. Pollution assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in sediment of Lake Tuohu in Huaihe River Basin. China J. Lake Sci. 2024, 37, 889–901. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Yang, K.; Lu, J.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, L. Contamination and ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of urban rivers in a typical economic development zone, southern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 153, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Pan, K. Migration and diffusion for pollutants across the sediment-water interface in lakes: A review. China J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 1489–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C. Advances and prospect in sediment-water interface of lakes: A review. China J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 1191–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Long, Y.; Li, J.; Wen, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Current state, sources, and potential risk of heavy metals in sediments of typical inner lakes in the Dongting Lake Area. Process Safety and Environmental Protection. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 190, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Z. Distribution characteristics, ecological risk assessment, and source tracing of heavy metals in the sediments of typical lakes in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 1402–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhu, S.; Liu, P. Spatial distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Dongting Lake. J. Yunnan Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2019, 41, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Sun, Z.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y. Character and assessment of heavy metals in the sediments from Lake Dongting. China J. Lake Sci. 2008, 04, 477–485. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X. Geochemical Study on Heavy-metal Contamination in Sediments From the Four River Inlets of Dongting Lake, China. China. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Peng, G.; Xie, Y.; Mo, Y.; Li, F.; Ouyang, M.; Huang, D. Characteristics and risk assessment of nutrients and heavy metals pollution in sediments of Dongting Lake. China Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 2399–2409. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Ma, T.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Yu, H. Pollution assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in agricultural soil around Zijiang River estuary. China Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2021, 40, 138–146. [Google Scholar]
- Zeb, M.; Khan, K.; Younas, M.; Farooqi, A.; Cao, X.; Kavil, Y.; Alelyani, S.; Alkasbi, M.; Al-Sehemi, A. A review of heavy metals pollution in riverine sediment from various Asian and European countries: Distribution, sources, and environmental risk. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zeng, W.; He, M. Distribution sources contamination risks of toxic metals in Zijiang River a typical tributary of the midstream of the Yangtze River in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 153, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, R.; Bolam, T.; Barry, J.; Mason, C.; Kröger, S.; Warford, L.; Silburn, B.; Sivyer, D.; Birchenough, S.; Mayes, A.; et al. The application of Diffusive Gradients in Thin Films (DGT) for improved understanding of metal behaviour at marine disposal sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pueyo, M.; Mateu, J.; Rigol, A.; Vidal, M.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.F.; Rauret, G. Use of the modified BCR three-step sequential extraction procedure for the study of trace element dynamics in contaminated soils. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins-Veränderungen seit 1971. Umsch. Wiss. Tech. 1979, 79, 133–149. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson, D.; Wilson, J.; Harris, C. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Mar. Res. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, G.; Craboledda, L.; Lucchese, M.; Cirillo, R.; Dotta, L. Heavy metal speciation in the sediments of Northern Adriatic Sea: A new approach for environmental toxicity determination. Heavy Met. Environ. 1985, 2, 454–456. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Luo, T.C.; Zhang, B.R.; Zhang, H.F.; Han, Y.W.; Zhao, Z.D.; Kern, H. Structure and composition of the continental crust in eastern China. Science in China Series D. China Sci. China Earth Sci. 1999, 3, 204–213. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, M. A comparison of chemical element abundances in sediments from the Yellow River, the Yangtze River, and China's shallow seas. China Chin. Sci. Bull. 1992, 13, 1202–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Tang, X.; Yu, C.; Tan, C.; Tu, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, K.; Xiao, M.; Xu, J. Heavy metal contamination of inlet sediments of the Xiangjiang River and Pb isotopic geochemical implication. China Acta Geol. Sin. 2011, 85, 282–299. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Tang, X.; Yu, C.; Tan, C.; Yin, C.; Yang, G.; Liu, Q.; Yang, K.; Tu, X. Geochemistry of trace metals and Pb isotopes of sediments from the lowermost Xiangjiang River, Hunan Province (P. R. China): Implications on sources of trace metals. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieniawski, S.; Macdonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G. A Guidance Manual to Support the Assessment of Contaminated Sediments in Freshwater Ecosystems; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA; Great Lakes National Program Office: Chicago, IL, USA, 2002.
- Zhang, G. Characteristics ecological risk assessment of nutrient heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of Dongting Lake China. J. Hydroecol. 2015, 36, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kachoueiyan, F.; Karbassi, A.; Nasrabadi, T.; Rashidiyan, M.; De-la-Torre, G.E. Speciation characteristics, ecological risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Gomishan wetland. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 198, 115835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madadi, R.; Mejjad, N.; De-la-Torre, G.E. Geochemical speciation, ecological risk, and source identification of heavy metal (loid) s in sediments and waters from Musa Estuary, Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 114836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, X.; Lin, L.; Bai, L.; Yang, M.; Wang, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, D. A retrospective analysis of heavy metals and multi elements in the Yangtze River Basin: Distribution characteristics, migration tendencies and ecological risk assessment. Water Res. 2024, 254, 121385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qin, Y.; Cao, W.; Wen, Q.; Shi, Y.; Ma, Y. Speciation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Dongting Lake. China Environ. Sci. Res. 2020, 33, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Dong, Z.; Chao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, H. Bioavailability and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Lake Chaohu, China. China Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.; Ji, J.; Wang, S. The influence of pH on the release behavior of heavy metal elements Cd and Pb in the sediments of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Geol. Bull. China 2012, 31, 594–600. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, F. A new index for assessing heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal (Zaozhuang Segment): A case study. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.; Wang, S. Distribution, risk and bioavailability of metals in sediments of Lake Yamdrok Basin on the Tibetan Plateau. China J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 97, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Variation Characteristics of Nutrients and Typical Heavy Metals at Sediment-Water Interface in the Outlet of Nansi Lake. China. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.; Shen, J.; Zhu, Y. Determination of heavy metal chemical forms by BCR method for Taihu Lake sediments. China Res. Environ. Sci. 2005, 18, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Zhang, C.; Mao, X.; Tang, H.; Liao, Q.; Chen, C. Distribution characteristics and risk of heavy metal pollution in the sediments of Dongting Lake and its tributaries and the impact factor analysis. China Geol. Rev. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, F.; Wang, Z.; Yin, F.; Cao, J.; Liao, Q.; Xu, X.; Guo, J. Ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in sediments of Dongting Lake. China China Geol. 2024, 1–14. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1167.P.20240815.1222.002 (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Izquierdo, M.; De Miguel, E.; Ortega, M.F.; Mingot, J. Bioaccessibility of metals and human health risk assessment in community urban gardens. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fang, P.; Huang, B.; Lu, S.; Wan, Q.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, G. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and heavy metals in surface sediments of typical internal lakes in Dongting Lake area. Sci. Res. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Zhan, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, L. Current status and temporal trend of heavy metals in farmland soil of the Yangtze River Delta Region: Field survey and meta-analysis. Sci. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Pan, Y.; Huang, Y. Spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in soils from a typical lead-zinc mining area in Yangshuo. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4545–4555. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Xie, F. Enrichment characteristics, risk evaluation, and source apportionment of heavy metals in Wabu Lake of Yangtze River to Huai River water diversion project. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 7111–7122. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, H.; Lu, Z.; Fu, G.; Lv, S.; Jiang, J.; Xie, Y.; Luo, X.; Zeng, J.; Xue, S. Pollution characteristics and quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals within a zinc smelting site by GIS-based PMF and APCS-MLR models. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 144, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Hou, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yu, T.; Yuan, J.; Dai, G.; Tang, Z. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from Xiang River, China. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 2230–2240. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, G.; Liu, B.; Xiong, L. Content of Cu Zn in pig feeds their residual character in pig manures from intensive piggery in Guangxi China. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2012, 40, 9280–9281+9284. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Han, Z.; Ben, W. Heavy metal contents in pig manure pig feeds from intensive pig farms in Shandong Province China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2013, 32, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Shen, Z.; Hu, H.; Shi, H.; He, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, A. Evaluation assessment source analysis of heavy metals in sediment near the stone coal mining area in the lower reaches of the Zi River, China. China J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2024, 43, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Qiu, L.; Shen, Y.; Ge, Y.; Hou, Y. Investigation and analysis of heavy metal contents from livestock feed and manure in North China. China Trans. China Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, B.; Fang, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Dai, Y. Geochemical background of elements in bed sediments from the lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River in Hunan Province, China. China Geol. Rev. 2021, 67, 504–522. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, S.; Che, F.; Jiang, X.; Niu, Y. Meta analysis of heavy metal pollution in sediments of Chaohu Lake, Dongting Lake and Poyang Lake, China. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Luo, J.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Geochemical fractionation, bioavailability, and potential risk of heavy metals in sediments of the largest influent river into Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cui, J.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Bai, Y.; Shi, X. Extensive study of potential harmful elements (Ag, As, Hg, Sb, and Se) in surface sediments of the Bohai Sea, China: Sources and environmental risks. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wan, H. Distribution, speciation, toxicity and bioavailability of antimony in the environment. China Trends Chem. 2004, 1, 131–135. [Google Scholar]





| Igeo | Pollution Level | PLI | Pollution Level | RAC | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Igeo < 0 | Unpolluted | PLI ≤ 1 | Unpolluted | RAC ≤ 1% | No risk |
| 0 < Igeo < 1 | Slightly polluted | 1 < PLI ≤ 2 | Moderately polluted | 1% < RAC ≤ 10% | Low risk |
| 1 < Igeo < 2 | Slightly to moderately polluted | 2 < PLI ≤ 3 | Heavily polluted | 10% < RAC ≤ 30% | Moderate risk |
| 2 < Igeo < 3 | Moderately polluted | PLI > 3 | Extremely polluted | 30% < RAC ≤ 50% | High risk |
| 3 < Igeo < 4 | Moderately to heavily polluted | RAC > 50% | Very high risk | ||
| 4 < Igeo < 5 | Heavily polluted | ||||
| Igeo > 5 | Extremely polluted | ||||
| Risk Level | RI | Ecological Risk | |||
| < 40 | Low risk | RI < 150 | Low ecological risk | ||
| 40 ≤ < 80 | Moderate risk | 150 ≤ RI < 300 | Moderate ecological risk | ||
| 80 ≤ < 160 | Considerable risk | 300 ≤ RI < 600 | High ecological risk | ||
| 160 ≤ < 320 | High risk | RI ≥ 600 | Very high ecological risk | ||
| ≥ 320 | Very high risk |
| Region | Sample | V | Cr | Cu | Pb | Tl | Bi | Co | Ni | As | Se | Cd | Sb | Mn | Zn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xiangjiang Estuary | D1 | 81.53 | 81.68 | 44.30 | 107.2 | 1.34 | 3.95 | 19.73 | 73.93 | 84.59 | 3.29 | 12.00 | 6.54 | 1033 | 184.7 | 50,238 |
| D7 | 65.18 | 50.46 | 23.33 | 36.34 | 0.92 | 3.07 | 13.54 | 84.60 | 19.89 | 15.76 | 1.32 | 5.42 | 581.8 | 83.43 | 30,502 | |
| D8 | 58.05 | 63.67 | 25.88 | 55.51 | 1.03 | 5.57 | 13.25 | 65.39 | 31.30 | 27.98 | 2.86 | 4.28 | 470.9 | 89.60 | 31,386 | |
| D14 | 53.18 | 50.74 | 27.38 | 80.95 | 1.32 | 1.13 | 16.06 | 59.33 | 48.28 | 11.44 | 5.92 | 3.37 | 419.8 | 103.8 | 33,048 | |
| Mean | 64.49 | 61.64 | 30.22 | 70.00 | 1.15 | 3.43 | 15.65 | 70.81 | 46.01 | 14.62 | 5.53 | 4.90 | 626.5 | 115.4 | 36,294 | |
| Cv | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.44 | 0.18 | 0.54 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.61 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.41 | 0.26 | |
| Zishui Estuary | D3 | 84.50 | 60.96 | 25.89 | 29.20 | 0.86 | 2.35 | 15.87 | 65.12 | 21.20 | 5.71 | 1.65 | 18.65 | 329.2 | 60.94 | 40,071 |
| D4 | 82.80 | 61.68 | 24.00 | 38.12 | 0.73 | 2.94 | 14.38 | 38.81 | 23.41 | 1.26 | 0.39 | 9.25 | 455.0 | 66.06 | 48,817 | |
| D5 | 89.33 | 67.65 | 26.92 | 34.97 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 15.31 | 51.12 | 21.48 | 10.91 | 1.19 | 11.97 | 365.0 | 66.32 | 37,143 | |
| D6 | 80.27 | 82.96 | 25.63 | 37.48 | 0.84 | 3.71 | 17.27 | 108.7 | 21.42 | 12.54 | 0.74 | 6.88 | 379.4 | 85.18 | 48,269 | |
| Mean | 84.23 | 68.31 | 25.61 | 34.94 | 0.83 | 2.46 | 15.71 | 65.93 | 21.88 | 7.60 | 0.99 | 11.69 | 382.2 | 69.63 | 43,575 | |
| Cv | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.49 | 0.08 | 0.46 | 0.05 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.44 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.13 | |
| Northeast of South Dongting Lake | D2 | 84.70 | 72.89 | 34.69 | 77.49 | 1.28 | 3.48 | 17.32 | 62.47 | 55.31 | 5.25 | 4.09 | 4.86 | 818.8 | 111.5 | 44,582 |
| D9 | 53.31 | 60.15 | 27.14 | 65.91 | 1.21 | 5.40 | 16.08 | 131.6 | 46.88 | 17.00 | 5.25 | 4.74 | 762.0 | 113.0 | 33,395 | |
| D10 | 84.47 | 82.68 | 34.18 | 72.82 | 0.54 | 9.93 | 18.02 | 71.69 | 40.37 | 11.53 | 1.89 | 4.48 | 391.0 | 95.04 | 41,563 | |
| D11 | 71.42 | 70.12 | 34.35 | 79.78 | 1.40 | 1.90 | 17.31 | 66.36 | 56.52 | 4.90 | 5.45 | 5.26 | 977.3 | 131.5 | 43,369 | |
| D12 | 74.51 | 75.14 | 26.82 | 89.39 | 0.87 | 3.64 | 15.64 | 88.74 | 22.27 | 11.60 | 0.88 | 3.40 | 470.8 | 73.28 | 43,219 | |
| D13 | 79.29 | 65.81 | 26.20 | 59.14 | 0.83 | 4.98 | 13.94 | 66.74 | 23.74 | 4.56 | 0.36 | 1.85 | 415.8 | 59.46 | 34,002 | |
| Mean | 74.62 | 71.13 | 30.56 | 74.09 | 1.02 | 4.89 | 16.38 | 81.27 | 40.85 | 9.14 | 2.98 | 4.10 | 639.3 | 97.31 | 40,022 | |
| Cv | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.32 | 0.57 | 0.09 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.12 |
| Xiangjiang Estuary | Zishui Estuary | Northeast of South Dongting Lake | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Mean | Level | Max | Min | Mean | Level | Max | Min | Mean | Level | |
| V | 0.37 | −0.24 | 0.01 | Sp | 0.50 | 0.35 | 0.42 | Sp | 0.43 | −0.24 | 0.23 | Sp |
| Cr | 0.31 | −0.39 | −0.13 | Up | 0.33 | −0.11 | 0.04 | Sp | 0.33 | −0.13 | 0.1 | Sp |
| Cu | 0.56 | −0.36 | −0.04 | Up | −0.16 | −0.32 | −0.23 | Up | 0.21 | −0.2 | 0.02 | Sp |
| Pb | 1.7 | 0.14 | 0.97 | Sp | 0.21 | −0.18 | 0.07 | Sp | 1.44 | 0.84 | 1.15 | Smp |
| Tl | 0.57 | 0.03 | 0.34 | Sp | −0.03 | −0.31 | −0.12 | Up | 0.64 | −0.73 | 0.11 | Sp |
| Bi | 3.63 | 1.32 | 2.71 | Mp | 3.04 | 0.93 | 2.27 | Mp | 4.46 | 2.08 | 3.26 | Mhp |
| Co | 0.35 | −0.22 | 0 | Up | 0.16 | −0.10 | 0.02 | Sp | 0.22 | −0.15 | 0.08 | Sp |
| Ni | 1.41 | 0.9 | 1.14 | Smp | 1.77 | 0.29 | 0.94 | Sp | 2.05 | 0.97 | 1.3 | Smp |
| As | 2.23 | 0.14 | 1.15 | Smp | 0.38 | 0.24 | 0.28 | Sp | 1.65 | 0.31 | 1.09 | Smp |
| Se | 3.3 | 0.21 | 1.99 | Smp | 2.14 | −1.18 | 0.97 | Sp | 2.58 | 0.68 | 1.49 | Smp |
| Cd | 4.6 | 1.41 | 3.03 | Mhp | 1.74 | −0.33 | 0.81 | Sp | 3.46 | −0.46 | 2.04 | Mp |
| Sb | 1.99 | 1.03 | 1.53 | Smp | 3.50 | 2.06 | 2.73 | Mp | 1.67 | 0.17 | 1.23 | Smp |
| Mn | 0.61 | −0.69 | −0.2 | Up | −0.57 | −1.04 | −0.83 | Up | 0.53 | −0.79 | −0.17 | Up |
| Zn | 0.7 | −0.45 | −0.06 | Up | −0.42 | −0.90 | −0.72 | Up | 0.21 | −0.94 | −0.28 | Up |
| Fe | 0.26 | −0.46 | −0.24 | Up | 0.22 | −0.18 | 0.04 | Sp | 0.09 | −0.33 | −0.08 | Up |
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D11 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Total | RAC | F1 | Total | RAC | F1 | Total | RAC | F1 | Total | RAC | |
| V | 0.03 | 77.44 | 0% | 0.03 | 74.84 | 0% | 0.02 | 73.15 | 0% | 0.06 | 80.31 | 0% |
| Cr | 0.20 | 53.12 | 0% | 0.24 | 54.49 | 0% | 0.27 | 37.30 | 1% | 0.20 | 54.46 | 0% |
| Cu | 1.90 | 46.20 | 4% | 2.62 | 56.70 | 5% | 2.26 | 38.98 | 6% | 1.93 | 50.37 | 4% |
| Pb | 1.08 | 68.96 | 2% | 0.48 | 54.59 | 1% | 0.63 | 34.37 | 2% | 0.51 | 36.13 | 1% |
| Tl | 0.01 | 0.69 | 1% | 0.01 | 1.25 | 1% | 0.01 | 0.83 | 1% | 0.01 | 1.12 | 0% |
| Bi | 0.00 | 3.23 | 0% | 0.00 | 2.16 | 0% | 0.00 | 2.03 | 0% | 0.00 | 2.18 | 0% |
| Co | 0.70 | 23.97 | 3% | 0.37 | 16.63 | 2% | 0.79 | 9.39 | 8% | 1.34 | 25.05 | 5% |
| Ni | 1.40 | 43.87 | 3% | 2.04 | 48.55 | 4% | 2.48 | 39.07 | 6% | 1.20 | 48.47 | 2% |
| As | 0.20 | 36.14 | 1% | 0.14 | 46.86 | 0% | 0.15 | 46.50 | 0% | 0.30 | 49.25 | 1% |
| Se | 0.11 | 3.80 | 3% | 0.13 | 6.50 | 2% | 0.21 | 4.64 | 5% | 0.11 | 3.34 | 3% |
| Cd | 2.08 | 7.35 | 28% | 2.95 | 5.66 | 52% | 1.66 | 2.88 | 58% | 0.89 | 3.17 | 28% |
| Sb | 0.09 | 6.36 | 1% | 0.09 | 3.55 | 3% | 0.15 | 4.70 | 3% | 0.13 | 4.39 | 3% |
| Mn | 505.18 | 992.48 | 51% | 134.95 | 766.19 | 18% | 13.41 | 317.23 | 4% | 112.88 | 913.18 | 12% |
| Zn | 82.57 | 148.38 | 56% | 27.73 | 120.41 | 23% | 22.19 | 77.26 | 29% | 10.82 | 88.56 | 12% |
| Xiangjiang Estuary | Zishui Estuary | Northeast of South Dongting Lake | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Mean | Risk Level | Max | Min | Mean | Risk Level | Max | Min | Mean | Risk Level | |
| V | 3.88 | 2.53 | 3.07 | Low | 4.25 | 3.82 | 4.01 | Low | 4.03 | 2.54 | 3.55 | Low |
| Cr | 3.71 | 2.29 | 2.80 | Low | 3.77 | 2.77 | 3.11 | Low | 3.76 | 2.73 | 3.23 | Low |
| Cu | 11.07 | 5.83 | 7.56 | Low | 6.73 | 6.00 | 6.40 | Low | 8.67 | 6.55 | 7.64 | Low |
| Pb | 24.37 | 8.26 | 15.91 | Low | 8.66 | 6.64 | 7.94 | Low | 20.32 | 13.44 | 16.84 | Low |
| Co | 9.58 | 6.43 | 7.59 | Low | 8.38 | 6.98 | 7.62 | Low | 8.75 | 6.77 | 7.95 | Low |
| Ni | 19.95 | 13.99 | 16.70 | Low | 25.63 | 9.15 | 15.55 | Low | 31.05 | 14.73 | 19.17 | Low |
| As | 70.49 | 16.57 | 38.35 | Low | 19.51 | 17.67 | 18.23 | Low | 47.10 | 18.56 | 34.04 | Low |
| Cd | 1091.07 | 119.75 | 502.44 | Vh | 149.82 | 35.70 | 90.28 | Cons | 495.06 | 32.63 | 271.30 | High |
| Mn | 2.30 | 0.93 | 1.39 | Low | 1.01 | 0.73 | 0.85 | Low | 2.17 | 0.87 | 1.42 | Low |
| Zn | 2.43 | 1.10 | 1.52 | Low | 1.12 | 0.80 | 0.92 | Low | 1.73 | 0.78 | 1.28 | Low |
| RI | 597.32 | High | 154.91 | Mod | 366.43 | High | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, X.; Han, X.; Tang, C.; Peng, B.; Peng, Q.; Hu, L.; Zhong, Y.; Shi, S. Distribution Characteristics, Mobility, and Influencing Factors of Heavy Metals at the Sediment–Water Interface in South Dongting Lake. Water 2025, 17, 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152331
Fang X, Han X, Tang C, Peng B, Peng Q, Hu L, Zhong Y, Shi S. Distribution Characteristics, Mobility, and Influencing Factors of Heavy Metals at the Sediment–Water Interface in South Dongting Lake. Water. 2025; 17(15):2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152331
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Xiaohong, Xiangyu Han, Chuanyong Tang, Bo Peng, Qing Peng, Linjie Hu, Yuru Zhong, and Shana Shi. 2025. "Distribution Characteristics, Mobility, and Influencing Factors of Heavy Metals at the Sediment–Water Interface in South Dongting Lake" Water 17, no. 15: 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152331
APA StyleFang, X., Han, X., Tang, C., Peng, B., Peng, Q., Hu, L., Zhong, Y., & Shi, S. (2025). Distribution Characteristics, Mobility, and Influencing Factors of Heavy Metals at the Sediment–Water Interface in South Dongting Lake. Water, 17(15), 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152331





